Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Runoff Dynamics and Its Drivers in a Water Conservation Area of the Upper Yellow River Basin over the Past 35 Years
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
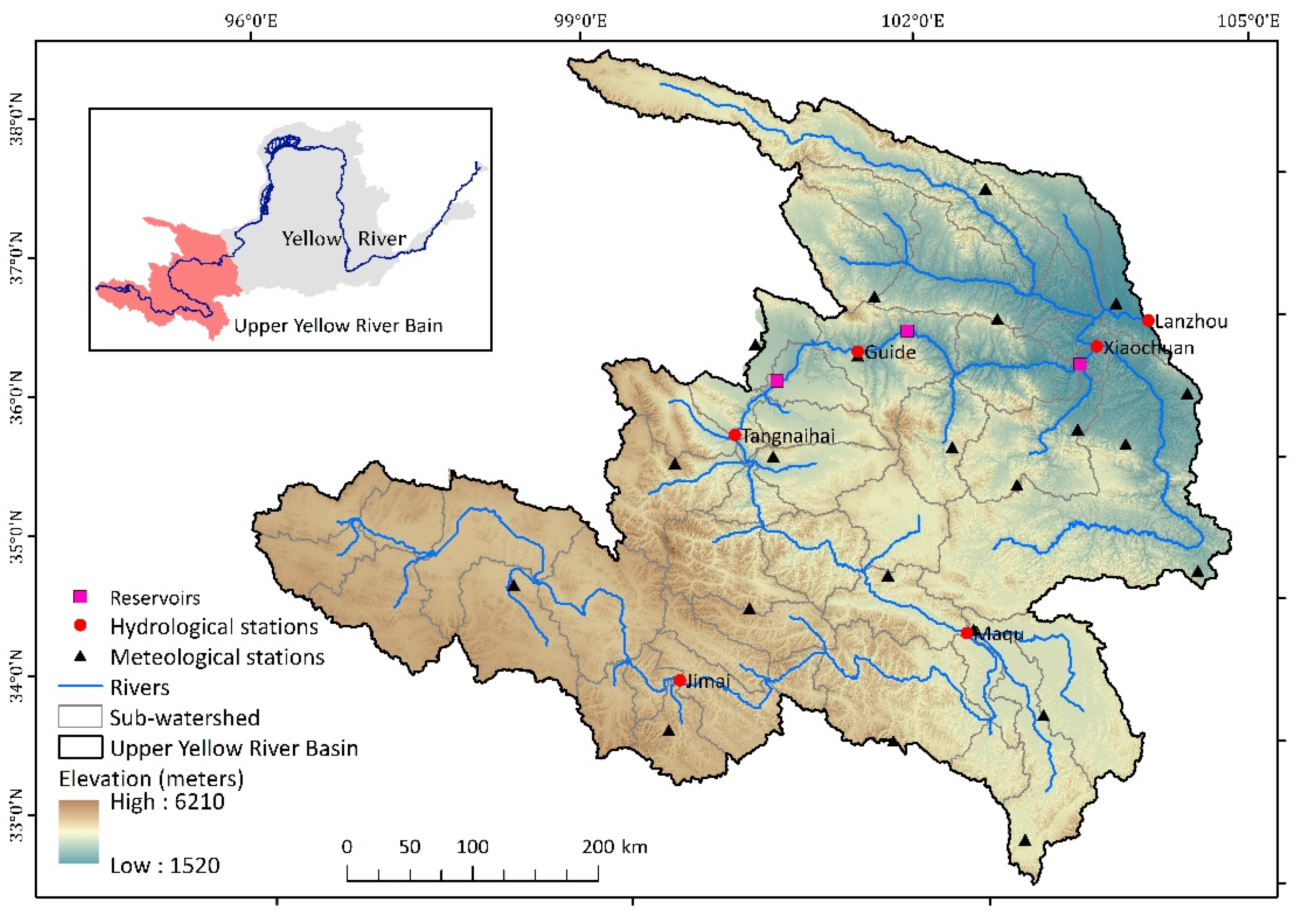
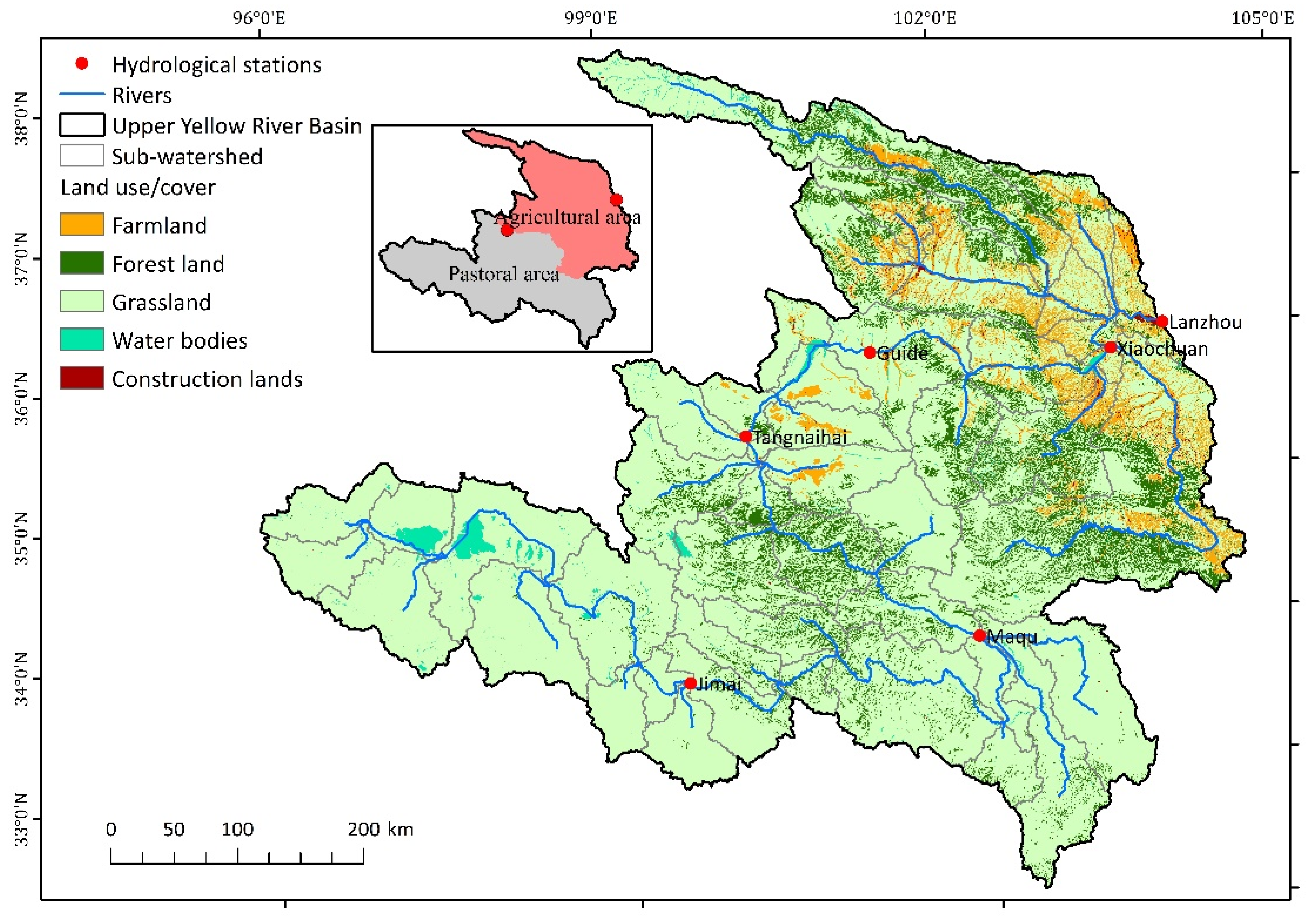
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Observed Runoff Series
2.2.2. Driving Datasets for Simulating Runoff Dynamics
2.2.3. Anthropogenic Water Consumption Data
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Scenario Simulations for Quantifying Contributions of Individual Drivers to Runoff Dynamics
- (1)
- Model parameterization and validation
- (2)
- Scenario simulations
2.3.2. Quantifying the Contributions of Climate Change, Land-Use Change and Anthropogenic Water Consumption to Runoff Changes
3. Results
3.1. Reliability of Runoff Simulations
3.2. Runoff Characteristics and Their Spatiotemporal Variability
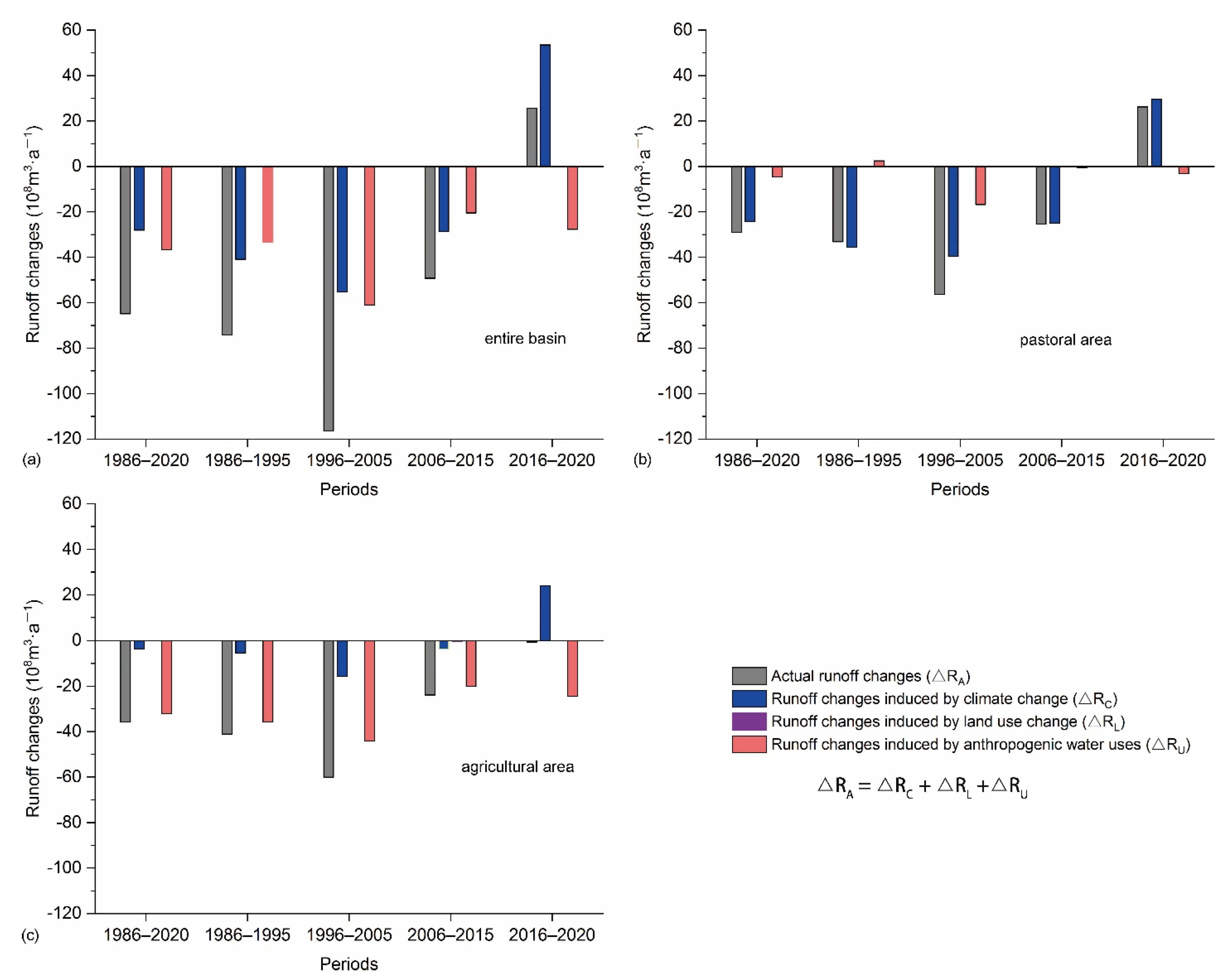
3.3. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of the Individual Contributions to Runoff Changes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Q.; Lan, C.; Su, F.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Ding, J.; Wang, L.; Leng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, Y.; et al. Streamflow change on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its impacts. China Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 807–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Gao, G.; Huang, J.; Jiang, E. Water Cycle and Soil-water Coupling Processes in the Yellow River Basin. Bull. Natl. Nat. Sci. Found. China 2021, 35, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Chen, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, G.; Han, C. Runoff evolution characteristics and driving factors of Yellow River above Lanzhou station from 1956 to under changing environment. Adv. Earth Sci. 2022, 37, 726–741. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Song, H.; An, Z.; Sun, C.; Trouet, V.; Cai, Q.; Liu, R.; Leavitt, S.W.; Song, Y.; Li, Q.; et al. Recent anthropogenic curtailing of Yellow River runoff and sediment load is unprecedented over the past 500 y. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18251–18257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafton, R.; Pittock, J.; Davis, R.; Williams, J.; Fu, G.; Warburton, M.; Udall, B.; McKenzie, R.; Yu, X.; Che, N.; et al. Global insights into water resources, climate change and governance. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Fu, C.; Zhou, T.; Yan, Z.; Li, M.