Using Remote Sensing Methods to Study Active Geomorphologic Processes on Cantabrian Coastal Cliffs
Abstract
1. Introduction
Settings of Study Area
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis of Landscape Deformations from Photogrammetric Surveys
2.2. Ground Motion Detection Applying A-DInSAR Techniques and Sentinel-1 Satellite Data
2.3. Electrical Resistivity Tomography Lines
2.4. Geomorphological Mapping and Geological Interpretation of the Tazones Lighthouse Slope
3. Results
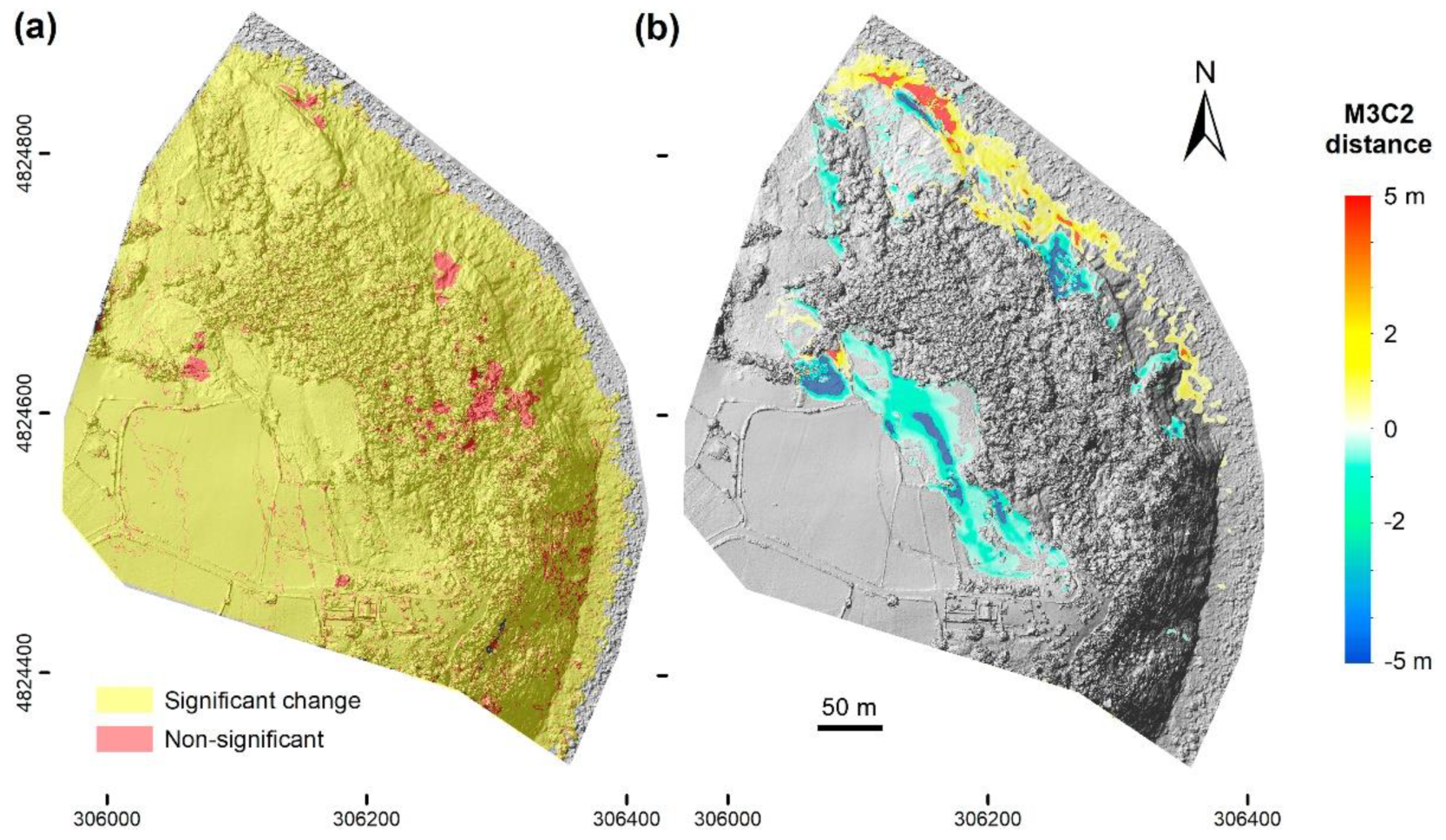
3.1. Analysis of Landscape Deformations from Photogrammetric Surveys
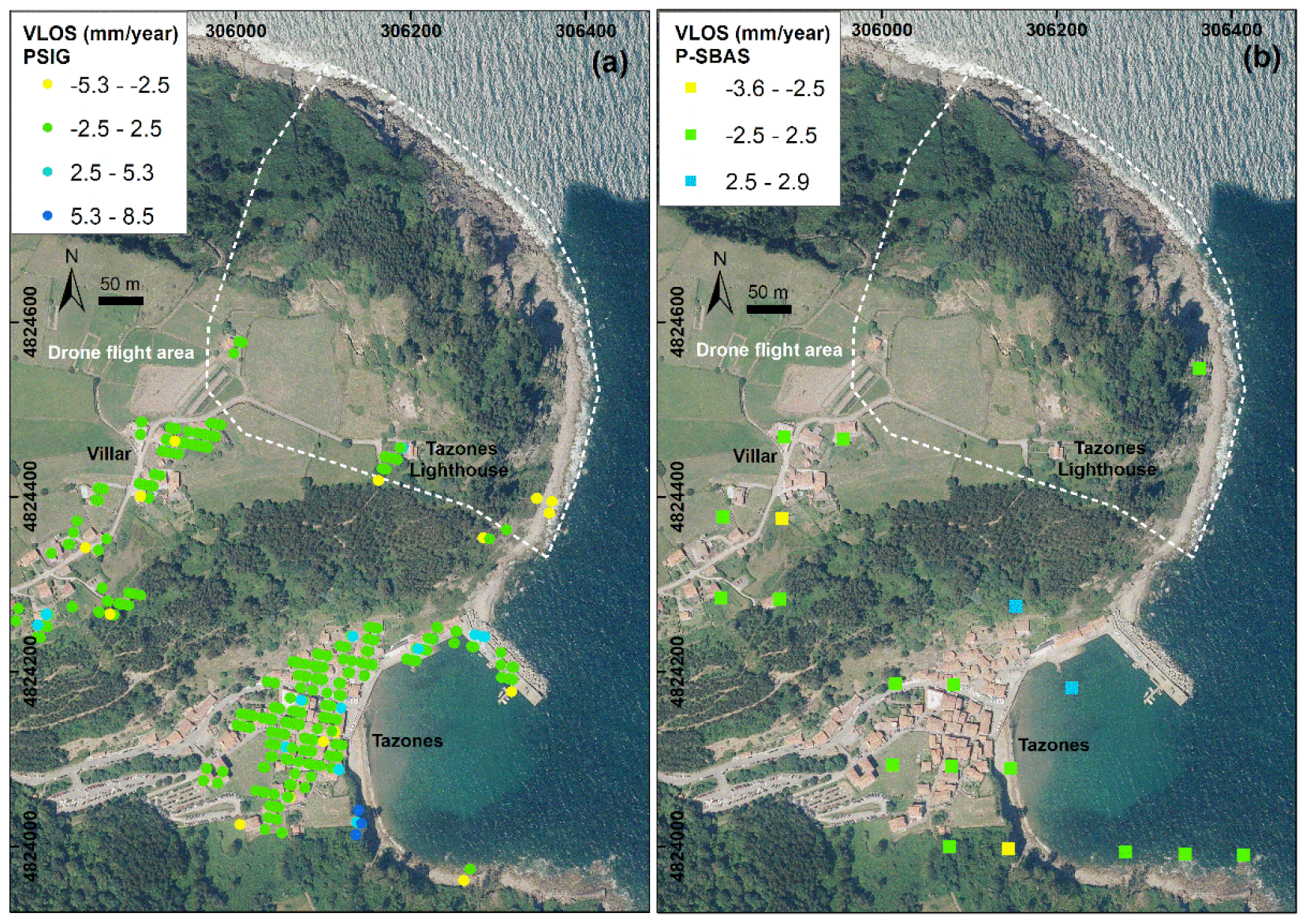
3.2. Ground Motion Detection Applying A-DInSAR Techniques and Sentinel-1 Satellite Data
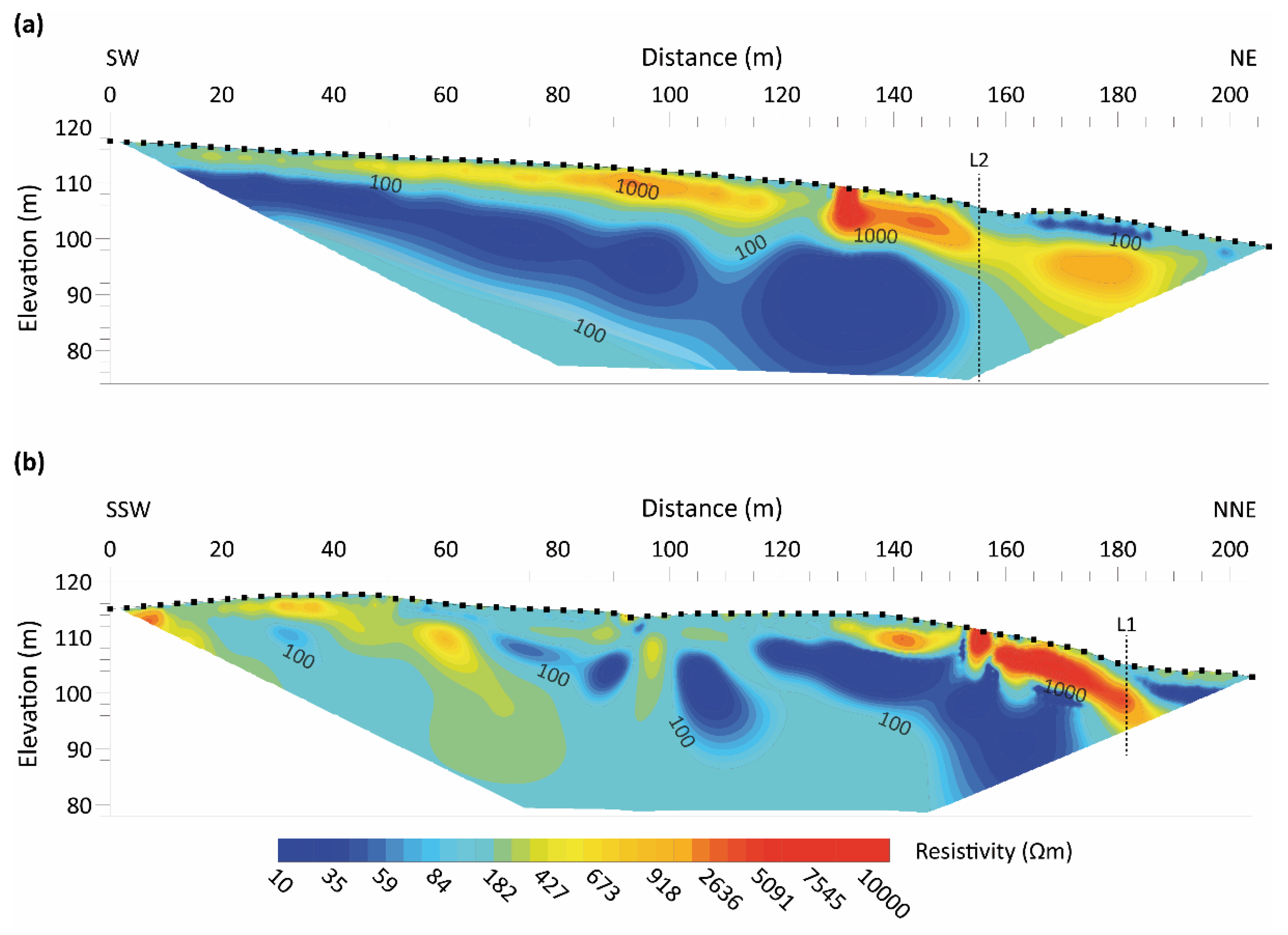
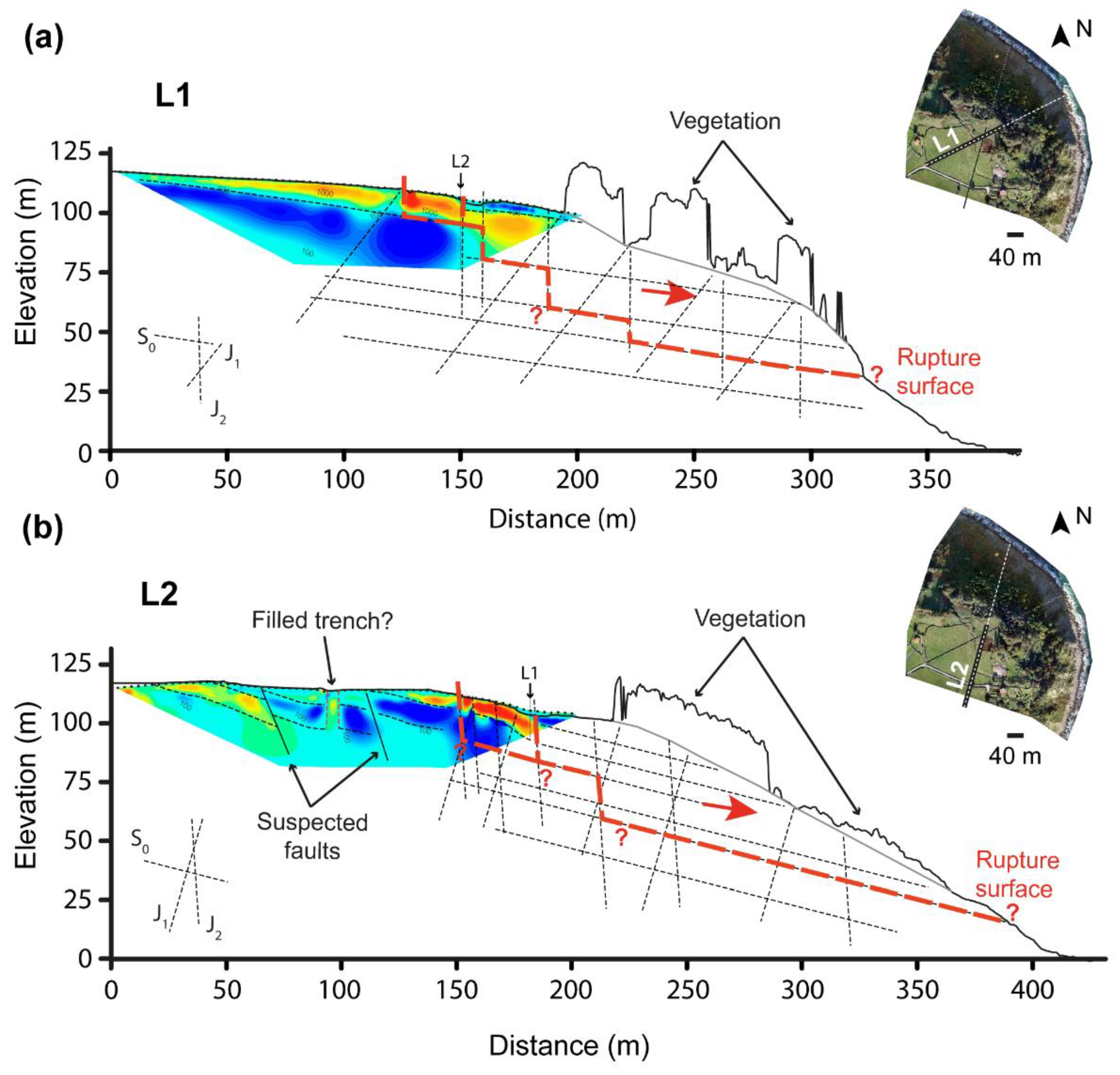
3.3. Interpretation of the Electrical Resistivity Tomography Lines
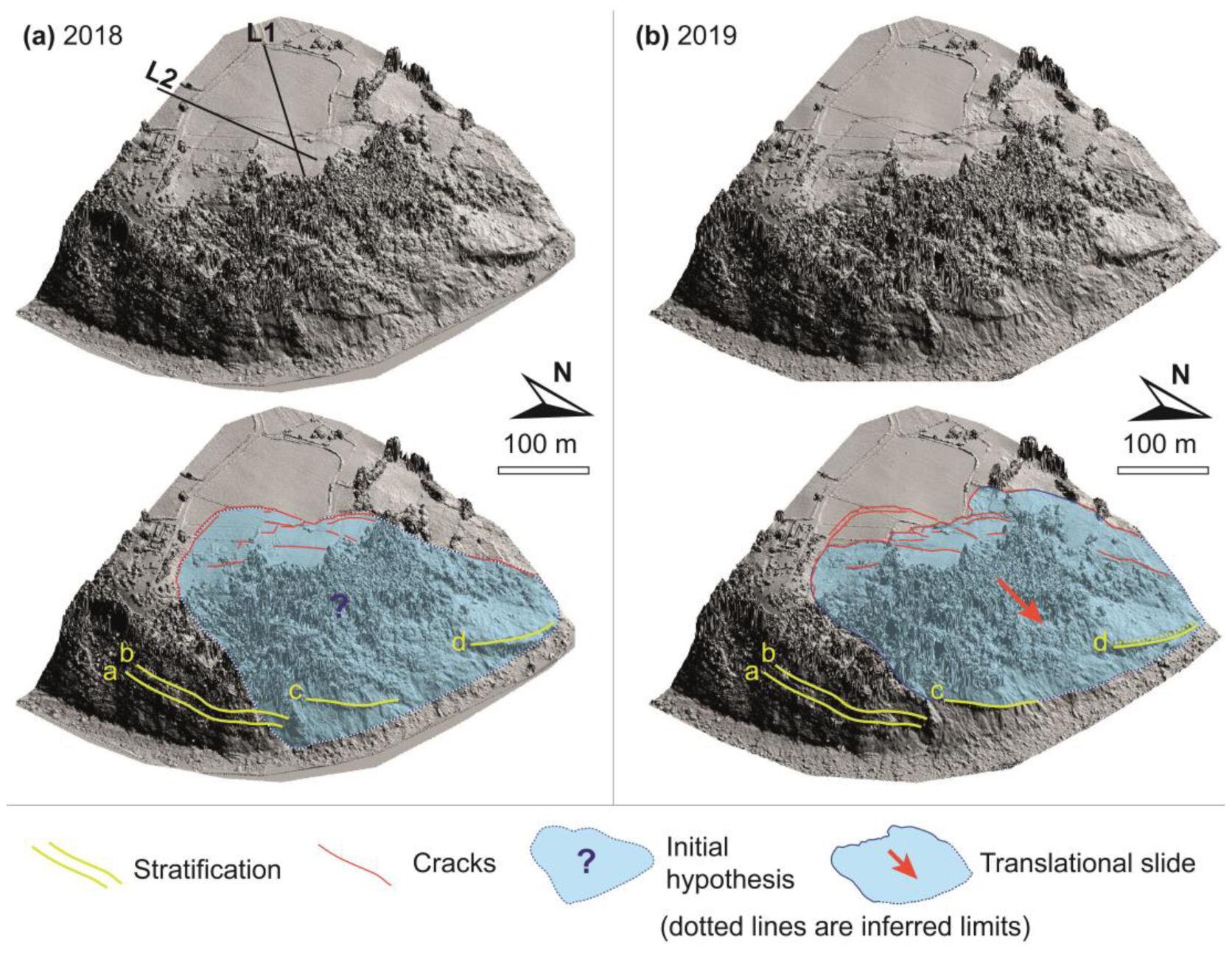
3.4. Geological and Geomorphological Interpretation of the Tazones Lighthouse Slope
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cendrero, A.; Remondo, J.; Bonachea, J.; Rivas, V.; Soto, J. Sensitivity of Landscape Evolution and Geomorphic Processes to Direct and Indirect Human Influence. Geogr. Fis. E Din. Quat. 2006, 29, 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Gariano, S.L.; Guzzetti, F. Landslides in a Changing Climate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 162, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Sanderson, A.; Tyson, P.D.; Jäger, J.; Matson, P.A.; Moore, B., III; Oldfield, F.; Richardson, K.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; Turner, B.L., II; et al. Global Change and the Earth System: A Planet under Pressure; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Korup, O.; Clague, J.J.; Hermanns, R.L.; Hewitt, K.; Strom, A.L.; Weidinger, J.T. Giant Landslides, Topography, and Erosion. