Deep Learning Aided Time–Frequency Analysis Filter Framework for Suppressing Ionosphere Clutter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Multicomponent Echoes Signal Decomposition with Synchrosqueezing
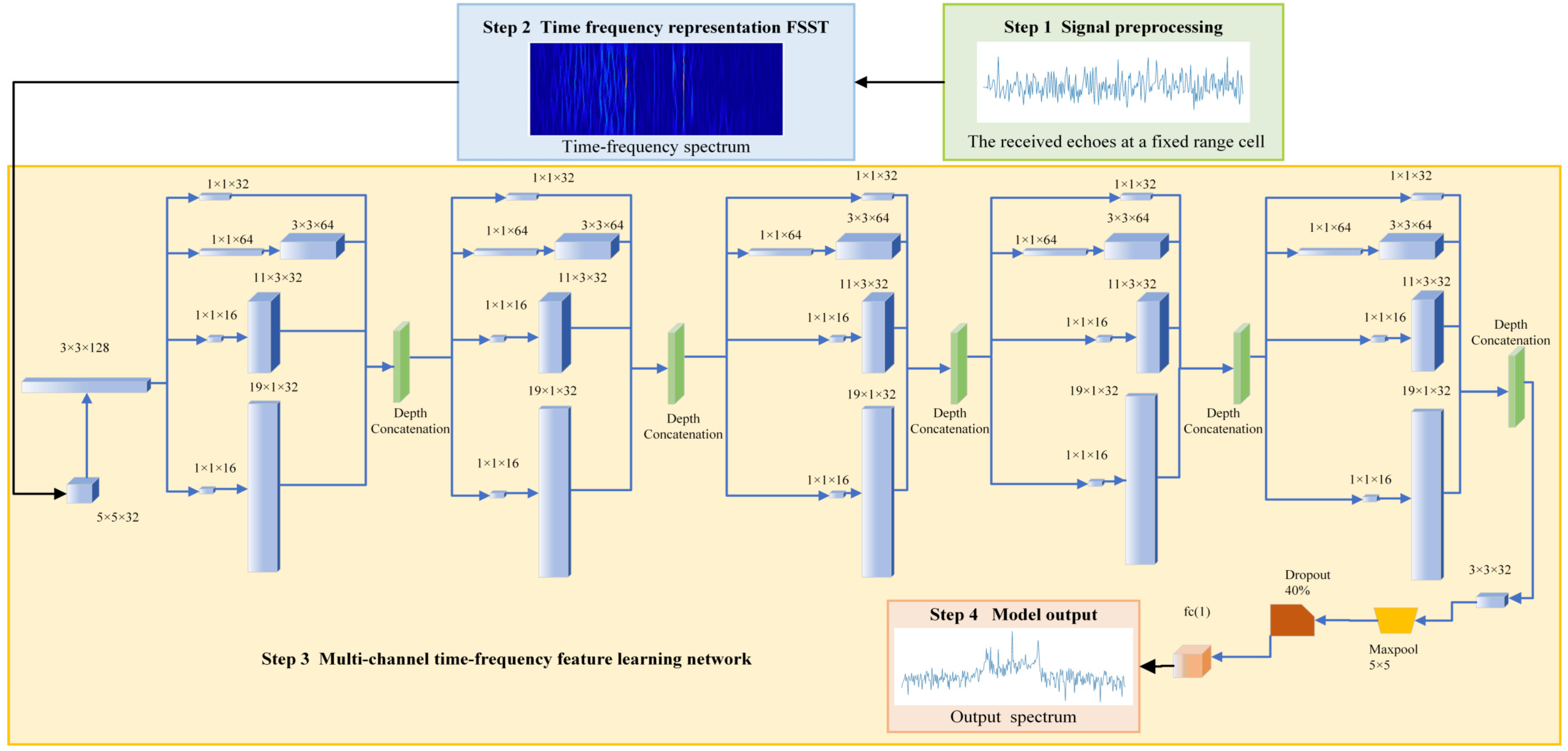
2.2. Proposed Deep Learning Aided Time–Frequency Analysis Filter Framework
2.2.1. Signal Preprocessing
2.2.2. Time–Frequency Representation of the Received Echoes
2.2.3. Feature Learning of Different Types of Echo Components
3. Results
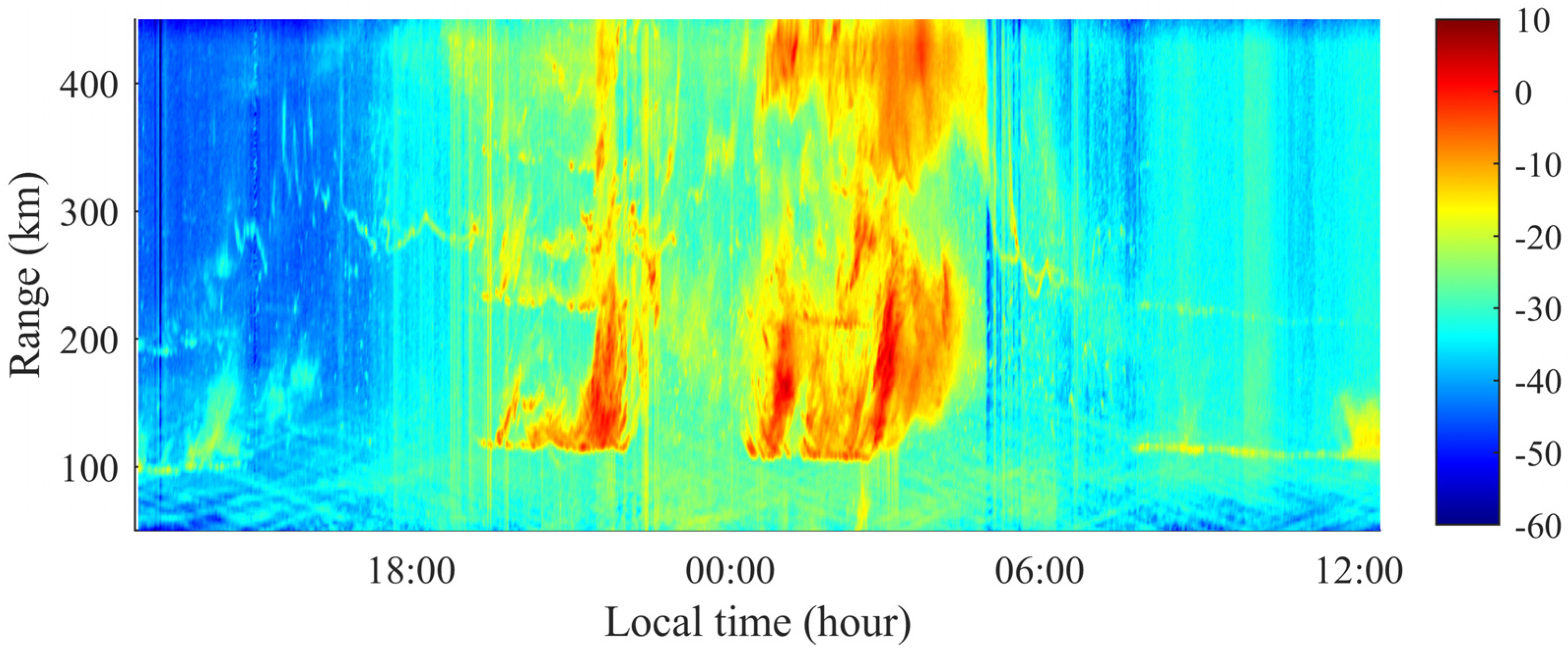
3.1. Data Sets
3.2. The Parameter Analysis of Time–Frequency Representation
3.3. Time–Frequency Representation of Radar Received Echoes
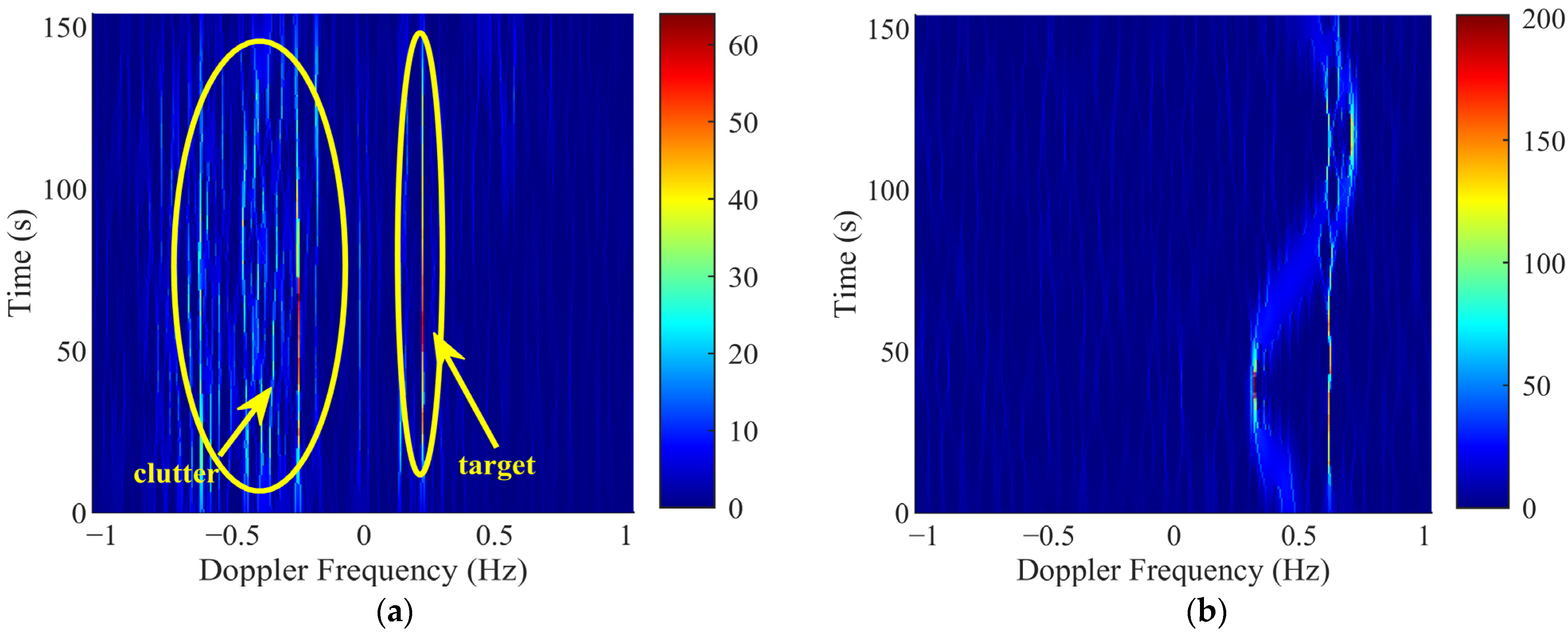
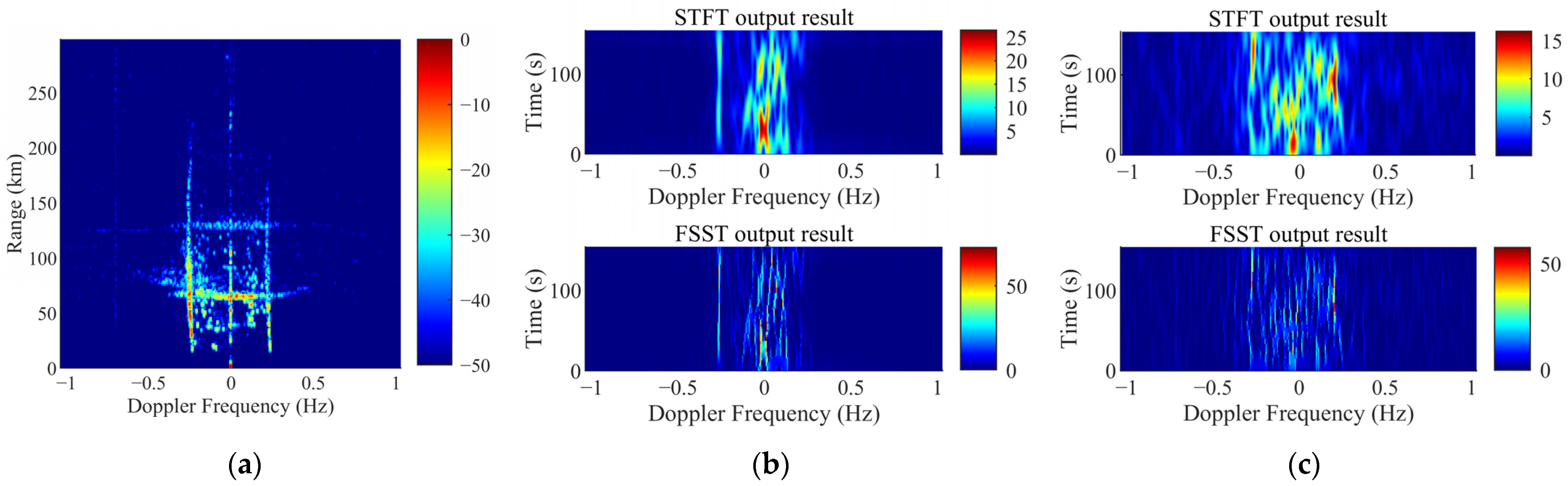
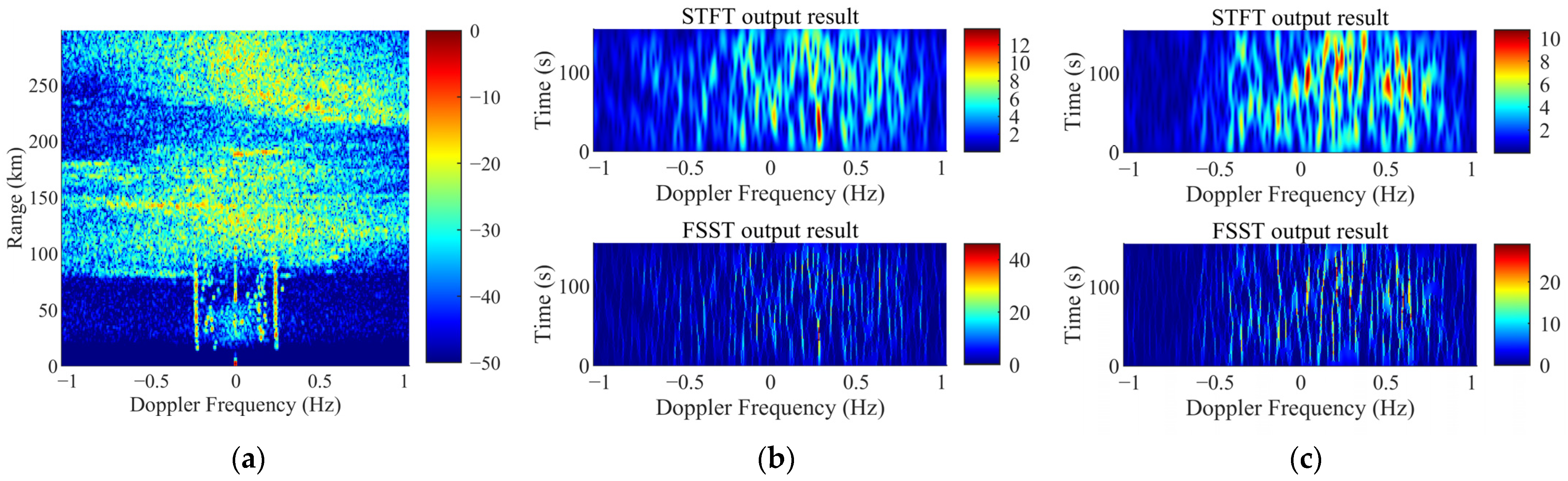
3.3.1. The Time–Frequency Analysis of Targets Echoes
3.3.2. The Time–Frequency Analysis of Ionosphere Clutter
3.4. Model Training Details
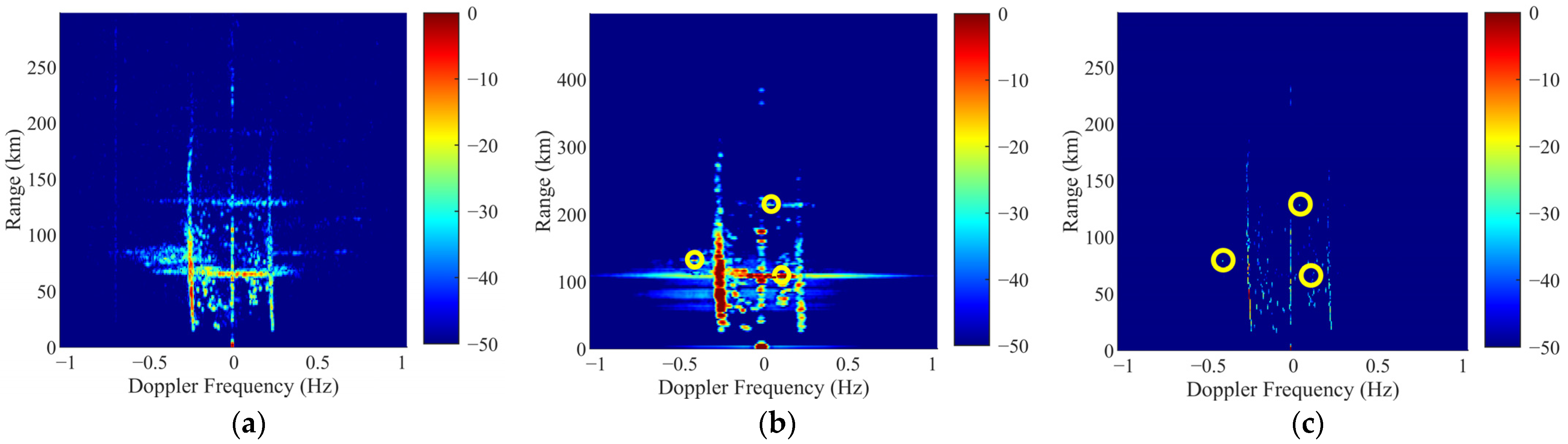
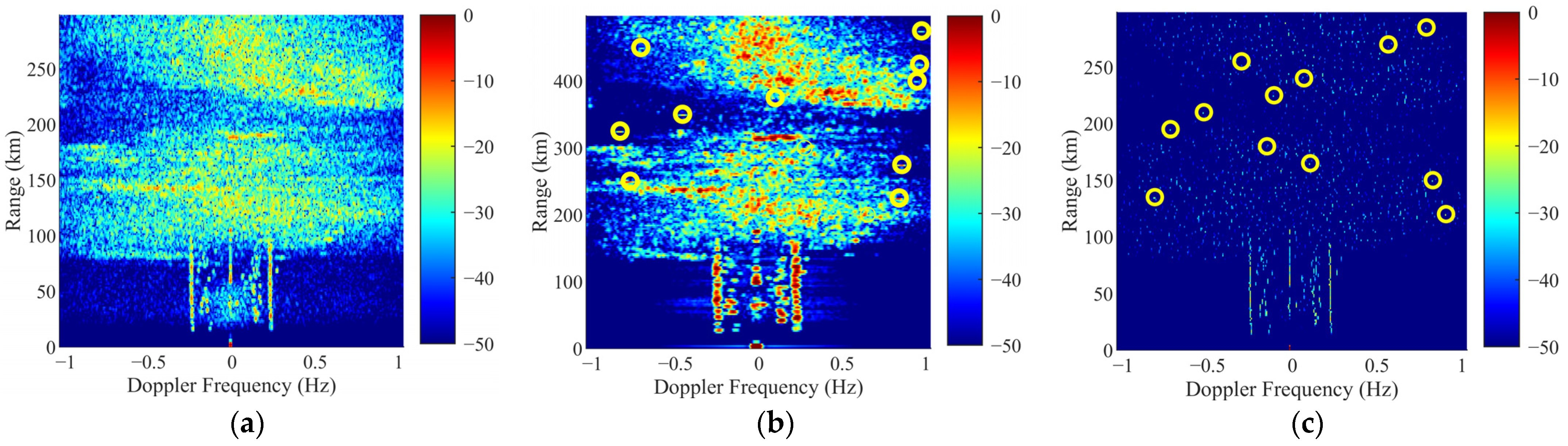
3.5. The Global Region Suppression Results of Ionosphere Clutter by Using Proposed Framework
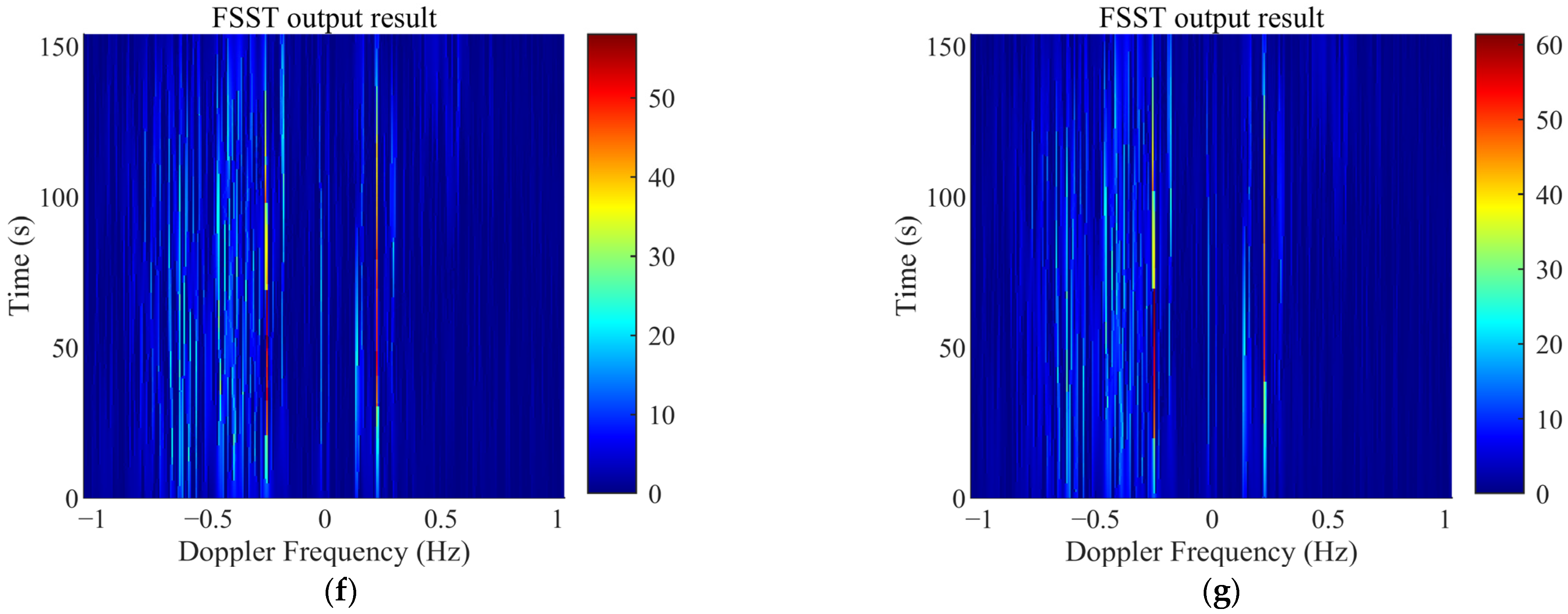
3.5.1. The Suppression Results of Specular Reflection Ionosphere Clutter
3.5.2. The Suppression Results of Spread Ionosphere Clutter
4. Discussion
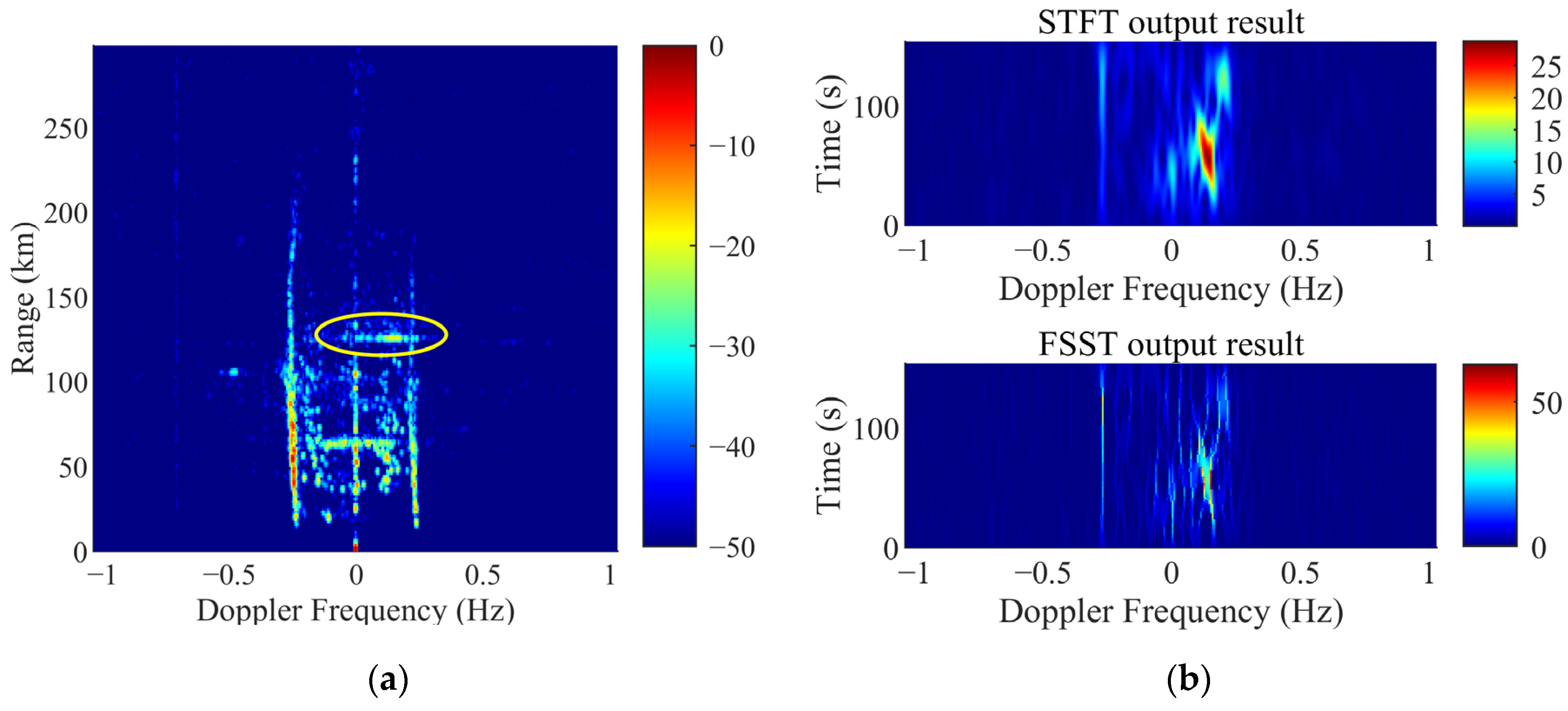
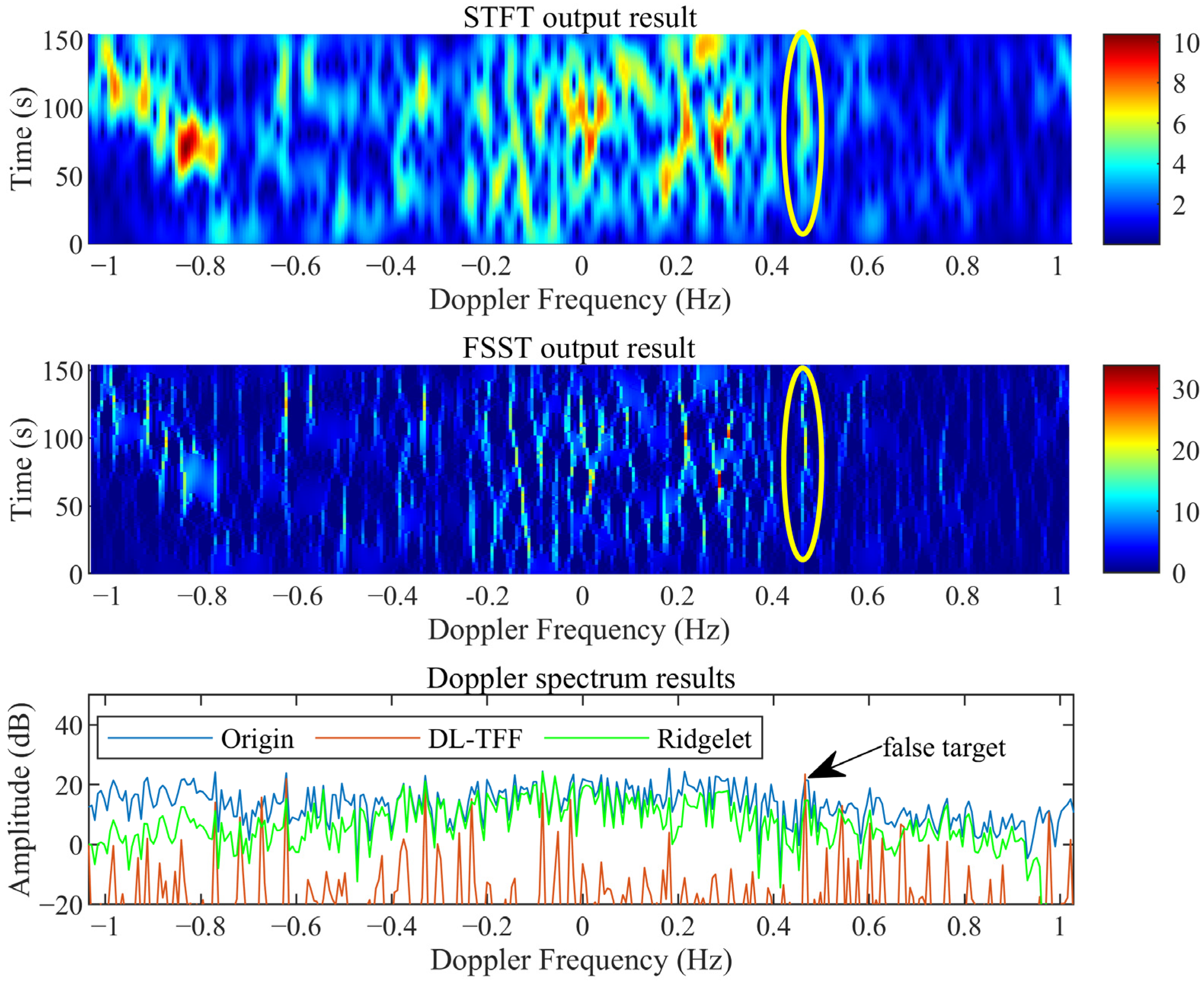