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, L.; Lv, M. Status and Ponder of Climate and Hydrology Changes in the Yellow River Basin. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2020, 35, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; An, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, M. Ecological network construction of the heterogeneous agro-pastoral areas in the upper Yellow River basin. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mu, X.; Gao, P. Dynamic response of runoff to soil and water conservation measures and precipitation based on VAR model. Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Q. Decadal water storage decrease driven by vegetation changes in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1859–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Han, L.; Cao, W.; Liu, L. Target-based Assessment on Effects of First-stage Ecological Conservation and Restoration Project in Three-river Source Region, China and Policy Recommendations. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Lv, Y.; Hao, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, R.; Xue, K.; Fu, B. Ecosystem Change and Its Ecohydrological Effect in the Yellow River Basin. Bull. Natl. Nat. Sci. Found. China 2021, 35, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Mckenzie, J.M. Climate-induced hydrologic change in the source region of the yellow river: A new assessment including varying permafrost. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2018, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Wu, G.; Xu, B.; Wang, W.; Gao, J.; An, B. Asian Water Tower Change and Its Impacts. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tian, W.; Liu, X.; Liang, K.; Bai, P. Analysis and understanding of runoff variation of the Yellow River in recent 100 years. Yellow River 2019, 41, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; LV, M.; Ma, Z. Climate, Hydrology, and Vegetation Coverage Changes in Source Region of Yellow River and Countermeasures for Challenges. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2020, 35, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Corte-Real, J.; Moreira, M.; Kilsby, C.; Birkinshaw, S.; Burton, A.; Fowler, H.J.; Forsythe, N.; Nunes, J.P.; Sampaio, E.; et al. Downscaling climate change of water availability, sediment yield and extreme events: Application to a mediterranean climate basin. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 2947–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y. Mechanisms of Human-natural System Coupling and Optimization of the Yellow River Basin. Bull. Natl. Nat. Sci. Found. China 2021, 35, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Ma, Z.; Lv, M. Effects of climate/land surface changes on streamflow with consideration of precipitation intensity and catchment characteristics in the Yellow River Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1942–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaake, J.C. From climate to flow. In Climate Change and U.S. Water Resources; Waggoner, P.E., Ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 177–206. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X. Attribution analysis for runoff decline in Yellow River Basin during past fifty years based on Budyko hypothesis. Sci. Sin. Technol. 2015, 45, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, K. Contribution of ecological conservation programs and climate change to hydrological regime change in the source region of the Yangtze River in China. Reg. Environ. Change 2022, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; McVicar, T.R.; Zhang, Z.; Brunner, T.; Strauss, P. Globally partitioning the simultaneous impacts of climate-induced and human-induced changes on catchment streamfow: A review and meta-analysis. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Tao, F.; Moiwo, J.P.; Xiao, D. Attribution of hydrological change in Heihe River Basin to climate and land use change in the past three decades. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Xia, J.; Li, X.; Yang, D.; Hu, Z.; Sun, S.; Sun, X. Critical advances in understanding ecohydrological processes of terrestrial vegetation: From leaf to watershed scale. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 3667–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Charles, S.P.; Viney, N.R.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.Q. Impacts of climate variability on stream-flow in the Yellow River. Hydrol. Processes 2007, 21, 3431–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Fohrer, N. SWAT2000: Current capabilities and research opportunities in applied watershed modelling. Hydrol. Processes 2005, 19, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yeo, I.Y.; Lang, M.W.; McCarty, G.W.; Sadeghi, A.M.; Sharifi, A.; Jin, H.; Liu, Y. Improving the catchment scale wetland modeling using remotely sensed data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 122, 104069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Long, A.; Deng, X.; Yin, Z.; Den, M.; An, Q.; Gu, X.; Li, S.; Liu, G. The Impact of Climate Change on Hydrological Processes of the Glacierized Watershed and Projections. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Shepard, D. Hydro-Climatic Trends of the Yellow River Basin for the last 50 years. Clim. Change 2004, 65, 149–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Duan, R.; Wang, H.; Li, A.; Shi, Y.; Jing, H.; Fang, J. Farming-Pastoral ecotone of Northern China plays important role in ensuring national food security. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/IIASA/ISRIC/ISSCAS/JRC. Harmonized World Soil Database Version 1.2; FAO: Rome, Italy; IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Winchell, M.; Srinivasan, R.; Di Luzio, M.; Arnold, J. ArcSWAT Interface for SWAT2009 User’s Guide; Texas Agricultural Experiment Station and U.S. Department of Agriculture: Temple, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tachikawa, T.; Hato, M.; Kaku, M.; Iwasaki, A. The Characteristics of ASTER GDEM Version 2. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute Technical Report; Texas A&M University System: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour, K.; Vaghefi, S.; Srinivasan, R. A Guideline for Successful Calibration and Uncertainty Analysis for Soil and Water Assessment: A Review of Papers from the 2016 International SWAT Conference. Water 2017, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzman, J.A.; Shirmohammadi, A.; Sadeghi, A.M.; Wang, X.; Chu, M.L.; Jha, M.; Parajuli, P.B.; Harmel, R.D.; Khare, Y.; Hernandez, J.E. Uncertainty Considerations in Calibration and Validation of Hydrologic and Water Quality Models. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1745–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Bolch, T.; Chen, D.; Gao, J.; Immerzeel, W.; Piao, S.; Su, F.; Thompson, L.; Wada, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M. A coordinated three-dimensional network for observing large-scale terrestrial ecosystem status changes and the consequences on resources and environment. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Climatic Datasets | Time Resolution | Unit | Timespan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean temperature | day | °C·day−1 | 1964–2020 |
| Total precipitation | day | mm·day−1 | |
| Mean solar radiation | day | W·m−2·day−1 | |
| Mean relative humidity | day | % | |
| Mean wind speed | day | m·s−1 |
| Parameters | Description | Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| r_CN2 | Initial SCS runoff curve number for moisture condition II | [−0.2, 0.2] |
| v_ALPHA_BF | Baseflow alpha factor | [0, 1] |
| v_GW_DELAY | Groundwater delay time | [0, 500] |
| v_GW_REVAP | Groundwater “revap” coefficient | [0.02, 0.2] |
