Processing Missile-Borne SAR Data by Using Cartesian Factorized Back Projection Algorithm Integrated with Data-Driven Motion Compensation
Abstract
1. Introduction
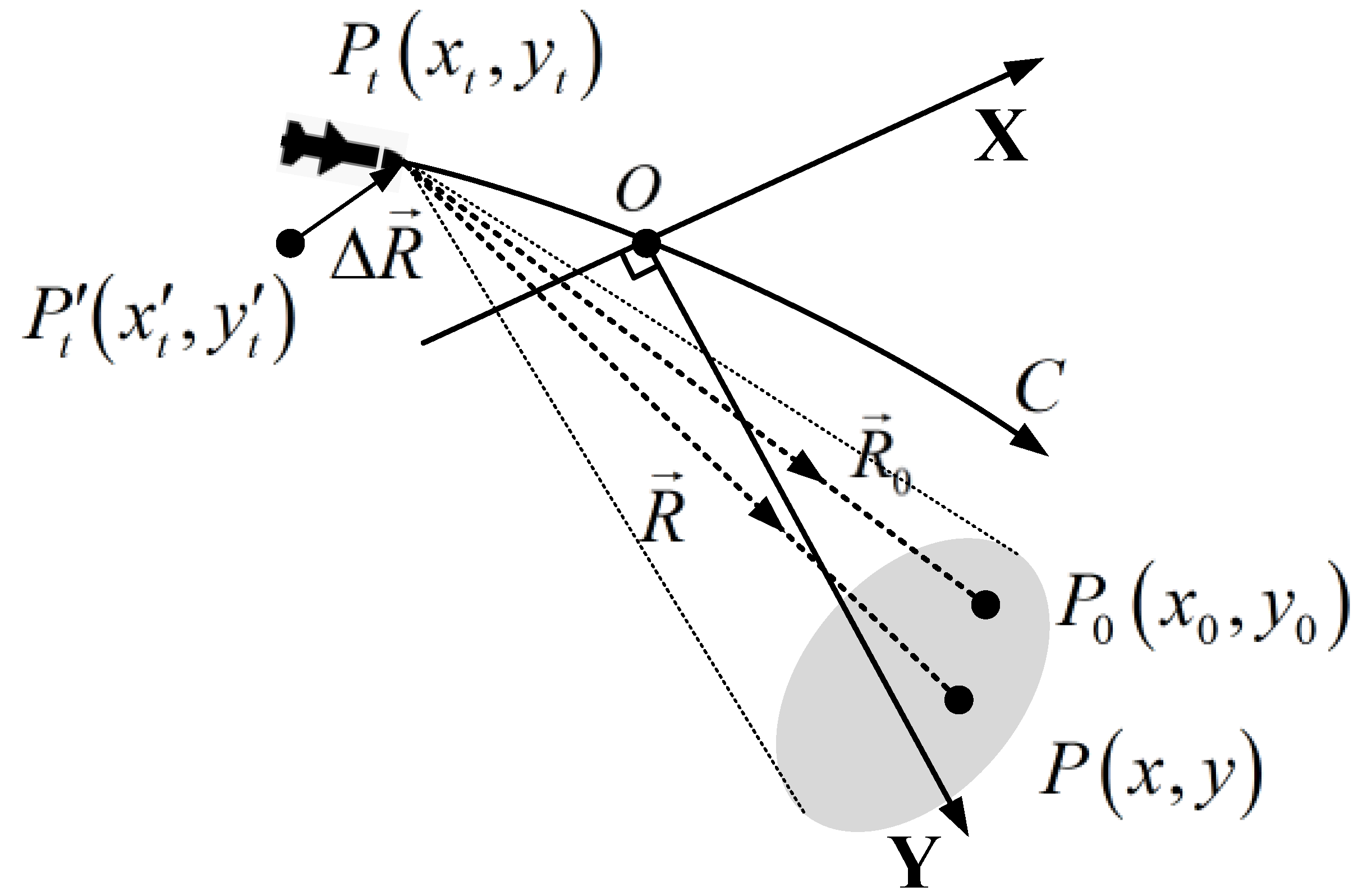
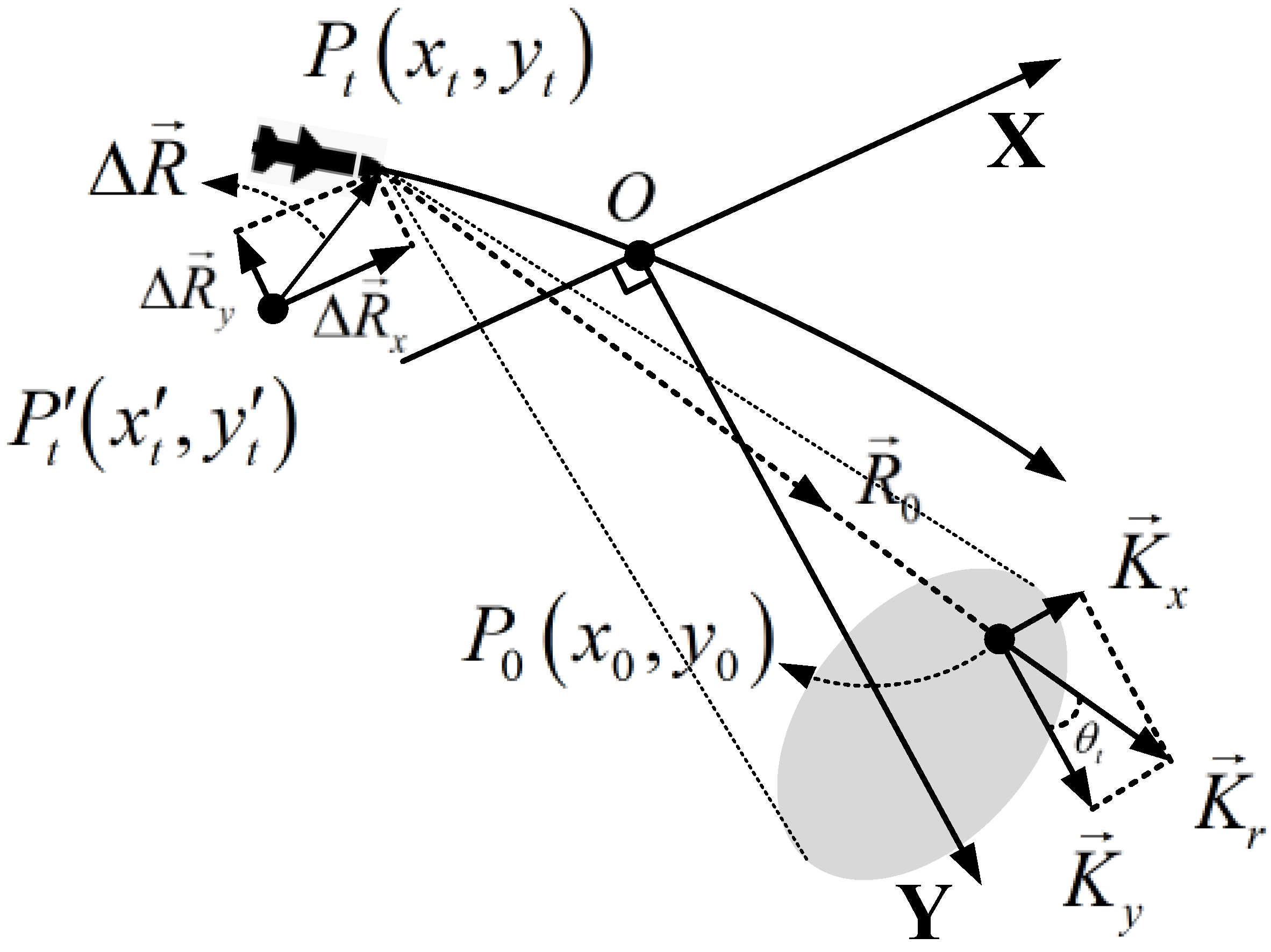
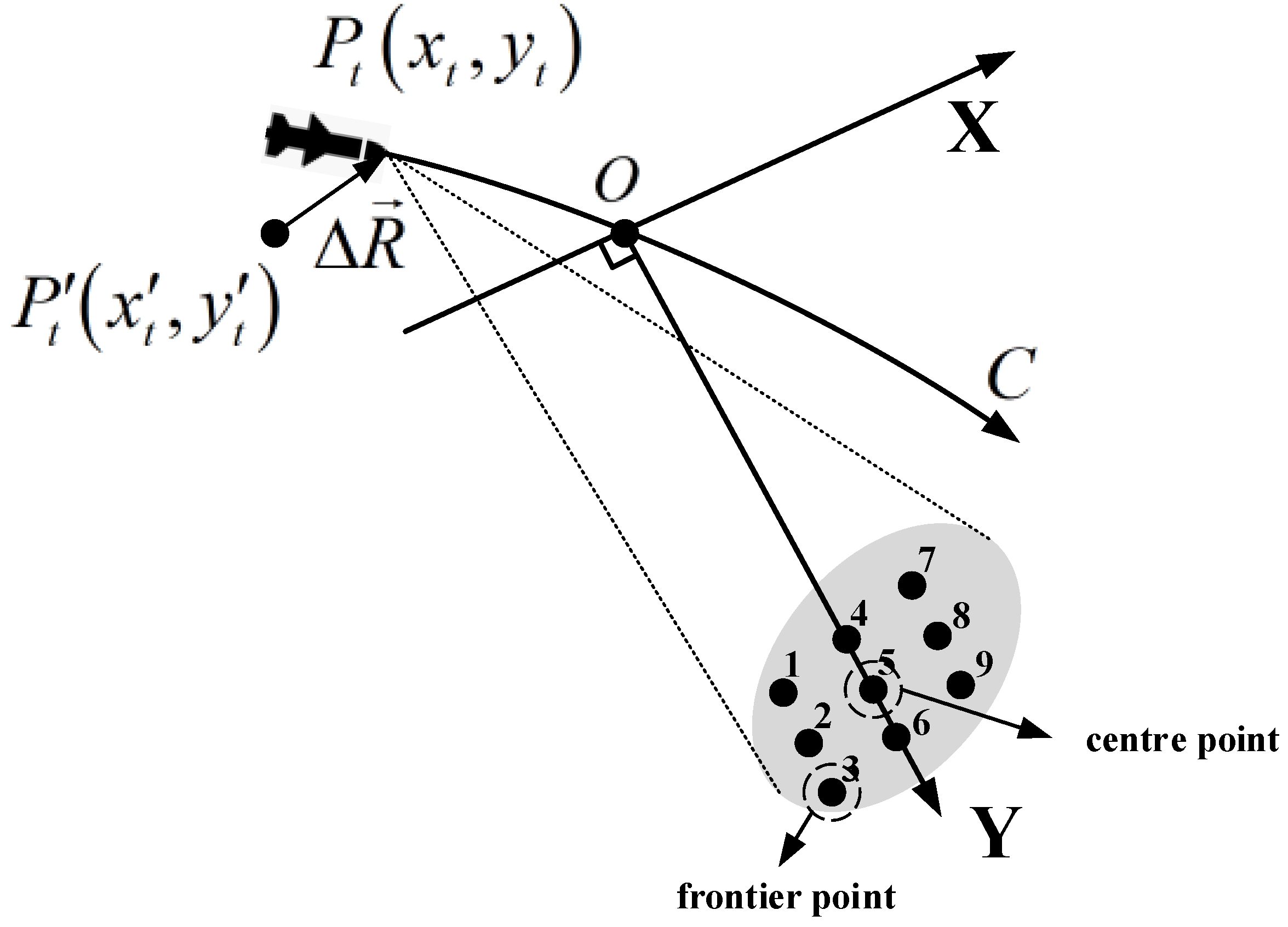
2. Geometry and Signal Model
3. Spectrum Analysis
4. Data-Driven MOCO in the Spectrum-Compressed Domain
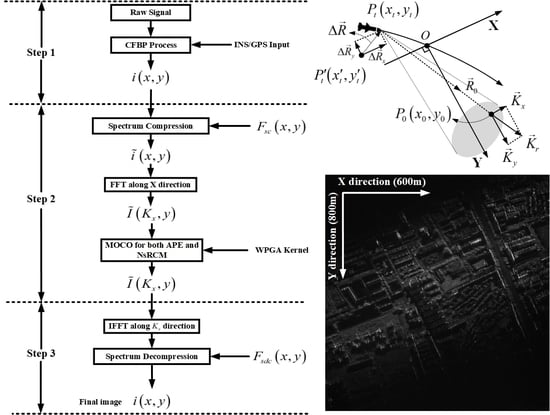
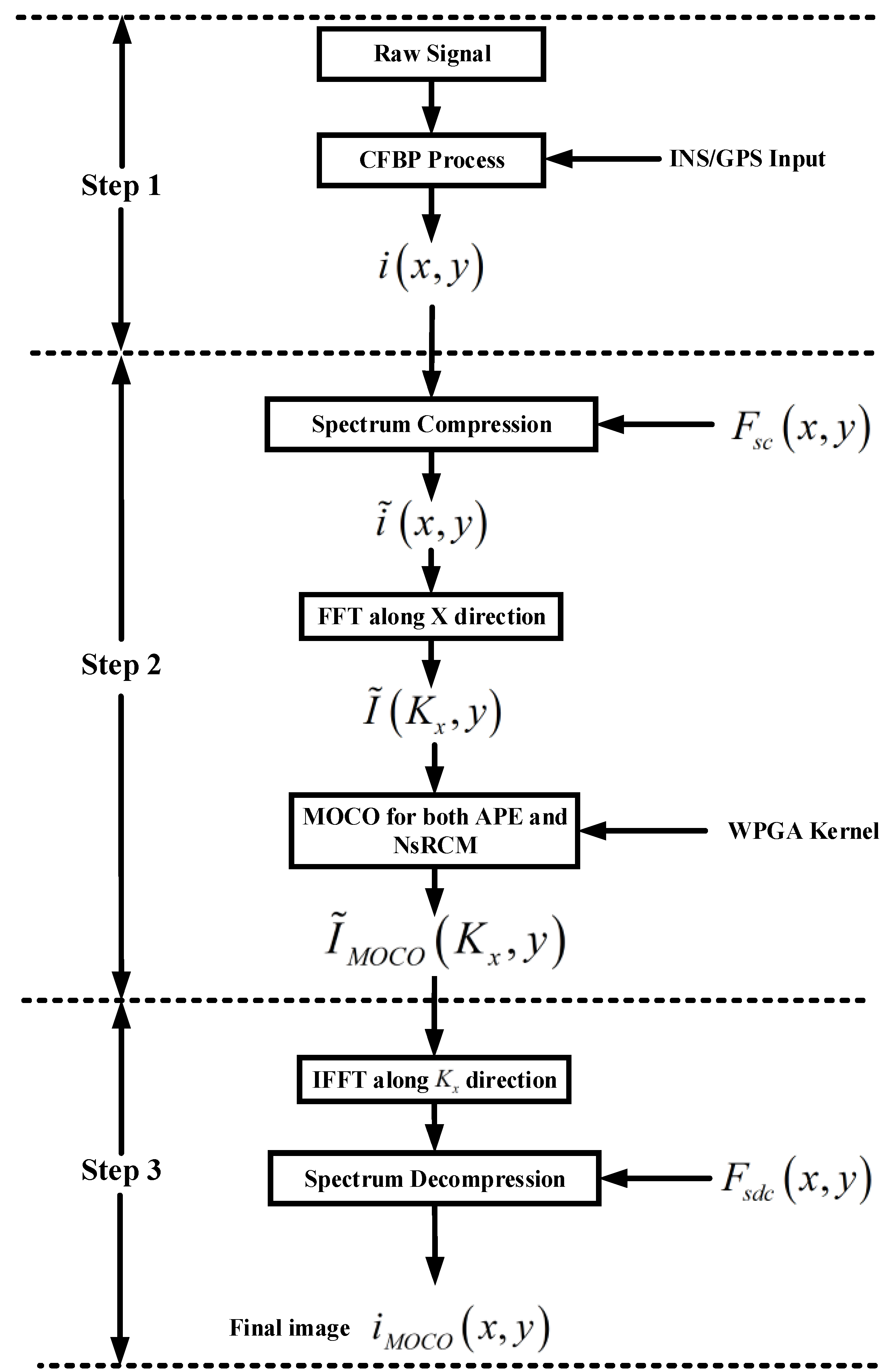
5. Processing Procedures
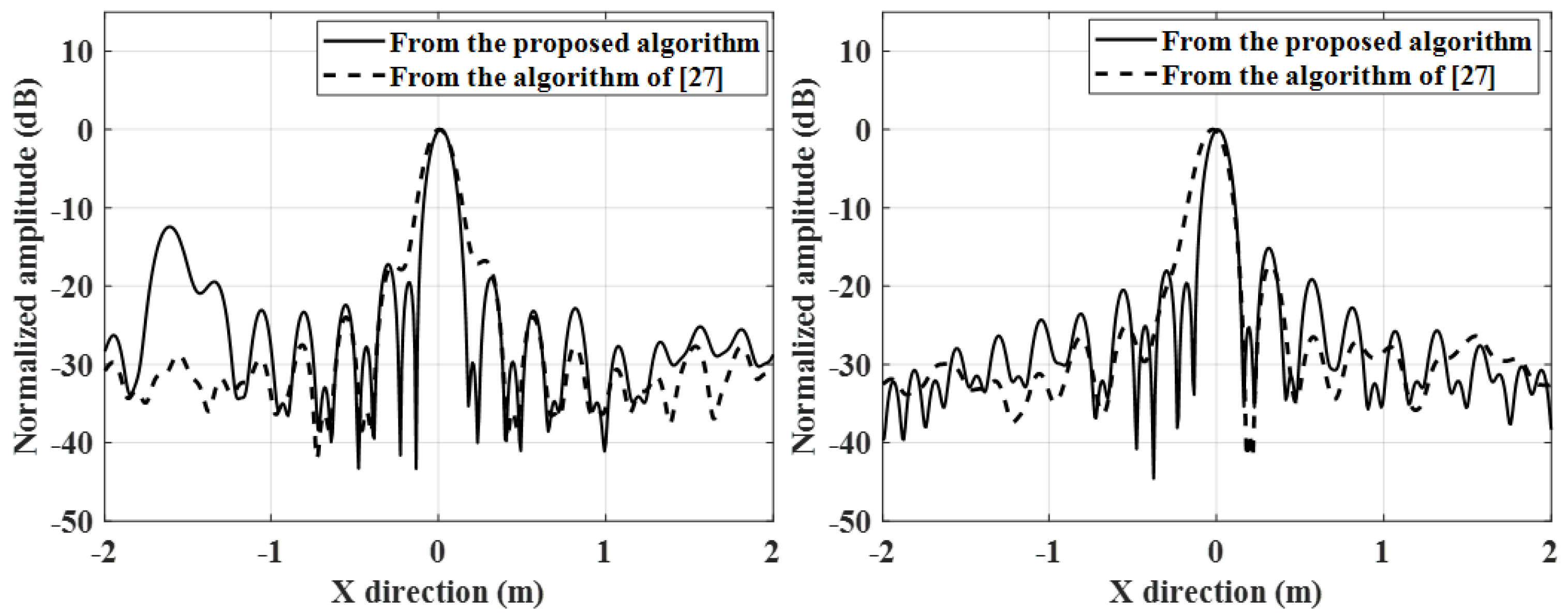
6. Simulations and Raw Data Experiments
6.1. Simulations for Missile-Borne SAR
6.2. Raw Data Experiments for Airborne SAR
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LD | linear dichroism |
| SAR | synthetic aperture radar |
| FFBP | fast factorized back-projection |
| CFBP | Cartesian factorized back projection |
| MOCO | motion compensation |
| FDA | frequency-domain algorithm |
| TDA | time-domain algorithm |
| RDA | range-doppler algorithm |
| CSA | chirp-scaling algorithm |
| BP | back-projection |
| INS/GPS | inertial navigation system/global positioning system |
| UAV | unmanned aerial vehicle |
| FT | Fourier transformation |
| SA | sub image |
| POSP | principle of stationary phase |
| PGA | phase gradient autofocusing |
| MDA | map-drift autofocusing |
| WPGA | weighted PGA |
| APC | antenna phase center |
| NsRCM | nonsystematic range cell migration |
| PRF | pulse repetition frequency |
| PSLR | peak sidelobe ratio |
| ISLR | integrated sidelobe ratio |
References
