The Computational Optimization of the Invariant Imbedding T Matrix Method for the Particles with N-Fold Symmetry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Invariant Imbedding T-Matrix Algorithm
3. Optimization Method for Calculating Scattering Parameters of Particles with N-Fold Symmetric Geometry
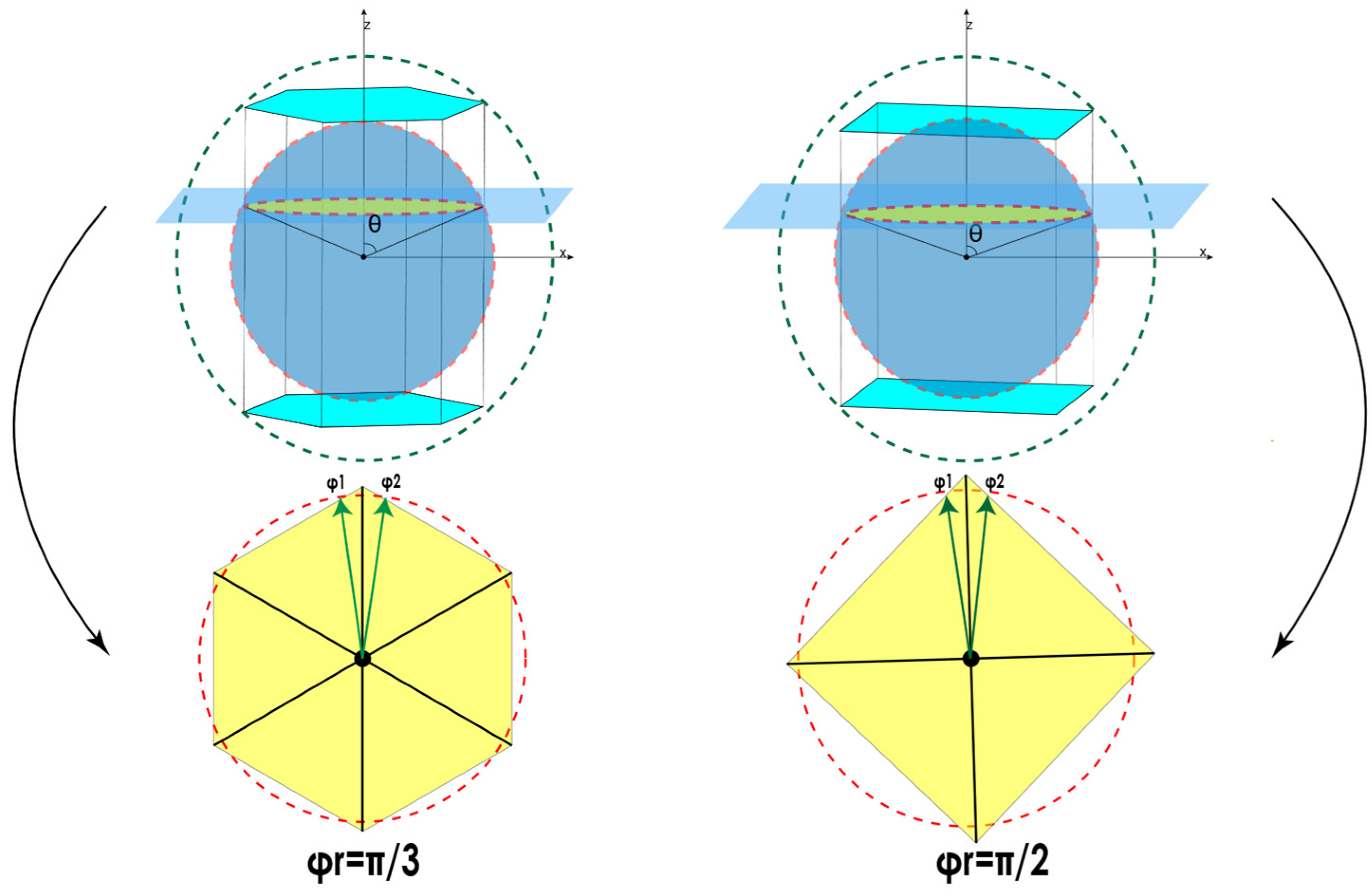
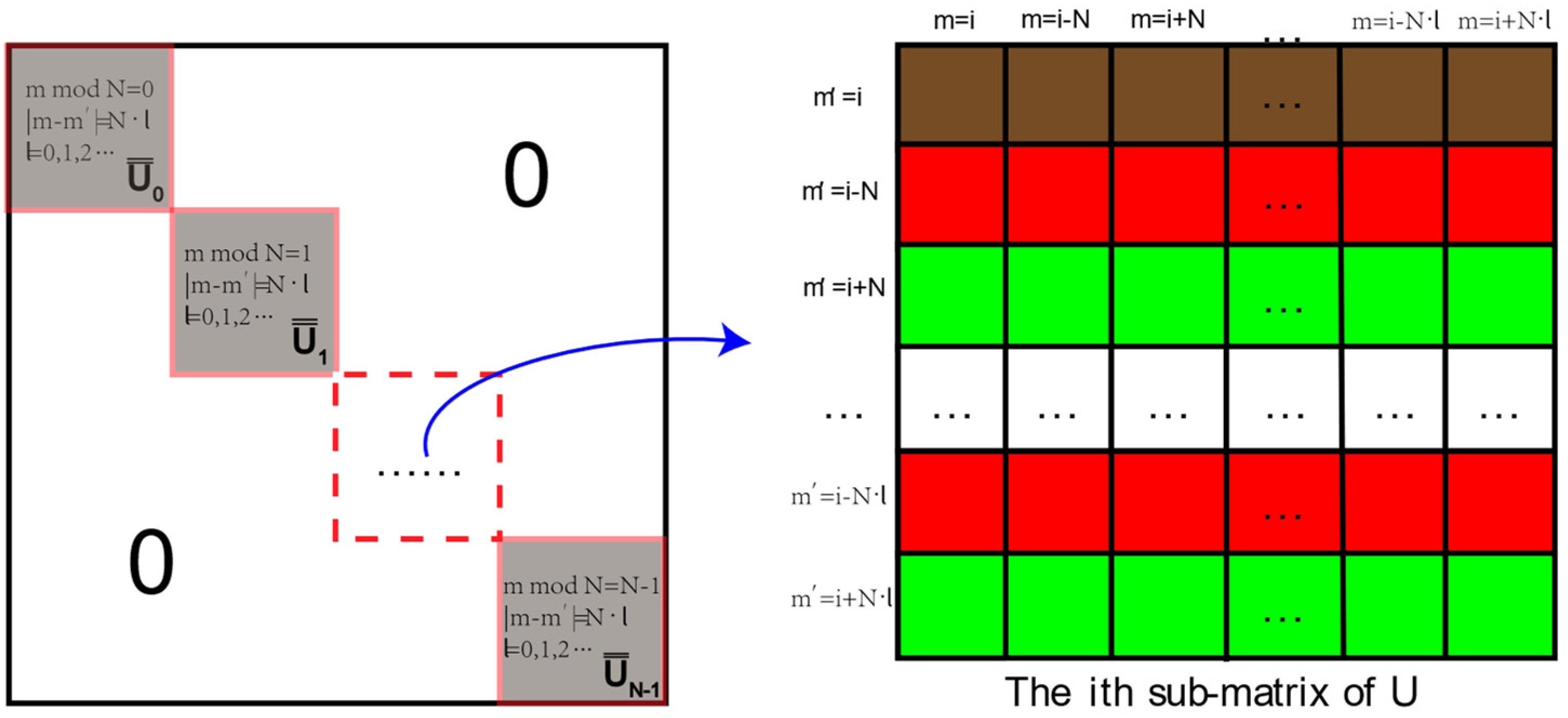
3.1. Computational Optimization Based on Symmetry Property of U Matrix
