Improving the Evapotranspiration Estimation under Cloudy Condition by Extending the Ts-VI Triangle Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets and Pre-Processing
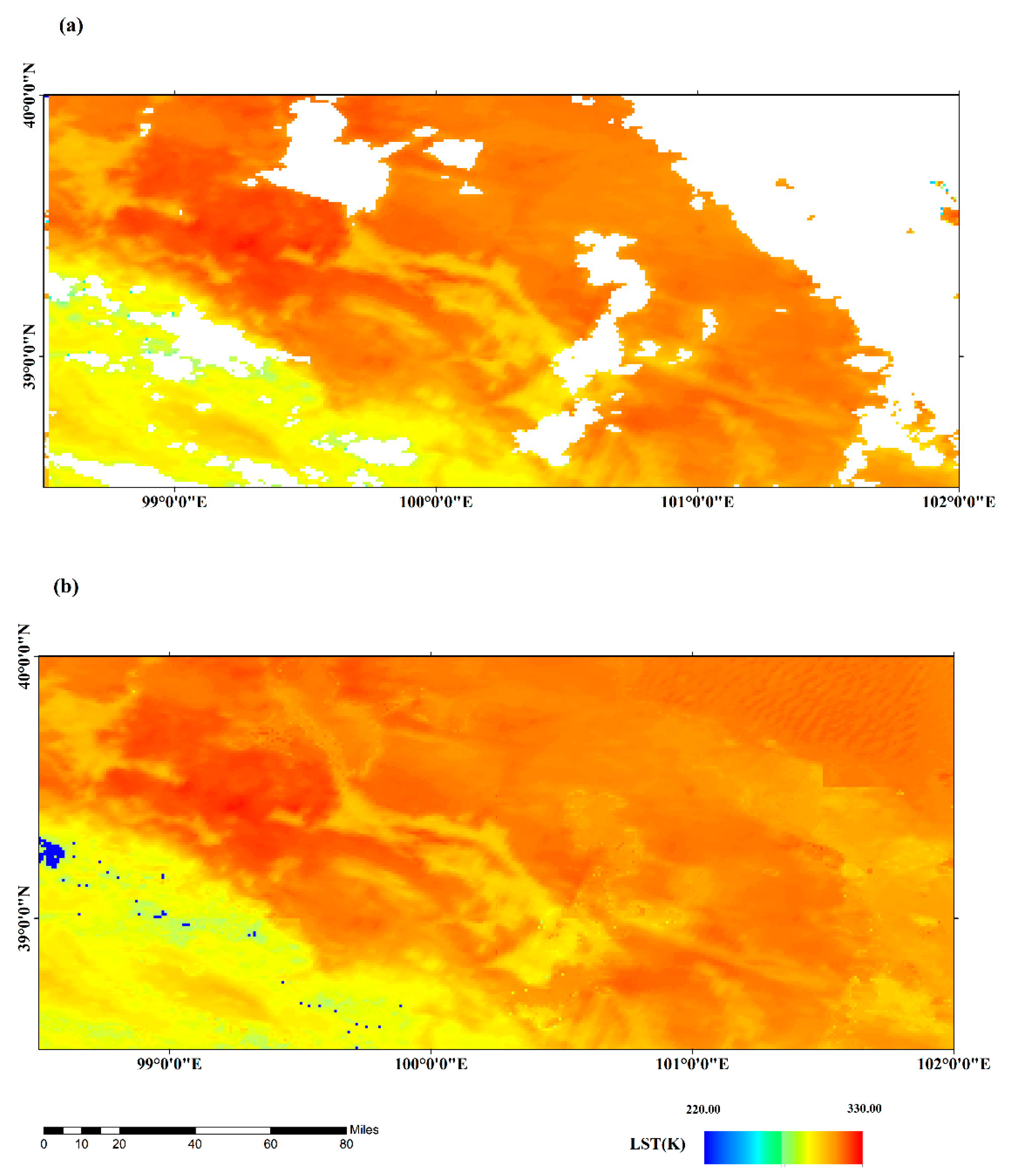
2.2.1. MODIS LST
2.2.2. Cloud-Free MODIS NDVI
2.2.3. GLASS Albedo
2.2.4. MICLCover Land Cover Map
2.2.5. China Meteorological Forcing Dataset
2.2.6. In Situ Measurements
2.2.7. Ground Truth of Land Surface Evapotranspiration at the Satellite Pixel
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. LST Reconstruction Method
2.3.2. Ts-VI ET Model
2.3.3. Performance Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Performance of LST Reconstruction
3.2. Overall Performance of ET Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages of This Study
4.2. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trenberth, K.; Fasullo, J.; Kiehl, J. Earth’s global energy budget. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R. A Review of Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration: Observation, Modeling, Climatology, and Climatic Variability. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Miltenburg, I.J.; Pelgrum, H. Surface energy balance and actual evapotranspiration of the transboundary Indus Basin estimated from satellite measurements and the ET Look model. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.D.; Reginato, R.J.; Idso, S.B. Wheat Canopy Temperature-Practical Tool for Evaluating Water Requirements. Water Resour. Res. 1977, 13, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liang, S.L.; Yuan, W.P.; Chen, Z.X. Improving a Penman-Monteith evapotranspiration model by incorporating soil moisture control on soil evaporation in semiarid areas. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 134–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S. A methodology for estimation of surface evapotranspiration over large areas using remote sensing observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2773–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System SEBS for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, G.; Entekhabi, D.; Castelli, F. Land data assimilation with satellite measurements for the estimation of surface energy balance components and surface control on evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Torn, R.D.; Kustas, W.P.; Basara, J.B. A multiscale remote sensing model for disaggregating regional fluxes to micrometeorological scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoca, M.E.; Senay, G.B.; Maupin, M.A.; Kenny, J.F.; Perry, C.A. Actual Evapotranspiration Modeling Using the Operational Simplified Surface Energy Balance (SSEBop) Approach: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2013-5126, 16p. 2013. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/sir/2013/5126 (accessed on 29 January 2021).
- Melton, F.S.; Johnson, L.F.; Lund, C.P.; Pierce, L.L.; Michaelis, A.R.; Hiatt, S.H.; Guzman, A.; Adhikari, D.; Purdy, A.J.; Rosevelt, C.; et al. Satellite Irrigation Management Support With the Terrestrial Observation and Prediction System: A Framework for Integration of Satellite and Surface Observations to Support Improvements in Agricultural Water Resource Management. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, Z.L.; Tang, B. An application of the Ts–VI triangle method with enhanced edges determination for evapotranspiration estimation from MODIS data in arid and semi-arid regions: Implementation and validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Song, L.; Fan, W. Generation of spatio-temporally continuous evapotranspiration and its components by coupling a two-source energy balance model and a deep neural network over the Heihe River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kimball, J.S.; Running, S.W. A review of remote sensing based actual evapotranspiration estimation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2016, 3, 834–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S. Estimation of surface evaporation map over Southern Great Plains using remote sensing data. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Shen, H.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, P. Reconstructing MODIS LST Based on Multitemporal Classification and Robust Regression. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, S.; Kustas, W.P.; Nieto, H.; Sun, L.; Xu, Z.; Skaggs, T.H.; Yang, Y.; Ma, M.; Xu, T.; et al. Monitoring and validating spatially and temporally continuous daily evaporation and transpiration at river basin scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Long, D.; Shen, H.; Wu, P.; Cui, Y.; Hong, Y. A two-step framework for reconstructing remotely sensed land surface temperatures contaminated by cloud. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 141, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzbach, J.E.; Prell, W.L.; Ruddiman, W.F. Sensitivity of Eurasian Climate to Surface Uplift of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Shang, H.; Hu, G.; Menenti, M. Phenological response of vegetation to upstreamriver flow in the Heihe Rive basin by time series analysis of MODIS data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1047–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Z.; Xu, M.; Gao, W.; Kunkel, K.; Slusser, J.; Dai, Y.J.; Min, Q.L.; Houser, P.R.; Rodell, M.; Schaaf, C.B.; et al. Development of land surface albedo parameterization based on Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectro radiometer MODIS data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Wen, J. A Temporal Filtering Algorithm to Reconstruct Daily Albedo Series Based on GLASS Albedo Product. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Y.H.; Li, X.; Lu, L.; Li, Z.Y. Large-scale land cover mapping with the integration of multi-source information based on the Dempster-Shafer theory. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2012, 26, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, K.; Tang, W.; Lu, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. The first high-resolution meteorological forcing dataset for land process studies over China. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; He, J.; Qin, J.; Shi, J.; Du, J.; He, Q. Improving land surface temperature modeling for dry land of China. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Long, D.; Li, Z. Estimation of daily actual evapotranspiration from remotely sensed data under complex terrain over the upper Chao river basin in North China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3295–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Jia, L. Monitoring of Evapotranspiration in a Semi Arid Inland River Basin by Combining Microwave and Optical Remote Sensing Observations. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3056–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, K.; Moore, R.; Floyer, J.; Asplin, M.; McKendry, I. Comparison of approaches for spatial interpolation of daily air temperature in a large region with complex topography and highly variable station density. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 139, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, M.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Che, T.; Chen, E.; Yan, G.; et al. Watershed Allied Telemetry Experimental Research. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xu, T.; Song, L.; Yang, X.; et al. Intercomparison of Six Upscaling Evapotranspiration Methods: From Site to the Satellite Pixel. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6777–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Song, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ge, Y.; Xu, T.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, F. Upscaling evapotranspiration measurements from multi-site to the satellite pixel scale over heterogeneous land surfaces. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.P. Robust Regression Computation Using Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 1990, 11, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, C.H.B.; Taylor, R.J. On the assessment of surface heat flux and evaporation using large-scale parameters. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1972, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Brutsaert, W. Daily evaporation over a region from lower boundary layer profiles measured with radiosondes. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J. Using spatial context in satellite data to infer regional scale evapotranspiration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ma, S.; Yao, Z.; Chen, X.; Luo, Z.; Fan, W.; Hong, Y. Developing a Gap-Filling Algorithm Using DNN for the Ts-VI Triangle Model to Obtain Temporally Continuous Daily Actual Evapotranspiration in an Arid Area of China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihodko, L.; Goward, S.N. Estimation of air temperature from remotely sensed surface observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 60, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S. An intercomparison of regional latent heat flux estimation using remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T. An overview of the “Triangle Method” for estimating surface evapotranspiration and soil moisture from satellite imagery. Sensors 2007, 7, 1612–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S.; Carlson, T.N. Uncertainties in latent heat flux measurement and estimation: Implications for using a simplified approach with remote sensing data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 769–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D.; Crow, W.T. Performance Metrics for Soil Moisture Retrievals and Application Requirements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, L.; Yang, W.; Cheng, G. Estimation of evapotranspiration in an arid region by remote sensing—A case study in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 17, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Hou, J.; Gu, J.; Zhu, G.; Li, X. Mapping daily evapotranspiration based on spatiotemporal fusion of ASTER and MODIS images over irrigated agricultural areas in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 244, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, S. Estimation of regional irrigation water requirement and water supply risk in the arid region of Northwestern China 1989–2010. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 128, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xia, J.; Liang, S.; Feng, J.; Fisher, J.B.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Ma, Z.; Miyata, A.; et al. Comparison of satellite-based evapotranspiration models over terrestrial ecosystems in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. Source Approach for Estimating Soil and Vegetation Energy Fluxes In Observations Of Directional Radiometric Surface-Temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Cui, Y.; Geng, X.; Li, H. Improving the Evapotranspiration Estimation under Cloudy Condition by Extending the Ts-VI Triangle Model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081516
Li B, Cui Y, Geng X, Li H. Improving the Evapotranspiration Estimation under Cloudy Condition by Extending the Ts-VI Triangle Model. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(8):1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081516
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Boyang, Yaokui Cui, Xiaozhuang Geng, and Huan Li. 2021. "Improving the Evapotranspiration Estimation under Cloudy Condition by Extending the Ts-VI Triangle Model" Remote Sensing 13, no. 8: 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081516
APA StyleLi, B., Cui, Y., Geng, X., & Li, H. (2021). Improving the Evapotranspiration Estimation under Cloudy Condition by Extending the Ts-VI Triangle Model. Remote Sensing, 13(8), 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081516