4.1. The Suppression Results Comparison of Local Stable Ionosphere Clutter
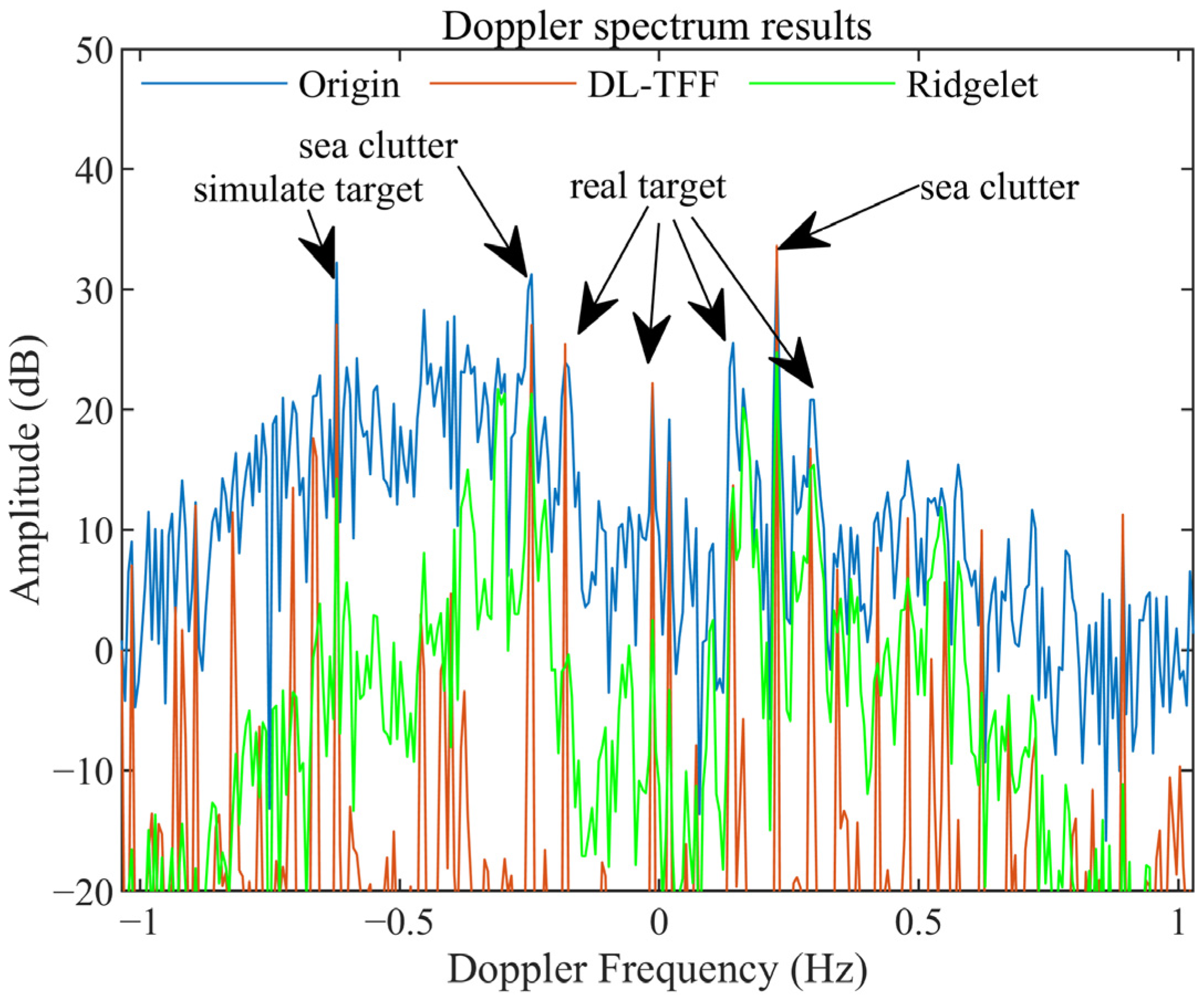
4.2. The Suppression Results Comparsion of Local Region Ionosphere Clutter
4.3. Analysis of Detection Properties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, H.C. Characterization of Ionospheric Clutter in HF Surface Wave Radar; Rep. TR 2003-114; Defence Research and Development Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2003.
- Ravan, M.; Adve, R.S. Ionospheric clutter model for high frequency surface wave radar. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–11 May 2012; pp. 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Ono, Y.; Peng, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H. Target Detection Within Nonhomogeneous Clutter Via Total Bregman Divergence-Based Matrix Information Geometry Detectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 4326–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Ono, Y.; Peng, L.; Xu, Y. Unsupervised Learning Discriminative MIG Detectors in Nonhomogeneous Clutter. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 4107–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Bi, G.; Yang, X. Super-Resolution ISAR Imaging for Maneuvering Target Based on Deep-Learning-Assisted Time–Frequency Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5201514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, H. Radar Target Detection with Multi-Task Learning in Heterogeneous Environment. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4021405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, N.; Zhu, J.; Xie, G.; Yang, L.; Huang, Z. Z-Transform-Based FDTD Implementations of Biaxial Anisotropy for Radar Target Scattering Problems. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, D.; Wei, N. Research on ionospheric phase decontamination for OTHR. In Proceedings of the 2014 XXXIth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS), Beijing, China, 16–23 August 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, Z.X.; Guo, W.L. An improved time-frequency distribution method for ionosphere phase decontamination. In Proceedings of the ISAPE2012, Xi’an, China, 22–26 October 2012; pp. 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Y. A cascaded approach for correcting ionospheric contamination with large amplitude in HF sky-wave radars. Sci. World J. 2013, 100, 693872. [Google Scholar]
- Stockwell, R.G.; Mansinha, L.; Lowe, R.P. Localisation of the complex spectrum: The S transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1996, 44, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.V.; Sahu, S.S.; Mansinha, L.; Tiampo, K.F.; Panda, G. Time Localised Band Filtering Using Modified S-Transform. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Signal Processing Systems, Singapore, 15–17 May 2009; pp. 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. Ocean surface current measurement with high-frequency hybrid sky-surface wave radar. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yue, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, L. Correction of ionospheric distortion on HF hybrid sky-surface wave radar calibrated by direct wave. Radio Sci. 2019, 54, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, R. Cascaded method for ionospheric decontamination and sea clutter suppression for high-frequency hybrid sky-surface wave radar. IET Signal Process. 2015, 9, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, A.; Xia, X.; Chen, D. Spread Sea Clutter Suppression in HF Hybrid Sky-Surface Wave Radars Based on General Parameterized Time–Frequency Analysis. Int. J. Antenn. Propag. 2020, 2020, 7627521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xu, R. A novel ionospheric clutter mitigation method through time-frequency image processing based on ridgelet analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 10–13 October 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Starck, J.L.; Candes, E.J.; Donoho, D.L. The curvelet transform for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2002, 11, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estevez, P.G.; Marchi, P.; Galarza, C.; Elizondo, M. Non-Stationary Power System Forced Oscillation Analysis Using Synchrosqueezing Transform. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 2021, 36, 1583–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, N.; Zhu, X. Synchroextracting transform: The theory analysis and comparisons with the synchrosqueezing transform. Signal Process. 2020, 166, 107243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I.; Lu, J.; Wu, H.-T. Synchrosqueezed wavelet transforms: An empirical mode decomposition-like tool. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2011, 30, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oberlin, T.; Meignen, S.; Perrier, V. The fourier-based synchrosqueezing transform. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- Auger, F.; Flandrin, P. Improving the readability of time-frequency and time-scale representations by the reassignment method. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1995, 43, 1068–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.-T.; Chan, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-T.; Yeh, Y.-H. Using synchrosqueezing transform to discover breathing dynamics from ECG signals. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2014, 36, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xianrong, W.; Hengyu, K.; Biyang, W. Adaptive ionospheric clutter suppression based on subarrays in monostatic HF surface wave radar. Proc. Inst. Elect. Eng.—Radar Sonar Navigat. 2005, 152, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arienzo, A.; Argenti, F.; Alparone, L.; Gherardelli, M. Accurate Despeckling and Estimation of Polarimetric Features by Means of a Spatial Decorrelation of the Noise in Complex PolSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basit, A.; Qureshi, I.M.; Khan, W.; ur Rehman, S.; Khan, M.M. Beam Pattern Synthesis for an FDA Radar with Hamming Window-Based Nonuniform Frequency Offset. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 2283–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Peng, X. Spectra Analysis of Sampling and Reconstructing Continuous Signal Using Hamming Window Function. In Proceedings of the 2008 Fourth International Conference on Natural Computation, Jinan, China, 18–20 October 2008; pp. 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, X.; Peng, L. MIG Median Detectors with Manifold Filter. Signal Process. 2021, 188, 108176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, S. OS-CFAR theory for multiple targets and nonuniform clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1988, 24, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Properties | Specification |
|---|---|
| Frequency bandwidth | 60 kHz |
| Carrier frequency | 4.7 MHz |
| Coherent integration time | 144 s |
| Waveform | FMICW |
| Range resolution | 1.5 km |
