Abstract
Infrastructure is a fundamental sector for sustainable development and Earth observation has great potentials for sustainable infrastructure development (SID). However, implementations of the timely, large–scale and multi–source Earth observation are still limited in satisfying the huge global requirements of SID. This study presents a systematical literature review to identify trends of Earth observation for sustainable infrastructure (EOSI), investigate the relationship between EOSI and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and explore challenges and future directions of EOSI. Results reveal the close associations of infrastructure, urban development, ecosystems, climate, Earth observation and GIS in EOSI, and indicate their relationships. In addition, from the perspective of EOSI–SDGs relationship, the huge potentials of EOSI are demonstrated from the 70% of the infrastructure influenced targets that can be directly or indirectly derived from Earth observation data, but have not been included in current SDG indicators. Finally, typical EOSI cases are presented to indicate challenges and future research directions. This review emphasizes the contributions and potentials of Earth observation to SID and EOSI is a powerful pathway to deliver on SDGs.
1. Introduction
Sustainable infrastructure is one of the key paths, from research, policies, actions to impacts, for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of United Nations [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Infrastructure can impact about 72% of the 169 targets of 17 SDGs [1]. The investment of large–scale infrastructure, especially for developing countries, has been a priority for socio–economic development [4]. However, rapid infrastructure construction usually leads to different degrees of environmental and ecological issues, such as grassland, forest and wetland degradation [7,8,9], air, water and soil pollution [10,11], biodiversity loss [12] and temperature rise [13]. Sustainable infrastructure aims at developing methods and solutions for resilient and sustainable energy, water, solid waste, transport and digital communication facilities [1]. Therefore, sustainable infrastructure development (SID) is the key to address the infrastructure related environmental and ecological problems.
Emerging technologies become an increasingly critical support of current and future SID [14,15,16]. It is estimated that about 70% of SDG targets can be supported by technology innovation [15]. The recent advanced technologies for SID generally include following categories. First, clean and low–carbon technologies have been widely applied in industries to decrease emission intensive operations and reduce emissions during infrastructure construction and maintenance [17]. In addition, the development of artificial intelligence (AI) provides effective solutions and opportunities for SID [18,19]. More importantly, AI is helpful for the implementations of relevant technologies in SID, such as smart cities, internet of things, big data, cloud computing, BIM-GIS (building information modeling and geographical information science) integration, machine learning and deep learning [20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Studies have also demonstrated that AI may inhibit the achievement of 35% of SDG targets [18]. Third, blockchain can revolutionize knowledge and value of the whole life cycle of SID [22,27]. Blockchain technology is characterized in transparency, decentralization, openness, interconnection and sharing for more reliable and efficient life cycle assessment of SID [16,27,28]. The last but not least category of technologies for SID is the Earth observation technology, such as remote sensing [29,30], light detection and ranging (LiDAR) [31,32], unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) [33] and precise in–situ or ground observations [34,35]. In recent a few years, Earth observation has been increasingly applied in quantifying impacts of infrastructure on environment and ecosystems [30,32], due to its advantages in the timely and large–scale eco–environmental assessment [36,37,38,39]. In this study, the Earth observation technology for supporting SID will be systematically reviewed and analyzed.
There are still gaps and challenges in the Earth observation for sustainable infrastructure (EOSI). First, explicit goals of EOSI are increasingly required to guide decision making and actions. A key question is to convert requirements of SID to Earth observation based solutions to satisfy the requirements. Next, there are huge gaps between the global requirements of SID and limited Earth observation applications for the infrastructure sector. Sustainable infrastructure consists of diverse sectors, but the implementations of Earth observation in different sectors are unequal. For instance, topics of current EOSI studies primarily include green infrastructure [34], ecological assessment of infrastructure and surrounding environment [40,41], and developing sustainability indicators for infrastructure [42,43], but they are limited in solid waste and digital communication facilities. Finally, technology integration is a key difficulty for the implementation, leading to the lack of benchmark studies, due to the practical challenges in the interdisciplinary studies [44,45]. Thus, it is desired to develop innovative methodology and benchmark cases for reasonable implementations of technology integration in SID.
To address above issues, this study systematically reviews methods and applications of EOSI, identifies the imbalance between the requirements of sustainable infrastructure and the capacity of Earth observation, and explores challenges and future research directions for SID. Sections of this review are arranged as follows. Section 2 shows primary concepts and categories of sustainable infrastructure and the scope of this review. Section 3 analyzes trends of previous studies about EOSI using a bibliometric analysis from the perspective of the whole infrastructure system. Section 4 analyzes the relationship between EOSI and SDGs for each sector of infrastructure systems, and for each of the infrastructure influenced SDG targets. Section 5 summarizes five typical cases for the five sectors of infrastructure systems, respectively, to demonstrate the best practices of EOSI. Section 6 summarizes challenges and recommends future research directions about EOSI based on the literature review and analysis in this study. Section 7 concludes this review.
2. Concepts of Sustainable Infrastructure
Sustainable infrastructure can be described as infrastructure that is designed, constructed and maintained with socio–economic and environmental considerations and that can perpetuate and enhance the environment [46]. The objective of SID is to develop methods and solutions for resilient and sustainable infrastructure and facilities [1]. From the socio–economic perspective, sustainable infrastructure has benefits for adding value for infrastructure investment, finance and business [47,48], and for triggering the technology innovation [14,32] and the implementation of renewable energy [49]. Meanwhile, sustainable infrastructure should be delivered in compliance with labor standards and human rights [46,50]. From the eco–environmental perspective, the primary task of sustainable infrastructure is to decrease carbon and pollutant emissions during the whole life cycle of design, construction, maintenance and demolition [51,52,53]. More importantly, sustainable infrastructure should take an active role in protecting and enhancing ecosystems [54] and be resilient to global climate change [13].
3. Trends of Earth Observation for Sustainable Infrastructure (EOSI)
3.1. Data and Methods
The literature review of EOSI aims at describing application trends of previous studies and identifying research gaps between the requirements of SID and potentials of Earth observation. The data was collected from Web of Science using following search criteria:
- Topic (including title, abstract, and keywords): ((sustainab* OR green) AND infrastructure AND (“remote sensing” OR “Earth observation”))
- Publication Years: Before 2020 (inclusive)
- Research Areas: Areas in environment, geosiences, engineering, computer sciences and mathematics.
- Document types: Article and review
- Language: English
The analysis of literature in this part is presented from the perspective of the whole infrastructure systems, instead of sectors within infrastructure systems. Therefore, studies for individual sectors and specific cases of infrastructure, such as energy, transport, and water infrastructure, are not included in this analysis. Earth observation for individual sectors of infrastructure and typical cases are analyzed in Section 4 and Section 5, respectively.
A bibliometric analysis was applied to analyze research trends of EOSI in terms of publications, references, citations and information of literature. The bibliometric analysis is a quantitative method to describe and assess academic literature according to the information of bibliographies [55]. In this study, research trends and topics of EOSI were identified from the conceptual structure map regarding keywords and keyword co-occurrences network. The literature analysis was performed using R “bibliometrix” package [55]. The “bibliometrix” package is a powerful tool for statistical analysis and visualization of the bibliometric analysis.
3.2. Analysis
According to the search criteria, 271 academic publications have been collected. The publication years range from 1996 to 2020, where 74% of the research were published after 2015 (Figure 1). The rapid growth trend of publications demonstrates that studies of EOSI are attracting increasing research attentions in recent a few years and in the future, and they have great potentials for research and practice. In addition, in the publications, the top five most frequent keywords are “remote sensing”, “GIS”, “urbanization”, “green infrastructure” and “Earth observation”, which appear in 79, 23, 21, 18 and 14 publications, respectively. This means the collected publications are consistent with the topic and objective of the literature review. Top three areas in the Web of Science Categories are environmental sciences, remote sensing, and environmental studies. The total number of publications in the three areas accounts for 81% of all collected publications. Top ten countries of corresponding authors in terms of the number of publications include China (40), USA (40), India (22), Germany (20), Italy (16), United Kingdom (13), Australia (12), Turkey (11), Canada (7) and Spain (7).
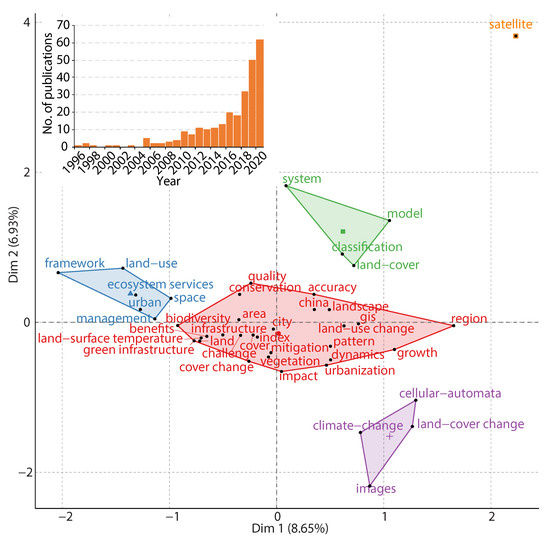
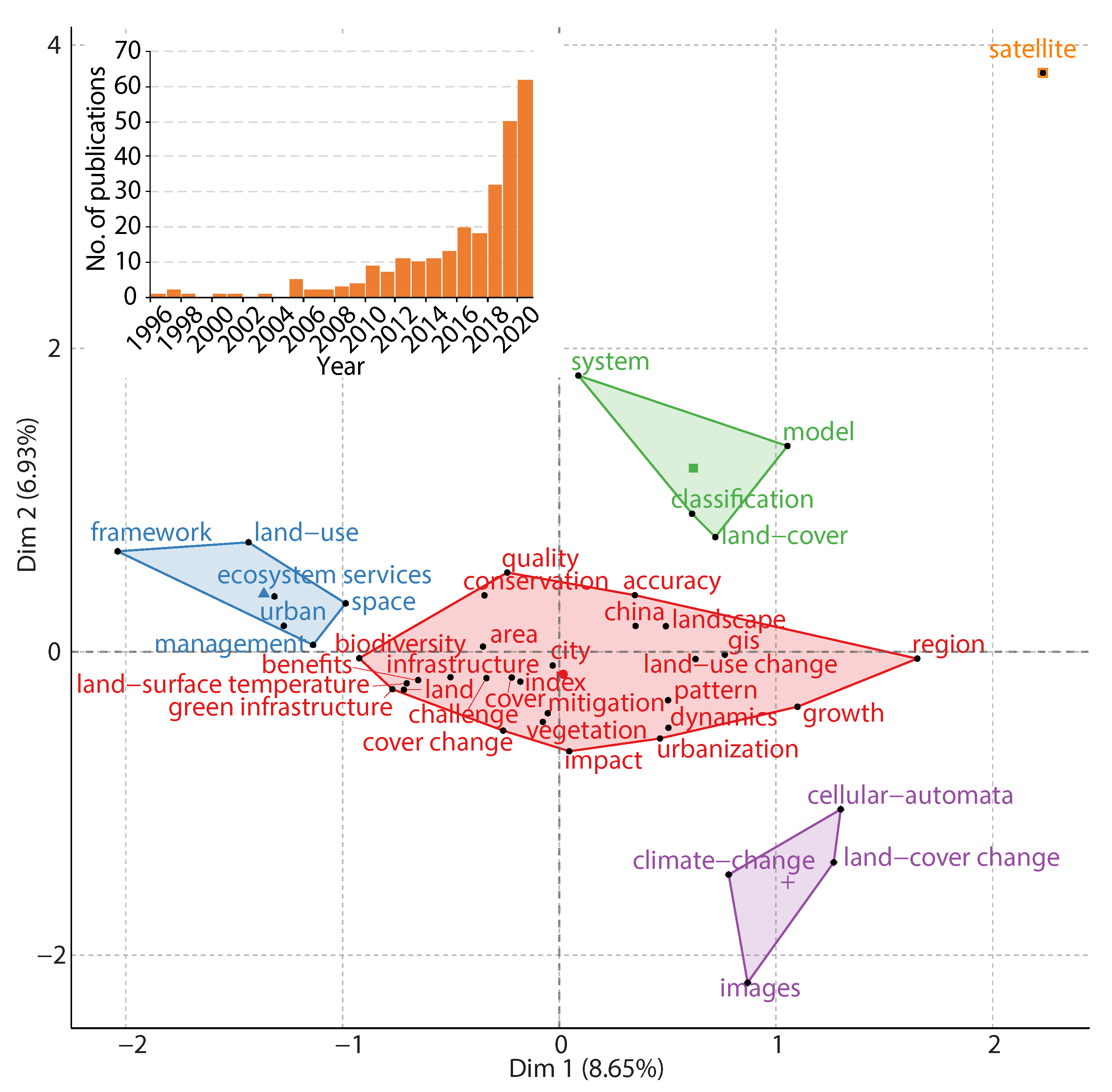
Figure 1.
