Multisource Data Fusion and Adversarial Nets for Landslide Extraction from UAV-Photogrammetry-Derived Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Overview of the Proposed Method
2.2. Proposed Adversarial Nets
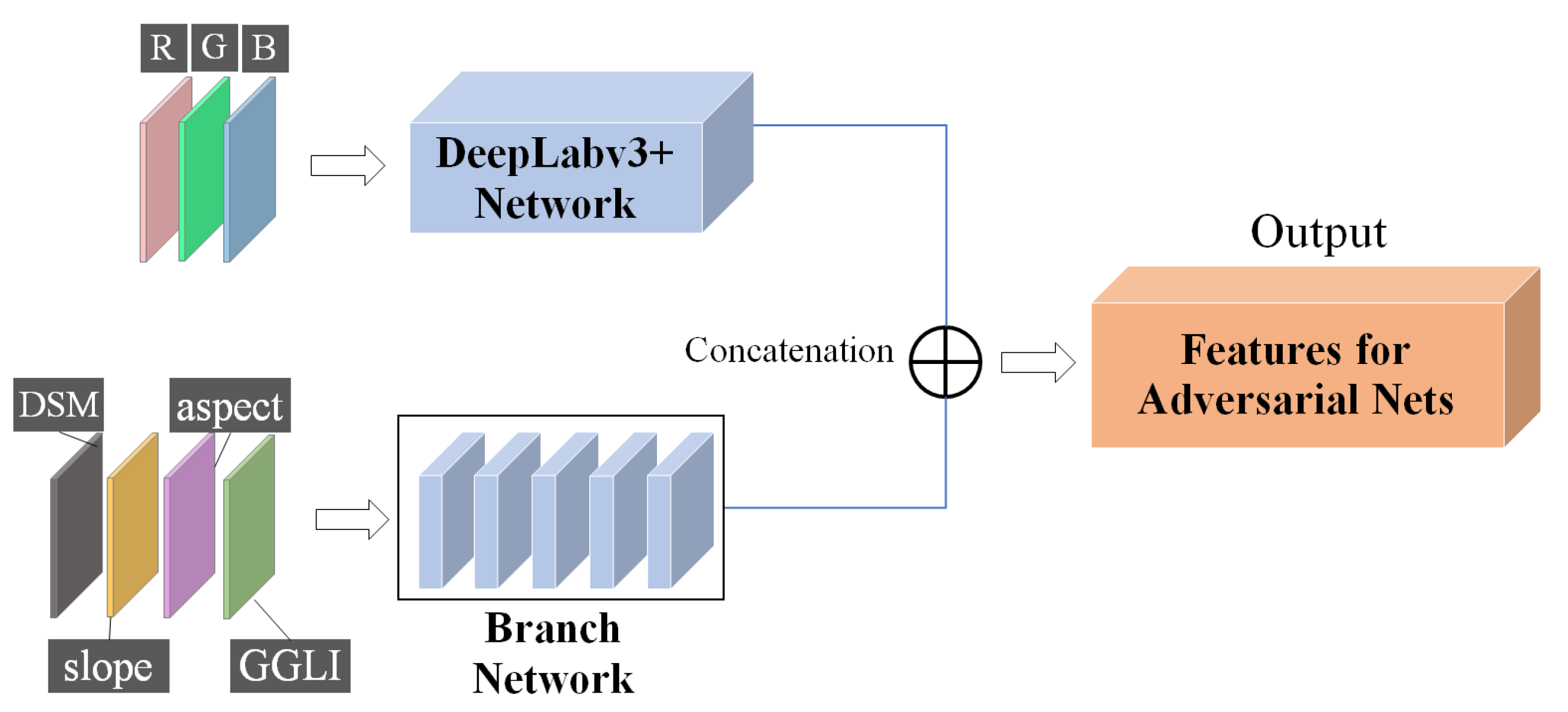
2.2.1. Multisource Data Fusion
2.2.2. Generative Network
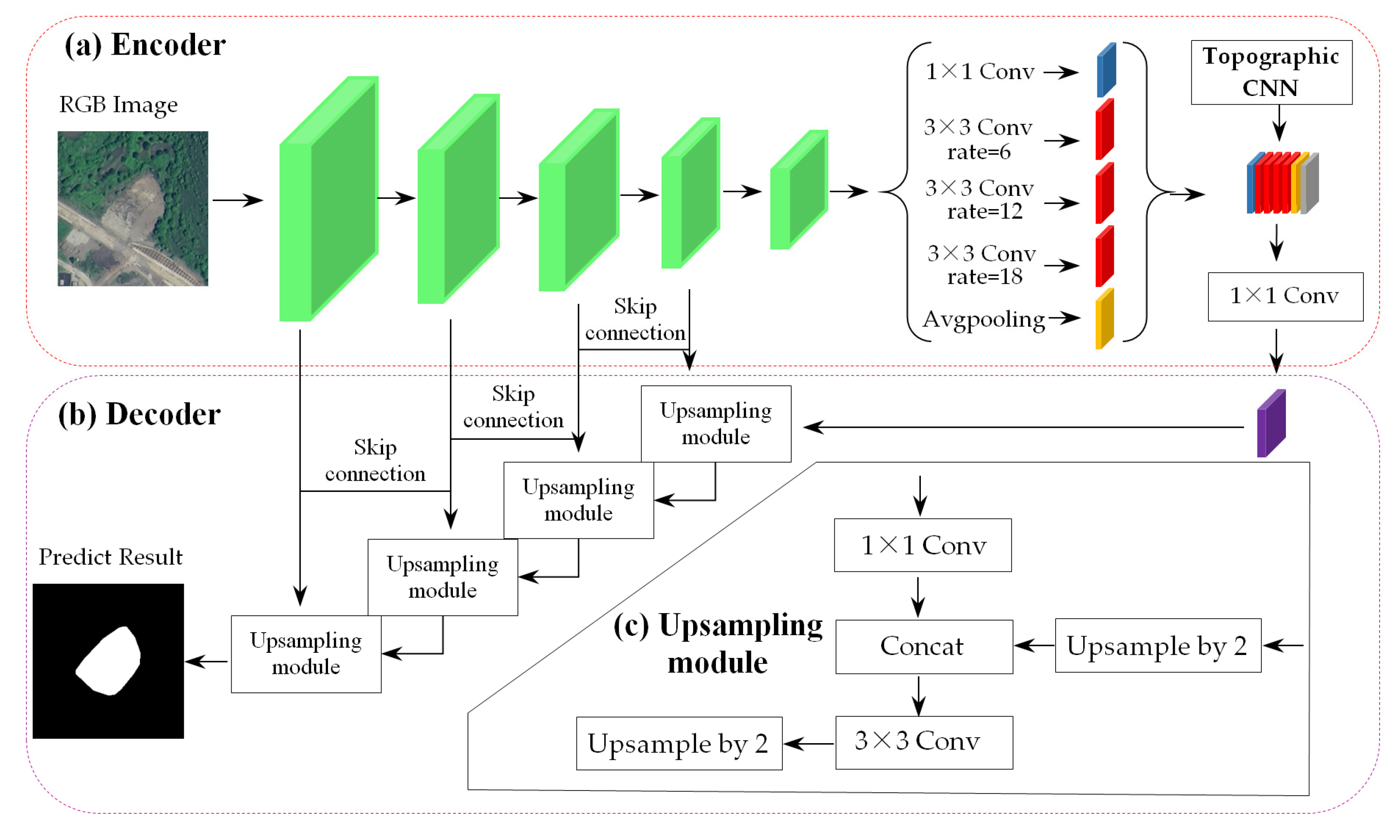
2.2.3. Improved DeepLabv3+ for Discriminator
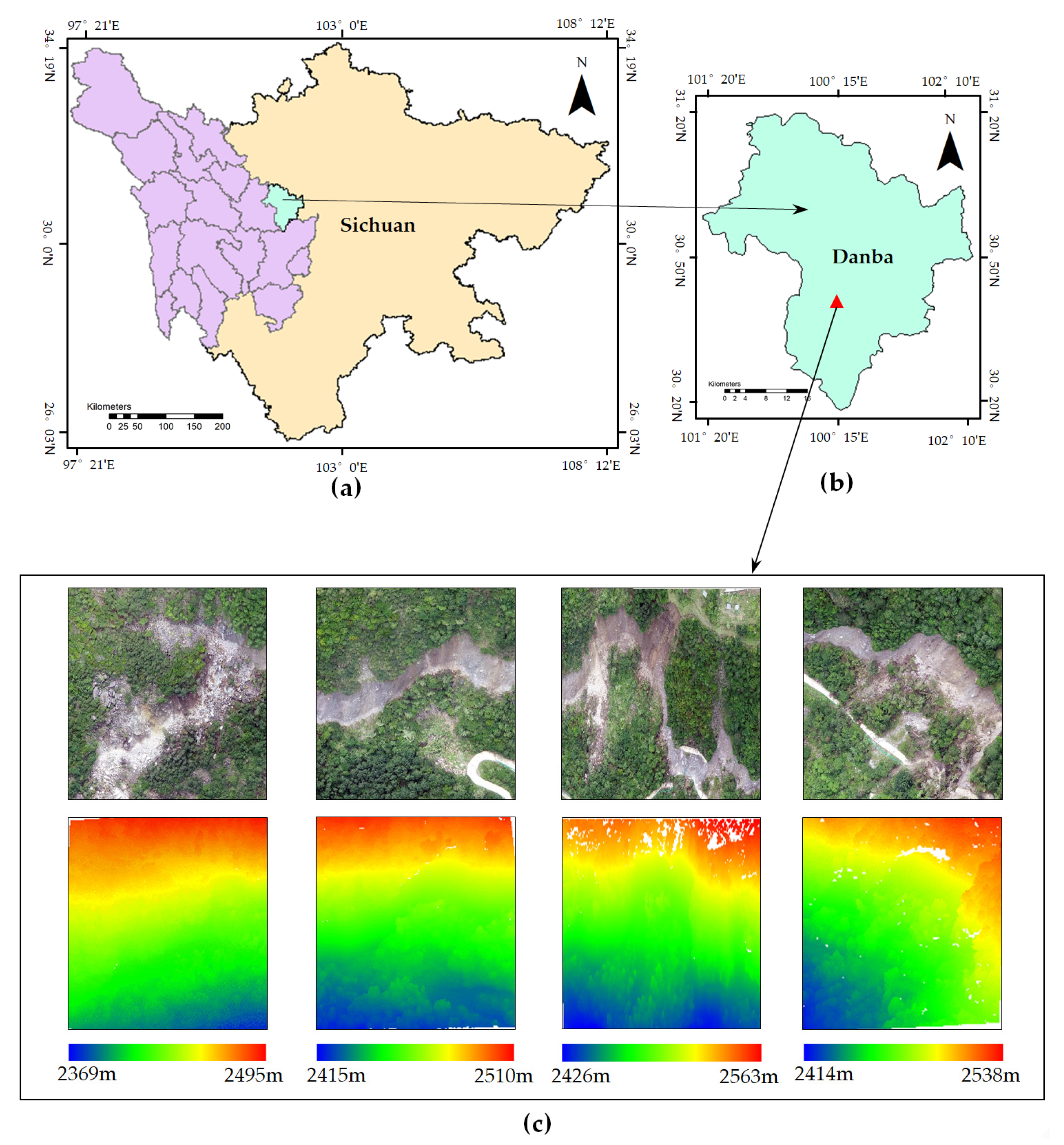
2.2.4. UAV Photogrammetry
3. Experiment Results and Analysis
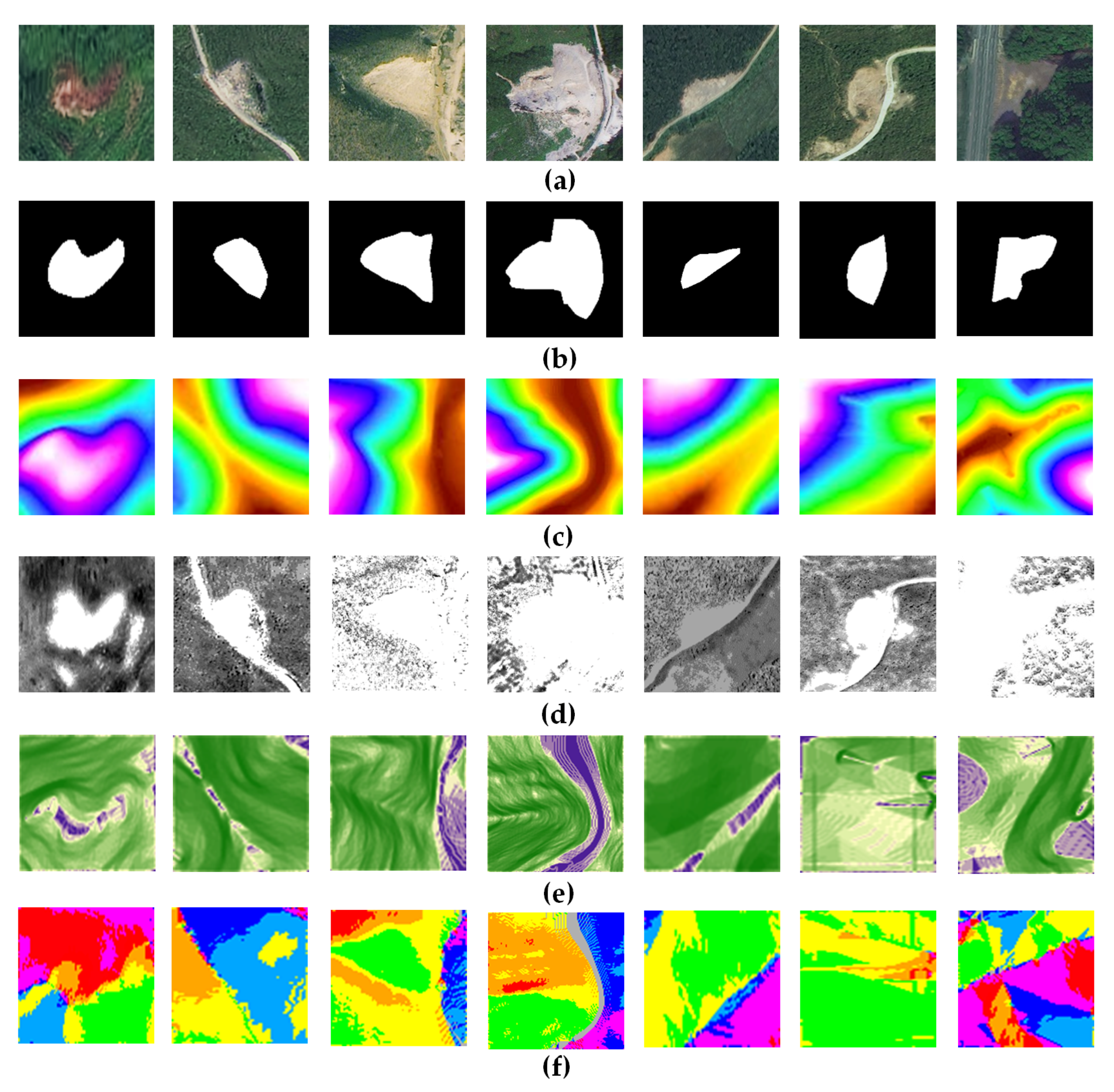
3.1. Dataset
3.1.1. Training Dataset
3.1.2. Test Dataset
3.2. Evaluation Criteria of Landslide Extraction Performance
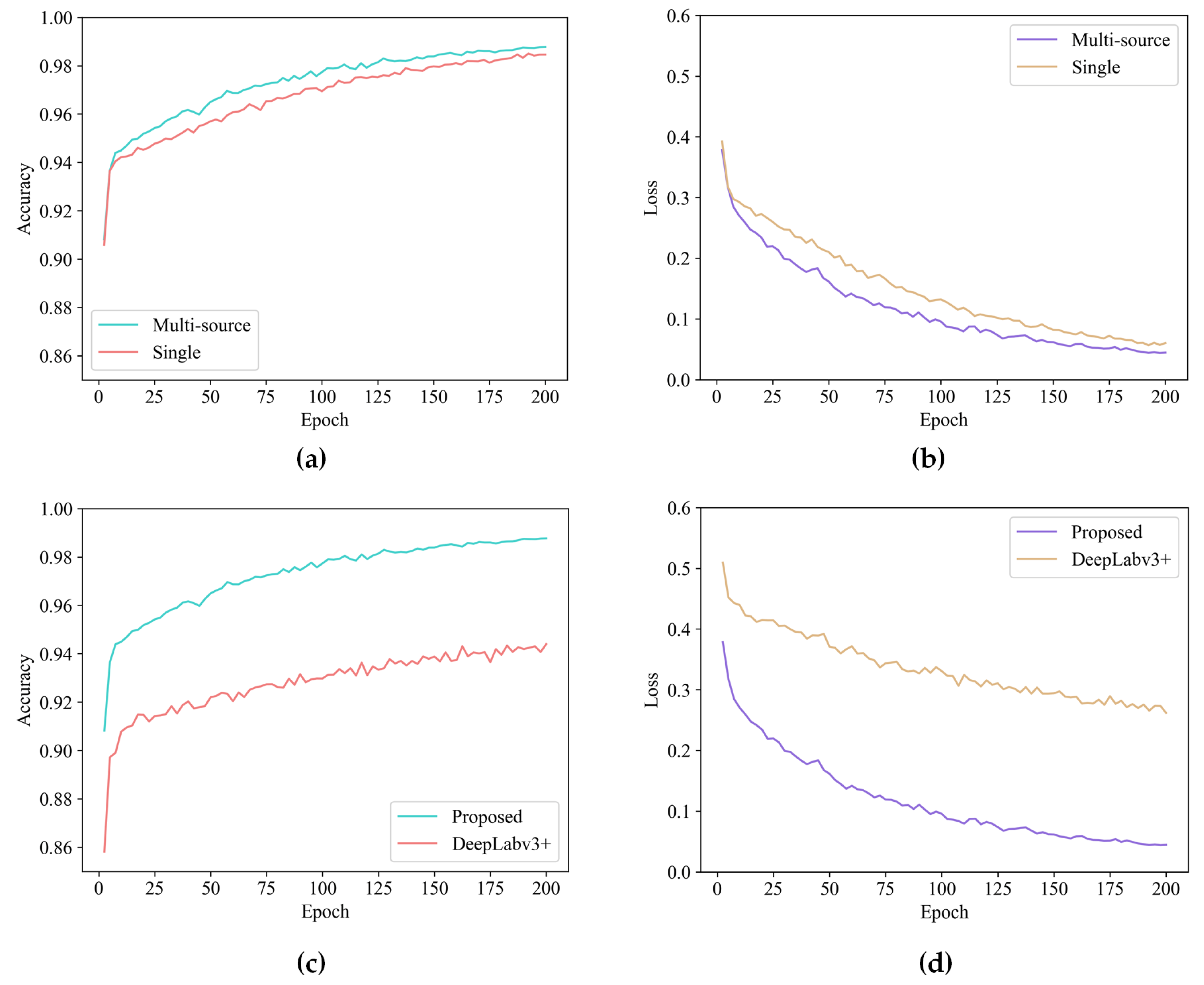
3.3. Training and Validation
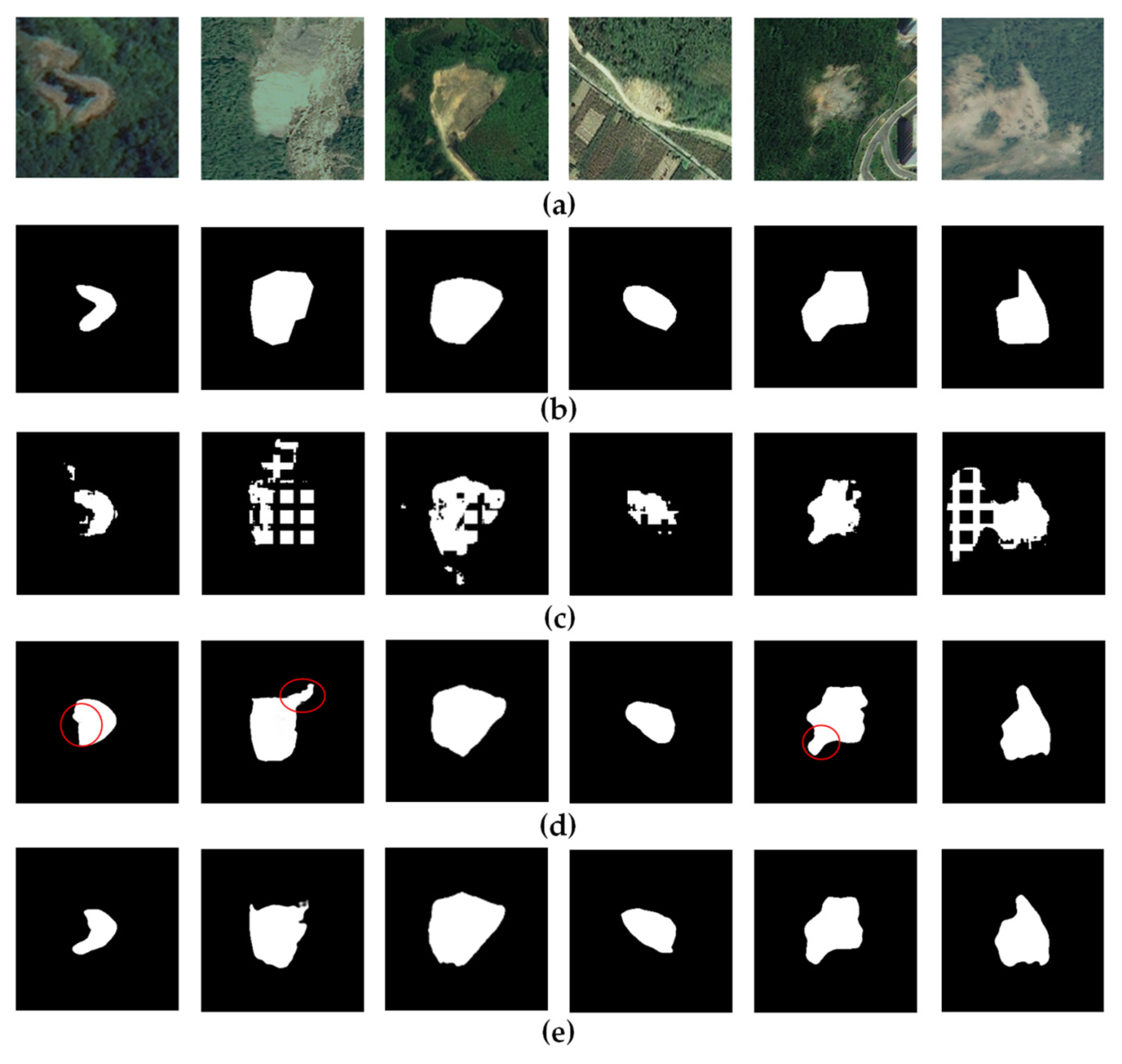
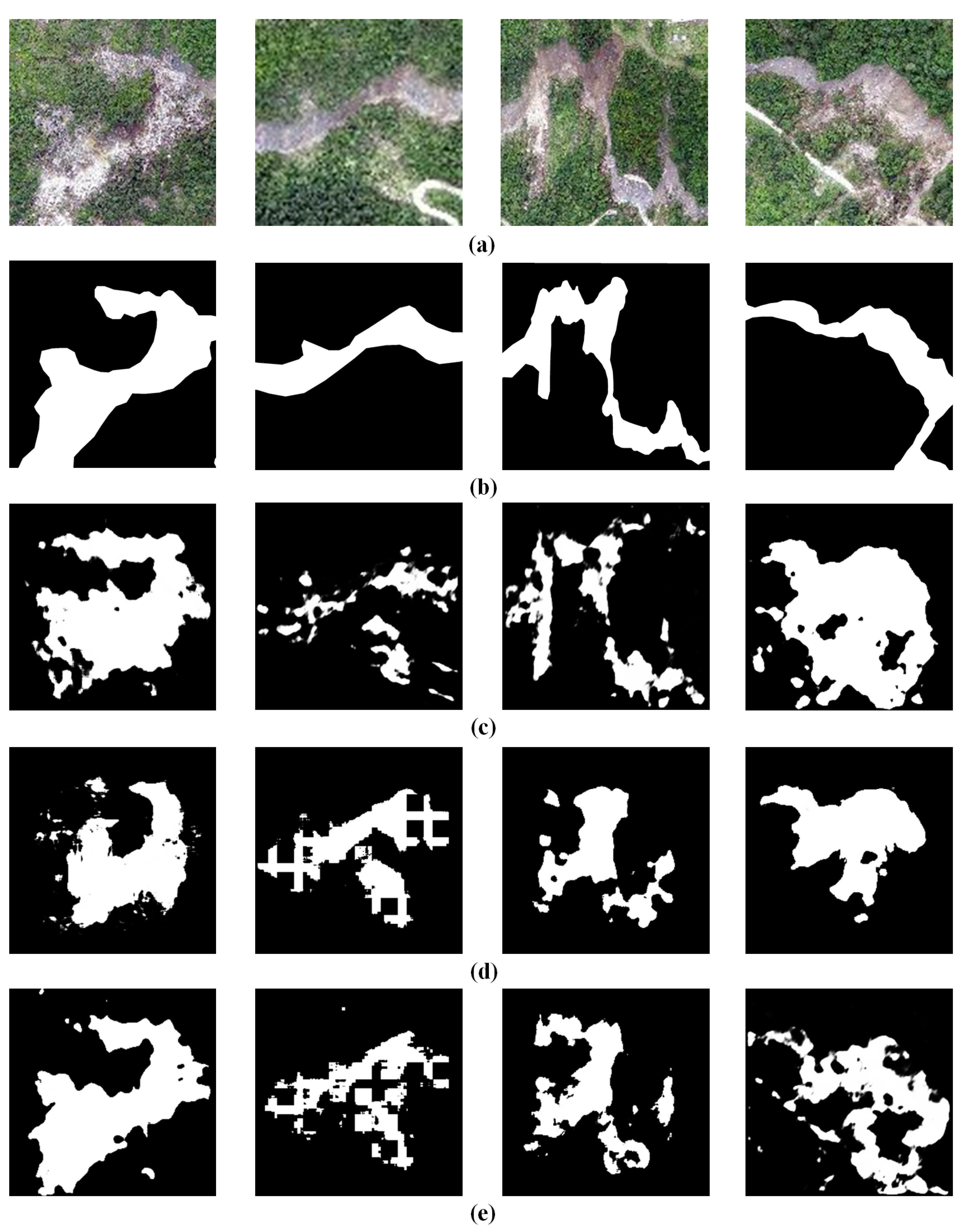
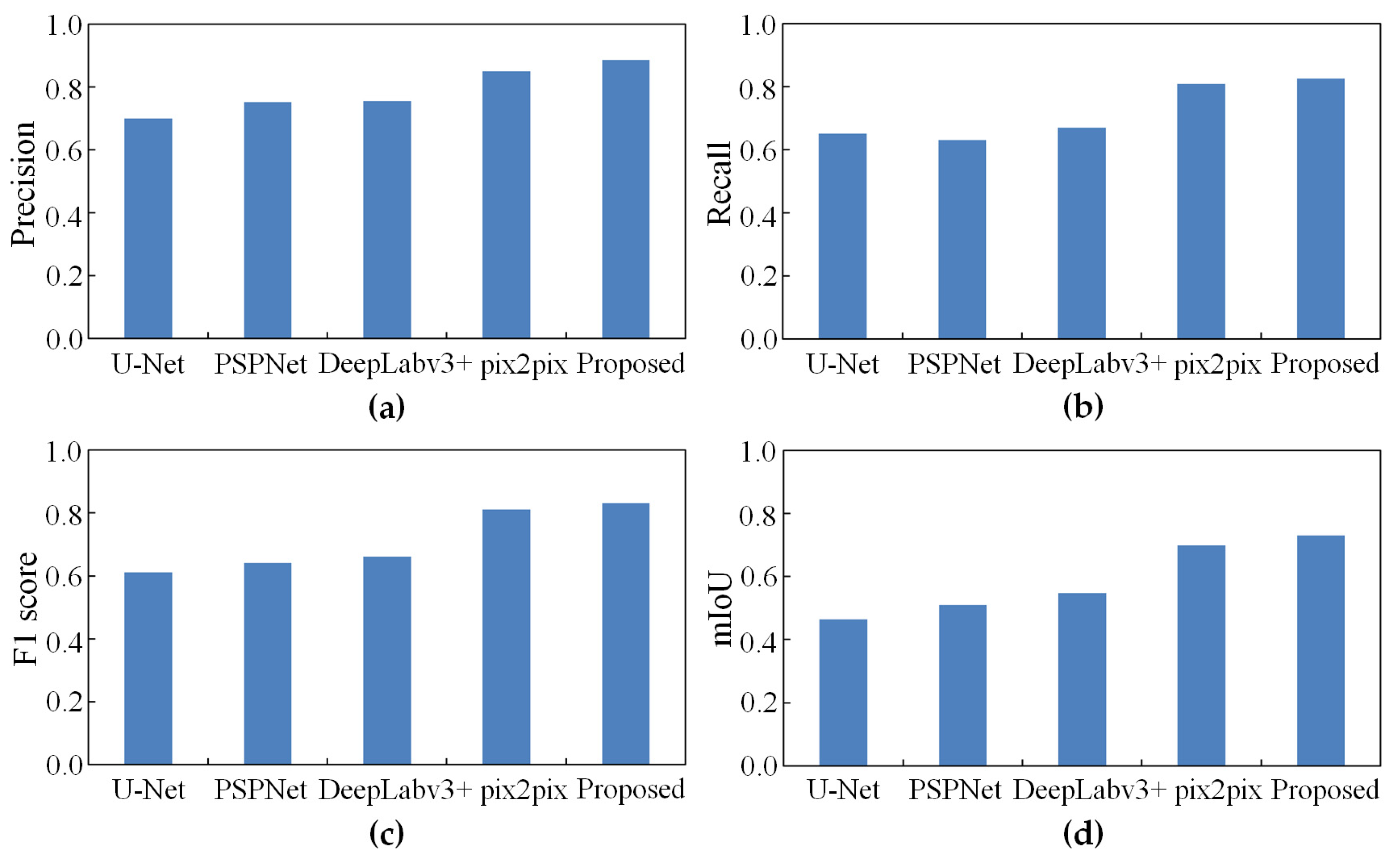
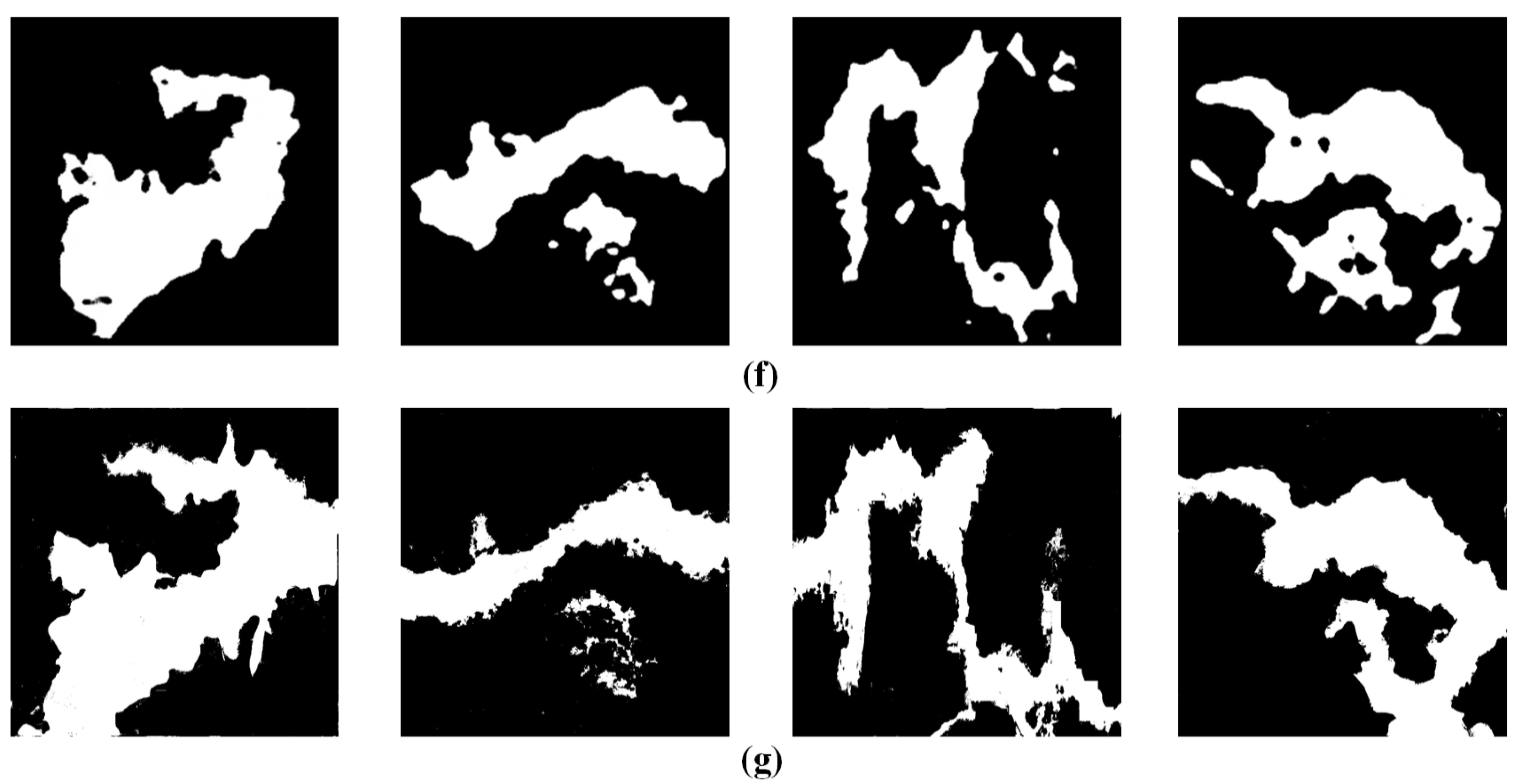
3.4. Comparisons with State-of-the-Art Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, D.; Peng, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, X. Influences of risk perception and sense of place on landslide disaster preparedness in southwestern China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2018, 9, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garnica-Peña, R.J.; Alcántara-Ayala, I. The use of UAVs for landslide disaster risk research and disaster risk management: A literature review. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froude, M.J.; Petley, D.N. Global fatal landslide occurrence from 2004 to 2016. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 2161–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bui, T.A.; Lee, P.J.; Lum, K.Y.; Loh, C.; Tan, K. Deep Learning for Landslide Recognition in Satellite Architecture. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 143665–143678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Gong, W.; Gao, L.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Z. An Interpretation Approach of Ascending–Descending SAR Data for Landslide Identification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Omidalizarandi, M.; Xu, X.; Neumann, I. Terrestrial laser scanning technology for deformation monitoring and surface modeling of arch structures. Compos. Struct. 2017, 169, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, Z.; Shu, C.; Yang, Y.; Wu, C.; Dong, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y. Time Series Surface Deformation of Changbaishan Volcano Based on Sentinel-1B SAR Data and Its Geological Significance. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ashraf, M.A. The application of the intelligent algorithm in the prevention and early warning of mountain mass landslide disaster. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Frodella, W.; Morelli, S.; Tofani, V.; Ciampalini, A.; Intrieri, E.; Raspini, F.; Rossi, G.; Tanteri, L.; Lu, P. Spaceborne, UAV and ground-based remote sensing techniques for landslide mapping, monitoring and early warning. Geoenviron. Disasters 2017, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, A.; Kerle, N. Object-oriented mapping of landslides using Random Forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2564–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Qiu, H.; Hu, S.; Yang, D.; Liu, Z. Characteristics