Abstract
The South China Sea is rich in hydrocarbon resources and has been exploited for decades by countries around it. However, little is known about the hydrocarbon exploitation (HE) activities in the South China Sea in recent years, especially its intensity changes and development trends. Here, a long-time series of monthly Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) nighttime light (NTL)images were applied to observe and analyze the HE dynamics in the South China Sea from 2012 to 2019. A target recognition method combining feature increment strategy and random forest model was proposed to obtain the spatial distribution of offshore HE targets, with an average comprehensive precision of 94.44%. Then, a spatio-temporal statistical analysis was carried out on the intensity changes and development trends of HE activities. The results showed that: (1) From 2012 to 2019, the quantity of HE targets in the South China Sea has increased from 215 to 310, from rapid to stable increasing taking 2014 as a turning point. (2) The distribution density of HE targets increases year by year, with the maximum density reaching 59/ 10,000 Km2, and with the most significant increase in the new hydrocarbon-bearing fields close to the deep-sea. (3) The quantity of HE targets shallower than -300m has been increasing with years, but showing a decreasing proportion trend, falling from 96.7% in 2012 to 94.2% of the total in 2019. (4) After 2015, the exploitation core of most hydrocarbon-bearing basins began to shift from shallow-sea to deep-sea, with gradually increasing exploitation depth, among which the maximum depth reaching −1580 m. Against the background of the changes in international crude oil prices and the vigorous development of deep-sea HE, this research provides important information and methodological references for the formulation and analysis of offshore hydrocarbon resource exploitation strategies.
1. Introduction
Currently, offshore hydrocarbon exploitation (HE) has become the hotspot of international energy development [1,2] and the main force of global hydrocarbon production growth [3]. Offshore HE activities reflect the situation, technical capabilities, and ownership of offshore hydrocarbon resources developed by different countries or companies [4,5,6]. Meanwhile, it has also posed potential threats to marine ecological diversity [7,8,9,10], environmental protection [5,11,12,13,14,15], and maritime safety [5,16,17]. Therefore, mastering the information of offshore HE activities can provide important references for energy development strategy formulation, marine ecosystem conservation, etc. [4,18,19,20].
The South China Sea is very rich in proven and probable hydrocarbon resource reserves [21], and has the reputation of “the second Persian Gulf” [22]. Countries surrounding the South China Sea have been exploiting its hydrocarbon resources for decades, but little is known about their exploitation activities due to commercial secrets or national interests [6]. Moreover, in recent years, few studies involved the HE activities in the South China Sea, and mainly providing information such as the occurrence year and quantity of offshore platforms or gas flaring sites [11,19,23]. Particularly, lacking the targeted, quantitative, and comprehensive analysis of deeper information such as the intensity changes and development trends of HE activities in recent years.
Dynamic monitoring of offshore HE targets (e.g., offshore platforms or gas flaring) is an important means of obtaining information on offshore HE activities. Compared with traditional survey approaches (e.g., aircraft inspections, ocean observations, etc.), in recent years, remote sensing observation technology has provided great convenience for the monitoring of the offshore HE activities in large-scale, inaccessible sea areas [4,5,6,24,25,26]. The mainly used data sources include nighttime light (NTL)/ infrared (IR), optical and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) remote sensing images.
For the advantages of SAR images on all-weather observation and the sensitivity to the detection of metal targets on the sea surface, it performs excellently in the sea surface targets’ recognition [24,26,27]. The Constant False-Alarm Rate (CFAR)/dual-parameter CFAR algorithm, which is commonly used for ship target detection, has been proposed for offshore platform extraction based on the “position-invariant” characteristic [26,28,29]. But uncertainties still exist in the optimization setting of the occurrence frequency (OF) threshold. Moreover, in the open and shared data list, SAR images have insufficient spatial coverage and low observation frequency, which limits their application in long-term series and large-scale offshore HE monitoring [6,30].
Compared with SAR images, there are relatively more data sources and data inventory for traditional optical remote sensing images, including Landsat1-8, SPOT1-7, GF1/2, ZY-3 [6], etc. For example, based on the characteristics of “position-invariant and size-invariant”, the Landsat images have been successfully applied to the extraction of offshore platforms through the combination of iterative threshold segmentation algorithm or transform-based algorithm and “time-series and multi-refinement strategies” [6,31]. Especially, Liu et al. [19] have obtained the spatio-temporal distribution of offshore platforms in the South China Sea from 1992 to 2014 by using long-time series Landsat images. While the existing methods still lacks a generalizable standard in the optimization setting of the OF threshold, and the processing process is complicated. Moreover, a problem that cannot be ignored is that traditional optical images are highly susceptible to cloud coverage [31,32]. In sea areas with a wide range and high cloud coverage, it is usually needed to collect a large number of high-quality images, which poses a challenge to the dynamic and up-to-date data update requirements.
Compared with the first two data sources, the NTL/ IR image data (e.g., the infrared band of MODIS and ATSR images, the DMSP/OLS, NPP/VIIRS) has been widely used in the monitoring of the gas flaring [11,15,23,32,33,34,35,36]. Due to its relatively low spatial resolution, it is limited in the fine discrimination of targets in the close range [6]. However, NTL/IR image data usually has a data inventory that can meet the large-scale, high-time resolution, and long-term sequence coverage, providing free and sufficient data for continuing to reveal the dynamics of global offshore HE activities [23]. For example, Elvidge et al. [23] obtained the global gas flaring distribution using four VIIRS IR bands data based on the VNF algorithm [37] and is currently continuously updating its annual product (https://eogdata.mines.edu/download_global_flare.html (accessed on 1 February 2021)). However, this method is not robust enough to recognize the targets with weaker radiation intensity, such as natural gas exploitation platforms with smaller gas flare. Moreover, the product does not include the “weak targets” without gas flaring, such as the central processing platform and the smaller wellhead platform, which will have a certain impact on the disclosure of offshore HE activities.
For the aforementioned problems, this study intends to use long-time series VIIRS NTL images from 2012 to 2019 to observe the dynamics of offshore hydrocarbon activities in the South China Sea, and to analysis its intensity changes and development trends. The specific objectives of this study were: (1) To make full use of the advantages and characteristics of time-series NTL remote sensing images to develop a new automatic extraction method for offshore HE targets (offshore gas flaring areas or offshore platforms); (2) to obtain the spatio-temporal distribution of HE targets in the South China Sea in recent years; (3) and to further reveal the spatio-temporal intensity changes of HE activities and the evolution of development trends in the South China Sea. The results will provide important information reference for research groups, managers, and decision makers to understand the situation and trends of HE in the South China Sea, as well as for subsequent energy structure assessment and development strategy formulation.
2. Study Area
This study focuses on the offshore HE activities carried out by the countries surrounding the South China Sea Basin. The South China Sea area east of 105°E was selected as the study area (Figure 1), with the extension of east to the coast of Philippines, west to the coast of Vietnam, north to the coast of Chinese mainland, and south to the coast of Malaysia and Brunei. It covers the entire South China Sea basin, with an average depth of −1212 m and a maximum depth of −5559 m [38]. Moreover, it has many coral islands and reefs, rich fishery resources [38], and one-third of the world’s ocean shipping passes through this area [39], especially the South China Sea bed is considered to have huge hydrocarbon deposits [21].
