The Outburst of a Lake and Its Impacts on Redistribution of Surface Water Bodies in High-Altitude Permafrost Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
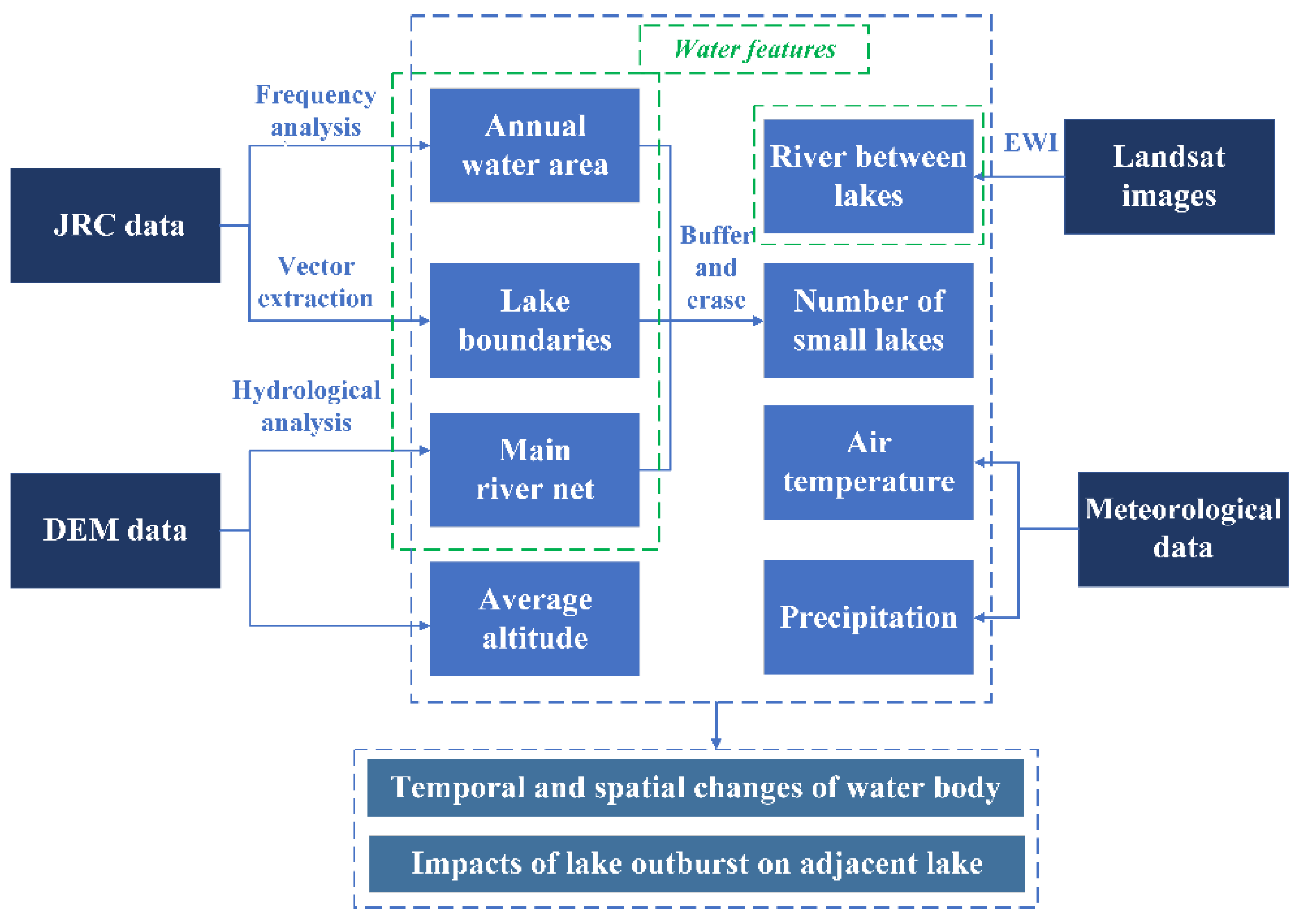
2. Materials and Methods
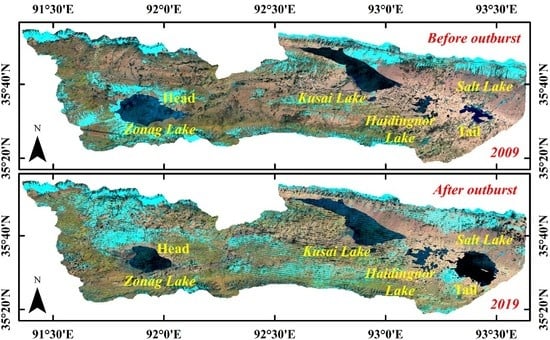
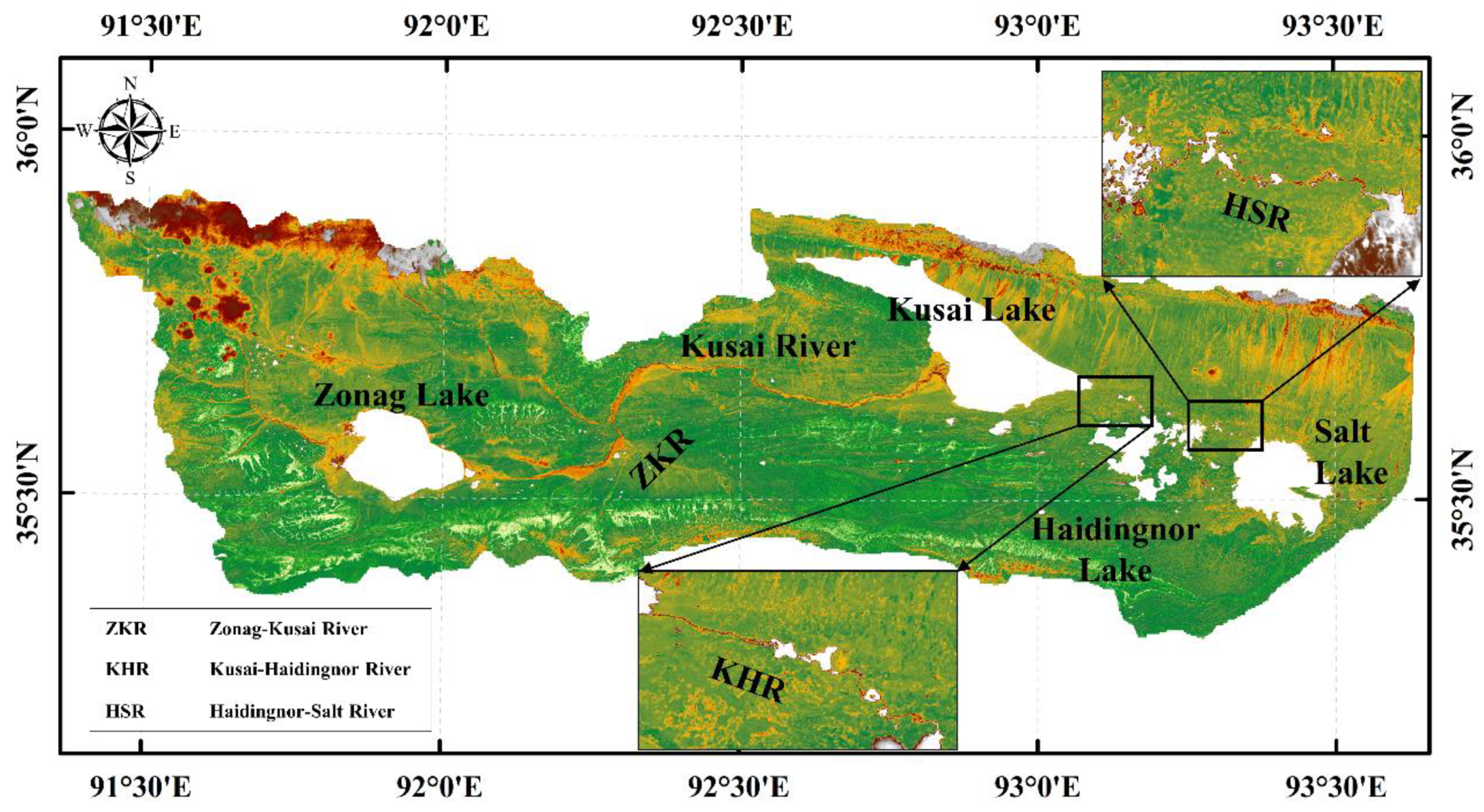
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Climate Data
2.3. Remote Sensing Data
2.4. Lake Volume Data
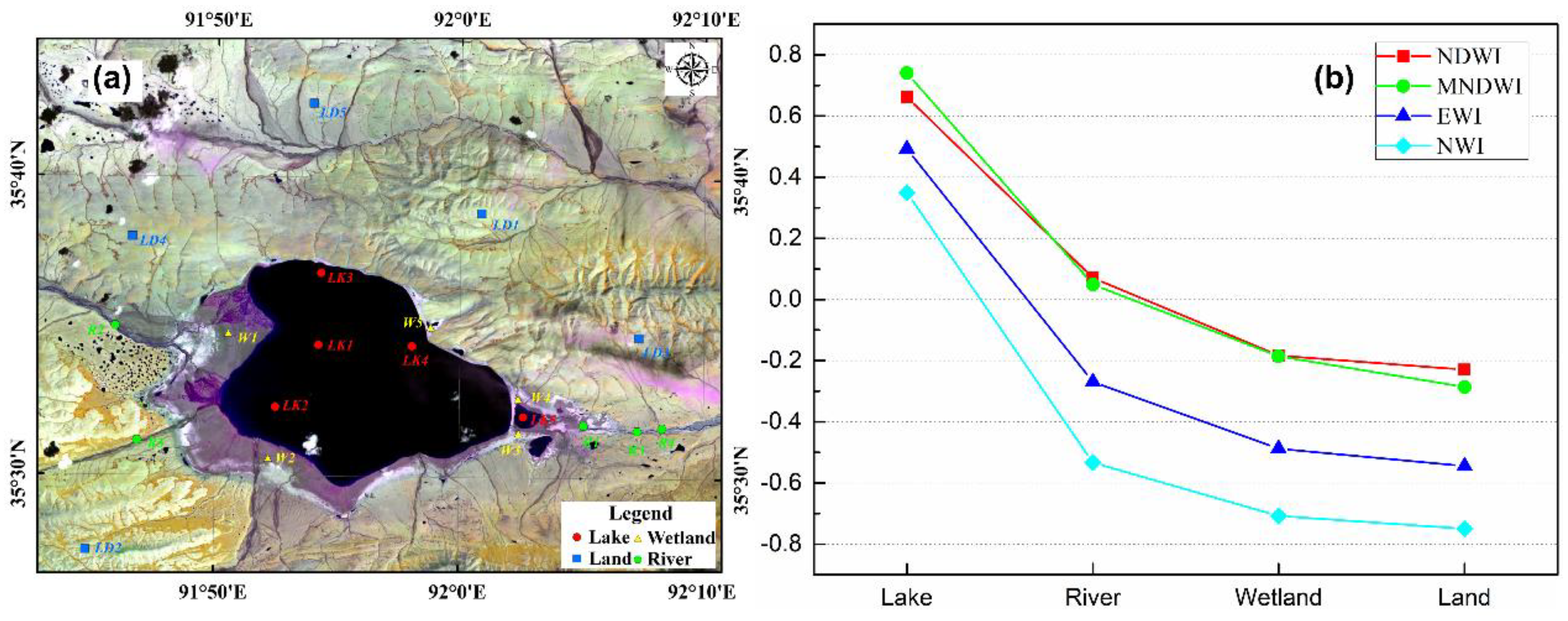
2.5. Methods
3. Results
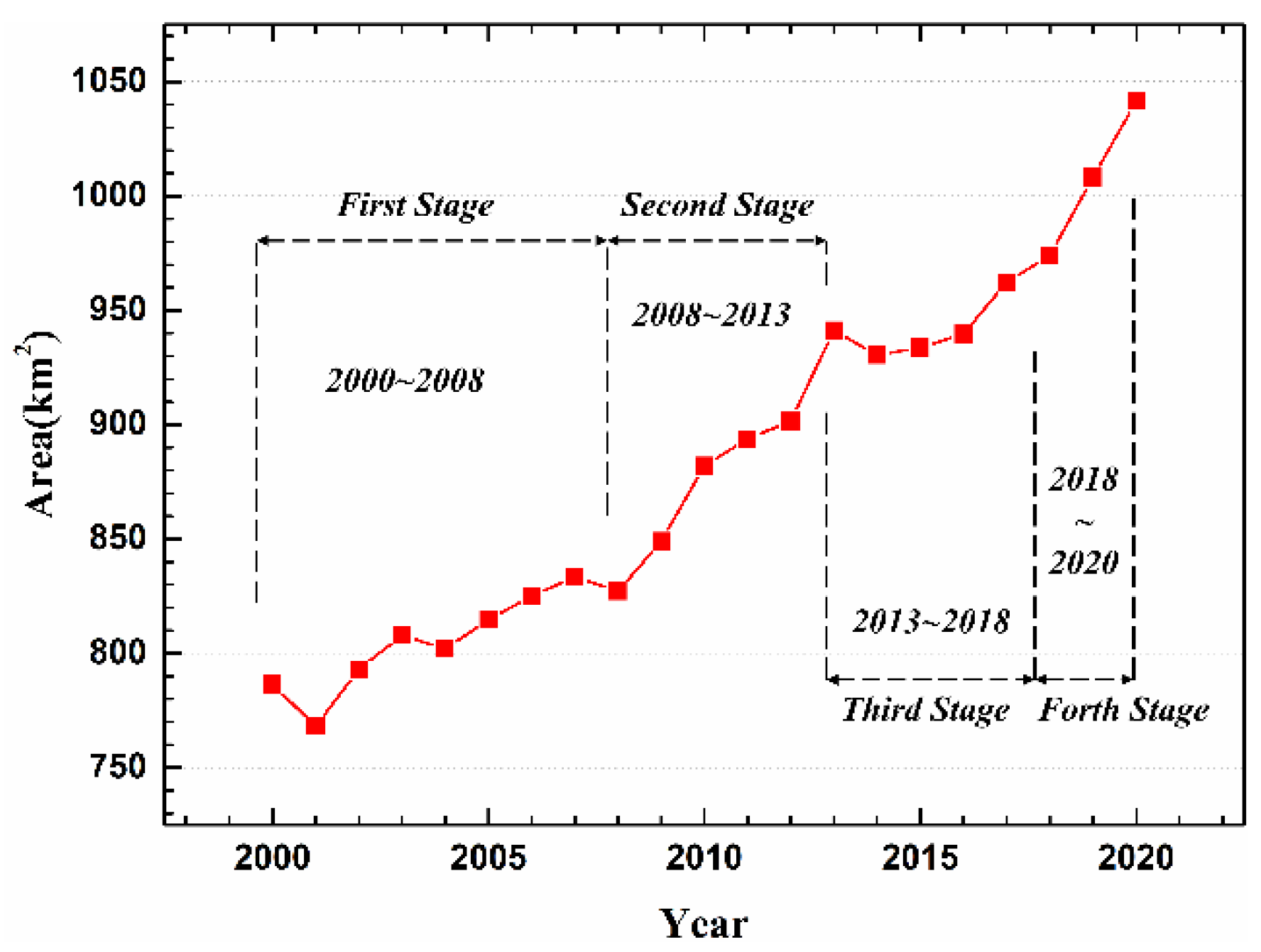
3.1. Changes in Total Surface Water Area in ZSLB
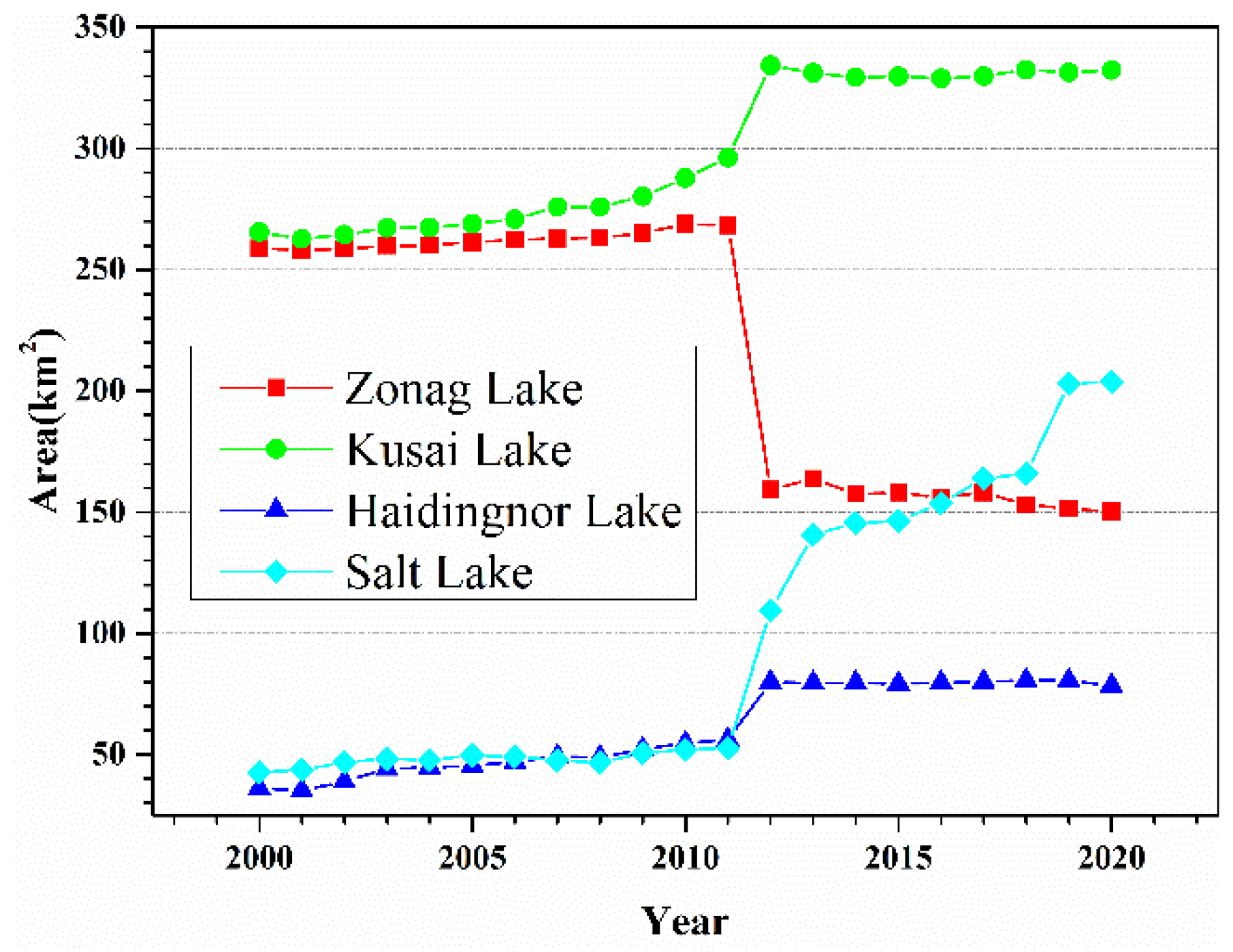
3.2. Changes in the Area of the Four Lakes
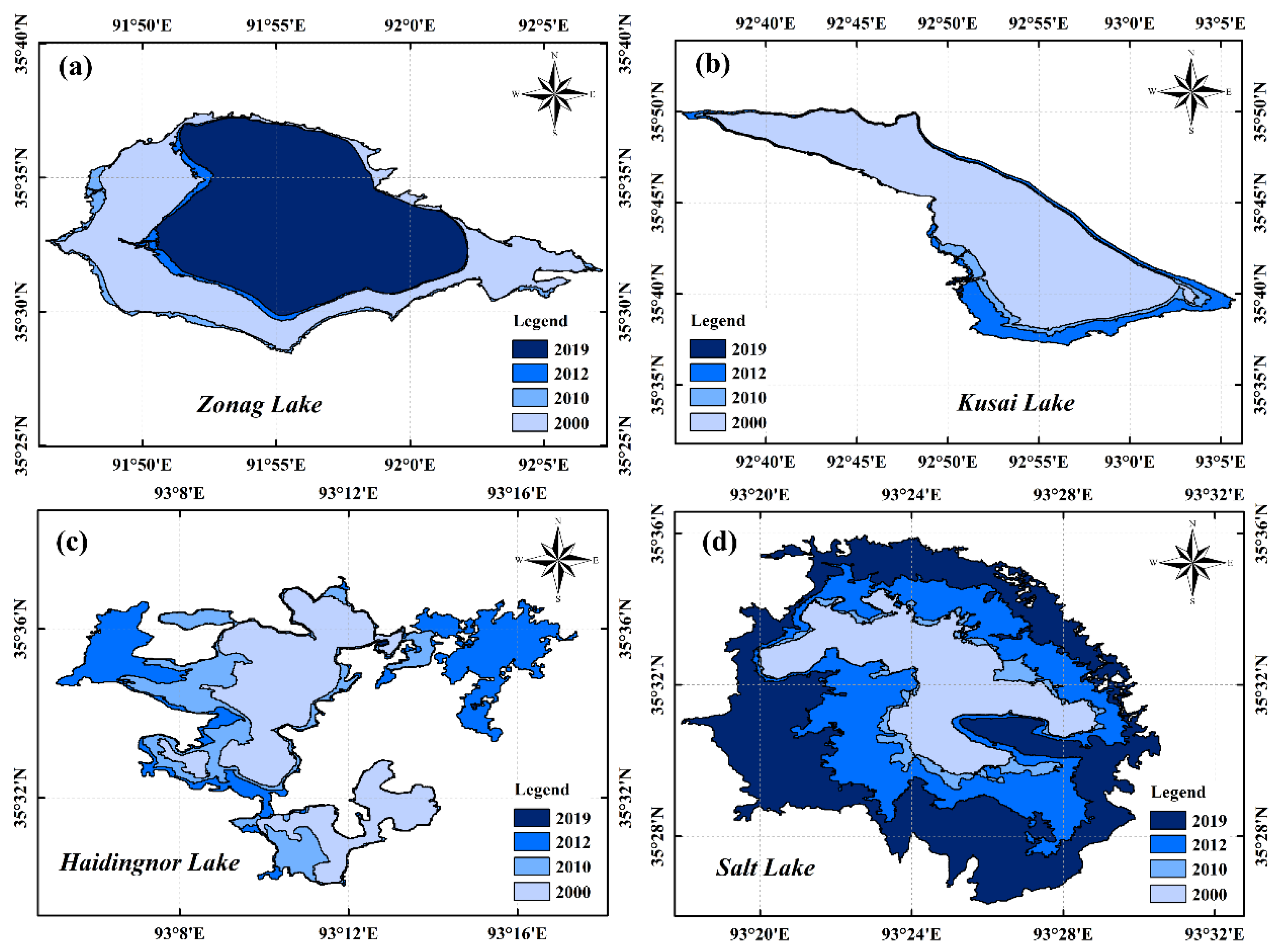
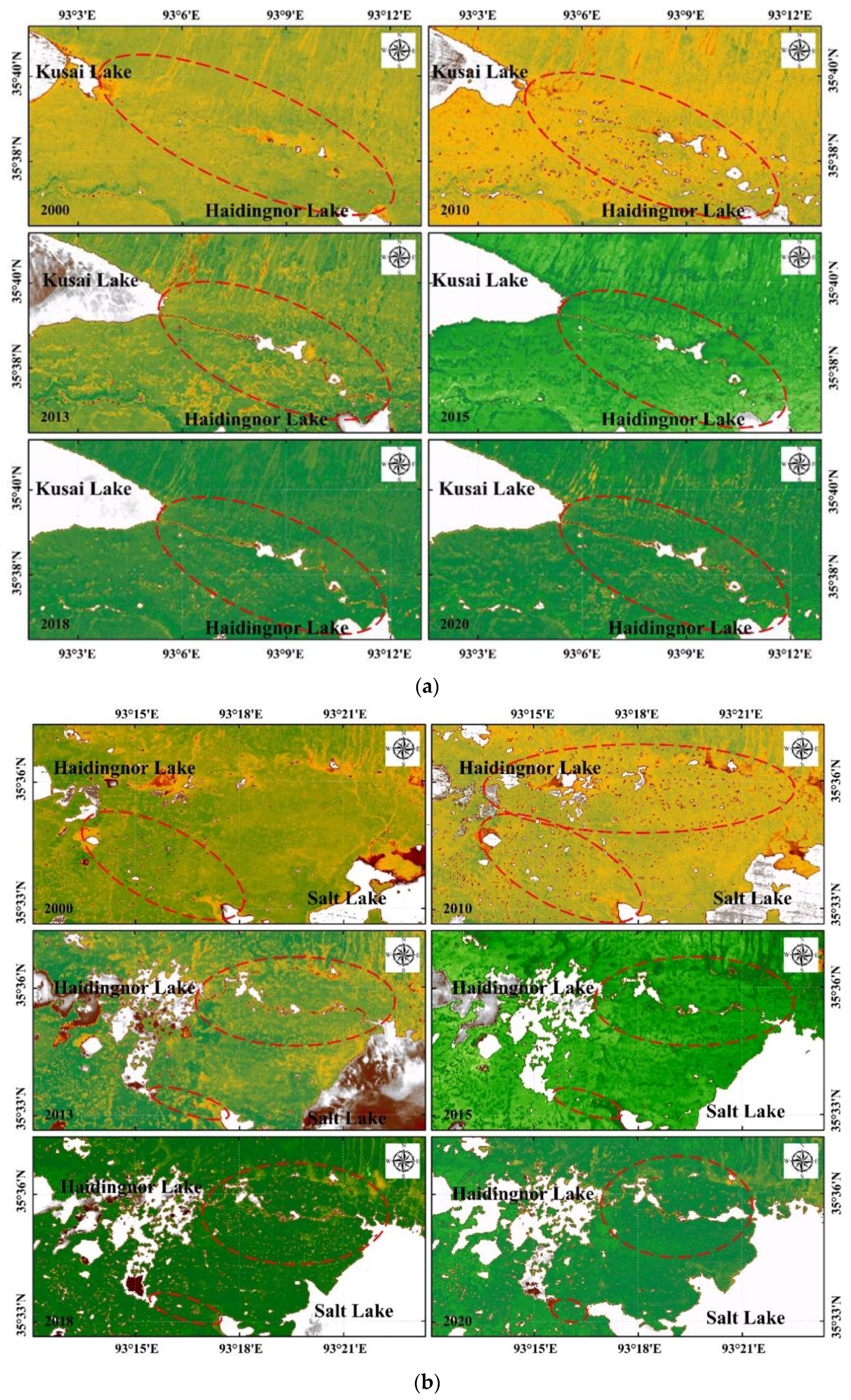
3.3. Changes in Shorelines of the Four Lakes in ZSLB
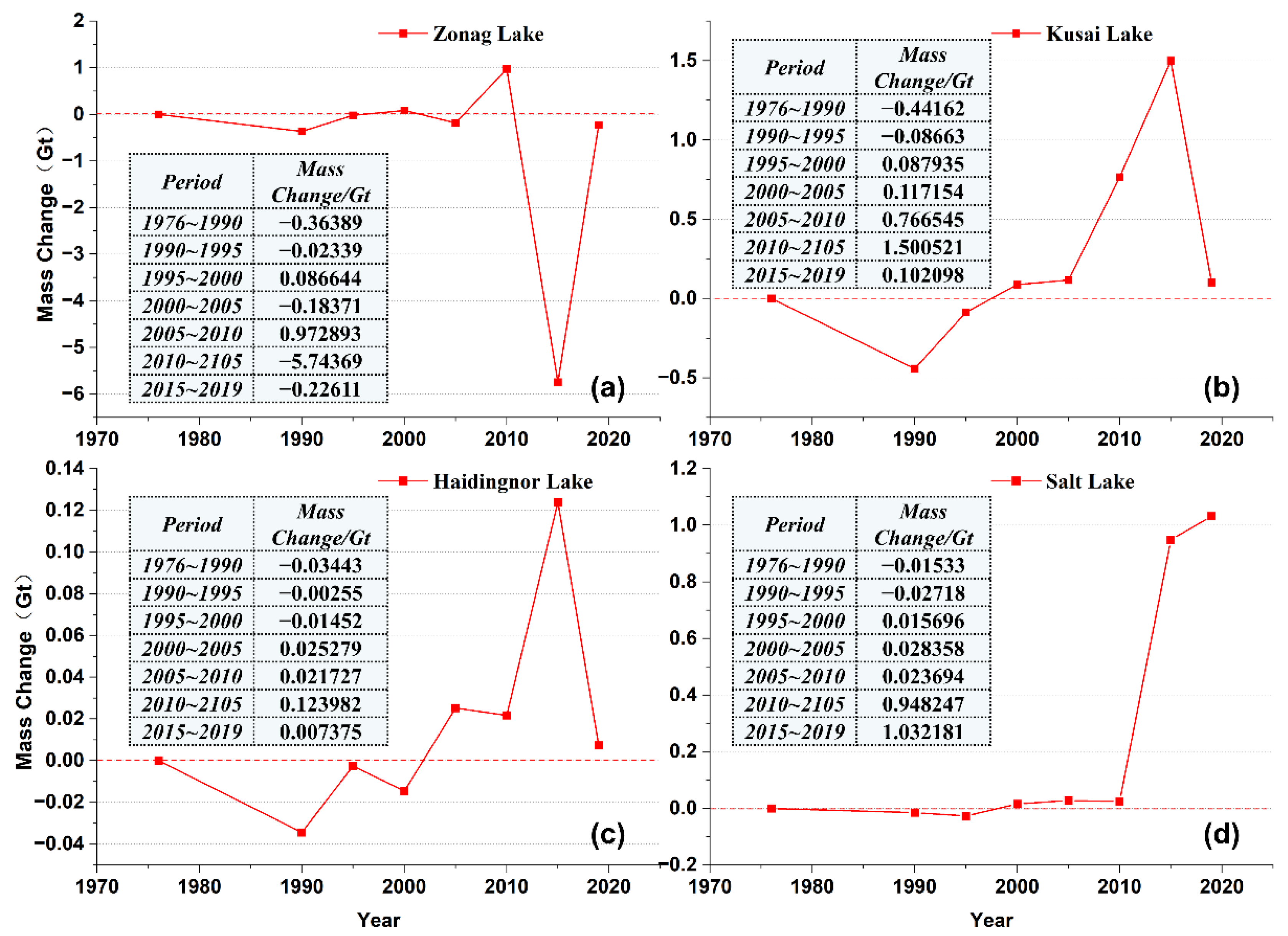
3.4. Changes in Water Volumes of the Four Lakes in ZLSB
3.5. Hydraulic Connection of the Four Lakes in ZSLB
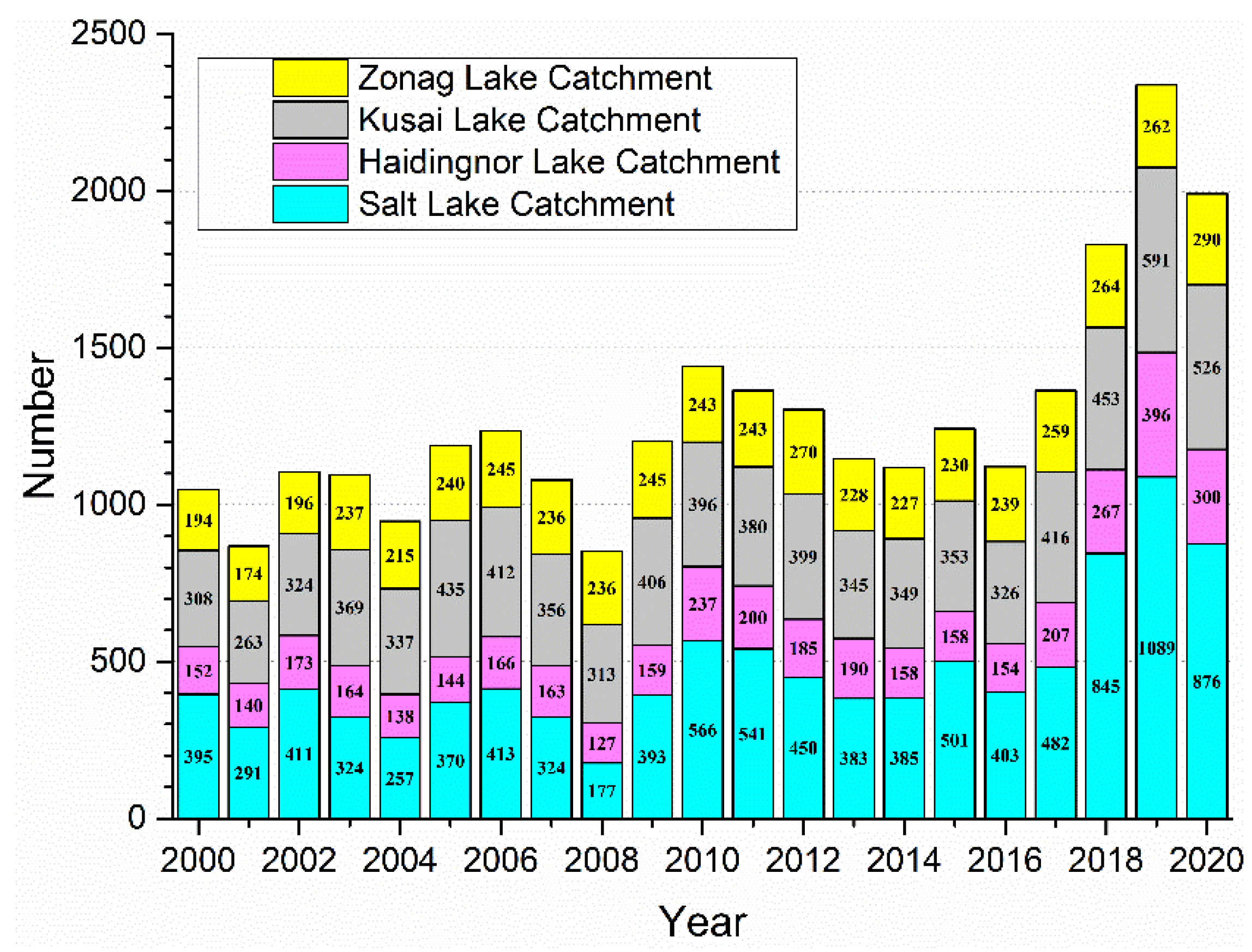
3.6. Variations in the Number of Small Lakes and Ponds in ZSLB
4. Discussion
4.1. Causes of Lake Expansion in the ZSLB
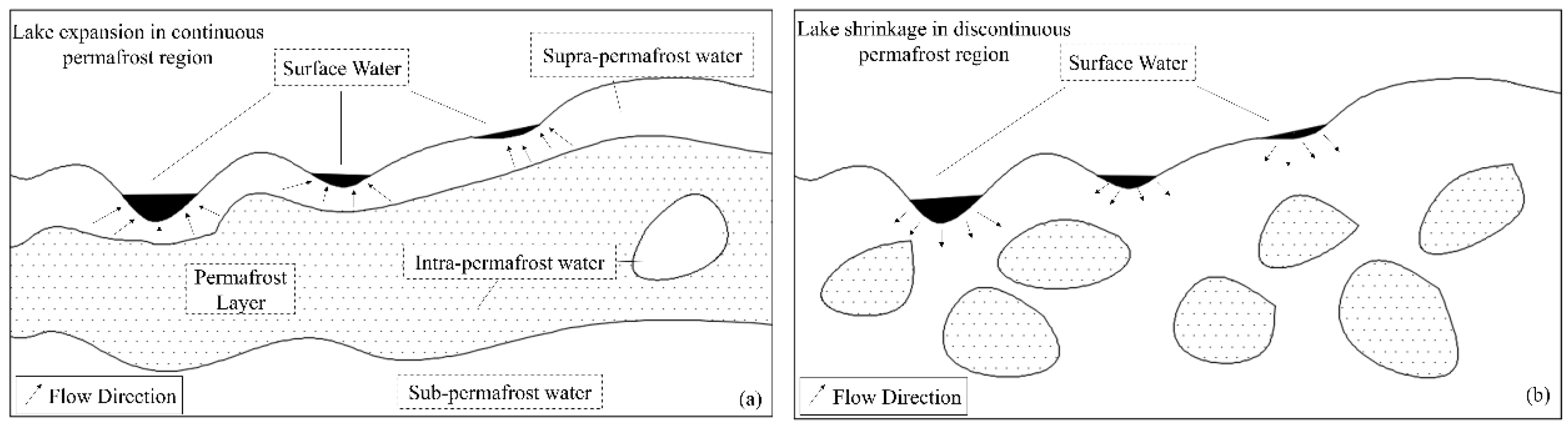
4.2. Roles of Permafrost Layer in Hydrology Process in Periglacial Environments
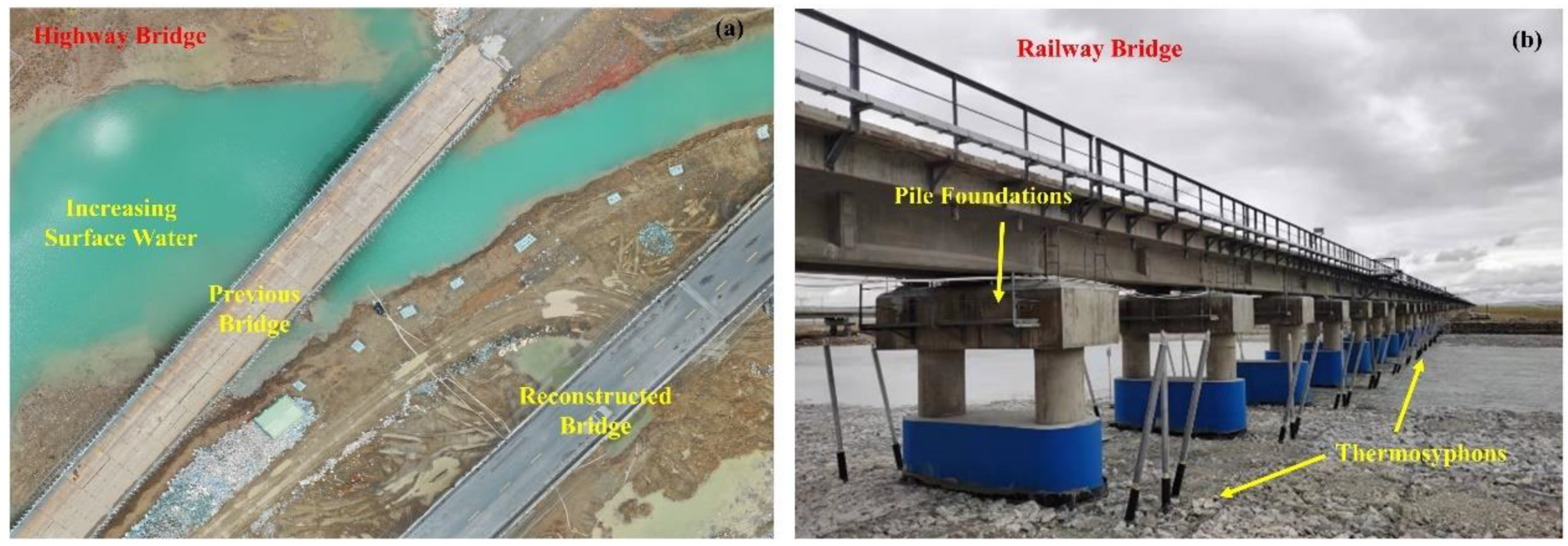
4.3. Influences of Lake Expansion and Outburst on Engineering
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Z. Dahe Qin: Time is limited to curb global warming. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, D.; Wang, N. Water cycle changes: Interpretation of IPCC AR6. Progress. Inquisitiones Mutat. Clim. 2021, 17, 699–704. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Qian, J. Changes of weather and climate extremes in the IPCC AR6. Progress. Inquisitiones Mutat. Clim. 2021, 17, 713–718. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Tang, H. Evidence of Warming and Wetting Climate over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2010, 42, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, P.A. Precipitation Extremes Under Climate Change. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2015, 1, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, W.; Nie, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, J. Recent glacier and glacial lake changes and their interactions in the Bugyai Kangri, southeast Tibet. Ann. Glaciol. 