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 261, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chang, K.T.; Lee, H.Y.; Chiang, S.H. Average Landslide Erosion Rate at the Watershed Scale in Southern Taiwan Estimated from Magnitude and Frequency of Rainfall. Geomorphology 2015, 228, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, B.G.; Park, H.J.; Catani, F.; Simoni, A.; Berti, M. Landslide Prediction, Monitoring and Early Warning: A Concise Review of State-of-the-Art. Geosci. J. 2017, 21, 1033–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pourghasemi, H.R. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Machine Learning Algorithms and Comparison of Their Performance at Abha Basin, Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Qin, J.; Sheng, H.; Huang, L. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Land Subsidence in Wuhan, China from 2017 to 2021. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, J.; Dario, C.; Marc-Henri, D.; Thierry, O.; Ivanna Marina, P.; Bejamin, R. A Review of Methods Used to Estimate Initial Landslide Failure Surface Depths and Volumes. Eng. Geol. 2020, 267, 105478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Montes, I.; Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Sánchez-García, M.J.; Alcántara-Carrió, J.; Martín-Velázquez, S.; Gómez-Ortiz, D.; Martín-Crespo, T. Mapping of Landslide Susceptibility of Coastal Cliffs: The Mont-Roig Del Camp Case Study. Geol. Acta 2012, 10, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, T.; Clemente, J.A.; Damas Mollá, L.; Izagirre, E.; Uriarte, J.A. Analysis of Instabilities in the Basque Coast Geopark Coastal Cliffs for Its Environmentally Friendly Management (Basque-Cantabrian Basin, Northern Spain). Eng. Geol. 2021, 283, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prémaillon, M.; Regard, V.; Dewez, T.J.B.; Auda, Y. GlobR2C2 (Global Recession Rates of Coastal Cliffs): A Global Relational Database to Investigate Coastal Rocky Cliff Erosion Rate Variations. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2018, 6, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, M.D.; Rood, D.H.; Ellis, M.A.; Anderson, R.S.; Dornbusch, U. Recent Acceleration in Coastal Cliff Retreat Rates on the South Coast of Great Britain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13336–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeuw, R.; Rust, D.; Solana, C.; Dewdney, C.; Robertson, R. Large Coastal Landslides and Tsunami Hazard in the Caribbean. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2009, 90, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Cuesta, M.J.; Valenzuela, P.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, L.; Ballesteros, D.; Jiménez-Sánchez, M.; Piñuela, L.; García-Ramos, J.C. Cliff Coast of Asturias. In The Spanish Coastal Systems: Dynamic Processes, Sediments and Management; Morales, J.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Cuesta, M.; Ferrer-Serrano, A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, L.; López-Fernández, C.; Jiménez-Sánchez, M. Análisis Del Retroceso de La Costa Cantábrica En El Entorno Del Cabo Peñas. Geogaceta 2020, 68, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez-Cuesta, M.J.; González-Pumariega, P.; Valenzuela, P.; López-Fernández, C.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, L.; Ballesteros, D.; Mora, M.; Meléndez, M.; Herrera, F.; Marigil, M.A.; et al. Understanding the Retreat of the Jurassic Cantabrian Coast (N. Spain): Comprehensive Monitoring and 4D Evolution Model of the Tazones Lighthouse Landslide. Mar. Geol. 2022, 449, 106836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, M.; García-Ramos, J.C.; Suarez de Centi, C. The Jurassic Sedimentation in Asturias (N. Spain). Trab. Geol. 1986, 16, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramburu, C.; Bermúdez-Rochas, D.D.; Delvene, G.; Fürsich, F.T.; García-Ramos, J.C.; Piñuela, L.; Ruiz-Omeñaca, J.I.; Werner, W. Las Sucesiones Litorales y