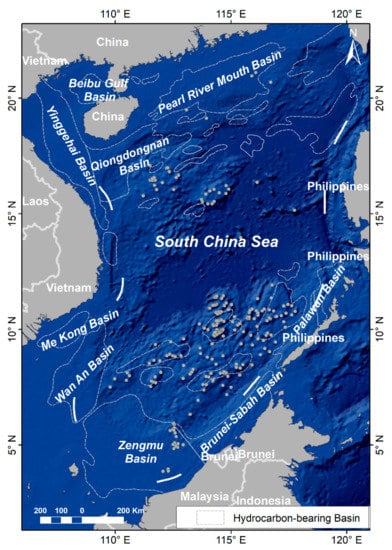
Figure 1.
Study area.
There are more than 30 hydrocarbon-bearing basins distributed from north to south in this sea area. The northern part mainly includes the Beibu Gulf Basin, the Pearl River Mouth Basin, the Yinggehai Basin, and the Qiongdongnan Basin; the southern part mainly includes the Me Kong Basin, Wan An Basin, Zengmu Basin, Brunei-Sabah Basin, and Palawan Basin. The basins located in the north are rich in natural gas resources; the basins located in the south are mainly rich in oil resources. In general, the reserves of hydrocarbon resources in the southern basins are more abundant than those in the northern basins [38]. Currently, the surrounding countries have all participated in the exploitation of hydrocarbon resources in the South China Sea, and the exploitation activities have continued for decades.
As the main facility for offshore HE, offshore platforms are in a variety of types, including oil platforms (Figure 2a), natural gas platforms (Figure 2b), central processing platforms (Figure 2c), wellhead platforms (Figure 2d), etc. The oil platforms are generally accompanied by gas flaring, and the radiation intensity is strong, showing bright halo areas on the NTL images (Figure 2(a-2)). Compared with the oil platforms, the gas flaring of the natural gas platforms is smaller, and it is usually smaller bright halo areas on the NTL images (Figure 2(b-2)). The central processing platforms and wellhead platforms usually have no gas flaring, and their radiation intensity are weaker (Figure 2(c-2,d-2)). Here, the gas flaring areas with halo characteristics and the offshore platforms with weak radiation intensity in the NTL images are collectively referred to as offshore HE targets.

Figure 2.
Image features of different HE targets: (a) is an oil platform group with gas flaring, (b) is a gas platform with gas flaring, (c) is a central processing platform without gas flaring, (d) is a wellhead platform without gas flaring; (a-1)–(d-1) are the corresponding panchromatic bands of high-resolution images; (a-2)–(d-2) are the corresponding NTL images.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Datasets
Datasets used in this study include VIIRS NTL images, Chinese high-resolution images, offshore platform records, and bathymetric data.
3.1.1. VIIRS Day/Night Band (DNB) Monthly Composite Images
The VIIRS sensor has a total of 22 bands, of which the day and night band (DNB)has the ability to detect both electric lighting and combustion sources [37], which can meet our detection requirements for the targets with gas flaring and targets without gas flaring. This band has long-term sequence, high-time resolution global observations, and has been applied to the detection of sea surface targets such as ships and gas flaring sites [40]. Considering the impact of environmental factors such as cloud coverage in the study area, we adopted VIIRS monthly composite products. It is a composite of effective observations under the condition of no cloud or less cloud selected from the monthly daily observations. In this study, a total of 117 images (resolution: 500m; range: Tie3_75N060E; Data format: VCMCFG) from April 2012 to December 2019 were downloaded from the Earth Observation Group, Payne Institute for Public Policy (https://eogdata.mines.edu/nighttime_light/monthly/v10/ (accessed on 1 February 2021)).
3.1.2. Chinese High-Resolution Images and Offshore Platform Records
To verify the accuracy of the recognition results of HE targets based on long time-series VIIRS images, we obtained high-spatial resolution images(Gaofen Satellite, GF; Resources satellite, ZY) from the China Center for Resources Satellite Data and Application (http://www.cresda.com/CN/ (accessed on 1 February 2021)), and obtained the offshore platform records from the State Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Information System (SKLREIS, http://www.lreis.ac.cn/ (accessed on 1 February 2021)), Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGSNRR, CAS). There are a total of 121 scenes of high-resolution images (39 scenes in 2015, 38 scenes in 2016, and 47 scenes in 2017), including GF-1 (2 m), GF-2 (1 m), ZY-1 (2.36 m), ZY-3 (2.1 m), mainly covering the southern sea areas of the Zengmu Basin, with cloud coverage ≤15%. The offshore platform records include CNOOC’s offshore platform records and field survey records, provided by the marine and coastal zone research team of the SKLREIS. It records the location distribution and photos of offshore platforms in the northern sea areas of the South China Sea from 2014 to 2017.
3.1.3. Bathymetric Data
To analyze the development trend of offshore HE activities and the technical capabilities of the surrounding countries, we downloaded the gridded bathymetric data set GEBCO_2020 Grid from CEBCO (https://www.gebco.net/data_and_products/gridded_bathymetry_data/ (accessed on 1 February 2021)) to extract the exploitation water depth of the HE targets in the study area. The GEBCO_2020 Grid is a global terrain model of the ocean and land, with an interval of 15 arc seconds, provided by the GEBCO Compilation Group.
3.2. Methods
Here, we propose a novel automatic method for recognizing the HE targets based on time-series VIIRS DNB images. First, a feature increment strategy is adopted to construct multi-dimension target features based on time-series DNB images, and then a machine learning model is used for target recognition to avoid the difficulty in the optimization setting of the OF threshold in previous studies. In addition, the tracking analysis of the intensity changes and development trends of HE activities in this study is mainly based on the spatio-temporal distribution of HE targets. Here, the methods of spatio-temporal statistical analysis (time filter, quantitative statistics, mesh statistics, standard deviation ellipse) are used to quantify the exploitation activities from the perspectives of quantity, speed, density, depth, and gravity center. The technical route is shown in Figure 3, which is mainly composed of four parts.
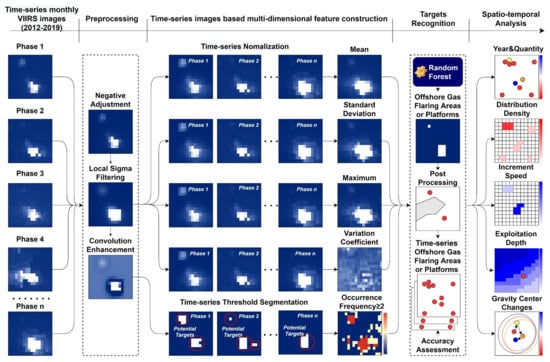
Figure 3.
Technical flowchart.
3.2.1. Data Preprocessing
The VIIRS monthly composite images provide pixel radiation value to represent the light intensity (unit is nW·cm−2·sr−1), pixel radiation value 0 and below are regarded as no light. To avoid affecting the subsequent calculations, the negative pixels in the original image (Figure 4a) are assigned to 0 (Figure 4b).
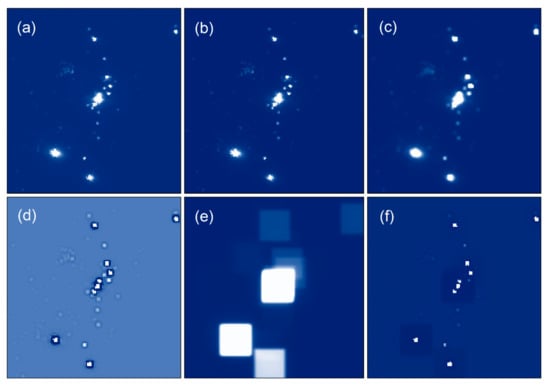
Figure 4.
