Multi-Path Interactive Network for Aircraft Identification with Optical and SAR Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A residual Sum-Max fusion strategy is proposed to reduce the effect of clouds. A new plug-and-play Interactive Attention Sum-Max Fusion Module (IASM) is thus constructed for synthesizing task-related features from multi-module images.
- A deep Multi-path Interactive Network (MIN) is proposed for aircraft identification with optical and SAR images by employing multi-modal IASM in the deep network. It can accurately identify aircraft with clouds, especially thick clouds.
- A new validation dataset consisting of 4720 scenes, named Fused Cloudy Aircraft Detection (FCAD), is constructed to evaluate the MIN performance by average accuracy.
2. Methodlogy
2.1. Overall Structure of MIN
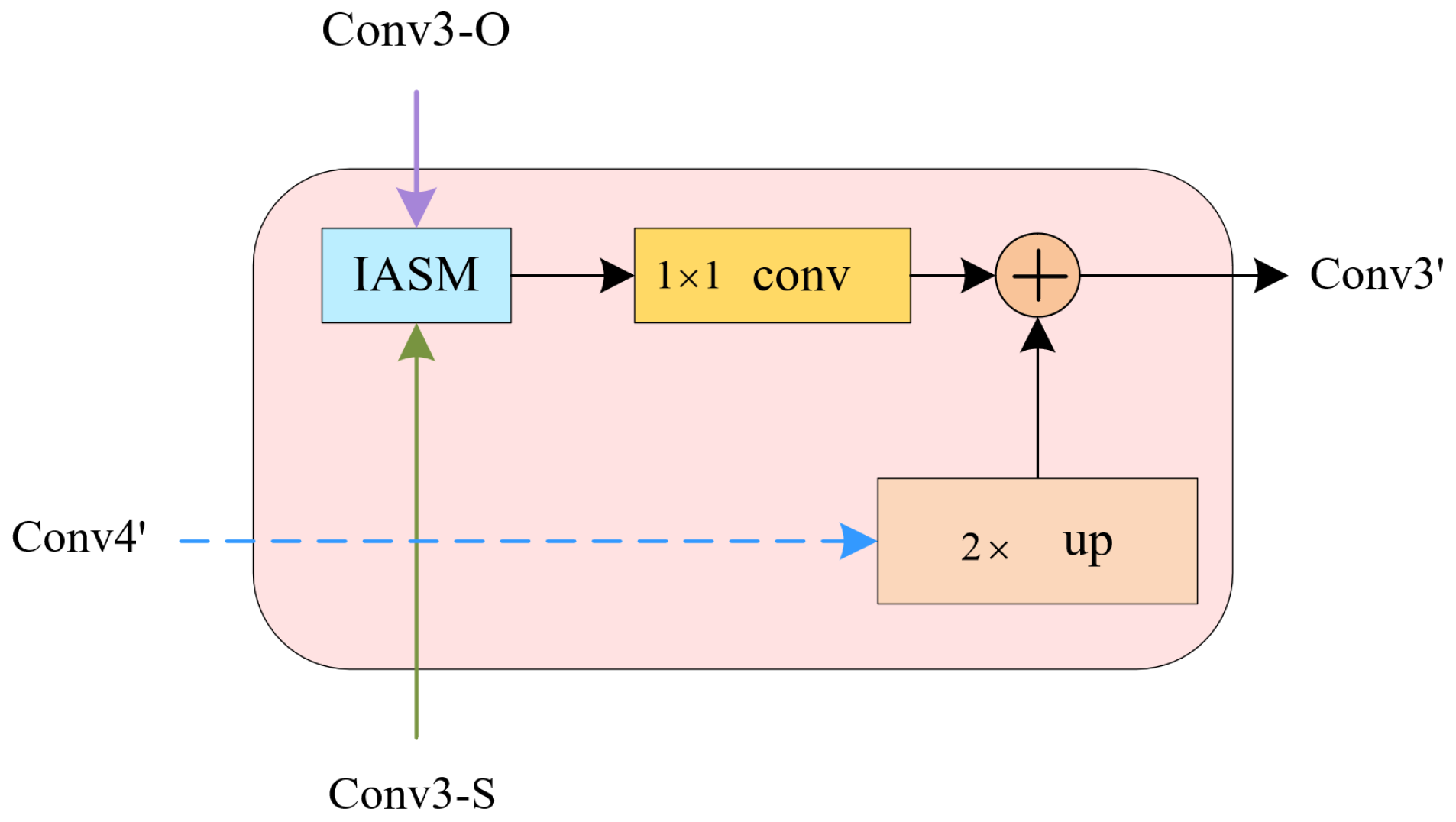
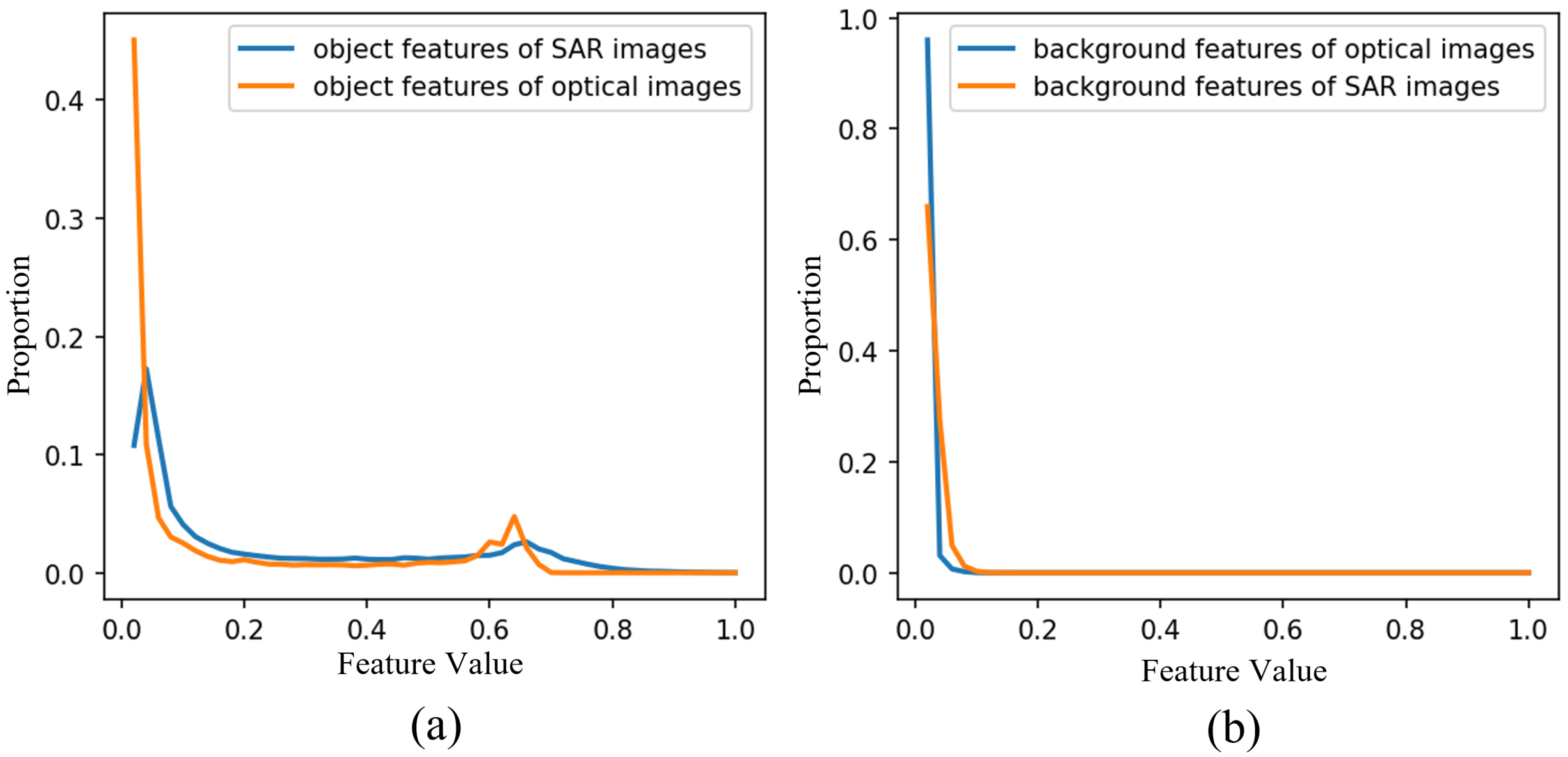
2.2. Residual SM (Sum-Max) Fusion
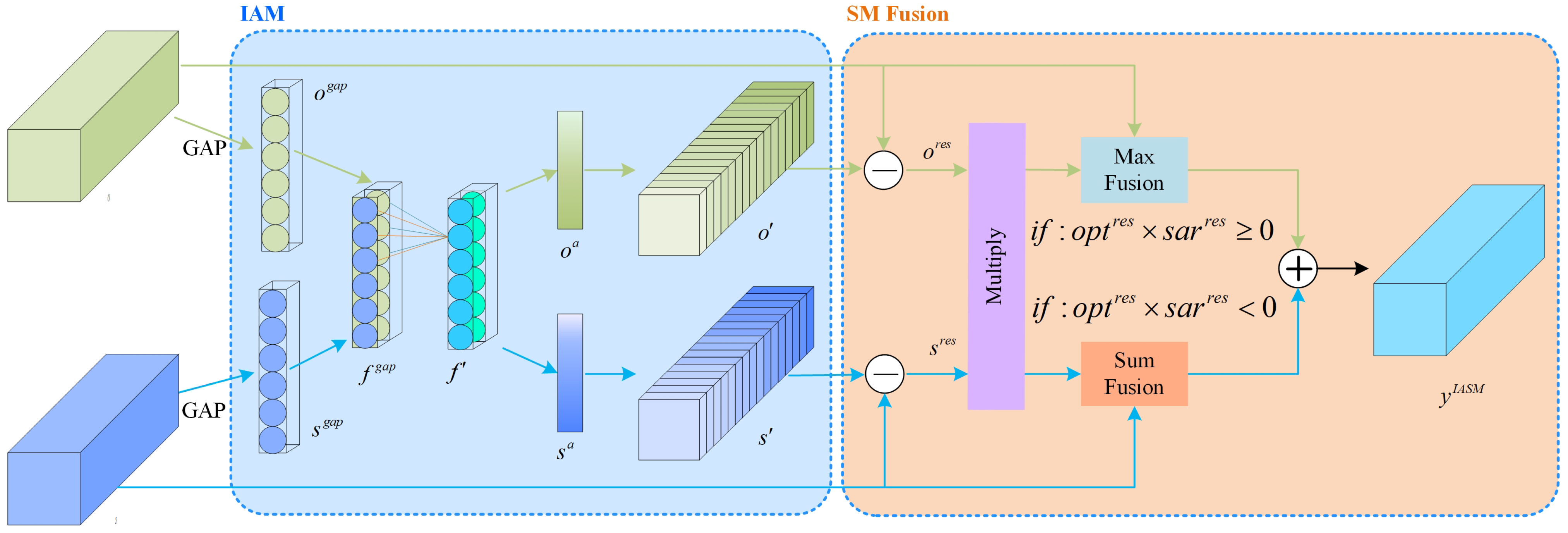
2.3. IASM (Interactive Attention Sum-Max Fusion Module)
2.4. Other Parts
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Datasets and Training Details
3.2. Experiments on Single-Modal and Multi-Modal Images
3.3. Experiments on Multi-Path IASM
3.4. Ablation Experiments
3.5. Comparison with SOTA Methods
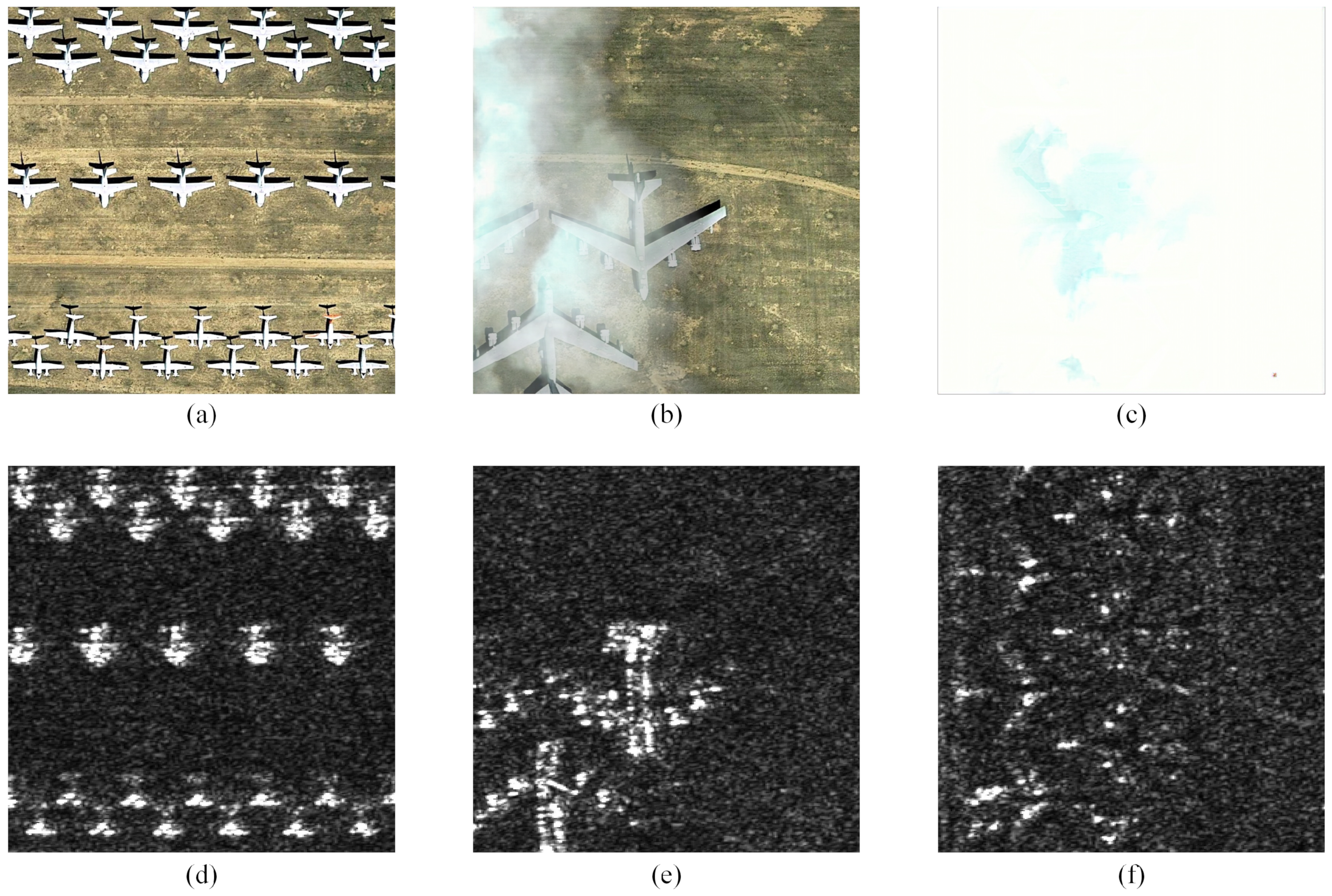
3.6. Visualization of Feature Maps of Different Fusion Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| MIN | Multi-path Interactive Network |
| SM | Sum-Max |
| IAM | Interactive Attention Module |
| IASM | Interactive Attention Sum-Max fusion module |
| FCAD | Fused Cloudy Aircraft Detection |
| FPN | Feature Pyramid Network |
| FPS | Frames Per Second |
| RPN | Region Proposal Network |
| SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| ISCCP-FD | the international satellite cloud climatology project-flux data |
References
- Zhang, Y.; Rossow, W.B.; Lacis, A.A.; Oinas, V.; Mishchenko, M.I. Calculation of radiative fluxes from the surface to top of atmosphere based on isccp and other global data sets: Refinements of the radiative transfer model and the input data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigang, L.; da Silva, N. A study of parallel neural networks. In Proceedings of the IJCNN’99 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Washington, DC, USA, 10–16 July 1999; pp. 1113–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of theEuropean Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, F.; Ming, D.; Zeng, B.; Yu, J.; Qing, Y.; Du, T.; Zhang, X. Aircraft detection in high spatial resolution remote sensing images combining multi-angle features driven and majority voting cnn. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Tang, Z.; Wang, T.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. Aircraft detection in remote sensing images based on deconvolution and position attention. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 4241–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Diao, W.; Fu, K. Fmssd: Feature-merged single-shot detection for multiscale objects in large-scale remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 3377–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, H. X-linenet: Detecting aircraft in remote sensing images by a pair of intersecting line segments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 1645–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yan, H.; Shan, Y.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Qiao, B. Aircraft detection for remote sensing images based on deep convolutional neural networks. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2021, 2021, 4685644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wen, G.; Deng, Z.; Fan, Y.; Hui, B. Automatic and fast pcm generation for occluded object detection in high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1730–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z.; Zeng, W.-J.; Gui, J. Local attention networks for occluded airplane detection in remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wen, G.; Fan, Y. Occluded object detection in high-resolution remote sensing images using partial configuration object model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1909–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xiao, S. Deformable faster r-cnn with aggregating multi-layer features for partially occluded object detection in optical remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wen, G.; Liu, J.; Deng, Z.; Fan, Y. Unified partial configuration model framework for fast partially occluded object detection in high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Pan, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J. Generative adversarial learning in yuv color space for thin cloud removal on satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Dai, P.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous cloud detection and removal from bitemporal remote sensing images using cascade convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, X.-Y.; Wang, X. Single image cloud removal using u-net and generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 6371–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, K.