Conceptual structure map of EOSI.
Figure 1 shows a conceptual structure map of EOSI in terms of keywords in literature. The two dimensions of the map demonstrate the highest variance for visualizing the average location of articles related to the keywords [55]. In this conceptual structure map, the dimensions 1 and 2 explain 8.7% and 6.9% of variances of the keywords, respectively. The location where dimension value is 0 indicates the midpoint of all articles of EOSI studies [55]. For instance, the keyword “city” is close to the midpoint, meaning that a large number of articles of EOSI highlight city studies. The conceptual structure map includes five groups of primary concepts related to EOSI. The largest group (red) of concepts located at the center of the map includes terms related to infrastructure (e.g., infrastructure and green infrastructure), ecosystems (e.g., biodiversity, landscape, conservation, and vegetation), urbanization (e.g., city, growth and urbanization), Earth observation (e.g., land surface temperature, land, land cover change, and land use change) and geospatial models (e.g., GIS and accuracy). This group of concepts demonstrates a general approach to address EOSI issues: using Earth observation data and geospatial models to assess contributions of infrastructure to urbanization and infrastructure impacts on ecosystems. Another four groups of concepts are urban space management and ecosystem services (blue), land cover modeling (green), climate change and land cover change investigation (purple), and satellite data (orange). These concepts present the essential technical and management topics in EOSI.
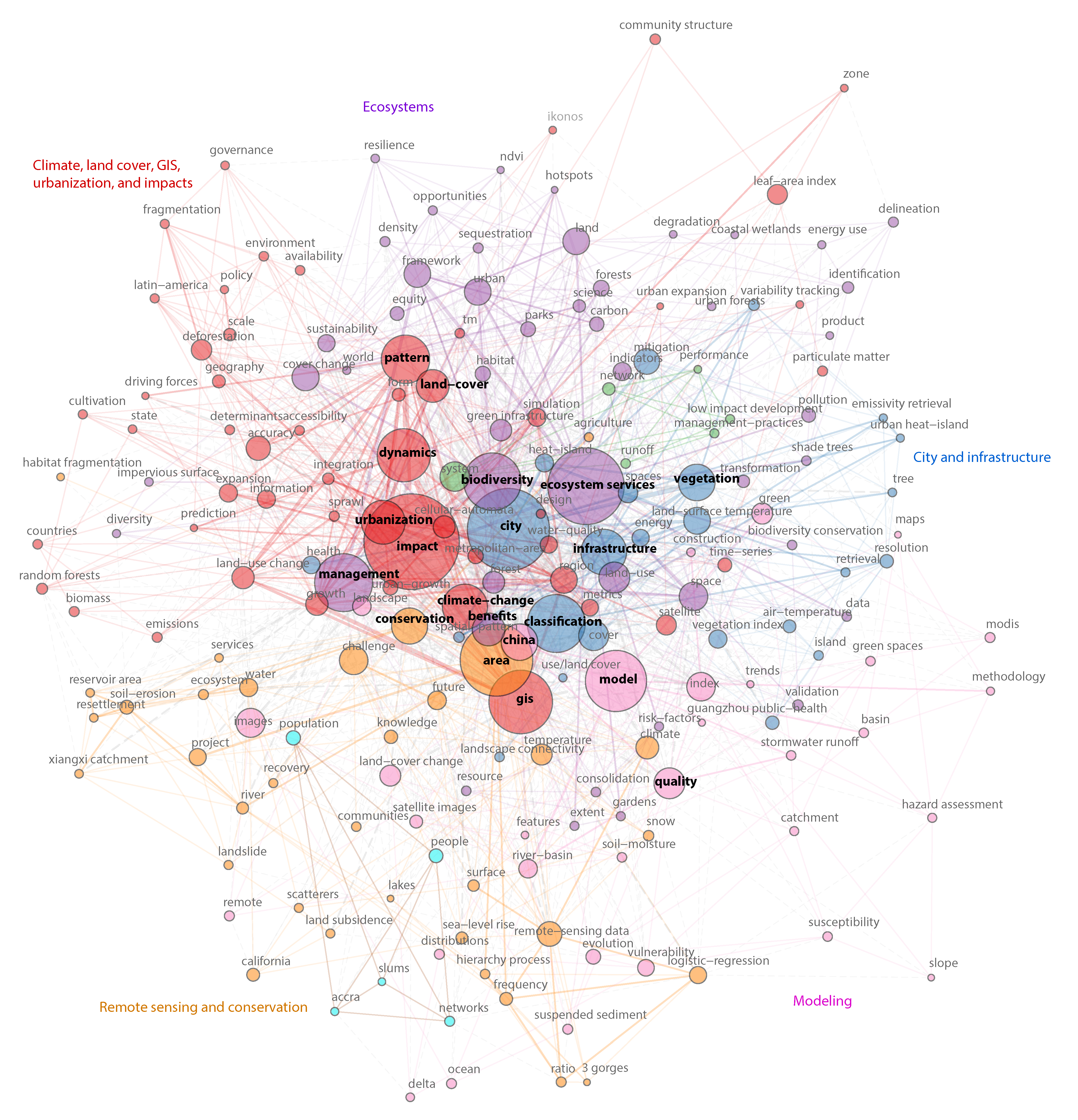
Figure 2 shows the keyword co–occurrences network of EOSI in a word cloud form, where the top 200 keywords according to frequency and their links are visualized. In the figure, top 20 keywords are marked with black color and other keywords are shown in gray color. The sizes of circles show the frequency of keywords, and the widths of lines and distances of circles illustrate the closeness of keywords, which were identified from co–citation information of publications. According to the distributions and links of keywords, the network includes five primary clusters. The first cluster primarily consists of keywords related to the “city and infrastructure” (blue), such as city, infrastructure, vegetation, classification, land surface temperature, heat island, health, mitigation, etc. The second cluster characterizes “ecosystems” (purple) with keywords ecosystem services, biodiversity, management, forest, land, habitat, sustainability, parks, etc. The third cluster presents the relationships of “climate, land cover, GIS, urbanization and impacts” (red), which includes seven of the top 20 keywords: impact, GIS, dynamics, pattern, climate change, urbanization and land cover. The fourth cluster contains keywords related to “remote sensing and conservation” (orange), such as area, conservation, remote sensing data, water, etc. The last cluster primarily covers “modeling” (light red) related keywords: model, quality, index, methodology, MODIS, etc. The brief summaries of clusters are not absolutely consistent with keywords within clusters, since all clusters are interacted with each other through locations and links on the network. This phenomenon is identical with practical issues of EOSI that contain different combinations of topics, objectives, data and methods.
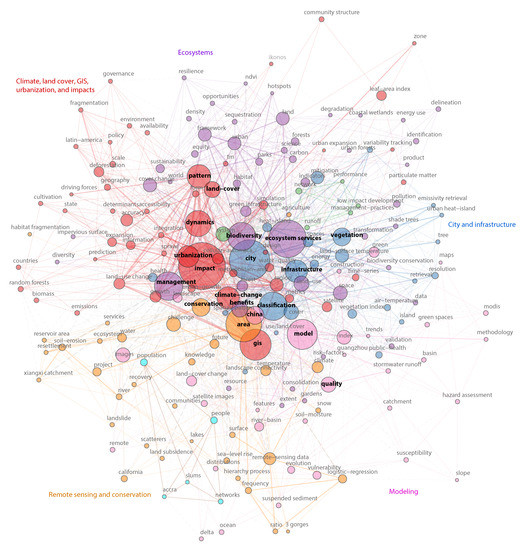
Figure 2.
Keyword co–occurrences network of EOSI.
In addition to above five primary clusters, the network also includes two small clusters. One cluster is the keywords with green circles distributed between “city and infrastructure” and “ecosystems”. The keywords include system, network, runoff, low impact development, management practices and performance. This cluster shows a few studies that apply strategies and management practices to reduce impacts of infrastructure and urban development on ecosystems, especially hydrologic performance [56,57,58]. Another cluster is the keywords with light blue circles, such as populations, people and slums, located near the cluster of remote sensing and conservation. This cluster highlights the relationship between human activities and environment.
In summary, the conceptual structure map and keyword co–occurrences network demonstrate the close associations of infrastructure, urban development, ecosystems, climate, Earth observation and GIS in EOSI. The interactions among the first three clusters reveal the trade–offs between the benefits of infrastructure to cities and urbanization, and the pressures on ecosystems and environment from infrastructure. In addition, it is common that Earth observation data and geospatial models are usually simultaneously utilized to address EOSI issues.
4. EOSI and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
4.1. Concepts and Scope
The targets of SDGs are effective indicator tools for identifying interactions, benchmark studies and gaps of EOSI [59]. Sustainable infrastructure is directly or indirectly associated with about 72% (121/169) of the targets of SDGs [1]. Simultaneously, Earth observation can contribute large-scale and timely data for about 18% (30/231) indicators across the targets of SDGs, where 70% of the data have been available in the Global SDG Indicators Database [60,61].
In this review, the relationship between EOSI and SDGs is analyzed by comparing each SDG target and previous Earth observation–based case studies. In the analysis, the relevant concepts and assumptions are presented. First, infrastructure is classified into five types according to the definition presented by [1], including energy, transport, water, solid waste and digital communications. The direct and indirect influences of infrastructure on SDG targets have been justified in [1]. Only the targets affected by infrastructure shown in [1] are assessed in this review.
