Effect of Number and Configuration of Participating Stations on Lightning Location outside the Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
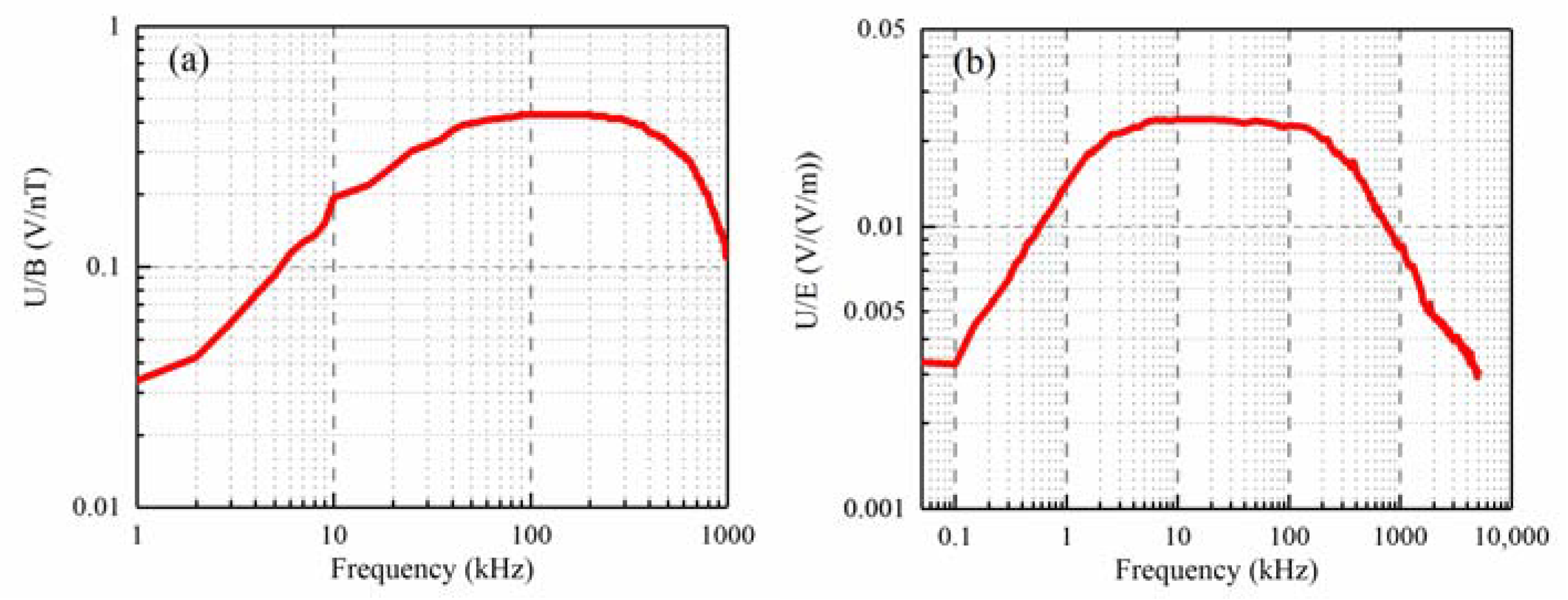
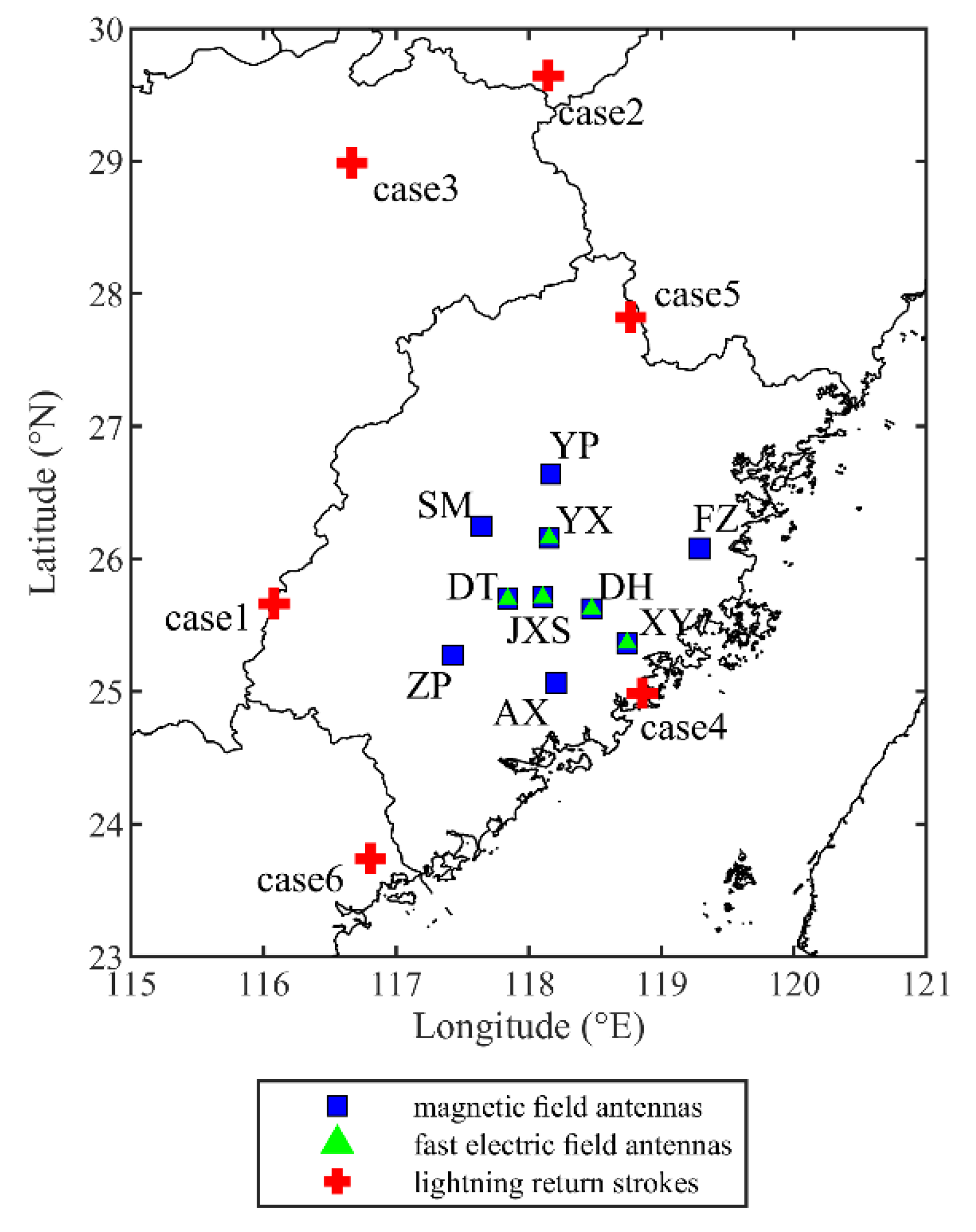
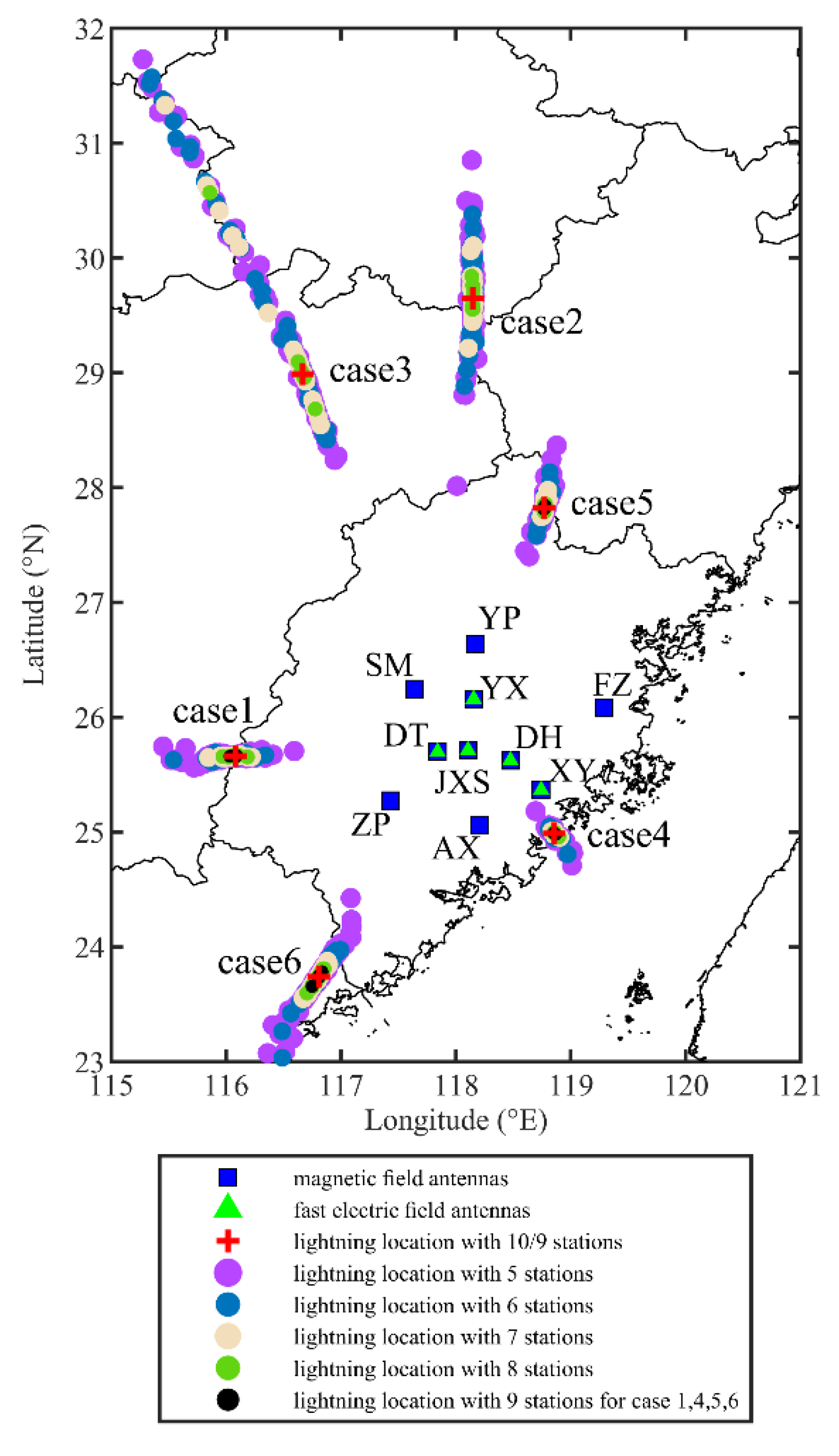
2.1. The Lightning Detection and Location Network
2.2. Lightning Location Algorithm
3. Results
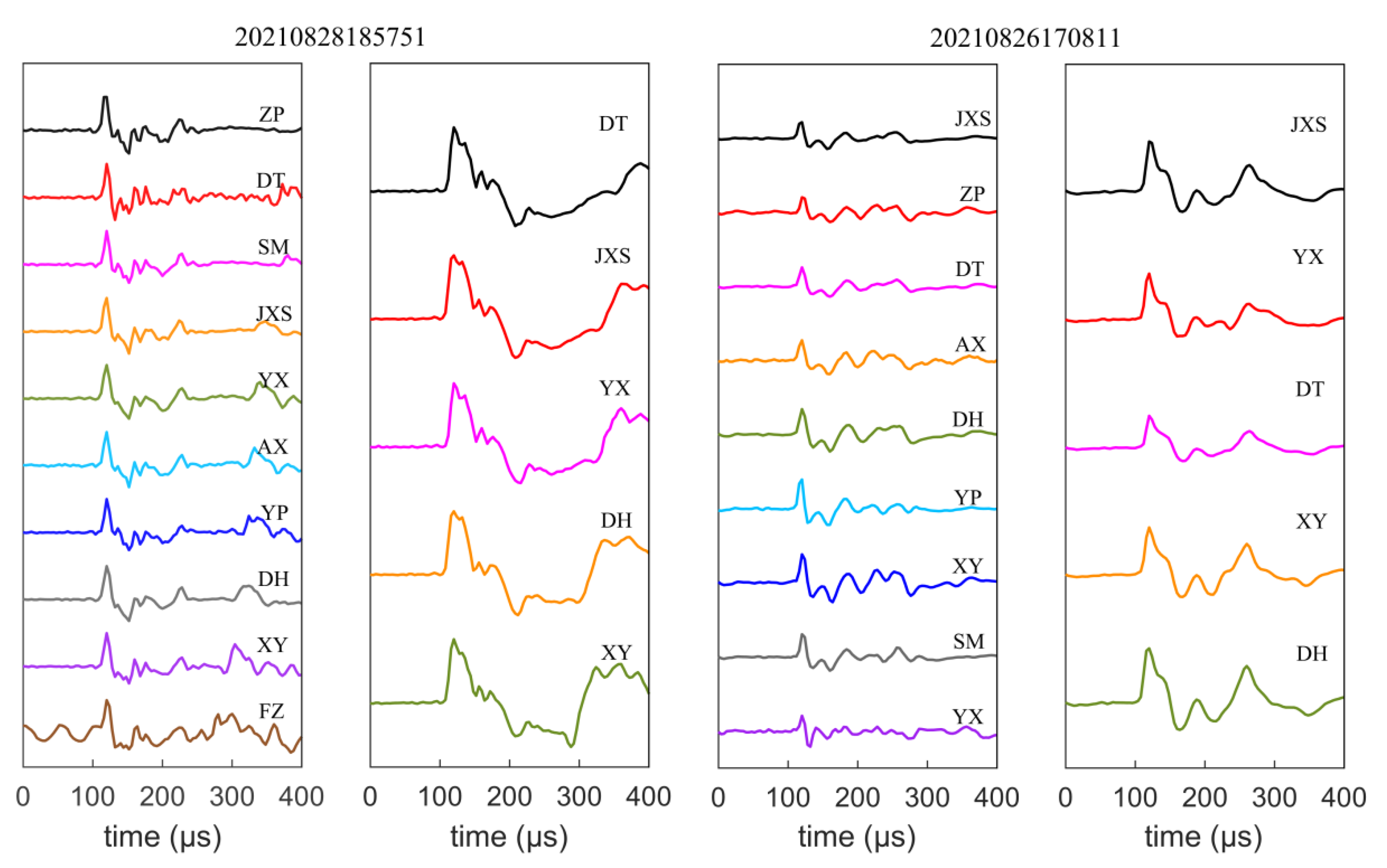
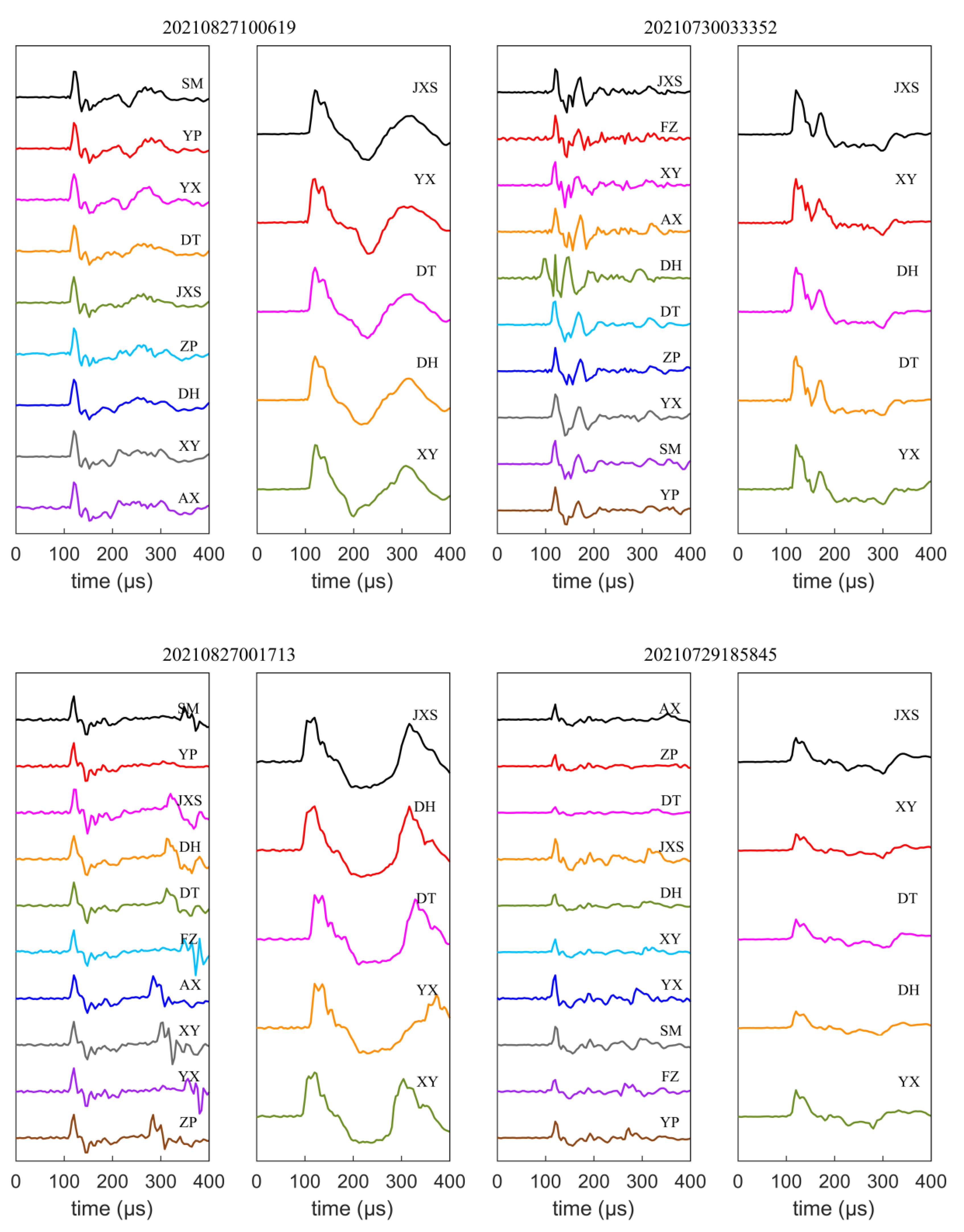
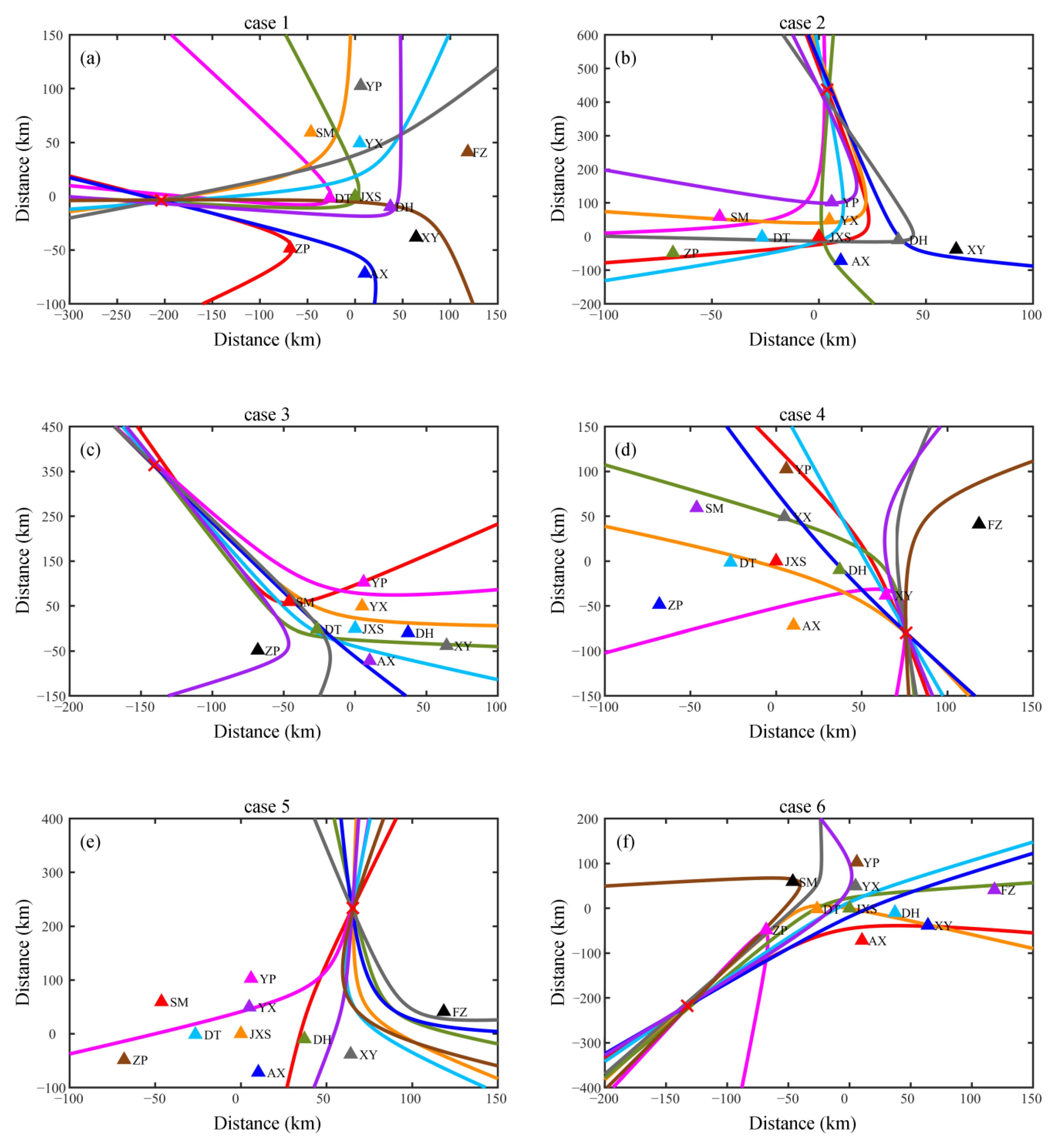
3.1. The Validation of Reference Location
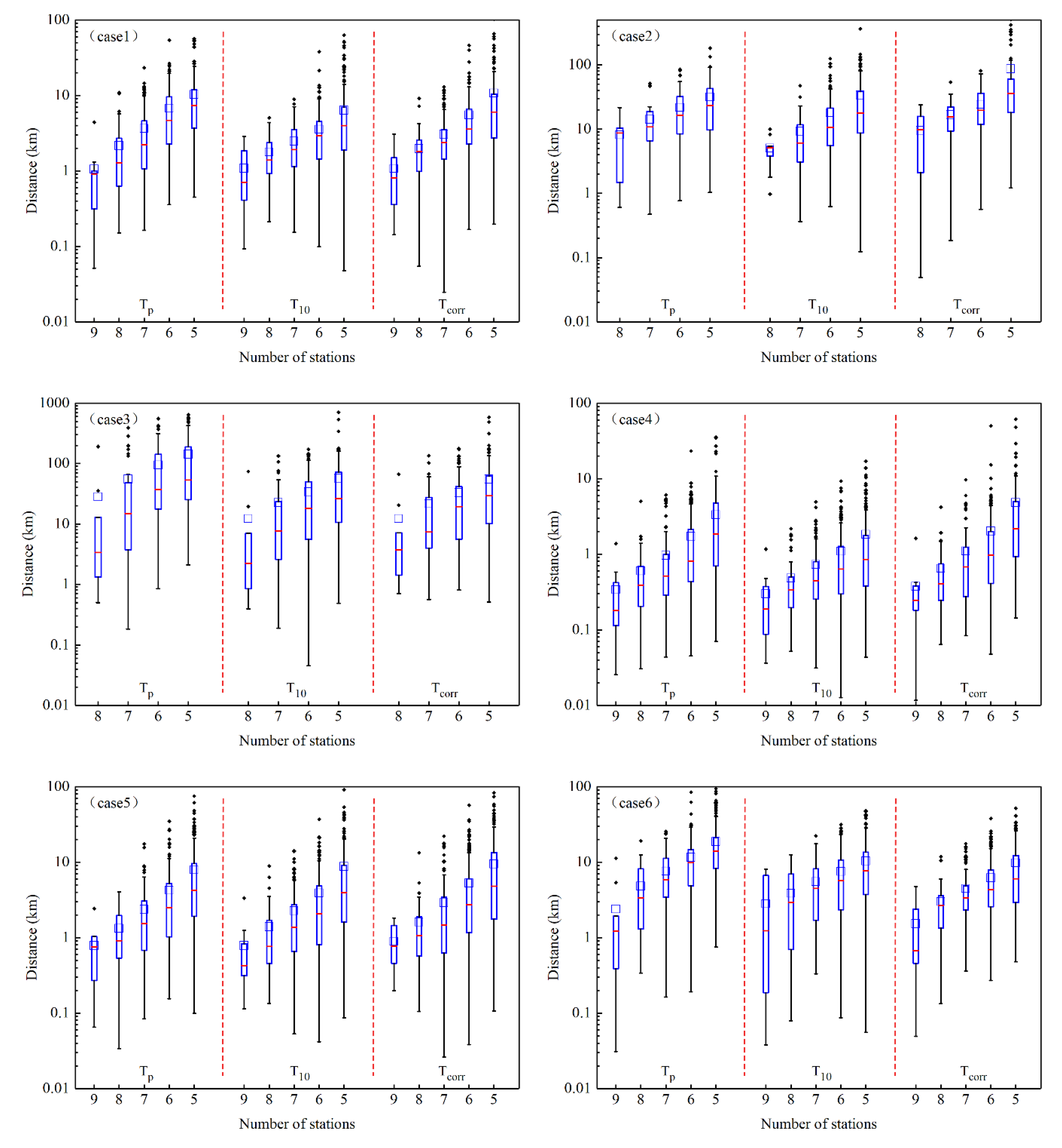
3.2. The Deviation Distance between the Reference Location and the Locations for Different Number and Configuration of Participating Stations
3.3. The Configuration of Five Stations under the Maximum and Minimum Deviation Distance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGRI | advanced geosynchronous radiation imager |
| AX | Anxi station |
| BLNET | Beijing Lightning Network |
| BOLT | Broadband Observation Network for Lightning and Thunderstorm positioning system |
| CTT | Cloud-Top Temperature |
| DE | detection efficiency |
| DH | Dehua station |
| DT | Datian station |
| EUCLID | European Cooperation for Lightning Detection |
| FALMA | Fast Antenna Lightning Mapping Array |
| FY4A | FengYun 4A meteorological satellite |
| FZ | Fuzhou station |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| IBP | initial breakdown processes |
| IC | intracloud lightning |
| JASA | Jianghuai Area Sferic Array |
| JXS | Jiuxianshan station |
| LA | location accuracy |
| LASA | Los Alamos Sferic Array |
| LDAR | Lightning Detection and Ranging |
| LF | low frequency |
| LFEDA | Low-frequency E-field Detection Array |
| LINET | Lightning detection network |
| LLSs | lightning location systems |
| LMA | Lightning Mapping Array |
| NBE | narrow bipolar event |
| NLDN | National Lightning Detection Network |
| SM | Sanming station |
| ToA | time of arrival |
| VHF | very high frequency |
| VLF | very low frequency |
| XY | Xianyou station |
| YP | Yanping station |
| YX | Youxi station |
| ZP | Zhangping station |