Data preprocessing: (a) original image; (b) negative adjustment image; (c) local Sigma filtered image, the window size is 3 × 3, Sigma factor is 4; (d) Hp image, convolution kernel is 3 × 3; (e) Lp image, convolution kernel is 27 × 27; (f) the difference between Hp image and Lp image. The parameters used in the above process are obtained through estimation and trial and error, and remain unchanged for all NTL images used.
In addition, because the VIIRS monthly composite images will generate a lot of noise during the generation process, it will cause false alarms in the subsequent target detection and recognition process, so filtering processing is required. Local Sigma filtering is a better method for noise processing among many filtering methods [41]. Therefore, here we perform local Sigma filtering on the images after negative adjustment to remove noises such as sea clutter (Figure 4c).
After the aforementioned processing, two convolution filters (high-pass filter and low-pass filter) in ENVI 5.3 are used to enhance their information based on the distance between the targets to ensure that offshore HE targets with weaker lights can be effectively detected. First, the high-pass filter (Hp) was used to increase the pixel values of some weakly-lit targets (Figure 4d), and then the low-pass filter (Lp) was used to obtain low-frequency background information such as light halo and sea water (Figure 4e), and finally the difference between the Hp and the Lp is calculated to enhance the separation of the sea surface target and the background (Figure 4f).
3.2.2. Multi-Features Construction of Offshore HE Targets
The spatial position of offshore HE targets is fixed [6] and will appear in the same position multiple times in the time-series NTL images, which is the most important feature that distinguishes them from moving targets (e.g., ships). Many studies believed that the higher the OF of a target at the same spatial position, the more probable it is to be a HE target [4,6,11,25]. Therefore, our first step is to obtain the OF feature of the targets. First, a fixed threshold t is used to binarize the convolution-enhanced time-series images to separate potential HE targets from the seawater background (Figure 5(a–l)). Then, the time-series of potential HE targets are added pixel by pixel to obtain statistical images of OF (Figure 5m). According to the “position-invariant” characteristic, targets that appear twice or more in the same poisons are more likely to be HE targets. Of course, we cannot rule out that different ships will appear in the same position at different times. Therefore, the targets with OF ≥ 2 are separated to form a purified set of potential HE targets (Figure 5n) to further reduce the impact of false alarm targets (e.g., ships, sea clutter).
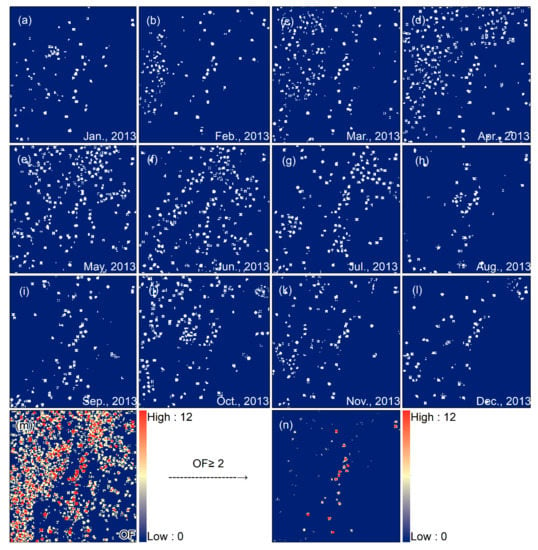
Figure 5.
Target OF statistics: (a–l) are the binarized segmentation results of time-series images in one year, with a threshold t = 0.5; (m) is the OF statistics; (n) is the purified result, the threshold f = 2. The parameters used in the above process refer to empirical values, which are obtained through estimation and trial and error, and remain unchanged for all NTL images used.
Next, existing studies usually use a larger OF threshold F to filter the set of potential targets, and identify those with a OF ≥ F as real HE targets [6,11,29]. However, an optimal threshold F is difficult to determine. Therefore, the feature increment strategy is adopted here: Besides the OF, four statistical indicators (average, maximum, standard deviation, and variation coefficient) of light brightness characteristics were established based on the pixels of time-series images to increase the features description of the offshore HE targets from multiple dimensions. Here, the time-series images involved in the calculation of the above multi-dimensional features refer to all monthly images in one year.
Since the monthly composite images have different value ranges, we normalized the time series images after negative adjustment by using Min-Max Normalization (Figure 6(a–l)), and then calculate their average (Figure 6m), maximum (Figure 6o), standard deviation (Figure 6n) and variation coefficient (Figure 6p). After that, the novelty of our method is that we combined them with the OF feature into a 5-band image as a new data source for HE targets recognition, which creates conditions for the application of machine learning models.
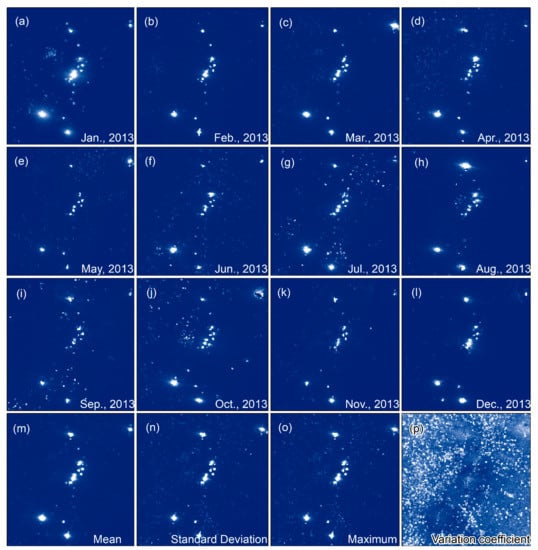
Figure 6.
Target brightness feature statistics: (a–l) are the normalized results of time-series images; (m) is the mean value; (n) is the standard deviation; (o) is the maximum value; (p) is the variation coefficient.
3.2.3. Offshore HE Targets Recognition Based on Random Forest Model
After constructing multiple features of offshore HE targets, the random forest model from many machine learning models was choose to automatically recognize them. The main reason for our choosing is that the random forest model has built-in randomly selected features and testing methods, which will not overfit when the number of trees increases, and does not require any additional feature selection or model performance testing methods [42,43]. It is currently widely used to describe remote sensing data sets that span time and space [44,45,46,47].
Before recognition, we obtained the spatial distribution of offshore HE targets in the southern Zengmu Basin and the northern South China Sea through visual interpretation from high-resolution remote sensing images and offshore platform records. We selected a part of them as a reference for visual labeling of training samples in the new composited multi-feature images, and the rest part provided us with reference for testing and verification. Taking 2017 as an example, we have labeled 115 samples (9770 pixels), including 43 HE targets samples (118 pixels) and 72 seawater samples (9652 pixels). Since the offshore HE targets will change over time, we used the training samples of 2017 as the standard and modified the training samples based on the composite multi-feature image of each year, and finally generated the training samples in 2012–2019.
It should be noted that the random forest model is applied pixel-based. After the target recognition calculation, the edge of the target or the area far away from the target will still contain many isolated pixels. Those isolated pixels that are unlikely to become offshore HE targets will cause misrecognition [6,25], and need to use morphological filtering techniques such as erode, dilate, and opening operations to eliminate them. Due to the relatively low spatial resolution of the VIIRS images, the offshore HE targets consists of only a few pixels, so the size of the morphological filter kernel is set to 3 × 3.