- Zink, M.; Moreira, A.; Hajnsek, I.; Rizzoli, P.; Bachmann, M.; Kahle, R.; Fritz, T.; Huber, M.; Krieger, G.; Lachaise, M. TanDEM-X: 10 Years of Formation Flying Bistatic SAR Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3546–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Tan, X.; Chen, Z.; Dong, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L. Refocusing of Ground Moving Targets with Doppler Ambiguity Using Keystone Transform and Modified Second-Order Keystone Transform for Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2021, 2, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Zink, M.; Caro, E.; Moreira, A.; Veilleux, L.; Werner, M. The legacy of the SIR-C/X-SAR radar system: 25 years on. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebeck, D.; Wimmer, C.; Moreira, L.F.; Alcântara, M.; Oré, G.; Góes, J.A.; Oliveira, L.P.; Teruel, B.; Bins, L.S.; Gabrielli, L.H. Drone-borne differential SAR interferometry. Sensors 2020, 12, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, B.; Sun, G.C.; Xia, X.G.; Xing, M.; Guo, L.; Bao, Z. High-speed maneuvering platforms squint beam-steering SAR imaging without subaperture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6974–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, X. Maneuvering platform high-squint SAR imaging method based on perturbation KT and subregion phase filtering. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 1, 016502. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.; An, D.; Huang, X. An extended fast factorized back projection algorithm for missile-borne bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 2724–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Guo, P.; Zhang, L.; Lin, C. Modeling and Precise Processing for Spaceborne