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Ren, P. Cloudy image arithmetic: A cloudy scene synthesis paradigm with an application to deep learning based thin cloud removal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. 2021, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, P.; Meraner, A.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X.X. Multisensor data fusion for cloud removal in global and all-season sentinel-2 imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 5866–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Weng, Q.; Tang, L.; Zhang, X.; Bilal, M.; Li, Q. Thick clouds removing from multitemporal landsat images using spatiotemporal neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Lu, S.; Ye, Y.; Ban, Y. Gcdb-unet: A novel robust cloud detection approach for remote sensing images. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 238, 107890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luotamo, M.; Metsämäki, S.; Klami, A. Multiscale cloud detection in remote sensing images using a dual convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 4972–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Jian, C.; Luo, S.; Mou, L.; Zhu, X.X.; Molinier, M. A lightweight deep learning-based cloud detection method for sentinel-2a imagery fusing multiscale spectral and spatial features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Yue, H.; Tan, H.; Hou, C.; Li, K. Cdnetv2: Cnn-based cloud detection for remote sensing imagery with cloud-snow coexistence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Li, Y. Cnn cloud detection algorithm based on channel and spatial attention and probabilistic upsampling for remote sensing image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5404613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Sun, X.; Yan, Z.; Fu, K. Dabnet: Deformable contextual and boundary-weighted network for cloud detection in remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5601216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, F. Scattering enhanced attention pyramid network for aircraft detection in sar images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 7570–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Xing, J.; Chen, L.; Pan, Z.; Cai, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Ford, A. Glassboxing deep learning to enhance aircraft detection from sar imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, H.; Tian, T.; Gao, P.; Tian, J. Sfre-net: Scattering feature relation enhancement network for aircraft detection in sar images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, J.; Sun, X.; Fu, K. Sfr-net: Scattering feature relation