Offshore platforms are located in hydrocarbon-bearing basins that have been explored in advance, so it is necessary to manually remove significant false alarm targets (e.g., islands, coral reefs, ships) far away from the hydrocarbon-bearing basins. Besides, due to the presence of many port facilities, docked ships close to the coastline, and artificial facilities on islands and reefs, these objects will also show the characteristics of position-invariant, which will generate many false alarm targets. Therefore, based on prior knowledge and reference to existing research, we have established buffer zones (10 Km towards the sea [6]) and made masks for countries along the coastline, islands and reefs. The false alarm targets in the area covered by the mask are eliminated to reduce interference from islands, reefs, coastal facilities, and docked ships.
After the aforementioned processing, two areas from the northern and southern parts of the South China Sea were selected for precision evaluation, one of which is located in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, and the other is located in the Zengmu Basin. Meanwhile, to verify the reliability of the proposed method, this study used three periods (2015, 2016 and 2017) of offshore platform records and high-resolution remote sensing images to verify the recognition results in the evaluation areas. In order to quantitatively evaluate the reliability of the proposed method, we use the F1-measure index to comprehensively evaluate the precision of target recognition. The F1-measure index is widely used in natural language processing, machine learning and other fields [48,49,50], its common form as shown in Equation (1).
In Equation (1), (precision) is the proportion of correct recognitions in all recognitions, (recall) is the proportion of correct recognitions in all that should be correctly recognized, (true positives) is the quantity of correct recognitions, (false positives) is the quantity of incorrect recognitions, (false negatives) is the quantity of omissive recognitions. Limited by the spatial resolution of the VIIRS images, here we regard the offshore platforms or platform groups within the range of twice the pixel distance (with a radius of 1 Km) as one HE target. Therefore, in the Equation (1) are the statistical results based on the total amount obtained through proximity analysis on the real offshore platforms.
3.2.4. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Offshore HE Activities
The construction year and quantity of offshore HE targets directly reflect the sequence and intensity of exploitation activities in areas containing hydrocarbon resources, which can be obtained through the time filter and quantitative statistic. Combining the scope of hydrocarbon-bearing basins can further count the quantity of HE targets in each basin. The increment speed represents the time difference in the intensity of HE activities, which is calculated by the annual increase of HE targets. In addition, the increment speed is gridding-spatialized here to reflect its spatial difference. Since the minimum division scale of the bidding blocks for HE in the surrounding countries is generally 0.5°, the spatial grid division scale is set to 0.5° × 0.5° here. Similarly, the distribution density is obtained by calculating the ratio of the quantity of targets in each grid to the grid area, which is used to characterize the spatial pattern of the overall intensity of HE activities.
The standard deviation ellipse are commonly used indicators in the study of the spatial distribution characteristics of geographic entities, and its center reflects the gravity center or distribution center of geographic entities. The moving direction and distance of the gravity center can reflect the range of changes and the spatial differences of the geographical entities within a certain period. Therefore, it is used here to describe the spatio-temporal shift process of the gravity center of HE targets to reveal the development characteristics of HE activities in the plane space over time. The change of exploitation water depth characterizes the development trend of offshore HE activities in the vertical space, and represents the technical level of offshore HE in various countries or companies. We first combined the two major marine HE depth classification standards currently used in the world (NORSOK standard and Occident standard), and considered the characteristics of the steep transition between the continental shelf and ocean basin of the South China Sea, and further divided the offshore HE depths into four levels (Figure 7). Then, based on the bathymetry data, the annual variation of the quantity of HE targets within each depth level and the annual variation of the depth information (including minimum, average, and maximum depths) of HE targets within each basin were counted respectively.
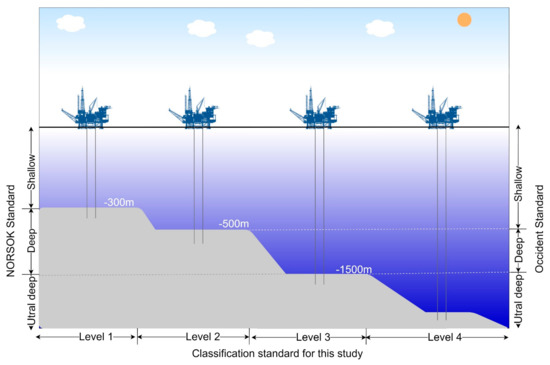
Figure 7.
Depth classification for offshore HE in this study. Level 1: ≥−300 m, Level 2: −300 m > d ≥ −500 m, Level 3: −500 m >d ≥ −1500 m, d <− 1500 m.
4. Results
4.1. Precision Evaluation of Target Recognition for Offshore HE
Target recognition verification (Figure 8) and precision evaluation (Table 1) were carried out for the two regions in three periods. The results show that the average precision is 96.58%, the average recall is 93.16%, and the average F1-measure is 94.44%, indicating that the method proposed in this study is reliable. In addition, we compared this result with the Global Gas Flaring product (https://eogdata.mines.edu/download_global_flar-e.html (accessed on 1 February 2021)) released by the Earth Observation Group (Figure 8). It can be seen from the figure that the released product can only calibrate targets with obvious gas flaring, and the F1-measure is relatively low, and it cannot meet the calibration of various types of offshore HE targets. Our method can recognize the HE targets without gas flaring, and is more conducive to obtaining information about actual offshore HE activities.
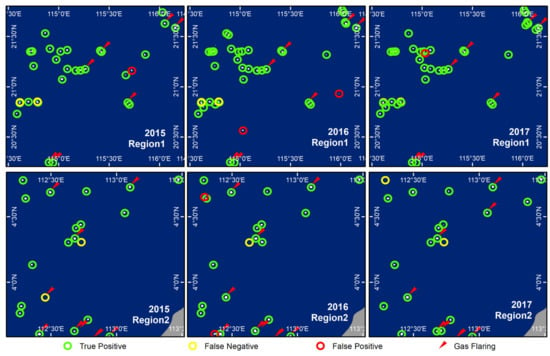
Figure 8.
Target recognition verification: Region1 is located in the northern part of the Pearl River Mouth Basin and Region2 is located in the southern part of the Zengmu Basin. Green circles indicate correctly recognized targets, yellow circles indicate omissive targets, and red circles indicate incorrectly recognized targets. The red arrows indicate the Global Gas Flaring Product released by the Earth Observations Group.

Table 1.
Precision evaluation.
4.2. Recognition Results of Offshore HE Targets from 2012 to 2019
Based on the VIIRS monthly composite images from 2012 to 2019, we obtained the distribution of offshore HE targets within the study area (Figure 9). From 2012 to 2019, the overall quantity of HE targets is increasing year by year, from 215 to 310. From the perspective of the entire South China Sea, HE targets present an asymmetrical distribution pattern of “more in the south and less in the north”, of which the targets in the southern basins account for about 60% of the total.
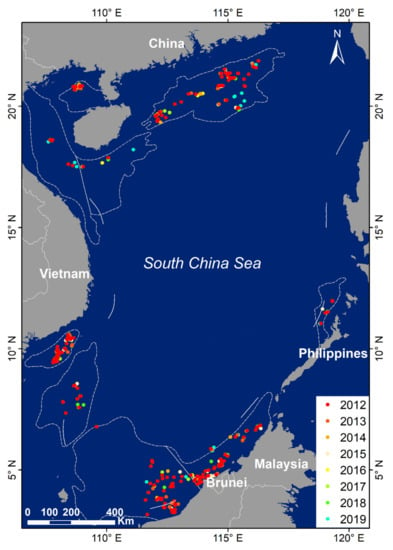
Figure 9.
Recognition results of offshore HE targets from 2012 to 2019.