References
- Rakov, V.A.; Uman, M.A. Lightning: Physics and Effects; Cambridge University Press: Cambidge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, K.L.; Murphy, M.J.; Bardo, E.A.; Hiscox, W.L.; Pyle, R.B.; Pifer, A.E. A combined TOA/MDF technology upgrade of the US National Lightning Detection Network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 9035–9044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, K.L.; Murphy, M.J. An Overview of Lightning Locating Systems: History, Techniques, and Data Uses, With an In-Depth Look at the U.S. NLDN. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2009, 51, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.A.; Eack, K.B.; Harlin, J.; Heavner, M.J.; Jacobson, A.R.; Massey, R.S.; Shao, X.M.; Wiens, K.C. The Los Alamos Sferic Array: A research tool for lightning investigations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, ACL-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.M.; Stanley, M.; Regan, A.; Harlin, J.; Pongratz, M.; Stock, M. Total lightning observations with the new and improved Los Alamos Sferic Array (LASA). J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2006, 23, 1273–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, H.D.; Schmidt, K.; Laroche, P.; Blanchet, P.; Oettinger, W.P.; Defer, E.; Dziewit, Z.; Konarski, J. LINET—An international lightning detection network in Europe. Atmos. Res. 2009, 91, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, H.D.; Meneux, B. LINET systems—10 years experience. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2014 International Conference on Lightning Protection (ICLP), Shanghai, China, 11–18 October 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Heckman, S. Using total lightning data in severe storm prediction: Global case study analysis from North America, Brazil and Australia. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Symposium on Lightning Protection (XI SIPDA), Fortaleza, Brazil, 3–7 October 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, W.; Diendorfer, G.; Pedeboy, S.; Poelman, D.R. The European lightning location system EUCLID—Part 1: Performance analysis and validation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowden, R.L.; Holzworth, R.H.; Rodger, C.J.; Lichtenberger, J.; Thomson, N.R.; Jacobson, A.R.; Lay, E.; Brundell, J.B.; Lyons, T.J.; O’keefe, S. World-Wide Lightning Location Using VLF Propagation in the Earth-Ionosphere Waveguide. IEEE Antennnas Propag. Mag. 2008, 50, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodger, C.J.; Werner, S.W.; Brundell, J.B.; Thomas, N.R.; Lay, E.H.; Holzworth, R.H.; Dowden, R.L. Detection efficiency of the VLF World-Wide Lightning Location Network (WWLLN): Initial case study. Ann. Geophys. 2004, 24, 3197–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Said, R.K.; Inan, U.S.; Cummins, K.L. Long-Range Lightning Geolocation Using a VLF Radio Atmospheric Waveform Bank. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D23108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessi, A.T.; Businger, S.; Cummins, K.L.; Demetriades, N.W.S.; Murphy, M.; Pifer, B. Development of a Long-Range Lightning Detection Network for the Pacific: Construction, Calibration, and Performance. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2009, 26, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronis, T.G.; Anagnostou, E.N. Error Analysis for a Long-Range Lightning Monitoring Network of Ground-Based Receivers in Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustan, P.L.; Uman, M.A.; Childers, D.G.; Beasley, W.H.; Lennon, C.L. Lightning source locations from VHF radiation data for a flash at Kennedy Space Center. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1980, 85, 4893–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.J.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Rison, W.; Hunyady, S.J.; Winn, W.P.; Hamlin, T.; Harlin, J. Accuracy of the Lightning Mapping Array. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D14207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.M.; Holden, D.N.; Rhodes, C.T. Broad band radio interferometry for lightning observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Biagi, C.J.; Rakov, V.A.; Hill, J.D.; Stapleton, M.V.; Jordan, D.M.; Uman, M.A.; Morimoto, T.; Ushio, T.; Kawasaki, Z.I. Three-dimensional imaging of upward positive leaders in triggered lightning using VHF broadband digital interferometers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L05805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.G.; Akita, M.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Rison, W.; Edens, H.E.; Kawasaki, Z.; Stanley, M.A. Continuous broadband digital interferometry of lightning using a generalized cross—Correlation algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3134–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunarathne, S.; Marshall, T.C.; Stolzenburg, M.; Karunarathna, N.; Vickers, L.E.; Warner, T.A.; Orville, R.E. Locating initial breakdown pulses using electric field change network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7129–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzer, P.M.; Christian, H.J.; Stewart, M.; Burchfield, J.; Podgorny, S.; Corredor, D.; Hall, J.; Kuznetsov, E.; Franklin, V. Characterization and applications of VLF/LF source locations from lightning using the Huntsville Alabama Marx Meter Array. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 3120–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bitzer, P.M.; Stewart, M.; Podgorny, S.; Corredor, D.; Burchfeld, J.; Carey, L.; Medina, B.; Stock, M. Huntsville Alabama Marx meter array 2: Upgrade and capability. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.C.; Cummer, S.A.; Solanki, R.; Weinert, J.; McTague, L.; Katko, A.; Barrett, J.; Zigoneanu, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, W. A low-frequency near-field interferometric-TOA 3-D Lightning Mapping Array. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 7777–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Wu, T.; Ushio, T.; Kusunoki, K.; Nakamura, Y. Initial results of LF sensor network for lightning observation and characteristics of lightning emission in LF band. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 12034–12051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Wu, T.; Yoshida, S. Review of recent progress in lightning and thunderstorm detection techniques in Asia. Atmos. Res. 2015, 154, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.H.; Takagi, N. Lightning mapping with an array of fast antennas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3698–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Chang, S.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, F.; Gao, C. Classification of VLF/LF Lightning Signals Using Sensors and Deep Learning Methods. Sensors 2020, 20, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Du, Y.; Fan, L.; He, H.; Zhong, D. A lightning location system in China: Its performances and applications. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2002, 44, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qie, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Su, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Tian, Y. Beijing Lightning Network (BLNET) and the observation on preliminary breakdown processes. Atmos. Res. 2016, 171, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Qie, X.; Jiang, R.; Wang, D.; Sun, Z.; Srivastava, A.; Williams, E. Origin of an uncommon multiple-stroke positive cloud-to-ground lightning flash with different terminations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD032098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lyu, W.; Chen, S.; Yan, X. Low-frequency E-field Detection Array (LFEDA)—Construction and preliminary results. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 1896–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhu, B.; Lyu, F.; Ma, M.; Ma, D. Using time domain waveforms of return strokes to retrieve the daytime fluctuation of ionospheric D layer. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Qin, Z.; Zhu, B.; Ma, M.; Chen, M.; Shen, P. Observations of ionospheric D layer fluctuations during sunrise and sunset by using time domain waveforms of lightning narrow bipolar events. Chin. J. Geophys. 