3.2. Calculation Optimization of T-Matrix Iteration Process
4. Results
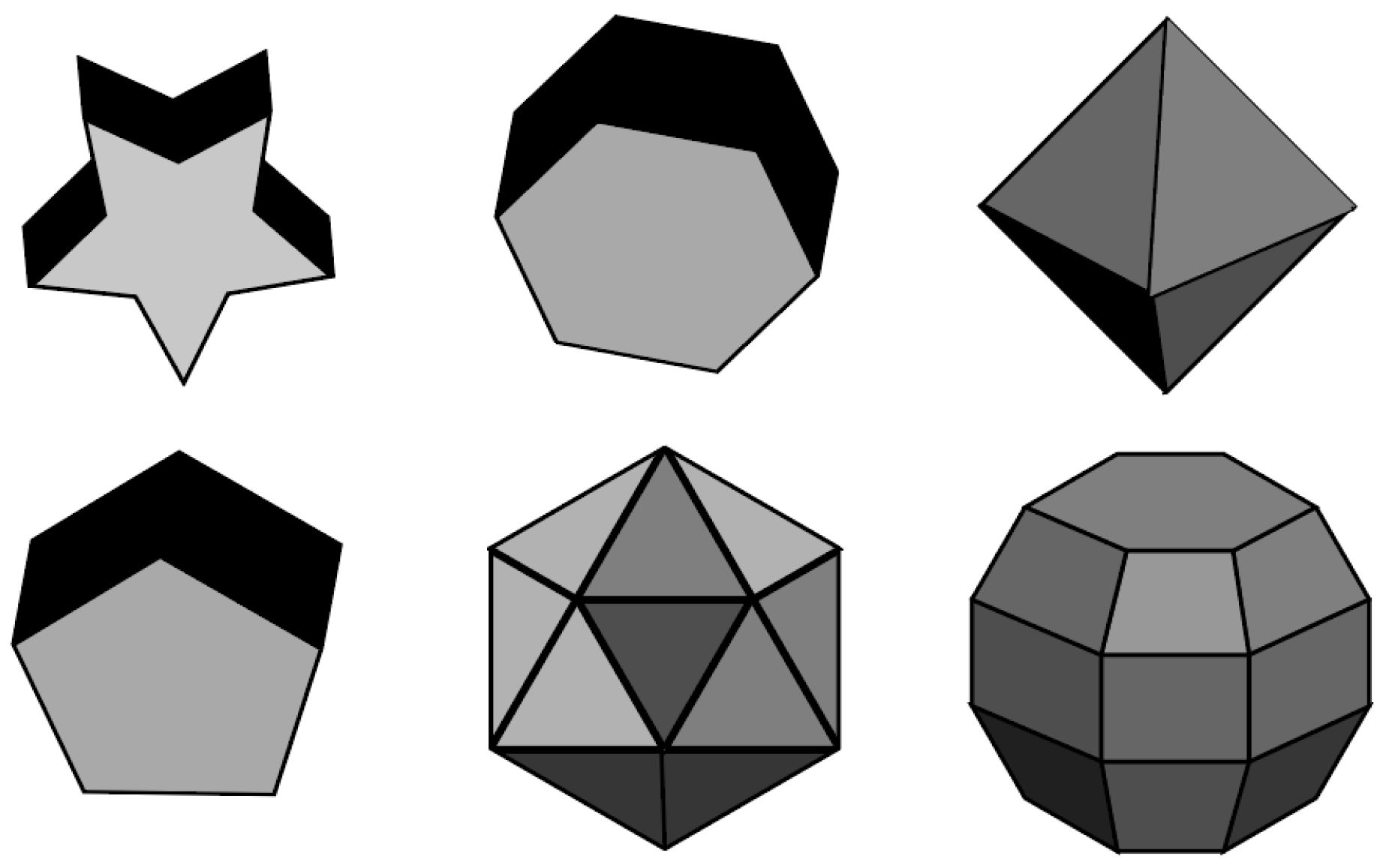
4.1. Small Particle Case
- (1)
- Hexagonal prism case
- (2)
- Octagonal prism case
- (3)
- Twelve prism case
- (4)
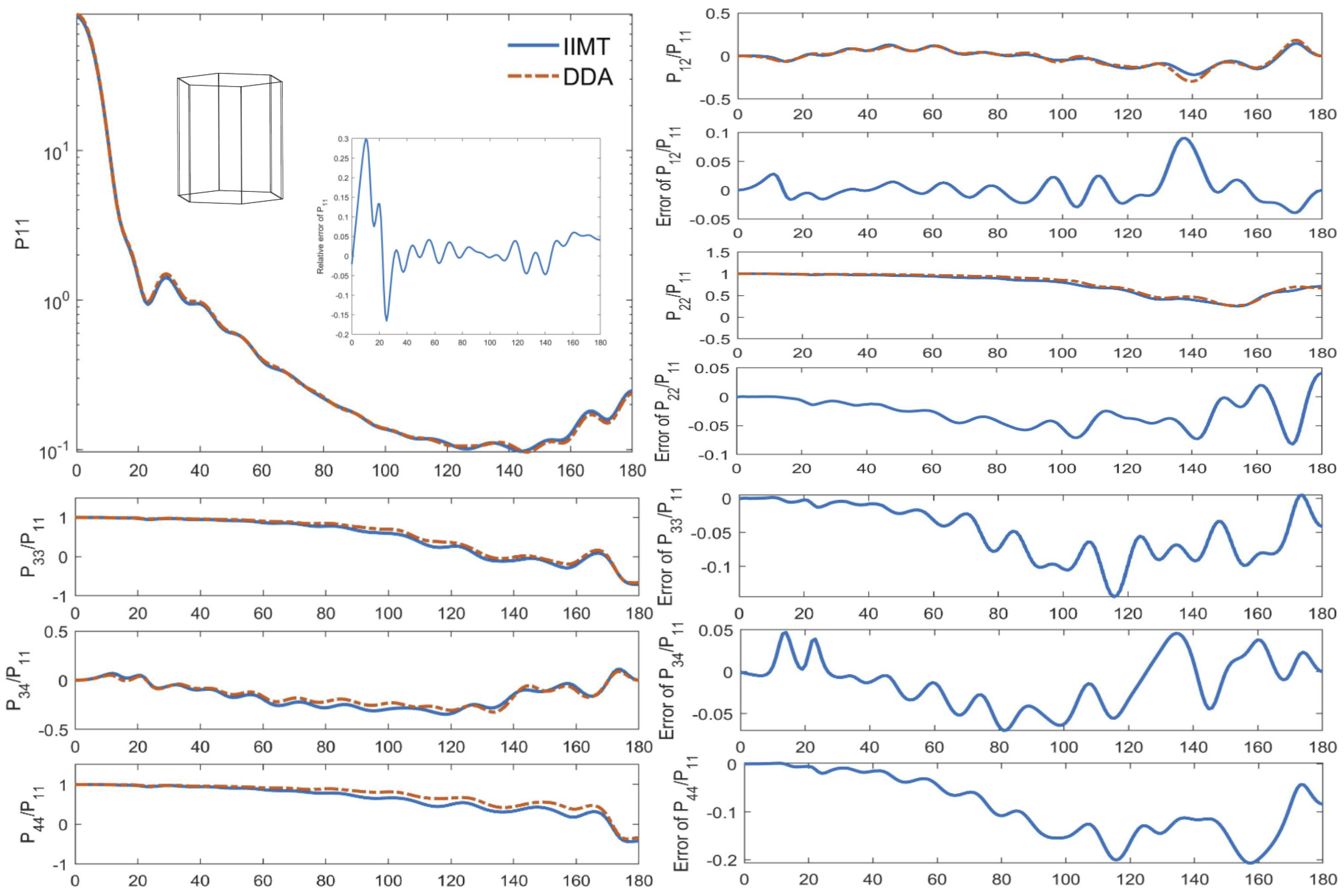
- The comparison of the improved and traditional T-matrix method
4.2. Large Particle Case
4.3. Calculation Efficiency by IIM T-Matrix Model before and after Optimization
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The improved IIM T-matrix method can accurately simulate the light scattering parameters of the particles with N-fold symmetry. The scattering properties obtained by the IIM T-matrix method demonstrated excellent agreement with those of the well-test scattering models, especially for the polarization characteristics of which absolute differences between our model and DDA were within 0.02.
