Improved Model-Based Forest Height Inversion Using Airborne L-Band Repeat-Pass Dual-Baseline Pol-InSAR Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Test Sites and Datasets
2.1. Test Sites
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. UAVSAR
2.2.2. LVIS
2.2.3. PolSARproSim+
3. Methodology
3.1. Physical Model
3.2. PolInSAR Coherence Function
3.3. Forest Height Inversion
4. Experiment Result
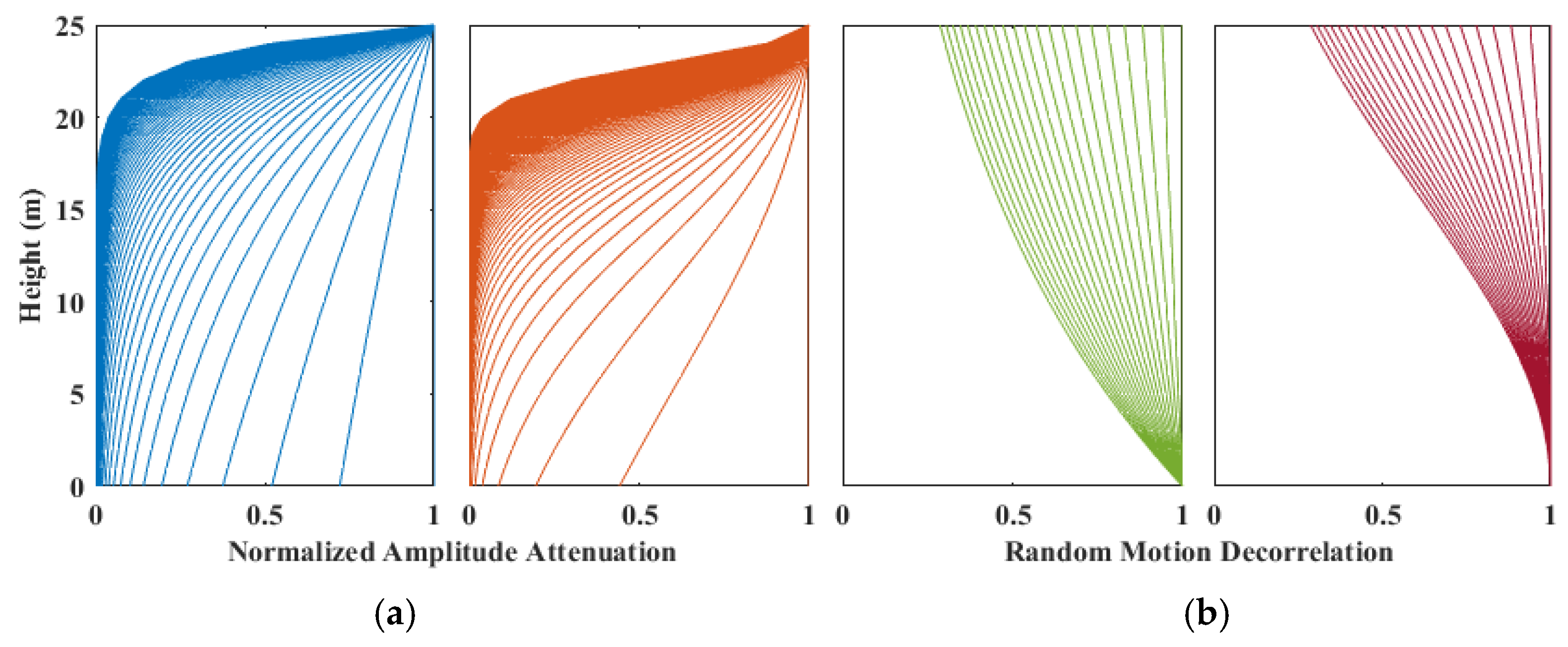
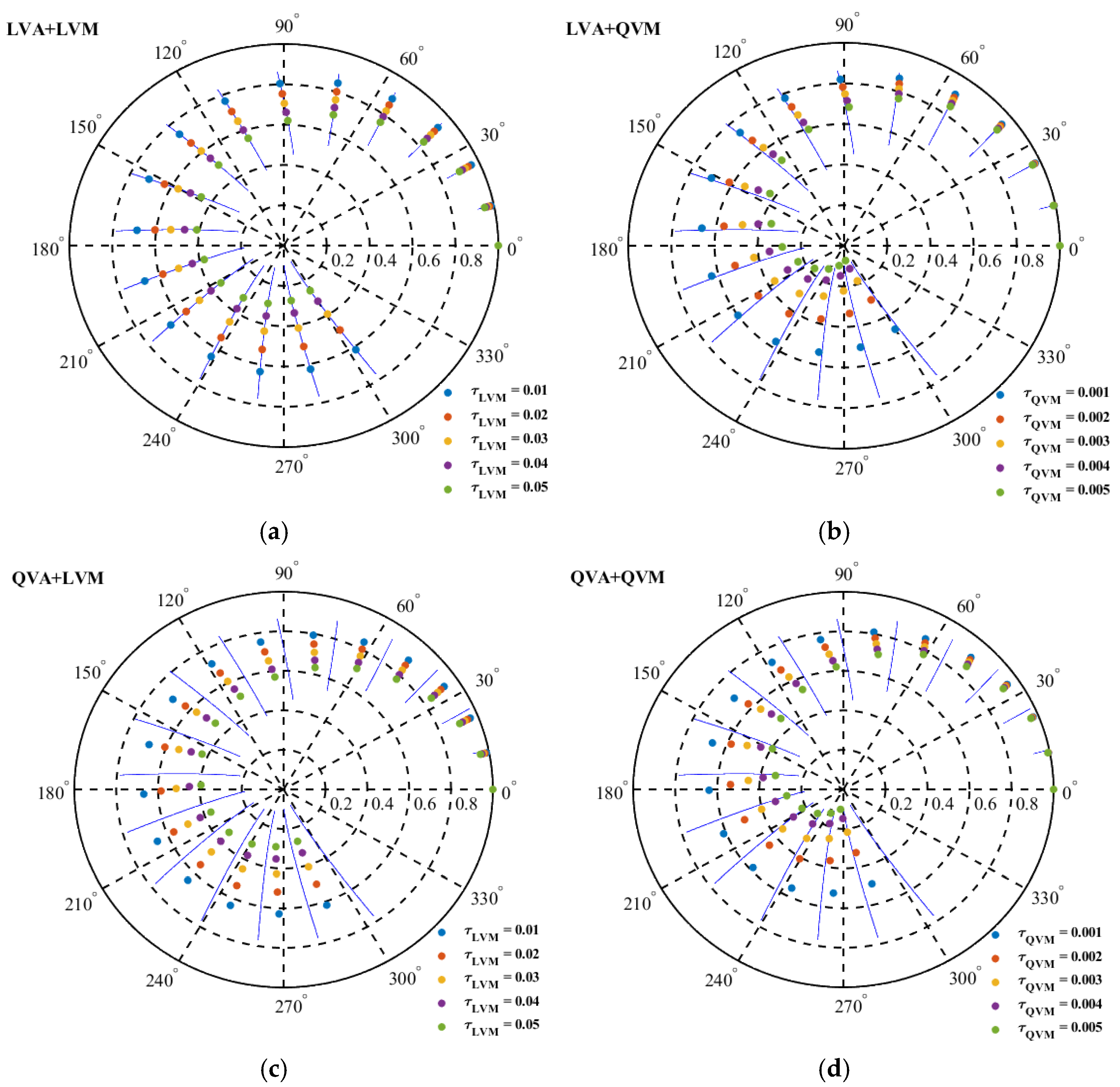
4.1. Scattering Attenuation Fitting
4.2. Forest Height Inversion
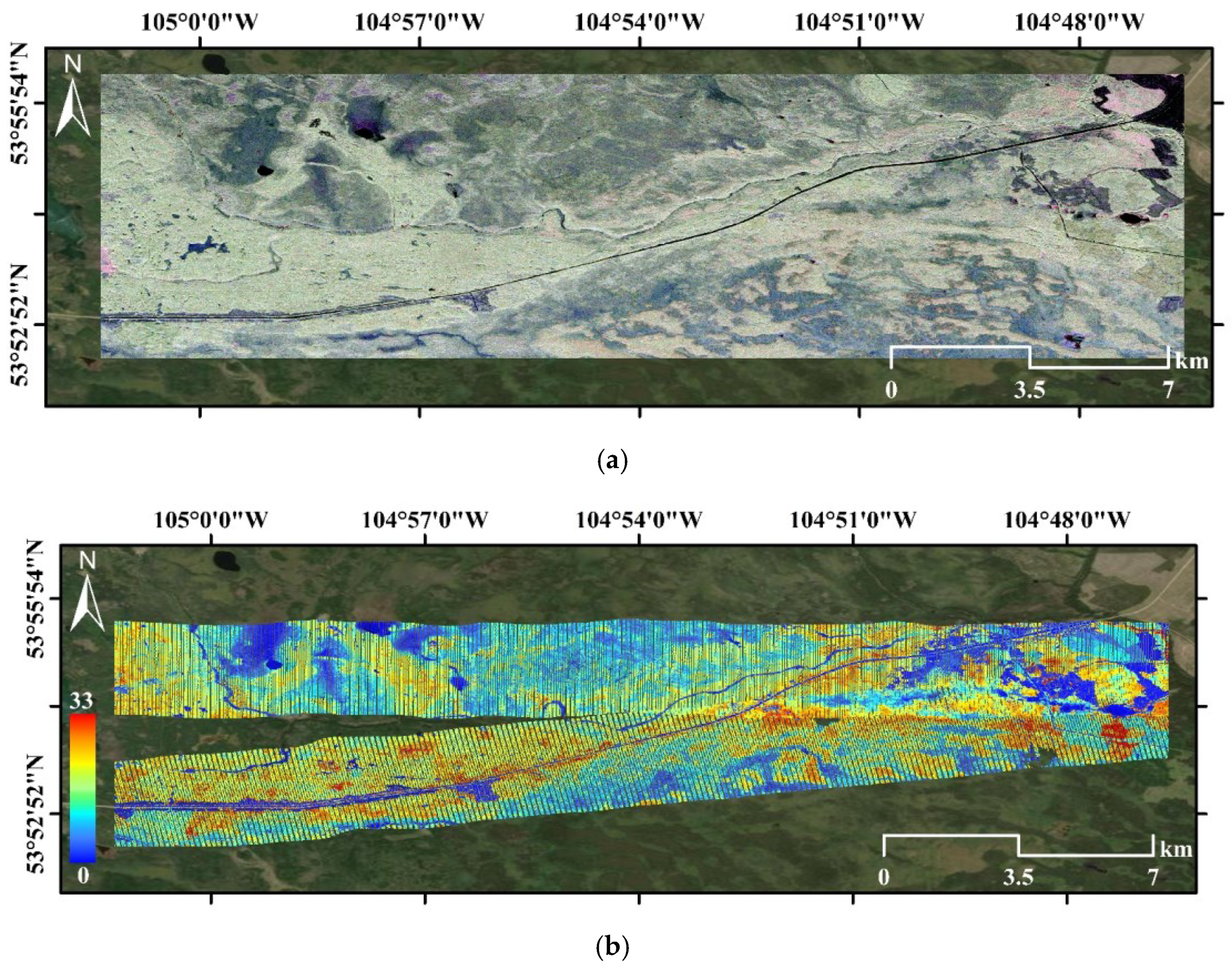
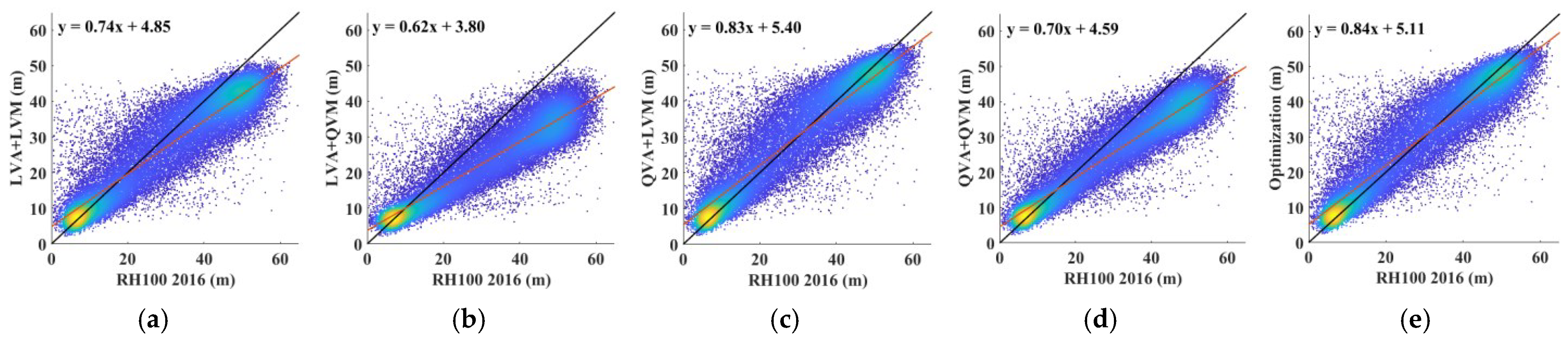
4.2.1. Boreal Ecosystem Research and Monitoring Sites
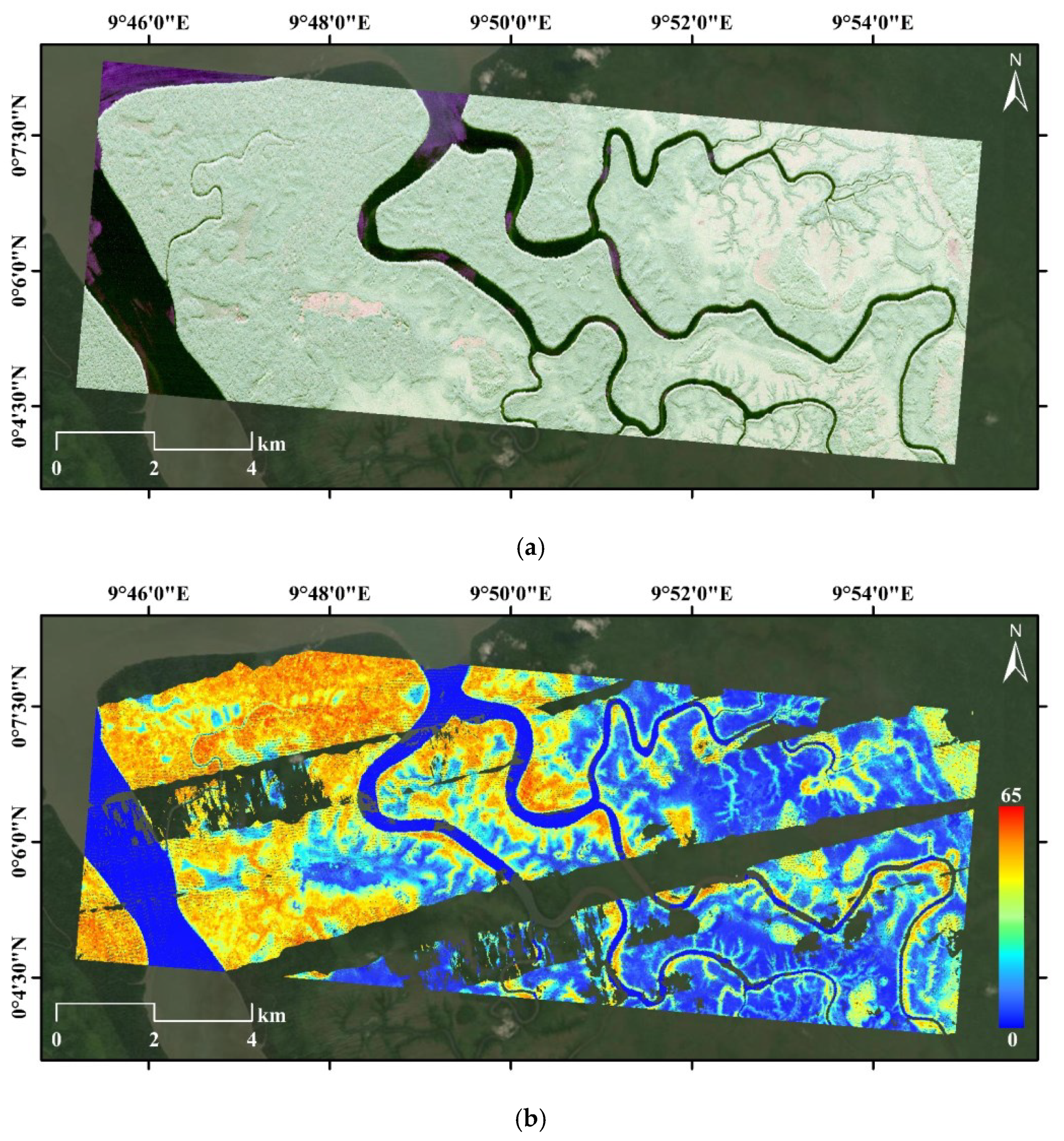
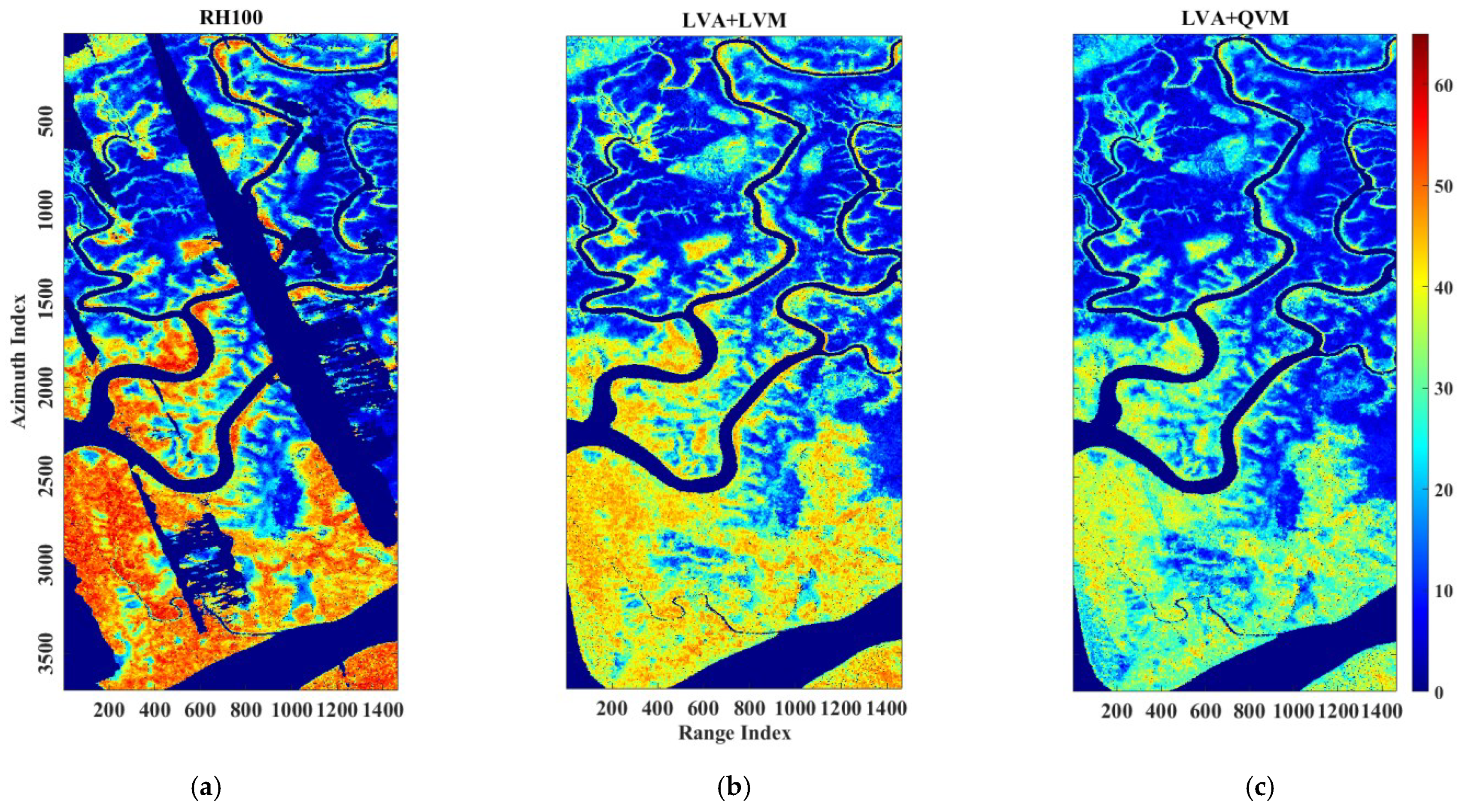
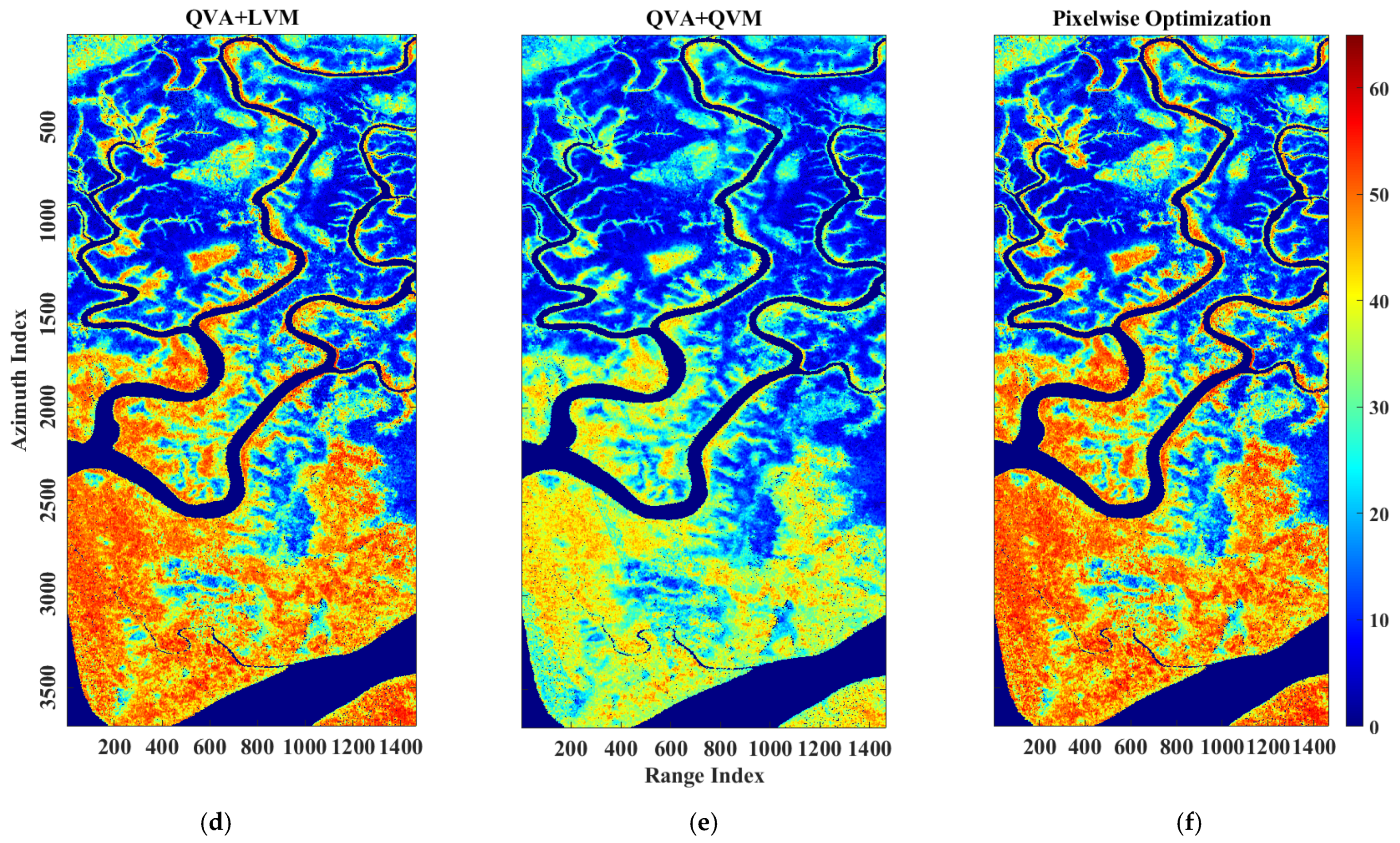
4.2.2. Pongara National Park
5. Discussion
5.1. Boreal Ecosystem Research and Monitoring Sites
5.2. Pongara National Park
5.3. Model Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreira, A.; Hajnsek, I.; Krieger, G.; Papathanassiou, K.; Eineder, M.; De Zan, F.; Younis, M.; Werner, M. Tandem-L: Monitoring the earth’s dynamics with InSAR and Pol-InSAR. In Proceedings of the PolInSAR 2009, Frascati, Italy, 26–30 January 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Siqueira, P.; Treuhaft, R. A physical scattering model of repeat-pass InSAR correlation for vegetation. Waves Random Complex Media 2017, 27, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garestier, F.; Le Toan, T. Forest modeling for height inversion using single-baseline InSAR/Pol-InSAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 1528–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A. Estimation of forest structure, ground, and canopy layer characteristics from multibaseline polarimetric interferometric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 1086–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garestier, F.