Reconstruction of Monthly Surface Nutrient Concentrations in the Yellow and Bohai Seas from 2003–2019 Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
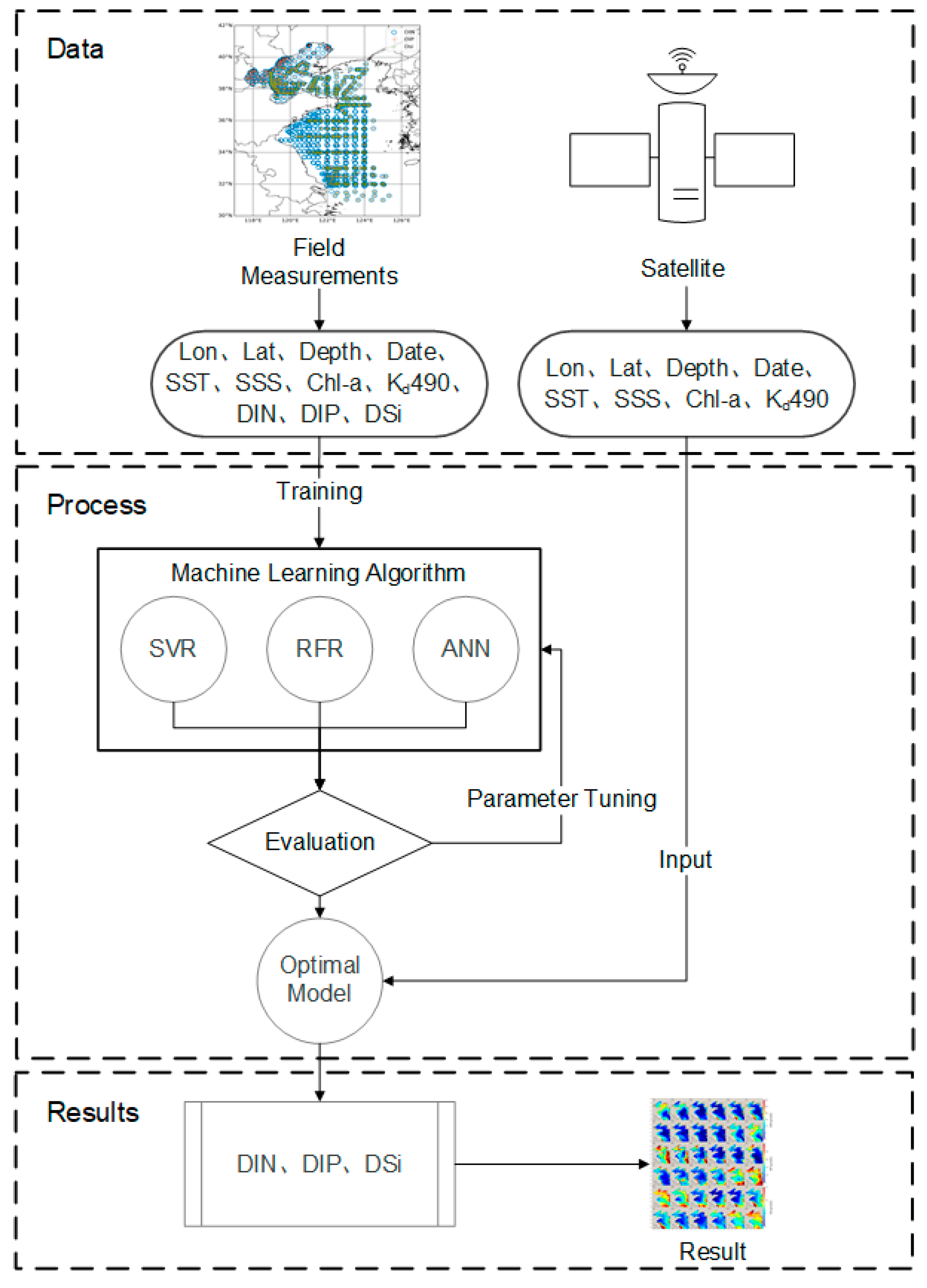
2.1. Design of the Machine-Learning Model for Sea Surface Nutrient Concentrations
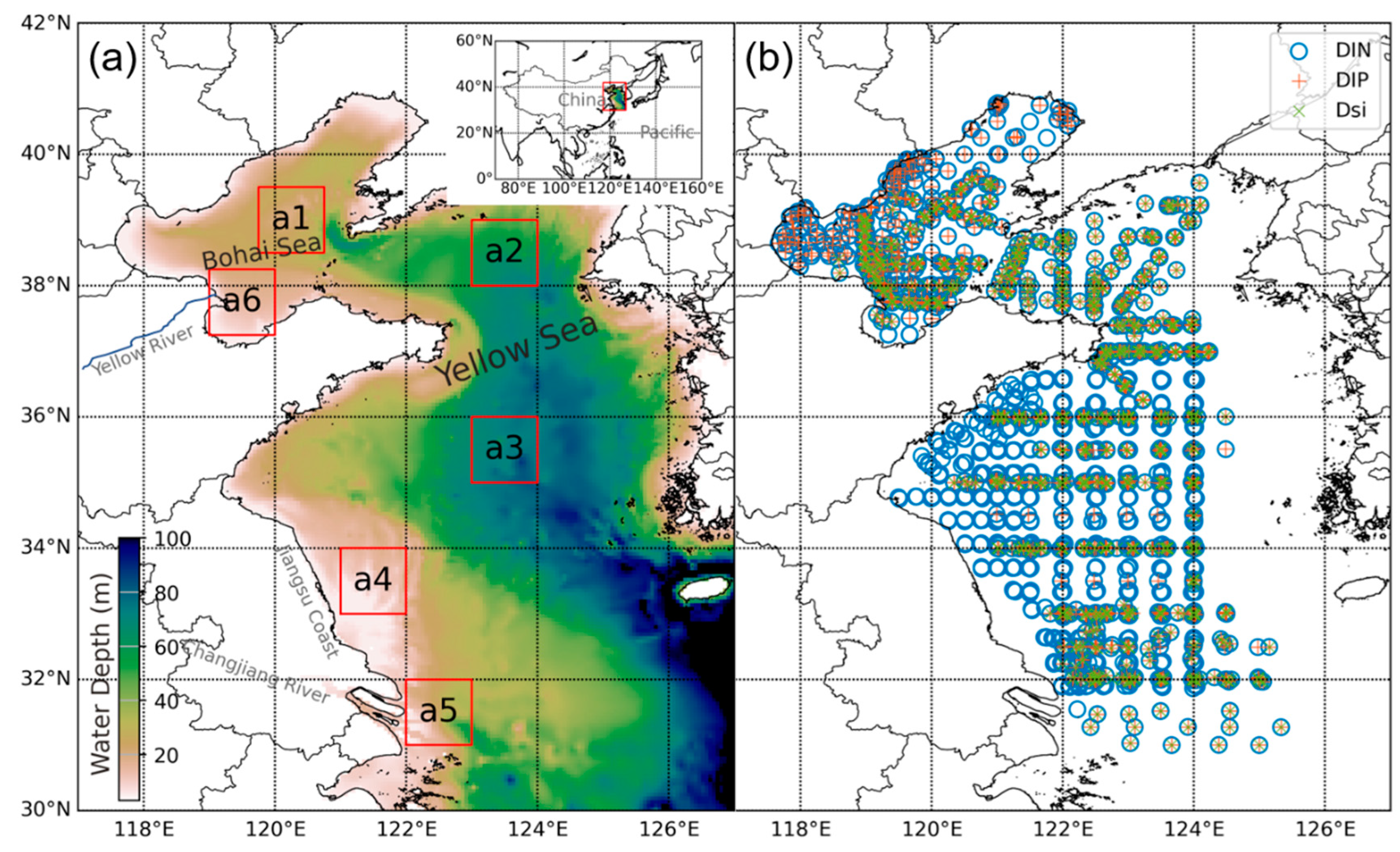
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. In Situ Measured Data
2.2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. Machine-Learning Algorithms
2.4. Evaluation of Machine-Learning Models
2.5. Analysis of Effects of Environmental Factors
3. Results
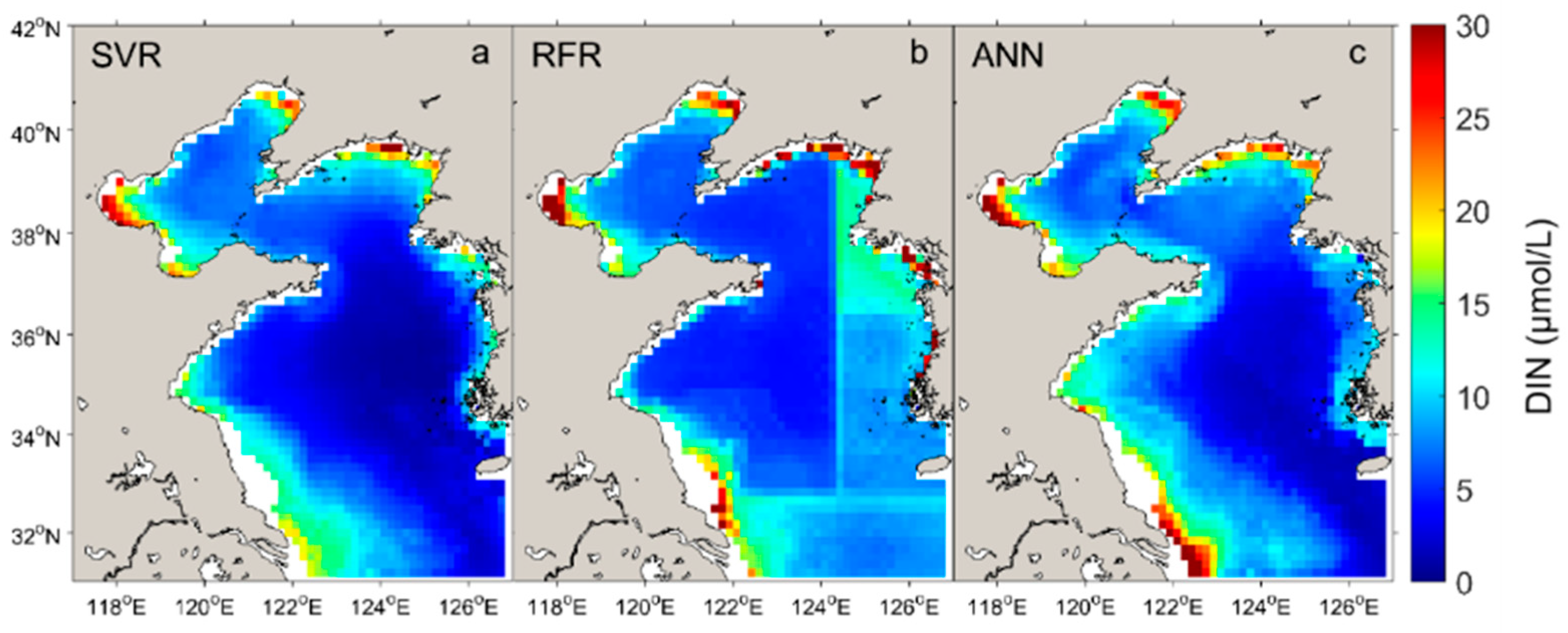
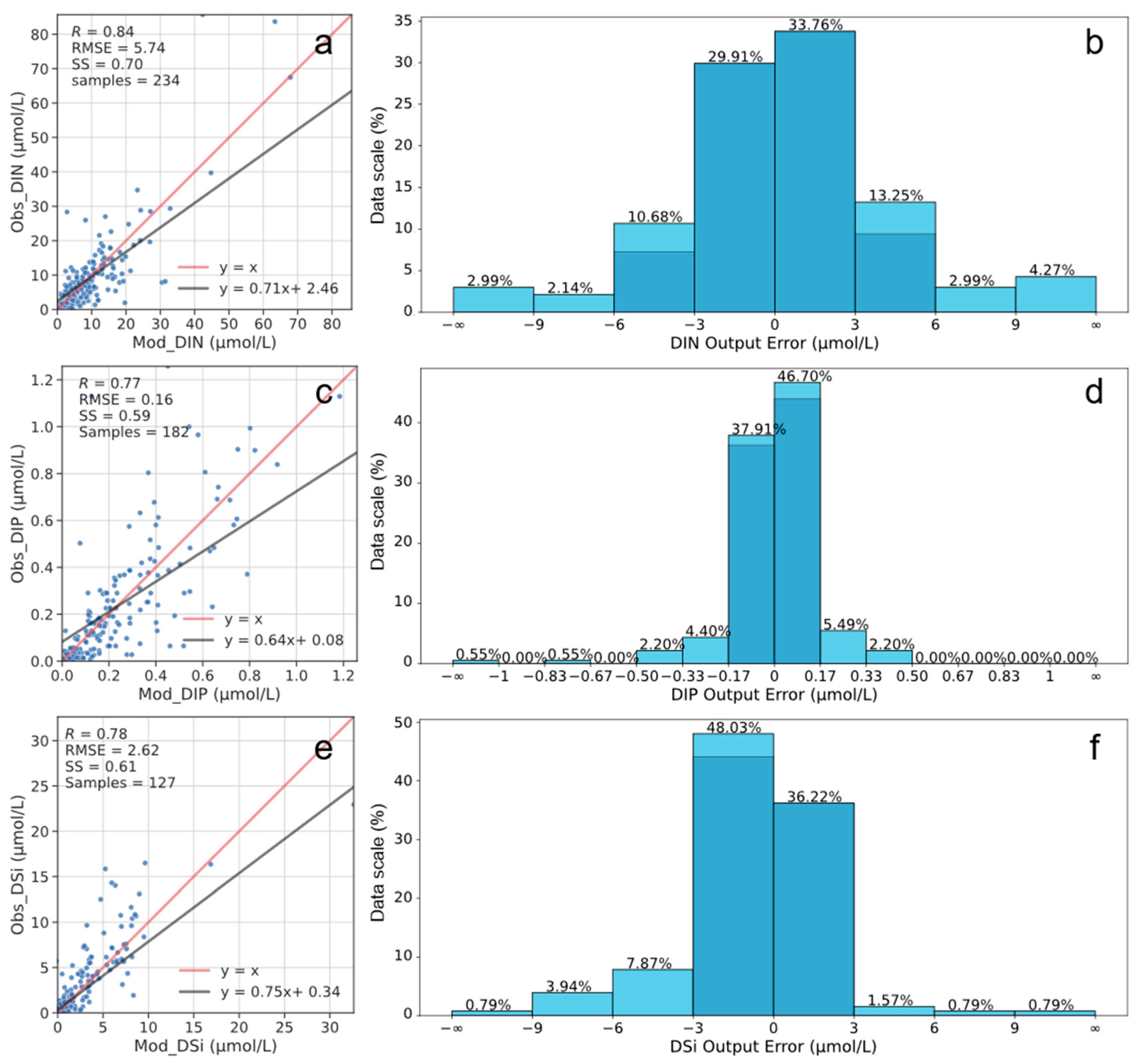
3.1. Evaluation of Machine-Learning Models
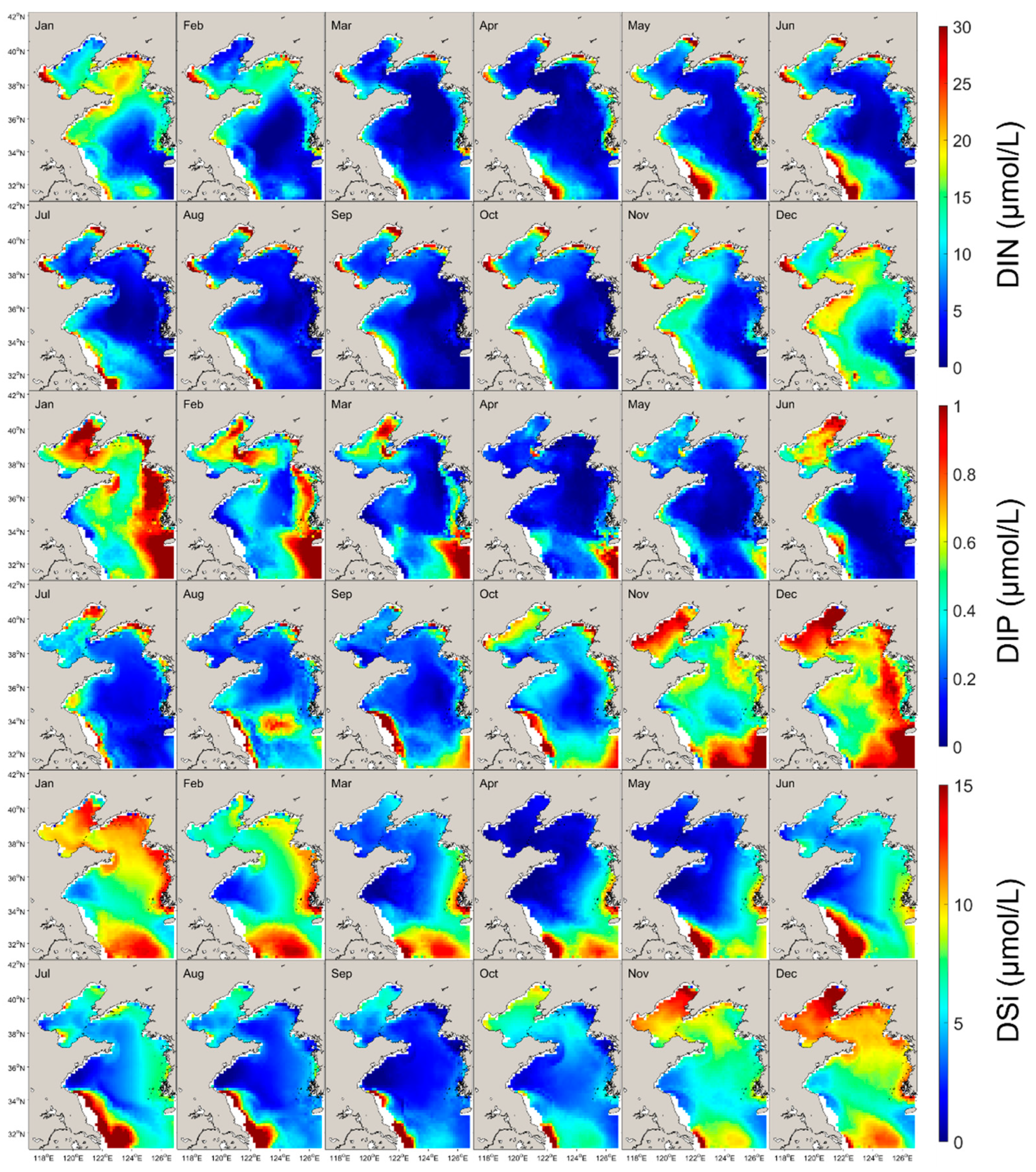
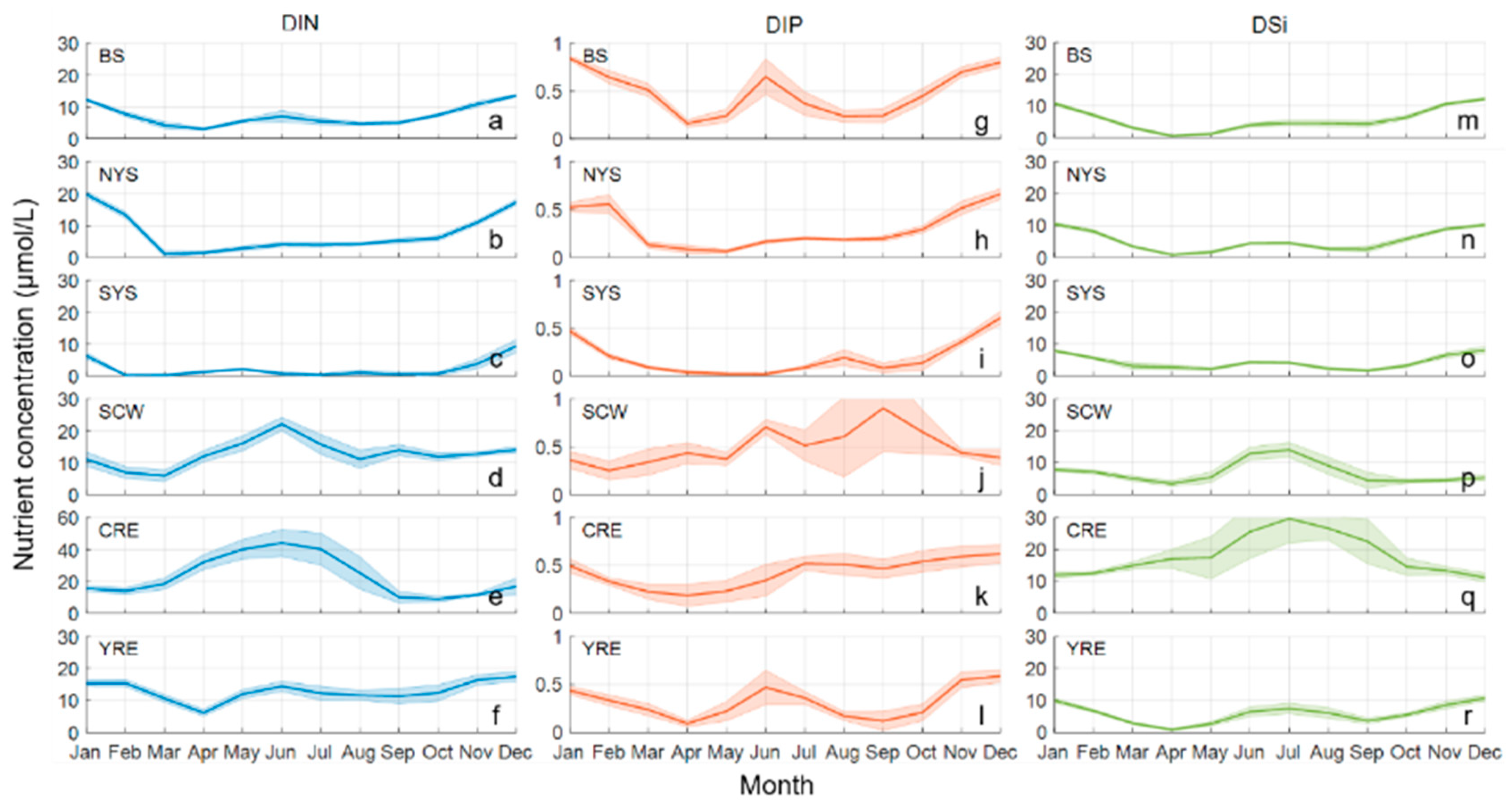
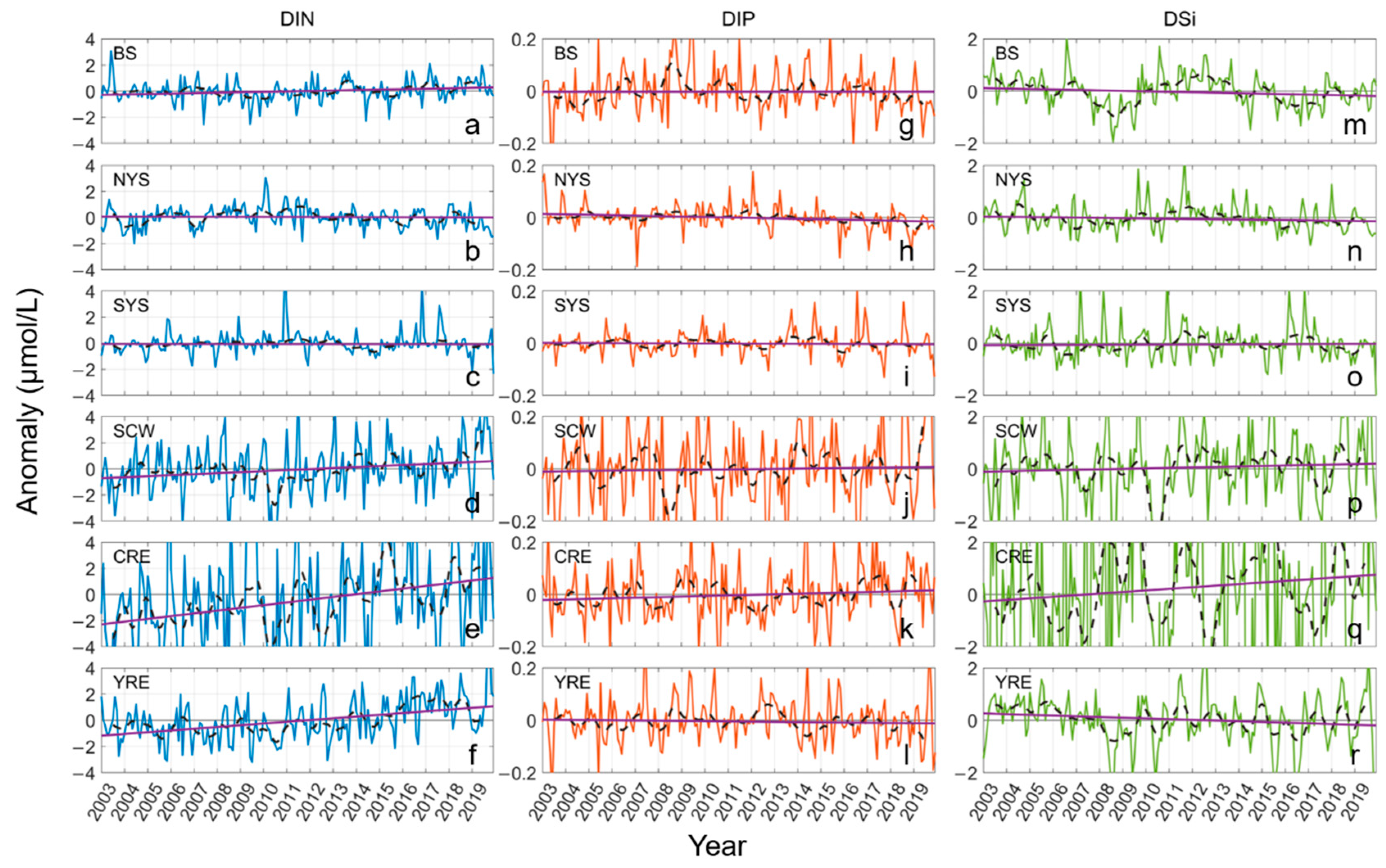
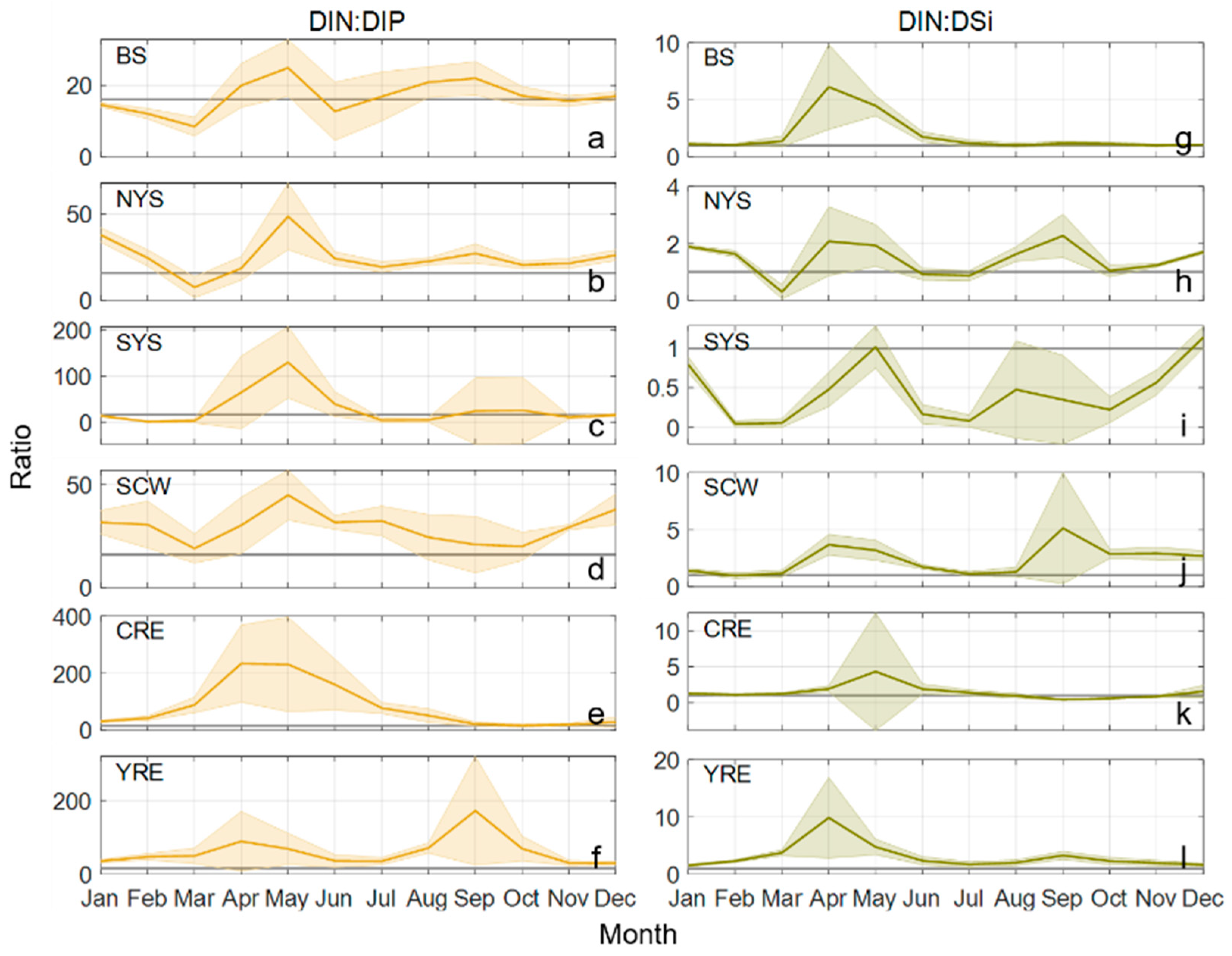
3.2. Surface Nutrient Concentrations of the YBS from 2003–2019
3.2.1. Regional and Seasonal Variations
3.2.2. Interannual Trends
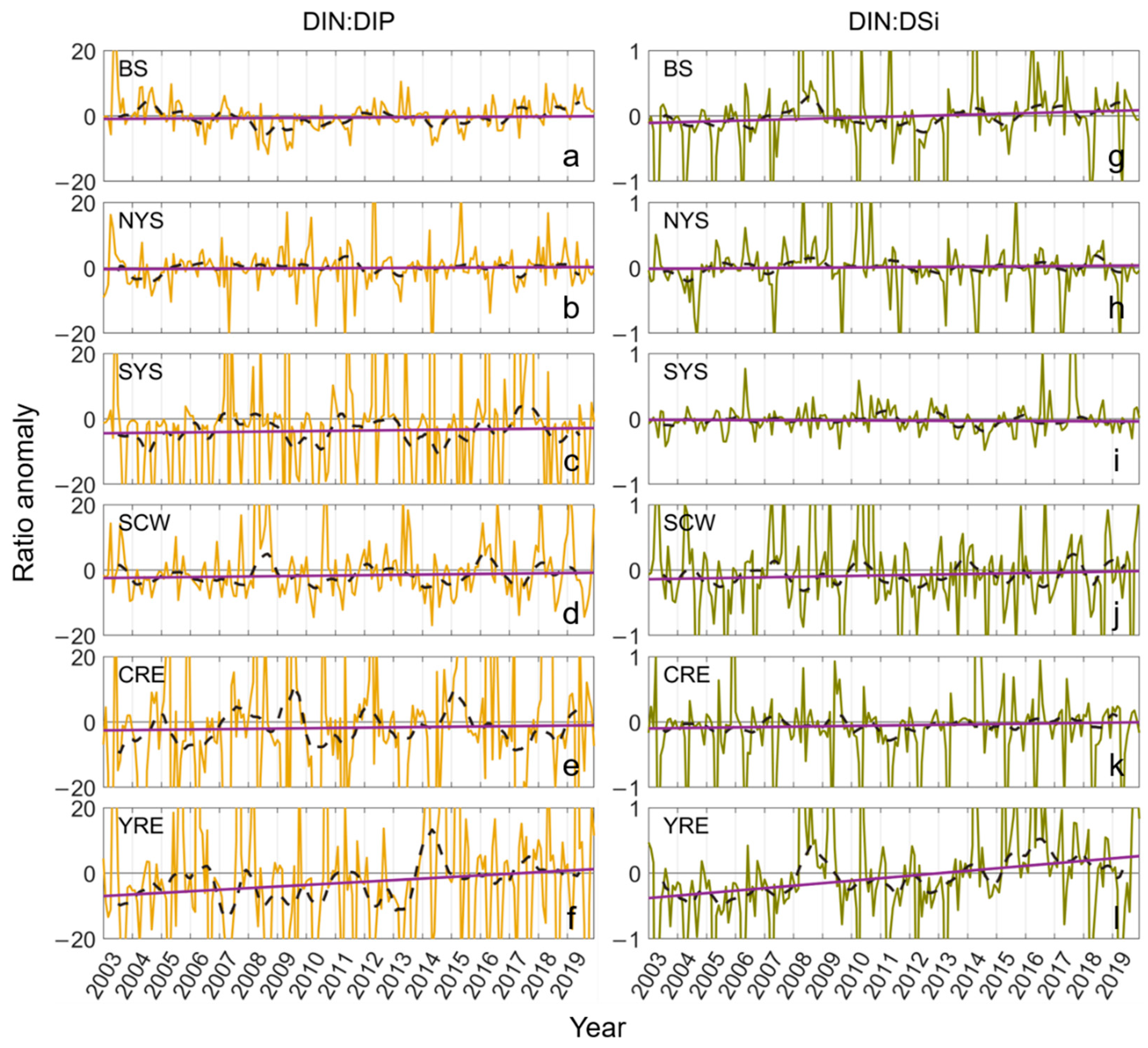
3.2.3. Nutrient Ratios
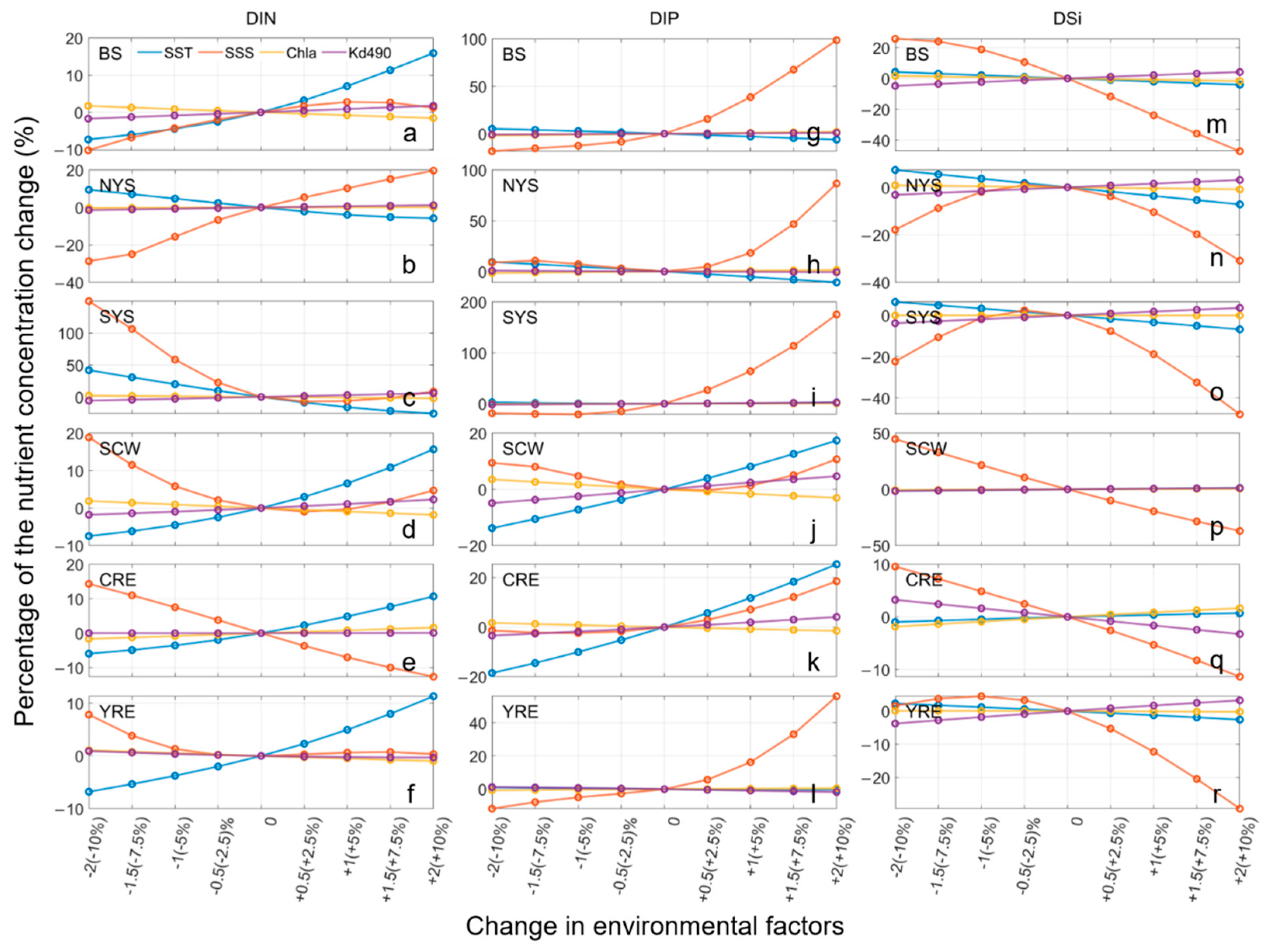
3.3. Effects of Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages and Limitations of the Machine-Learning Approach
4.2. Dynamics of Spatiotemporal Variability of Nutrients in the YBS
4.2.1. Regional and Seasonal Variations
4.2.2. Interannual Trends
4.2.3. Nutrient Ratios
4.2.4. Effects of Environmental Factors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Redfield, A.C.; Ketchum, B.H.; Richards, F.A. The Influence of Organisms on the Composition of Sea-Water. Sea Ideas Obs. Prog. Study Seas 1963, 2, 26–77. [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, R.W. Nutrient Limitation of Net Primary Production in Marine Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1988, 19, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, S.; Hoell, E.E. The Importance of Silicon for Marine Production. Hydrobiologia 2002, 484, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, T. The Relative Influences of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Oceanic Primary Production. Nature 1999, 400, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessen, C.; Bednarz, V.N.; Rix, L.; Teichberg, M.; Wild, C. Marine Eutrophication. In Environmental Indicators; Armon, R.H., Hänninen, O., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 177–203. ISBN 978-94-017-9499-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Liu, H. Relationships between Phytoplankton Growth and Cell Size in Surface Oceans: Interactive Effects of Temperature, Nutrients, and Grazing. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.A.; Lonsdale, D.J.; Merlo, L.R.; Gobler, C.J. The Interactive Roles of Temperature, Nutrients, and Zooplankton Grazing in Controlling the Winter–Spring Phytoplankton Bloom in a Temperate, Coastal Ecosystem, Long Island Sound. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, A.; Hashihama, F.; Kanda, J.; Horimoto-Miyazaki, N.; Ishimaru, T. Long-Term Variability of Nutrient and Dissolved Organic Matter Concentrations in Tokyo Bay between 1989 and 2015. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, S209–S222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkiewicz, S.; Follows, M.J.; Bragg, J.G. Modeling the Coupling of Ocean Ecology and Biogeochemistry. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2009, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Gou, H.; Li, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Lin, W.; Li, K. Numerical Simulation on Marine Environmental Capacity in the Open Sea Area of Northern Jiangsu Province Using a Three-Dimensional Water Quality Model Based on FVCOM. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 45, 101856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Flynn, K.J. Promotion of Harmful Algal Blooms by Zooplankton Predatory Activity. Biol. Lett. 2006, 2, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutkiewicz, S.; Cermeno, P.; Jahn, O.; Follows, M.J.; Hickman, A.E.; Taniguchi, D.A.A.; Ward, B.A. Dimensions of Marine Phytoplankton Diversity. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 609–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, P.J.S. Planktonic Ecosystem Models: Perplexing Parameterizations and a Failure to Fail. J. Plankton Res. 2009, 31, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Xiao, W.; Wang, L.; Huang, B. A Machine-Learning Approach to Modeling Picophytoplankton Abundances in the South China Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 189, 102456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, W.L.; Bode, M.; Doherty, T.S.; Fulton, E.A.; Nimmo, D.G.; Tulloch, A.I.T.; Tulloch, V.J.D.; Ritchie, E.G. A Guide to Ecosystem Models and Their Environmental Applications. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piroddi, C.; Coll, M.; Liquete, C.; Macias, D.; Greer, K.; Buszowski, J.; Steenbeek, J.; Danovaro, R.; Christensen, V. Historical Changes of the Mediterranean Sea Ecosystem: Modelling the Role and Impact of Primary Productivity and Fisheries Changes over Time. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.-H.; Liu, B. Purely Satellite Data–Driven Deep Learning Forecast of Complicated Tropical Instability Waves. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, T.R.; Hosking, J.S.; Pérez-Ortiz, M.; Paige, B.; Elliott, A.; Russell, C.; Law, S.; Jones, D.C.; Wilkinson, J.; Phillips, T.; et al. Seasonal Arctic Sea Ice Forecasting with Probabilistic Deep Learning. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannata, A.; Cannavò, F.; Moschella, S.; Gresta, S.; Spina, L. Exploring the Link between Microseism and Sea Ice in Antarctica by Using Machine Learning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Schalles, J.; Binding, C.; Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Alikas, K.; Kangro, K.; Gurlin, D.; Hà, N.; et al. Seamless Retrievals of Chlorophyll-a from Sentinel-2 (MSI) and Sentinel-3 (OLCI) in Inland and Coastal Waters: A Machine-Learning Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, C.; Barnes, B.B.; Wanninkhof, R.; Cai, W.