- (2)
- The computational time of the model was notably shortened by nearly 50%. As the particle size increased, the improvement in the modeling efficiency was much more remarkable, reaching approximately 75% for large particles.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Herman, M.; Deuzé, J.L.; Marchand, A.; Roger, B.; Lallart, P. Aerosol remote sensing from POLDER/ADEOS over the ocean: Improved retrieval using a nonspherical particle model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D10S02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.F.; Stephens, G.L. A new polarized atmospheric radiative transfer model. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1991, 46, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.H.; Gu, X.F.; Yu, T.; Tian, G.L. The reflection and polarization properties of non-spherical aerosol particles. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Muñoz, O.; Veihelmann, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Liou, K.-N.; Bi, L.; Liu, C.; Yi, B.; Baum, B.A. On the radiative properties of ice clouds: Light scattering, remote sensing, and radiation parameterization. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 32, 32–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinson, Y.W.; Maughan, J.B.; Ding, J.; Chakrabarti, A.; Yang, P.; Sorensen, C.M. Q-space analysis of light scattering by ice crystals. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2016, 185, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, K.N.; Takano, Y. Light scattering by nonspherical particles: Remote sensing and climatic implications. Atmos. Res. 1994, 31, 271–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Lin, W.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yi, B. Optical Modeling of Sea Salt Aerosols: The Effects of Nonsphericity and Inhomogeneity. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterman, P.C. Matrix formulation of electromagnetic scattering. Proc. IEEE 1965, 53, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.I. Infrared absorption by shape distributions of NH3 ice particles: An application to the Jovian atmosphere. Earth Moon Planets 1991, 53, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S. Research on the Numerical Computational Models and Application of the scattering Properties of Nonspherical Atmospheric Particles. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, B.; Ström, S. T Matrix for Electromagnetic Scattering from an Arbitrary Number of Scatterers and Representations of E(3). Phys. Rev. D 1973, 8, 3661–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.I.; Travis, L.D. T-matrix computations of light scattering by large spheroidal particles. Opt. Commun. 1994, 109, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielaard, D.J.; Mishchenko, M.I.; Macke, A.; Carlson, B.E. Improved T-matrix computations for large, nonabsorbing and weakly absorbing nonspherical particles and comparison with geometrical-optics approximation. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 4305–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishchenko, M.I.; Travis, L.D. Capabilities and limitations of a current FORTRAN implementation of the T-matrix method for randomly oriented, rotationally symmetric scatterers. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1998, 60, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havemann, S.; Baran, A.J. Extension of T-matrix to scattering of electromagnetic plane waves by non-axisymmetric dielectric particles: Application to hexagonal ice cylinders. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2001, 70, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, F.M.; Stamnes, K.; Stamnes, J.J. Scattering of electromagnetic waves by spheroidal particles: A novel approach exploiting the T matrix computed in spheroidal coordinates. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 7875–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackowski, D.W. Discrete dipole moment method for calculation of the T matrix for nonspherical particles. J. Opt. Soc. America. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2002, 19, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, V.L.Y.; Nieminen, T.A.; Heckenberg, N.R.; Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H. T-matrix calculation via discrete dipole approximation, point matching and exploiting symmetry. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.R. Invariant imbedding T matrix approach to electromagnetic scattering. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, 4861–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Yang, P.; Kattawar, G.W.; Mishchenko, M.I. A numerical combination of extended boundary condition method and invariant imbedding method applied to light scattering by large spheroids and cylinders. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 123, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Yang, P.; Kattawar, G.W.; Mishchenko, M.I. Efficient implementation of the invariant imbedding T-matrix method and the separation of variables method applied to large nonspherical inhomogeneous particles. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 116, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Yang, P. Accurate simulation of the optical properties of atmospheric ice crystals with the invariant imbedding T-matrix method. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 138, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Gao, T.; Zhang, F. An investigation of the symmetrical properties in the invariant imbedding T-matrix method for the nonspherical particles with symmetrical geometry. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2021, 259, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Gao, T.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X. Efficient design of the realization scheme of the Invariant Imbedding (IIM) T-matrix light scattering model for atmospheric nonspherical particles. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2020, 251, 106999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, L.; Gao, T.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X. An efficient implementation of the light scattering simulation for random-oriented non-rotationally symmetric particles using invariant imbedding T-matrix method. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2020, 241, 106734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Yang, P.; Kattawar, G.W. Many-body iterative T-matrix method for large aspect ratio particles. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 127, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doicu, A.; Wriedt, T.; Khebbache, N. An overview of the methods for deriving recurrence relations for T-matrix calculation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2019, 224, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, F.M.; Stamnes, K.; Stamnes, J.J. Point-group symmetries in electromagnetic scattering. J. JOSA A 1999, 16, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.I. Light scattering by randomly oriented axially symmetric particles. JOSA A 1991, 8, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doicu, A.; Wriedt, T. The Invariant Imbedding T Matrix Approach. In The Generalized Multipole Technique for Light Scattering: Recent Developments; Wriedt, T., Eremin, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 35–47. [Google Scholar]


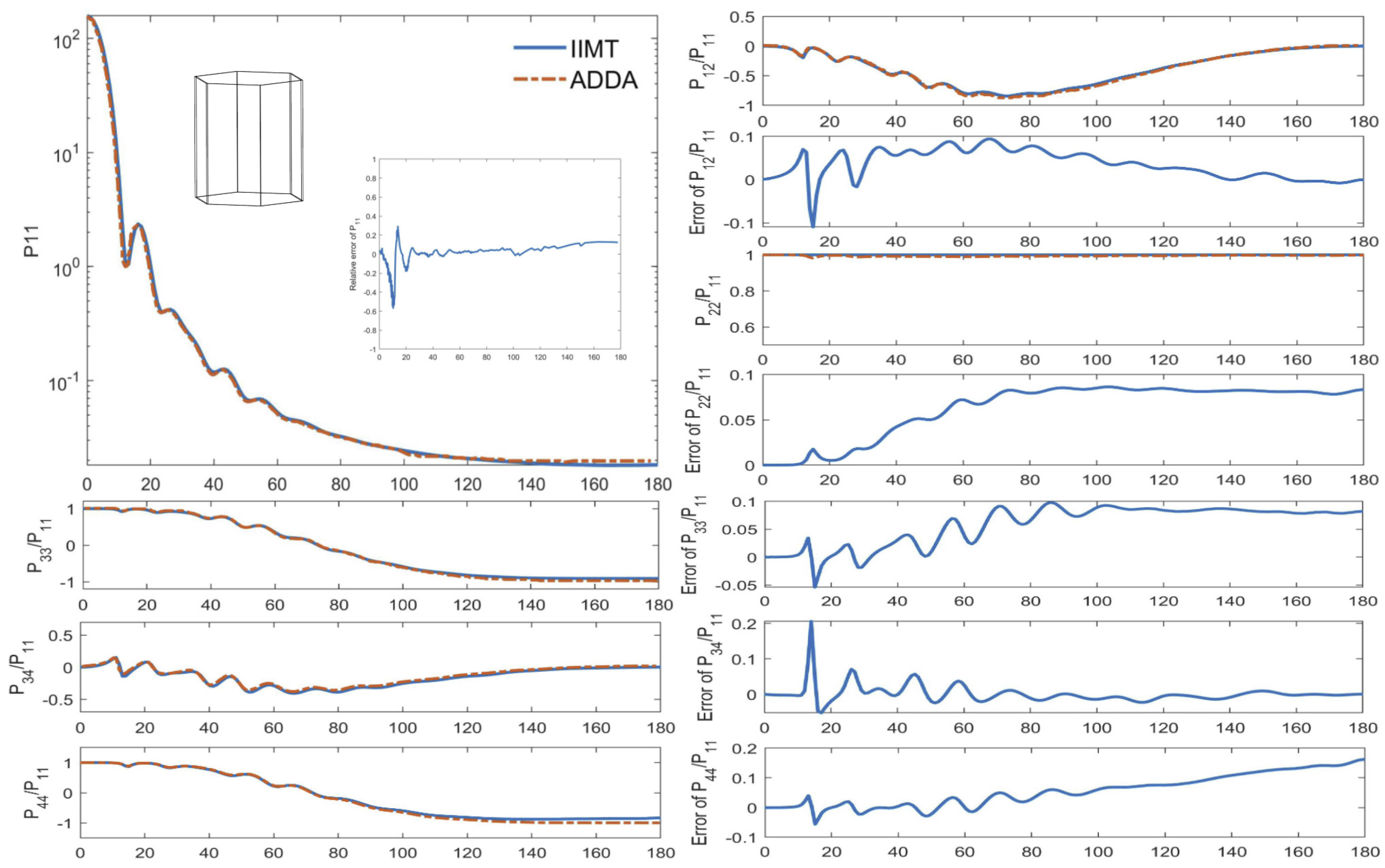

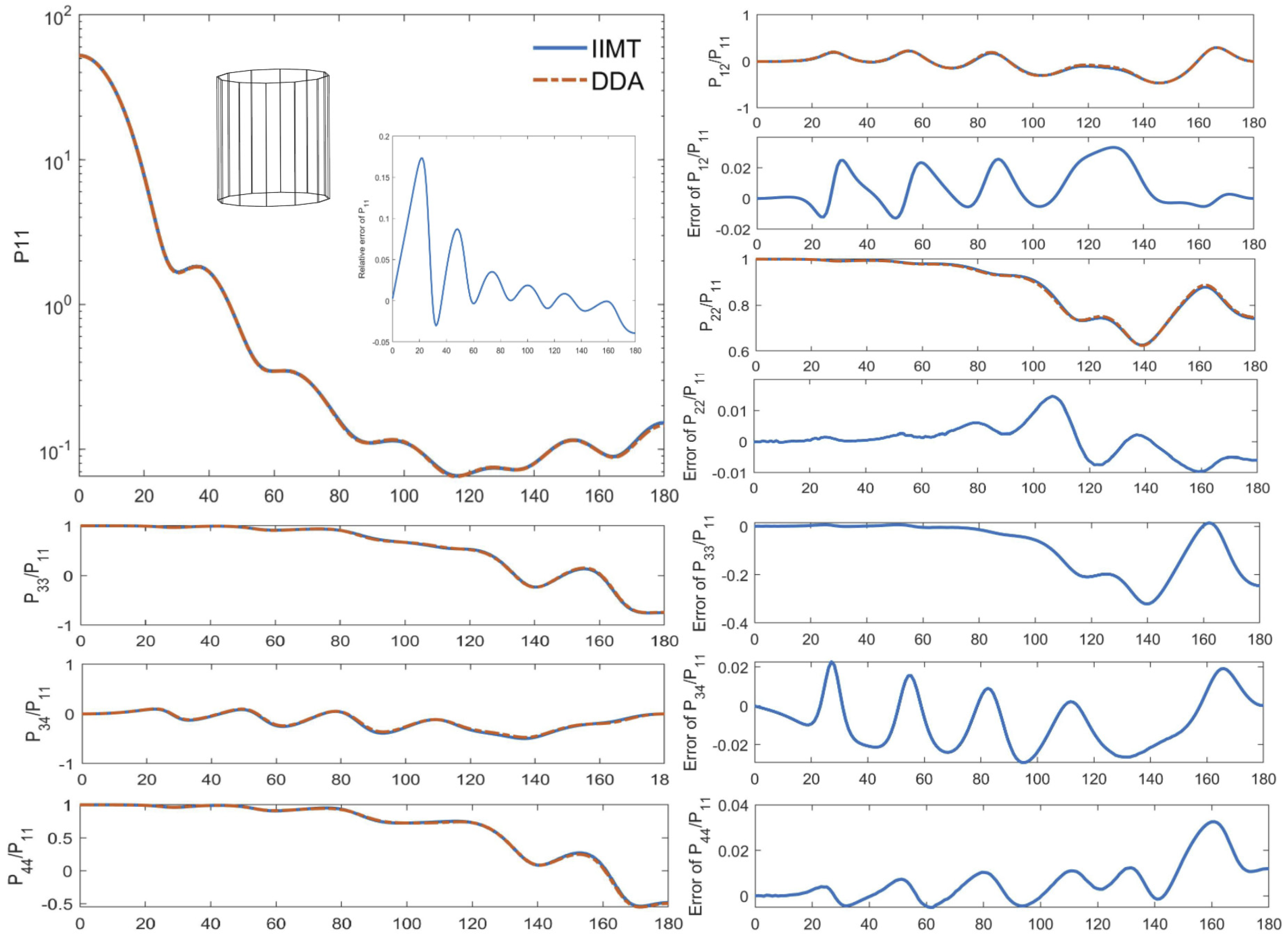
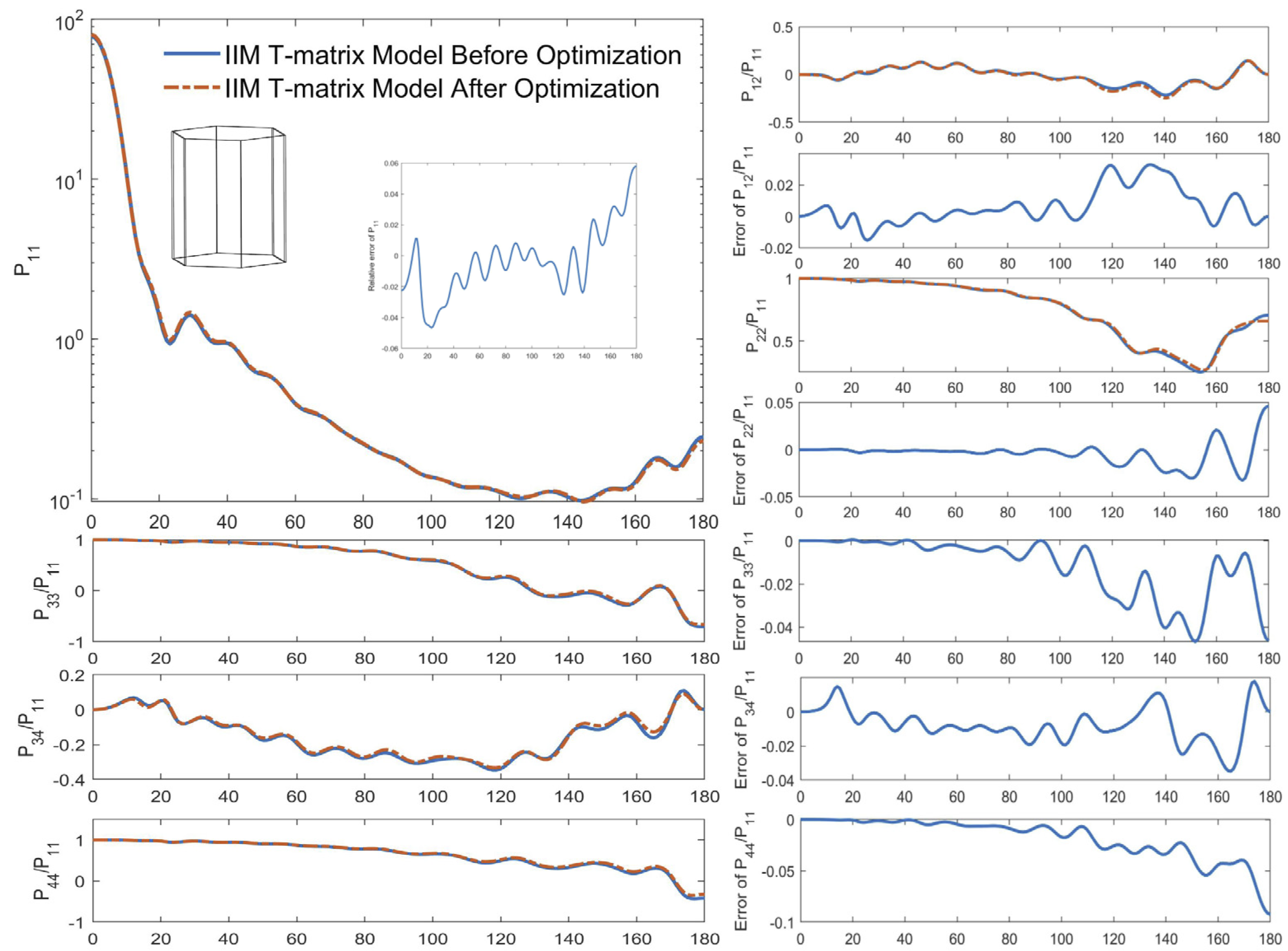

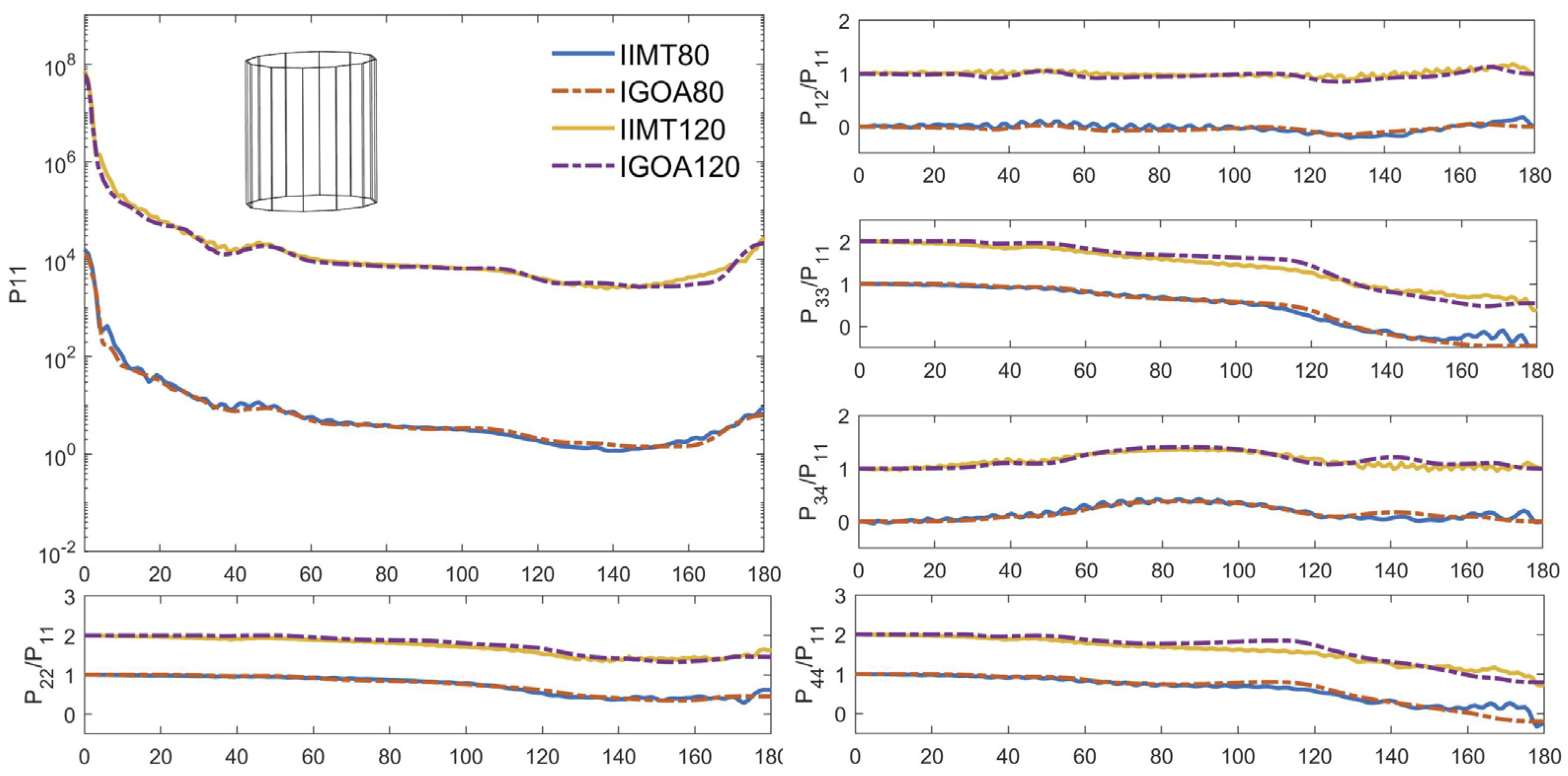
| IIM T-Matrix | DDA | Relative Errors/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cext/um2 | 8.5940 | 8.6097 | 0.1820 |
| Csca/um2 | 8.4313 | 8.4348 | 0.0419 |
| Cabs/um2 | 0.1627 | 0.1751 | 7.6205 |
| IIM T-Matrix | ADDA | Relative Errors/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cext/um2 | 8.8100 | 8.8168 | 0.0770 |
| Csca/um2 | 4.3903 | 4.4134 | 0.5252 |
| Cabs/um2 | 4.4197 | 4.4036 | 0.3640 |
| IIM T-Matrix | DDA | Relative Errors/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cext/um2 | 19.8603 | 19.8724 | 0.0607 |
| Csca/um2 | 19.7228 | 19.7343 | 0.4366 |
| Cabs/um2 | 0.1375 | 0.13816 | 0.0582 |
| IIM T-Matrix | DDA | Relative Errors/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cext/um2 | 14.3633 | 14.3704 | 0.0500 |