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Champion, I. Forest height inversion using high-resolution P-band Pol-InSAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3544–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichierri, M.; Hajnsek, I. Comparing performances of RVoG and OVoG crop height inversion schemes from multi-frequency SAR data. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2016: 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 6–9 June 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cloude, S.; Papathanassiou, K. Three-stage inversion process for polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Proc.-Radar Sonar Navig. 2003, 150, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Guo, H.; Song, P.; Tian, B.; Li, X.; Sun, Z. Combination of PolInSAR and LiDAR techniques for forest height estimation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praks, J.; Kugler, F.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Hajnsek, I.; Hallikainen, M. Height estimation of boreal forest: Interferometric model-based inversion at L-and X-band versus HUTSCAT profiling scatterometer. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, S.; Michel, T.; Nuemann, M.; Lavalle, M.; Muellerschoen, R.; Chapman, B.; Jones, C.; Ahmed, R.; Lombardini, F.; Siqueira, P. Some first polarimetric-interferometric multi-baseline and tomographic results at Harvard forest using UAVSAR. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 5202–5205. [Google Scholar]
- Hajnsek, I.; Kugler, F.; Lee, S.-K.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Tropical-forest-parameter estimation by means of Pol-InSAR: The INDREX-II campaign. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugler, F.; Lee, S.-K.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Forest height estimation by means of Pol-InSAR data inversion: The role of the vertical wavenumber. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5294–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garestier, F.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Pine forest height inversion using single-pass X-band PolInSAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanassiou, K.; Cloude, S.R. The effect of temporal decorrelation on the inversion of forest parameters from PoI-InSAR data. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 1429–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Lavalle, M.; Hensley, S. Extraction of structural and dynamic properties of forests from polarimetric-interferometric SAR data affected by temporal decorrelation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4752–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, S.; Wheeler, K.; Sadowy, G.; Jones, C.; Shaffer, S.; Zebker, H.; Miller, T.; Heavey, B.; Chuang, E.; Chao, R. The UAVSAR instrument: Description and first results. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 26–30 May 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-K.; Kugler, F.; Papathanassiou, K.; Hajnsek, I. Quantification and compensation of temporal decorrelation effects in polarimetric SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 3106–3109. [Google Scholar]
