A Sensor Bias Correction Method for Reducing the Uncertainty in the Spatiotemporal Fusion of Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
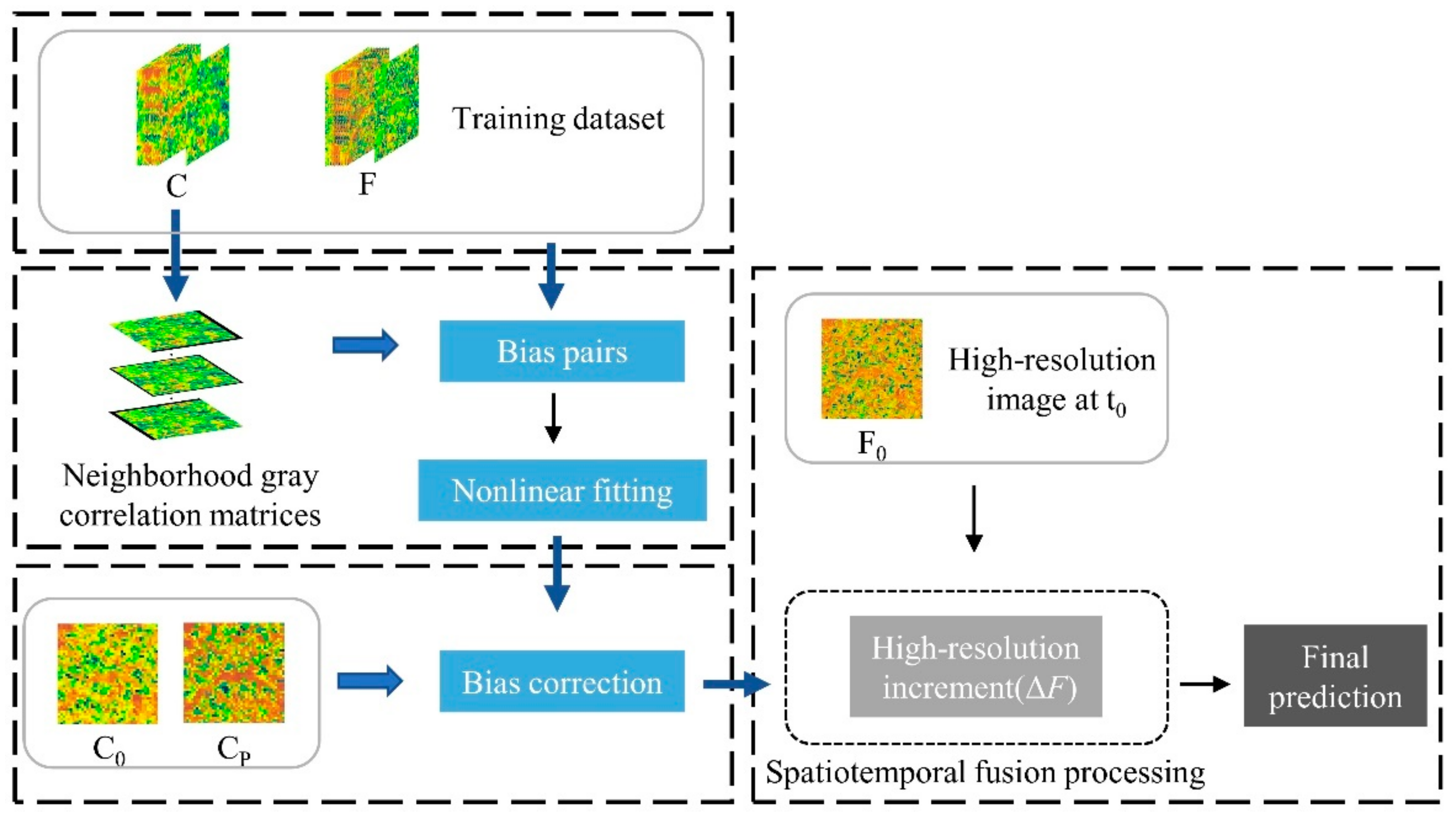
2. Methodology
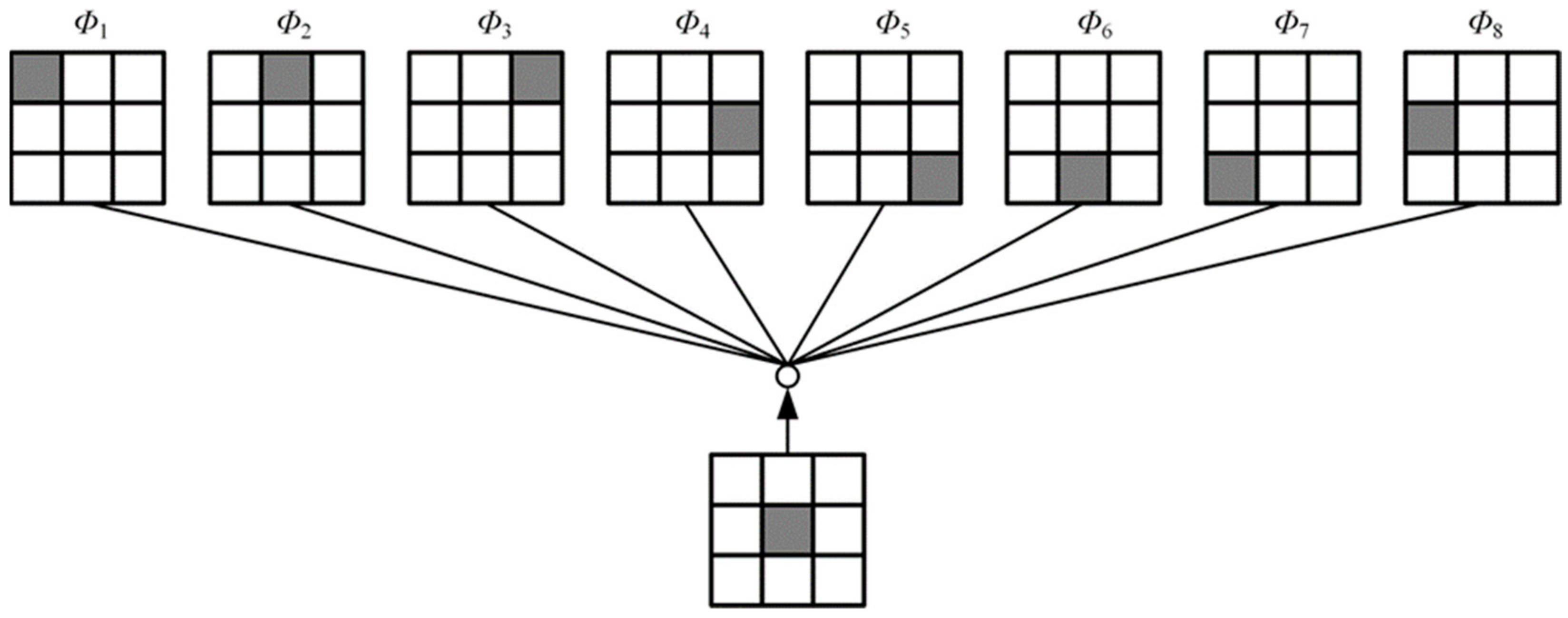
2.1. Generating Neighborhood Gray Correlation Matrices
2.2. Establishing Bias Pairs of Different Sensors
2.3. Nonlinear Fitting of Image Bias Pairs
2.4. Correcting the Low-Spatial-Resolution Images
2.5. Predicting High-Resolution Image with Spatiotemporal Fusion Models
3. Experiment
3.1. Experimental Area and Data
3.2. Experimental Design and Evaluation
4. Results
4.1. Fusion of the NDVI after Sensor Bias Correction in Heterogeneous Landscape Areas
4.2. Fusion of NDVI Images after Sensor Bias Correction in Areas of Dramatic Land Cover Change
4.3. NDVI Fusion after Sensor Bias Correction in Homogeneous Regions
5. Discussion
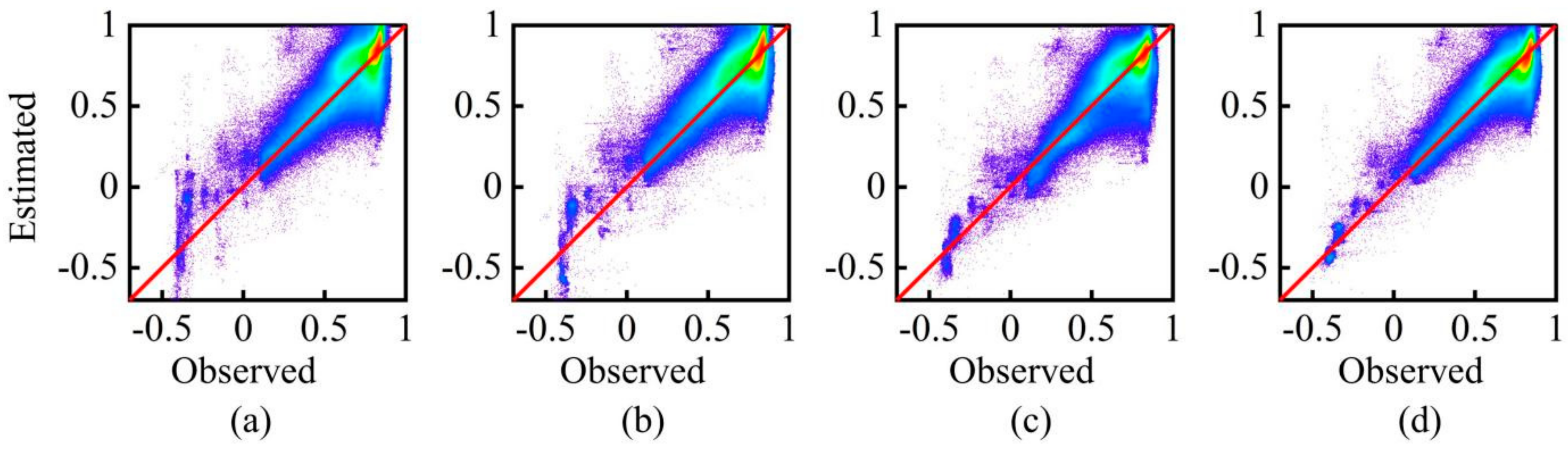
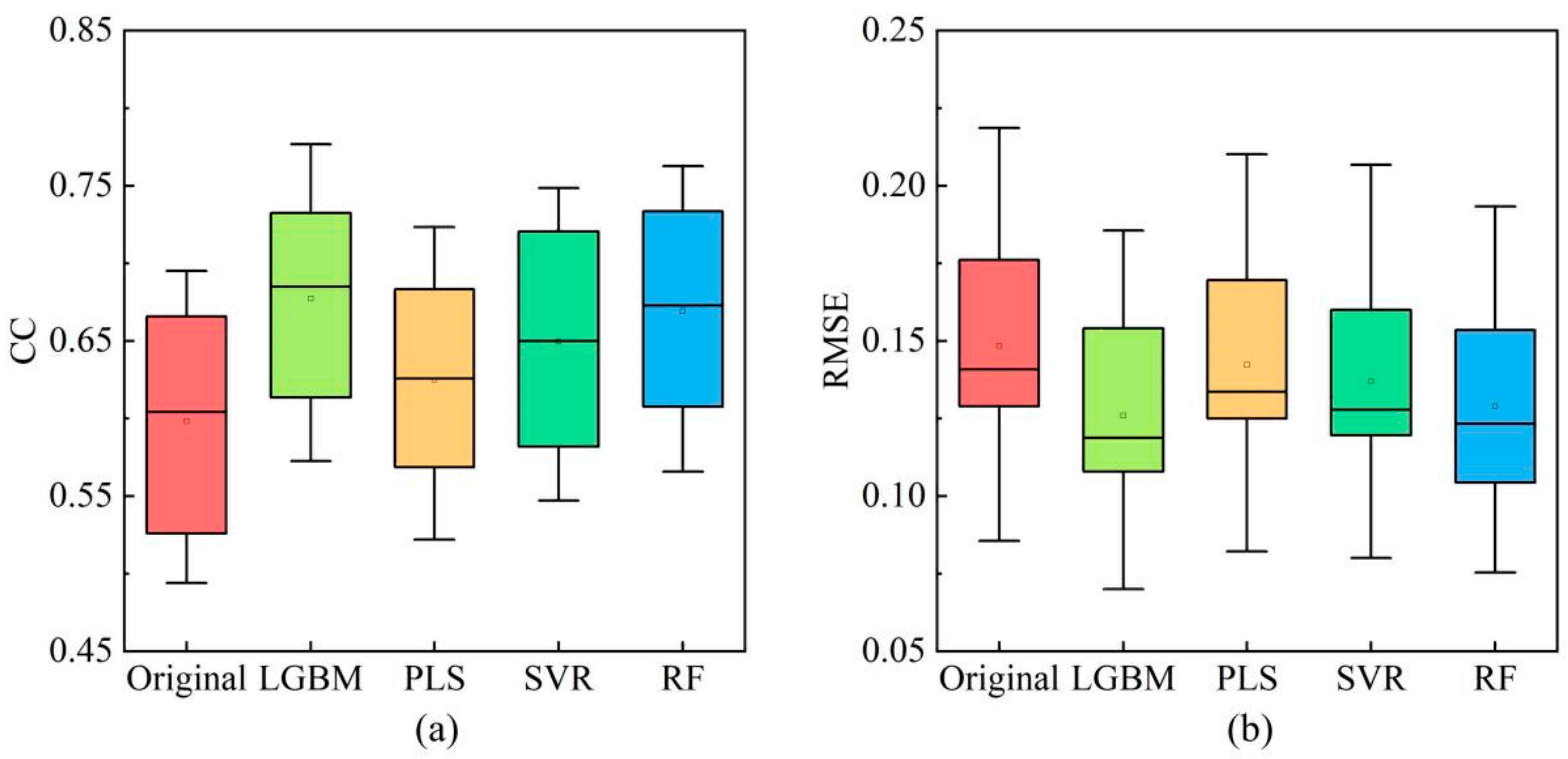
5.1. Effect of Different Regression Algorithms on Correction Models
5.2. Effect of Bias Correction on the Input Image for Spatiotemporal Fusion
5.3. Effect of Bias Correction on the Spatiotemporal Fusion Results
5.4. Applicability of the Bias Correction Method
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The machine learning algorithm is introduced to quantify sensor bias, which mitigates the uncertain effects of sensor differences and preprocessing on fusion results and provides optimized input data for spatiotemporal fusion.
- (2)
- Sensor bias correction helps to improve the robustness and usability of spatiotemporal fusion algorithms in different types of landscapes.
- (3)
- The bias correction method reduces the misjudgment of pixels and occurrence of blocky or blurring effects induced by the spatiotemporal fusion model in areas with high heterogeneity or drastic land cover changes, thus, effectively recovering the changed features and retaining more spatial details.
- (4)
- By bias correction, the availability of high- and low-spatial-resolution image pairs for adjacent dates without large-scale land cover changes will be improved, providing convenience for generating large-scale high-spatiotemporal-resolution datasets through spatiotemporal fusion models.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Song, H.; Fu, D.; Wong, K. Generating high spatiotemporal resolution land surface temperature for urban heat island monitoring. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Schmitz, O.; Lu, M.; Karssenberg, D. Thermal unmixing based downscaling for fine resolution diurnal land surface temperature analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 161, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Fu, P.; Gao, F. Generating daily land surface temperature at Landsat resolution by fusing Landsat and MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Du, X.; Wu, B. Generation of high spatial and temporal resolution NDVI and its application in crop biomass estimation. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewes, A.; Thonfeld, F.; Schmidt, M.; Oomen, R.J.; Zhu, X.; Dubovyk, O.; Menz, G.; Schellberg, J. Using RapidEye and MODIS data fusion to monitor vegetation dynamics in semi-arid rangelands in South Africa. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6510–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Chen, L.; Huang, B.; Michishita, R.; Xu, B. Dynamic monitoring of the Poyang Lake wetland by integrating Landsat and MODIS observations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Gong, H. Spatiotemporal downscaling approaches for monitoring 8-day 30 m actual evapotranspiration. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 126, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Gong, H. Downscaling of MODIS One kilometer evapotranspiration using Landsat-8 data and machine learning approaches. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houborg, R.; McCabe, M.F.; Gao, F. A spatio-temporal enhancement method for medium resolution LAI (STEM-LAI). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 47, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, H.; Huang, F.; Qi, H. Generating high resolution LAI based on a modified FSDAF model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.M.; Huang, B.; Song, H.; Li, Y. Reconstructing seasonal variation of Landsat vegetation index related to leaf area index by fusing with MODIS data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busetto, L.; Meroni, M.; Colombo, R. Combining medium and coarse spatial resolution satellite data to improve the estimation of sub-pixel NDVI time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, B.; Xu, Y.; Cao, K.; Guo, C.; Meng, D. Spatial and temporal image fusion via regularized spatial unmixing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1362–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, B.; Oertel, D.; Lanzl, F.; Reinhäckel, G. Unmixing-based multisensor multiresolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, S.; Zand-Parsa, S.; Jahromi, M.N.; Niyogi, D. Application of a simple Landsat-MODIS fusion model to estimate evapotranspiration over a heterogeneous sparse vegetation region. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Helmer, E.H.; Gao, F.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Lefsky, M.A. A flexible spatiotemporal method for fusing satellite images with different resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 172, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Song, H. Spatiotemporal reflectance fusion via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3707–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, G.; Hang, R.; Huang, B. Spatiotemporal satellite image fusion using deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cai, F.; Tian, J.; Williams, T.K.A. Spatiotemporal fusion of multisource remote sensing data: Literature survey, taxonomy, principles, applications, and future directions. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Guan, K.; Peng, J. STAIR: A generic and fully-automated method to fuse multiple sources of optical satellite data to generate a high-resolution, daily and cloud-/gap-free surface reflectance product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileva, N.; Mecklenburg, S.; Gascon, F. New tool for spatio-temporal image fusion in remote sensing: A case study approach using Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3 data. In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXIV; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2018; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, W.; Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Helmer, E.H. An Improved Flexible Spatiotemporal DAta Fusion (IFSDAF) method for producing high spatiotemporal resolution normalized difference vegetation index time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 227, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Foody, G.M.; Boyd, D.S.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Ling, F. SFSDAF: An enhanced FSDAF that incorporates sub-pixel class fraction change information for spatio-temporal image fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Shi, W.; Hao, M.; Zhu, X. FSDAF 2.0: Improving the performance of retrieving land cover changes and preserving spatial details. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Song, H.; Sun, L.; Wu, Z.; Jeon, B. Spatiotemporal fusion of satellite images via very deep convolutional networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Han, C.; Zhang, L. Remote Sensing Image Spatiotemporal Fusion Using a Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 4273–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Yue, P.; Di, L.; Tang, J. Deriving high spatiotemporal remote sensing images using deep convolutional network. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, D.; Cheng, C.; Shen, S.; Ning, L. Multitask Deep Learning Framework for Spatiotemporal Fusion of NDVI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5616313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanova, I.V.; McVicar, T.R.; Van Niel, T.G.; Li, L.T.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M. Assessing the accuracy of blending Landsat-MODIS surface reflectances in two landscapes with contrasting spatial and temporal dynamics: A framework for algorithm selection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Atkinson, P.M. Spatio-temporal fusion for daily Sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Ke, Y.; Yin, Q.; Chen, X.; Im, J. Comparison of five spatio-temporal satellite image fusion models over landscapes with various spatial heterogeneity and temporal variation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Song, H.; Rao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cao, X.; Cui, X. Sensitivity of six typical spatiotemporal fusion methods to different influential factors: A comparative study for a normalized difference vegetation index time series reconstruction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privette, J.L.; Fowler, C.; Wick, G.A.; Baldwin, D.; Emery, W.J. Effects of orbital drift on advanced very high resolution radiometer products: Normalized difference vegetation index and sea surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 53, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teillet, P.M.; Staenz, K.; Williams, D.J. Effects of spectral, spatial, and radiometric characteristics on remote sensing vegetation indices of forested regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teillet, P.M.; Fedosejevs, G.; Thome, K.J.; Barker, J.L. Impacts of spectral band difference effects on radiometric cross-calibration between satellite sensors in the solar-reflective spectral domain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, Y. Multisensor Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Intercalibration: A Comprehensive Overview of the Causes of and Solutions for Multisensor Differences. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2018, 6, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.E.; Pinzón, J.E.; Didan, K.; Morisette, J.T.; Tucker, C.J. Evaluation of the consistency of Long-term NDVI time series derived from AVHRR, SPOT-vegetation, SeaWiFS, MODIS, and Landsat ETM+ sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Strahler, A.H.; Barnsley, M.J.; Borel, C.C.; Gerstl, S.A.W.; Diner, D.J.; Prata, A.J.; Walthall, C.L. Multiangle remote sensing: Past, present and future. Remote Sens. Rev. 2000, 18, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Yoshioka, H. Development and Demonstration of a Method for Geo-to-Leo NDVI Transformation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifovic, R.; Cihlar, J.; Chen, J. A comparison of BRDF models for the normalization of sallite optical data to a standard sun-target-sensor geometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, J.; Heinzel, V.; Menz, G. Assessment of NDVI- Differences caused by sensor-specific relative spectral response functions. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Denver, CO, USA, 31 July 2006–4 August 2006; pp. 1130–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Trishchenko, A.P.; Cihlar, J.; Li, Z. Effects of spectral response function on surface reflectance and NDVI measured with moderate resolution satellite sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, B. A rigorously-weighted spatiotemporal fusion model with uncertainty analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, W.; Guo, D.; Zhang, H. A reliable and adaptive spatiotemporal data fusion method for blending multi-spatiotemporal-resolution satellite images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 268, 112770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, C.M.; García-Haro, F.J. A comparison of STARFM and an unmixing-based algorithm for Landsat and MODIS data fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.Y. LightGBM: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. Adv. Neural Inf. Processing Syst. 2017, 30, 3147–3155. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Q. Small Aerial Target Detection for Airborne Infrared Detection Systems Using LightGBM and Trajectory Constraints. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9959–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, F.