and geomorphology change detection analysis of the Jiangdingya landslide on July 12, 2018, China. Landslides 2021, 18, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Xu, Q.; Jin, S.; Li, W.; Su, Y.; Dong, X.; Guo, Q. Loess Landslide Detection Using Object Detection Algorithms in Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghuis, A.M.; Chang, K.; Lee, H.Y. Comparison between automated and manual mapping of typhoon-triggered landslides from SPOT-5 imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Yasir, M.; Xu, C.; Nazir, S.; Hossain, M.S.; Ullah, S.; Khan, S. Extraction of Landslide Information Based on Object-Oriented Approach and Cause Analysis in Shuicheng, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Stumpf, A.; Kerle, N.; Casagli, N. Object-oriented change detection for landslide rapid mapping. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martha, T.R.; Kamala, P.; Jose, J.; Kumar, K.V.; Sankar, G.J. Identification of new landslides from high resolution satellite data covering a large area using object-based change detection methods. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, W.; Lu, P.; Yan, L.; Wang, Q.; Miao, Z. Landslide mapping from aerial photographs using change detection-based Markov random field. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, P.; Qin, Y.; Li, Z.; Mondini, A.; Casagli, N. Landslide mapping from multi-sensor data through improved change detection-based Markov random field. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondini, A.C.; Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P.; Rossi, M.; Cardinali, M.; Ardizzone, F. Semi-automatic recognition and mapping of rainfall induced shallow landslides using optical satellite images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1743–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanos, A.M.; Pradhan, B.; Mansor, S.; Yusoff, Z.M.; Abdullah, A.F. A hybrid model using machine learning methods and GIS for potential rockfall source identification from airborne laser scanning data. Landslides 2018, 15, 1833–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Yu, D.; Shen, C.; Li, W.; Xu, Q. Landslide detection from an open satellite imagery and digital elevation model dataset using attention boosted convolutional neural networks. Landslides 2020, 17, 1337–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, M.; Ke, H.; Fang, X.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, S. Landslide recognition by deep convolutional neural network and change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 4654–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Blaschke, T.; Gholamnia, K.; Meena, S.R.; Tiede, D.; Aryal, J. Evaluation of Different Machine Learning Methods and Deep-Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Landslide Detection. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, W.; Wei, M.; Yang, W.; Xu, C.; Ma, C. Automatic Mapping of Landslides by the ResU-Net. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Tanatipuknon, A.; Aimmanee, P.; Watanabe, Y.; Murata, K.T.; Wakai, A.; Sato, G.; Hung, H.V.; Tungpimolrut, K.; Keerativittayanun, S.; Karnjana, J. Study on Combining Two Faster R-CNN Models for Landslide