In addition, Earth observation data for indicators and targets of SDGs is classified into four categories according to their contributions to SDG targets, consisting of available, direct, indirect and irrelevant indicators. A direct relationship exists when EOSI can be used to calculate or directly contribute to relevant SDG targets. For instance, nighttime lights obtained through EO can be used to calculate economic indicators, thus a direct relationship is observed. On the other hand, an indirect relationship exists when EOSI data cannot do so. For example, EOSI can support the access of fishers to markets (SDG 14.b) by providing physical and virtual access through transport and digital communications, and support the development of effective, accountable, and transparent institutions (SDG 16.6) by assessing performance of public infrastructure, but it is not the predominant factor of these targets. Therefore, the classification of EOSI in terms of SDG targets is carried out according to following steps.
- If Earth observation data has been used in the Global SDG Indicators Database?
- –
- If “Yes”, the EOSI is an available indicator.
- –
- If “No”, are there any direct relationships between EOSI and SDG targets according to case studies in literature?
- ∗
- If “Yes”, the EOSI is a direct indicator that can be potentially used in SDG targets.
- ∗
- If “No”, are there any indirect relationships between EOSI and SDG targets according to case studies in literature?
- ·
- If “Yes”, the EOSI is an indirect indicator that can be potentially used to support achieving SDG targets.
- ·
- If “No”, the EOSI is an irrelevant indicator.
The available indicators are data of Earth observation that can exactly match the required indicators of SDGs [60] and have been used in the Global SDG Indicators Database [61]. Currently, at least 21 Earth observation based SDG indicators have been implemented in the SDG Indicators Database [60]. The direct indicators that can be potentially used in SDG targets are derived from Earth observation-based data products and models from case studies in literature, such as global raster data of population, economy, poverty and disease. A large number of data products are currently available at open data portals for direct applications and other data should be computed using mathematical and geospatial models according to literature. The potential indicators also can be indirect indicators of SDG targets. They may have indirect, partial or weak associations with SDG targets, but they can still be applied to support achieving SDGs. In general, data of indirect indicators should be processed and analyzed to derive parts of SDG indicators. The data processing generally includes data collection, processing, modeling, computations, assessment and validation.
4.2. Analysis
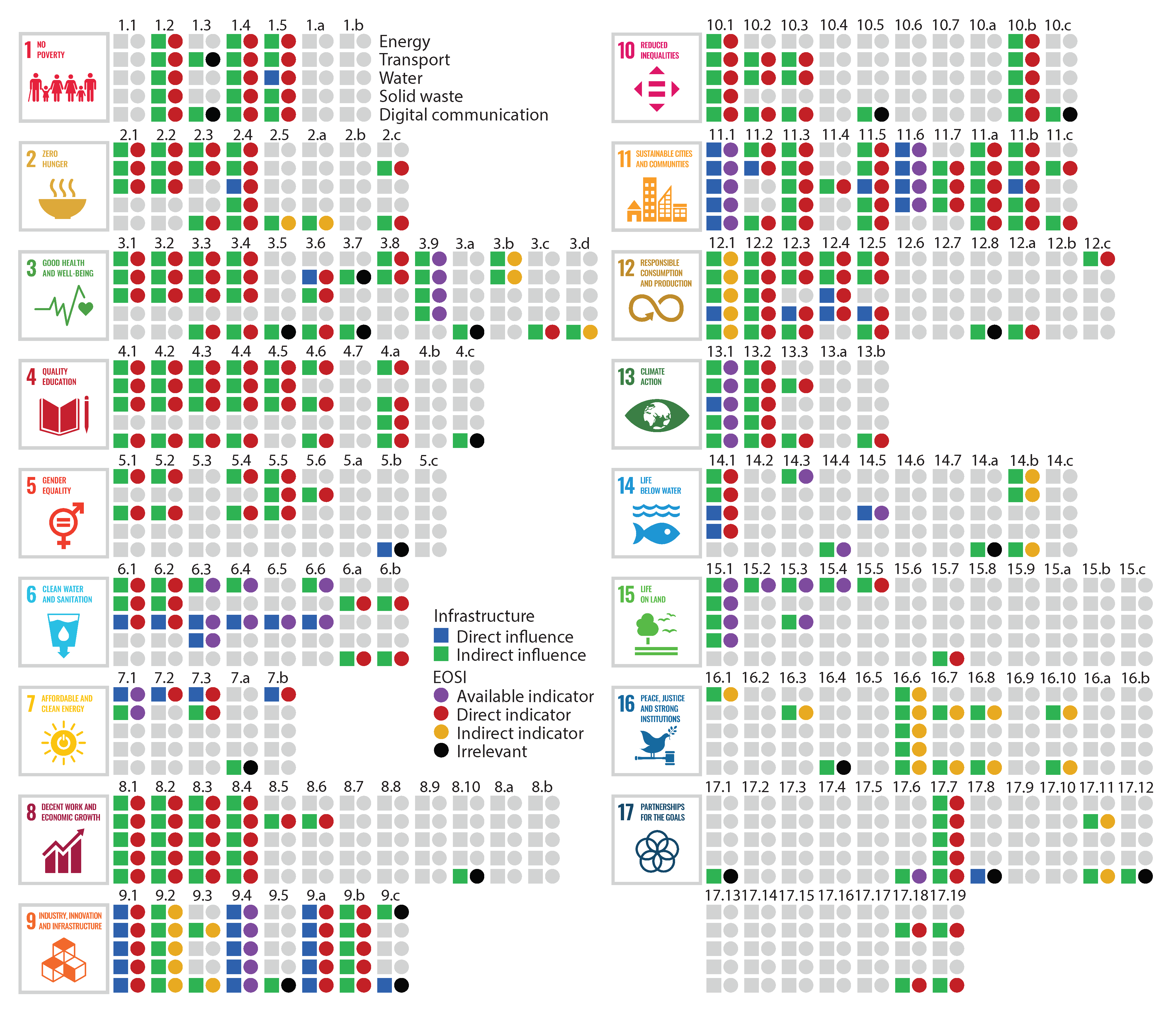
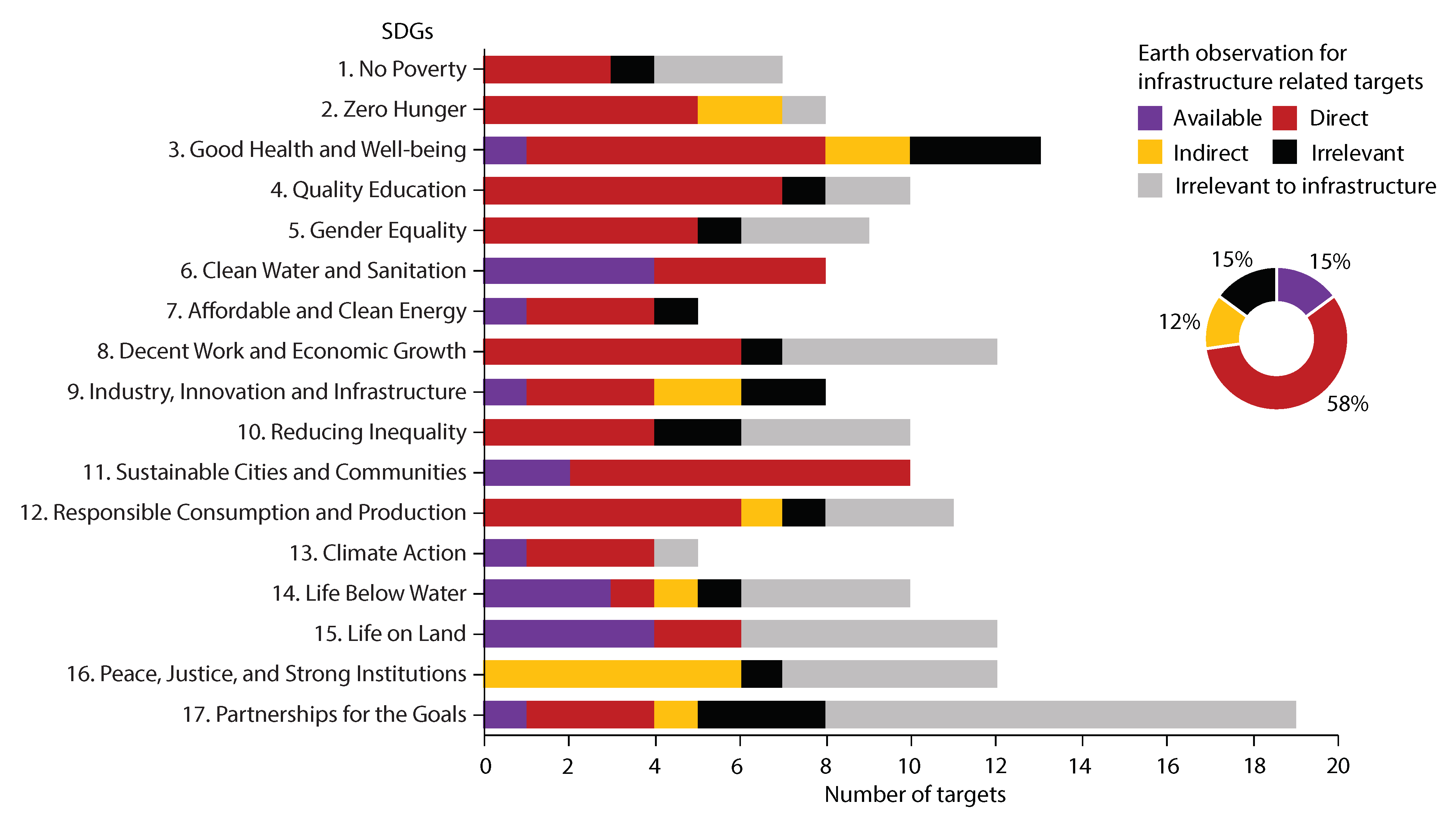
Figure 3 shows the relationship between EOSI and SDGs according to targets and indicators clarified in [61] and case studies in literature, such as [39,60,62,63,64,65]. In the figure, data of the direct and indirect influences of infrastructure on SDG targets are sourced from the infrastructure influence justification presented in [1]. Results show that the distribution of EOSI categories is critically varied for different targets. For instance, Earth observation based indicators have been available for at least two infrastructure influenced targets for SDG 6, 11, 14 and 15, but more than half of the infrastructure influenced targets cannot be derived from available or direct Earth observation indicators for SDG 9 and 16.
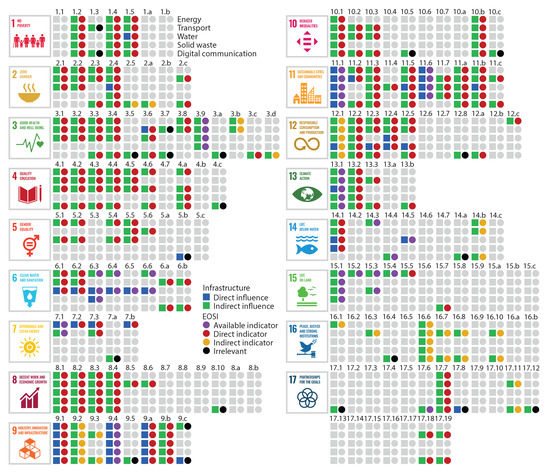
Figure 3.