In addition, we have also made statistics in each hydrocarbon-bearing basin (Table 2). The quantity of targets in the Brunei-Sabah Basin is the largest, with more concentrated distribution in the southwest part of the basin and sparse distribution in the northeast part. The second-largest quantity is in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, which is relatively evenly distributed. The quantity of targets in the Zengmu Basin and the Mekong Basin are similar, and they are mainly distributed on the east side of their respective basins, but the targets distribution in the Me Kong Basin is more concentrated. The quantity of targets in the Wan An Basin and the Beibu Gulf Basin are also similar, the targets in the Beibu Gulf Basin are mainly concentrated in the north, while the targets in the Wan An Basin are scattered in the middle. The targets in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan Basins are distributed along the coast of Hainan Island. Similarly, the targets in the Palawan Basin are distributed along the strike of Palawan Island, but the quantity of targets is the least.

Table 2.
Statistics of offshore HE targets in each basin.
4.3. Increment Speed Changes of Offshore HE Targets from 2012 to 2019
As can be seen from the statistical results (Figure 10), the total amount of offshore HE targets is increasing year by year, but it shows two different growth stages. From 2012 to 2014, it was in a stage of rapid increase. After 2014, the increment speed began to slow down and entered a period of stable increase. This may be related to the decline in international oil prices. Different from the overall trend, the quantity of offshore HE targets in the Beibu Gulf Basin and the Me Kong Basin was in a rapid growth stage during 2012–2014 and began to slowly decrease after 2014. While the targets in the remaining basins have been increasing year by year from 2012 to 2019. In particular, the quantity of targets in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, the Zengmu Basin and the Brunei-Sabah Basin has increased significantly.
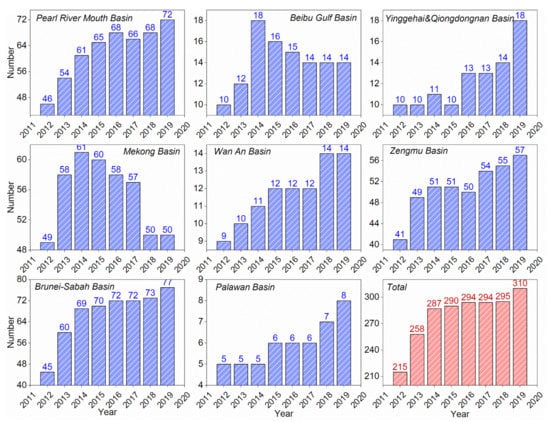
Figure 10.
Changes in the quantity of offshore HE targets from 2012 to 2019.
Subsequently, we spatialized the increment speed, as shown in Figure 11. Before 2014, the quantity of targets for all hydrocarbon-bearing fields in each basin had positive growth. After 2014, in addition to emerging hydrocarbon-bearing fields close to the deep sea, some other hydrocarbon-bearing fields began to show negative growth, especially the fields closer to the coast. This result also explains why the increment speed has slowed down after 2014. From this, we can also find that the increment speed of hydrocarbon-bearing fields closer to the coast is not all in a state of decline, and there are still growth areas in the sea areas near the coasts of Malaysia, Brunei, Vietnam, and Philippines. For example, after 2014, hydrocarbon-bearing fields in the Zengmu Basin and Brunei-Sabah Basin that are close to the coast have experienced a decline and growth in targets increment speed, indicating that these areas are still important HE areas for Malaysia and Brunei.
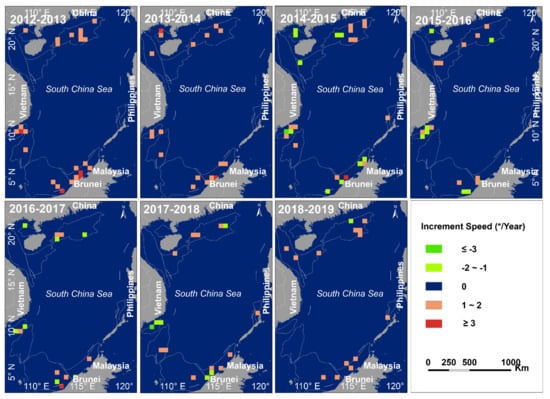
Figure 11.
Spatial differentiation in the increment speed of offshore HE targets in each basin from 2012 to 2019.
4.4. Distribution Density Changes of Offshore HE Targets from 2012 to 2019
We further conducted mesh statistics on the distribution density of HE targets (Figure 12). Overall, the distribution of HE targets generally presents the characteristics of “high density in shallow-sea and low density in deep-sea”, and the distribution density in each basin has been increasing year by year from 2012 to 2019, especially in the deep-sea areas. For example, the distribution density of HE targets in the southwestern Pearl River Mouth Basin, the northern Beibu Gulf Basin, the central Me Kong Basin, the southeastern Zengmu Basin, and the southwestern Brunei-Basha Basin has been relatively high, reaching 27–59/10,000 Km², indicating that these areas close to the coast have been exploited heavily and have always been a hot spot for offshore HE. In addition, the distribution density in the northern Pearl River Mouth Basin, the central Yinggehai Basin, and the eastern Zengmu Basin has increased with years, and has gradually become new hot spots for HE. Meanwhile, the distribution density in the southeastern Pearl River Mouth Basin, the northern Qiongdongnan Basin, the central and eastern Wan An Basin, the northeastern Brunei-Sabah Basin, and the western Palawan Basin also showed a trend of increasing with years. Moreover, these areas are close to the deep-sea, indicating that most of the countries surrounding the South China Sea have the same strategy in increasing deep-sea HE.
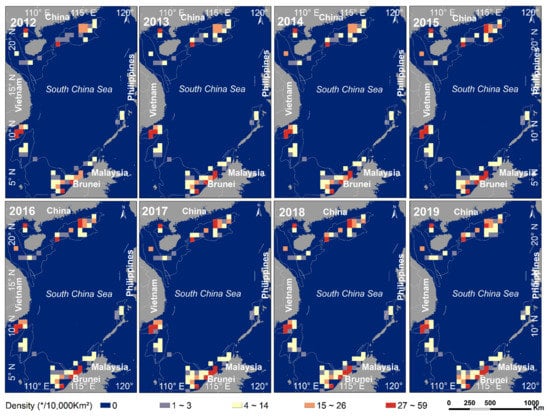
Figure 12.
The spatial pattern of distribution density of offshore HE targets in each basin from 2012 to 2019.
4.5. Development Trends in the Depth of Offshore HE from 2012 to 2019
The statistics of the quantity of HE targets for each depth level from 2012 to 2019 (Figure 13) show that targets shallower than −300 m account for most of the total. Although its quantity is increasing year by year, its proportion is declining with years, down from 96.7% in 2012 to 94.2% in 2019. In contrast, the quantity and proportion of targets deeper than −300 m are increasing year by year, mainly in the southern Pearl River Mouth Basin and the northern Brunei-Sabah Basin. Although the quantity of targets in the narrow interval between −300 m and −500 m has remained unchanged for many years, it has increased rapidly after 2018. The quantity of targets located between −500 m and −1500 m has maintained steady growth, while after 2018, there have been ultra-deep targets exceeding −1500 m. The above results show that the exploitation of hydrocarbon resources in the South China Sea is still in the shallow water stage in recent years, but the signs of development to the deep sea and even ultra-deep sea stages are very obvious, which is consistent with the trend of the world’s offshore HE.