Detection with a Classification Decision Tree to Improve the Detection Performance. J. Disaster Res. 2021, 16, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Chen, F.; Xu, C. Landslide detection based on contour-based deep learning framework in case of national scale of Nepal in 2015. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 135, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J. Research on Post-Earthquake Landslide Extraction Algorithm Based on Improved U-Net Model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Liu, W. Landslide Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery Using Fully Convolutional Spectral–Topographic Fusion Network. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, M.A.; Vizilter, Y.V.; Vygolov, O.V.; Knyaz, V.A.; Rubis, A.Y. Change Detection in Remote Sensing Images Using Conditional Adversarial Networks. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Mou, L.; Chen, J.; Bo, Y.; Emery, W. Incorporating metric learning and adversarial network for seasonal invariant change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 2720–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Snavely, N.; Seitz, S.M.; Szeliski, R. Bundle adjustment in the large. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, T.; Li, D.; Cheng, P. Building Extraction from UAV Images Jointly Using 6D-SLIC and Multiscale Siamese Convolutional Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, N.; Fang, L.; Li, S.; Plaza, A.; Plaza, J. Remote sensing scene classification using multilayer stacked covariance pooling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6899–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Han, G.; Liu, P.; Yang, H.; Sun, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, J. A Novel 2D-3D CNN with Spectral-Spatial Multi-Scale Feature Fusion for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameen, M.I.; Pradhan, B. Landslide detection using residual networks and the fusion of spectral and topographic information. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 114363–114373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yang, L.; Chen, F. Semantic segmentation for high spatial resolution remote sensing images based on convolution neural network and pyramid pooling module. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3252–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergado, J.R.; Persello, C.; Stein, A. Recurrent multiresolution convolutional networks for VHR image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6361–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Dai, F.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, K. Symmetrical dense-shortcut deep fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation of very-high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Gao, L.; Marinoni, A.; Zhang, B.; Yang, F.; Gamba, P. Semantic Labeling of High Resolution Aerial Imagery and LiDAR Data with Fine Segmentation Network. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marmanis, D.; Datcu, M.; Esch, T.; Stilla, U. Deep learning earth observation classification using ImageNet pretrained networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 13, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marmanis, D.; Schindler, K.; Wegner, J.D.; Galliani, S.; Datcu, M.; Stilla, U. Classification with an edge: Improving semantic image segmentation with boundary detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 135, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, H.; Yan, Y.; Chen, T.; Cheng, P. Tree Height Estimation of Forest Plantation in Mountainous Terrain from Bare-Earth Points Using a DoG-Coupled Radial Basis Function Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, H.; Chen, M.; Chen, T.; Li, D. Matching of Remote Sensing Images with Complex Background Variations via Siamese Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Souly, N.; Spampinato, C.; Shah, M. Semi supervised semantic segmentation using generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5688–5696. [Google Scholar]




| Layer | Kernel | Stride | Padding | Feature | Activation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| conv1 | 4 × 4 | 3 | 1 | 64 | None |
| conv2 | 4 × 4 | 2 | 1 | 128 | ReLU |
| conv3 | 4 × 4 | 2 | 1 | 256 | ReLU |
| conv4-8 | 4 × 4 | 2 | 1 | 512 | ReLU |
| dconv9-12 | 4 × 4 | 2 | 1 | 512 | ReLU |
| dconv13 | 4 × 4 | 2 | 1 | 256 | ReLU |
| dconv14 | 4 × 4 | 2 | 1 | 128 | ReLU |
| dconv15 | 4 × 4 | 2 | 1 | 64 | ReLU |
| dconv16 | 4 × 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | tanh |
| Network | Input | Precision | Recall | F1_Score | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLabv3+ | Multisource | 0.7552 | 0.6689 | 0.6612 | 0.5482 |
| Proposed | Single | 0.8237 | 0.7846 | 0.7925 | 0.6825 |
| Multisource | 0.8859 | 0.8254 | 0.8308 | 0.7305 |