Marinas Restringidas Del Jurásico Superior. Acantilados de Tereñes (Ribadesella) y de La Playa de La Griega (Colunga); García-Ramos, J.C., Aramburu, C., Eds.; Universidad de Oviedo: Colunga, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Uzkeda, H.; Bulnes, M.; Poblet, J.; García-Ramos, J.C.; Piñuela, L. Jurassic Extension and Cenozoic Inversion Tectonics in the Asturian Basin, NW Iberian Peninsula: 3D Structural Model and Kinematic Evolution. J. Struct. Geol. 2016, 90, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde, J.; Cossio, J.; Muñoz de la Nava, P.; Cembranos, V. Posibilidades de Azabaches en Asturias; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 1986; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Monte Carreño, V. El Azabache. Piedra Mágica, Joya, Emblema Jacobeo; Picu Urriellu: Gijón, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- López, M.T. Mapa de Rocas y Minerales Industriales de Asturias. Escala 1:200.000; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo, S.; Sierra, M.; Fernández, S.; Herrera, D. Plan Especial de Protección y Rehabilitación de Tazones-Villaviciosa; Ayuntamiento de Villaviciosa: Villaviciosa, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli, R.; Giannini, G.; Ramírez del Pozo, J.; Beroiz, C.; Barón, A. Mapa Geológico de España Escala 1:50.000, No 15 (14-3) Lastres; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Spanish National Geographic Institute. Reseña de Estación Permanente—ERGNSS (XIX1). Available online: https://datos-geodesia.ign.es/ERGNSS/fichas/XIX1.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Taddia, Y.; Stecchi, F.; Pellegrinelli, A. Coastal Mapping Using Dji Phantom 4 RTK in Post-Processing Kinematic Mode. Drones 2020, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, G.; Gonçalves, D.; Gómez-gutiérrez, Á.; Andriolo, U.; Pérez-alvárez, J.A. 3D Reconstruction of Coastal Cliffs from Fixed-wing and Multi-rotor Uas: Impact of Sfm-mvs Processing Parameters, Image Redundancy and Acquisition Geometry. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grottoli, E.; Biausque, M.; Rogers, D.; Jackson, D.W.T.; Cooper, J.A.G. Structure-from-Motion-Derived Digital Surface Models from Historical Aerial Photographs: A New 3D Application for Coastal Dune Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lague, D.; Brodu, N.; Leroux, J. Accurate 3D Comparison of Complex Topography with Terrestrial Laser Scanner: Application to the Rangitikei Canyon (N-Z). ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 82, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gutiérrez, Á.; Gonçalves, G.R. Surveying Coastal Cliffs Using Two UAV Platforms (Multirotor and Fixed-Wing) and Three Different Approaches for the Estimation of Volumetric Changes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 8143–8175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, L.; Cellone, F. SfM-MVS and GIS Analysis of Shoreline Changes in a Coastal Wetland, Parque Costero Del Sur Biosphere Reserve, Argentina. Geocarto Int. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A.; Solari, L.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Monserrat, O.; Bianchini, S.; Herrera, G.; Crosetto, M.; Sarro, R.; González-Alonso, E.; Mateos, R.M.; et al. A Methodology to Detect and Update Active Deformation Areas Based on Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanthéry, N.; Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Crippa, B.; Mróz, M. Data Analysis Tools for Persistent Scatterer Interferometry Based on Sentinel-1 Data. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52 (Suppl. 1), 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biescas, E.; Crosetto, M.; Agudo, M.; Monserrat, O.; Crippa, B. Two Radar Interferometric Approaches to Monitor Slow and Fast Land Deformation. J. Surv. Eng. 2007, 133, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanthéry, N.; Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Crippa, B. An