-J.; Barbero, L.; Pierrot, D. A Machine Learning Approach to Estimate Surface Ocean PCO2 from Satellite Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 228, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Bhoot, V.N.; Kumbier, K.; Sison-Mangus, M.P.; Brown, J.B.; Kudela, R.; Newcomer, M.E. A Novel Random Forest Approach to Revealing Interactions and Controls on Chlorophyll Concentration and Bacterial Communities during Coastal Phytoplankton Blooms. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, F.H.; Thompson, C.C.; Cabral, A.S.; Paranhos, R.; Dutilh, B.E.; Thompson, F.L. Modelling the Influence of Environmental Parameters over Marine Planktonic Microbial Communities Using Artificial Neural Networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 677, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cui, Q.; Gong, F.; Wang, L.; He, X.; Bai, Y. Satellite Retrieval of Surface Water Nutrients in the Coastal Regions of the East China Sea. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Liu, N.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y. Remote Estimation of Total Phosphorus Concentration in the Taihu Lake Using a Semi-Analytical Model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 7993–8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Gong, F.; Bai, Y.; He, X. Changes in Nutrient Concentrations in Shenzhen Bay Detected Using Landsat Imagery between 1988 and 2020. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartino, M.; Marullo, S.; Santoleri, R.; Scardi, M. Modelling the Vertical Distribution of Phytoplankton Biomass in the Mediterranean Sea from Satellite Data: A Neural Network Approach. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Du, C.; Zeng, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Kd(490) and Its Response to Precipitation and Wind in Lake Hongze Based on MODIS Data. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Tang, D. Application of a Generalized Additive Model (GAM) for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentration from MODIS Data in the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 639–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D. Vertical Average Irradiance Shapes the Spatial Pattern of Winter Chlorophyll-a in the Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 224, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Bin, X.; Hanbing, X.; Yi, C.; Bijuan, C.; Zhengguo, C.; Dongsheng, D. Study on Temporal and Spatial Variation of Nutrients and Evaluation on Eutrophication in the Seawater of the Bohai Sea in Winter and Spring of 2014. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2016, 37, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, T.Z.; Yao, Q.; Meng, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Liu, S.M. Distributions of Nutrients in the Southern Yellow Sea and East China Sea in Spring and Summer 2011. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 43, 678–688. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, Q.; Huang, G.; Niu, Z. Distribution of Dissolved Silicate and Changes of Si: N and Si: P Ratio in Yangtze River Estuary before and after Impoundment of Three Gorges Reservoir. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2013, 33, 1974–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Liu, S.; Ren, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Preliminary Estimates of Cross Shelf Transport Flux of Nutrients in the East China Sea in Spring. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ye, X. Temporal and Spatial Distributions of Nutrient Structure and Limitation on Phytoplankton in The East China Sea. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2015, 46, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, S.; Li, C. Distribution of Chlorophyll a and Its Correlation with the Formation of Hypoxia in the Changjiang River Estuary and Its Adjacent Waters. Mar. Sci. 2016, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, S.; Li, C.; Yu, Z. Preliminary Discussion on the Phytoplankton Assemblages and Its Response to the Environmental Changes in the Changjiang (Yangtze)River Estuary and Its Adjacent Waters during the Dry Season and the Wet Season. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 39, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Song, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. The 2015-2016 Annual Variation of Dinoflagellate Community and Amoebophrya Infections in The Changjiang (Yangtze) River Estuary and Adjacent Waters. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2019, 50, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Luan, Q.; Peng, L.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J. Assemblages of Phytoplankton in the Yellow Sea in Response to the Physical Processes During the Summer of 2014. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2016, 35, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.-S.; Yu, Z.-G.; Wang, B.-D.; Fu, M.-Z.; Xia, C.-S.; Liu, L.; Ge, R.-F.; Wang, H.-W.; Zhan, R. Coupling of the Spatial–Temporal Distributions of Nutrients and Physical Conditions in the Southern Yellow Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 156, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, G.; Sun, J.; Leng, X.; Xu, W.; Wu, C.; Li, X.; Pujari, L. Seasonal Responses of Nutrient to Hydrology and Biology in the Southern Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 206, 104207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gao, H.; Shi, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, G. Diurnal Forcing Induces Variations in Seasonal Temperature and Its Rectification Mechanism in the Eastern Shelf Seas of China. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 9870–9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, W.S. What Is a Support Vector Machine? Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1565–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vapnik, V.N. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-387-98780-4. [Google Scholar]
