Vehicle Re-Identification Based on UAV Viewpoint: Dataset and Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
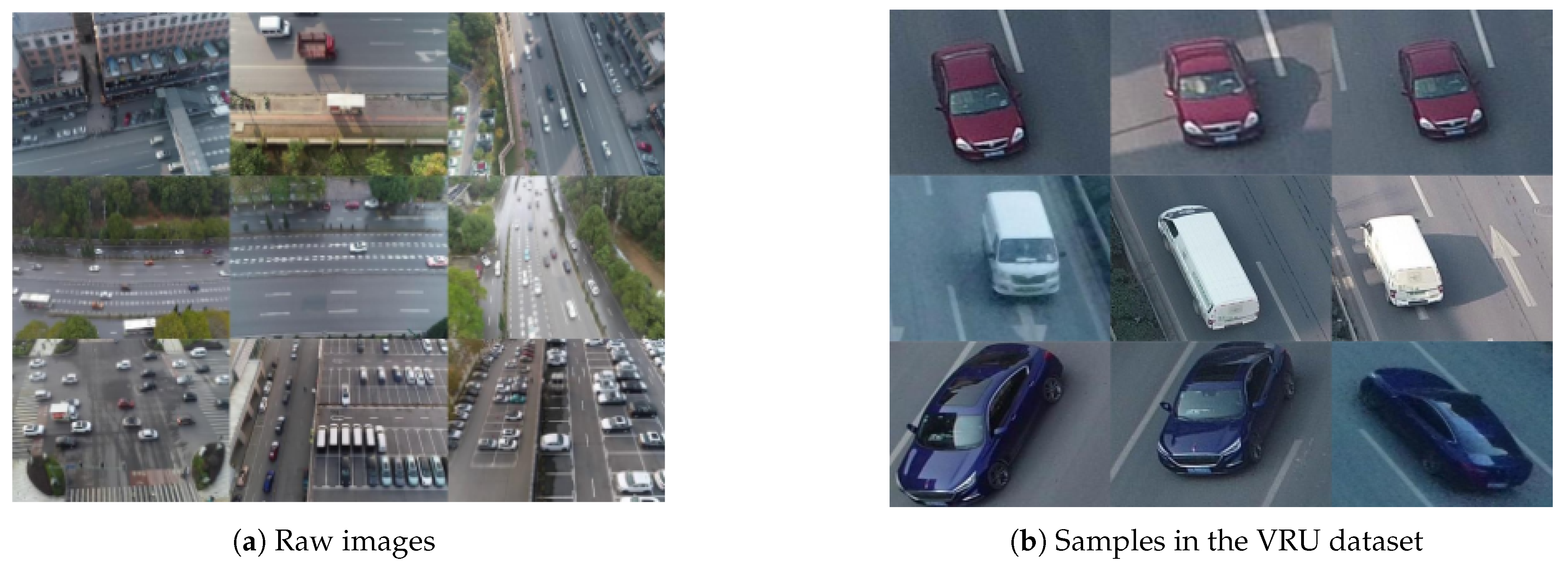
3.1.1. Data Collection
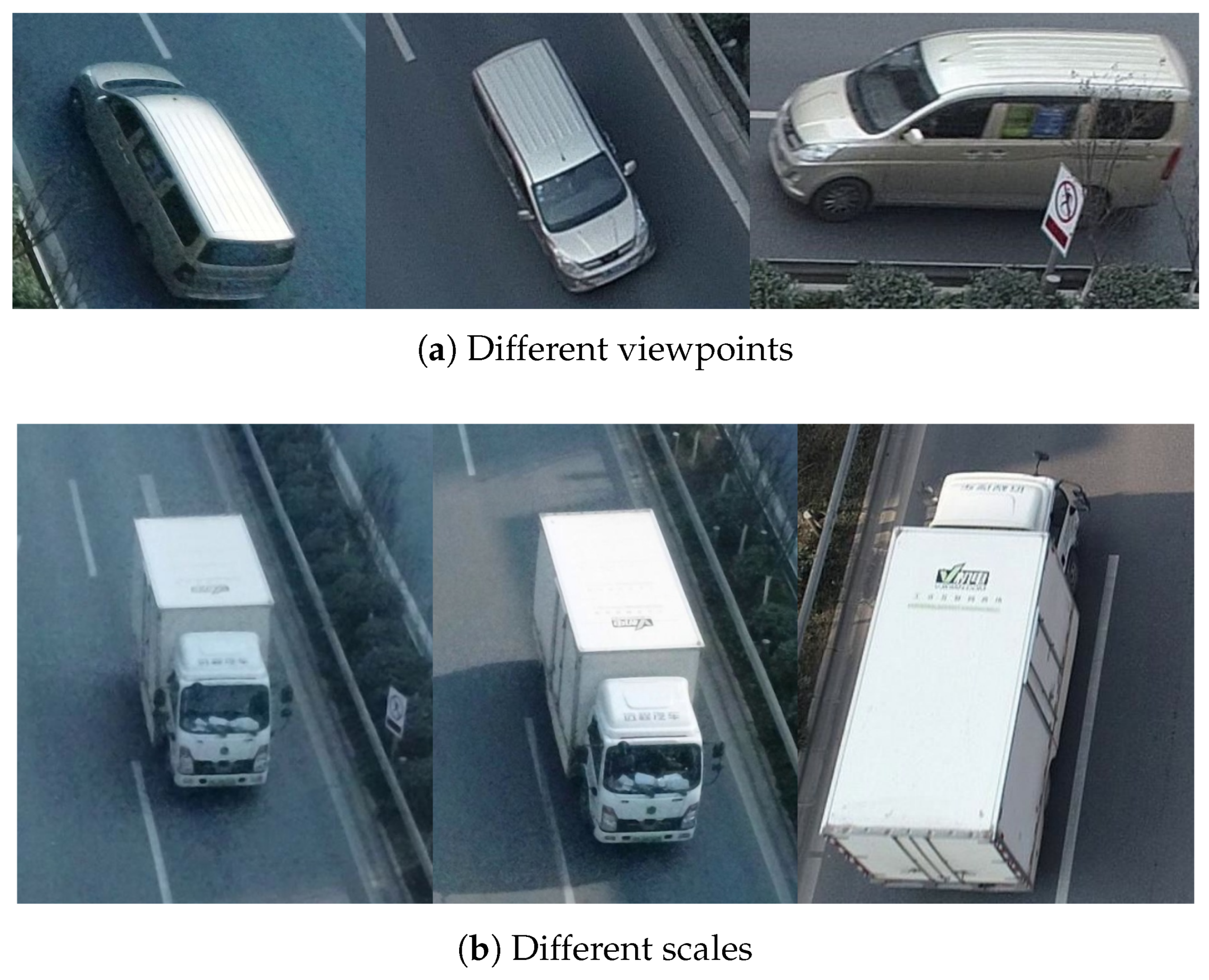
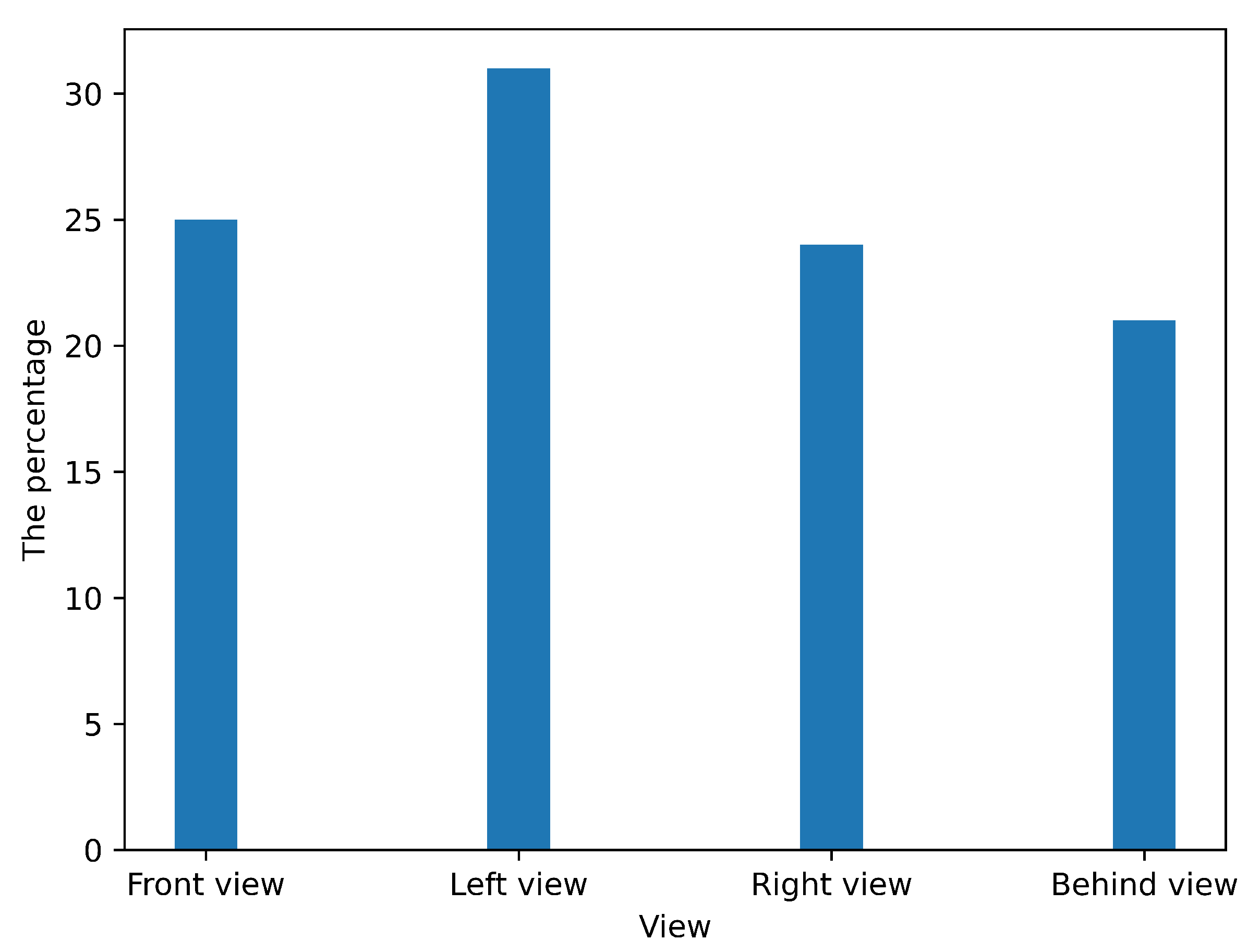
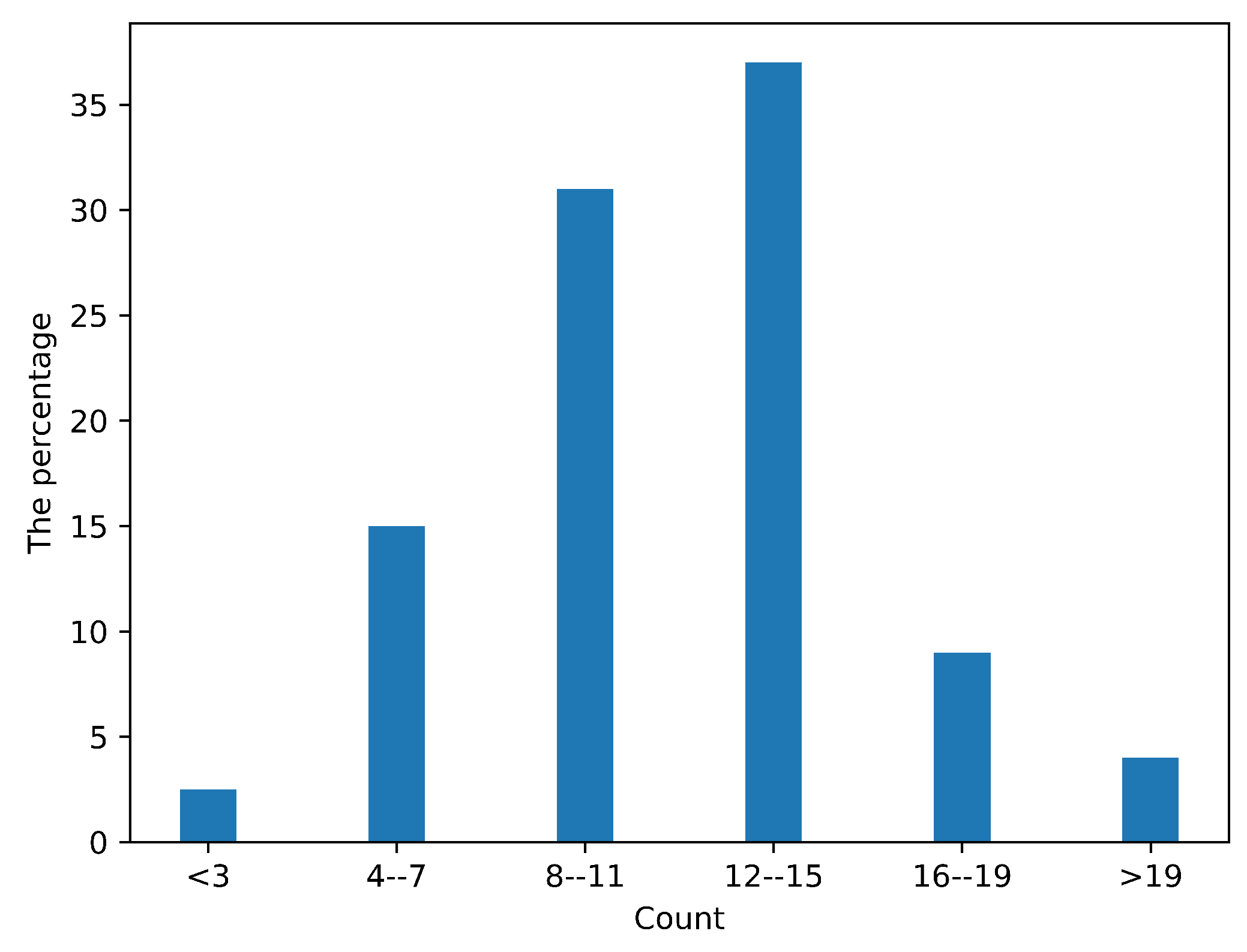
3.1.2. Multi-View and Multi-Scale
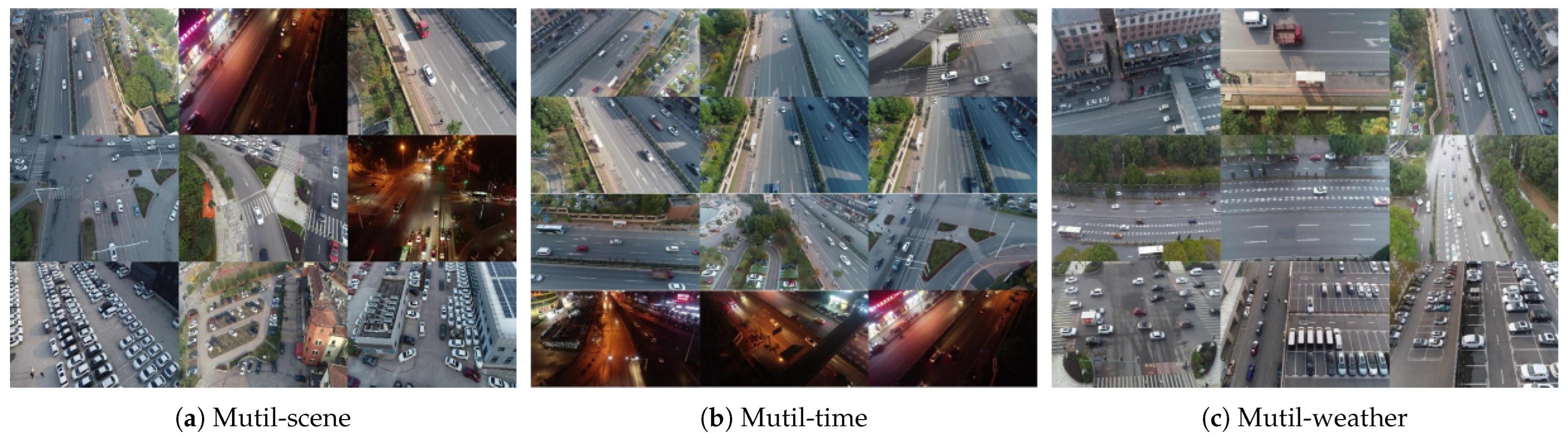
3.1.3. Multi-Scene, Multi-Time, and Multi-Weather
3.1.4. Data Processing
3.1.5. Data Annotation
3.1.6. Dataset Partitioning
3.1.7. Dataset Comparison
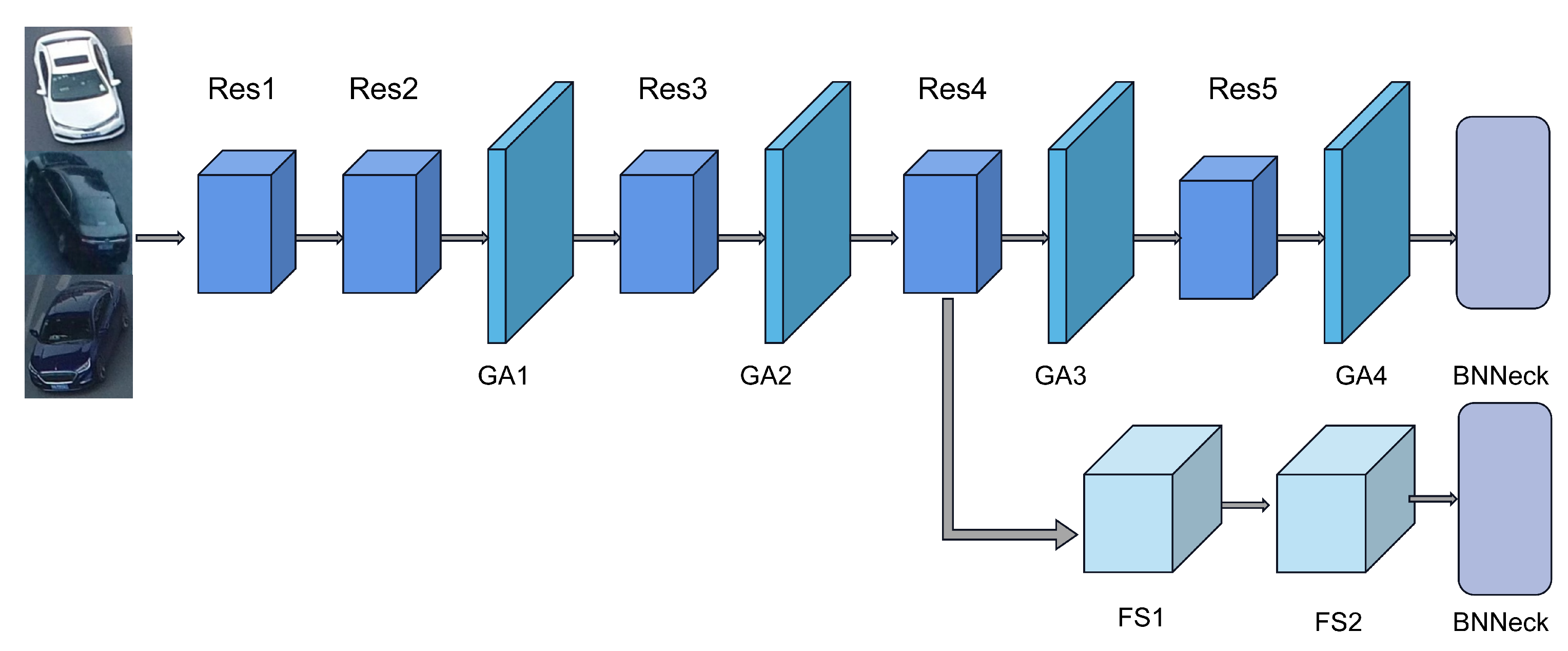
3.2. GASNet
3.2.1. Overall Structure of GASNet
3.2.2. Global Attention Module
3.2.3. Full-Scale Module
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation Indicators
4.2. Ablation Experiments
4.2.1. The Ablation Experiment for GA
4.2.2. The Ablation Experiments for FS
4.3. The Performance Comparison Experiment
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| Models | VRU | Batchsize | Rank-1 (%) | Rank-5 (%) | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Small | 32 | 88.25 | 98.95 | 92.98 |
| Medium | 32 | 83.17 | 97.44 | 89.41 | |
| Big | 32 | 70.23 | 92.04 | 79.77 | |
| Baseline+GA | Small | 32 | 95.24 | 99.65 | 97.28 |
| Medium | 32 | 92.84 | 99.13 | 95.68 | |
| Big | 32 | 86.00 | 97.45 | 91.04 |
| Models | VRU | Batchsize | Rank-1 (%) | Rank-5 (%) | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Small | 64 | 94.24 | 99.70 | 96.78 |
| Medium | 64 | 90.56 | 99.04 | 94.34 | |
| Big | 64 | 82.78 | 96.91 | 89.00 | |