| Doppler frequency resolution | 6.5 mHz |
| Transmit power | 8 kW |
| Antenna system | Uniform linear monopole array |
| Blocks | Layer | Filter Size | Stride | Padding | Output Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Input | 320 × 5 × 128 | |||
| Conv 5 × 5 | 5 × 5 × 32 | 1, 1 | Same | ||
| ReLU1 | |||||
| Conv 3 × 3 | 3 × 3 × 128 | 1, 1 | Same | ||
| ReLU2 | |||||
| crossChannelNorm | |||||
| Inception 1 | Inception | 320 × 5 × 160 | |||
| depthConcatenation | 2, 1 | Same | |||
| maxpool 3 × 3 | |||||
| Inception 2 | Inception | 80 × 5 × 160 | |||
| depthConcatenation | 2, 1 | Same | |||
| maxpool 3 × 3 | |||||
| Inception 3 | Inception | 80 × 5 × 160 | |||
| depthConcatenation | 2, 1 | Same | |||
| maxpool 3 × 3 | |||||
| Inception 4 | Inception | 40 × 5 × 160 | |||
| depthConcatenation | 2, 1 | Same | |||
| maxpool 3 × 3 | |||||
| Inception5 | Inception | 20 × 5 × 160 | |||
| depthConcatenation | 2, 1 | Same | |||
| maxpool 3 × 3 | |||||
| Conv 3 × 3 | 3 × 3 × 32 | 1, 1 | Same | 2 × 1 × 32 | |
| ReLu | |||||
| Maxpool 5 × 5 | |||||
| Output | Dropout 40% | 1 | |||
| Full | |||||
| connected (1) | |||||
| Regression |
| Channel | Layer | Filter Size | Stride | Padding | Output Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel 1 | Conv 1 × 1 | 1 × 1 × 32 | 1, 1 | Same | 320 × 5 × 32 |
| ReLU | |||||
| Channel 2 | Conv 1 × 1 | 1 × 1 × 64 | 1, 1 | Same | 320 × 5 × 64 |
| ReLu | |||||