- Lavalle, M.; Simard, M.; Hensley, S. A temporal decorrelation model for polarimetric radar interferometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2880–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatoyinbo, T.; Armston, J.; Simard, M.; Saatchi, S.; Denbina, M.; Lavalle, M.; Hofton, M.; Tang, H.; Marselis, S.; Pinto, N. The NASA AfriSAR campaign: Airborne SAR and lidar measurements of tropical forest structure and biomass in support of current and future space missions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.B.; Rabine, D.L.; Hofton, M.A. The Laser Vegetation Imaging Sensor: A medium-altitude, digitisation-only, airborne laser altimeter for mapping vegetation and topography. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denbina, M.; Simard, M.; Hawkins, B. Forest height estimation using multibaseline PolInSAR and sparse lidar data fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3415–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, M.; Denbina, M. An Assessment of Temporal Decorrelation Compensation Methods for Forest Canopy Height Estimation Using Airborne L-Band Same-Day Repeat-Pass Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, C.M.; Bhatti, J.S.; Norris, C.E. Chemical quality of aboveground litter inputs for jack pine and black spruce stands along the Canadian Boreal Forest Transect Case Study. Écoscience 2014, 21, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, A.K.; Ball, J.H.; Barr, A.G.; Black, T.A.; McCaughey, J.H.; Viterbo, P. Assessing land-surface-atmosphere coupling in the ERA-40 reanalysis with boreal forest data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 140, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsaranta, J.M.; Lieffers, V.J. Inequality of size and size increment in Pinus banksiana in relation to stand dynamics and annual growth rate. Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsaranta, J.M.; Lieffers, V.J. A fifty-year reconstruction of annual changes in the spatial distribution of Pinus banksiana stands: Does pattern fit competition theory? Plant Ecol. 2008, 199, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, C.; Ochieng, E.; Tieszen, L.L.; Zhu, Z.; Singh, A.; Loveland, T.; Masek, J.; Duke, N. Status and distribution of mangrove forests of the world using earth observation satellite data. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trettin, C.C.; Dai, Z.; Tang, W.; Lagomasino, D.; Thomas, N.; Lee, S.K.; Simard, M.; Ebanega, M.O.; Stoval, A.; Fatoyinbo, T.E. Mangrove carbon stocks in Pongara National Park, Gabon. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 259, 107432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.; Griffith, P.; Goetz, S.; Hoy, E.; Pinto, N.; McCubbin, I.; Thorpe, A.; Hofton, M.; Hodkinson, D.; Hansen, C. An overview of ABoVE airborne campaign data acquisitions and science opportunities. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 080201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Toan, T.; Quegan, S.; Davidson, M.; Balzter, H.; Paillou, P.; Papathanassiou, K.; Plummer, S.; Rocca, F.; Saatchi, S.; Shugart, H. The BIOMASS mission: Mapping global forest biomass to better understand the terrestrial carbon cycle. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.; Hensley, S.; Shaffer, S.; Edelstein, W.; Kim, Y.; Kumar, R.; Misra, T.; Bhan, R.; Sagi, R. The NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) mission dual-band radar instrument preliminary design. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 3832–3835. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, S.; Armston, J.; Hofton, M.; Sun, X.; Tang, H.; Duncanson, L.I.; Kellner, J.R.; Dubayah, R. The GEDI simulator: A large-footprint waveform lidar simulator for calibration and validation of spaceborne missions. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, S.; Ahmed, R.; Chapman, B.; Hawkins, B.; Lavalle, M.; Pinto, N.; Pardini, M.; Papathanassiou, K.; Siqueria, P.; Treuhaft, R. A Comparison of L-band and S-band Interferometry and Tomography of the BERMS Borel Forest with UAVSAR and F-SAR Datasets. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2021 13th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Online, 29 March–1 April 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hensley, S.; Michel, T.; Neumann, M.; Lavalle, M.; Ahmed, R.; Muellerschoen, R.; Chapman, B. A Comparison of Multi-Baseline Polarimetric Inteferometry at La Amistad and La Selva, Costa Rica with a Modified PolSARProSim Scattering Tool. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2014 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 3–5 June 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Treuhaft, R.N.; Siqueira, P.R. Vertical structure of vegetated land surfaces from interferometric and polarimetric radar. Radio Sci. 2000, 35, 141–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanassiou, K.P.; Cloude, S.R. Single-baseline polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denbina, M.; Simard, M. Kapok: An open source Python library for PolInSAR forest height estimation using UAVSAR data. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 4314–4317. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Canada. Historical Data-Climate-Environment and Climate Change Canada; Government of Canada: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2018.