| Baseline+GA | Small | 64 | 96.19 | 99.63 | 97.61 |
| Medium | 64 | 94.28 | 99.25 | 96.59 | |
| Big | 64 | 88.32 | 98.07 | 92.63 |
| Models | VRU | Batchsize | Rank-1 (%) | Rank-5 (%) | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Small | 96 | 95.38 | 99.60 | 97.33 |
| Medium | 96 | 92.86 | 99.23 | 95.77 | |
| Big | 96 | 85.10 | 97.78 | 90.70 | |
| Baseline+GA | Small | 96 | 96.40 | 99.76 | 97.95 |
| Medium | 96 | 94.92 | 99.24 | 96.92 | |
| Big | 96 | 88.99 | 98.26 | 93.11 |
| Models | VRU | Batchsize | Rank-1 (%) | Rank-5 (%) | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Small | 128 | 96.08 | 99.64 | 97.74 |
| Medium | 128 | 93.33 | 99.25 | 96.02 | |
| Big | 128 | 86.86 | 98.05 | 91.85 | |
| Baseline+GA | Small | 128 | 96.93 | 99.63 | 98.20 |
| Medium | 128 | 94.62 | 99.37 | 96.79 | |
| Big | 128 | 88.97 | 98.19 | 93.09 |
| Models | VRU | Batchsize | Rank-1 (%) | Rank-5 (%) | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Small | 32 | 88.25 | 98.95 | 92.98 |
| Medium | 32 | 83.17 | 97.44 | 89.41 | |
| Big | 32 | 70.23 | 92.04 | 79.77 | |
| Baseline+FS | Small | 32 | 90.55 | 99.22 | 96.17 |
| Medium | 32 | 90.33 | 98.45 | 93.98 | |
| Big | 32 | 82.24 | 95.90 | 88.21 |
| Models | VRU | Batchsize | Rank-1 (%) | Rank-5 (%) | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Small | 64 | 94.24 | 99.70 | 96.78 |
| Medium | 64 | 90.56 | 99.04 | 94.34 | |
| Big | 64 | 82.78 | 96.91 | 89.00 | |
| Baseline+FS | Small | 64 | 95.87 | 99.61 | 97.61 |
| Medium | 64 | 93.70 | 99.22 | 96.18 | |
| Big | 64 | 87.91 | 97.58 | 92.21 |
