Change Detection Techniques with Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: Experiments with Random Forests and Sentinel-1 Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals of Coherent and Incoherent Change Detection Methods
2.1. Incoherent CD Approaches
2.2. Coherent CD Approaches
2.3. Introduction to AI-Aided Change Detection Methods
- The development of methodologies capable of ingesting and analyzing a large amount of data automated and extrapolating useful new information [110].
3. Proposed Multi-Temporal SAR Change Detection Strategy
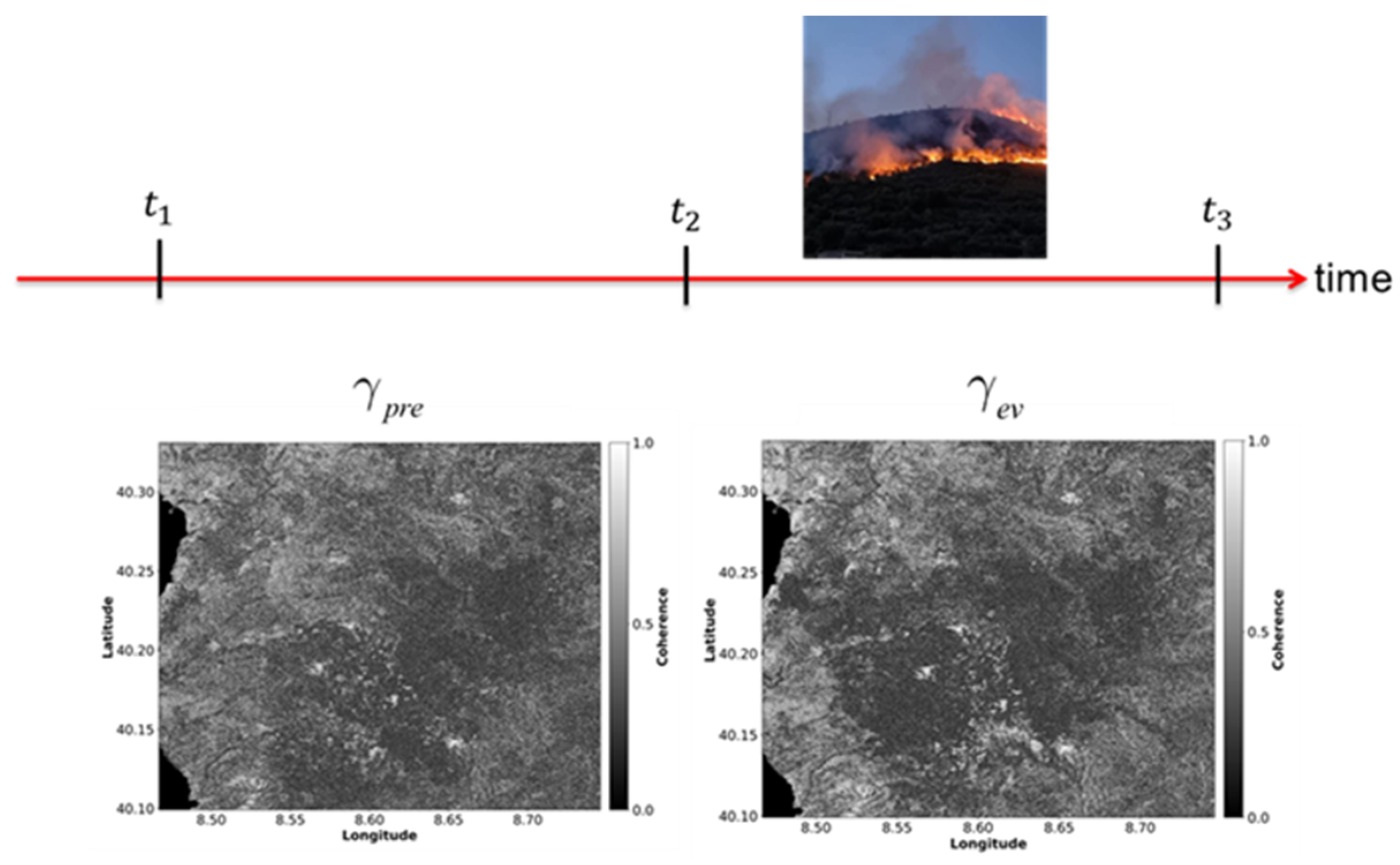
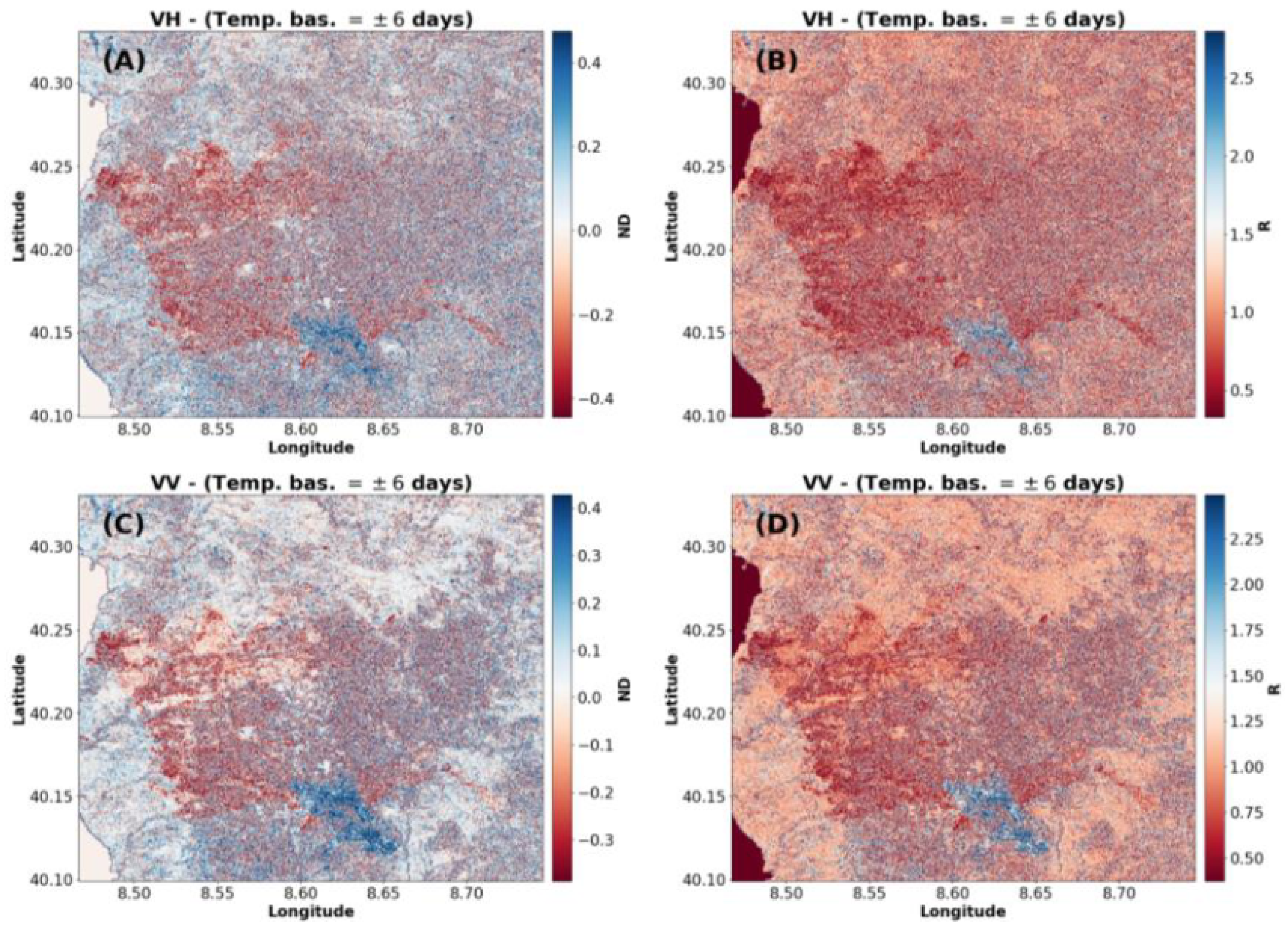
3.1. Coherent Change Detection Indices
3.2. Temporal Decorrelation Models: Implications for Change Detection
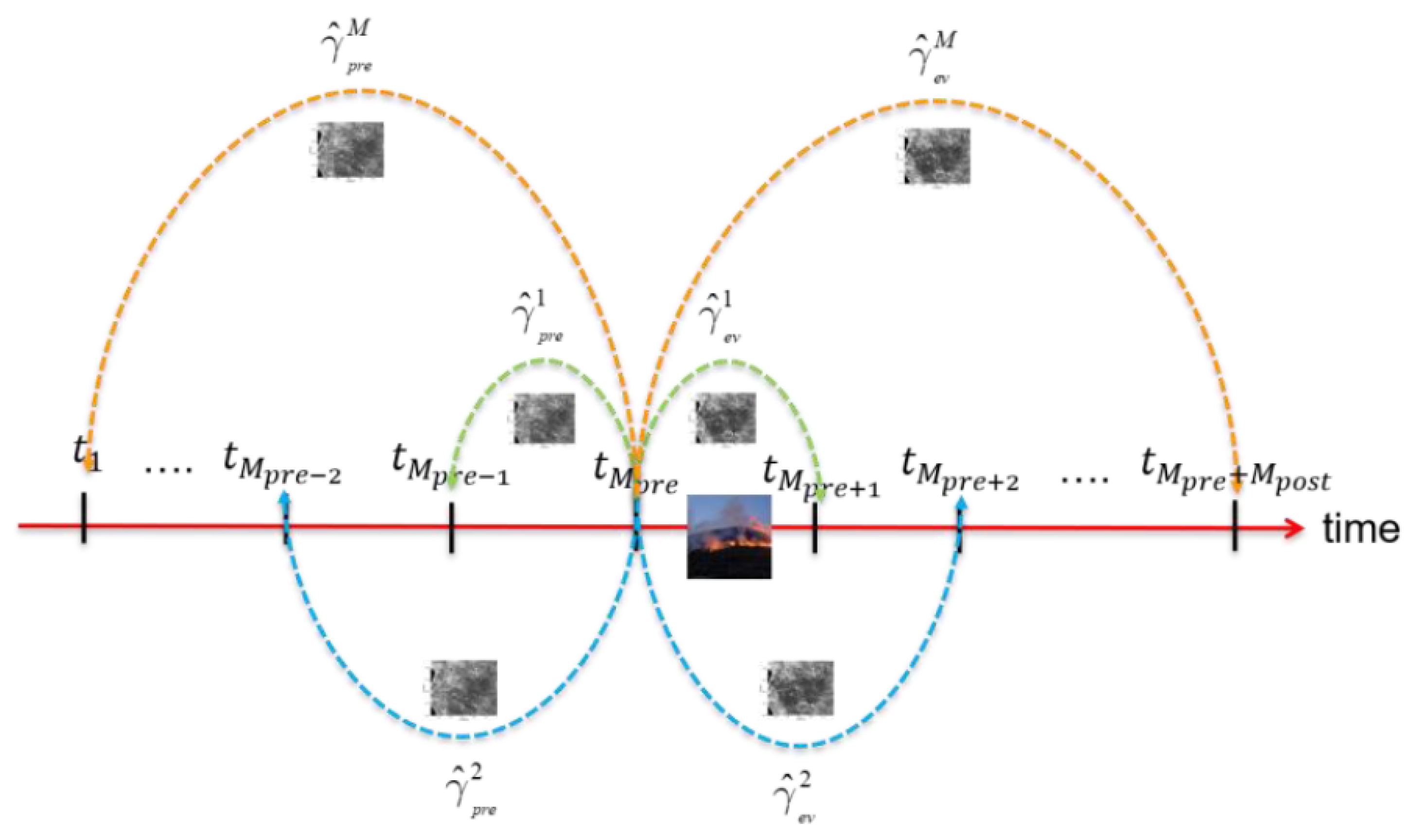
3.3. Extension to the Multi-Pass Case