Transmitter/Missile-Borne Receiver SAR Signals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Yang, L. A New Fast Factorized Back-Projection Algorithm with Reduced Topography Sensibility for Missile-Borne SAR Focusing with Diving Movement. Remote Sens. 2020, 16, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Signal Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xing, M.; Sun, G.; Li, Z. A 2D space-variant motion estimation and compensation method for ultrahigh-resolution airborne stepped-frequency SAR with long integration time. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6390–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Cassola, M.; Prats, P.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Efficient time-domain image formation with precise topography accommodation for general bistatic SAR configurations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 2949–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.D.; Jenkins, W.K. Convolution backprojection image reconstruction for spotlight mode synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1992, 1, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. Fast split bregman based deconvolution algorithm for airborne radar imaging. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaibel, A.; Boag, A. Backprojection Imaging of Moving Objects. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, P. Focusing High-Resolution Airborne SAR with Topography Variations Using an Extended BPA Based on a Time/Frequency Rotation Principle. Remote Sens. 2018, 8, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.L.; Qiao, Z.J.; Xing, M.D.; Bao, Z. Integrating autofocus techniques with fast factorized back-projection for high-resolution spotlight SAR imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Ding, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, R.; Li, S. Knowledge-Aided 2D Autofocus for Spotlight SAR Filtered Backprojection Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9041–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulander, L.M.H.; Hellsten, H.; Stenstrom, G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 760–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shippey, G.; Banks, S.; Pihl, J. SAS image reconstruction using fast polar back projection: Comparisons with fast factored back projection and Fourier-domain imaging. Eur. Ocean. 2005, 1, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, G.-C.; Xing, M. A new fast back-projection algorithm using polar format algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2013 Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Tsukuba, Japan, 23–27 September 2013; Volume 1, pp. 373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, V.T.; Pettersson, M.I. Nyquist sampling requirements for polar grids in bistatic time-domain algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 63, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yang, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, L.; Xing, M. A New Fast Factorized Back Projection Algorithm for Bistatic Forward-Looking SAR Imaging Based on Orthogonal Elliptical Polar Coordinate. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1508–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Sun, G.; Yang, Z.; Guo, L.; Xing, M. Cartesian factorized backprojection algorithm for high-resolution spotlight SAR imaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 3, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, F.; Li, N.; Zhang, H. A modified cartesian factorized back-projection algorithm for highly squint spotlight synthetic aperture radar imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 6, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, G.; Xing, M.; Li, B.; Yang, J.; Bao, Z. Ground Cartesian Back-Projection Algorithm for High Squint Diving TOPS SAR Imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, F.; Li, N.; Zhang, H. An autofocus cartesian factorized backprojection algorithm for spotlight synthetic aperture radar imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 8, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Jiang, X.; Wu, R.; Zhou, F.; Bao, Z. Motion compensation for UAV SAR based on raw radar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 8, 2870–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, Z.; Xing, M.; Yang, L.; Bao, Z. A robust motion compensation approach for UAV SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 8, 3202–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W. Deep SAR Imaging and Motion Compensation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2232–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yang, L.; Zhao, L.; Bi, G. Quasi-polar-based FFBP algorithm for miniature UAV SAR imaging without navigational data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 7053–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, H. Fast Factorized Backprojection Imaging Algorithm Integrated With Motion Trajectory Estimation for Bistatic Forward-Looking SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3949–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, S.; Xing, M. Cooperative Multitask Learning for Sparsity-Driven SAR Imagery and Nonsystematic Error Autocalibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5132–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.; Eichel, P.H.; Ghiglia, D.C.; Jakowatz, C.V. Phase gradient autofocus-a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 3, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Yeo, T.; Bao, Z. Weighted least-squares estimation of phase errors for SAR/ISAR autofocus. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 5, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Zhou, S.; Yang, L.; Xing, M.; Zhao, L. Data-driven Motion Compensation for Airborne Bistatic SAR Imagery under Fast Factorized Back Projection Framework. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
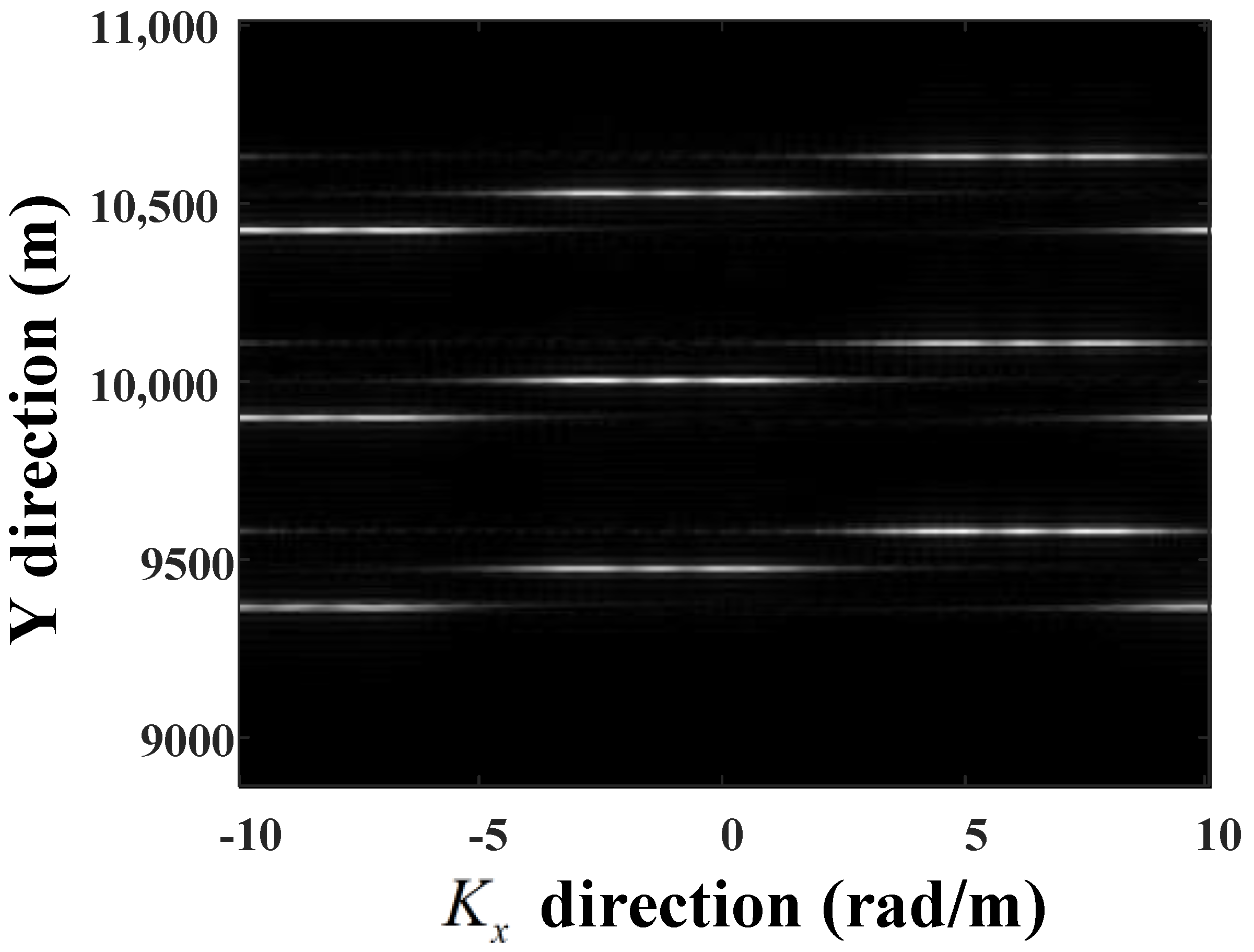
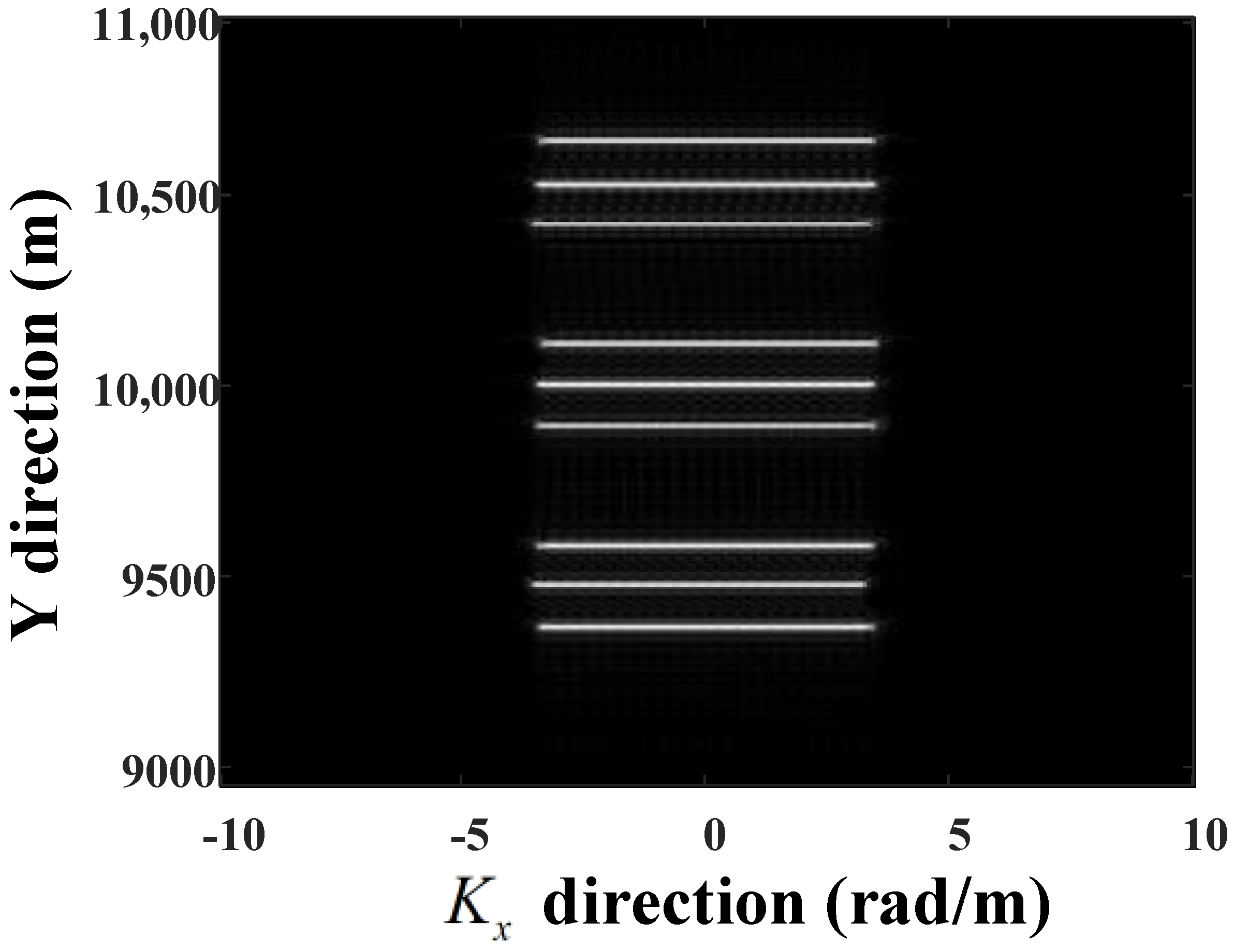

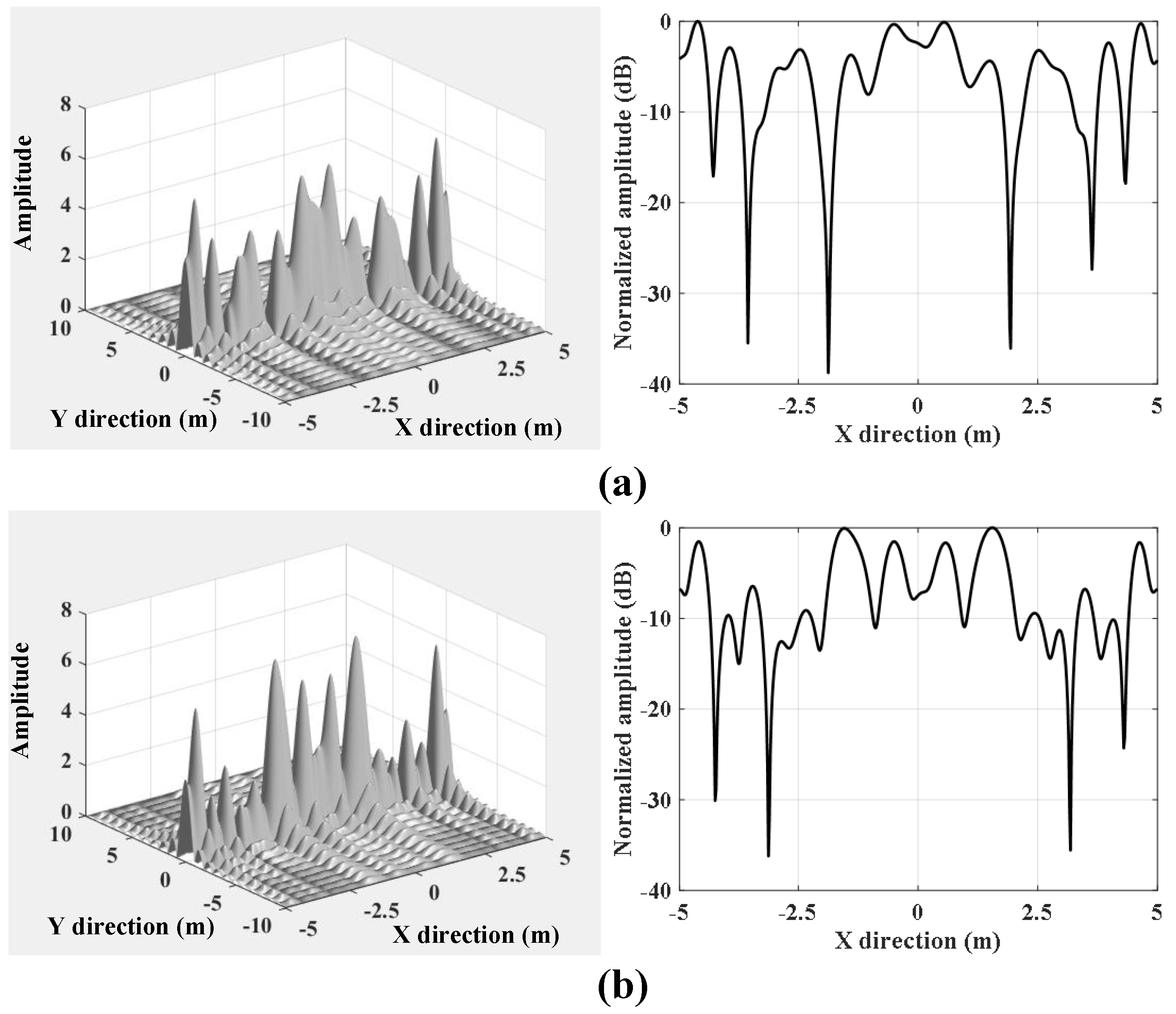
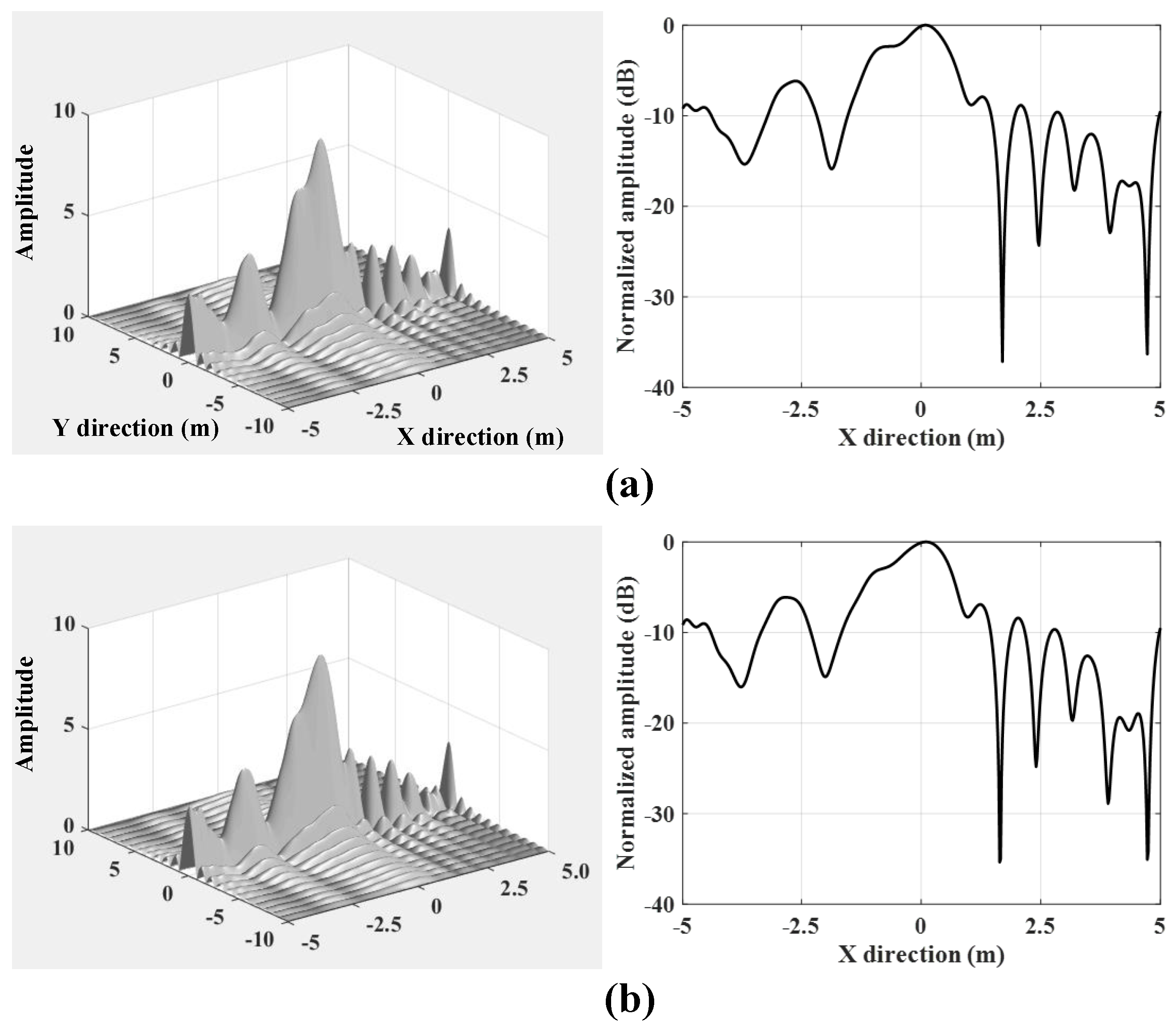
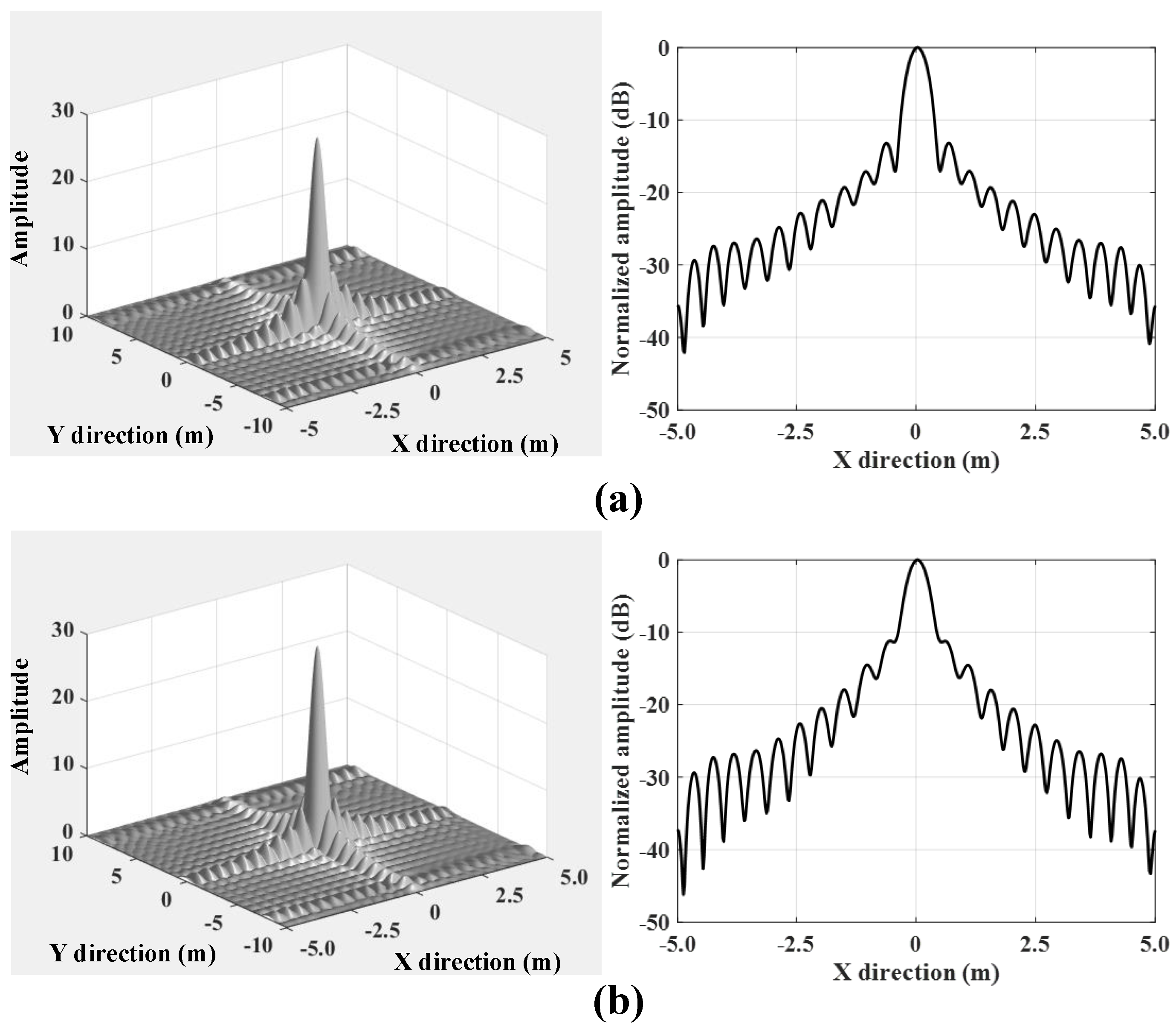
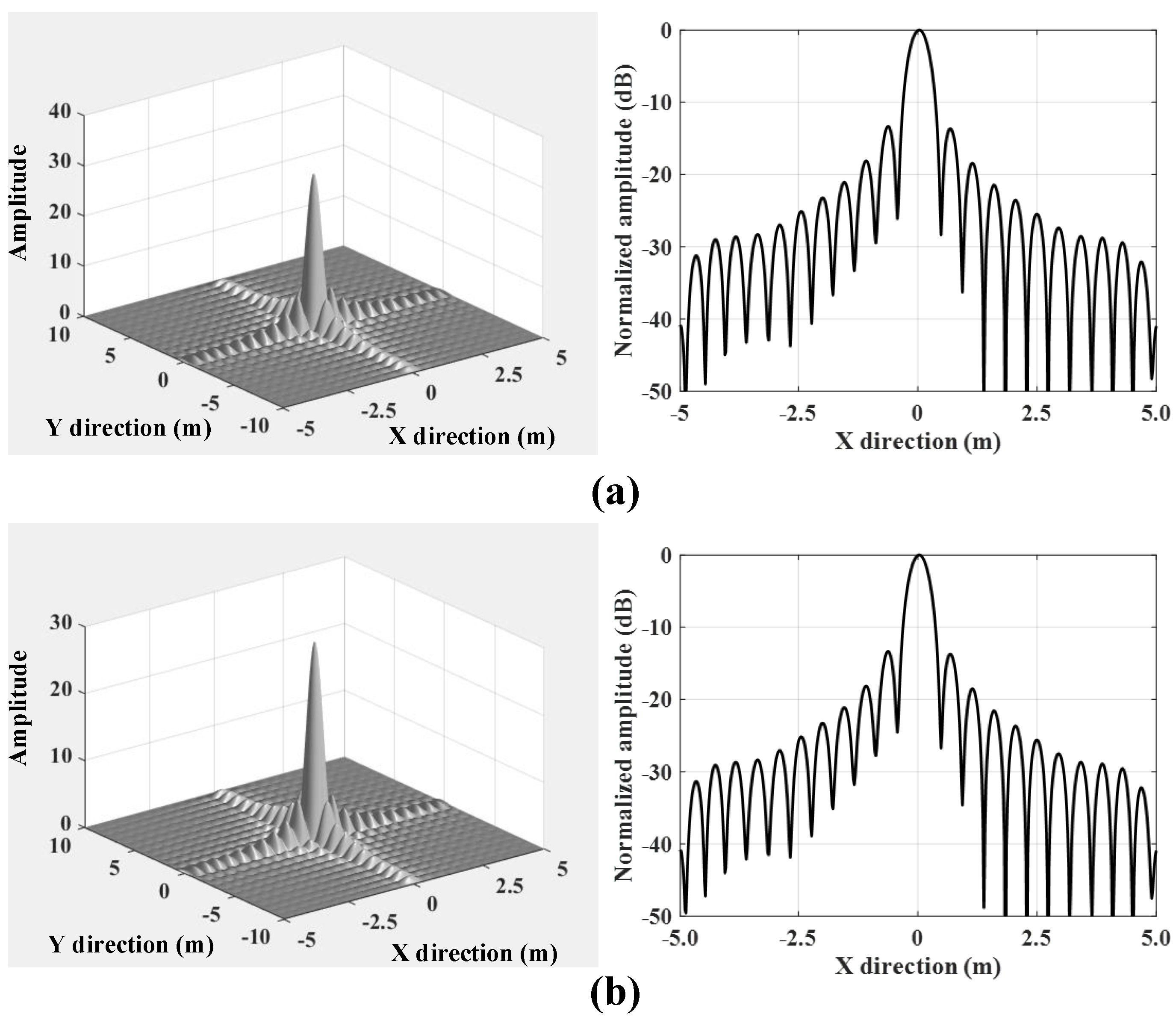
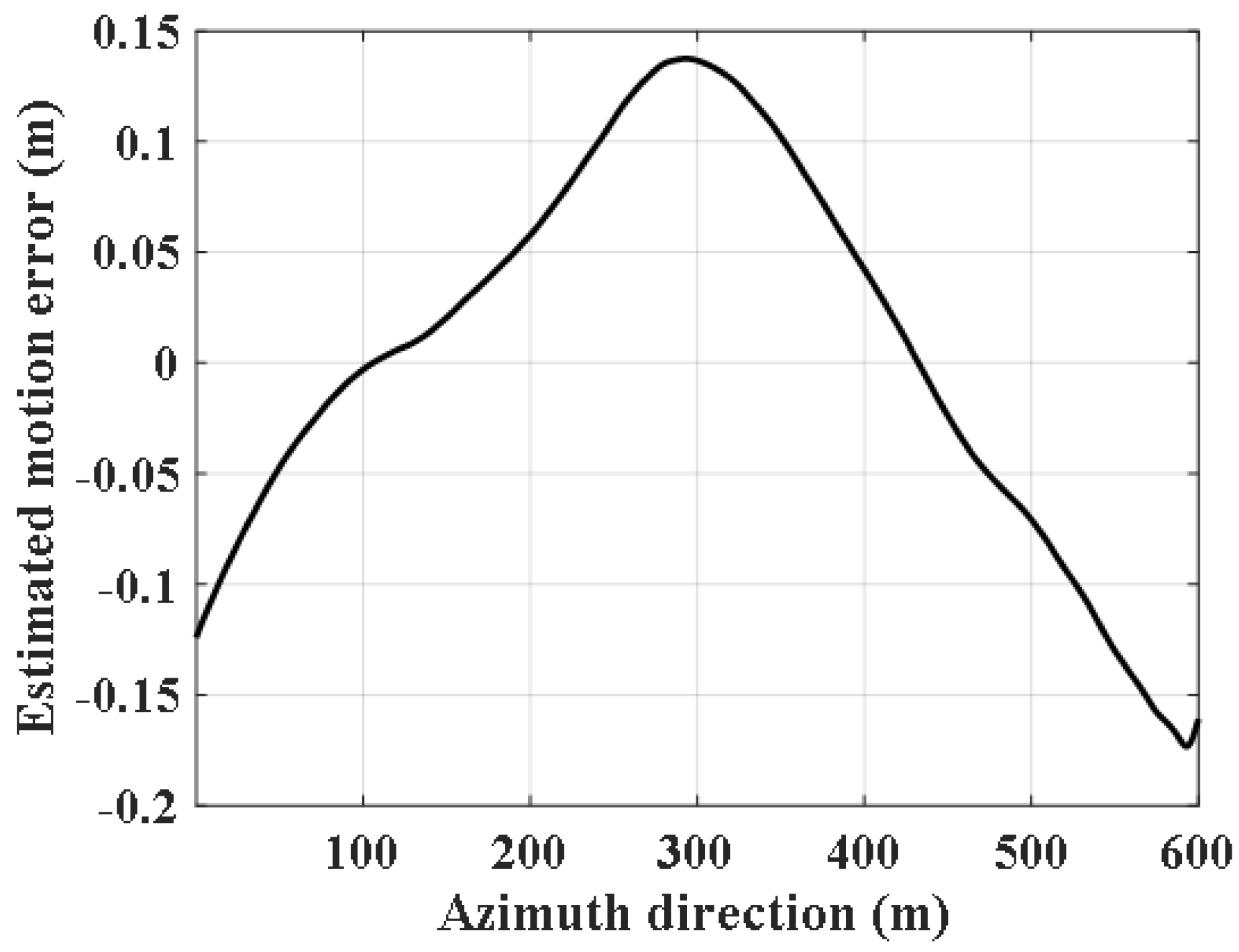


| Wave Band | Ku |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth | 180 MHz |
| Range Center | about 10,000 m |
| Velocity in the x-Direction | 500 m/s |
| Acceleration in x-Direction | −15 m/s |
| Velocity in y-Direction | 120 m/s |
| Acceleration in y-Direction | −12 m/s |
| Synthetic Duration | 0.5 s |
