Automatic Registration for Panoramic Images and Mobile LiDAR Data Based on Phase Hybrid Geometry Index Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A registration method for panoramic images and mobile LiDAR data based on the hybrid geometric structure index feature of phase is proposed.
- A multi-scale and multi-directional feature descriptor called HGIFP is developed to capture the shape and structural features of the image and combined with a robust false matching point elimination algorithm to complete the corresponding feature points extraction work of the multimodal images.
- The assumption of local motion invariance of 3D–2D corresponding feature points is proposed to solve the registration process of the mobile LiDAR data and panoramic image.
- The method in this paper can correct the rotation error within 12° and the translation error within 2 m, and the average error is within 3 pixels.
2. Related Works
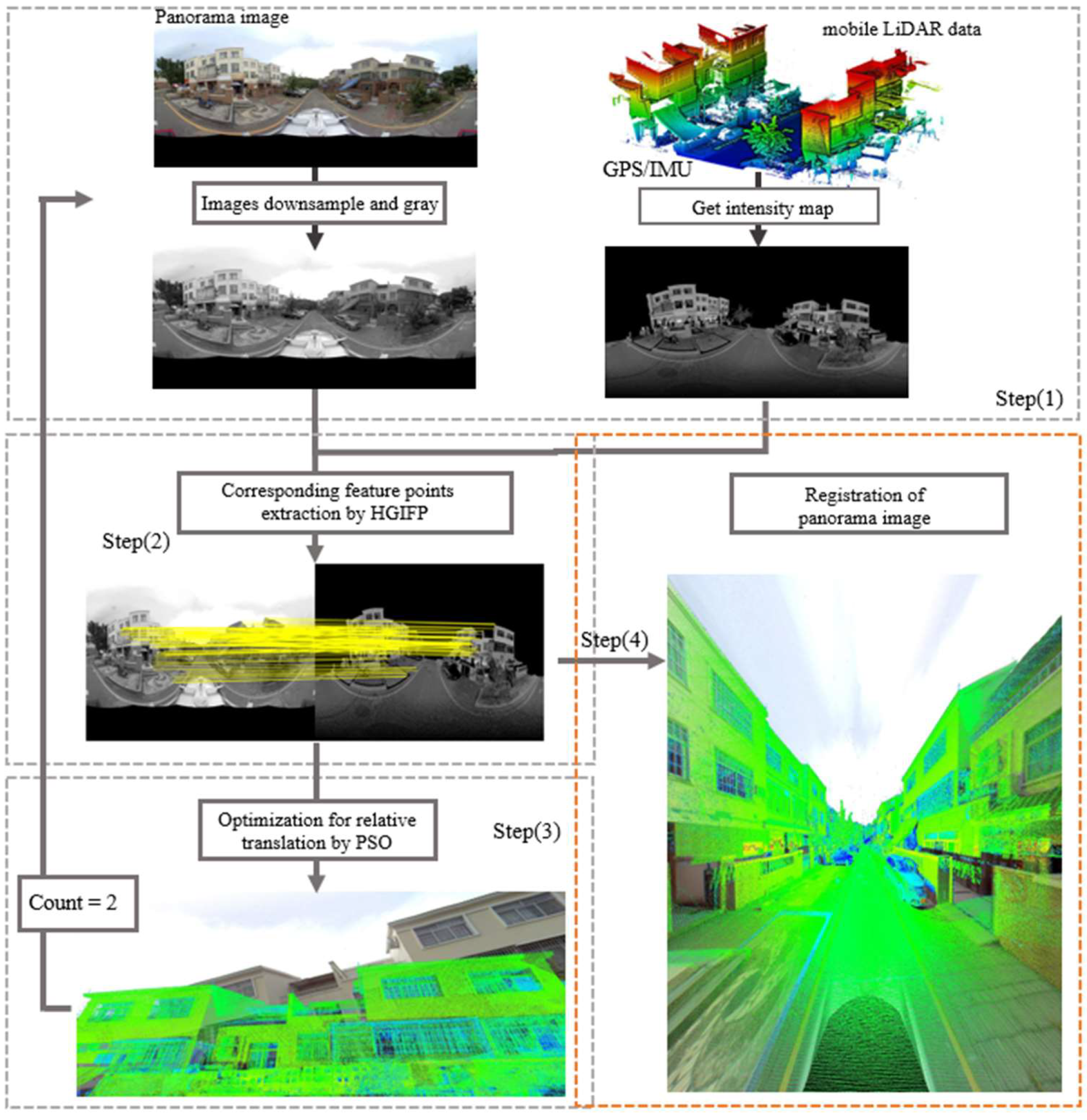
3. Methodology
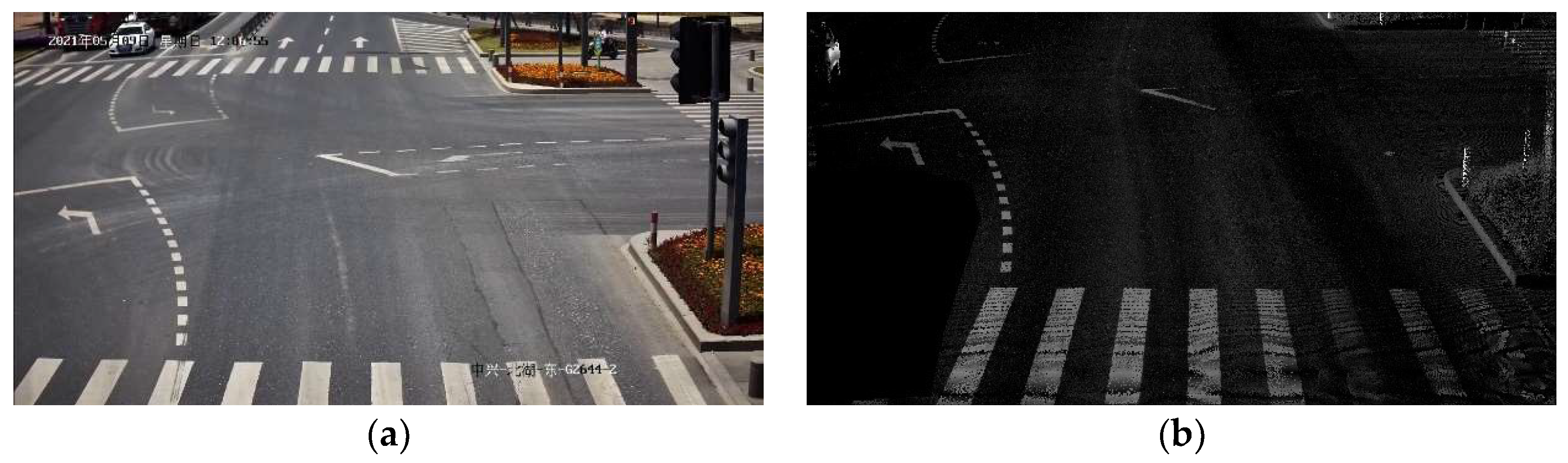
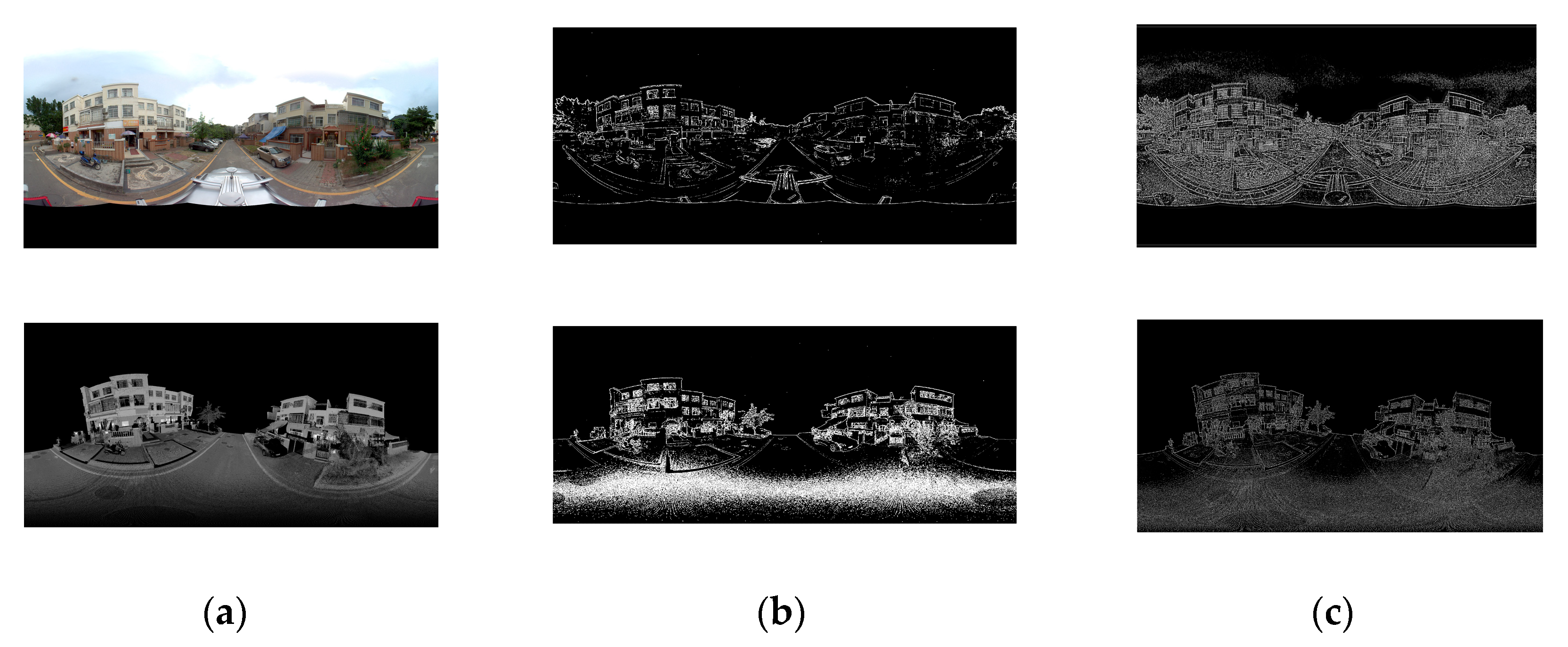
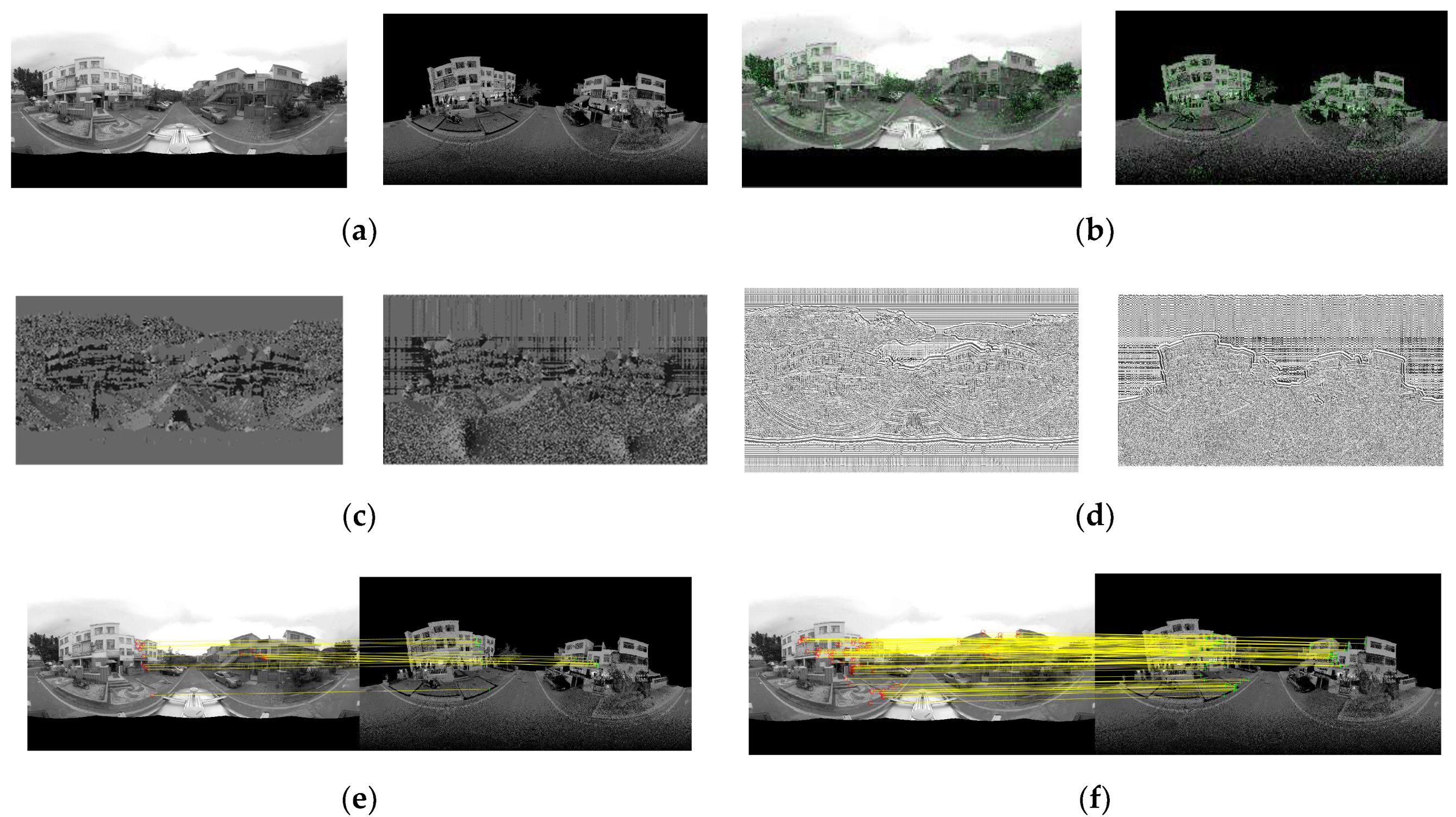
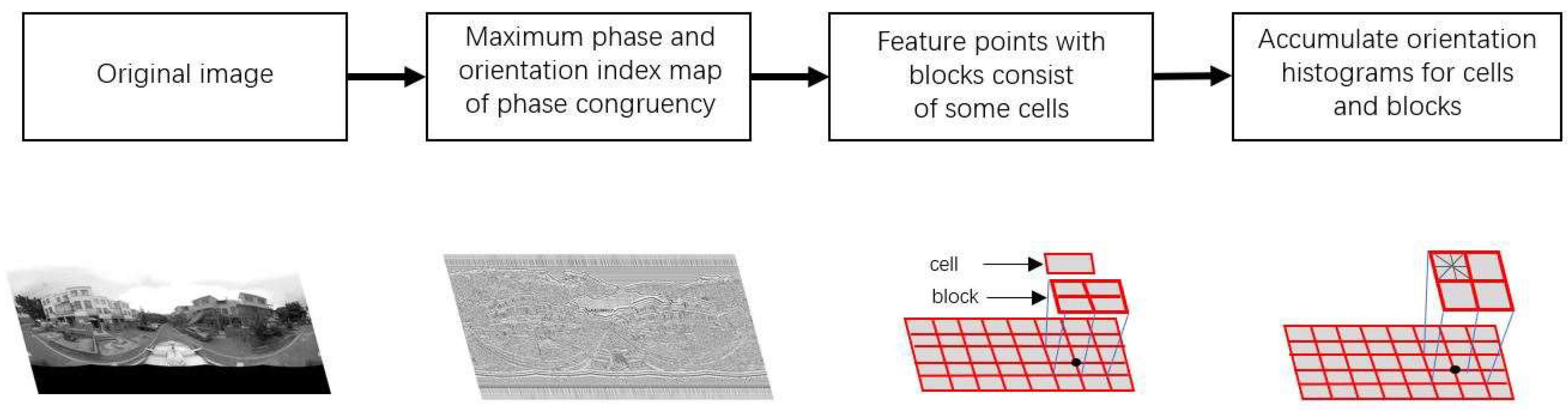
3.1. Multimodal Image Corresponding Feature Points Extraction
3.1.1. Point Feature Detection
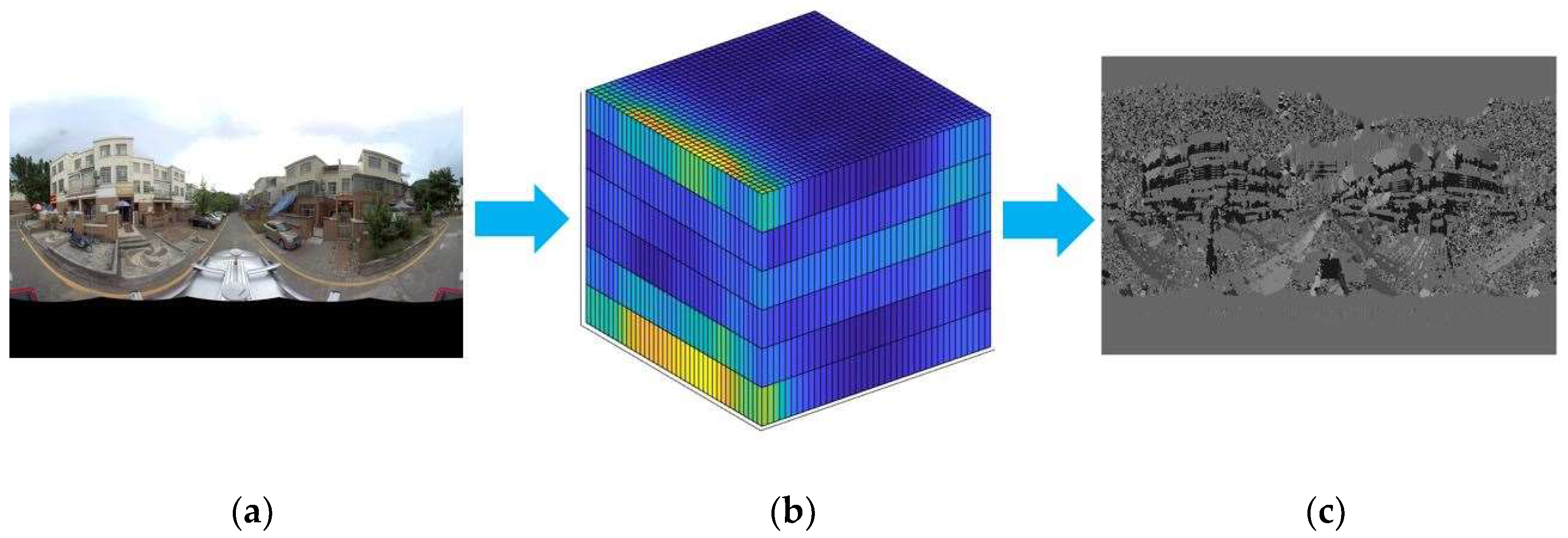
3.1.2. Feature Description Based on Mixed Index Map and Orientation of Phase Congruency Index Map
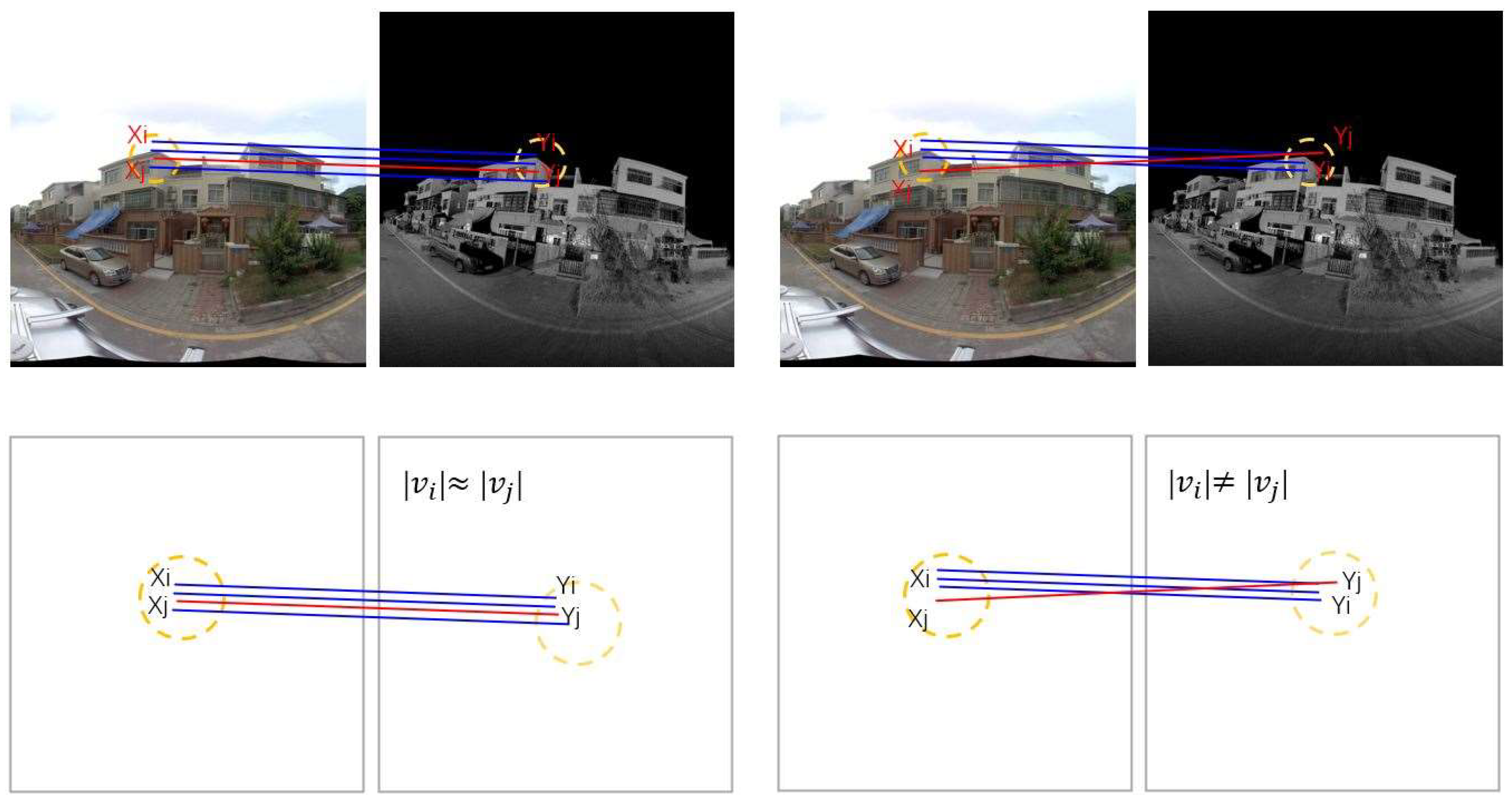
3.1.3. Elimination of Mismatched Points Based on Local Preserving Matching
3.2. Panoramic Image and the Mobile LiDAR Data Registration Model Based on Local Motion Invariance in 3D–2D Corresponding Feature Points
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Setting of Experiments
4.2. Parameter Study
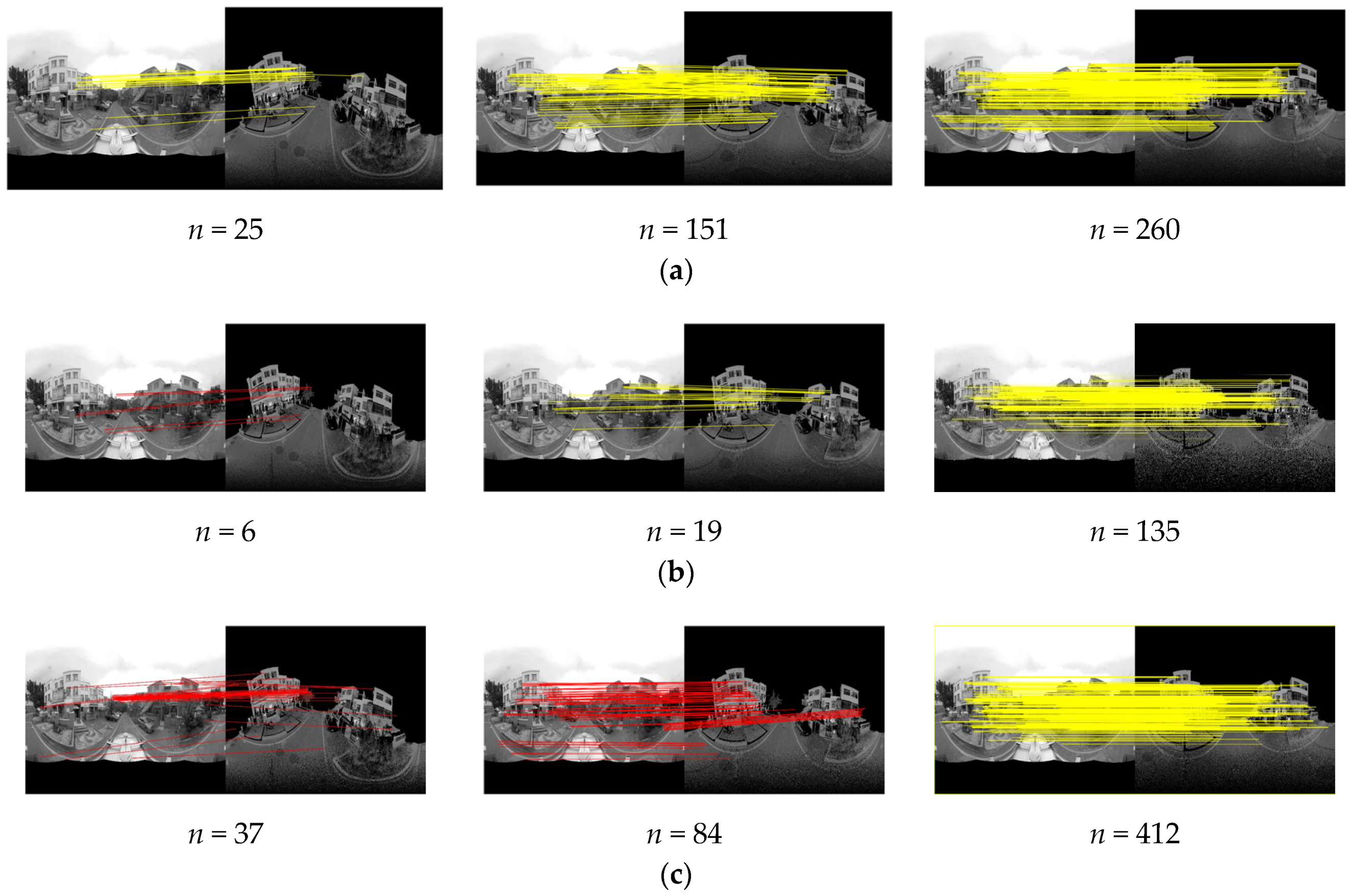
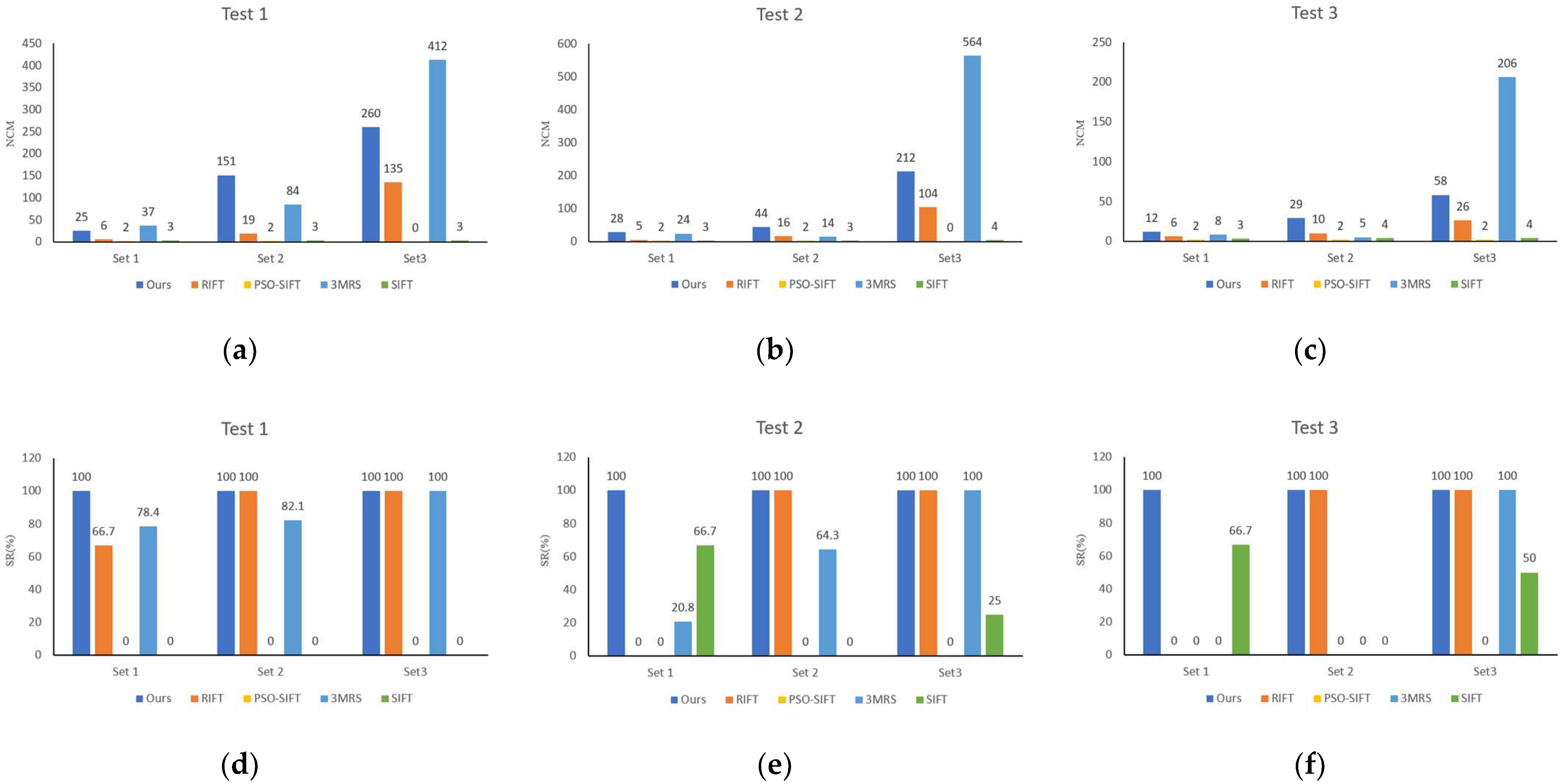
4.3. Matching Performance Analysis and Comparison
5. Discussion
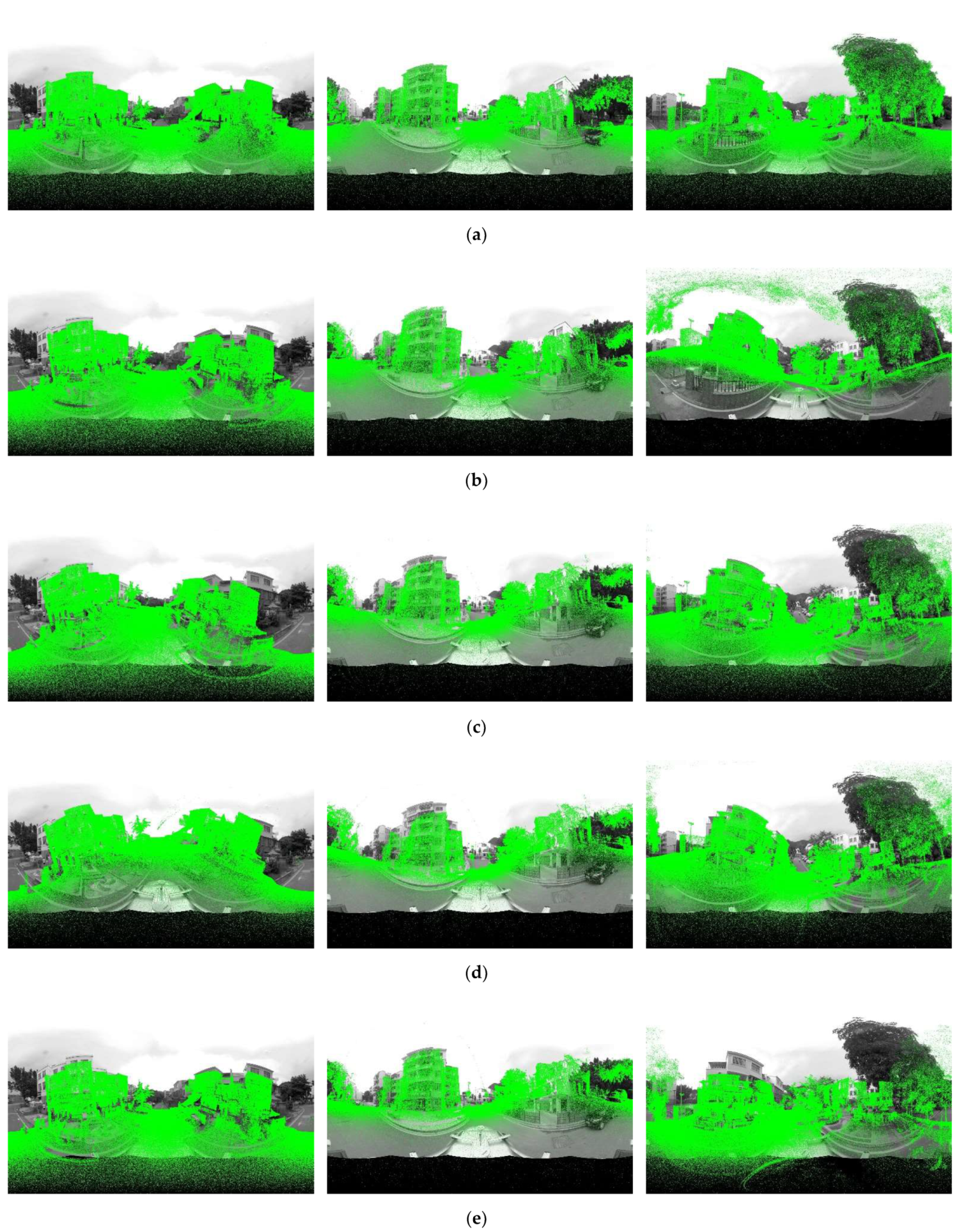
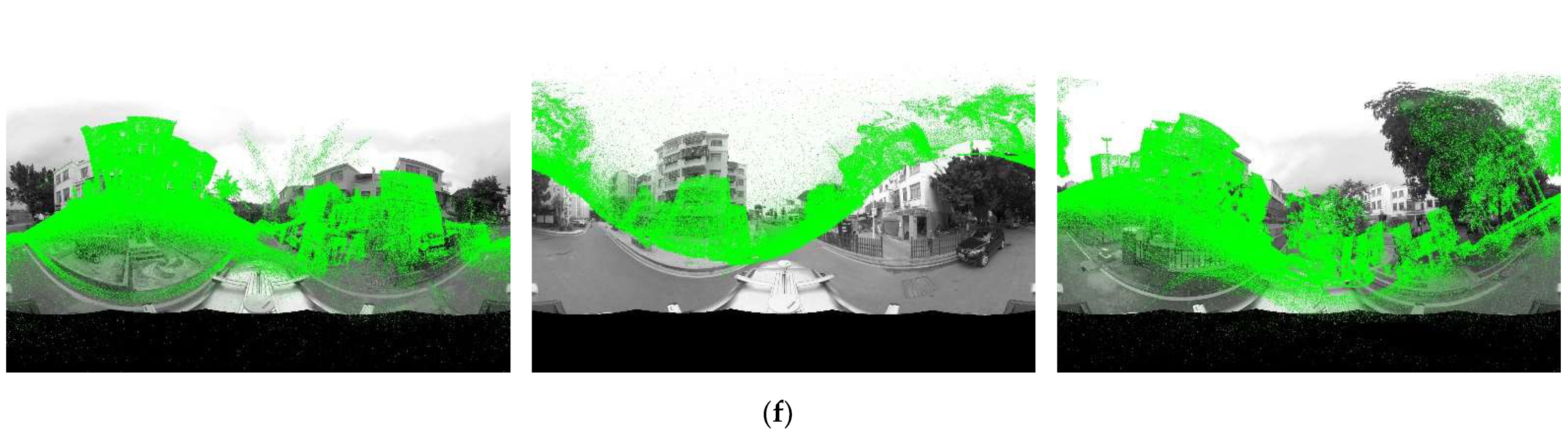
5.1. Pixel Error and Runtime Evaluation