The relationship between Earth observation for sustainable infrastructure (EOSI) and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The direct and indirect influences of infrastructure on SDG targets are adapted from the infrastructure influence justification in [1] and the relationship between EOSI and each target is identified from case studies in literature, such as [39,60,62,63,64,65]. Meanings of SDG targets, explanations to each target, and corresponding references are available at Supplementary Materials Table S1 (https://yongzesong.github.io/EOSI, accessed on 10 April 2021) [1,2,20,39,50,60,62,63,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164,165,166,167,168,169,170,171,172].
More importantly, the interaction between different categories of infrastructure and the support of Earth observation shows a full picture of current efforts and future potentials of EOSI (Figure 4). In total, there are 30 types of interactions regarding infrastructure category, direct or indirect influence of infrastructure and EOSI. The interactions are explained from following aspects. First, the available indicators are confirmed data that can support SID and most of the case studies in literature about EOSI have been performed for this type of indicators. For instance, for SDG 11.1 that the access to living space and services should be ensured [6], all infrastructure have direct influence on the target and Earth observation based indicators have been available in the official database [60,61], where the data have been assessed in recent case studies [173,174]. In addition, the summary indicates that the Earth observation for indirect influenced targets of infrastructure is the predominant one for all five categories of infrastructure. This means a considerable part of SDG targets will be achieved with the indirect influence of infrastructure, and these targets can be assessed with direct Earth observation data that have not yet been formally used in the Global SDG Indicators Database. For instance, SDG 11.3 is to enhance “sustainable urbanization and human settlement planning” [6] and all infrastructure have indirect influence on this target. Earth observation data, such as Landsat satellite images, Land–Use/Cover data, Defense Meteorological Satellite Program/Operational Linescan System (DMSP/OLS) nighttime light data, Human Settlement data, urban impervious surface data, and population grid data, have been applied in estimating land consumption rate [175] and identifying urban land use efficiency [176,177,178,179]. Finally, the indirect Earth observation indicators are primarily used for assessing targets indirectly influenced by infrastructure. For instance, SDG 9.2 is to “promote sustainable industrialization” and improve industry–related employment and economic growth [6], which is indirectly affected by infrastructure sectors since studies have demonstrated that the infrastructure quality can impact industrial productivity and economic growth [180,181]. Earth observation data, such as climate, soil, flood and storm data, have been used to assess the quality of different types of infrastructure in case studies of literature [71,182,183,184].
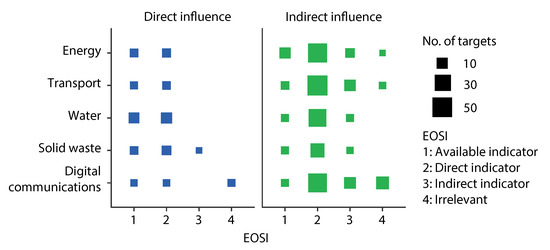
Figure 4.
A summary of the interaction between different categories of infrastructure and EOSI.
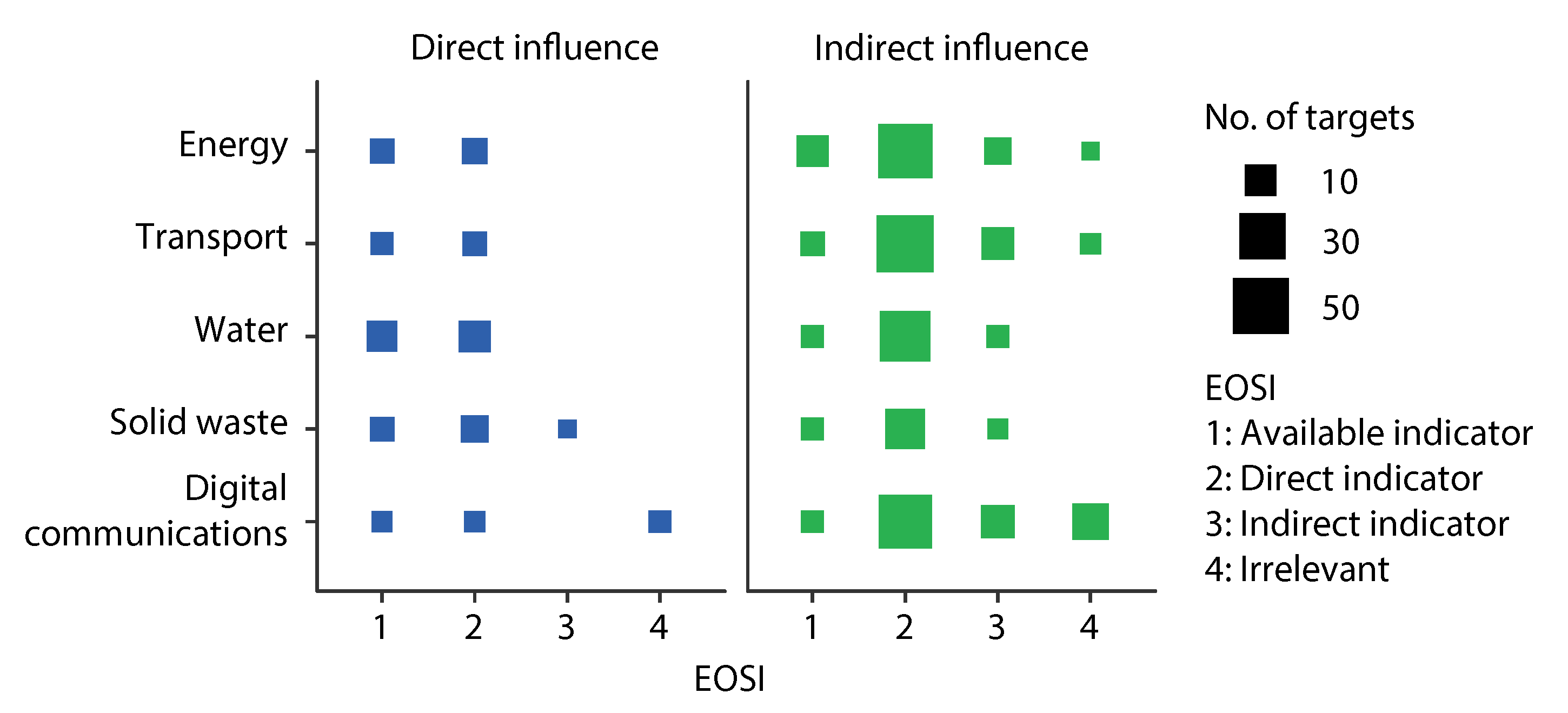
Figure 5 shows a statistical summary of the relationship between EOSI and SDGs. The analysis demonstrates that among the 121 infrastructure influenced SDG targets, about 15% of the targets already have Earth observation based indicators and 15% of the targets are currently irrelevant to Earth observation according to the literature that we have collected. About 58% and 12% of the targets have direct and indirect indicators, respectively, that potentially can be applied in SDG assessment, characterization and decision making. This means about 70% of the infrastructure influenced targets can be directly or indirectly supported by Earth observation, but have not been included in current SDG indicators, which indicates a huge potential of Earth observation in achieving SID. The literature also show a critical challenge that benchmark case studies are only available for a part of the indicators.
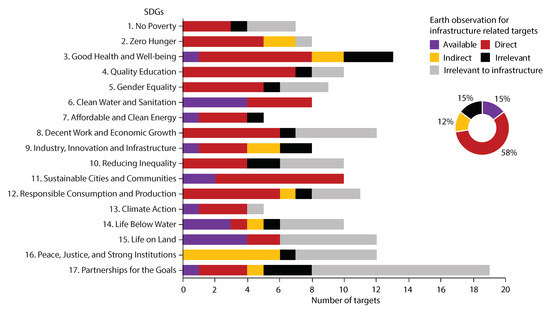
Figure 5.
A statistical summary of the relationship between EOSI and SDGs.
5. Typical Cases of EOSI
According to the analysis of literature, a few typical cases of EOSI were presented for each of the five categories of infrastructure, including energy, transport, water, solid waste, and digital communication facilities, with the consideration of SDGs. First, Earth observation has been used in the sustainable infrastructure assessment of both traditional and renewable energy. For instance, Earth observation has been applied in site selection and the estimation of carbon emissions and air pollution for both traditional fossil fuel power plant [185,186] and renewable-energy power plants, such as hydroelectric power plant [187], wind power plant [188], thermal power plant [189], solar power plant [119] and nuclear power plant [190]. In general, the issues of implementing Earth observation for satisfying requirements of policy and planning of renewable energy infrastructure contain four aspects: addressing scalar discordance across various regions, estimating interactions of complex geographical factors for determining potentials of renewable energy, developing technical plans regarding distributions of energy resources, and generating geospatial indicators for identifying priorities of recovery lands [191].
Second, Earth observation has been applied in the whole life cycle assessment of transportation infrastructure, such as roads, railways, ports and airports. As analyzed in Figure 3, a large number of SDG targets can be directly or indirectly achieved by improving population accessibility to facilities through transport. Earth observation for more efficient and accurate modeling have been applied in improving the provision of urban green space for residents [192], minimizing urban–rural inequality in accessing public facilities [53,71], engaging rural and remote residents to work to decrease poverty incidences and achieve gender equality [1,193,194], etc. In addition, land, climate and environmental factors of infrastructure performance have been derived from Earth observation to estimate risks, disasters and future scenarios of performance [195,196].
Third, a number of cases have demonstrated the capacity of Earth observation in the sustainable water infrastructure development. For instance, Delanka–Pedige, H.M.K., et al. developed a sustainability evaluation system for wastewater infrastructure that aimed at delivering on SDG 6 for ensuring water and sanitation availability for all, SDG 11 for enabling resilient future cities, and other wastewater related SDGs [197]. The sustainability evaluation system contains 36 parameters in five categories: high–quality water, safe pathogen, energy, biofertilizers, and emissions during the recovery from wastewater [197]. This study demonstrates the active contributions of sustainable wastewater infrastructure to the urban sustainable development. In addition, a study performed in China indicates that 60% of greenhouse gas emissions can be decreased from the water infrastructure under the most productive urbanization scenario that is characterized in a free migration rule, firmly planned space of cities, and the utilization of water techniques [198].
Fourth, Earth observation data can help direct and evaluate infrastructure for solid waste. Solid waste is critically increased in recent years, and the efficiency of regional and inter–regional solid waste management has been significantly improved with the support of Earth observation techniques. The applications include the optimization of placing landfill and waste bins, simplification of waste disposal, and assessment of ecological impacts of buried waste [147].
Finally, the integration of Earth observation and digital communication facilities can provide powerful solutions for achieving SDGs. Digital communication infrastructure is one of the key components of sustainable and smart cities, which aim at improving the quality of life of residents with technological solutions. Petrova–Antonova D., et al. developed a digital twin based methodological framework for developing smart solutions for cities with a cycle of sensing, data collection, analysis and actions [199], where digital communication facilities and Earth observation techniques can provide multi–source and multi–scale data for various elements of cities. The digital twin based framework brings physical and virtual sectors together to address the issues of sustainable and smart cities, such as green space, safe community, happy cities, and accessible public facilities [199].