network for aircraft detection in complex sar images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5218317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M. Weakly supervised learning based on coupled convolutional neural networks for aircraft detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5553–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Hu, D.; Kuang, G.; Liu, L. Attentional feature refinement and alignment network for aircraft detection in sar imagery. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.07124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.; Maurer, M.; Fraundorfer, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.X. Buildings detection in vhr sar images using fully convolution neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 1100–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. Building change detection in vhr sar images via unsupervised deep transcoding. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 1917–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, V.; Inglada, J.; Spigai, M.; Tourneret, J.-Y.; Marthon, P. High-resolution optical and sar image fusion for building database updating. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2900–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; He, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.-P. Building damage detection via superpixel-based belief fusion of space-borne sar and optical images. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 2008–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, D.; Lemoine, G.; Bruzzone, L. Earthquake damage assessment of buildings using vhr optical and sar imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2403–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Laganière, R.; Huang, D.; Luo, X.; Zhang, H. A robust and fast multispectral pedestrian detection deep network. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 227, 106990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bruzzone, L. Self-supervised sar-optical data fusion of sentinel-1/-2 images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2021, 60, 5406011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.; Biswas, M.; Pal, M. Fusion and classification of multi-temporal sar and optical imagery using convolutional neural network. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2022, 13, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ban, Y.; Nascetti, A. Learning u-net without forgetting for near real-time wildfire monitoring by the fusion of sar and optical time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 261, 112467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druce, D.; Tong, X.; Lei, X.; Guo, T.; Kittel, C.M.; Grogan, K.; Tottrup, C. An optical and sar based fusion approach for mapping surface water dynamics over mainland china. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, J.; Sagan, V.; Maimaitijiang, M. Sentinel sar-optical fusion for crop type mapping using deep learning and google earth engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Qu, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, W. Joint detection of airplane targets based on sar images and optical images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 1366–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Spröhnle, K.; Fuchs, E.-M.; Pelizari, P.A. Object-based analysis and fusion of optical and sar satellite data for dwelling detection in refugee camps. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1780–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, D.; Jing, M.; Liu, H.; Sun, F.; Jiang, L. A fast retinanet fusion framework for multi-spectral pedestrian detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 105, 103178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Tisse, C.-L. Exploiting fusion architectures for multispectral pedestrian detection and segmentation. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, D108–D116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, H.; Shin, H. Multi-layer fusion techniques using a cnn for multispectral pedestrian detection. IET Comput. Vis. 2018, 12, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friederici, A.D. Language in Our Brain: The Origins of a Uniquely Human Capacity; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. Eca-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11531–11539. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Bali, Indonesia, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Mmdetection: Open mmlab detection toolbox and benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07155. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Qiao, H.; Huang, K.; Hussain, A. Cross-modality interactive attention network for multispectral pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Guo, S.; Li, L. Attention fusion for one-stage multispectral pedestrian detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Methods | Cloudless | Thin Clouds | Thick Clouds | Total | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN (O) | 0.887 | 0.807 | 0.352 | 0.707 | 23.2 |
| Faster R-CNN (S) | - | - | - | 0.721 | 23.2 |
| MIN | 0.931 | 0.913 | 0.733 | 0.925 | 15.4 |