Approach to Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6662–6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, F.; Elefante, S.; Imperatore, P.; Zinno, I.; Manunta, M.; De Luca, C.; Lanari, R. SBAS-DInSAR Parallel Processing for Deformation Time-Series Computation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.; Cuccu, R.; Elefante, S.; Zinno, I.; Manunta, M.; Casola, V.; Rivolta, G.; Lanari, R.; Casu, F. An On-Demand Web Tool for the Unsupervised Retrieval of Earth’s Surface Deformation from SAR Data: The P-SBAS Service within the ESA G-POD Environment. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15630–15650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manunta, M.; Bonano, M.; Buonanno, S.; Casu, F.; De Luca, C.; Fusco, A.; Lanari, R.; Manzo, M.; Ojha, C.; Pepe, A.; et al. Unsupervised Parallel SBAS-DInSAR Chain for Massive and Systematic Sentinel-1 Data Processing. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. 2016, 2016, 3890–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galve, J.P.; Pérez-Peña, J.V.; Azañón, J.M.; Closson, D.; Caló, F.; Reyes-Carmona, C.; Jabaloy, A.; Ruano, P.; Mateos, R.M.; Notti, D.; et al. Evaluation of the SBAS InSAR Service of the European Space Agency’s Geohazard Exploitation Platform (GEP). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geohazards-TEP. Geohazard Exploitation Platform. Available online: https://geohazards-tep.eu/#! (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Ragan, D.M. Structural Geology: An Introduction to Geometrical Techniques; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz de Argandoña, V.G.; Calleja, L.; Suárez Del Río, L.M.; Rodríguez-Rey, A.; Celorio, C. Durabilidad En Ambientes Húmedos de La Arenisca de La Marina (Formación Lastres, Jurásico Superior de Asturias). Trab. Geol. 2005, 25, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ramos, J.C. El Jurásico de