- Aparna, S.G.; D’Souza, S.; Arjun, N.B. Prediction of Daily Sea Surface Temperature Using Artificial Neural Networks. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 4214–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.I.; Somerfield, P.J.; Gilbert, F.J. Quantifying Uncertainty in High-Resolution Coupled Hydrodynamic-Ecosystem Models. J. Mar. Syst. 2007, 64, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landschützer, P.; Gruber, N.; Bakker, D.C.E.; Schuster, U.; Nakaoka, S.; Payne, M.R.; Sasse, T.P.; Zeng, J. A Neural Network-Based Estimate of the Seasonal to Inter-Annual Variability of the Atlantic Ocean Carbon Sink. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7793–7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R. Species Distribution Models: Ecological Explanation and Prediction Across Space and Time. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 677–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, R.; Lv, Z.; Dang, S.; Su, T.; Li, X. Application of Machine Learning in Ocean Data. Multimed. Syst. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Zheng, G.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, F. Deep-Learning-Based Information Mining from Ocean Remote-Sensing Imagery. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1584–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, S.A. The Problem of Pattern and Scale in Ecology: The Robert H. MacArthur Award Lecture. Ecology 1992, 73, 1943–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparella, F.; Vichi, M. Stirring, Mixing, Growing: Microscale Processes Change Larger Scale Phytoplankton Dynamics. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liu, D.; Luo, C.; Xie, L. Double Fronts in the Yellow Sea in Summertime Identified Using Sea Surface Temperature Data of Multi-Scale Ultra-High Resolution Analysis. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 175, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Gao, Z. Evolution of Satellite Derived Chlorophyll-a Trends in the Bohai and Yellow Seas during 2002–2018: Comparison between Linear and Nonlinear Trends. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 259, 107449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Qi, M.; Tang, H.; Han, X. Spatial and Temporal Nutrient Variations in the Yellow Sea and Their Effects on Ulva Prolifera Blooms. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Farnsworth, K.L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean: A Global Synthesis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-1-107-61218-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.H.; Van, S.P.; Choi, B.-J.; Chang, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H. The Physical Processes in the Yellow Sea. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2014, 102, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Yao, Z.; Wang, X.; Jia, C. Long-Term Nutrient Variation Trends and Their Potential Impact on Phytoplankton in the Southern Yellow Sea, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-H.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Lee, J.; Wu, C.-R.; Wang, Y.-L.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Wang, S.-L.; Kandasamy, S.; Lou, J.