Estimating Irrigation Water Consumption Using Machine Learning and Remote Sensing Data in Kansas High Plains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Methodology
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
| Variables | Product | Temporal Aggregation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ET | MOD16A | Sum of MJJA | [64] |
| ET | ECOSTRESS PT-JPL | Sum of MJJA | [65] |
| ET | ECOSTRESS dis-ALEXI | Sum of MJJA | [66] |
| NDVI, NDWI, GI | LANDSAT | Mean of MJJA | [67] |
| Precipitation | GRIDMET | Sum of MJJA | [62] |
| Daily maximum temperature | GRIDMET | Mean of MJJA | [62] |
| Water vapor deficit (VPD) | GRIDMET | Mean of MJJA | [62] |
| Irrigated area | AIM-HPA | Annual | [46] |
| Crop fraction | CDL | Annual | [63] |
| In situ irrigation water use | WIMAS | Annual | [48] |
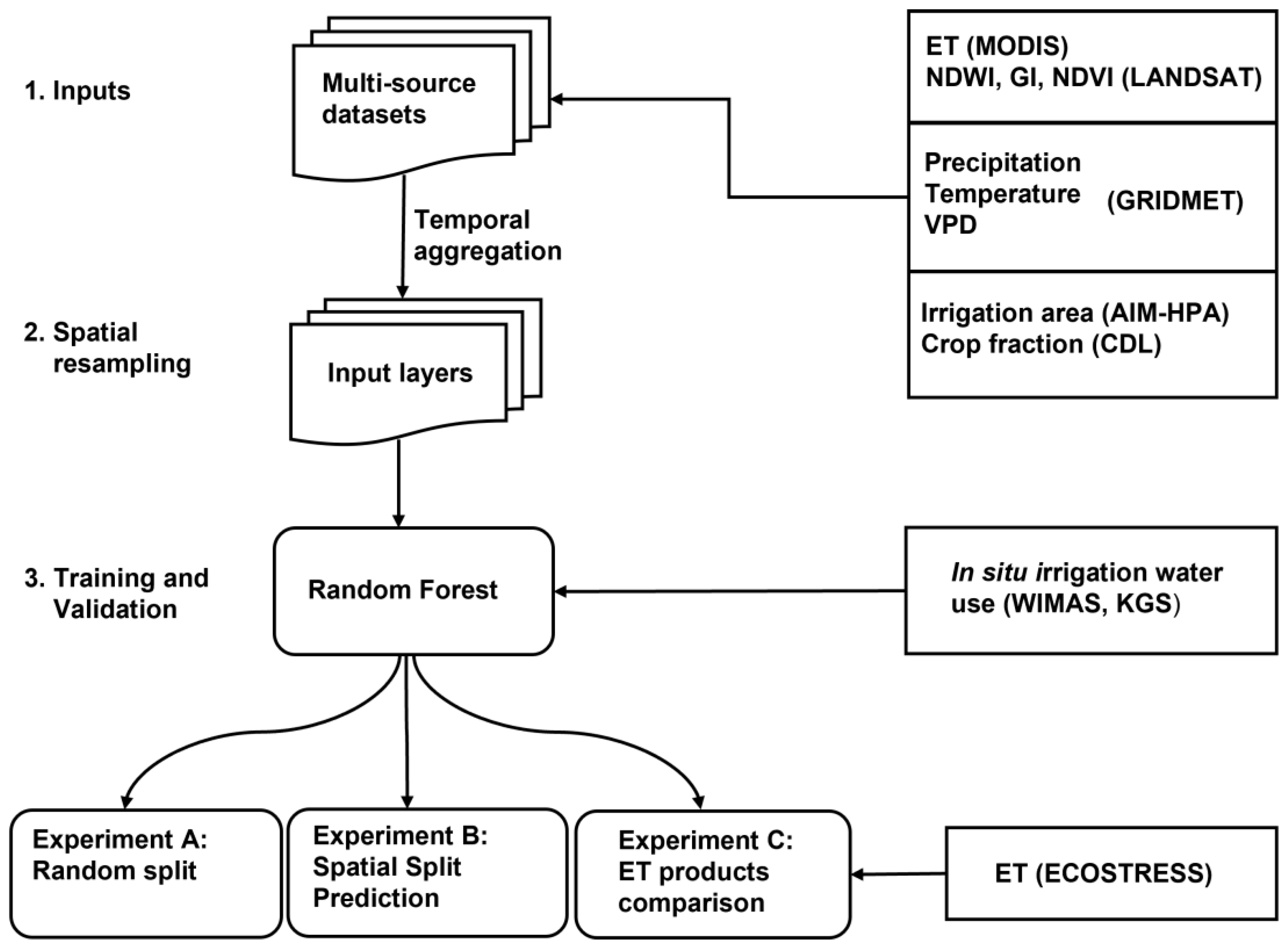
2.3. Methods
3. Results
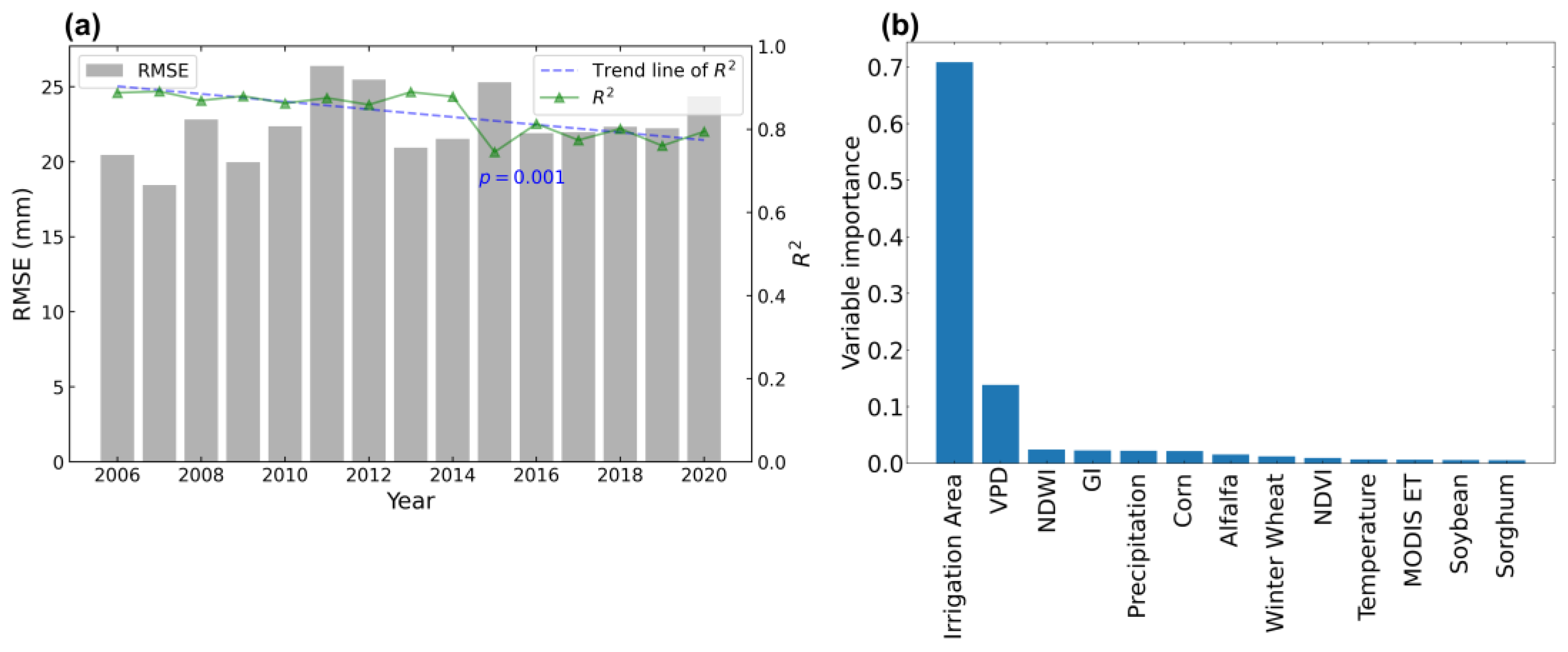
3.1. Experiment A: Random Split
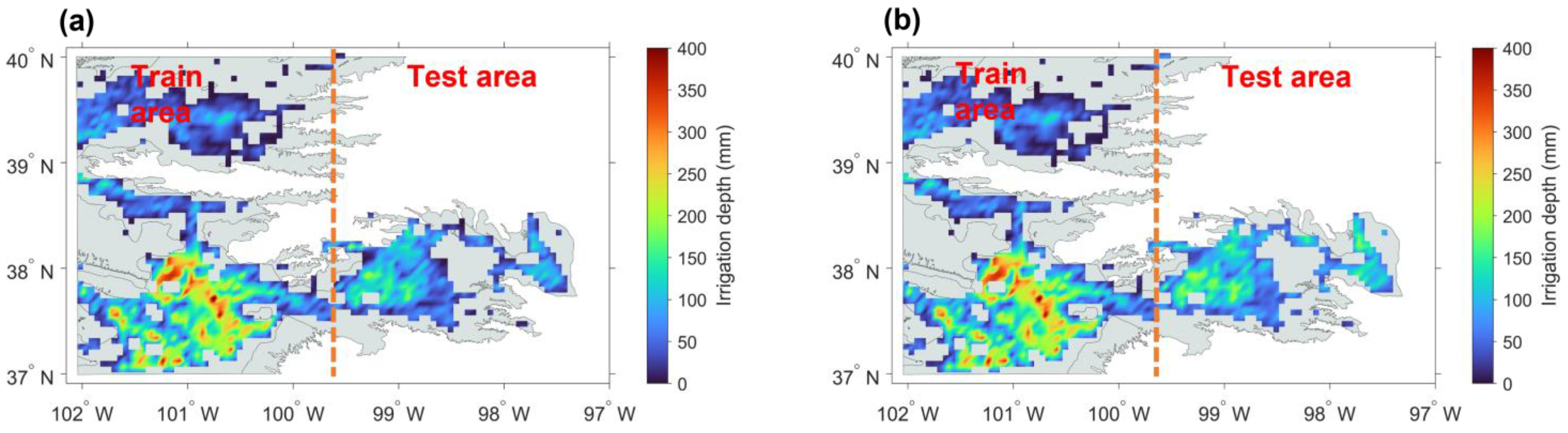
3.2. Experiment B: Spatial Split
3.3. Experiment C: ECOSTRESS and MODIS ET Comparison
4. Discussion
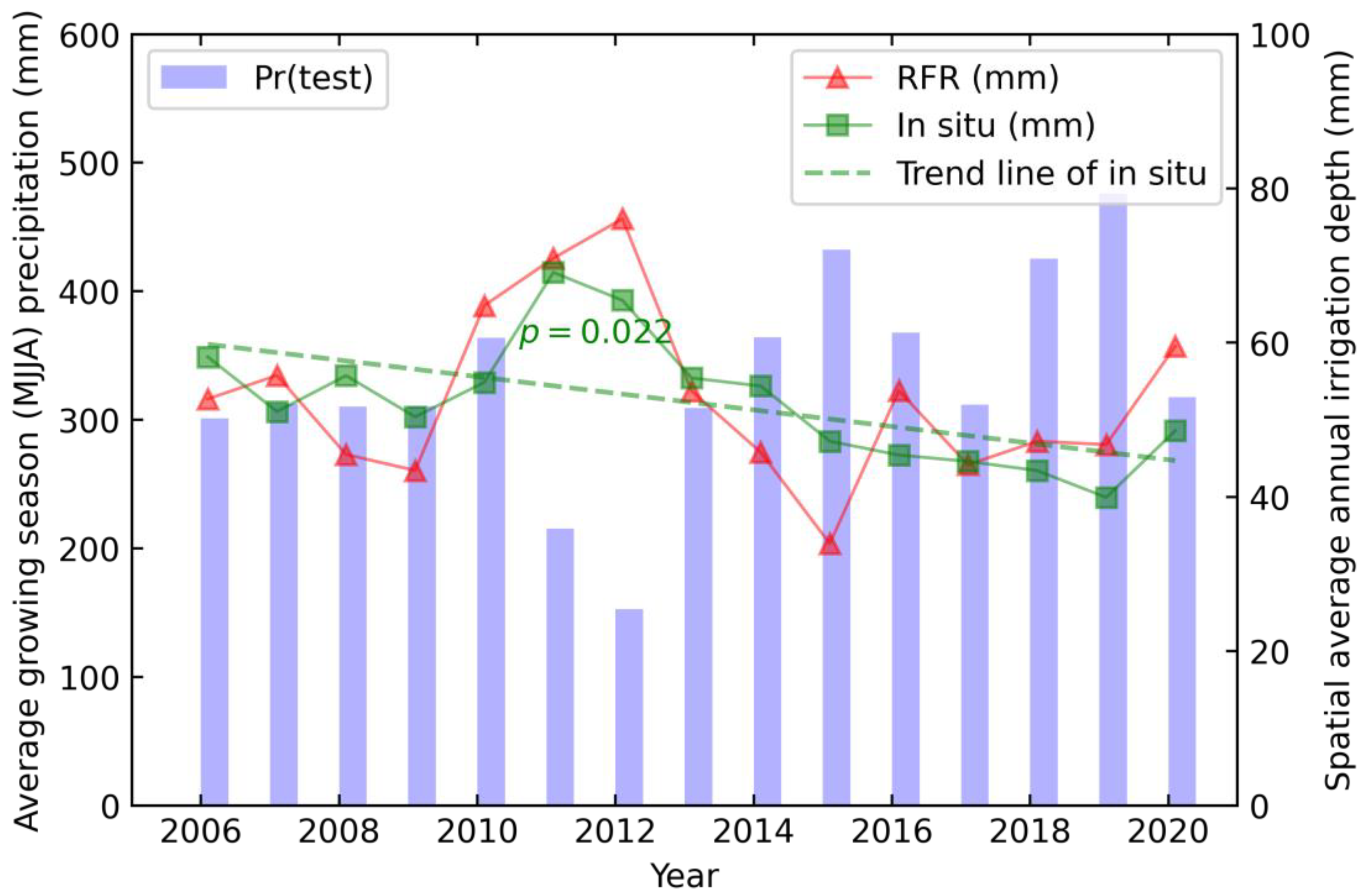
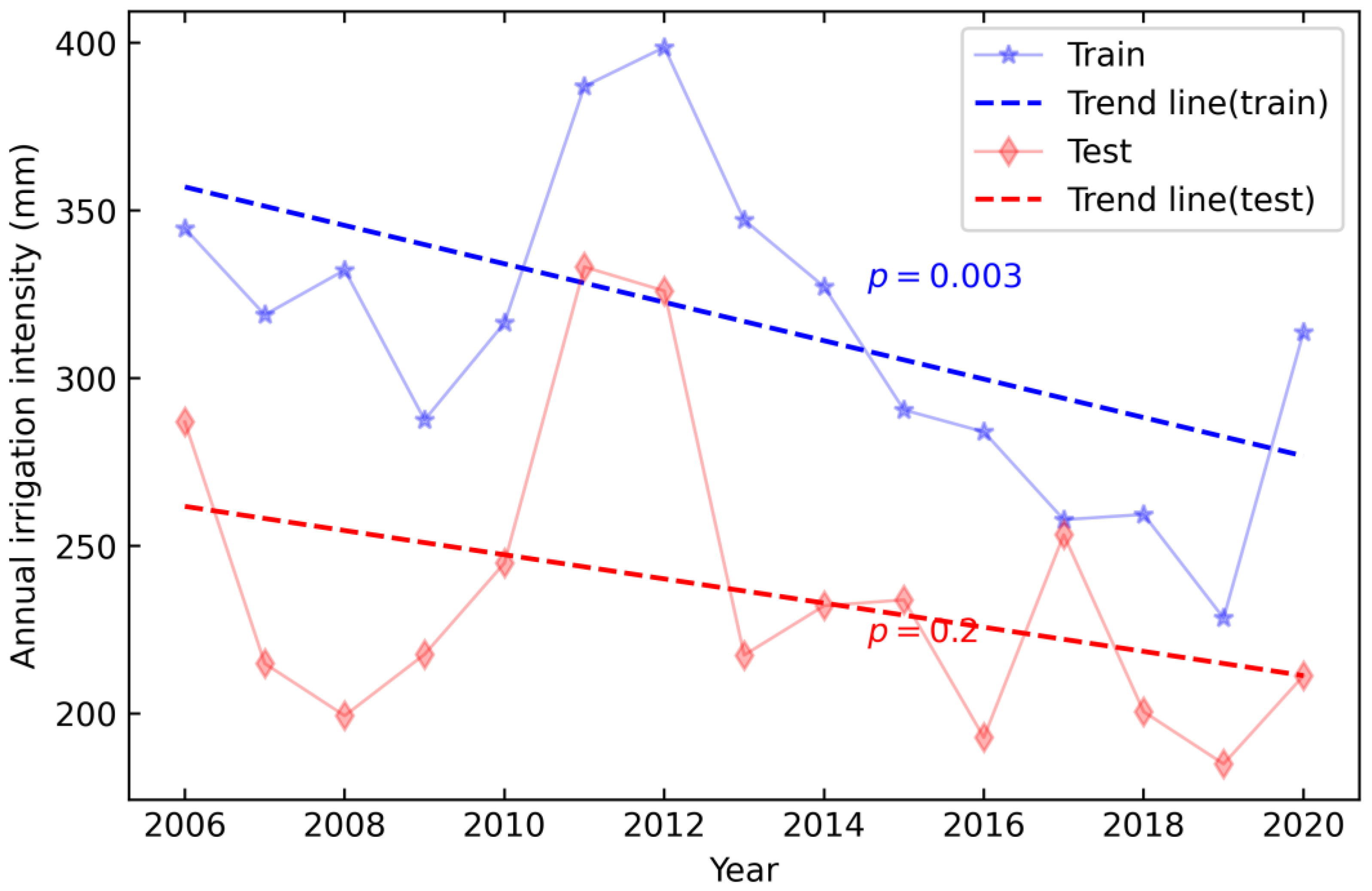
4.1. Groundwater Irrigation Trend
4.2. Spatial Transferability
4.3. ECOSTRESS ET Utility for Irrigation Amount Estimation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siebert, S.; Burke, J.; Faures, J.M.; Frenken, K.; Hoogeveen, J.; Döll, P.; Portmann, F.T. Groundwater Use for Irrigation—A Global Inventory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1863–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gleick, P.H.; Cooley, H.; Morikawa, M.; Morrison, J.; Cohen, M.J. The World’s Water, 2008–2009: The Biennial Report on Freshwater Resources; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; p. 402. [Google Scholar]
- Postel, S.L.; Daily, G.C.; Ehrlich, P.R. Human Appropriation of Renewable Fresh Water. Science 1996, 271, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haacker, E.M.K.; Kendall, A.D.; Hyndman, D.W. Water Level Declines in the High Plains Aquifer: Predevelopment to Resource Senescence. Ground Water 2016, 54, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Wilson, B.; Whittemore, D.; Jin, W.; Butler, J. Ground-Water Model for Southwest Kansas Groundwater Management District No. 3. 