2016, 57, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, D.; Lei, H. Reconciling the Attribution of Changes in Streamflow Extremes from a Hydroclimate Perspective. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 3886–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shen, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Geng, X. Changes in Precipitation and Drought Extremes over the Past Half Century in China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Guo, W.; Wu, T.; Zhong, X.; Chen, R.; Xu, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, R. Cryospheric Changes and Their Impacts onWater Resources in the Belt and Road Regions. Adv. Earth Sci. 2020, 35, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Hao, Z.; Tang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Zhang, X.; Hao, F. Projected increase in compound dry and hot events over global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.L.; French, H.M. Climate controls and high-altitude permafrost, Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau, China. Permafr. Periglac. Processes 1994, 5, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Zhuang, Q. Quantifying the Role of Snowmelt in Stream Discharge in an Alaskan Watershed: An Analysis Using a Spatially Distributed Surface Hydrology Model. J. Geophys. Res.-Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 2183–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Piao, S.; Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Fu, B. Permafrost thawing puts the frozen carbon at risk over the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Q.; Wu, T.; Shen, L.; Pepin, N.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Kang, S.; AghaKouchak, A. Review of snow cover variation over the Tibetan Plateau and its influence on the broad climate system. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Shum, C.K.; Yi, S.; Yang, K.; Xie, H.; Feng, W.; Bolch, T.; Wang, L.; Behrangi, A.; et al. Lake volume and groundwater storage variations in Tibetan Plateau’s endorheic basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5550–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, G.; Duan, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Li, A.; Kong, F.; Xue, B.; Wu, J.; et al. China’s lakes at present: Number, area and spatial distribution. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, L. The problems associated with permafrost in the development of the Qinghai-Xizang plateau. Quat. Sci. 2000, 20, 521. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Xu, B.; Yao, T.; Guo, Z.; Cui, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J.; et al. Assessment of past, present and future environmental changes on the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 3025–3035. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhen, X.; Sun, J. Environmental impacts and response strategies on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under global change. China Tibetol. 2021, 4, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Zheng, G. Lake-area mapping in the Tibetan Plateau: An evaluation of data and methods. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 742–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, M.; Geng, L. Monitoring the recent trend of aeolian desertification using Landsat TM and Landsat 8 imagery on the north-east Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in the Qinghai Lake basin. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 1753–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, L.; Du Yu, E.; Liang, T.; Duan, S.; Hou, F.; Ren, J. Causes of the outburst of Zonag Lake in Hoh Xil, Tibetan Plateau, and its impact on surrounding environment. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2016, 38, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Jin, R.; Lin, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, Z. Automatic Algorithm for Extracting Lake Boundaries in Qinghai- Tibet Plateau based on Cloudy Landsat TM/OLI Image and DEM. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2020, 35, 882–892. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Luo, W.; Chen, W.; Zheng, G. A robust but variable lake expansion on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 1306–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, D.L.; Jin, H.J.; Du, H.Q.; Li, C.; Ma, Q.; Duan, S.Q.; Li, G.S. Variation of alpine lakes from 1986 to 2019 in the Headwater Area of the Yellow River, Tibetan Plateau using Google Earth Engine. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2020, 11, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Liu, G.; Pang, Q.; Zou, D.; Liu, H. The Impact of Permafrost Degradation on Lake Changes in the Endorheic Basin on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Water 2020, 12, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Ohata, T.; Kadota, T. Land-surface hydrological processes in the permafrost region of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2003, 283, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bolch, T.; Chen, W.; Cretaux, J.-F. Comprehensive estimation of lake volume changes on the Tibetan Plateau during 1976-2019 and basin-wide glacier contribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Jin, H. Groundwater in the permafrost regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and it changes. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2013, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Jin, H.; Bense, V.F.; Jin, X.; Li, X. Hydrothermal processes of near-surface warm permafrost in response to strong precipitation events in the Headwater Area of the Yellow River, Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Liu, S.; Sun, M.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X. Changes of Kusai Lake in Hoh Xil Region and Causes of Its Water Overflowing. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 689–698. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.; Pang, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Liu, W. The formation of permafrost in the bottom of the Zonag Lake in Hoh Xil on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau after an outburst: Monitoring and simulation. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2017, 39, 949–956. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.e.; Liu, B.; He, W.; Duan, S.; Hou, F.; Wang, Z. Dynamic change and cause analysis of Salt Lake area in Hoh Xil on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during 1976–2017. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2018, 40, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.h.; Xie, C.w.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.h.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.x.; Yang, G.q.; Zhu, X.f.; Yue, G.y. Dynamic changes in lakes in the Hoh Xil region before and after the 2011 outburst of Zonag Lake. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Han, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, R.; Li, R.; Hao, T.; Qiao, G. Lake outburst accelerated permafrost degradation on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 112011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, W.; Liu, G. Environmental changes caused by the outburst of Zonag Lake and the possible outburst mode of Yanhu Lake in the Hoh Xil region. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2020, 42, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.; Sun, M.; Gong, P.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; An, L.; Ma, C. Overflow probability of the Salt Lake in Hoh Xil Region. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, W.; Xie, H. Tibetan Plateau’s Lake Level and Volume Changes from NASA’s ICESat/ICESat-2 and Landsat Missions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 13107–13118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ran, Y.; Wan, W.; Luo, W.; Chen, W.; Xu, F.; Li, X. 100 years of lake evolution over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3951–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mao, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C. Monitoring 40-Year Lake Area Changes of the Qaidam Basin, Tibetan Plateau, Using Landsat Time Series. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sha, J. Characteristics of stratigraphy and palaeontology of HohXil, Qinghai: Geographic significance. Acta Palaeontol. Sin. 1998, 37, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Shude, L.; Shijie, L. Permafrost and Periglacial Landforms in Kekexili Area of Qinghai Province. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 1993, 15, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; He, L.; Ye, L.; Chen, H.; Li, K. Micro-Area Analysis and Mechanism of Varves from Lake Kusai in the Hoh Xil Area, Northern Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Markham, B.L.; Storey, J.C.; Williams, D.L.; Irons, J.R. Landsat sensor performance: History and current status. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2691–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.C. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pci, Y.A.N.; Youjing, Z.; Yuan, Z. A Study on Information Extraction of Water Enhanced Water Index (EWI) and GIS System in Semi-arid Regions with the Based Noise Remove Techniques. Remote Sens. Inf. 2007, 6, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D. Study on information extraction of water body with a new water index (NWI). Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2009, 34, 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Xie, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, F. Lakes’ state and abundance across the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 3010–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Huang, B.; Richards, K.; Ke, L.; Vu Hien, P. Accelerated lake expansion on the Tibetan Plateau in the 2000s: Induced by glacial melting or other processes? Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 3170–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Piao, S.; Bolch, T.; Xie, H.; Chen, D.; Gao, Y.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Shum, C.K.; Yang, K.; et al. Extensive and drastically different alpine lake changes on Asia’s high plateaus during the past four decades. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Lu, H.; Yue, S.Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Lei, Y.B.; La, Z.; Wang, W. Quantifying recent precipitation change and predicting lake expansion in the Inner Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Chang. 2018, 147, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Zhu, L.; Yang, R. Temporal-spatial differences in lake water storage changes and their links to climate change throughout the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ding, Y.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Wang, S.L.; Jin, H.J. Estimates of the Reserves of Ground Ice in Permafrost Regions on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2010, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Sheng, Y.; Cao, W.; Li, J.; Ma, S.; Hu, X. Estimation of permafrost ice reserves in the source area of the Yellow River using landform classification. Adv. Water Sci. 2017, 28, 801–810. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Sheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Huang, L. Based on geomorphic classification to estimate the permafrost ground ice reserves in the source area of the Datong River, Qilian Mountains. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2020, 42, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Wu, Q.B.