5.2. Registration Parameters Error Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornelis, N.; Leibe, B.; Cornelis, K.; Van Gool, L. 3D urban scene modeling integrating recognition and reconstruction. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 78, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenakis, C.; Gao, Y.; Sohn, G. Co-registration of aerial photogrammetric and LiDAR point clouds in urban environments using automatic plane correspondence. Appl. Geomat. 2013, 5, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, Y.; Yan, W.Y.; Shaker, A. A phase-congruency-based scene abstraction approach for 2d-3d registration of aerial optical and LiDAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 964–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Li, S.K.; Jiang, L.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X. A new method of gold foil damage detection in stone carving relics based on multi-temporal 3D LiDAR point clouds. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feraco, S.; Bonfitto, A.; Amati, N.; Tonoli, A. A LIDAR-Based Clustering Technique for Obstacles and Lane Boundaries Detection in Assisted and Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the ASME 2020 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 16–19 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, E.; Yoshihara, Y.; Yoshiki, N. Blind Area Traffic Prediction Using High Definition Maps and LiDAR for Safe Driving Assist. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Las Palmas, Spain, 15–18 September 2015; pp. 2311–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, P. Automatic building extraction from high-resolution aerial images and LiDAR data using gated residual refinement network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, H.; Wei, M.; Remil, O.; Wang, B.; Wang, J. Automatic 3D reconstruction of electrical substation scene from LiDAR point cloud. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 143, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Niu, J. A cgans-based scene reconstruction model using lidar point cloud. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing and Communications (ISPA/IUCC), Guangzhou, China, 12–15 December 2017; pp. 1107–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Boehm, J.; Becker, S. Automatic Marker-free Registration of Terrestrial Laser Scans using Reflectance Features. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference Optical 3-D Measurement Techniques, Zurich, Switzerland, 9–12 July 2007; Volume I, pp. 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Dong, Z. A shape-based segmentation method for mobile laser scanning point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 81, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, H.; Wan, J.; Li, B.; Xia, T. Multi-view 3D object detection network for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; Volume 1, p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Schlosser, J.; Chow, C.K.; Kira, Z. Fusing LIDAR and images for pedestrian detection using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Premebida, C.; Carreira, J.; Batista, J.; Nunes, U. Pedestrian Detection Combining RGB and Dense LIDAR Data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Telling, J.; Lyda, A.; Hartzell, P.; Glennie, C. Review of earth science research using terrestrial laser scanning. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 169, 35–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Huang, R.; Dong, Z.; Xiao, W. Automatic registration of panoramic image sequence and mobile laser scanning data using semantic features. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 136, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ma, H.; Zhang, L. Automatic Registration of Optical Images with Airborne LiDAR Point Cloud in Urban Scenes Based on Line-Point Similarity Invariant and Extended Collinearity Equations. Sensors 2019, 19, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Yin, G. Robust registration of aerial images and LiDAR data using spatial constraints and Gabor structural features. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 181, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmehr, E.G.; Fraser, C.S.; Zhang, C.; Leach, J. Automatic registration of optical imagery with 3D LIDAR data using statistical similarity. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 88, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Gong, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, T. Point Cloud Depth Map and Optical Image Registration Based on Improved RIFT Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 13th International Conference on Computer Research and Development (ICCRD), Beijing, China, 5–7 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, Z.; Nieto, J. Automatic calibration of lidar and camera images using normalized mutual information. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2013), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Ferrie, F.P.; Macfarlane, J. Automatic registration of mobile lidar and spherical panoramas. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Providence, RI, USA, 18–20 June 2012; pp. 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Shan, J. A local descriptor based registration method for multispectral remote sensing images with non-linear intensity differences. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 90, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, A. Fast registration of terrestrial LiDAR point cloud and sequence images. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences—ISPRS Archives, Wuhan, China, 18–22 September 2017; Volume 42, pp. 875–879. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, N.; Jia, Y.; Ji, S. Registration of Panoramic/Fish-Eye Image Sequence and LiDAR Points Using Skyline Features. Sensors 2018, 18, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, T.; Ji, S.; Shan, J.; Gong, J.; Liu, K. Line-based registration of panoramic images and LiDAR point clouds for mobile mapping. Sensors 2017, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Jia, Y.; Huang, X. Semiautomatically register MMS LiDAR points and panoramic image sequence using road lamp and lane. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2019, 85, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, R.S.; Snavely, N.; Seitz, S.T.; Szeliski, R. Alignment of 3D Point Clouds to Overhead Images. In Proceedings of the Second IEEE Workshop on Internet Vision, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Huang, R.; Zhou, Y. Registration of optical images with LiDAR data and its accuracy assessment. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Nister, D.; Hsu, S. Alignment of continuous video onto 3D point clouds. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1305–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abayowa, B.O.; Yilmaz, A.; Hardie, R.C. Automatic registration of optical aerial imagery to a LiDAR point cloud for generation of city models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2015, 106, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tsai, Y. 2D-image to 3D-range registration in urban environments via scene categorisation and combination of similarity measurements. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, Z.; Nieto, J.; Johnson, D. Automatic calibration of multimodal sensor systems using a gradient orientation measure. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots & Systems (IROS), Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 1293–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Chen, C. Automatic registration of UAV-borne sequent images and LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, M.; Lilienthal, A.; Duckett, T. Scan registration for autonomous mining vehicles using 3D-NDT. J. Field Robot. 2007, 24, 803–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.; McKay, N. A Method for Registration of 3-D Shapes. IEEE T rans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.-H.; Lichti, D.D. A method for automated registration of unorganised point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressin, A.; Mallet, C.; Demantké, J.; David, N. Towards 3D lidar point cloud registration improvement using optimal neighborhood knowledge. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Habib, A. NRLI-UAV: Non-rigid registration of sequential raw laser scans and images for low-cost UAV LiDAR point cloud quality improvement. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 158, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Ai, M. RIFT: Multi-modal image matching based on radiation-variation insensitive feature transform. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 3296–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, B.; Klaus, B.; Horn, P. Robot Vision; MIT Press: Cambridge, CA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Weickert, J.; ter Haar Romeny, B.M.; Viergever, M.A. Efficient and reliable schemes for nonlinear diffusion filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1998, 7, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, H.; Guo, X. Locality preserving matching. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 127, 512–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, H. Heterologous Images Matching Considering Anisotropic Weighted Moment and Absolute Phase Orientation. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 46, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar]
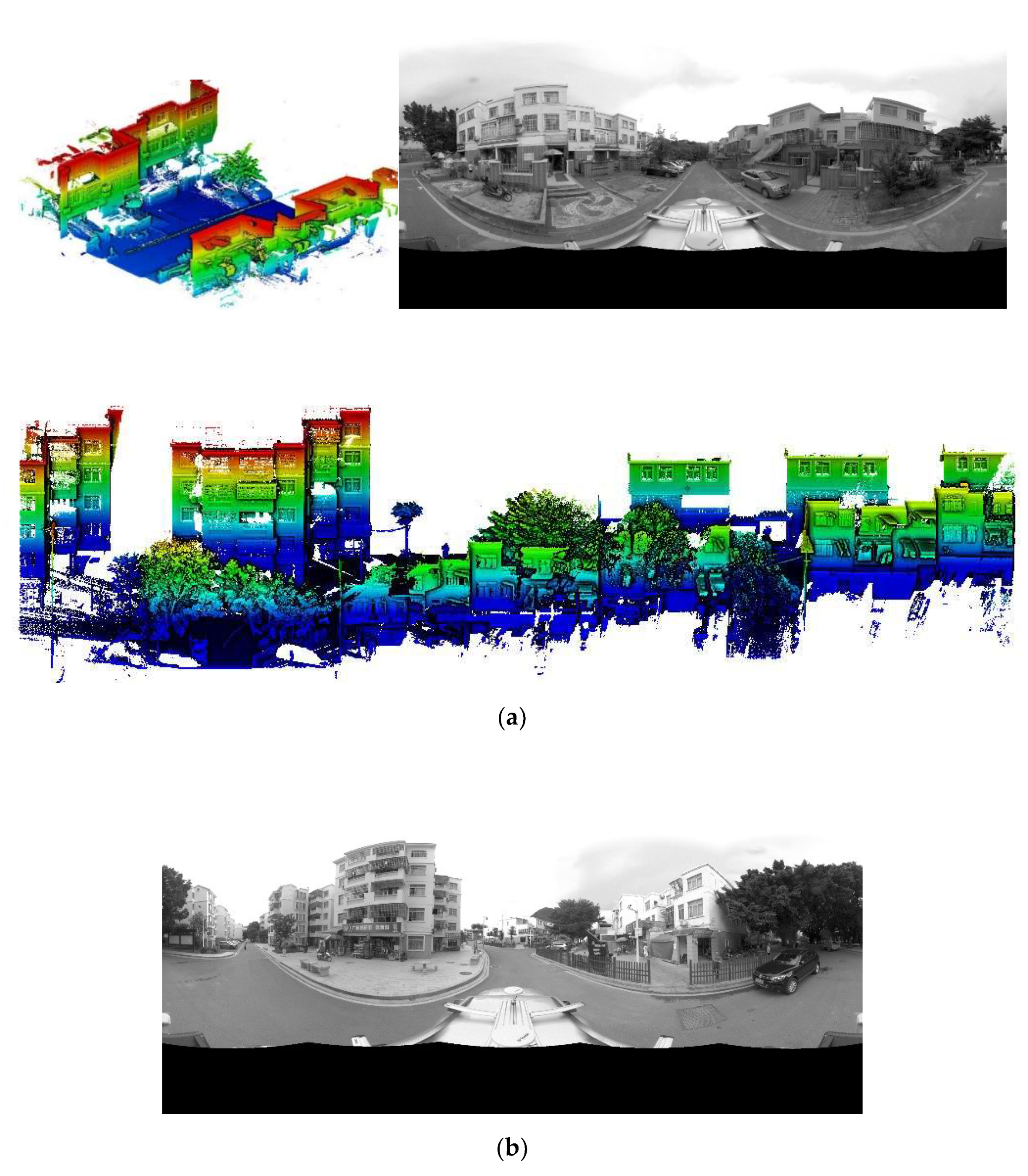
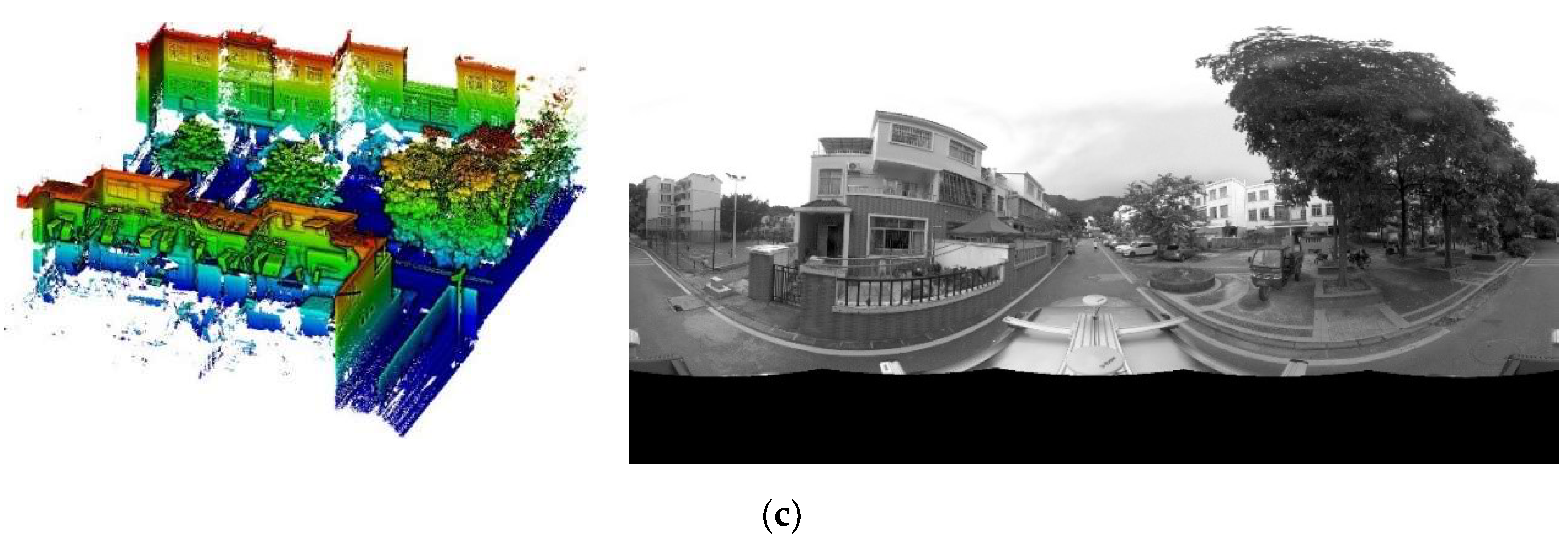



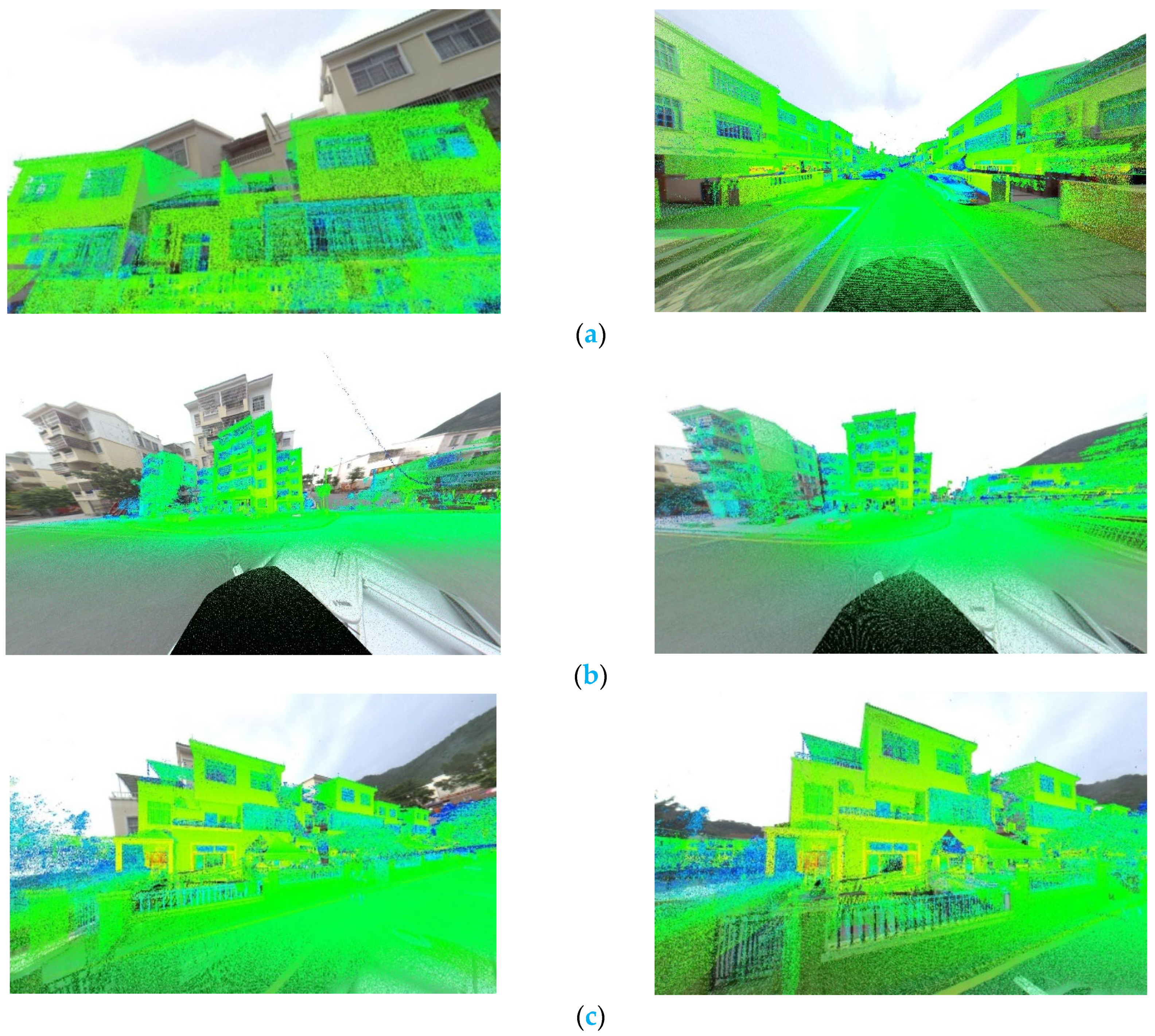
| Dataset Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Test Case | Data Resource | Size | Location |
| Test 1 | MMS LiDAR points | 7,802,955(points) | town |
| Panoramic image | 2731 × 1366(pixels) | ||
| Test 2 | MMS LiDAR points | 8,471,353(points) | town |
| Panoramic image | 2731 × 1366(pixels) | ||
| Test 3 | MMS LiDAR points | 9,067,519(points) | town |
| Panoramic image | 2731 × 1366(pixels) | ||
| Experiments | Variable | Fixed Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| parameterN | ||
| parameterμ | ||
| parameterJ | ||
| parameterr |
| Metric | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 19 | |
| NCM | 64 | 84 | 93 | 43 | 72 |
| SR/% | 98.4 | 100 | 100 | 93.5 | 92.3 |
| Metric | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | |
| NCM | 65 | 93 | 51 | 52 | 49 |