- The Global Historical Weather and Climate Data. Available online: https://tcktcktck.org/gabon/estuaire/libreville (accessed on 11 October 2022).


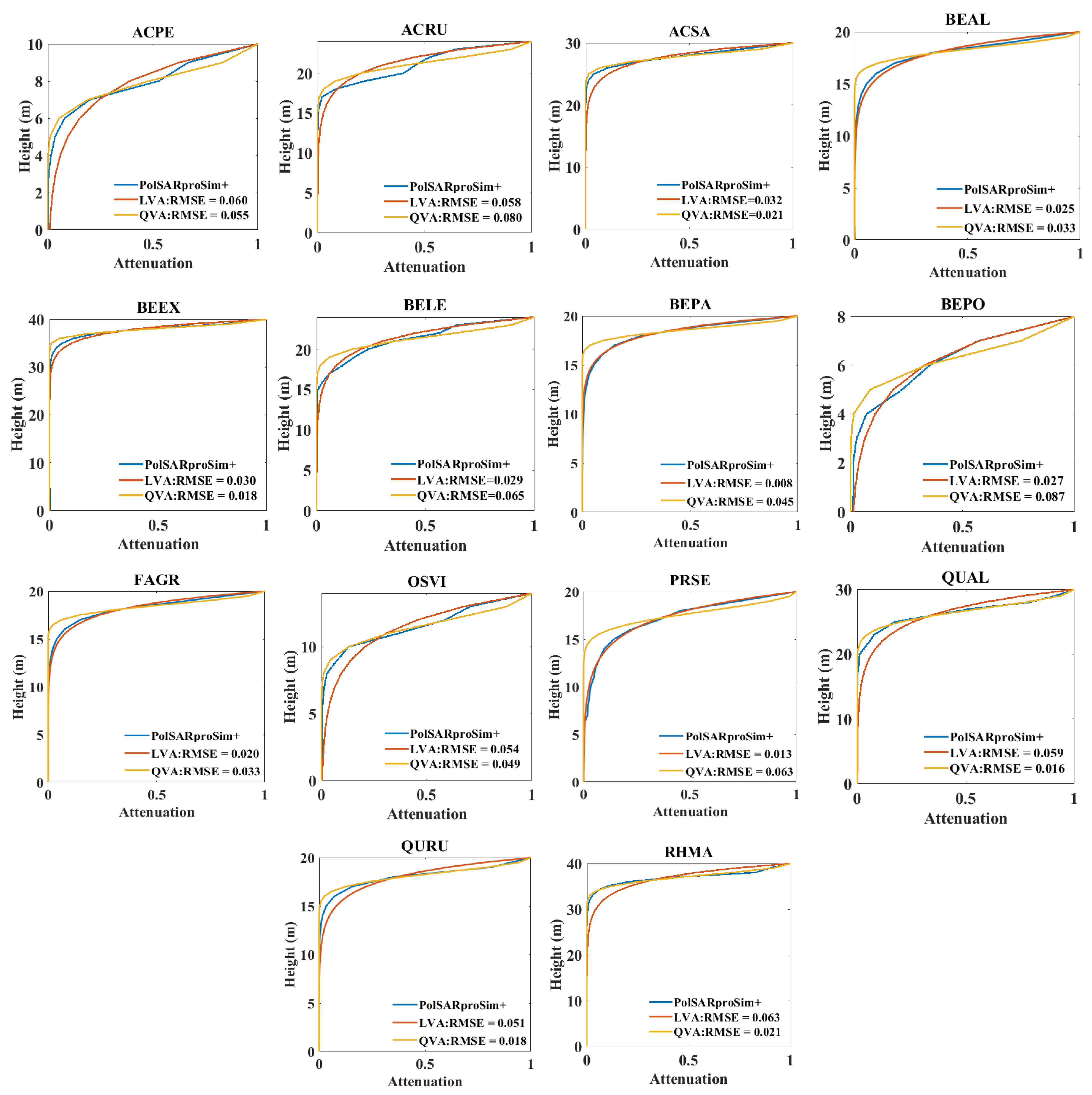
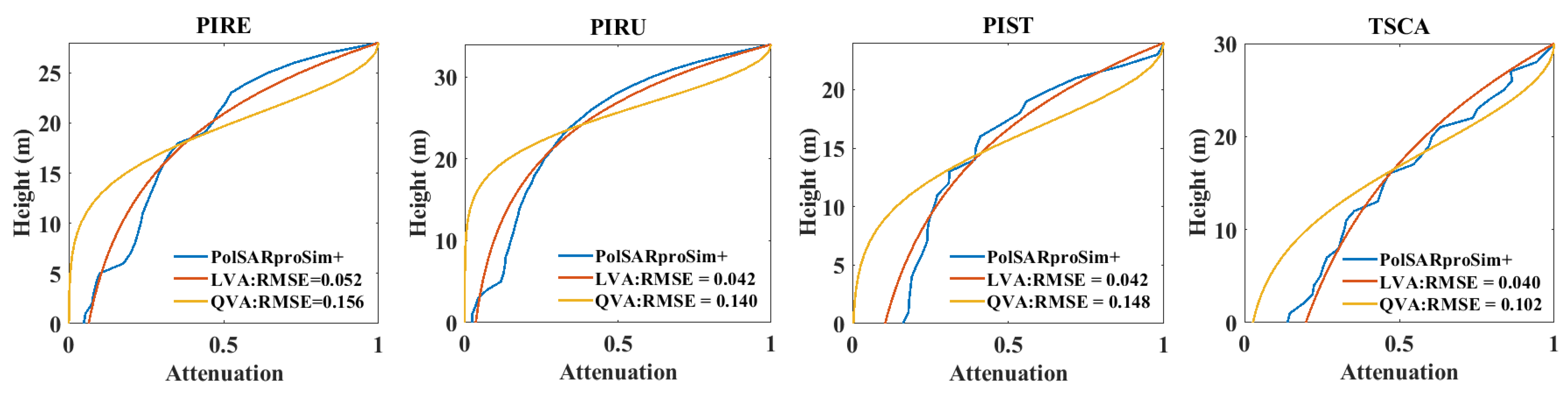


| Tree Species | Type | Average Height (m) | Density (Trees/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Striped maple (ACPE) | Deciduous | 10 | 36 |
| Red maple (ACRU) | Deciduous | 24 | 36 |
| Sugar maple (ACSA) | Deciduous | 30 | 33 |
| Yellow birch (BEAL) | Deciduous | 20 | 19 |
| Brazil nut (BEEX) | Deciduous | 40 | 36 |
| Sweet birch (BELE) | Deciduous | 24 | 51 |
| Paper birch (BEPA) | Deciduous | 20 | 51 |
| Grey birch (BEPO) | Deciduous | 8 | 51 |
| American beech (FAGR) | Deciduous | 20 | 33 |
| American hophornbeam (OSVI) | Deciduous | 14 | 60 |
| Red pine (PIRE) | Coniferous | 28 | 44 |
| Red spruce (PIRU) | Coniferous | 34 | 25 |
| White pine (PIST) | Coniferous | 24 | 26 |
| Black cherry (PRSE) | Deciduous | 20 | 51 |
| White oak (QUAL) | Deciduous | 30 | 27 |
| Red oak (QURU) | Deciduous | 20 | 28 |
| Red mangrove (RHMA) | Deciduous | 40 | 69 |
| Eastern hemlock (TSCA) | Coniferous | 30 | 15 |
| Tree Species | Type | Best-Fit Model |
|---|---|---|
| ACPE | Deciduous | QVA |
| ACRU | Deciduous | LVA |
| ACSA | Deciduous | QVA |
| BEAL | Deciduous | LVA |
| BEEX | Deciduous | QVA |
| BELE | Deciduous | LVA |
| BEPA | Deciduous | LVA |
| BEPO | Deciduous | LVA |
| FAGR | Deciduous | LVA |
| OSVI | Deciduous | QVA |
| PRSE | Deciduous | LVA |
| QUAL | Deciduous | QVA |
| QURU | Deciduous | QVA |
| RHMA | Deciduous | QVA |
| PIRE | Coniferous | LVA |
| PIRU | Coniferous | LVA |
| PIST | Coniferous | LVA |