| Models | VRU | Batchsize | Rank-1 (%) | Rank-5 (%) | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Small | 96 | 95.38 | 99.60 | 97.33 |
| Medium | 96 | 92.86 | 99.23 | 95.77 | |
| Big | 96 | 85.10 | 97.78 | 90.7 | |
| Baseline+FS | Small | 96 | 96.55 | 99.50 | 97.95 |
| Medium | 96 | 94.39 | 99.11 | 96.53 | |
| Big | 96 | 88.84 | 98.01 | 92.92 |
| Models | VRU | Batchsize | Rank-1 (%) | Rank-5 (%) | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Small | 128 | 96.08 | 99.64 | 97.74 |
| Medium | 128 | 93.33 | 99.25 | 96.02 | |
| Big | 128 | 86.86 | 98.05 | 91.85 | |
| Baseline+FS | Small | 128 | 96.43 | 99.66 | 97.89 |
| Medium | 128 | 94.76 | 99.10 | 96.76 | |
| Big | 128 | 89.38 | 98.07 | 93.27 |
Appendix A.2
| Aircraft | |
|---|---|
| Parameters | Value |
| Takeoff Weight | 907 g |
| Dimensions | Folded: 214 × 91 × 84 mm Unfolded: 322 × 42 × 84 mm |
| Diagonal Distance | 354 mm |
| Max Ascent Speed | 5 m/s (S-mode), 4 m/s (P-mode) |
| Max Descent Speed | 3 m/s (S-mode), 3 m/s (P-mode) |
| Max Speed | 72 km/h (S-mode) (near sea level, no wind) |
| Max Service Ceiling Above Sea Level | 6000 m |
| Max Flight Time | 31 min (at a consistent 25 kph, no wind) |
| Overall Flight Time | 25 min (in normal flight, 15% remaining battery level) |
| Max Flight Distance | 18 km (at a consistent 50 kph, no wind) |
| Hovering Accuracy Range | Vertical: ±0.1 m (when vision positioning is active) ±0.5 m (with GPS positioning) Horizontal: ±0.3 m (when vision positioning is active) ±1.5 m (with GPS positioning) |
| Camera | |