| SR/% | 79.2 | 100 | 96.2 | 94.5 | 98 |
| Metric | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 84 | 96 | 108 | 120 | 132 | |
| NCM | 76 | 80 | 93 | 72 | 51 |
| SR/% | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Metric | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | |
| NCM | 57 | 93 | 92 | 129 | 121 |
| SR/% | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.3 |
| Test | Elements | Correct Value | Initial Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | X/m | 472,133.143 | 472,135.143 |
| Y/m | 2,622,689.476 | 2,622,690.876 | |
| Z/m | 70.920 | 72.120 | |
| Roll/rad | −0.015755 | −0.205755 | |
| Pitch/rad | −0.020855 | −0.190855 | |
| Yaw/rad | −1.565119 | −1.395119 | |
| Test 2 | X/m | 471,980.115 | 471,982.115 |
| Y/m | 2,622,760.311 | 2,622,761.811 | |
| Z/m | 65.443 | 64.043 | |
| Roll/rad | −0.009265 | 0.179265 | |
| Pitch/rad | 0.028898 | 0.208898 | |
| Yaw/rad | 0.807724 | 0.627724 | |
| Test 3 | X/m | 472,089.330 | 472,091.401 |
| Y/m | 2,622,689.692 | 2,622,687.734 | |
| Z/m | 69.654 | 70.154 | |
| Roll/rad | −0.002380 | −0.200804 | |
| Pitch/rad | 0.045244 | 0.205244 | |
| Yaw/rad | 1.597508 | 1.397508 |
| Test | Method | RMSE (Pixel) | RT (Second) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | Ours | 0.997 | 184.414 |
| RIFT + PSO | 93.813 | 118.803 | |
| MI | 107.721 | 507.088 | |
| PSO-SIFT + PSO | 188.919 | 255.598 | |
| 3MRS + PSO | 91.426 | 267.647 | |
| SIFT + PSO | 94.818 | 110.800 | |
| Test 2 | Ours | 1.606 | 187.174 |
| RIFT + PSO | 51.153 | 100.743 | |
| MI | 65.89 | 637.487 | |
| PSO-SIFT + PSO | 85.335 | 217.802 | |
| 3MRS + PSO | 53.924 | 283.901 | |
| SIFT + PSO | 198.992 | 98.392 | |
| Test 3 | Ours | 2.531 | 192.024 |
| RIFT + PSO | 111.961 | 104.788 | |
| MI | 74.089 | 632.097 | |
| PSO-SIFT + PSO | 93.483 | 291.207 | |
| 3MRS + PSO | 176.542 | 256.630 | |
| SIFT + PSO | 143.185 | 124.225 |
| Test | Elements | Correct Value | Initial Value | Final Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | X/m | 472,133.143 | 472,135.143 | 472,133.127 |
| Y/m | 2,622,689.476 | 2,622,690.876 | 2,622,689.486 | |