2010. Available online: https://www.kgs.ku.edu/Hydro/Publications/2010/OFR10_18/index.html (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Scanlon, B.R.; Faunt, C.C.; Longuevergne, L.; Reedy, R.C.; Alley, W.M.; McGuire, V.L.; McMahon, P.B. Groundwater Depletion and Sustainability of Irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9320–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konikow, L.F. Contribution of Global Groundwater Depletion since 1900 to Sea-Level Rise. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 2011GL048604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kueppers, L.M.; Snyder, M.A.; Sloan, L.C. Irrigation Cooling Effect: Regional Climate Forcing by Land-Use Change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 2006GL028679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sacks, W.J.; Cook, B.I.; Buenning, N.; Levis, S.; Helkowski, J.H. Effects of Global Irrigation on the Near-Surface Climate. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 33, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobell, D.; Bala, G.; Mirin, A.; Phillips, T.; Maxwell, R.; Rotman, D. Regional Differences in the Influence of Irrigation on Climate. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2248–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdogan, M.; Salvucci, G.D. Irrigation-Induced Changes in Potential Evapotranspiration in Southeastern Turkey: Test and Application of Bouchet’s Complementary Hypothesis. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, 2003WR002822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozdogan, M.; Rodell, M.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Toll, D.L. Simulating the Effects of Irrigation over the United States in a Land Surface Model Based on Satellite-Derived Agricultural Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, M.; Wu, X.; Yang, H. Snow Cover and Vegetation-Induced Decrease in Global Albedo from 2002 to 2016. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wada, Y.; Lo, M.H.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Reager, J.T.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Wu, R.J.; Tseng, Y.H. Fate of Water Pumped from Underground and Contributions to Sea-Level Rise. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puma, M.J.; Cook, B.I. Effects of Irrigation on Global Climate during the 20th Century. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 16120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Niu, G.Y.; Xia, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Fang, Y. A Systematic Evaluation of Noah-MP in Simulating Land-Atmosphere Energy, Water, and Carbon Exchanges Over the Continental United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 12245–12268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ikeda, K.; Rasmussen, R.; Barlage, M.; Newman, A.J.; Prein, A.F.; Chen, F.; Chen, L.; Clark, M.; Dai, A.; et al. Continental-Scale Convection-Permitting Modeling of the Current and Future Climate of North America. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Save, H.; Sun, A.Y.; Schmied, H.M.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Wiese, D.N.; Wada, Y.; Long, D.; Reedy, R.C.; et al. Global Models Underestimate Large Decadal Declining and Rising Water Storage Trends Relative to GRACE Satellite Data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1080–E1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, W.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Rodell, M.; Kumar, S.V.; Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C. Groundwater Withdrawals under Drought: Reconciling GRACE and Land Surface Models in the United States High Plains Aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 5282–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, C.; Modanesi, S.; Dari, J.; Gruber, A.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Girotto, M.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Le Page, M.; Jarlan, L.; Zribi, M.; et al. A Review of Irrigation Information Retrievals from Space and Their Utility for Users. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Santanello, J.A.; Reichle, R.H.; Draper, C.S.; Koster, R.D.; Nearing, G.; Jasinski, M.F. Evaluating the Utility of Satellite Soil Moisture Retrievals over Irrigated Areas and the Ability of Land Data Assimilation Methods to Correct for Unmodeled Processes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4463–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escorihuela, M.J.; Quintana-Seguí, P. Comparison of Remote Sensing and Simulated Soil Moisture Datasets in Mediterranean Landscapes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, D.; Gupta, P.K.; Pradhan, R.; Dubey, A.K.; Singh, R.P. Discerning Shifting Irrigation Practices from Passive Microwave Radiometry over Punjab and Haryana. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2017, 8, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, J.; Gao, Q.; Wang, S.; Su, Z. Comparison of Temporal Trends from Multiple Soil Moisture Data Sets and Precipitation: The Implication of Irrigation on Regional Soil Moisture Trend. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 48, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawston, P.M.; Santanello, J.A.; Kumar, S.V. Irrigation Signals Detected from SMAP Soil Moisture Retrievals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11860–11867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocca, L.; Tarpanelli, A.; Filippucci, P.; Dorigo, W.; Zaussinger, F.; Gruber, A.; Fernández-Prieto, D. How Much Water Is Used for Irrigation? A New Approach Exploiting Coarse Resolution Satellite Soil Moisture Products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilvand, E.; Tajrishy, M.; Ghazi Zadeh Hashemi, S.A.; Brocca, L. Quantification of Irrigation Water Using Remote Sensing of Soil Moisture in a Semi-Arid Region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dari, J.; Brocca, L.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Stefan, V.; Morbidelli, R. Exploiting High-Resolution Remote Sensing Soil Moisture to Estimate Irrigation Water Amounts over a Mediterranean Region. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dari, J.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Giugliarelli, E.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Stefan, V.; Brocca, L. Irrigation Estimates from Space: Implementation of Different Approaches to Model the Evapotranspiration Contribution within a Soil-Moisture-Based Inversion Algorithm. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 265, 107537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaussinger, F.; Dorigo, W.; Gruber, A.; Tarpanelli, A.; Filippucci, P.; Brocca, L. Estimating Irrigation Water Use over the Contiguous United States by Combining Satellite and Reanalysis Soil Moisture Data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 897–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zappa, L.; Schlaffer, S.; Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; Nendel, C.; Zimmerman, B.; Dorigo, W. Detection and Quantification of Irrigation Water Amounts at 500 m Using Sentinel-1 Surface Soil Moisture. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droogers, P.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Lorite, I.J. Estimating Actual Irrigation Application by Remotely Sensed Evapotranspiration Observations. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaguera, M.; Krol, M.S.; Salama, M.S.; Su, Z.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Application of a Remote Sensing Method for Estimating Monthly Blue Water Evapotranspiration in Irrigated Agriculture. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10033–10050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Eekelen, M.W.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Jarmain, C.; Jackson, B.; Ferreira, F.; van der Zaag, P.; Saraiva Okello, A.; Bosch, J.; Dye, P.; Bastidas-Obando, E.; et al. A Novel Approach to Estimate Direct and Indirect Water Withdrawals from Satellite Measurements: A Case Study from the Incomati Basin. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 200, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valencia, O.M.L.; Johansen, K.; Solorio, B.J.L.A.; Li, T.; Houborg, R.; Malbeteau, Y.; Almashharawi, S.; Altaf, M.U.; Fallatah, E.M.; Dasari, H.P.; et al. Mapping Groundwater Abstractions from Irrigated Agriculture: Big Data, Inverse Modeling, and a Satellite-Model Fusion Approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 5251–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, M.F.A.; de Jong, S.M.; Sterk, G.; Wanders, N.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Addink, E.A. An Object-Based Image Analysis Approach to Assess Irrigation-Water Consumption from MODIS Products in Ethiopia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 88, 102067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Rodell, M.; Kumar, S.V.; Arsenault, K.R.; Badr, H.S. Irrigation Water Demand Sensitivity to Climate Variability Across the Contiguous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, 2020WR027738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, S.E.; Haacker, E.M.K.; Smidt, S.J. Influence of Irrigation Drivers Using Boosted Regression Trees: Kansas High Plains. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, 2020WR028867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.; Mieno, T.; Brozović, N. Satellite-Based Monitoring of Irrigation Water Use: Assessing Measurement Errors and Their Implications for Agricultural Water Management Policy. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, 2020WR028378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deines, J.M.; Kendall, A.D.; Butler, J.J.; Hyndman, D.W. Quantifying Irrigation Adaptation Strategies in Response to Stakeholder-Driven Groundwater Management in the US High Plains Aquifer. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 044014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deines, J.M.; Kendall, A.D.; Hyndman, D.W. Annual Irrigation Dynamics in the U.S. Northern High Plains Derived from Landsat Satellite Data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 9350–9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Deines, J.M.; Kendall, A.D.; Basso, B.; Hyndman, D.W. Addressing Challenges for Mapping Irrigated Fields in Subhumid Temperate Regions by Integrating Remote Sensing and Hydroclimatic Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Liang, F. Machine Learning for Hydrologic Sciences: An Introductory Overview. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2021, 8, e1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Lark, T.J. Mapping Annual Irrigation from Landsat Imagery and Environmental Variables across the Conterminous United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 260, 112445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, J.; Zuo, L.; Ge, Q. Tracking Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Irrigated Croplands in China from 2000 to 2019 through the Synergy of Remote Sensing, Statistics, and Historical Irrigation Datasets. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deines, J.M.; Kendall, A.D.; Crowley, M.A.; Rapp, J.; Cardille, J.A.; Hyndman, D.W. Mapping Three Decades of Annual Irrigation across the US High Plains Aquifer Using Landsat and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Smith, R.; Butler, J.J.; Lakshmi, V. Groundwater Withdrawal Prediction Using Integrated Multitemporal Remote Sensing Data Sets and Machine Learning. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, 2020WR028059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansas Geological Survey. Water Information Management and Analysis System (WIMAS). Available online: https://geohydro.kgs.ku.edu/geohydro/wimas/query_setup.cfm (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Peck, J.C. Groundwater Management in Kansas: A Brief History and Assessment. Kans. J. Law Public Policy 2006, 15, 441. [Google Scholar]
- United States Department of Agriculture. 2021 State Agriculture Overview for Kansas. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Quick_Stats/Ag_Overview/stateOverview.php?state=KANSAS (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Whittemore, D.O.; Butler, J.J.; Brownie Wilson, B. Status of the High Plains Aquifer in Kansas; Technical Series 22; Kansas Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lanning-Rush, J.L. Irrigation Water Use in Kansas, 2013; Data Series 981; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2016; 12p.