6. Challenges and Future Directions
Earth observation techniques have great advantages over long–term and large–scale infrastructure planning, management and environmental impact assessment for delivering on the SDGs. However, methods and typical cases are still limited to address EOSI issues. In this study, the literature analysis on the relationship between EOSI and SDGs reveals that 70% of potential Earth observation based indicators are still not available for the infrastructure influenced SDG targets. In addition, EOSI studies still face numerous challenges, such as the data availability of large–scale infrastructure, gaps between SDGs and practical actions, the development of innovative solutions to deliver on SDGs, gaps between advanced research and practices, gaps between Earth observation big data and local implementations and decisions, the integration of emerging technologies, the development of innovative methods to address the sophisticated issues in developing countries, etc. To resolve the challenges, we have summarized the advanced topics of EOSI in future studies.
First, methods are required to integrate multi–source and multi–scale Earth observation data and geospatial models to develop social indicators for practical SID solutions, making decisions, and benefiting communities. In recent a few years, the scope of Earth observation has been enlarged, covering space–borne, airborne, ground–based and internet–based earth big data [3,200]. This means Earth observation not only consists of optimal remote sensing, synthetic–aperture radar (SAR), drone photogrammetry, light detection and ranging (LiDAR), in–situ and ground observations, but also include web, mobile and social media based geotagged text, images and videos [3,201]. In addition, the development of geospatial models, machine learning and deep learning, provides opportunities to investigate and reasonably apply Earth observation in SID. Typical examples are the social issues indirectly influenced by infrastructure and can be partially supported by Earth observation. For instance, SDG 5.5, “ensuring women’s participation and equal opportunities for leadership and decision making” [6], is primarily delivered through policies about gender equality. However, it is also indirectly affected by energy, transport and water infrastructure, since the provision of accessible energy and water infrastructure through transport enables time and opportunities for women to be more engaged in public life and activities [1]. As we summarized in the typical cases, Earth observation has been applied in the site selection and environmental impact assessment of energy and water infrastructure [185,186], the identification of poverty and remote communities [202,203,204], and the population accessibility analysis through transport network [71]. Therefore, it is highly recommended to spend efforts in implementing the multi–source Earth observation based outcomes of infrastructure development to social issues and SDGs in future research.
Next, methods and typical case studies are increasingly needed to integrate Earth observation with other emerging technologies in the EOSI field. The complexity of implementing the technologies in infrastructure development practice and the concepts for seamless and effective integration are primary challenges for the applications of technology integration. Recent cases have demonstrated the potentials of the emerging technology integration for improving capacity and applicability of Earth observation. For instance, Google Earth Engine (GEE) is an innovative cloud computing platform of Earth observation big data for research, practice and decision making [205,206], such as mapping flood [207], land cover [208,209,210], and natural hazards [211]. However, few cases are available about GEE for supporting infrastructure development. Therefore, it is expected that the creative technology integration can be applied in EOSI issues, such as cloud computing for earth big data applications, digital twin for sustainable and smart cities, and blockchain for sustainable infrastructure management. In the process, stakeholders from various fields and stages should work together for SID, including authorities, professionals, project investigators, construction sectors, as well as individuals [212,213].
Third, actions should be taken to enable Earth observation data driven resilient infrastructure in response to climate change and natural hazards. The quality of infrastructure systems are essentially affected by temperature rise [13], temperature extremes, cyclones, storms [214], earthquakes, flooding [2], bushfire, heavy rain and snow, landslides, and volcanic eruptions [215]. A primary role of Earth observation in natural hazards management is to map, assess and predict risks and impacts of the hazards on infrastructure [216]. In addition, Earth observation also has active contributions to the recovery of infrastructure and communities after the hazards [217].
The last but not least opportunity for future research is to satisfy the critically increased requirements of SID in developing countries. In recent a few years, developing countries have the largest market of infrastructure investment and construction. However, they still suffer from difficulties and inequality of accessing infrastructure of electricity, water, health care and education [218]. At the same time, they are facing high environmental pressure from infrastructure construction, together with the related densely populated cities and the shortage of low–emission technologies of construction and energy. The middle–income, low–income and small island developing countries may face more severe and sophisticated challenges [219,220]. To address the issues, localization strategies and whole systems of plans, policies, technologies, talents, standards, measurements and methods should be built for EOSI [50,221,222,223].
There are still limitations in EOSI. As discussed in this review, it is impossible to deliver all sustainable development strategies and actions with EOSI. Thus, it is essential to identify the direct, indirect, and irrelevant relationships between EOSI and issues of sustainable development, and integrate EOSI with other technologies to develop effective solutions for sustainable development.
7. Conclusions
Earth observation has great potentials for sustainable infrastructure development. Infrastructure can contribute to 72% of SDGs, and EOSI can benefit about 85% of infrastructure influenced SDGs and 61% of all SDGs. This review first uses a conceptual structure map and keyword co–occurrences network to reveal the close associations of infrastructure, urban development, ecosystem, climate, Earth observation and GIS in EOSI. The interactions of keyword clusters indicate the relationship between the increased needs of infrastructure to cities and urbanization, and the high pressures on ecosystems and environment from infrastructure, especially in developing countries. It is common that Earth observation data and geospatial models are usually simultaneously utilized to address EOSI issues. In addition, this review reveals that the Earth observation has been implemented in only 15% of infrastructure influenced SDG targets. From the perspective of EOSI-SDGs relationship, the huge potentials of EOSI are demonstrated from the 58% and 12% infrastructure influenced targets that can be directly or indirectly derived from Earth observation data, respectively, but have not been included in SDG indicators. Finally, typical EOSI cases of five types of infrastructure have been explained to identify challenges and future research directions.
In future studies, this review recommends that more Earth observation–related indicators can be developed for SDG targets, emerging technologies and Earth observation can be integrated to develop more typical cases, actions of EOSI are required to address climate change and natural hazards related challenges, and methods and strategies should be developed to satisfy the increased requirements of SID in developing countries. This review emphasizes the contributions and potentials of latest Earth observation to the infrastructure sector of sustainable development and EOSI is a powerful pathway to deliver on SDGs.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://yongzesong.github.io/EOSI, accessed on 10 April 2021, Table S1. Explanations to the relationship between Earth observation for sustainable infrastructure (EOSI) and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S. and P.W.; methodology, Y.S.; software, Y.S.; formal analysis, Y.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.S.; writing—review and editing, P.W.; visualization, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by the Australian Government through the Australian Research Council’s Discovery Project grant number DP180104026.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in Supplementary Materials at https://yongzesong.github.io/EOSI, accessed on 10 April 2021.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Thacker, S.; Adshead, D.; Fay, M.; Hallegatte, S.; Harvey, M.; Meller, H.; O’Regan, N.; Rozenberg, J.; Watkins, G.; Hall, J.W. Infrastructure for sustainable development. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koks, E.E.; Rozenberg, J.; Zorn, C.; Tariverdi, M.; Vousdoukas, M.; Fraser, S.; Hall, J.; Hallegatte, S. A global multi-hazard risk analysis of road and railway infrastructure assets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asensio, O.I.; Alvarez, K.; Dror, A.; Wenzel, E.; Hollauer, C.; Ha, S. Real-time data from mobile platforms to evaluate sustainable transportation infrastructure. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebbington, A.; Chicchon, A.; Cuba, N.; Greenspan, E.; Hecht, S.; Bebbington, D.H.; Kandel, S.; Osborne, T.; Ray, R.; Rogan, J.; et al. Opinion: Priorities for governing large-scale infrastructure in the tropics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21829–21833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chester, M.; Underwood, B.S.; Allenby, B.; Garcia, M.; Samaras, C.; Markolf, S.; Sanders, K.; Preston, B.; Miller, T.R. Infrastructure resilience to navigate increasingly uncertain and complex conditions in the Anthropocene. Npj Urban Sustain. 2021, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN General Assembly. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; UN General Assembly: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hosonuma, N.; Herold, M.; De Sy, V.; De Fries, R.S.; Brockhaus, M.; Verchot, L.; Angelsen, A.; Romijn, E. An assessment of deforestation and forest degradation drivers in developing countries. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 044009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebbington, A.J.; Bebbington, D.H.; Sauls, L.A.; Rogan, J.; Agrawal, S.; Gamboa, C.; Imhof, A.; Johnson, K.; Rosa, H.; Royo, A.; et al. Resource extraction and infrastructure threaten forest cover and community rights. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 13164–13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatowitsch, S.M. Natural and anthropogenic drivers of wetland change. In The Wetland Book II: Distribution, Description, and Conservation; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 359–367. [Google Scholar]
- Balaguera, A.; Carvajal, G.I.; Albertí, J.; Fullana-i Palmer, P. Life cycle assessment of road construction alternative materials: A literature review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 132, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, J. Urban traffic infrastructure investment and air pollution: Evidence from the 83 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- zu Ermgassen, S.O.S.E.; Utamiputri, P.; Bennun, L.; Edwards, S.; Bull, J.W. The role of “no net loss” policies in conserving biodiversity threatened by the global infrastructure boom. One Earth 2019, 1, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, B.S.; Guido, Z.; Gudipudi, P.; Feinberg, Y. Increased costs to US pavement infrastructure from future temperature rise. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, D.; Lu, Z.; Crittenden, J.; Mao, G.; Wang, S.; Zou, H. Research Development on Sustainable Urban Infrastructure From 1991 to 2017: A Bibliometric Analysis to Inform Future Innovations. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herweijer, C.; Combes, B.; Gawel, A.; Larsen, A.E.; Davies, M.; Wrigley, J.; Donnelly, M. Unlocking Technology for the Global Goals; World Economic Forum, PwC: Cologny, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Di Vaio, A.; Varriale, L. Blockchain technology in supply chain management for sustainable performance: Evidence from the airport industry. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.W.; Celia, M.A. Infrastructure to enable deployment of carbon capture, utilization, and storage in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8815–E8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinuesa, R.; Azizpour, H.; Leite, I.; Balaam, M.; Dignum, V.; Domisch, S.; Felländer, A.; Langhans, S.D.; Tegmark, M.; Nerini, F.F. The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, D.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dai, N.; Song, Y.; Chen, H. Artificial Intelligence in Sustainable Energy Industry: Status Quo, Challenges and Opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshri, B.; Hu, A.; Adelson, P.; Chen, X.; Dupas, P.; Weinstein, J.; Burke, M.; Lobell, D.; Ermon, S. Infrastructure quality assessment in africa using satellite imagery and deep learning. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 616–625. [Google Scholar]