| Z/m | 70.920 | 72.120 | 70.928 | |
| Roll/rad | −0.015755 | −0.205755 | −0.0174915 | |
| Pitch/rad | −0.020855 | −0.190855 | −0.0187945 | |
| Yaw/rad | −1.565119 | −1.395119 | −1.5604139 | |
| Test 2 | X/m | 471,980.115 | 471,982.115 | 471,980.115 |
| Y/m | 2,622,760.311 | 2,622,761.811 | 2,622,760.322 | |
| Z/m | 65.443 | 64.043 | 65.456 | |
| Roll/rad | −0.009265 | 0.179265 | −0.011067 | |
| Pitch/rad | 0.028898 | 0.208898 | 0.027423 | |
| Yaw/rad | 0.807724 | 0.627724 | 0.812992 | |
| Test 3 | X/m | 472,089.330 | 472,091.401 | 472,089.323 |
| Y/m | 2,622,689.692 | 2,622,687.734 | 2,622,689.669 | |
| Z/m | 69.654 | 70.154 | 69.628 | |
| Roll/rad | −0.002380 | −0.200804 | −0.002570 | |
| Pitch/rad | 0.045244 | 0.205244 | 0.044744 | |
| Yaw/rad | 1.597508 | 1.397508 | 1.602342 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhu, N.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, R. Automatic Registration for Panoramic Images and Mobile LiDAR Data Based on Phase Hybrid Geometry Index Features. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4783. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194783
Wan G, Wang Y, Wang T, Zhu N, Zhang R, Zhong R. Automatic Registration for Panoramic Images and Mobile LiDAR Data Based on Phase Hybrid Geometry Index Features. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4783. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194783
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Genyi, Yong Wang, Tao Wang, Ningning Zhu, Ruizhuo Zhang, and Ruofei Zhong. 2022. "Automatic Registration for Panoramic Images and Mobile LiDAR Data Based on Phase Hybrid Geometry Index Features" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4783. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194783
APA StyleWan, G., Wang, Y., Wang, T., Zhu, N., Zhang, R., & Zhong, R. (2022). Automatic Registration for Panoramic Images and Mobile LiDAR Data Based on Phase Hybrid Geometry Index Features. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4783. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194783