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, G.L. Stable isotopic evolutions of ground ice in permafrost of the Hoh Xil regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Quat. Int. 2017, 444, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Hinzman, L.D. Disappearing Arctic lakes. Science 2005, 308, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Hinzman, L.D. Shrinking thermokarst ponds and groundwater dynamics in discontinuous permafrost near Council, Alaska. Permafr. Periglac. Processes 2003, 14, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, B.; Verbyla, D.; McGuire, A.D. Shrinking ponds in subarctic Alaska based on 1950-2002 remotely sensed images. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Ma, W.; Li, G.; Niu, F.; Liu, Y.; Mao, Y. Impacts of supra-permafrost water ponding and drainage on a railway embankment in continuous permafrost zone, the interior of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 154, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Niu, F.; Luo, J.; Liu, M.; Yin, G. Thermal Regime at Bottom of Thermokarst Lakes along Qinghai-Tibet Engineering Corridor. Earth Sci. 2015, 40, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Zhelezniak, M.; Wang, D.; Ma, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhirkov, Z.A.; Gao, Q. Thermal interaction between a thermokarst lake and a nearby embankment in permafrost regions. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 155, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Landsat-5 TM | Landsat-7 ETM+ | Landsat-8 OLI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bands | Wavelength (μm) | Resolution (m) | Bands | Wavelength (μm) | Resolution (m) | Bands | Wavelength (μm) | Resolution (m) |
| 1-Blue | 0.45–0.52 | 30 | 1-Blue | 0.45–0.52 | 30 | 1-Coastal aerosol | 0.43–0.45 | 30 |
| 2-Green | 0.52–0.60 | 30 | 2-Green | 0.52–0.60 | 30 | 2-Blue | 0.45–0.51 | 30 |
| 3-Red | 0.63–0.69 | 30 | 3-Red | 0.63–0.69 | 30 | 3-Green | 0.53–0.59 | 30 |
| 4-NIR 1 | 0.76–0.90 | 30 | 4-NIR | 0.77–0.90 | 30 | 4-Red | 0.64–0.67 | 30 |
| 5-SWIR1 2 | 1.55–1.75 | 30 | 5-SWIR1 | 1.55–1.75 | 30 | 5-NIR | 0.85–0.88 | 30 |
| 6-Thermal | 10.40–12.5 | 120 | 6-Thermal | 10.40–12.5 | 60 | 6-SWIR1 | 1.57–1.65 | 30 |
| 7-SWIR2 | 2.08–2.35 | 30 | 7-SWIR2 | 2.08–2.35 | 30 | 7-SWIR2 | 2.11–2.29 | 30 |
| 8-Panchromatic | 0.52–0.9 | 15 | 8-Panchromatic | 0.50–0.68 | 15 | |||
| 9-Cirrus | 1.36–1.38 | 30 | ||||||
| TM/ETM+ Bands | OLI Bands | Equations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDWI | b2, b4 | b3, b5 | |