| Conv 3 × 3 | 3 × 3 × 64 | 1, 1 | Same | ||
| ReLu | |||||
| Channel 3 | Conv 1 × 1 | 1 × 1 × 16 | 1, 1 | Same | 320 × 5 × 32 |
| ReLu | |||||
| Conv 11 × 3 | 11 × 3 × 32 | 1, 1 | Same | ||
| ReLu | |||||
| Channel 4 | Conv 1 × 1 | 1 × 1 × 16 | 1, 1 | Same | 320 × 5 × 32 |
| ReLu | |||||
| Conv 19 × 1 | 19 × 1 × 32 | 1, 1 | Same | ||
| ReLu |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Suo, Y.; Wu, X. Deep Learning Aided Time–Frequency Analysis Filter Framework for Suppressing Ionosphere Clutter. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143424
Ji X, Li J, Yang Q, Wang L, Suo Y, Wu X. Deep Learning Aided Time–Frequency Analysis Filter Framework for Suppressing Ionosphere Clutter. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(14):3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143424
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Xiaowei, Jiaming Li, Qiang Yang, Linwei Wang, Ying Suo, and Xiaochuan Wu. 2022. "Deep Learning Aided Time–Frequency Analysis Filter Framework for Suppressing Ionosphere Clutter" Remote Sensing 14, no. 14: 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143424
APA StyleJi, X., Li, J., Yang, Q., Wang, L., Suo, Y., & Wu, X. (2022). Deep Learning Aided Time–Frequency Analysis Filter Framework for Suppressing Ionosphere Clutter. Remote Sensing, 14(14), 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143424