| v_GWQMN | Groundwater baseflow threshold (mm) | [0, 2000] |
| v_REVAPMN | Groundwater “revap” threshold (mm) | [0, 500] |
| v__CH_N2 | Manning’s “n” value for the main channel | [0, 0.3] |
| v_OV_N | Manning’s “n” value for overland flow | [−0.01, 30] |
| v__CH_K2 | Effective hydraulic conductivity in main channel alluvium | [0, 150] |
| v__ESCO | Soil evaporation compensation factor | [0.01, 1] |
| v__EPCO | Plant uptake compensation factor | [0.01, 1] |
| v__SMFMX | Maximum melt rate for snow during year | [0, 10] |
| v__SFTMP | Snowfall temperature | [−5, 5] |
| Simulated Periods | Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1986–1995 | observed climatic series and 1990 land use | observed climatic series and | 1990 land use |
| 1996–2005 | 2000 land use | ||
| 2006–2015 | 2010 land use | ||
| 2016–2020 | 2020 land use | ||
| Hydrological Stations | Calibration Period | Validation Period | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSE | R2 | PBIAS (%) | NSE | R2 | PBIAS (%) | |
| Jimai | 0.84 | 0.85 | 2.10 | 0.77 | 0.79 | −3.25 |
| Maqu | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.86 | −6.52 |
| Tangnaihai | 0.89 | 0.90 | −0.64 | 0.85 | 0.86 | −8.81 |
| Guide | 0.90 | 0.91 | −2.04 | 0.86 | 0.87 | −9.03 |
| Xiaochuan | 0.90 | 0.90 | −2.12 | 0.85 | 0.85 | −0.84 |
| Lanzhou | 0.90 | 0.90 | −3.7 | 0.87 | 0.87 | −4.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, B.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, W.; Yan, K.; Cui, C. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Runoff Dynamics and Its Drivers in a Water Conservation Area of the Upper Yellow River Basin over the Past 35 Years. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153628
Zeng B, Zhang F, Zeng W, Yan K, Cui C. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Runoff Dynamics and Its Drivers in a Water Conservation Area of the Upper Yellow River Basin over the Past 35 Years. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153628
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Biao, Fuguang Zhang, Weifeng Zeng, Ke Yan, and Chengyu Cui. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Runoff Dynamics and Its Drivers in a Water Conservation Area of the Upper Yellow River Basin over the Past 35 Years" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153628
APA StyleZeng, B., Zhang, F., Zeng, W., Yan, K., & Cui, C. (2022). Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Runoff Dynamics and Its Drivers in a Water Conservation Area of the Upper Yellow River Basin over the Past 35 Years. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153628