-Y.; et al. East China Sea Increasingly Gains Limiting Nutrient P from South China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Shim, J.; Yoo, S. Seasonal Variations in Nutrients and Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in the Northern East China Sea. Ocean Sci. J. 2006, 41, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obenour, D.R.; Michalak, A.M.; Zhou, Y.; Scavia, D. Quantifying the Impacts of Stratification and Nutrient Loading on Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5489–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doney, S.C. Plankton in a Warmer World. Nature 2006, 444, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Song, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, W.; Chi, L.; Cao, X.; Yu, Z. Intrusion of the Kuroshio Subsurface Water in the Southern East China Sea and Its Variation in 2014 and 2015 Traced by Dissolved Inorganic Iodine Species. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 165, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, T.; Kattner, G. The Biogeochemistry of the River and Shelf Ecosystem of the Arctic Ocean: A Review. Mar. Chem. 2003, 83, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.J.; Kroeze, C. Past and Future Trends in Nutrients Export by Rivers to the Coastal Waters of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xin, M.; Wei, Q.; Xie, L. A Historical Overview of Coastal Eutrophication in the China Seas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Saito, Y.; Liu, J.P.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Stepwise Decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) Sediment Load (1950–2005): Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2007, 57, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Wei, Q.; Yao, Q. Long-Term Nutrient Variations in the Bohai Sea Over the Past 40 Years. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Yu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H. Silicon and Sediment Transport of the Changjiang River (Yangtze River): Could the Three Gorges Reservoir Be a Filter? Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Wu, W.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Yao, Q.; Xin, M.; Liu, P.; Yu, Z. Decadal Change in Dissolved Silicate Concentration and Flux in the Changjiang (Yangtze) River. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Ran, X.; Liu, X.-M.; Bataille, C.P.; Su, N. Response of the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Water Chemistry to the Impoundment of Three Gorges Dam during 2010–2011. Chem. Geol. 2018, 487, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Zhan, R. Nutrient Conditions in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 58, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Altabet, M.A.; Zhao, L.; Larkum, J.; Song, G.D.; Zhang, G.L.; Jin, H.; Han, L.J. Tracing Nitrogen Biogeochemistry During the Beginning of a Spring Phytoplankton Bloom in the Yellow Sea Using Coupled Nitrate Nitrogen and Oxygen Isotope Ratios. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2490–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhen, G.; Chi, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yao, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W. Nutrient Loads Flowing into Coastal Waters from the Main Rivers of China (2006–2012). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P.J.; Hu, M.H.; Yang, Y.P.; Lu, X. Phosphate Limitation in Estuarine and Coastal Waters of China. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1990, 140, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.G.; Raabe, T.; Liu, S.M.; Starke, A.; Zou, L.; Gao, H.W.; Brockmann, U. Dynamics of Inorganic Nutrient Species in the Bohai Seawaters. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 44, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Shen, Z.; Yu, R. Responses of a Coastal Phytoplankton Community to Increased Nutrient Input from the Changjiang (Yangtze) River. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justić, D.; Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Dortch, Q. Changes in Nutrient Structure of River-Dominated Coastal Waters: Stoichiometric Nutrient Balance and Its Consequences. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Wang, B.; Xie, L.; Sun, X.; Wei, Q.; Liang, S.; Chen, K. Long-Term Changes in Nutrient Regimes and Their Ecological Effects in the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Webster, I.T.; Revill, A.T.; Kenyon, R.A.; Whittle, M.; Curwen, G. Controls on Phytoplankton Productivity in a Wet–Dry Tropical Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paetsch, J.; Gouretski, V.; Hinrichs, I.; Koul, V. Distinct Mechanisms Underlying Interannual to Decadal Variability of Observed Salinity and Nutrient Concentration in the Northern North Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2020, 125, e2019JC015825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainol, Z.; Akhir, M.F.; Abdullah, S. Hydrodynamics, Nutrient Concentrations, and Phytoplankton Biomass in a Shallow and Restricted Coastal Lagoon under Different Tidal and Monsoonal Environmental Drivers. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 38, 101376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.-H. Phosphorus Speciation and Budget of the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1285–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carritt, D.E.; Goodgal, S. Sorption Reactions and Some Ecological Implications. Deep. Sea Res. 1954, 1, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Yu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Bianchi, T.S.; Paytan, A.; Zhao, B.; Pan, H.; Yao, P. Distribution, Mixing Behavior, and Transformation of Dissolved Inorganic Phosphorus and Suspended Particulate Phosphorus along a Salinity Gradient in the Changjiang Estuary. Mar. Chem. 2015, 168, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data Source | Sampling Time | Number of Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIN | DIP | DSi | ||
| Cruise 1 in this study | 29 April–4 May 2010 | 91 | 89 | 91 |
| Cruise 2 in this study | 2–20 May 2012 | 116 | 115 | 116 |
| Cruise 3 in this study | 2–19 November 2012 | 105 | 105 | 105 |
| Cruise 4 in this study | 28 April–18 May 2014 | 106 | 123 | 122 |
| Cruise 5 in this study | 8–23 November 2014 | 123 | 123 | 123 |
| Cruise 6 in this study | 14–30 January 2016 | 77 | 77 | 77 |