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Y.; Han, J.; Li, Z. Identifying the contributions of multi-source data for winter wheat yield prediction in China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuia, D.; Verrelst, J.; Alonso, L.; Perez-Cruz, F.; Camps-Valls, G. Multioutput support vector regression for remote sensing biophysical parameter estimation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P.; Kowalski, B.R. Partial least-squares regression: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 1986, 185, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Liang, X.; Niu, L.; Han, H.; Zhu, X. A comprehensive and automated fusion method: The enhanced flexible spatiotemporal data fusion model for monitoring dynamic changes of land surface. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Methods | Image | CC | RMSE | AD | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSDAF | uncorrected | 0.7974 | 0.1563 | −0.0072 | 0.6837 |
| corrected | 0.8269 | 0.1449 | 0.0002 | 0.6901 | |
| STARFM | uncorrected | 0.7990 | 0.1577 | −0.0133 | 0.6976 |
| corrected | 0.8406 | 0.1416 | −0.0056 | 0.7186 |
| Methods | Image | CC | RMSE | AD | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSDAF | uncorrected | 0.7586 | 0.1507 | −0.0448 | 0.4561 |
| corrected | 0.7960 | 0.1315 | −0.0013 | 0.5027 | |
| STARFM | uncorrected | 0.7817 | 0.1432 | -0.0458 | 0.5006 |
| corrected | 0.8316 | 0.1204 | −0.0013 | 0.5556 |
| Methods | Image | CC | RMSE | AD | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSDAF | uncorrected | 0.8525 | 0.1149 | 0.0220 | 0.6257 |
| corrected | 0.8742 | 0.1055 | 0.0003 | 0.6538 | |
| STARFM | uncorrected | 0.8693 | 0.1066 | 0.0207 | 0.6582 |
| corrected | 0.8869 | 0.0967 | −0.0016 | 0.6684 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Huang, F.; Hong, X.; Wang, P. A Sensor Bias Correction Method for Reducing the Uncertainty in the Spatiotemporal Fusion of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143274
Zhang H, Huang F, Hong X, Wang P. A Sensor Bias Correction Method for Reducing the Uncertainty in the Spatiotemporal Fusion of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(14):3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143274
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hongwei, Fang Huang, Xiuchao Hong, and Ping Wang. 2022. "A Sensor Bias Correction Method for Reducing the Uncertainty in the Spatiotemporal Fusion of Remote Sensing Images" Remote Sensing 14, no. 14: 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143274
APA StyleZhang, H., Huang, F., Hong, X., & Wang, P. (2022). A Sensor Bias Correction Method for Reducing the Uncertainty in the Spatiotemporal Fusion of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 14(14), 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143274