|---|---|
| Parameters | Value |
| Sensor | 1″ CMOS Effective Pixels: 20 million |
| Lens | FOV: approx. 77° 35 mm Format Equivalent: 28 mm Aperture: f/2.8–f/11 Shooting Range: 1 m to |
| ISO Range | Video: 100–6400 Photo: 100–3200 (auto) 100–12,800 (manual) |
| Shutter Speed | Electronic Shutter: 8-1/8000 s |
| Still Image Size | 5472 × 3648 |
| Still Photography Modes | Single shot Burst shooting: 3/5 frames Auto Exposure Bracketing (AEB): 3/5 bracketed frames at 0.7 EV Bias Interval: 2/3/5/7/10/15/20/30/60 s (JPEG) 5/7/10/15/20/30/60 s (RAW) |
| Video Resolution | 4 K: 3840 × 2160 24/25/30 p 2.7 K: 2688 × 1512 24/25/30/48/50/60 p FHD: 1920 × 1080 24/25/30/48/50/60/120 p |
| Color Mode | Dlog-M (10-bit) support HDR video (HLG 10-bit) |
| Max Video Bitrate | 100 Mbps |
| Photo Format | JPEG/DNG (RAW) |
| Video Format | MP4/MOV |
References
- Zhang, S.; Shao, H.; Li, X.; Xian, W.; Shao, Q.; Yin, Z.; Lai, F.; Qi, J. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecological Security Pattern of Urban Agglomerations in Yangtze River Delta Based on LUCC Simulation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L. A Spliced Satellite Optical Camera Geometric Calibration Method Based on Inter-Chip Geometry Constraints. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, M.; Velastin, S. Intelligent distributed surveillance systems: A review. IEEE Proc.-Vis. Image Signal Process. 2005, 152, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, F.Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, W.H.; Xu, X.; Chen, C. Data-Driven Intelligent Transportation Systems: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2011, 12, 1624–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Capra, L.; Wolfson, O.; Yang, H. Urban Computing: Concepts, Methodologies, and Applications. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2014, 5, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Jiao, B.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Y. Vehicle Re-identification in Aerial Imagery: Dataset and Approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Sebe, N. Viewpoint and Scale Consistency Reinforcement for UAV Vehicle Re-Identification. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, X. Learning Discriminative Features with Multiple Granularities for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM Multimedia Conference (MM), Seoul, Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q. SCAN: Spatial and Channel Attention Network for Vehicle Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 19th Pacific-Rim Conference on Multimedia (PCM), Hefei, China, 21–22 September 2018; pp. 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Huang, T. Exploiting Multi-Grain Ranking Constraints for Precisely Searching Visually-Similar Vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.; Fu, H. Large-scale vehicle re-identification in urban surveillance videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 July 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiao, T.; Li, H.; Yi, S.; Wang, X. Learning Deep Neural Networks for Vehicle Re-ID with Visual-spatio-temporal Path Proposals. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Mei, T.; Ma, H. A Deep Learning-Based Approach to Progressive Vehicle Re-identification for Urban Surveillance. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pang, L.; Huang, T. Deep Relative Distance Learning: Tell the Difference Between Similar Vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Bai, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Duan, L.Y. VERI-Wild: A Large Dataset and a New Method for Vehicle Re-Identification in the Wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3230–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Yan, B.; Bare, B. Feature Super-Resolution: Make Machine See More Clearly. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3994–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shao, L. Cross-view GAN based vehicle generation for re-identification. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), London, UK, 4–7 September 2017; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, Y.; Cavallaro, A.; Xiang, T. Omni-Scale Feature Learning for Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3701–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S. Person Re-Identification by Deep Learning Multi-Scale Representations. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2590–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, L.; Liu, X.; Yao, Z.; Yi, S.; Shao, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Orientation Invariant Feature Embedding and Spatial Temporal Regularization for Vehicle Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Gu, Y.; Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Jiang, W. Bag of Tricks and A Strong Baseline for Deep Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Choi, J.Y. Deep Neural Networks Learning based on Multiple Loss Functions for Both Person and Vehicles Re-Identification. J. Korea Multimed. Soc. 2020, 23, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lagadec, B.; Bremond, F. Partition and reunion: A two-branch neural network for vehicle re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, A.O.R.; Soares, F.F.; Neto, A.V.L.; de Macedo, J.A.F.; Rego, P.A.L.; Gomes, F.A.C.; Maia, J.G.R. Vehicle Re-Identification by Deep Feature Embedding and Approximate Nearest Neighbors. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), New York, NY, USA, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z. Relation-Aware Global Attention for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




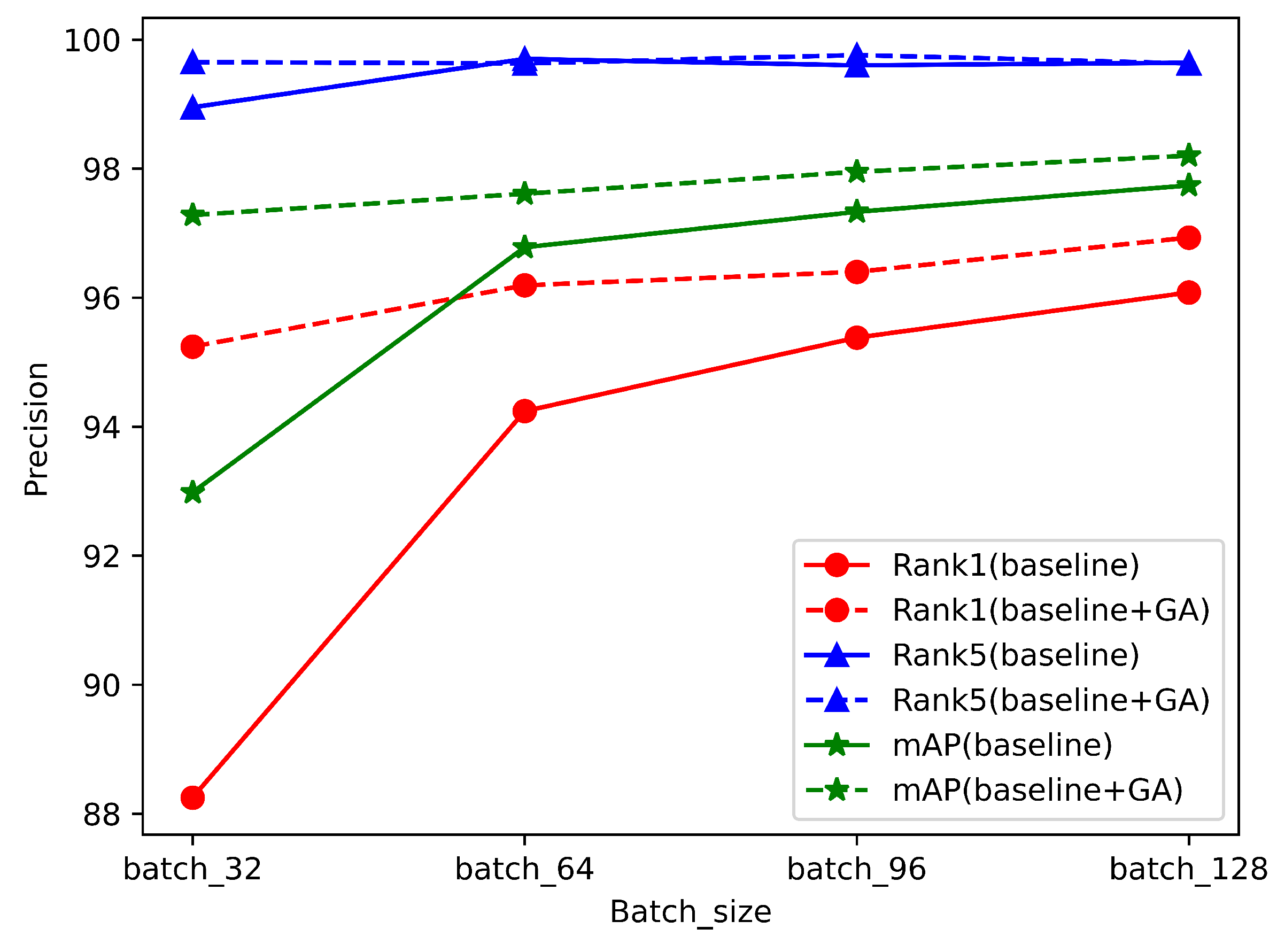
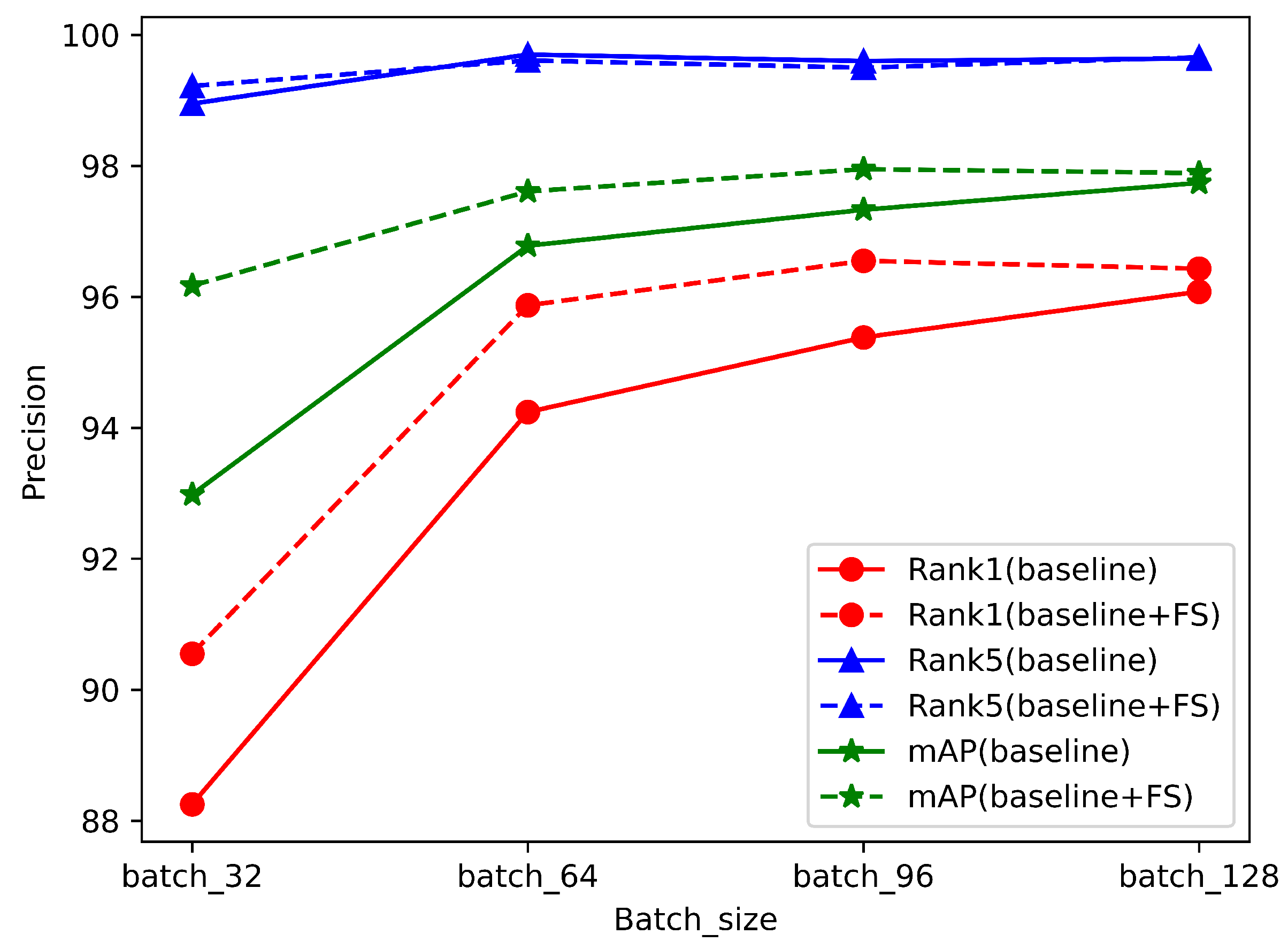
| Datasets | VRU | UAV-VeID | VRAI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identities | 15,085 | 4601 | 13,022 |
| Images | 172,137 | 41,917 | 137,613 |
| Multi-view | √ | √ | √ |
| Multi-scale | √ | √ | √ |
| Weather | √ | √ | × |
| Lighting | √ | √ | × |
| Open-source | √ | × | × |
| Models | VRU | Rank-1 (%) | Rank-5 (%) | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGN | Small | 81.72 | 95.08 | 82.48 |