- Alreshidi, E. Smart sustainable agriculture (SSA) solution underpinned by internet of things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI). Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogo, E.M.; Salami, A.F.; Nwulu, N.I.; Aigbavboa, C.O. Blockchain and internet of things-based technologies for intelligent water management system. In Artificial Intelligence in IoT; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 129–150. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Jeong, Y.S.; Park, J.H. A deep learning-based IoT-oriented infrastructure for secure smart city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 60, 102252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Tan, Y.; Wu, P.; Sutrisna, M.; Cheng, J.C.; Hampson, K. Trends and opportunities of BIM-GIS integration in the architecture, engineering and construction industry: A review from a spatio-temporal statistical perspective. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, B.; Horanont, T.; Aryal, J. Deep Learning-Based Semantic Segmentation of Urban Features in Satellite Images: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefrin, O.; Riese, F.M.; Keller, S. Deep Learning for Land Cover Change Detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, A.; Wang, J.; Fenner, A. Exploring the feasibility of blockchain technology as an infrastructure for improving built asset sustainability. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2019, 10, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Application of blockchain technology in smart city infrastructure. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Smart Internet of Things (SmartIoT), Xi’an, China, 17–19 August 2018; pp. 276–2766. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guindon, B. Using satellite remote sensing to survey transport-related urban sustainability: Part 1: Methodologies for indicator quantification. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2006, 8, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, L.; Friesen, J.; Altherr, L.C.; Meck, M.; Pelz, P.F. A holistic concept to design optimal water supply infrastructures for informal settlements using remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonczak, B.; Kontokosta, C.E. Large-scale parameterization of 3D building morphology in complex urban landscapes using aerial LiDAR and city administrative data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 73, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacasse, S. Innovation Reduces Risk for Sustainable Infrastructure. In CIGOS 2019, Innovation for Sustainable Infrastructure; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Sestras, P.; Bilasco, S.; Roșca, S.; Dudic, B.; Hysa, A.; Spalevi, V. Geodetic and UAV Monitoring in the Sustainable Management of Shallow Landslides and Erosion of a Susceptible Urban Environment. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, S.; Georgiev, G.; Georgieva, M.; Gluschkova, M.; Chepisheva, V.; Mirchev, P.; Zhiyanski, M. Integrated assessment of urban green infrastructure condition in Karlovo urban area by in-situ observations and remote sensing. One Ecosyst. 2018, 3, e21610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattinzioli, T.; Sol-Sánchez, M.; Martínez, G.; Rubio-Gámez, M. A critical review of roadway sustainable rating systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.E. Remote Sensing for Sustainable Forest Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Foody, G.M. Remote sensing of tropical forest environments: Towards the monitoring of environmental resources for sustainable development. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4035–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, F.; Daniel, J.; Jackson, L.; Neale, A. Earth observation-based ecosystem services indicators for national and subnational reporting of the sustainable development goals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 244, 111796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J. Earth observations and geographic information science for sustainable development goals. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Dur, F. Developing a sustainability assessment model: The sustainable infrastructure, land-use, environment and transport model. Sustainability 2010, 2, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, T.L.; Shackleton, R.T.; Förster, J.; Dini, J.; Khan, A.; Gumula, M.; Kubiszewski, I. Achieving the national development agenda and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through investment in ecological infrastructure: A case study of South Africa. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 27, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wright, G.; Wu, P.; Thatcher, D.; McHugh, T.; Li, Q.; Li, S.J.; Wang, X. Segment-based spatial analysis for assessing road infrastructure performance using monitoring observations and remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Thatcher, D.; Li, Q.; McHugh, T.; Wu, P. Developing sustainable road infrastructure performance indicators using a model-driven fuzzy spatial multi-criteria decision making method. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswami, A.; Weible, C.; Main, D.; Heikkila, T.; Siddiki, S.; Duvall, A.; Pattison, A.; Bernard, M. A social-ecological-infrastructural systems framework for interdisciplinary study of sustainable city systems: An integrative curriculum across seven major disciplines. J. Ind. Ecol. 2012, 16, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, Z.; Matsler, A.; Thiel, C.; McPhillips, L.; Hum, R.; Bradshaw, A.; Miller, T.; Redman, C. Infrastructures as socio-eco-technical systems: Five considerations for interdisciplinary dialogue. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2017, 23, 02517002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, A.M.; McDougal, K.; Uzsoki, D. Sustainable Asset Valuation Tool; International Institute for Sustainable Development: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Choguill, C.L. Ten steps to sustainable infrastructure. Habitat Int. 1996, 20, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Peña-Mora, F.; Wang, X.R.; Shen, C.Q.; Riaz, Z. Social impact project finance: An innovative and sustainable infrastructure financing framework. Procedia Eng. 2015, 123, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Adesina, A.; Awoyera, P. Utilization of biomass energy in cement production: A pathway towards sustainable infrastructure. In Renewable Energy and Sustainable Buildings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 791–799. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Sarachaga, J.M.; Jato-Espino, D.; Castro-Fresno, D. Methodology for the development of a new Sustainable Infrastructure Rating System for Developing Countries (SIRSDEC). Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 69, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tian, J.; Chen, L. Managing energy infrastructure to decarbonize industrial parks in China. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadefors, A.; Lingegård, S.; Uppenberg, S.; Alkan-Olsson, J.; Balian, D. Designing and implementing procurement requirements for carbon reduction in infrastructure construction–international overview and experiences. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2021, 64, 611–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Chen, S. Dynamic energy and carbon footprints of urban transportation infrastructures: Differentiating between existing and newly-built assets. Appl. Energy 2020, 277, 115554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.M.; Motzny, A.E.; Majd, S.; Chavez, F.J.V.; Laimer, D.; Orlove, B.S.; Culligan, P.J. Identifying linkages between urban green infrastructure and ecosystem services using an expert opinion methodology. Ambio 2020, 49, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Chen, H.; Liao, Z.; Gu, X.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, J. An integrated assessment of urban flooding mitigation strategies for robust decision making. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chui, T.F.M. Linking hydrological and bioecological benefits of green infrastructures across spatial scales—A literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, M.; Fensholt, R.; Zhang, Y.; Bergen Jensen, M. Geographic object based image analysis of worldview-3 imagery for urban hydrologic modelling at the catchment scale. Water 2019, 11, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waage, J.; Yap, C.; Bell, S.; Levy, C.; Mace, G.; Pegram, T.; Unterhalter, E.; Dasandi, N.; Hudson, D.; Kock, R.; et al. Governing the UN Sustainable Development Goals: Interactions, infrastructures, and institutions. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e251–e252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C. A review of the sustainability concept and the state of SDG monitoring using remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA), United Nations. Global SDG Indicators Database. 2021. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/indicators/database/ (accessed on 20 February 2021).
- Prince, S.D. Challenges for remote sensing of the Sustainable Development Goal SDG 15.3. 1 productivity indicator. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 234, 111428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirici, G. Earth observation for the implementation of Sustainable Development Goals: The role of the European Journal of Remote Sensing. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 53, i–ii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimdavar, R.; Hubbard, A.; Policelli, F.; Pickens, A.; Hansen, M.; Fatoyinbo, T.; Lagomasino, D.; Pahlevan, N.; Unninayar, S.; Kavvada, A.; et al. Monitoring water-related ecosystems with earth observation data in support of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6 reporting. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishtiaque, A.; Masrur, A.; Rabby, Y.W.; Jerin, T.; Dewan, A. Remote sensing-based research for monitoring progress towards SDG 15 in Bangladesh: A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Report of the World Summit for Social Development; Technical Report; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Watmough, G.R.; Marcinko, C.L.; Sullivan, C.; Tschirhart, K.; Mutuo, P.K.; Palm, C.A.; Svenning, J.C. Socioecologically informed use of remote sensing data to predict rural household poverty. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwi, P.O.; Ndeng’e, G.; Kristjanson, P.; Arunga, M.; Notenbaert, A.; Omolo, A.; Henninger, N.; Benson, T.; Kariuki, P.; Owuor, J. Spatial determinants of poverty in rural Kenya. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16769–16774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gannon, C.A.; Liu, Z. Poverty and Transport; Technical Report; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Velaga, N.R.; Beecroft, M.; Nelson, J.D.; Corsar, D.; Edwards, P. Transport poverty meets the digital divide: Accessibility and connectivity in rural communities. J. Transp. Geogr. 2012, 21, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Tan, Y.; Song, Y.; Wu, P.; Cheng, J.C.; Kim, M.J.; Wang, X. Spatial and temporal variations of spatial population accessibility to public hospitals: A case study of rural–urban comparison. GISci. Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 718–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.; Rodríguez, D.; Wijnen, M.; Pakulski, I. Earth Observation for Water Resources Management: Current Use and Future Opportunities for the Water Sector; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammedshum, A.; Gebresilassiea, M.; Rulindaa, C.; Kahsaya, G.; Tesfay, M. Application of geographic information system and remote sensing in effective solid waste disposal sites selection in Wukro Town, Tigray, Ethiopia. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40-2, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenböck, H.; Staab, J.; Zhu, X.X.; Geiß, C.; Dech, S.; Wurm, M. Are the poor digitally left behind? Indications of urban divides based on remote sensing and twitter data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasowski, J.; Bovenga, F.; Nutricato, R.; Nitti, D.O.; Chiaradia, M.T. High resolution satellite multi-temporal interferometry for monitoring infrastructure instability hazards. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2017, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, L.; Chawla, I.; Mishra, A.K. A review of remote sensing applications in agriculture for food security: Crop growth and yield, irrigation, and crop losses. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppa, A.; Gebremichael, M. Improving the Applicability of Hydrologic Models for Food–Energy–Water Nexus Studies Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.E.; Grace, K.; Shively, G.; Johnson, K.B.; Carroll, M. Using satellite remote sensing and household survey data to assess human health and nutrition response to environmental change. Popul. Environ. 2014, 36, 48–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vittuari, M.; Pagani, M.; Johnson, T.G.; De Menna, F. Impacts and costs of embodied and nutritional energy of food waste in the US food system: Distribution and consumption (Part B). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanto, G.M. The Impact of Infrastructure on Agricultural Productivity; Technical Report, PIDS Discussion Paper Series; PIDS: Makati, Philippine, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bakht, Z. Poverty Impact of Rural Roads and Markets Improvement & Maintenance Project of Bangladesh; India Habitat Centre: New Delhi, India, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Deichmann, U.; Goyal, A.; Mishra, D. Will Digital Technologies Transform Agriculture in Developing Countries; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullahi, H.S.; Mahieddine, F.; Sheriff, R.E. Technology impact on agricultural productivity: A review of precision agriculture using unmanned aerial vehicles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless and Satellite Systems, Bradford, UK, 6–7 July 2015; pp. 388–400. [Google Scholar]