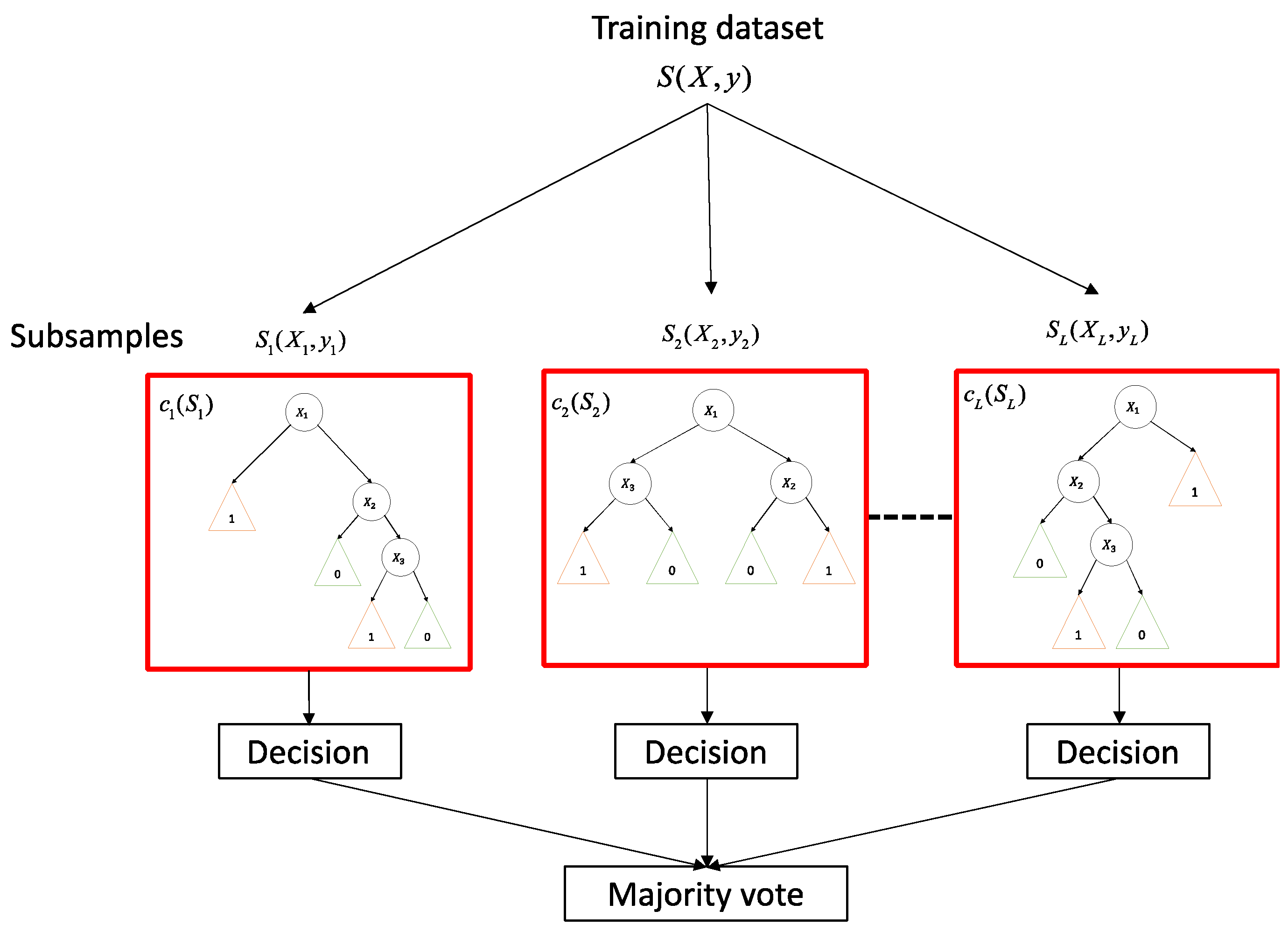
3.4. Random Decision Forest: Basic Rationale and Application to Change Detection Analyses
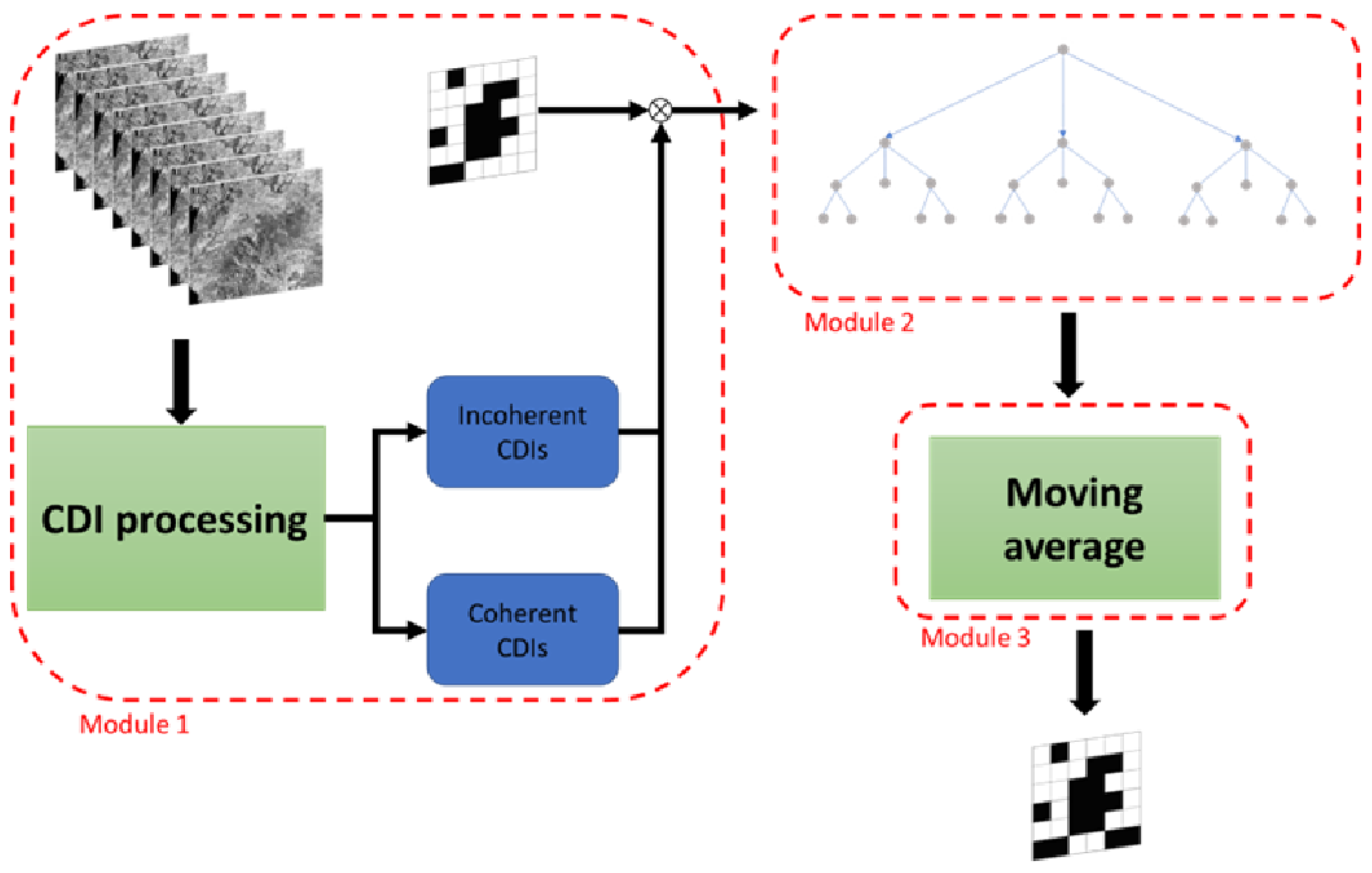
3.5. Proposed RF-Aided CD Strategy
- ➢
- Starting from a sequence of calibrated, co-registered, and geocoded SAR acquisitions, the first module consists of pre-processing data and calculating the incoherent and coherent change detection indices.