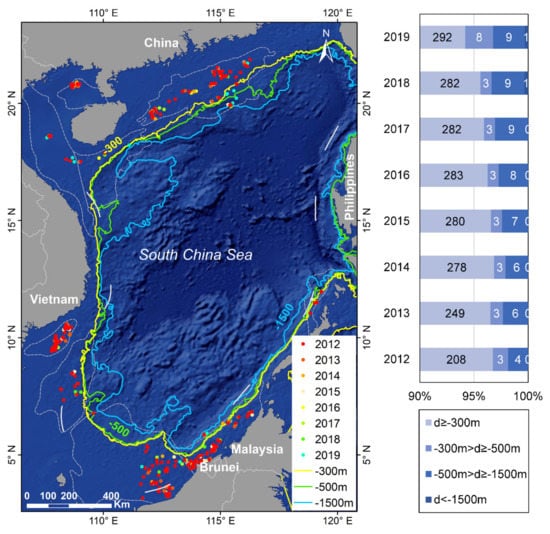
Figure 13.
Spatio-temporal changes in the quantity of HE targets in different exploitation depth levels from 2012 to 2019.
Judging from the HE water depth statistics of the basins (Figure 14), it have shown an increasing trend in most basins with years. This also confirms from a quantitative perspective that the offshore HE of countries around the South China Sea is gradually moving toward the deep-sea. Most of the HE targets in the study area are in sea areas shallower than −200 m. However, with the advancement of HE technology, the maximum exploitation depth has now broken the record of −1423 m in 2012, reaching −1580 m. What is more special is that the maximum HE water depth in the Me Kong Basin increased to −69 m in 2013 and continued until 2016, but fell back to −57 m after 2017.
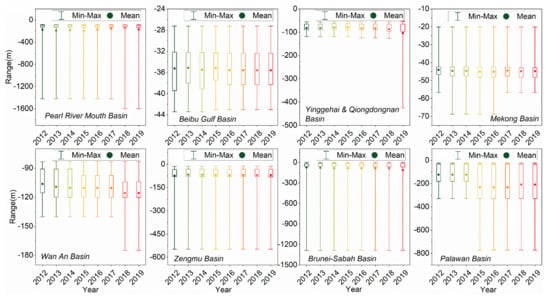
Figure 14.
Changes in the water depth of HE targets in each basin from 2012 to 2019.
4.6. Gravity Center Shift of Offshore HE Targets Distrbution from 2012 to 2019
Based on the spatial distribution of HE targets, we used the Directional Distribution tool of ArcGIS 10.0 to drew the gravity centers shift path and standard deviation ellipses of the HE targets in each basin (Figure 15) to further explore the overall development trend in HE activities of countries surrounding the South China Sea in recent years.
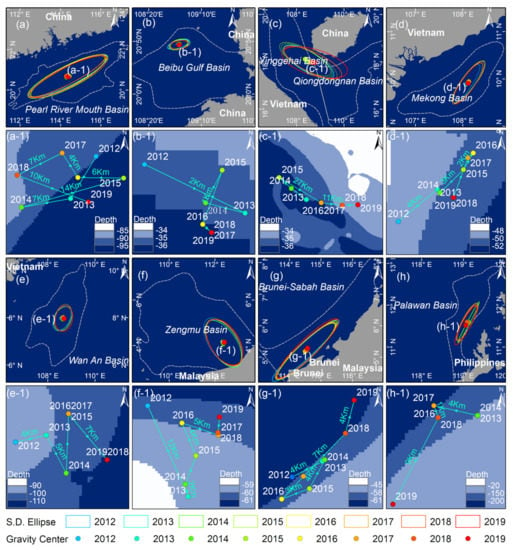
Figure 15.
Gravity center shift of offshore HE targets distribution in each basin from 2012 to 2019. (a–h) are the GCHETDs and standard deviation ellipses in each basin respectively; (a-1–h-1) are the corresponding shift paths of the GCHETDs in each basin respectively.
From 2012 to 2019, the shift path direction of the gravity center of HE targets distribution (GCHETD) in the Pearl River Mouth Basin was relatively circuitous. It is in a state where the exploitation of new and old hydrocarbon-bearing fields is carried out together, and the exploitation in shallow-sea and deep-sea go on simultaneously. The GCHETD in the Beibu Gulf Basin began to shift to the deep-sea away from the coast in 2015, but the overall change was not significant. The changes in the Yinggehai Basin and Qiongdongnan Basin show obvious characteristics of strike changes. Since 2014, it has gradually transfer to the Qiongdongnan Basin, which indicates that the Qiongdongnan Basin will become a new hot area. This is consistent with the previous study results.
The shift distance of GCHETD of the Me Kong Basin was relatively small during 2012–2019. However, the shift process still revolves around the Bach Ho oil field, indicating that it is still the most important offshore hydrocarbon producing areas of Vietnam at present. The shift path of the GCHETD in the Wan An Basin progressed in a “Z” shape from 2012 to 2019, and gradually moving from shallow-sea to deep-sea.
Different from Mei Kong Basin and Wan An Basin, the GCHETD in the Zengmu Basin experienced a relatively large-span shift to coast before 2013, indicating that hydrocarbon-bearing fields close to the coast still have great exploitation value. After 2013, it began to shift toward the deep-sea far away from coast. The GCHETD of the Brunei-Sabah Basin has been roundabout in the southwestern part of the basin from 2012 to 2017, and it was mainly carried out in batches around the old hydrocarbon-bearing fields. After 2017, its GCHETD began to follow the basin’s strike toward the deep-sea in the northeast.
Similar to the Brunei-Sabah Basin, the GCHETD of the Palawan Basin follows the strike of the basin. During 2012–2017, it changed from shallow-sea to deep-sea, but after 2017, it began to move across the shallow-sea area in the southwest, indicating that the Philippines’ HE in the Palawan Basin is still dominated by the sea areas near Palawan Island.
In general, the characteristics of the shift of the GCHETD in each basin are not the same, but the expansion of their standard deviation ellipse changes relatively small, indicating that most of the HE are carried out in batches around existing hydrocarbon-bearing fields. After 2015, except for several hydrocarbon-bearing basins, GCHETD of most of the basins have begun to shift to the deep-sea, which further confirms the development strategies of most countries around the South China Sea.
5. Discussion
With 2014 as the turning point, the increment speed of HE targets in the South China Sea generally presents two different phase characteristics. Before 2014, the quantity of HE targets showed a rapid growth trend, which is consistent with the trend analyzed by Liu et al. [19] on the increment speed of offshore platforms in the South China Sea. However, after 2014 this trend has changed and gradually stabilized. The main reason for this change is related to the decline in international crude oil prices since the second half of 2014. In response to the decline in profits brought about by low oil prices, some companies involved in HE in the South China Sea have slowed down the development of hydrocarbon resources by compressing exploration and drilling. For example, in the old hydrocarbon-bearing fields in the Beibu Gulf Basin and the Me Kong Basin, the increment speed of HE targets has shown a clear downward trend after 2014. In addition, although the increment speed of HE targets in most basins has generally shown an upward trend, some old hydrocarbon-bearing fields have also seen a significant decline after 2014 (as shown in Figure 10). It shows that compressing the exploitation of some old hydrocarbon-bearing fields may be the main way for many energy industries to cope with low oil prices.