- Cotterman, K.A.; Kendall, A.D.; Basso, B.; Hyndman, D.W. Groundwater Depletion and Climate Change: Future Prospects of Crop Production in the Central High Plains Aquifer. Clim. Chang. 2018, 146, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. Field Crops Usual Planting and Harvesting Dates 2010; National Agricultural Statistics Service Agricultural Handbook Number 628; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Mancino, G.; Ferrara, A.; Padula, A.; Nolè, A. Cross-Comparison between Landsat 8 (OLI) and Landsat 7 (ETM+) Derived Vegetation Indices in a Mediterranean Environment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, D.P.; Kovalskyy, V.; Zhang, H.K.; Vermote, E.F.; Yan, L.; Kumar, S.S.; Egorov, A. Characterization of Landsat-7 to Landsat-8 Reflective Wavelength and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Continuity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. MODIS Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration (ET) Product. In Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, Collection; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Halverson, G.H.; Fisher, J.B.; Lee, C.M. Level 3 Evapotranspiration Priestley-Taylor Jet Propulsion Laboratory (PT-JPL) Data User Guide; Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://ecostress.jpl.nasa.gov/downloads/atbd/ECOSTRESS_L3_ET_PT-JPL_ATBD_20180509.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- Cawse-Nicholson, K.; Anderson, M. ECOSTRESS Level-3 DisALEXI-JPL Evapotranspiration (ECO3ETALEXI) Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document; Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2021. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/documents/999/ECO3ETALEXI_User_Guide_V1.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- Fisher, J.B.; Tu, K.P.; Baldocchi, D.D. Global Estimates of the Land-Atmosphere Water Flux Based on Monthly AVHRR and ISLSCP-II Data, Validated at 16 FLUXNET Sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Oishi, A.C.; Miniat, C.F.; Bolstad, P. An Evaluation of ECOSTRESS Products of a Temperate Montane Humid Forest in a Complex Terrain Environment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J.T. Development of Gridded Surface Meteorological Data for Ecological Applications and Modelling. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. National Agricultural Statistics Service (USDA NASS) Cropland Data Layer. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Research_and_Science/Cropland/metadata/meta.php (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- United States Geological Survey. LP DAAC—MOD16A2. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod16a2v061/ (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- United States Geological Survey. LP DAAC—ECO3ETPTJPL. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/eco3etptjplv001/ (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- United States Geological Survey. LP DAAC—ECO3ETALEXI. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/eco3etalexiv001/ (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- United States Geological Survey. Landsat Data Access|U.S. Geological Survey. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions/landsat-data-access (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăgu, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louppe, G. Understanding Random Forests: From Theory to Practice. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1407.7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S.; Yapo, P.O. Status of Automatic Calibration for Hydrologic Models: Comparison with Multilevel Expert Calibration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Quesada, G.; Hendricks, N.P. Lessons from Local Governance and Collective Action Efforts to Manage Irrigation Withdrawals in Kansas. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 247, 106736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwickle, A.; Feltman, B.C.; Brady, A.J.; Kendall, A.D.; Hyndman, D.W. Sustainable Irrigation through Local Collaborative Governance: Evidence for a Structural Fix in Kansas. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 124, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansas Department of Agriculture. Sheridan County 6 LEMA. Available online: https://agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/dwr/managing-kansas-water-resources/local-enhanced-management-areas/sheridan-county-6-lema (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Butler, J.J.; Bohling, G.C.; Whittemore, D.O.; Wilson, B.B. Charting Pathways Toward Sustainability for Aquifers Supporting Irrigated Agriculture. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, D.; Caballero, E.; Jacobsen, J.-H.; Zhang, A.; Binas, J.; Zhang, D.; Priol, R.L.; Courville, A. Out-of-Distribution Generalization via Risk Extrapolation (REx). In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Yang, Y.; Xue, J.; Knipper, K.R.; Yang, Y.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Kustas, W.P.; Cawse-Nicholson, K.; Hulley, G.; et al. Interoperability of ECOSTRESS and Landsat for Mapping Evapotranspiration Time Series at Sub-Field Scales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


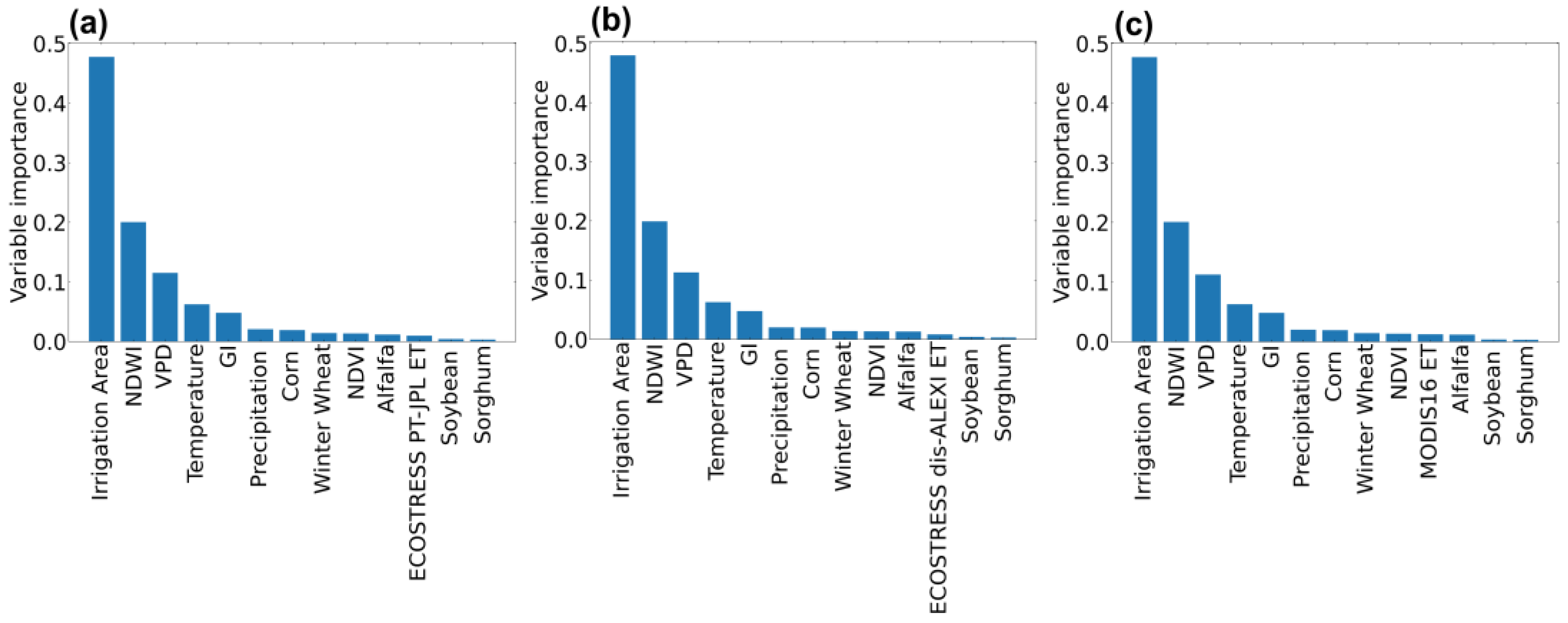

| ET Products | PBIAS | RMSE (mm) | R2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | STD | Mean | STD | Mean | STD | |
| ECOSTRESS PT-JPL Instantaneous | −0.12% | 2.0% | 22 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 0.013 |
| ECOSTRESS dis-ALEXI Daily | −0.12% | 2.0% | 22 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 0.013 |
| MOD16 | −0.13% | 2.0% | 22 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 0.013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, S.; Xu, T.; Niu, G.-Y.; Zeng, R. Estimating Irrigation Water Consumption Using Machine Learning and Remote Sensing Data in Kansas High Plains. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3004. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133004
Wei S, Xu T, Niu G-Y, Zeng R. Estimating Irrigation Water Consumption Using Machine Learning and Remote Sensing Data in Kansas High Plains. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):3004. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133004
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Shiqi, Tianfang Xu, Guo-Yue Niu, and Ruijie Zeng. 2022. "Estimating Irrigation Water Consumption Using Machine Learning and Remote Sensing Data in Kansas High Plains" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 3004. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133004
APA StyleWei, S., Xu, T., Niu, G.-Y., & Zeng, R. (2022). Estimating Irrigation Water Consumption Using Machine Learning and Remote Sensing Data in Kansas High Plains. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3004. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133004