- ➢
- In this work, we treated change detection as a pixel-based binary classification task that uses 1 and 0 to indicate changed and unchanged pixels. Therefore, we used an RF model combining CDIs and a reference change mask in the second module to perform supervised learning.
- ➢
- The final module applies a spatial average with a moving window to the RF predicted binary change mask. Eventually, the binary change mask is retrieved.
4. Material
- i.
- The Montiferru region in Sardinia (see Figure 6A). The territory is mainly characterized by a mountain chain and some valleys located in its inner parts, particularly in the municipalities of Santu Lussurgiu, Cuglieri, and Scano Montiferro. The terrain elevation of the investigated area ranges from the sea level to the highest point of Monte Urtigu, about 1050 m a.s.l., located in the municipality of Santu Lussurgiu. The site is historically characterized by the Mediterranean climate, presenting dry summers, cold and wet winters, and intermediate conditions in spring and autumn. In recent decades, due to global warming, the region has also been facing alterations drastically in precipitation regimes, with the most considerable precipitation runoff decrease [147].
- ii.
- The Sicilian Apennines, specifically the area of the “Madonie” (see Figure 6B). Within this area is situated the Parco delle Madonie, which is the second nature reserve in Sicily. Its 35,000 hectares are home to towering mountains (at 1979 m, the highest peak is Pizzo Carbonara), large expanses of woodland, and a flourishing variety of flora and fauna. In terms of flora, there are over 2600 different species of plants, many of which are endemic to the area. Specifically, at an altitude of 1500 m, the land is entirely covered by the Madonie Forest. Below, on the hillsides, the area is mainly characterized by crops, including the cultivation of wheat, olives, and fruits. The area incorporates several historic towns and villages such as Polizzi Generosa, Petralia Soprana and Sottana, Gangi and Castelbuono.
- iii.
- The Houston metropolitan area (see Figure 6C) is the fifth-most populous urban area in the USA. The region contains the city of Houston (the most significant economic and cultural center of the South). Its port (the second largest port in the United States and the 16th largest globally) leads the US international trade. The metropolitan area is in the Mexico Gulf Coastal Plains. Much of the urbanized area was built on forested land, marshes, and prairie.
5. Experimental Results
6. Discussion on Random Forest Training and Research Outcomes
- (i)
- Short temporal InSAR baselines are preferred to long-baselines because coherence rapidly varies after a primary event and tends to achieve a new (random) state, not linked to the primary event under investigation, just a few days after the event itself. This finding is in accordance with the fact that temporal decorrelation is sensitive not only to random changes (linked to the event) but also to composite ground and volumetric changes that determine a systematic decay of the coherence over time (see the model in Section 3.2).
- (ii)
- The normalized coherence difference has generally an enhanced importance than the coherence ratio. This finding was also expected, and it agrees with theory (see Section 3.2). Indeed, the normalized coherence difference has the beneficial effect of including in a unique estimator the advantage of the coherence difference and coherence ratio to discriminate and better isolate the random coherent components.
- (iii)
- The co-pol and cross-pol channels have almost the same importance, with a slight marked preference versus the co-pol VV polarization.
7. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansen, M.C.; Loveland, T.R. A Review of Large Area Monitoring of Land Cover Change Using Landsat Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasyev, A.; Zamyatin, A.; Cabral, P. Land Cover Change Analysis Using Change Detection Methods. In Information Technologies and Mathematical Modelling: Proceedings of the 13th International Scientific Conference, Anzhero-Sudzhensk, Russia, 20–22 November 2014; Dudin, A., Nazarov, A., Yakupov, R., Gortsev, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone, L.; Prieto, D.F. Automatic Analysis of the Difference Image for Unsupervised Change Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Mausel, P.; Brondizio, E.; Moran, E. Change Detection Techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2365–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z. Change Detection Using Landsat Time Series: A Review of Frequencies, Preprocessing, Algorithms, and Applications. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, P.; Jonckheere, I.; Nackaerts, K.; Muys, B.; Lambin, E. Digital Change Detection Methods in Ecosystem Monitoring: A Review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 1565–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Digital Change Detection Techniques Using Remotely-Sensed Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1989, 10, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radke, R.J.; Andra, S.; Al-Kofahi, O.; Roysam, B. Image Change Detection Algorithms: A Systematic Survey. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunetta, R.S.; Knight, J.F.; Ediriwickrema, J.; Lyon, J.G.; Worthy, L.D. Land-Cover Change Detection Using Multi-Temporal MODIS NDVI Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, V. Object-Based Classification of Remote Sensing Data for Change Detection. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2004, 58, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.; Quegan, S. Understanding Synthetic Aperture Radar Images; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-89006-850-2. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, T. Unsupervised Change Detection in Satellite Images Using Principal Component Analysis and K-Means Clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, G.; Chiroiu, L.; Mering, C.; Chopin, F. Building Destruction and Damage Assessment after Earthquake Using High Resolution Optical Sensors. The Case of the Gujarat Earthquake of January 26, 2001. In Proceedings of the Igarss 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume I–VII, pp. 2398–2400. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, D.; Lemoine, G.; Bruzzone, L. Earthquake Damage Assessment of Buildings Using VHR Optical and SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2403–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wieland, M.; Pittore, M.; Parolai, S.; Zschau, J. Exposure Estimation from Multi-Resolution Optical Satellite Imagery for Seismic Risk Assessment. ISPRS Int. Geo-Inf. 2012, 1, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Hajj, M.; Begue, A.; Guillaume, S.; Martine, J.-F. Integrating SPOT-5 Time Series, Crop Growth Modeling and Expert Knowledge for Monitoring Agricultural Practices—The Case of Sugarcane Harvest on Reunion Island. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.; Dorigo, W.A.; Bauer, T.; Eitzinger, J.; Haumann, J.; Kaiser, G.; Linke, R.; Postl, W.; Rischbeck, P.; Schneider, W.; et al. Changes in Spectral Reflectance of Crop Canopies Due to Drought Stress. In Earth Observation for Vegetation Monitoring and Water Management; D’Urso, G., Jochum, M.A.O., Moreno, J., Eds.; Amer Inst Physics: Melville, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 852, p. 258. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, C.; White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A. Optical Remotely Sensed Time Series Data for Land Cover Classification: A Review. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 116, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Moran, E. A Survey of Remote Sensing-Based Aboveground Biomass Estimation Methods in Forest Ecosystems. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 63–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.O.; Malhi, Y.; Aragao, L.E.O.C.; Ladle, R.; Arai, E.; Barbier, N.; Phillips, O. Remote Sensing Detection of Droughts in Amazonian Forest Canopies. New Phytol. 2010, 187, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.M.C. Remote Sensing of Burned Areas in Tropical Savannas. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2003, 12, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, T.; Su, Y.; Xue, B.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Fang, J.; Guo, Q. Mapping Global Forest Aboveground Biomass with Spaceborne LiDAR, Optical Imagery, and Forest Inventory Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapete, D.; Cigna, F. Appraisal of Opportunities and Perspectives for the Systematic Condition Assessment of Heritage Sites with Copernicus Sentinel-2 High-Resolution Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Wong, L.N.Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, T. Using Multitemporal Landsat Imagery to Monitor and Model the Influences of Landscape Pattern on Urban Expansion in a Metropolitan Region. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, S.; Nascetti, A.; Azizpour, H.; Ban, Y. Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data Fusion for Urban Change Detection Using a Dual Stream U-Net. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4019805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarro, C.; Cerra, D.; Auer, S.; Ullo, S.L.; Reinartz, P. Urban Sprawl and COVID-19 Impact Analysis by Integrating Deep Learning with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and Expansion of the Fmask Algorithm: Cloud, Cloud Shadow, and Snow Detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckerstorfer, M.; Buehler, Y.; Frauenfelder, R.; Malnes, E. Remote Sensing of Snow Avalanches: Recent Advances, Potential, and Limitations. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2016, 121, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.; Bolch, T.; Gafurov, A.; Prechtel, N. Snow Cover Distribution in the Aksu Catchment (Central Tien Shan) 1986-2013 Based on AVHRR and MODIS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 5361–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhuri, A.; Gascoin, S.; Menzel, L.; Kostadinov, T.S.; Harpold, A.A.; Sanmiguel-Vallelado, A.; Lopez-Moreno, J. Performance Assessment of Optical Satellite-Based Operational Snow Cover Monitoring Algorithms in Forested Landscapes. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7159–7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.P. Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective; Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning Series; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-262-01802-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. Speckle Analysis and Smoothing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1981, 17, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Wen, J.-H.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Chen, K.-S.; Chen, A.J. Improved Sigma Filter for Speckle Filtering of SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Pierce, L.E.; Ulaby, F.T. SAR Speckle Reduction Using Wavelet Denoising and Markov Random Field Modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2196–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazi, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Melgani, F. An Unsupervised Approach Based on the Generalized Gaussian Model to Automatic Change Detection in Multitemporal SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rignot, E.; Vanzyl, J. Change Detection Techniques for Ers-1 Sar Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conradsen, K.; Nielsen, A.A.; Sehou, J.; Skriver, H. A Test Statistic in the Complex Wishart Distribution and Its Application to Change Detection in Polarimetric SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De, S.; Pirrone, D.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L.; Bhattacharya, A. A Novel Change Detection Framework Based on Deep Learning for the Analysis of Multi-Temporal Polarimetric SAR Images. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 5193–5196. [Google Scholar]
- Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. A Detail-Preserving Scale-Driven Approach to Change Detection in Multitemporal SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, G.; Serpico, S.B. Generalized Minimum-Error Thresholding for Unsupervised Change Detection from SAR Amplitude Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2972–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Hostache, R.; Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.J.-P.; Bates, P.D.; Mason, D.C. A Change Detection Approach to Flood Mapping in Urban Areas Using TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Dong, J.; Li, B.; Xu, Q.; Xie, C. Change Detection from Synthetic Aperture Radar Images Based on Neighborhood-Based Ratio and Extreme Learning Machine. JARS 2016, 10, 046019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carincotte, C.; Derrode, S.; Bourennane, S. Unsupervised Change Detection on SAR Images Using Fuzzy Hidden Markov Chains. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, W.; Skriver, H. Change Detection for Thematic Mapping by Means of Airborne Multitemporal Polarimetric SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 618–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, P.B.; Preiss, M. Coherent Change Detection Under a Forest Canopy. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Brisbane, Australia, 27–31 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, V.S.; Stiles, J.A.; Shanmugan, K.S.; Holtzman, J.C. A Model for Radar Images and Its Application to Adaptive Digital Filtering of Multiplicative Noise. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1982, 4, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Berglund, J.; Jensen, J.R.; Thakkar, P.; Ren, D. Speckle Noise Reduction in SAR Imagery Using a Local Adaptive Median Filter. GISci. Remote Sens. 2004, 41, 244–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuan, D.; Sawchuk, A.; Strand, T.; Chavel, P. Adaptive Restoration of Images with Speckle. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1987, 35, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, A.; Tabbara, K.; Yaacoub, C. An Enhanced Kuan Filter for Suboptimal Speckle Reduction. In Proceedings of the 2012 2nd International Conference on Advances in Computational Tools for Engineering Applications (ACTEA), Beirut, Lebanon, 12–15 December 2012; pp. 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Baraldi, A.; Parmiggiani, F. A Refined Gamma MAP SAR Speckle Filter with Improved Geometrical Adaptivity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A.; Bousquet, P. A Statistical and Geometrical Edge Detector for SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S. A Simple Speckle Smoothing Algorithm for Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1983, 1, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S. Statistical Modelling and Suppression of Speckle in Synthetic Aperture Radar Images; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 2, pp. 1331–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Adaptive Speckle Filtering in Radar Imagery. IntechOpen. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/46699 (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Bruzzone, L.; Serpico, S.B. An Iterative Technique for the Detection of Land-Cover Transitions in Multitemporal Remote-Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- A Variational Change Detection Method for Multitemporal SAR Images: Remote Sensing Letters: Vol 5, No 4. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/2150704X.2014.904970 (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing Active and Passive. Rader Remote Sens. Surf. Scatt. Emiss. Theory 1982, 2, 848–902. [Google Scholar]
- Chini, M.; Hostache, R.; Giustarini, L.; Matgen, P. A Hierarchical Split-Based Approach for Parametric Thresholding of SAR Images: Flood Inundation as a Test Case. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6975–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazi, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Melgani, F. Automatic Identification of the Number and Values of Decision Thresholds in the Log-Ratio Image for Change Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Ban, Y. Unsupervised Change Detection in Multitemporal SAR Images Over Large Urban Areas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3248–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, J. Change Detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar Images Based on Image Fusion and Fuzzy Clustering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Su, L.; Jia, M.; Chen, W. Fuzzy Clustering With a Modified MRF Energy Function for Change Detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 22, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hou, B.; Liu, G. Using Combined Difference Image and K-Means Clustering for SAR Image Change Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kittler, J.; Illingworth, J. Minimum Error Thresholding. Pattern Recognit. 1986, 19, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Shi, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, C. Unsupervised Change Detection With Expectation-Maximization-Based Level Set. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lei, L.; Li, X.; Tan, X.; Kuang, G. Structure Consistency-Based Graph for Unsupervised Change Detection With Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Sierra, D.A.; Benítez-Restrepo, H.D.; Vargas-Cardona, H.D.; Chanussot, J. Graph-Based Data Fusion Applied to: Change Detection and Biomass Estimation in Rice Crops. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, U.; Lavanant, L.; Liuzzi, G.; Masiello, G.; Serio, C.; Stuhlmann, R.; Tjemkes, S.A. Cloud Mask via Cumulative Discriminant Analysis Applied to Satellite Infrared Observations: Scientific Basis and Initial Evaluation. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2014, 7, 3355–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, W.; Shi, S.; Pan, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L. Unsupervised Change Detection in SAR Images Based on Frequency Difference and a Modified Fuzzy C-Means Clustering. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 3055–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J. A Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test for Coherent Change Detection in Polarimetric SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1873–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Chen, J.M.; Kuang, G. A Change Detection Measure Based on a Likelihood Ratio and Statistical Properties of SAR Intensity Images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 3, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, D.O. Satellite Remote Sensing of Biomass Burning with Optical and Thermal Sensors. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2000, 24, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentile, L.B.; Morgan, P.; Hudak, A.T.; Bobbitt, M.J.; Lewis, S.A.; Smith, A.M.S.; Robichaud, P.R. Post-Fire Burn Severity and Vegetation Response Following Eight Large Wildfires Across the Western United States. Fire Ecol. 2007, 3, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, F.; Ruecker, G. Use of Multitemporal ERS-2 SAR Images for Identification of Burned Scars in South-East Asian Tropical Rainforest. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Kasischke, E.S.; Brunzell, S.; Mudd, J.P.; Tukman, M. Mapping Fire Scars in Global Boreal Forests Using Imaging Radar Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 4211–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, M.A.; Belenguer-Plomer, M.A.; Roteta, E.; Bastarrika, A.; Wheeler, J.; Fernandez-Carrillo, A.; Tansey, K.; Wiedemann, W.; Navratil, P.; Lohberger, S.; et al. Burned Area Detection and Mapping: Intercomparison of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Based Algorithms over Tropical Africa. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imperatore, P.; Azar, R.; Calo, F.; Stroppiana, D.; Brivio, P.A.; Lanari, R.; Pepe, A. Effect of the Vegetation Fire on Backscattering: An Investigation Based on Sentinel-1 Observations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4478–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifi, L.; Mignotte, M. Deep Learning for Change Detection in Remote Sensing Images: Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 126385–126400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S.; Zhan, Z. Change Detection Based on Artificial Intelligence: State-of-the-Art and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, M.; Liu, W.; Yamazaki, F. Learning Change from Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: Performance Evaluation of a Support Vector Machine to Detect Earthquake and Tsunami-Induced Changes. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Gong, M.; Qin, K.; Zhang, P. A Deep Convolutional Coupling Network for Change Detection Based on Heterogeneous Optical and Radar Images. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiss, M.; Gray, D.; Stacy, N. A Change Detection Statistic for Repeat Pass Interferometric SAR. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, (ICASSP ’03), Hong Kong, China, 6–10 April 2003; Volume 5, p. V-241. [Google Scholar]
- Bamler, R.; Hartl, P. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Inverse Probl. 1998, 14, R1–R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiss, M.; Gray, D.A.; Stacy, N.J.S. Detecting Scene Changes Using Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2041–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pepe, A.; Calò, F. A Review of Interferometric Synthetic Aperture RADAR (InSAR) Multi-Track Approaches for the Retrieval of Earth’s Surface Displacements. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Detecting Scene Changes Using Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. IEEE Journals & Magazine. IEEE Xplore. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1661793 (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in Interferometric Radar Echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mercier, G.; Derrode, S. SAR Image Change Detection Using Distance between Distributions of Classes. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2004, 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; Volume 6, pp. 3872–3875. [Google Scholar]
- Amitrano, D.; Di Martino, G.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G. Unsupervised Rapid Flood Mapping Using Sentinel-1 GRD SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3290–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Gong, M.; Zhou, Z. Wavelet Fusion on Ratio Images for Change Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti-Guarnieri, A.V.; Brovelli, M.A.; Manzoni, M.; Mariotti d’Alessandro, M.; Molinari, M.E.; Oxoli, D. Coherent Change Detection for Multipass SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6811–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Hao, M.; Deng, K.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Yao, G. Change Detection in SAR Images via Ratio-Based Gaussian Kernel and Nonlocal Theory. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.C.; Dobbs, K.; Koehler, F.W. Sentinel-1 Spatially Varying Maximum-Likelihood Coherent Change Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 1234–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, A. Sar Calibration—An Overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Huang, S.; Xiong, H.; Torre, A.; Rubertone, F. Study on Speckle Reduction in Multi-Look Polarimetric SAR Image. J. Electron. 1999, 16, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, D.L.; Lee, J.-S.; Ainsworth, T.L. Compensation of Terrain Azimuthal Slope Effects in Geophysical Parameter Studies Using Polarimetric SAR Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 69, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A. Statistics of the Stokes Parameters and of the Complex Coherence Parameters in One-Look and Multilook Speckle Fields. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martinez, C.; Fabregas, X. Modeling and Reduction of SAR Interferometric Phase Noise in the Wavelet Domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2553–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pepe, A.; Mastro, P.; Jones, C.E. Adaptive Multilooking of Multitemporal Differential SAR Interferometric Data Stack Using Directional Statistics. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 6706–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupp, P.E.; Mardia, K.V. Directional Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-470-31781-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bouaraba, A.; Younsi, A.; Aissa, A.B.; Acheroy, M.; Milisavljevic, N.; Closson, D. Robust Techniques for Coherent Change Detection Using Cosmo-Skymed SAR Images. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2012, 22, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebremichael, E.; Molthan, A.L.; Bell, J.R.; Schultz, L.A.; Hain, C. Flood Hazard and Risk Assessment of Extreme Weather Events Using Synthetic Aperture Radar and Auxiliary Data: A Case Study. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvaras, M.; Danezis, C.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Small Scale Landslide Detection Using Sentinel-1 Interferometric SAR Coherence. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaraba, A.; Belhadj-Aissa, A.; Closson, D. Man-Made Change Detection Using High-Resolution Cosmo-SkyMed SAR Interferometry. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.; Froger, J.-L.; Baghdadi, N.; Ho Tong Minh, D. Volcanic Eruption Monitoring Using Coherence Change Detection Matrix. In Proceedings of the Igarss 2020—2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 324–327. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, D.E.; Yocky, D.A.; Jakowatz, C.V.; Simonson, K.M. A New Maximum-Likelihood Change Estimator for Two-Pass SAR Coherent Change Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, O.; Perissin, D. Detection of Multitransition Abrupt Changes in Multitemporal SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3239–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, B.; Ranjan, R.; Zomaya, A.; Jie, W. Remote Sensing Big Data Computing: Challenges and Opportunities. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2015, 51, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, A.Y.; Scanlon, B.R. How Can Big Data and Machine Learning Benefit Environment and Water Management: A Survey of Methods, Applications, and Future Directions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 073001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data Fusion: Status and Trends. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2010, 1, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pohl, C.; Van Genderen, J.L. Review Article Multisensor Image Fusion in Remote Sensing: Concepts, Methods and Applications. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 823–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, M.; Chen, D.; Cheng, A.; Wei, H.; Stanley, D. Change Detection from Remotely Sensed Images: From Pixel-Based to Object-Based Approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 80, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Song, K.; Kim, S.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Davis, P.; Masek, J.G.; Goward, S.N. Use of a Dark Object Concept and Support Vector Machines to Automate Forest Cover Change Analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 970–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, D.; Lin, H.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, Y. A SVM-Based Change Detection Method from Bi-Temporal Remote Sensing Images in Forest Area. In Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (WKDD 2008), Adelaide, Australia, 23–24 January 2008; pp. 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support Vector Machines in Remote Sensing: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Lu, H.; Mou, L. Learning a Transferable Change Rule from a Recurrent Neural Network for Land Cover Change Detection. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, P. Feature Learning and Change Feature Classification Based on Deep Learning for Ternary Change Detection in SAR Images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 129, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lathrop, R.G. Urban Change Detection Based on an Artificial Neural Network. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Liu, J.; Gong, J. Urban Flood Mapping Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing and Random Forest Classifier—A Case of Yuyao, China. Water 2015, 7, 1437–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Wyner, A.J.; Olson, M.; Bleich, J.; Mease, D. Explaining the Success of AdaBoost and Random Forests as Interpolating Classifiers. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2017, 18, 1558–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Liu, X.; Shi, J.; Lei, C.; Wang, J. Multiscale Superpixel Segmentation With Deep Features for Change Detection. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36600–36616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Ru, L.; Wu, C.; Zhang, L. Unsupervised Deep Slow Feature Analysis for Change Detection in Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9976–9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touazi, A.; Bouchaffra, D. A K-Nearest Neighbor Approach to Improve Change Detection from Remote Sensing: Application to Optical Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the 2015 15th International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications (ISDA), Marrakech, Morocco, 14–16 December 2015; pp. 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, M.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, A. A Novel Approach for Change Detection of Remotely Sensed Images Using Semi-Supervised Multiple Classifier System. Inf. Sci. 2014, 269, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, A. A Neural Approach Under Active Learning Mode for Change Detection in Remotely Sensed Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedjam, R.; Abdesselam, A.; Melgani, F. Change Detection from Unlabeled Remote Sensing Images Using SIAMESE ANN. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 1530–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, A. Change Detection of Remote Sensing Images with Semi-Supervised Multilayer Perceptron. Fundam. Inform. 2008, 84, 429–442. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Yin, G.; Johnson, B.A. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing Applications: A Meta-Analysis and Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potin, P.; Rosich, B.; Roeder, J.; Bargellini, P. Sentinel-1 Mission Operations Concept. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (Igarss), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1465–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, Y.; Hosokawa, M. Damage Estimation Model Using Temporal Coherence Ratio. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; Volume 5, pp. 2859–2861. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, P.; Gokon, H.; Meguro, K. A Review on Synthetic Aperture Radar-Based Building Damage Assessment in Disasters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Liu, J.G. Analysis of Topographic Decorrelation in SAR Interferometry Using Ratio Coherence Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kim, D.; Yun, S.; Lavalle, M. Damage Mapping Based on Coherence Model Using Multi-Temporal Polarimetric-Interferometric UAVSAR Data. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-315-13947-0. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Delgado, M.; Cernadas, E.; Barro, S.; Amorim, D. Do We Need Hundreds of Classifiers to Solve Real World Classification Problems? J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 3133–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, S.; Heutte, L.; Adam, S. A Study of Strength and Correlation in Random Forests. In Advanced Intelligent Computing Theories and Applications; Huang, D.-S., McGinnity, M., Heutte, L., Zhang, X.-P., Eds.; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 93, pp. 186–191. ISBN 978-3-642-14830-9. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by RandomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, C.; Hutter, F.; Hoos, H.H.; Leyton-Brown, K. Auto-WEKA: Combined Selection and Hyperparameter Optimization of Classification Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–14 August 2013; ACM: Chicago, IL, USA, 2013; pp. 847–855. [Google Scholar]
- Akiba, T.; Sano, S.; Yanase, T.; Ohta, T.; Koyama, M. Optuna: A Next-Generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; ACM: Anchorage, AK, USA, 2019; pp. 2623–2631. [Google Scholar]
- Scornet, E. Tuning Parameters in Random Forests. ESAIM Proc. Surv. 2017, 60, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Victoria, A.H.; Maragatham, G. Automatic Tuning of Hyperparameters Using Bayesian Optimization. Evol. Syst. 2021, 12, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstra, J.; Bengio, Y. Random Search for Hyper-Parameter Optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Montaldo, N.; Oren, R. Changing Seasonal Rainfall Distribution With Climate Directs Contrasting Impacts at Evapotranspiration and Water Yield in the Western Mediterranean Region. Earth’s Future 2018, 6, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Freeman, V.; Cao, S.; Matgen, P.; Chini, M.; Salamon, P.; McCormick, N.; Martinis, S.; Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; Navacchi, C.; et al. Data Processing Architectures for Monitoring Floods Using Sentinel-1. In Proceedings of the 24th ISPRS Congress, Nice, France, 4–10 July 2020; pp. 641–648. [Google Scholar]
- Twele, A.; Martinis, S.; Cao, W.; Plank, S. Automated Flood Mapping and Monitoring Using Sentinel-1 Data. In Proceedings of the ESA Living Planet Symposium 2016, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; Ouwehand, L., Ed.; Volume SP-740, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Martinis, S.; Kuenzer, C.; Twele, A. Flood Studies Using Synthetic Aperture Radar Data. In Remote Sensing Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-429-08943-5. [Google Scholar]
- Giustarini, L.; Hostache, R.; Kavetski, D.; Chini, M.; Corato, G.; Schlaffer, S.; Matgen, P. Probabilistic Flood Mapping Using Synthetic Aperture Radar Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6958–6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D. Flattening Gamma: Radiometric Terrain Correction for SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Lanari, R. Synthetic Aperture Radar Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-8493-7899-7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.L.; Wen, J.; Zhang, Y. A New Algorithm for SAR Image Despeckling Using an Enhanced Lee Filter and Median Filter. In Proceedings of the 2013 6th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing (CISP), Hangzhou, China, 16–18 December 2013; Volume 1, pp. 224–228. [Google Scholar]
- STEP—Science Toolbox Exploitation Platform. Available online: http://step.esa.int/main/ (accessed on 4 June 2022).