However, we can also find that, except for the Me Kong Basin, the increase in the exploitation depth in most basins has not slowed down. Study has found that the maximum exploitation water depth in the South China Sea in 2015 was −1469 m [19], which is close to the ultra-deep sea standard. Our study found that in 2019, the maximum exploitation water depth in the South China Sea has exceeded the ultra-deep sea standard and reached −1580 m. Compared with the past, although the pattern dominated by shallow sea HE [19] has not undergone major changes, the exploitation density in the deep-sea has gradually increased. This, on the other hand, also confirms the development strategy of many energy companies under the background of low oil prices. That is, in addition to compressing the exploitation of those old hydrocarbon-bearing fields with reduced output, while relying on technological innovation to reduce project costs to ensure the normal progress of deep-water HE projects. This shows that persisting in deep-water HE has become an important strategy for many energy companies, because deep-water HE represents the future. However, according to EIA’s analysis, the Me Kong Basin, as one of Vietnam’s major offshore hydrocarbon producing areas, has nearly exhausted its reserves [51]. Unless more challenging deep-water areas can be explored, Vietnam’s production will face a decline in the next few years. While lower oil prices have hindered investment in these more technically challenging areas since late 2014 [51], which may be an important reason why exploitation depth has declined even as the increment speed of HE targets has decreased in the Me Kong basin.
The South China Sea is located in the tropics, with vast sea areas and high cloud coverage. The VIIRS DNB monthly composite product is generated by selecting the effective observations with no cloud or low cloud cover from the daily observations of each month [15,52], and can completely cover the entire South China Sea without a gap. The observations on the monthly time scale are an important data basis to satisfy our proposed method, especially the construction of multi-dimensional features. Considering the spatial coverage advantages and the unique advantages in detecting both electric lighting and combustion sources [37], this is another important reason why we choose to use the VIIRS DNB monthly composite product.
Actually, under the influence of the image resolution and gas flaring halo, those platforms that are close together are sometimes not distinguished into a single platform or a platform group, which may cause omissions (i.e., the false negative targets of Region 1 in Figure 7). The processing strategy of this study is to regard a platform or a platform group within 2 times the pixel distance (with a radius of 1Km) as one HE target, which is similar to the concept of gas flaring area that proposed in the existing research [5,6,11,32,53] and released products (https://eogdata.mines.edu/download_global_flare.html (accessed on 1 February 2021)). Although it is inevitable that the quantity of HE targets will be less than the real quantity of platforms, the recognized targets are not affected in reflecting actual HE activities. The HE targets in this study include the object (platforms without gas flaring) that is very critical to reflect the HE activities, which is superior to the existing research and products. In future research, we will comprehensively consider collecting and using multi-source and multi-sensor remote sensing images to obtain more finer results. Of course, we also face many problems, such as differences in spatial coverage, differences in spatial resolution, differences in data quality, differences in positioning accuracy, etc.
In the existing methods using time-series strategies, the OF based on position-invariant characteristic is one of the most critical parameters for recognizing offshore HE targets, and its optimal threshold is generally difficult to determine. In the existing studies, the determination of the optimal threshold usually requires some experience or prior knowledge [6,11,26], and may be affected by regional differences. However, the method proposed in this study avoids the difficulty in the optimal threshold setting of the parameters of OF in the existing research. Especially, it is reflected in the parameter settings for the recognition of “weak targets” with weak light intensity and low OF, and the removal of false alarm targets in sea areas with large differences in navigation and fishing operations. The uniqueness of the proposed method is that the high-dimensional features of offshore HE targets are constructed based on the long time-series NTL images of a single DNB, which provides feature variables for the effective application of machine learning models.
In the process of using this method, besides the selection of samples, the performance of machine learning is also closely related to the construction of feature variables. For example, there may be false high-frequency features in sea areas with high fishing intensity, or the addition of some other relatively low-importance feature variables may have a certain impact on the recognition effect (i.e., the false-positive targets of Region 1 in Figure 7). Therefore, in the following research, we will consider combining the features of other data sources and analyzing the effectiveness of the features to solve this problem. Compared with existing research, this method explores the feasibility and effectiveness of machine learning models in using low-spatial resolution NTL remote sensing images to recognize punctiform offshore HE targets. This technical idea has the potential to be extended to other medium and low-spatial resolution remote sensing images, and can provide methodological references for similar research such as route analysis and fishery activity monitoring.
6. Conclusions
A clear understanding of the intensity changes and development trends of the exploitation of hydrocarbon resources in the South China Sea is essential to a series of work such as the formulation of energy strategies and environmental protection. Therefore, this study used the long time-series VIIRS NTL monthly composite image products to track and analyze the HE activities in the South China Sea from 2012 to 2019.
In this study, a novel and reliable method for recognizing offshore HE targets based on random forest model and feature increment strategy is proposed, which can detect offshore HE targets with and without gas flaring from time-series VIIRS NTL images. It was used to obtain the dynamic changes of HE targets in the South China Sea from 2012 to 2019. The analysis of the quantity, increment speed, and distribution density of the HE targets in the South China Sea shows that the intensity of HE activities has increased rapidly and then gradually stabilized. The drop in international crude oil prices in 2014 may be an important reason for the change in the intensity of HE activities. The analysis in the shifts of GCHETD and the changes of HE water depth in each basin shows that “gong to the deep-sea” is the development trend of HE in the South China Sea. The proportion of deep-sea HE targets is increasing, and the ultra-deep sea HE has reached −1580 m.
This study explored the application of combining low-spatial resolution VIIRS NTL images and machine learning models in the recognition of offshore HE targets, and tried to further use them for the analysis of offshore HE activities. In future research work, we will focus on the collaborative application of multi-source remote sensing images and machine learning models, with a view to improving the methodology and providing more detailed and comprehensive basic data for the analysis of offshore HE activities. In addition, we also hope to further study the characteristics and impact of offshore HE activities on environmental pollution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.W. and F.S.; methodology, Q.W.; software, W.W.; validation, W.W. and Q.W.; formal analysis, Q.W.; investigation, Q.W. and F.S.; resources, F.S.; data curation, F.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.W.; writing—review and editing, H.X. and W.W.; visualization, Y.W. and Q.W.; supervision, F.S.; project administration, F.S., G.Y. and Q.W.; funding acquisition, F.S., G.Y. and Q.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by “Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Science, grant number XDA19060300” and “Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Shandong Jianzhu University, grant number XNBS1984”.
Data Availability Statement
The field survey data and offshore platform records presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. Those data are not publicly available due to commercial secrets. The image data and bathymetric data presented in this study are available from the website link within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Earth Observation Group, Payne Institute for Public Policy, Colorado School of Mines for providing the VIIRS/DNB monthly composite images; to the China Center for Resource Satellite Data and Applications (CRESDA, China) for providing the GF-1, GF-2, ZY-1 and ZY-3 images; to the GEBCO Compilation Group for providing the bathymetric data set GEBCO_2020 Grid; to the State Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Information System (SKLREIS), Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGSNRR, CAS) for providing the offshore platform records data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sandrea, I.; Sandrea, R. Growth expected in global offshore crude oil supply. Oil Gas J. 2007, 105, 34–36, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinder, D. Offshore oil and gas: Global resource knowledge and technological change. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2001, 44, 579–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIA. Offshore Production Nearly 30% of Global Crude Oil Output in 2015. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=28492 (accessed on 25 October 2016).