| TSCA | Coniferous | LVA |
| LVA + LVM | LVA+QVM | QVA + LVM | QVA + QVM | Optimization | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 5.31 m | 3.56 m | 6.56 m | 4.43 m | 3.21 m |
| Bias | 4.43 m | 2.05 m | 5.74 m | 3.13 m | 1.45 m |
| R2 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.65 |
| LVA + LVM | LVA + QVM | QVA + LVM | QVA + QVM | Optimization | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 7.71 m | 10.83 m | 6.83 m | 8.09 m | 6.48 m |
| Bias | −2.74 m | −7.29 m | 0.43 m | −4.25 m | 0.41 m |
| R2 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Hensley, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Ge, L. Improved Model-Based Forest Height Inversion Using Airborne L-Band Repeat-Pass Dual-Baseline Pol-InSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205234
Zhang Q, Hensley S, Zhang R, Liu C, Ge L. Improved Model-Based Forest Height Inversion Using Airborne L-Band Repeat-Pass Dual-Baseline Pol-InSAR Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(20):5234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205234
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qi, Scott Hensley, Ruiheng Zhang, Chang Liu, and Linlin Ge. 2022. "Improved Model-Based Forest Height Inversion Using Airborne L-Band Repeat-Pass Dual-Baseline Pol-InSAR Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 20: 5234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205234
APA StyleZhang, Q., Hensley, S., Zhang, R., Liu, C., & Ge, L. (2022). Improved Model-Based Forest Height Inversion Using Airborne L-Band Repeat-Pass Dual-Baseline Pol-InSAR Data. Remote Sensing, 14(20), 5234. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205234