| Medium | 78.75 | 93.75 | 80.06 | |
| Big | 66.25 | 87.15 | 71.53 | |
| SCAN | Small | 75.22 | 95.03 | 83.95 |
| Medium | 67.27 | 90.51 | 77.34 | |
| Big | 52.44 | 79.63 | 64.51 | |
| Baseline | Small | 96.08 | 99.64 | 97.74 |
| Medium | 93.33 | 99.25 | 96.02 | |
| Big | 86.86 | 98.05 | 91.85 | |
| Baseline+GA | Small | 96.93 | 99.63 | 98.20 |
| Medium | 94.62 | 99.37 | 96.79 | |
| Big | 88.97 | 98.19 | 93.09 | |
| Baseline+FS | Small | 96.43 | 99.66 | 97.89 |
| Medium | 94.76 | 99.10 | 96.76 | |
| Big | 89.38 | 98.07 | 93.27 | |
| GASNet | Small | 97.45 | 99.66 | 98.51 |
| Medium | 95.59 | 99.33 | 97.31 | |
| Big | 90.29 | 98.40 | 93.93 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, H. Vehicle Re-Identification Based on UAV Viewpoint: Dataset and Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184603
Lu M, Xu Y, Li H. Vehicle Re-Identification Based on UAV Viewpoint: Dataset and Method. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(18):4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184603
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Mingming, Yongchuan Xu, and Haifeng Li. 2022. "Vehicle Re-Identification Based on UAV Viewpoint: Dataset and Method" Remote Sensing 14, no. 18: 4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184603
APA StyleLu, M., Xu, Y., & Li, H. (2022). Vehicle Re-Identification Based on UAV Viewpoint: Dataset and Method. Remote Sensing, 14(18), 4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184603