| Point | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | −500 m | 9600 m |
| Point 2 | −500 m | 10,100 m |
| Point 3 | −500 m | 10,600 m |
| Point 4 | 0 m | 9500 m |
| Point 5 | 0 m | 10,000 m |
| Point 6 | 0 m | 10,500 m |
| Point 7 | 500 m | 9400 m |
| Point 8 | 500 m | 9900 m |
| Point 9 | 500 m | 10,400 m |
| y-Direction | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Point | 3-dB width | PSLR | ISLR |
| Point 1 | 0.86 m | −12.91 dB | −9.98 dB |
| Point 2 | 0.85 m | −13.11 dB | −9.91 dB |
| Point 3 | 0.86 m | −13.02 dB | −9.84 dB |
| Point 4 | 0.85 m | −13.10 dB | −9.88 dB |
| Point 5 | 0.85 m | −13.05 dB | −9.89 dB |
| Point 6 | 0.86 m | −13.02 dB | −9.91 dB |
| Point 7 | 0.86 m | −12.94 dB | −9.77 dB |
| Point 8 | 0.87 m | −13.12 dB | −9.84 dB |
| Point 9 | 0.87 m | −13.07 dB | −9.81 dB |
| x-Direction | |||
| Point | 3-dB width | PSLR | ISLR |
| Point 1 | 0.48 m | −11.68 dB | −9.67 dB |
| Point 2 | 0.47 m | −11.83 dB | −9.49 dB |
| Point 3 | 0.53 m | −11.64 dB | −9.57 dB |
| Point 4 | 0.45 m | −12.04 dB | −9.48 dB |
| Point 5 | 0.46 m | −12.17 dB | −9.37 dB |
| Point 6 | 0.47 m | −11.41 dB | −9.60 dB |
| Point 7 | 0.49 m | −10.79 dB | −9.43 dB |
| Point 8 | 0.52 m | −11.80 dB | −9.40 dB |
| Point 9 | 0.52 m | −12.24 dB | −9.59 dB |
| y-Direction | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Point | 3-dB width | PSLR | ISLR |
| Point 1 | 0.86 m | −13.11 dB | −9.88 dB |
| Point 2 | 0.85 m | −12.99 dB | −9.98 dB |
| Point 3 | 0.86 m | −13.09 dB | −9.87 dB |
| Point 4 | 0.85 m | −13.11 dB | −9.99 dB |
| Point 5 | 0.85 m | −13.10 dB | −9.97 dB |
| Point 6 | 0.86 m | −12.96 dB | −9.84 dB |
| Point 7 | 0.86 m | −13.01 dB | −9.88 dB |