- Seelan, S.K.; Laguette, S.; Casady, G.M.; Seielstad, G.A. Remote sensing applications for precision agriculture: A learning community approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaghat, S.; Balasundram, S.K. A review: The role of remote sensing in precision agriculture. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2010, 5, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulla, D.J. Twenty five years of remote sensing in precision agriculture: Key advances and remaining knowledge gaps. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 114, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Jacob, F.; Duveiller, G. Remote sensing for agricultural applications: A meta-review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benami, E.; Jin, Z.; Carter, M.R.; Ghosh, A.; Hijmans, R.J.; Hobbs, A.; Kenduiywo, B.; Lobell, D.B. Uniting remote sensing, crop modelling and economics for agricultural risk management. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihervaara, P.; Auvinen, A.P.; Mononen, L.; Törmä, M.; Ahlroth, P.; Anttila, S.; Böttcher, K.; Forsius, M.; Heino, J.; Heliölä, J.; et al. How essential biodiversity variables and remote sensing can help national biodiversity monitoring. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 10, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gamon, J.A. Remote sensing of terrestrial plant biodiversity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arastounia, M. Automated recognition of railroad infrastructure in rural areas from LiDAR data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14916–14938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysoulakis, N.; Grimmond, S.; Feigenwinter, C.; Lindberg, F.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P.; Marconcini, M.; Mitraka, Z.; Stagakis, S.; Crawford, B.; Olofson, F.; et al. Urban energy exchanges monitoring from space. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Han, D. Water quality monitoring in smart city: A pilot project. Autom. Constr. 2018, 89, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A. Internet of Things for Sustainable Community Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shang, L.; Wang, D. Risksens: A multi-view learning approach to identifying risky traffic locations in intelligent transportation systems using social and remote sensing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Seattle, WA, USA, 10–13 December 2018; pp. 1544–1553. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, J.A.; Gonçalves, G.R.; Rangel, J.M.G.; Ortega, P.F. Accuracy and effectiveness of orthophotos obtained from low cost UASs video imagery for traffic accident scenes documentation. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2019, 132, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.Y.; Lee, S.H. Data fusion, ensemble and clustering to improve the classification accuracy for the severity of road traffic accidents in Korea. Saf. Sci. 2003, 41, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Q.; Yoo, E.H.; Rothstein, D.H.; Cairo, S.; Malemo, L. Improving the spatial accessibility of healthcare in North Kivu, Democratic Republic of Congo. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 121, 102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation, United Nations Children Fund. State of the World’s Vaccines and Immunisation; Technical Report; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, T.F. The Spatial Distribution of Health Services in Zambia; IGC: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.; Liao, Y.; Peng, J. Spatial distribution estimation of malaria in northern China and its scenarios in 2020, 2030, 2040 and 2050. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimi, F.; Soebiyanto, R.P.; Safi, N.; Kiang, R. Towards malaria risk prediction in Afghanistan using remote sensing. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, S.I.; Snow, R.W. The Malaria Atlas Project: Developing Global Maps of Malaria Risk. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, M.V.A.B.; Sampaio, R.M.B.; Sampaio, L.M.B. Dynamic efficiency of primary education in Brazil: Socioeconomic and infrastructure influence on school performance. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2020, 70, 100738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergüzen, A.; Erdal, E.; Ünver, M.; Özcan, A. Improving Technological Infrastructure of Distance Education through Trustworthy Platform-Independent Virtual Software Application Pools. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaklader, S.; Alam, J.; Islam, M.; Sabbir, A.S. Bridging Digital Divide: ‘Village wireless LAN’, a low cost network infrastructure solution for digital communication, information dissemination & education in rural Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 2013 2nd International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering (ICAEE), Dkaka, Bangladesh, 19–21 December 2013; pp. 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Briceno, C.; Estache, A.; Shafik, N.T. Infrastructure Services in Developing Countries: Access, Quality, Costs, and Policy Reform; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bussemakers, C.; van Oosterhout, K.; Kraaykamp, G.; Spierings, N. Women’s worldwide education–employment connection: A multilevel analysis of the moderating impact of economic, political, and cultural contexts. World Dev. 2017, 99, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Wang, X.; Sutton, P. Can Nighttime Satellite Imagery Inform Our Understanding of Education Inequality? Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbury, Z.; Aly, M.H. A geospatial study of the drought impact on surface water reservoirs: Study cases from Texas, USA. GISci. Remote Sens. 2019, 56, 894–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, M.; van Soesbergen, A.; Hole, D.G.; Brooks, T.M.; Burke, S.; Hutton, J. Mapping nature’s contribution to SDG 6 and implications for other SDGs at policy relevant scales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.T.D.; Mitsch, W.J.; Martin, J.F.; Lee, J. Towards sustainable protection of public health: The role of an urban wetland as a frontline safeguard of pathogen and antibiotic resistance spread. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.A. Renewable energy and water sustainability: Lessons learnt from TUISR19. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32153–32156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, S.; Hamdaoui, B.; Guizani, M.; Rayes, A. Enabling smart cloud services through remote sensing: An internet of everything enabler. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014, 1, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valbuena, R.; Hernando, A.; Manzanera, J.A.; Görgens, E.B.; Almeida, D.R.; Silva, C.A.; García-Abril, A. Evaluating observed versus predicted forest biomass: R-squared, index of agreement or maximal information coefficient? Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duren, R.M.; Miller, C.E. Measuring the carbon emissions of megacities. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Han, Q.; de Vries, B. A geographic carbon emission estimating framework on the city scale. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.M.; Suliman, A.E.R.E.; Al Nahry, A.H.; Abd El Rahman, E.N. Spatial modeling for the optimum site selection of solar photovoltaics power plant in the northwest coast of Egypt. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 18, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparović, I.; Gašparović, M. Determining optimal solar power plant locations based on remote sensing and GIS methods: A case study from Croatia. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, J.; Bera, A.K.; Joseph, M.; Singh, V.; Singh, T.; Pradhan, B.; Das, S. Potential zones identification for harvesting wind energy resources in desert region of India—A multi criteria evaluation approach using remote sensing and GIS. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Weng, Q. Measuring the quality of life in city of Indianapolis by integration of remote sensing and census data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B.; Randerson, J.T.; Malmström, C.M. Global net primary production: Combining ecology and remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 51, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.; Odum, H.; Brown, M.; Alling, A. “Living off the land”: Resource efficiency of wetland wastewater treatment. Adv. Space Res. 2001, 27, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, C.M.; Brovelli, M.A.; Coetzee, S. Monitoring SDG 9 with global open data and open software—A case study from rural Tanzania. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Geospatial Week 2019, Enschede, The Netherlands, 10–14 June 2019; Volume 42, pp. 1551–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Wu, M.; Niu, Z.; Tang, B.; Mu, Y. Monitoring of UN sustainable development goal SDG-9.1. 1: Study of Algerian “Belt and Road” expressways constructed by China. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arowosafe, O.; Ceranic, B.; Dean, A. A sustainable infrastructure delivery model: Value added strategy in the Nigerian construction industry. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual ARCOM Conference, Lincoln, UK, 7–9 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Turnovsky, S.J. Infrastructure and inequality. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2012, 56, 1730–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, M.; Kabiri, M.; Saadatmanesh, H. Impact of socio-economic infrastructure investments on income inequality in Iran. J. Policy Model. 2020, 42, 1146–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, C. Energy infrastructure investment and regional inequality: Evidence from China’s power grid. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, V.; Ribeiro, R.S.M.; do Amaral, P.V.M. Infrastructure and household poverty in Brazil: A regional approach using multilevel models. World Dev. 2021, 137, 105118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Yang, D.; Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Xia, F. Regional inequality in China based on NPP-VIIRS night-time light imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.S.; Qiu, X.; Wang, L. Population estimation methods in GIS and remote sensing: A review. GISci. Remote Sens. 2005, 42, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R.; Cowen, D.C. Remote sensing of urban/suburban infrastructure and socio-economic attributes. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1999, 65, 611–622. [Google Scholar]
- Warth, G.; Braun, A.; Assmann, O.; Fleckenstein, K.; Hochschild, V. Prediction of socio-economic indicators for urban planning using VHR satellite imagery and spatial analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Diao, C.; Xian, G.; Yin, D.; Lu, Y.; Zou, S.; Erickson, T.A. A summary of the special issue on remote sensing of land change science with Google earth engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.; Zhang, Q.; de Miguel, A.S.; Román, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfadaly, A.; Lasaponara, R. Cultural heritage management using remote sensing data and GIS techniques around the archaeological area of ancient Jeddah in Jeddah City, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulvi, A. Documentation, Three-Dimensional (3D) Modelling and visualization of cultural heritage by using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) photogrammetry and terrestrial laser scanners. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 1994–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trier, Ø.D.; Reksten, J.H.; Løseth, K. Automated mapping of cultural heritage in Norway from airborne lidar data using faster R-CNN. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 95, 102241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, L.; Lei, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, B.; Zuo, Z.; Li, Z. Dynamic analysis of the Wenchuan Earthquake disaster and reconstruction with 3-year remote sensing data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2010, 3, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tralli, D.M.; Blom, R.G.; Zlotnicki, V.; Donnellan, A.; Evans, D.L. Satellite remote sensing of earthquake, volcano, flood, landslide and coastal inundation hazards. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2005, 59, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicht, M.; Kuffer, M. The continuous built-up area extracted from ISS night-time lights to compare the amount of urban green areas across European cities. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbich, M.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, R. Using deep learning to examine street view green and blue spaces and their associations with geriatric depression in Beijing, China. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. Using Google Street View to investigate the association between street greenery and physical activity. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 191, 103435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbyla, D.L. Satellite Remote Sensing of Natural Resources; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Pettorelli, N. Satellite Remote Sensing and the Management of Natural Resources; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A. Remote sensing and GIS applications for municipal waste management. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hanbali, A.; Alsaaideh, B.; Kondoh, A. Using GIS-based weighted linear combination analysis and remote sensing techniques to select optimum solid waste disposal sites within Mafraq City, Jordan. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2011, 3, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusworth, D.H.; Duren, R.M.; Thorpe, A.K.; Tseng, E.; Thompson, D.; Guha, A.; Newman, S.; Foster, K.T.; Miller, C.E. Using remote sensing to detect, validate, and quantify methane emissions from California solid waste operations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhong, X.; Liu, S.; Mao, Y.; Li, J. Analysis of mining waste dump site stability based on multiple remote sensing technologies. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ma, M.; Thompson, J.R.; Flower, R.J. Waste management, informal recycling, environmental pollution and public health. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2018, 72, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlat, N.; Motola, V.; Dallemand, J.F.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Mofor, L. Evaluation of energy potential of municipal solid waste from African urban areas. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 1269–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Tang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Yi, L. The Spatial Distribution and Potential for Energy Recovery of Urban-Rural Wastes in Guangdong Province, Southern China. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 555, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tanguy, A.; Glaus, M.; Laforest, V.; Villot, J.; Hausler, R. A spatial analysis of hierarchical waste transport structures under growing demand. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zalk, J.; Behrens, P. The spatial extent of renewable and non-renewable power generation: A review and meta-analysis of power densities and their application in the US. Energy Policy 2018, 123, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gong, P.; Fu, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Liang, S.; Xu, B.; Shi, J.; Dickinson, R. The role of satellite remote sensing in climate change studies. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelman, I.; West, J.J. Climate change and small island developing states: A critical review. Ecol. Environ. Anthropol. 2009, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, C.D. Satellite remote sensing of marine pollution. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 2985–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, S.; Wong, M.S.; Abbas, S.; Kwok, C.Y.T.; Nichol, J.; Lee, K.H.; Tang, D.; Pun, L. Detection and monitoring of marine pollution using remote sensing technologies. In Monitoring of Marine Pollution; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Davaasuren, N.; Marino, A.; Boardman, C.; Alparone, M.; Nunziata, F.; Ackermann, N.; Hajnsek, I. Detecting microplastics pollution in world oceans using SAR remote sensing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 938–941. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, M.J.; Colna, K.E.; El-Mezayen, M.M.; Laureano-Rosario, A.E.; Méndez-Lázaro, P.; Otis, D.B.; Toro-Farmer, G.; Vega-Rodriguez, M.; Muller-Karger, F.E. Satellite remote sensing for coastal management: A review of successful applications. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.; Lin, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. Grassland degradation remote sensing monitoring and driving factors quantitative assessment in China from 1982 to 2010. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Rosenqvist, A.; Mora, B. Current remote sensing approaches to monitoring forest degradation in support of countries measurement, reporting and verification (MRV) systems for REDD+. Carbon Balance Manag. 2017, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhou, Q. Remote sensing and evaluation of the wetland ecological degradation process of the Zoige Plateau Wetland in China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, M. Key Technologies and Applications of Wild Animal Satellite Tracking. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1757, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Linchant, J.; Lisein, J.; Semeki, J.; Lejeune, P.; Vermeulen, C. Are unmanned aircraft systems (UAS s) the future of wildlife monitoring? A review of accomplishments and challenges. Mammal Rev. 2015, 45, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.D.; Krivo, L.J. Divergent Social Worlds: Neighborhood Crime and the Racial-Spatial Divide; Russell Sage Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gorman, D.M.; Speer, P.W.; Gruenewald, P.J.; Labouvie, E.W. Spatial dynamics of alcohol availability, neighborhood structure and violent crime. J. Stud. Alcohol 2001, 62, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilford, R.; Kyobutungi, C.; Ndugwa, R.; Sartori, J.; Watson, S.I.; Sliuzas, R.; Kuffer, M.; Hofer, T.; de Albuquerque, J.P.; Ezeh, A. Because space matters: Conceptual framework to help distinguish slum from non-slum urban areas. BMJ Glob. Health 2019, 4, e001267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, J.; Friesen, V.; Dietrich, I.; Pelz, P.F. Slums, space, and state of health—A link between settlement morphology and health data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Thomson, D.R.; Boo, G.; Mahabir, R.; Grippa, T.; Vanhuysse, S.; Engstrom, R.; Ndugwa, R.; Makau, J.; Darin, E.; et al. The role of earth observation in an integrated deprived area mapping “System” for low-to-middle income countries. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonne, C.; Adair, L.; Adlakha, D.; Anguelovski, I.; Belesova, K.; Berger, M.; Brelsford, C.; Dadvand, P.; Dimitrova, A.; Giles-Corti, B.; et al. Defining pathways to healthy sustainable urban development. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilino, M.; Tarantino, C.; Adamo, M.; Barbanente, A.; Blonda, P. Earth Observation for the Implementation of Sustainable Development Goal 11 Indicators at Local Scale: Monitoring of the Migrant Population Distribution. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Wang, J.; Nagenborg, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Kohli, D.; Sliuzas, R.; Persello, C. The scope of earth-observation to improve the consistency of the SDG slum indicator. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, M.; Gu, J. Using Earth Observation for Monitoring SDG 11.3. 1-Ratio of Land Consumption Rate to Population Growth Rate in Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cai, G.; Du, M. Big Data Supported the Identification of Urban Land Efficiency in Eurasia by Indicator SDG 11.3. 1. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorri, M.; Pesaresi, M.; Florczyk, A.J.; Corbane, C.; Kemper, T. Principles and applications of the global human settlement layer as baseline for the land use efficiency indicator—SDG 11.3. 1. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Zhang, J.; Du, M.; Li, C.; Peng, S. Identification of urban land use efficiency by indicator-SDG 11.3. 1. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavina, M.; Melchiorri, M.; Corbane, C.; Florczyk, A.J.; Freire, S.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T. Multi-scale estimation of land use efficiency (SDG 11.3. 1) across 25 years using global open and free data. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estache, A. Infrastructure: A Survey of Recent and Upcoming Issues; World Bank Mimeo: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Estache, A.; Garsous, G. The Impact of Infrastructure on Growth in Developing Countries; IFC Economics Notes; IFC: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Xu, C. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Gersonius, B.; Kapelan, Z.; Vojinovic, Z.; Sanchez, A. Assessing the Co-Benefits of green-blue-grey infrastructure for sustainable urban flood risk management. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 239, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raei, E.; Alizadeh, M.R.; Nikoo, M.R.; Adamowski, J. Multi-objective decision-making for green infrastructure planning (LID-BMPs) in urban storm water management under uncertainty. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, Q. Deep learning based fossil-fuel power plant monitoring in high resolution remote sensing images: A comparative study. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovensmann, H.; Buchwitz, M.; Burrows, J.; Reuter, M.; Krings, T.; Gerilowski, K.; Schneising, O.; Heymann, J.; Tretner, A.; Erzinger, J. A remote sensing technique for global monitoring of power plant CO2 emissions from space and related applications. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 781–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, H.G.; Alganci, U.; Eris, E.; Agıralioglu, N.; Cigizoglu, H.K.; Yilmaz, L.; Toprak, Z.F. Remote sensing and GIS innovation with hydrologic modelling for hydroelectric power plant (HPP) in poorly gauged basins. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3757–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamanehpour, E. Site selection of wind power plant using multi-criteria decision-making methods in GIS: A case study. Comput. Ecol. Softw. 2017, 7, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Shi, P.; Mao, Q. Application of remote sensing techniques for monitoring the thermal pollution of cooling-water discharge from nuclear power plant. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2003, 38, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Kester, D.R.; Wang, Z.; Lian, J.; Kawamura, H. AVHRR satellite remote sensing and shipboard measurements of the thermal plume from the Daya Bay, nuclear power station, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, K.; Pearce, J.M.; Mabee, W.E. Toward renewable energy geo-information infrastructures: Applications of GIScience and remote sensing that build institutional capacity. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, G.; Petri, E.; Interwies, E.; Vysna, V.; Guigoz, Y.; Ray, N.; Dickie, I. Modelling Accessibility to Urban Green Areas Using Open Earth Observations Data: A Novel Approach to Support the Urban SDG in Four European Cities. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Fu, L. Do charitable foundations spend money where people need it most? A spatial analysis of China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Singh, R.; Kaur, R. SDG 9: Case Study–Infrastructure Assessment for Sustainable Development. In Spatial Information Technology for Sustainable Development Goals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Wu, P.; Gilmore, D.; Li, Q. A Spatial Heterogeneity-Based Segmentation Model for Analyzing Road Deterioration Network Data in Multi-Scale Infrastructure Systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wu, P. An Interactive Detector for Spatial Associations. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanka-Pedige, H.; Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.; Abeysiriwardana-Arachchige, I.; Nirmalakhandan, N. Wastewater infrastructure for sustainable cities: Assessment based on UN sustainable development goals (SDGs). Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Dai, X.; Baninla, Y.; Nakatani, J.; Moriguchi, Y. Urbanization impacts on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of the water infrastructure in China: Trade-offs among sustainable development goals (SDGs). J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova-Antonova, D.; Sylvia, I. Methodological framework for digital transition and performance assessment of smart cities. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech), Split, Croatia, 18–21 June 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sudmanns, M.; Tiede, D.; Lang, S.; Bergstedt, H.; Trost, G.; Augustin, H.; Baraldi, A.; Blaschke, T. Big Earth data: Disruptive changes in Earth observation data management and analysis? Int. J. Digit. Earth 2020, 13, 832–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Sumari, N.S.; Portnov, A.; Ujoh, F.; Musakwa, W.; Mandela, P.J. Urban sprawl and its impact on sustainable urban development: A combination of remote sensing and social media data. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shi, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Poverty evaluation using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data at the county level in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.C.; Ghosh, T.; Tuttle, B.T.; Baugh, K.E.; Bhaduri, B.; Bright, E. A global poverty map derived from satellite data. Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, N.; Burke, M.; Xie, M.; Davis, W.M.; Lobell, D.B.; Ermon, S. Combining satellite imagery and machine learning to predict poverty. Science 2016, 353, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiminia, H.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Quackenbush, L.; Adeli, S.; Brisco, B. Google Earth Engine for geo-big data applications: A meta-analysis and systematic review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Kumar, V.; Matin, M.A.; Thapa, A.; Ellenburg, W.L.; Gupta, N.; Thapa, S. Flood inundation mapping-Kerala 2018; Harnessing the power of SAR, automatic threshold detection method and Google Earth Engine. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanelli, R.; Nascetti, A.; Cirigliano, R.V.; Di Rico, C.; Leuzzi, G.; Monti, P.; Crespi, M. Monitoring the impact of land cover change on surface urban heat island through Google Earth Engine: Proposal of a global methodology, first applications and problems. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Qiu, C.; Ma, L.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X.X. Mapping the land cover of Africa at 10 m resolution from multi-source remote sensing data with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Stow, D.; Chen, H.L.; Lewison, R.; An, L.; Shi, L. Mapping vegetation and land use types in fanjingshan national nature reserve using google earth engine. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheip, C.M.; Wegmann, K.W. HazMapper: A global open-source natural hazard mapping application in Google Earth Engine. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2020, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansell, P.; Philbin, S.P.; Broyd, T.; Nicholson, I. Assessing the impact of infrastructure projects on global sustainable development goals. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Engineering Sustainability; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2019; Volume 173, pp. 196–212. [Google Scholar]
- Mansell, P.; Philbin, S.P.; Konstantinou, E. Delivering UN Sustainable Development Goals’ Impact on Infrastructure Projects: An Empirical Study of Senior Executives in the UK Construction Sector. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegatte, S. Storm damages and inter-city trade. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, E. Natural hazard impacts on transport infrastructure in Russia. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 1969–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achillopoulou, D.V.; Mitoulis, S.A.; Argyroudis, S.A.; Wang, Y. Monitoring of transport infrastructure exposed to multiple hazards: A roadmap for building resilience. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xu, J. Observing community resilience from space: Using nighttime lights to model economic disturbance and recovery pattern in natural disaster. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 57, 102115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N. Closing the Gaps in Social and Physical Infrastructure for Achieving Sustainable Development Goals in Asia and the Pacific. Millenn. Asia 2019, 10, 372–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurara, D.; Klyuev, V.; Mwase, N.; Presbitero, A.F. Trends and challenges in infrastructure investment in developing countries. Int. Dev. Policy Rev. Int. Polit. Dév. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuldauer, L.I.; Ives, M.C.; Adshead, D.; Thacker, S.; Hall, J.W. Participatory planning of the future of waste management in small island developing states to deliver on the Sustainable Development Goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, C. Creating a Common Language: How Does the Sustainable Infrastructure Criteria Compare to the SDGs? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Infrastructure 2019: Leading Resilient Communities through the 21st Century. American Society of Civil Engineers, Reston, VA, USA, 11–13 June 2019; pp. 671–688. [Google Scholar]
- Adshead, D.; Thacker, S.; Fuldauer, L.I.; Hall, J.W. Delivering on the Sustainable Development Goals through long-term infrastructure planning. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2019, 59, 101975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, S.E. The Sustainable Development Goals confront the infrastructure of measurement. Glob. Policy 2019, 10, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).