| Fusion Stages | FPS | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.646 | 0.902 | 0.721 | 0.254 | 0.738 | 0.678 | 0.678 | 0.678 | 0.299 | 0.773 | 17.9 |
| 2 | 0.672 | 0.911 | 0.775 | 0.338 | 0.749 | 0.703 | 0.703 | 0.703 | 0.383 | 0.783 | 17.4 |
| 3 | 0.677 | 0.907 | 0.791 | 0.328 | 0.757 | 0.710 | 0.710 | 0.710 | 0.387 | 0.792 | 16.8 |
| 4 | 0.689 | 0.925 | 0.800 | 0.363 | 0.764 | 0.723 | 0.723 | 0.723 | 0.417 | 0.801 | 15.8 |
| 5 | 0.680 | 0.921 | 0.799 | 0.331 | 0.760 | 0.713 | 0.713 | 0.713 | 0.383 | 0.796 | 15.0 |
| 6 | 0.659 | 0.919 | 0.737 | 0.278 | 0.745 | 0.691 | 0.691 | 0.691 | 0.340 | 0.779 | 14.4 |
| Index | Optical Image | SAR Image | SM Fusion | IAM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ✓ | 0.707 | |||
| 2 | ✓ | ✓ | 0.913 | ||
| 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.921 | |
| 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.925 |
| Methods | FPS | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum Fusion | 0.671 | 0.913 | 0.784 | 0.308 | 0.754 | 0.704 | 0.704 | 0.704 | 0.358 | 0.792 | 16.1 |
| Max Fusion | 0.675 | 0.909 | 0.790 | 0.328 | 0.757 | 0.709 | 0.709 | 0.709 | 0.369 | 0.795 | 16.0 |
| Concat Fusion | 0.669 | 0.909 | 0.786 | 0.309 | 0.750 | 0.704 | 0.704 | 0.704 | 0.363 | 0.789 | 15.3 |
| SM Fusion | 0.680 | 0.921 | 0.798 | 0.331 | 0.760 | 0.713 | 0.713 | 0.713 | 0.383 | 0.796 | 15.5 |
| CIAN [57] | 0.588 | 0.867 | 0.621 | 0.152 | 0.694 | 0.616 | 0.616 | 0.616 | 0.179 | 0.727 | 15.9 |
| MCFF [58] | 0.676 | 0.917 | 0.774 | 0.315 | 0.751 | 0.703 | 0.703 | 0.703 | 0.377 | 0.785 | 15.6 |
| MIN | 0.689 | 0.925 | 0.800 | 0.363 | 0.764 | 0.723 | 0.723 | 0.723 | 0.417 | 0.801 | 15.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Q.; Feng, Z.; Yang, S.; Chang, Z.; Wang, R. Multi-Path Interactive Network for Aircraft Identification with Optical and SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163922
Gao Q, Feng Z, Yang S, Chang Z, Wang R. Multi-Path Interactive Network for Aircraft Identification with Optical and SAR Images. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(16):3922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163922
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Quanwei, Zhixi Feng, Shuyuan Yang, Zhihao Chang, and Ruyu Wang. 2022. "Multi-Path Interactive Network for Aircraft Identification with Optical and SAR Images" Remote Sensing 14, no. 16: 3922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163922
APA StyleGao, Q., Feng, Z., Yang, S., Chang, Z., & Wang, R. (2022). Multi-Path Interactive Network for Aircraft Identification with Optical and SAR Images. Remote Sensing, 14(16), 3922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163922






