Investigation of Polar Mesospheric Summer Echoes Using Linear Discriminant Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
2.2. Skewness and Kurtosis
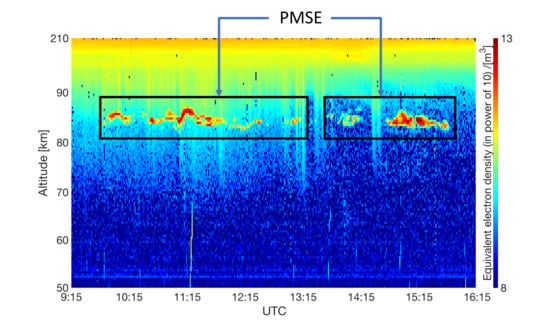
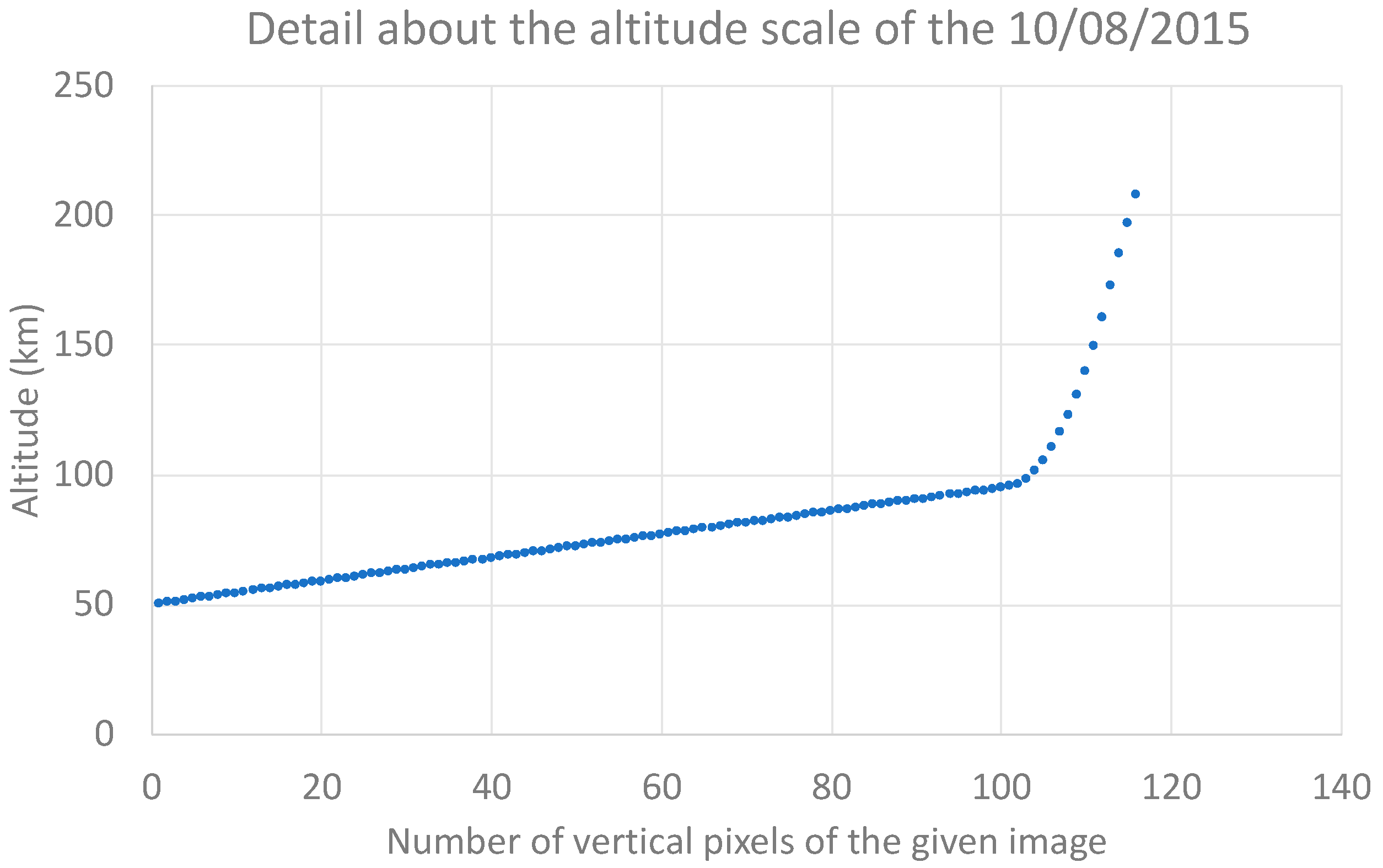
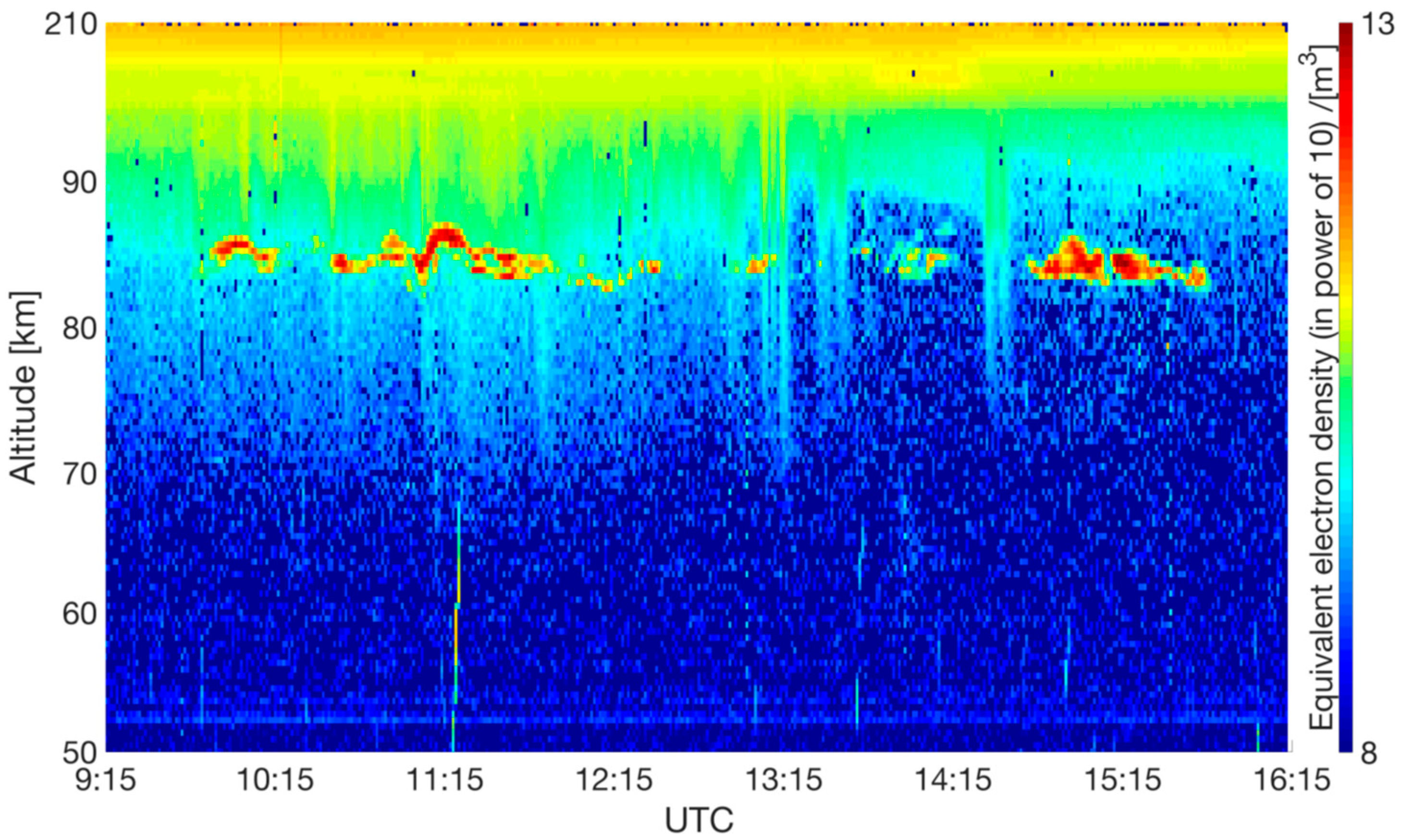
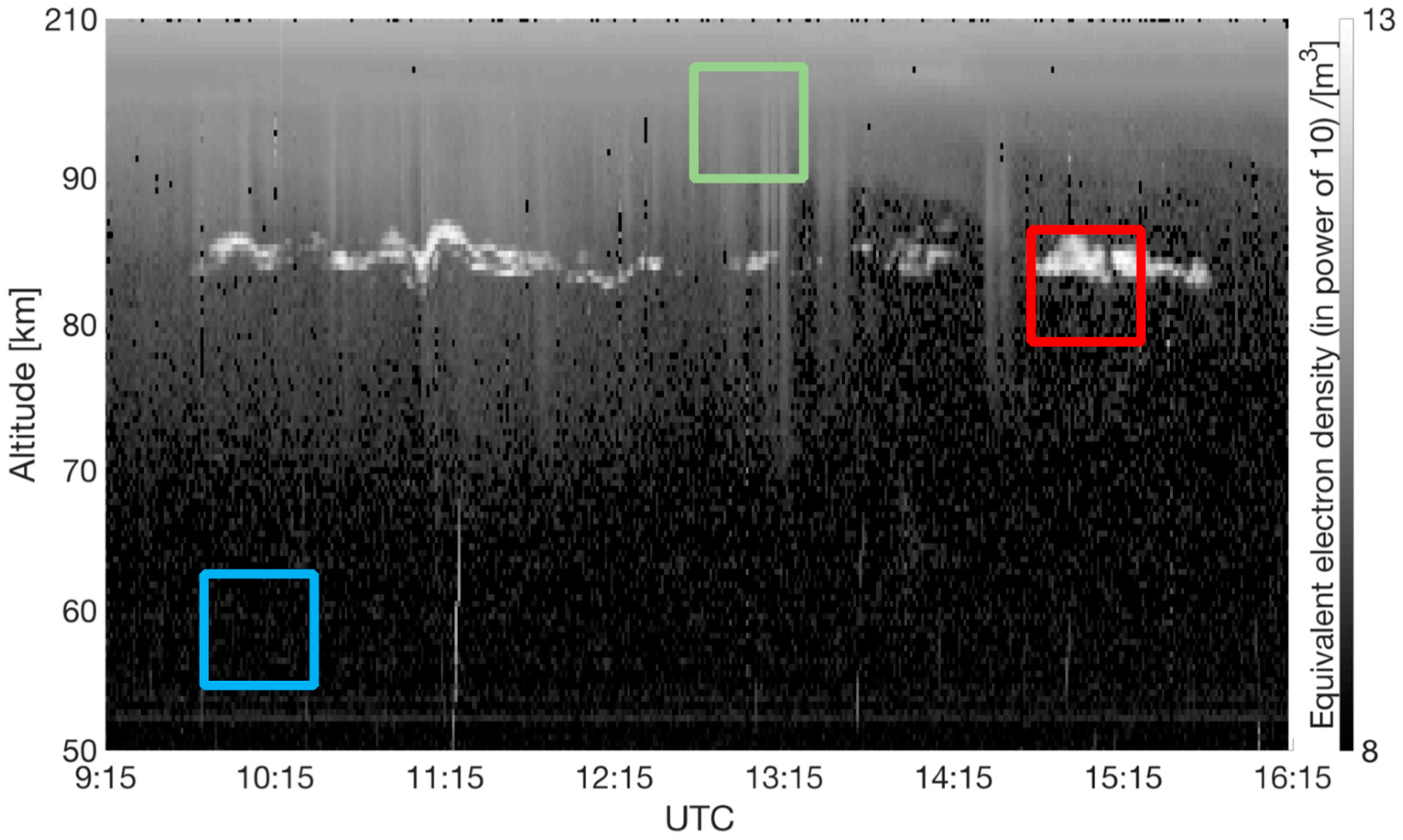