| Convolutional Layer | Precision | Recall | F1_Score | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 × 3 layers | 0.8488 | 0.7569 | 0.7534 | 0.6631 |
| 5 × 3 layers | 0.8859 | 0.8254 | 0.8308 | 0.7305 |
| 6 × 3 layers | 0.8900 | 0.8024 | 0.7756 | 0.6572 |
| Method | Precision | Recall | F1_Score | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net [25] | 0.6867 | 0.6515 | 0.6140 | 0.4767 |
| PSPNet [47] | 0.7362 | 0.6299 | 0.6271 | 0.4802 |
| DeepLabv3+ [33] | 0.7421 | 0.6830 | 0.6764 | 0.5800 |
| pix2pix [30,48] | 0.8052 | 0.8102 | 0.7740 | 0.6496 |
| Proposed | 0.8490 | 0.8204 | 0.8146 | 0.7002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, H.; Li, C.; Yang, R.; Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y. Multisource Data Fusion and Adversarial Nets for Landslide Extraction from UAV-Photogrammetry-Derived Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133059
He H, Li C, Yang R, Zeng H, Li L, Zhu Y. Multisource Data Fusion and Adversarial Nets for Landslide Extraction from UAV-Photogrammetry-Derived Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133059
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Haiqing, Changcheng Li, Ronghao Yang, Huaien Zeng, Lin Li, and Yufeng Zhu. 2022. "Multisource Data Fusion and Adversarial Nets for Landslide Extraction from UAV-Photogrammetry-Derived Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133059
APA StyleHe, H., Li, C., Yang, R., Zeng, H., Li, L., & Zhu, Y. (2022). Multisource Data Fusion and Adversarial Nets for Landslide Extraction from UAV-Photogrammetry-Derived Data. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133059