La Costa Centro-Oriental de Asturias. Un Monumento Natural de Alto Interés Patrimonial. Geo-Temas 2013, 14, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Varnes, D.J. Slope Movement Types and Processes. In Landslides: Analysis and Control; Special Rep., 17; Schuster, R.L., Krizek, R.J., Eds.; The National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; pp. 11–33. [Google Scholar]
- Crosetto, M.; Luzi, G.; Monserrat, O.; Barra, A.; Cuevas-González, M.; Palamá, R.; Krishnakumar, V.; Wassie, Y.; Mirmazloumi, S.M.; Espín-López, P.; et al. Deformation Monitoring Using SAR Interferometry and Active and Passive Reflectors. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. ISPRS Arch. 2020, 43, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, G.; Espín-López, P.F.; Pérez, F.M.; Monserrat, O.; Crosetto, M. A Low-Cost Active Reflector for Interferometric Monitoring Based on Sentinel-1 Sar Images. Sensors 2021, 21, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Gili, J.A.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Corominas, J.; Serral, D. Interferometric SAR Monitoring of the Vallcebre Landslide (Spain) Using Corner Reflectors. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, M.; Schlögel, R.; Bruzzone, L.; Cuozzo, G. Integration of PSI, MAI, and Intensity-Based Sub-Pixel Offset Tracking Results for Landslide Monitoring with X-Band Corner Reflectors-Italian Alps (Corvara). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Toyos, L.; Domínguez-Cuesta, M.J.; Piñuela, L. Procesos de Gravedad y Hallazgos Paleontológicos En La Costa de Los Dinosaurios (Asturias, N España). Geogaceta 2021, 70, 15–18. [Google Scholar]

| 2018 | 2019 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCP (9) | CP (12) | GCP (8) | CP (7) | |
| X | 0.028 | 1.445 | 0.528 | 2.863 |
| Y | 0.061 | 1.604 | 0.711 | 2.761 |
| Z | 0.014 | 3.438 | 0.341 | 1.538 |
| Satellite | Sentinel-1 |
|---|---|
| Sensor | A/B |
| Band | C |