| Point 8 | 0.87 m | −13.02 dB | −9.76 dB |
| Point 9 | 0.87 m | −13.13 dB | −9.93 dB |
| x-Direction | |||
| Point | 3-dB width | PSLR | ISLR |
| Point 1 | 0.46 m | −12.91 dB | −9.78 dB |
| Point 2 | 0.48 m | −13.03 dB | −9.87 dB |
| Point 3 | 0.51 m | −12.91 dB | −9.91 dB |
| Point 4 | 0.43 m | −13.03 dB | −9.93 dB |
| Point 5 | 0.43 m | −13.02 dB | −9.92 dB |
| Point 6 | 0.46 m | −12.99 dB | −9.87 dB |
| Point 7 | 0.48 m | −12.91 dB | −9.81 dB |
| Point 8 | 0.50 m | −13.00 dB | −9.89 dB |
| Point 9 | 0.51 m | −12.89 dB | −9.79 dB |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, M.; Zhou, S.; Xing, M. Processing Missile-Borne SAR Data by Using Cartesian Factorized Back Projection Algorithm Integrated with Data-Driven Motion Compensation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081462
Bao M, Zhou S, Xing M. Processing Missile-Borne SAR Data by Using Cartesian Factorized Back Projection Algorithm Integrated with Data-Driven Motion Compensation. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(8):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081462
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Min, Song Zhou, and Mengdao Xing. 2021. "Processing Missile-Borne SAR Data by Using Cartesian Factorized Back Projection Algorithm Integrated with Data-Driven Motion Compensation" Remote Sensing 13, no. 8: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081462
APA StyleBao, M., Zhou, S., & Xing, M. (2021). Processing Missile-Borne SAR Data by Using Cartesian Factorized Back Projection Algorithm Integrated with Data-Driven Motion Compensation. Remote Sensing, 13(8), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081462