- Sun, C.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, S.S.; Jin, S. Estimating offshore oil production using DMSP-OLS annual composites. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 165, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Sun, C.; Zhan, W.; Sun, S.; Xu, B.; Dong, Y. Assessment of offshore oil/gas platform status in the northern Gulf of Mexico using multi-source satellite time-series images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhan, W.; Cheng, W. Automatic extraction of offshore platforms using time-series Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claisse, J.T.; Pondella, D.J., II; Love, M.; Zahn, L.A.; Williams, C.M.; Williams, J.P.; Bull, A.S. Oil platforms off California are among the most productive marine fish habitats globally. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15462–15467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.P.; Jaidah, M.Y.; Jabado, R.W.; Lee-Brooks, K.; El-Din, N.M.N.; Malki, A.A.A.; Elmeer, K.; McCormick, P.A.; Henderson, A.C.; Pierce, S.J.; et al. Whale Sharks, Rhincodon typus, Aggregate around Offshore Platforms in Qatari Waters of the Arabian Gulf to Feed on Fish Spawn. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, C.M.; Montevecchi, W.A.; Wiese, F.K. Inadequate environmental monitoring around offshore oil and gas platforms on the Grand Bank of Eastern Canada: Are risks to marine birds known? J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 104, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlizzi, A.; Bevilacqua, S.; Scuderi, D.; Fiorentino, D.; Guarnieri, G.; Giangrande, A.; Licciano, M.; Felline, S.; Fraschetti, S. Effects of offshore platforms on soft-bottom macro-benthic assemblages: A case study in a Mediterranean gas field. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, J.Z.; Xu, W.X.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhao, B.X.; Li, H.T.; Li, P. Global proliferation of offshore gas flaring areas. J. Maps 2020, 16, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, H.; Tanimoto, H.; Tohjima, Y.; Mukai, H.; Nojiri, Y.; Machida, T. Emissions of methane from offshore oil and gas platforms in Southeast Asia. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingas, M.; Brown, C. Review of oil spill remote sensing. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifer, I.; Lehr, W.J.; Simecek-Beatty, D.; Bradley, E.; Clark, R.; Dennison, P.; Hu, Y.; Matheson, S.; Jones, C.E.; Holt, B.; et al. State of the art satellite and airborne marine oil spill remote sensing: Application to the BP Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A Fifteen Year Record of Global Natural Gas Flaring Derived from Satellite Data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, K.; Christie, N.; Burdon, D.; Atkins, J.P.; Barnes, R.; Elliott, M. Renewables-to-reefs?—Decommissioning options for the offshore wind power industry. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, W.; Cheng, L. Safety assessment of shipping routes in the South China Sea based on the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Saf. Sci. 2014, 62, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, Q.-T.; Shapiro, J.N.; Elvidge, C.D.; Abdel-Jelil, M.; Ahn, D.P.; Baugh, K.; Hansen-Lewis, J.; Zhizhin, M.; Bazilian, M.D. Terrorism, geopolitics, and oil security: Using remote sensing to estimate oil production of the Islamic State. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2018, 44, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Zhan, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S. Satellite data lift the veil on offshore platforms in the South China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyman, E. Offshore oil development and maritime conflict in the 20th century: A statistical analysis of international trends. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIA. South China Sea Analysis Brief. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/international/analysis/regions-of-interest/South_China_Sea (accessed on 7 February 2013).
- Jie, C.; Ning, W.; Xuejie, L.I. The status of the resource potential and petroleum exploration of The South China Sea. Prog. Geophys. 2007, 22, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.-C.; Ghosh, T. Methods for Global Survey of Natural Gas Flaring from Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Data. Energies 2015, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Su, F. Automatic Extraction of Offshore Platforms in Single SAR Images Based on a Dual-Step-Modified Model. Sensors 2019, 19, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, B.A.; Thomas, C.; Halpin, P. Automating offshore infrastructure extractions using synthetic aperture radar & Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Su, F. Offshore Platform Extraction Using RadarSat-2 SAR Imagery: A Two-Parameter CFAR Method Based on Maximum Entropy. Entropy 2019, 21, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Dong, Y.; Lu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, H.; Yang, R. Proliferation of offshore wind farms in the North Sea and surrounding waters revealed by satellite image time series. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 133, 110167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, K.; Tong, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, M. Invariant triangle-based stationary oil platform detection from multitemporal synthetic aperture radar data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadio, S.; Arino, O.; Minchella, A. Use of ATSR and SAR measurements for the monitoring and characterisation of night-time gas flaring from off-shore platforms: The North Sea test case. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Dong, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhan, W.; Sun, C. Geometric accuracy of remote sensing images over oceans: The use of global offshore platforms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 244–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Meng, R.; Lou, M.; Bing, L.; Liu, X. Remote Sensing of Ships and Offshore Oil Platforms and Mapping the Marine Oil Spill Risk Source in the Bohai Sea. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 3, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anejionu, O.C.D.; Blackburn, G.A.; Whyatt, J.D. Detecting gas flares and estimating flaring volumes at individual flow stations using MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, P.; Schroeder, W. Assessment of VIIRS 375 m active fire detection product for direct burned area mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, D.C.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.-C.; Baugh, E.K. Rapid Fire Detection, Characterization and Reporting from VIIRS Data. In Time-Sensitive Remote Sensing; Lippitt, D.C., Stow, A.D., Coulter, L.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csiszar, I.; Schroeder, W.; Giglio, L.; Ellicott, E.; Vadrevu, K.P.; Justice, C.O.; Wind, B. Active fires from the Suomi NPP Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite: Product status and first evaluation results. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadio, S.; Arino, O.; Serpe, D. Gas flaring monitoring from space using the ATSR instrument series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 116, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.-C.; Baugh, K.E. VIIRS nightfire: Satellite pyrometry at night. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4423–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qiu, W.T.; Qu, W.L. Countermeasure Study on Deep-sea Oil Exploitation in the South China Sea-A Comparison between Deep-sea Oil Exploitation in the South China Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advances in Energy Resources and Environment Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 113. [Google Scholar]
- Team, C.P. How Much Trade Transits the South China Sea? Available online: https://chinapower.csis.org/much-trade-transits-south-china-sea/ (accessed on 13 December 2020).
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.-C. Automatic boat identification system for VIIRS low light imaging data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3020–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Wen, J.H.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Chen, K.S.; Chen, A.J. Improved Sigma Filter for Speckle Filtering of SAR Imagery. Ieee Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Vastaranta, M.; Holopainen, M.; Viitala, R. Predicting individual tree attributes from airborne laser point clouds based on the random forests technique. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random Forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Weiguo, J.; Zhenghong, T.; Jiahong, L.; Jinxia, L.; Zheng, C.; Kai, J. Spatio-Temporal Change of Lake Water Extent in Wuhan Urban Agglomeration Based on Landsat Images from 1987 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulbure, M.G.; Broich, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Kommareddy, A. Surface water extent dynamics from three decades of seasonally continuous Landsat time series at subcontinental scale in a semi-arid region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielsen, C.G.; Murphy, M.A.; Evans, J.S. Using a multiscale, probabilistic approach to identify spatial-temporal wetland gradients. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, P.; Liang, L. A 30-year (1984–2013) record of annual urban dynamics of Beijing City derived from Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 166, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, C.; Pavlu, V.; Aslam, J. A Pipeline for Optimizing F1-Measure in Multi-label Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Orlando, FL, USA, 17–20 December 2018; pp. 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammut, C.; Webb, G.I. F1-Measure. In Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining; Sammut, C., Webb, G.I., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; p. 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, D. Complementarity, F-score, and NLP Evaluation. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; pp. 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- EIA. VIETNAM. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/international/analysis/country/VNM (accessed on 7 February 2020).
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. VIIRS night-time lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5860–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.; Chau, K.; Cushing, L.J.; Johnston, J.E. Characterizing Flaring from Unconventional Oil and Gas Operations in South Texas Using Satellite Observations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2220–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).