| Csca/um2 | 14.2720 | 14.2790 | 0.0486 |
| Cabs/um2 | 0.09123 | 0.09144 | 0.2298 |
| IIM T-Matrix before Optimization | IIM T-Matrix after Optimization | Relative Errors/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cext/um2 | 8.4843 | 8.5940 | 1.2771 |
| Csca/um2 | 8.3244 | 8.4313 | 1.2675 |
| Cabs/um2 | 0.1598 | 0.1627 | 1.7748 |
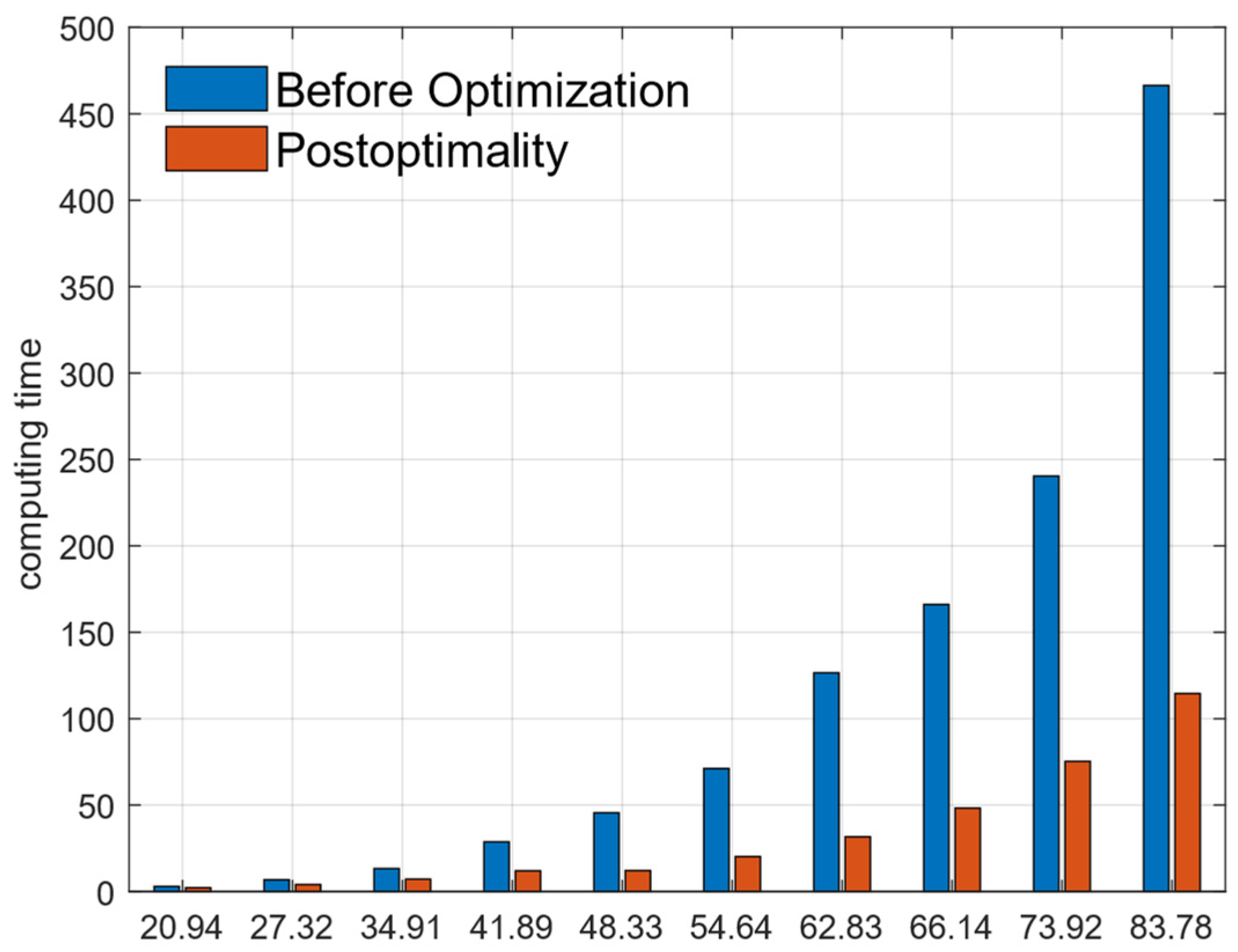
| Dimensional Parameters | Calculation Time T0 for Traditional IIM T-Matrix/min | Calculation Time T1 for the Improved IIM T-Matrix/min | (T0 − T1)/T0 × 100% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20.94 | 2.97 | 2.23 | 24.16% |
| 27.32 | 6.78 | 4.02 | 40.86% |
| 34.91 | 13.28 | 7.17 | 46.48% |
| 41.89 | 28.73 | 11.95 | 58.06% |
| 48.33 | 45.53 | 12.12 | 73.89% |
| 54.64 | 71.18 | 20.23 | 71.76% |
| 62.83 | 126.55 | 31.70 | 74.51% |
| 66.14 | 166.07 | 48.28 | 70.25% |
| 73.92 | 240.38 | 75.35 | 68.54% |
| 83.78 | 466.43 | 114.58 | 75.35% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Li, S. The Computational Optimization of the Invariant Imbedding T Matrix Method for the Particles with N-Fold Symmetry. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4061. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164061
Zhao J, Hu S, Liu X, Li S. The Computational Optimization of the Invariant Imbedding T Matrix Method for the Particles with N-Fold Symmetry. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(16):4061. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164061
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jiaqi, Shuai Hu, Xichuan Liu, and Shulei Li. 2022. "The Computational Optimization of the Invariant Imbedding T Matrix Method for the Particles with N-Fold Symmetry" Remote Sensing 14, no. 16: 4061. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164061
APA StyleZhao, J., Hu, S., Liu, X., & Li, S. (2022). The Computational Optimization of the Invariant Imbedding T Matrix Method for the Particles with N-Fold Symmetry. Remote Sensing, 14(16), 4061. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164061