| MNDWI | b2, b5 | b3, b6 | |
| EWI | b2, b4, b5 | b2, b4, b6 | |
| NWI | b1, b4, b5, b7 | b2, b5, b6, b7 |
| Points | NDWI | MNDWI | EWI | NWI | Points | NDWI | MNDWI | EWI | NWI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LK 11 | 0.832 | 0.893 | 0.742 | 0.672 | R 31 | −0.01 | 0.025 | −0.327 | −0.563 |
| LK2 | 0.785 | 0.857 | 0.67 | 0.569 | R2 | 0.346 | 0.441 | 0.067 | −0.281 |
| LK3 | 0.704 | 0.797 | 0.554 | 0.473 | R3 | 0.061 | −0.088 | −0.35 | −0.629 |
| LK4 | 0.41 | 0.493 | 0.138 | 0.004 | R4 | 0.077 | 0.062 | −0.27 | −0.503 |
| LK5 | 0.577 | 0.663 | 0.36 | 0.03 | R5 | −0.119 | −0.194 | −0.467 | −0.692 |
| Average | 0.662 | 0.741 | 0.493 | 0.35 | Average | 0.071 | 0.049 | −0.269 | −0.534 |
| LD 21 | −0.295 | −0.345 | −0.591 | −0.792 | W 41 | −0.150 | −0.185 | −0.475 | −0.715 |
| LD2 | −0.288 | −0.361 | −0.595 | −0.794 | W2 | −0.233 | −0.180 | −0.506 | −0.712 |
| LD3 | −0.211 | −0.215 | −0.510 | −0.700 | W3 | −0.246 | −0.281 | −0.549 | −0.767 |
| LD4 | −0.189 | −0.261 | −0.521 | −0.729 | W4 | −0.161 | −0.085 | −0.440 | −0.630 |
| LD5 | −0.167 | −0.250 | −0.508 | −0.732 | W5 | −0.125 | −0.199 | −0.471 | −0.714 |
| Average | −0.230 | −0.286 | −0.545 | −0.749 | Average | −0.183 | −0.186 | −0.488 | −0.708 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Z.; Niu, F.; Li, G.; Mu, Y.; Chai, M.; He, P. The Outburst of a Lake and Its Impacts on Redistribution of Surface Water Bodies in High-Altitude Permafrost Region. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122918
Ding Z, Niu F, Li G, Mu Y, Chai M, He P. The Outburst of a Lake and Its Impacts on Redistribution of Surface Water Bodies in High-Altitude Permafrost Region. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(12):2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122918
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Zekun, Fujun Niu, Guoyu Li, Yanhu Mu, Mingtang Chai, and Pengfei He. 2022. "The Outburst of a Lake and Its Impacts on Redistribution of Surface Water Bodies in High-Altitude Permafrost Region" Remote Sensing 14, no. 12: 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122918
APA StyleDing, Z., Niu, F., Li, G., Mu, Y., Chai, M., & He, P. (2022). The Outburst of a Lake and Its Impacts on Redistribution of Surface Water Bodies in High-Altitude Permafrost Region. Remote Sensing, 14(12), 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122918