| Wavelength | 5.55 cm |
| Acquisition mode | Interferometric Wide |
| Polarization | VV |
| SAR product | Single Look Complex |
| Acquisition orbit | Descending |
| Temporal period | 1 April 2018–2 May 2020 |
| Revisit period | 6–12 days |
| Resolution | 14 × 4 m |
| Incidence angle | 39° |
| Track | 154 |
| Number of SAR images | 113 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Domínguez-Cuesta, M.J.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, L.; López-Fernández, C.; Pando, L.; Cuervas-Mons, J.; Olona, J.; González-Pumariega, P.; Serrano, J.; Valenzuela, P.; Jiménez-Sánchez, M. Using Remote Sensing Methods to Study Active Geomorphologic Processes on Cantabrian Coastal Cliffs. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205139
Domínguez-Cuesta MJ, Rodríguez-Rodríguez L, López-Fernández C, Pando L, Cuervas-Mons J, Olona J, González-Pumariega P, Serrano J, Valenzuela P, Jiménez-Sánchez M. Using Remote Sensing Methods to Study Active Geomorphologic Processes on Cantabrian Coastal Cliffs. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(20):5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205139
Chicago/Turabian StyleDomínguez-Cuesta, María José, Laura Rodríguez-Rodríguez, Carlos López-Fernández, Luis Pando, José Cuervas-Mons, Javier Olona, Pelayo González-Pumariega, Jaime Serrano, Pablo Valenzuela, and Montserrat Jiménez-Sánchez. 2022. "Using Remote Sensing Methods to Study Active Geomorphologic Processes on Cantabrian Coastal Cliffs" Remote Sensing 14, no. 20: 5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205139
APA StyleDomínguez-Cuesta, M. J., Rodríguez-Rodríguez, L., López-Fernández, C., Pando, L., Cuervas-Mons, J., Olona, J., González-Pumariega, P., Serrano, J., Valenzuela, P., & Jiménez-Sánchez, M. (2022). Using Remote Sensing Methods to Study Active Geomorphologic Processes on Cantabrian Coastal Cliffs. Remote Sensing, 14(20), 5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205139