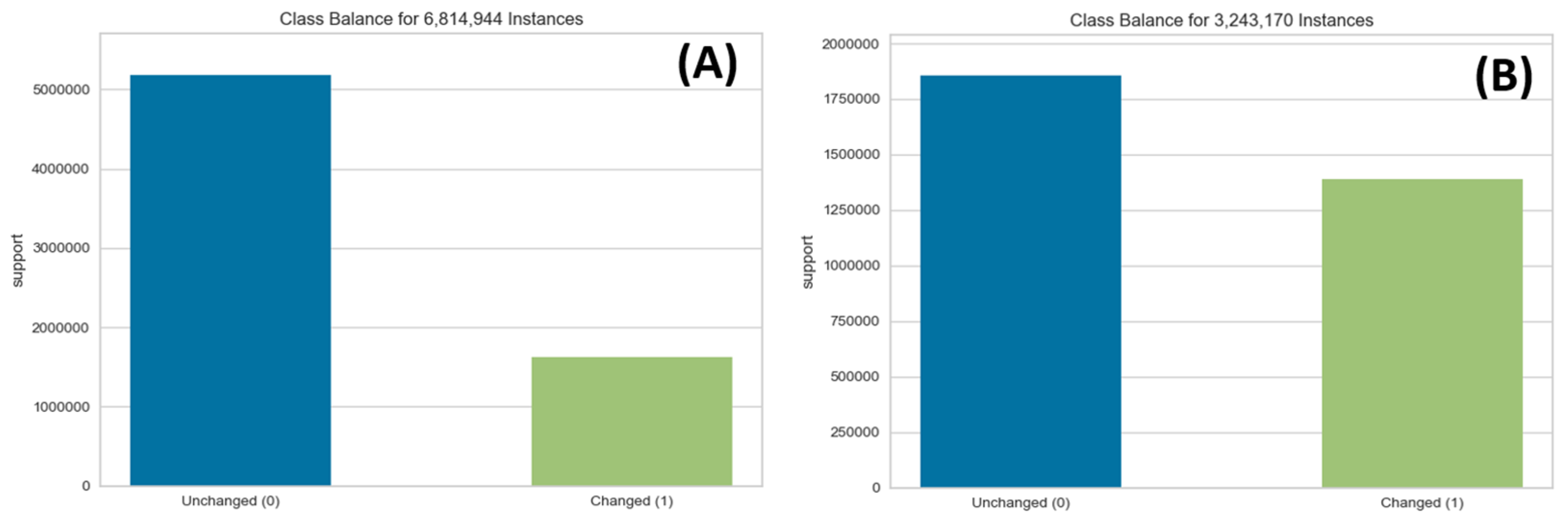
- Japkowicz, N. The Class Imbalance Problem: Significance and Strategies. In Proceedings of the 2000 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ICAI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–15 July 2000; pp. 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Ma, Y. (Eds.) Imbalanced Learning: Foundations, Algorithms, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781-118-07462-6. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, G.E.A.P.A.; Prati, R.C.; Monard, M.C. A Study of the Behavior of Several Methods for Balancing Machine Learning Training Data. SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2004, 6, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V. Data Mining for Imbalanced Datasets: An Overview. In Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook; Maimon, O., Rokach, L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 875–886. ISBN 978-0-387-09823-4. [Google Scholar]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. (Eds.) An Introduction to Statistical Learning: With Applications in R; Springer Texts in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4614-7137-0. [Google Scholar]
- Molinaro, A.M.; Simon, R.; Pfeiffer, R.M. Prediction Error Estimation: A Comparison of Resampling Methods. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3301–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cánovas-García, F.; Alonso-Sarría, F.; Gomariz-Castillo, F.; Oñate-Valdivieso, F. Modification of the Random Forest Algorithm to Avoid Statistical Dependence Problems When Classifying Remote Sensing Imagery. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, H.; Reudenbach, C.; Wöllauer, S.; Nauss, T. Importance of Spatial Predictor Variable Selection in Machine Learning Applications—Moving from Data Reproduction to Spatial Prediction. Ecol. Model. 2019, 411, 108815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Acquisition Dates | ||
|---|---|---|
| SARDINIA | SICILY | TEXAS |
| 2021-06-12 | 2021-06-27 | 2021-07-13 |
| 2021-06-18 | 2021-07-03 | 2021-07-19 |
| 2021-06-24 | 2021-07-06 | 2021-07-25 |
| 2021-07-06 | 2021-07-09 | 2021-07-31 |
| 2021-07-12 | 2021-07-21 | 2021-08-06 |
| 2021-07-18 | 2021-07-27 | 2021-08-12 |
| 2021-07-24 | 2021-08-02 | 2021-08-18 |
| 2021-07-30 | 2021-08-08 | 2021-08-24 |
| 2021-08-05 | 2021-08-14 | 2021-08-30 |
| 2021-08-11 | 2021-08-20 | 2021-09-05 |
| 2021-08-17 | 2021-08-26 | 2021-09-11 |
| 2021-08-23 | 2021-09-07 | 2021-09-17 |
| 2021-08-29 | 2021-09-13 | 2021-09-23 |
| 2021-09-04 | 2021-09-19 | 2021-09-29 |
| Sardinia | Sicily | Texas | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Precision | Recall | F1 | # | Precision | Recall | F1 | # | Precision | Recall | F1 | |
| Unchanged (0) | 3,164,393 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 2,108,222 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 2,726,416 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.93 |
| Changed (1) | 955,933 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 672,808 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 439,280 | 0.58 | 0.76 | 0.65 |
| Weighted avg. | 4,120,326 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 2,781,030 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 3,165,696 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mastro, P.; Masiello, G.; Serio, C.; Pepe, A. Change Detection Techniques with Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: Experiments with Random Forests and Sentinel-1 Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3323. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143323
Mastro P, Masiello G, Serio C, Pepe A. Change Detection Techniques with Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: Experiments with Random Forests and Sentinel-1 Observations. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(14):3323. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143323
Chicago/Turabian StyleMastro, Pietro, Guido Masiello, Carmine Serio, and Antonio Pepe. 2022. "Change Detection Techniques with Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: Experiments with Random Forests and Sentinel-1 Observations" Remote Sensing 14, no. 14: 3323. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143323
APA StyleMastro, P., Masiello, G., Serio, C., & Pepe, A. (2022). Change Detection Techniques with Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: Experiments with Random Forests and Sentinel-1 Observations. Remote Sensing, 14(14), 3323. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143323