2018, 61, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Jiang, R.; Qie, X.; Xing, H.; Liu, M.; Sun, Z.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. A low frequency 3D lightning mapping network in north China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 249, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohjola, H.; Mäkelä, A. The comparison of GLD360 and EUCLID lightning location systems in Europe. Atmos. Res. 2013, 123, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuk, B.J.; Kim, H.I.; Ha, J.S.; Lee, H.K. Intercomparison study of cloud-to-ground lightning flashes observed by KARITLDS and KLDN at South Korea. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 50, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Tian, Y.; Qie, X.; Wang, D.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; et al. Performance Assessment of Beijing Lightning Network (BLNET) and Comparison with Other Lightning Location Networks across Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, V. Propagation effects due to finitely conducting ground on lightning-generated magnetic fields evaluated using Sommerfeld’s integrals. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2009, 51, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ji, T.; Hou, W. Effect of frequency-dependent soil on the propagation of electromagnetic fields radiated by subsequent lightning strike to tall objects. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2015, 57, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Jing, X.; Li, D.; Wang, Z. Propagation effect of a fractal rough ground boundary on the lightning-radiated vertical electric field. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Rubinstein, M.; Rachidi, F.; Diendorfer, G.; Schulz, W.; Lu, G. Location Accuracy Evaluation of ToA-Based Lightning Location Systems Over Mountainous Terrain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 11760–11775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshak, W.J.; Solakiewicz, R.J.; Blakeslee, R.J.; Goodman, S.J.; Christian, H.J.; Hall, J.M.; Bailey, J.C.; Krider, E.P.; Bateman, M.G.; Boccippio, D.J.; et al. North Alabama lightning mapping array (LMA): VHF source retrieval algorithm and error analyses. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 2004, 21, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.T.; Ho, K.C. A simple and efficient estimator for hyperbolic location. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, W. Performance Evaluation of Lightning Location Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering at the Technical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Min, M.; Wu, C.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Xu, N.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, F.; Sun, F.; Qin, D.; et al. Developing the science product algorithm testbed for Chinese next-generation geostationary meteorological satellites: Fengyun-4 series. J. Meteorol. Res. 2017, 31, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhu, L.; Tang, S.; Gao, L.; Chen, L.; Zheng, W.; Han, X.; Chen, J.; Shao, J. General Comparison of FY-4A/AGRI with Other GEO/LEO Instruments and Its Potential and Challenges in Non-meteorological Applications. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 6, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Heymsfield, A.J.; DeMott, P.J.; Twohy, C.H.; Suski, K.J.; Toohey, D.W. High Ice Concentration Observed in Tropical Maritime Stratiform Mixed-Phase Clouds with Top Temperatures Warmer than −8 °C. Atmos. Res. 2020, 233, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, A.R.; Holzworth, R.; Harlin, J.; Dowden, R.; Lay, E. Performance assessment of the World Wide Lightning Location Network (WWLLN), using the Los Alamos Sferic Array (LASA) as ground truth. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, D.; Chandan, D.; Holzworth, R.H.; Strong, K.A. performance assessment of the World Wide Lightning Location Network (WWLLN) via comparison with the Canadian Lightning Detection Network (CLDN). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qie, X.; Xiong, Y.; Feng, G. Evolution of the total lightning activity in a leading line and trailing stratiform mesoscale convective system over Beijing. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Qie, X.; Liu, D.; Shi, H.; Srivastava, A. Lightning activity and its relationship with typhoon intensity and vertical wind shear for super typhoon Haiyan (1330). J. Meteorol. Res. 2016, 30, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


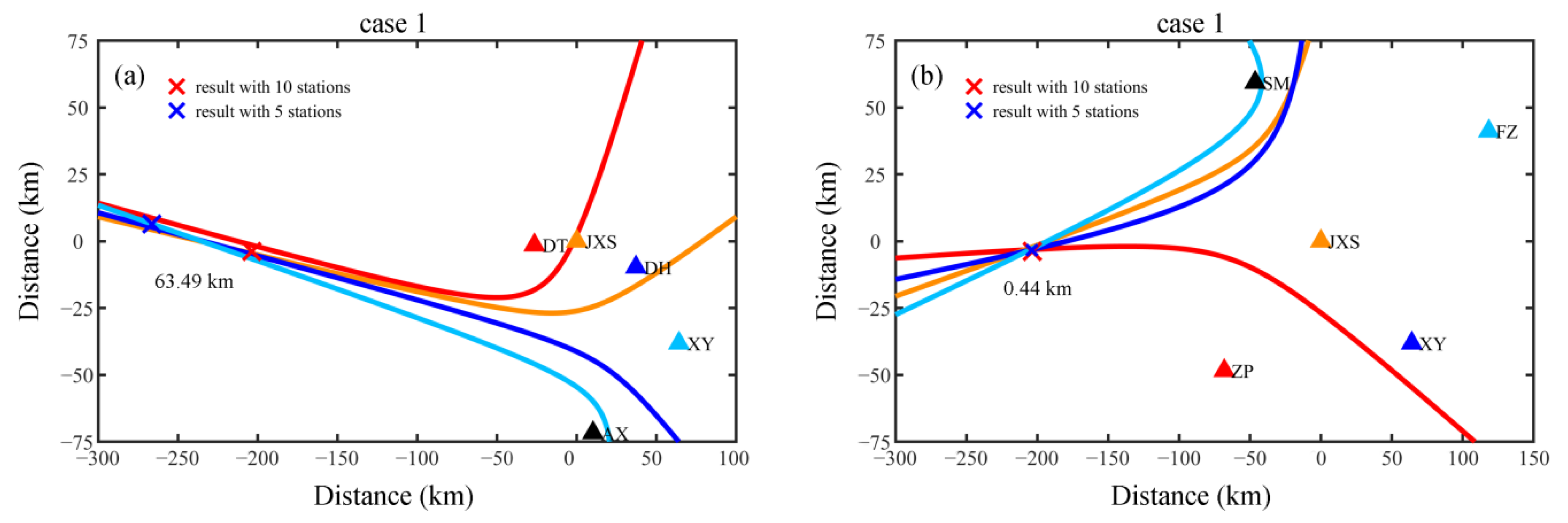

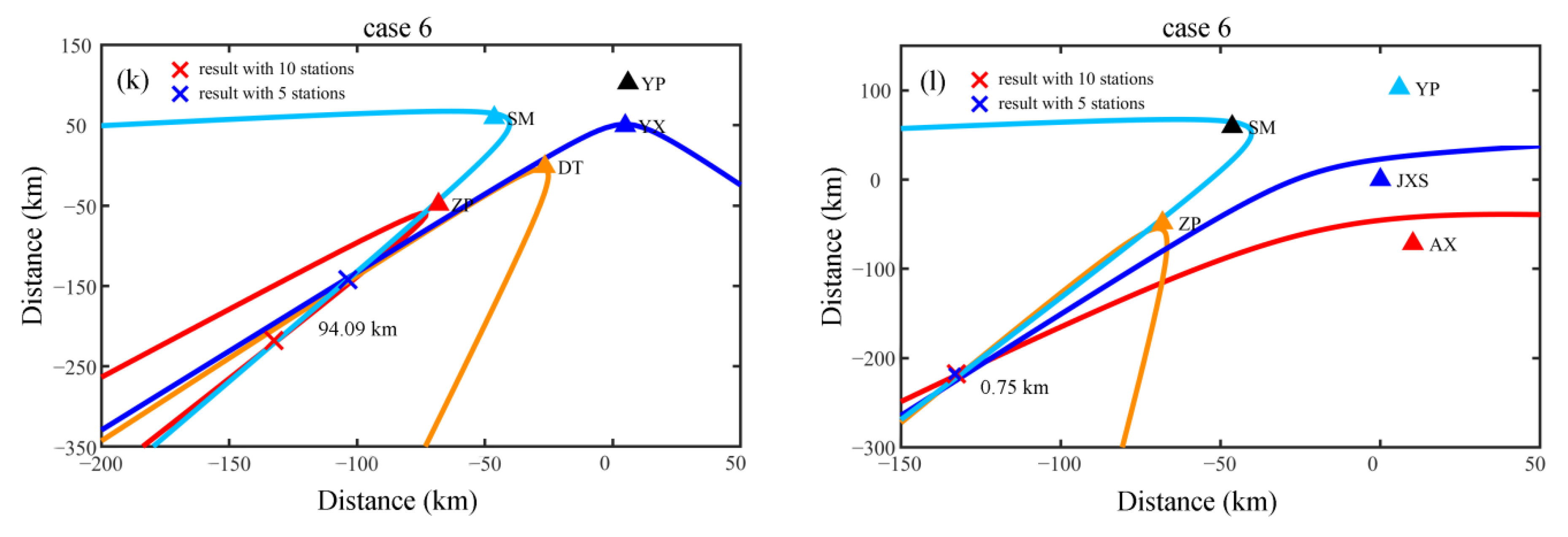

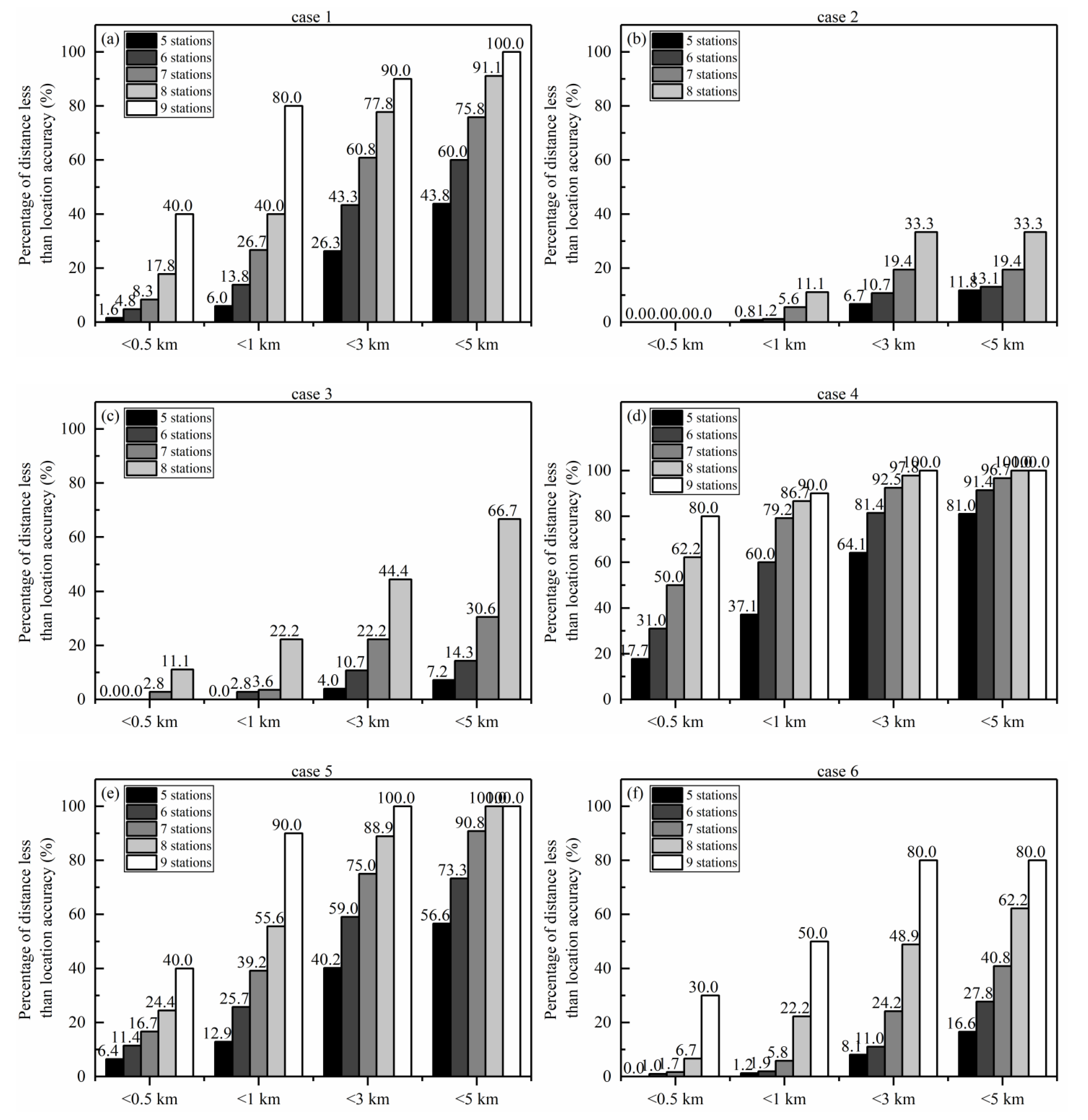
| Maximum Deviation Distance/km | Minimum Deviation Distance/km | |
|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 63.49 | 0.44 |
| Case 2 | 181.31 | 1.03 |
| Case 3 | 643.23 | 2.09 |
| Case 4 | 34.49 | 0.07 |
| Case 5 | 75.23 | 0.10 |
| Case 6 | 94.09 | 0.75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Dai, B.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; et al. Effect of Number and Configuration of Participating Stations on Lightning Location outside the Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174242
Gu J, Zhang Q, Li J, Zhang J, Zhou J, Dai B, Sun H, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhong Y, et al. Effect of Number and Configuration of Participating Stations on Lightning Location outside the Network. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(17):4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174242
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Jiaying, Qilin Zhang, Jie Li, Junchao Zhang, Jiahao Zhou, Bingzhe Dai, Hao Sun, Yao Wang, Jialei Wang, Yuqing Zhong, and et al. 2022. "Effect of Number and Configuration of Participating Stations on Lightning Location outside the Network" Remote Sensing 14, no. 17: 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174242
APA StyleGu, J., Zhang, Q., Li, J., Zhang, J., Zhou, J., Dai, B., Sun, H., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Zhong, Y., Li, Q., & Yang, J. (2022). Effect of Number and Configuration of Participating Stations on Lightning Location outside the Network. Remote Sensing, 14(17), 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174242