| Cruise 7 in this study | 17 August–5 September 2015 | 109 | 107 | 106 |
| Cruise 8 in this study | 28 March–16 April 2018 | 111 | 113 | 113 |
| Cruise 9 in this study | 24 July–8 September 2018 | 117 | 117 | 117 |
| Cruise 10 in this study | 8 April–6 May 2019 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
| Field Survey by EDSP | March–October 2016 | 425 | 425 | \ |
| Sui et al. [32] | February & May 2014 | 100 | 100 | \ |
| Mi et al. [33] | 6–25 April & 12–29 August 2011 | 74 | 74 | 74 |
| Cui et al. [34] | May 2011 | \ | \ | 1 |
| Dong et al. [35] | 10 May–5 June 2011 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Ye et al. [36] | February & May & August & November 2013 | 16 | 12 | 16 |
| Li et al. [37,38] | 4–20 March & 17–28 August 2013 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Chen et al. [39] | 2 February 2015–1 January 2016 | 21 | 36 | 22 |
| Lv et al. [40] | 5–23 August 2014 | 48 | 48 | \ |
| Wei et al. [41] | (21 January, 15 April, 21 October), 2007 & 24 July 2006 | 545 | \ | \ |
| Guo et al. [42] | (4 May, 12 November), 2014 & 4 September 2015 & 22 January 2016 | 93 | 93 | 93 |
| Total | 2372 | 1852 | 1271 | |
| Nutrient model | Indicator | SVR | RFR | ANN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIN | R | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.84 |
| RMSE (μmol/L) | 6.13 | 4.98 | 5.74 | |
| SS | 0.66 | 0.70 | 0.70 | |
| DIP | R | 0.71 | 0.84 | 0.77 |
| RMSE (μmol/L) | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.16 | |
| SS | 0.51 | 0.71 | 0.59 | |
| DSi | R | 0.73 | 0.87 | 0.78 |
| RMSE (μmol/L) | 2.87 | 2.05 | 2.62 | |
| SS | 0.54 | 0.76 | 0.61 |
| Indicator | DIN | DIP | DSi |
|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0.74 | 0.58 | 0.61 |
| RMSE (μmol/L) | 6.77 | 0.21 | 3.69 |
| SS | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, P.; Yu, Y.; Gong, X.; Lu, X. Reconstruction of Monthly Surface Nutrient Concentrations in the Yellow and Bohai Seas from 2003–2019 Using Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5021. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195021
Liu H, Lin L, Wang Y, Du L, Wang S, Zhou P, Yu Y, Gong X, Lu X. Reconstruction of Monthly Surface Nutrient Concentrations in the Yellow and Bohai Seas from 2003–2019 Using Machine Learning. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):5021. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195021
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hao, Lei Lin, Yujue Wang, Libin Du, Shengli Wang, Peng Zhou, Yang Yu, Xiang Gong, and Xiushan Lu. 2022. "Reconstruction of Monthly Surface Nutrient Concentrations in the Yellow and Bohai Seas from 2003–2019 Using Machine Learning" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 5021. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195021
APA StyleLiu, H., Lin, L., Wang, Y., Du, L., Wang, S., Zhou, P., Yu, Y., Gong, X., & Lu, X. (2022). Reconstruction of Monthly Surface Nutrient Concentrations in the Yellow and Bohai Seas from 2003–2019 Using Machine Learning. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 5021. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195021