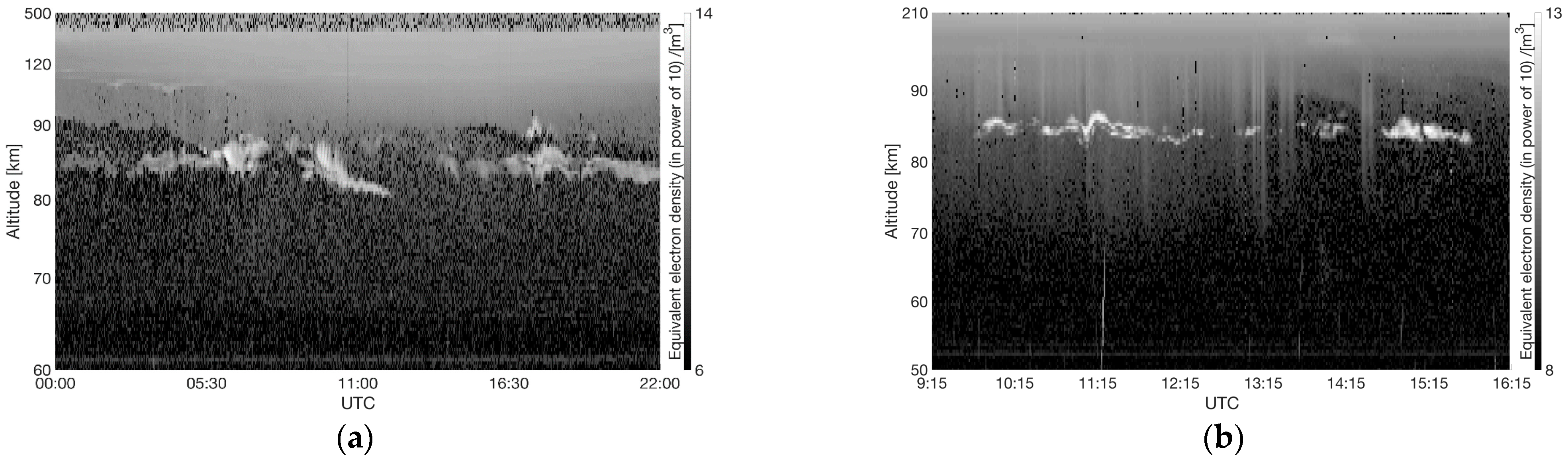
2.3. Input Data
3. Procedure
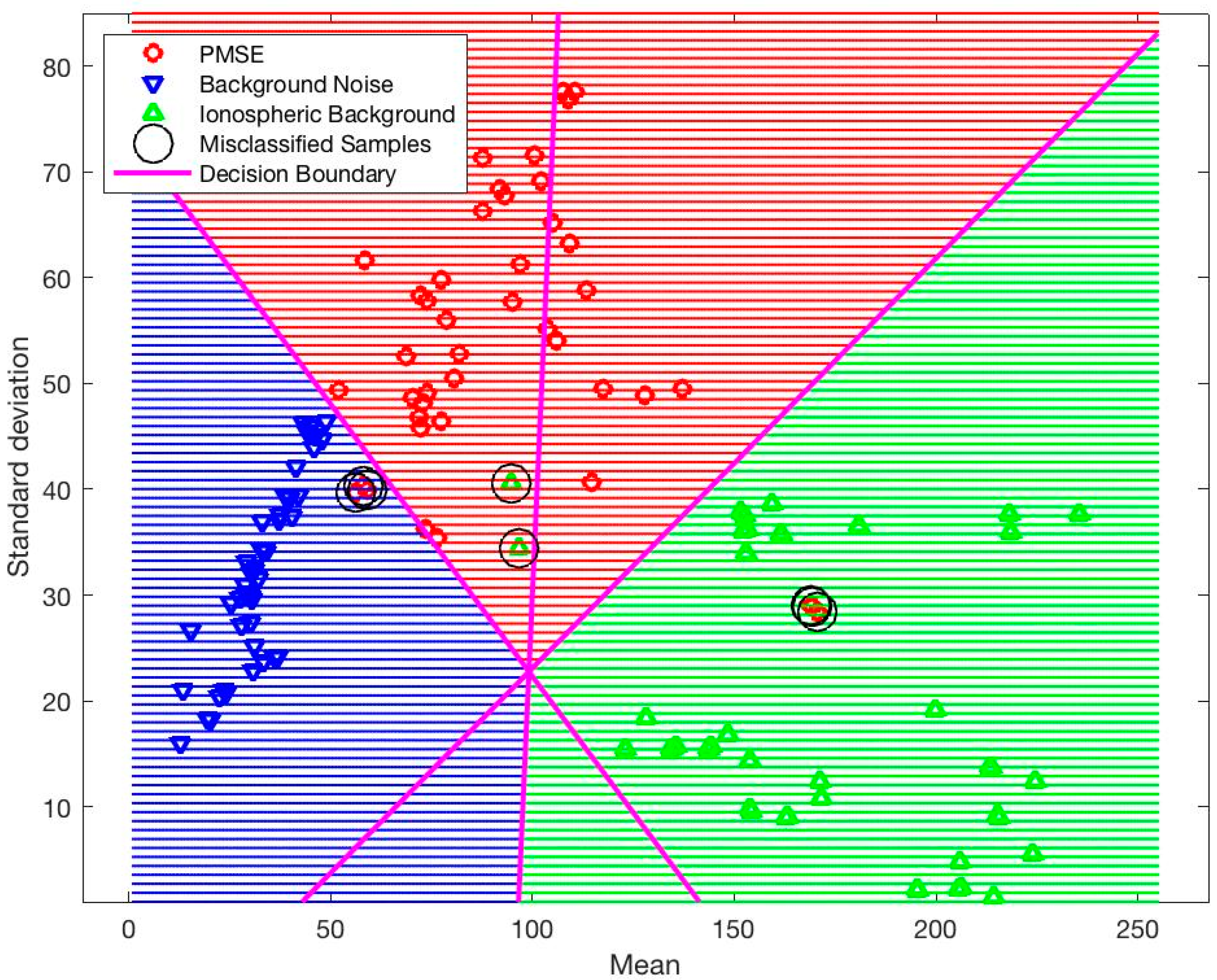
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Dates (dd.mm.yyyy) | Start Time in UTC 1 (hh:mm:ss) | End Time in UTC (hh:mm:ss) |
|---|---|---|
| 28.06.2008 | 07:58:33 | 08:36:18 |
| 30.06.2008 | 07:59:38 | 12:07:30 |
| 02.07.2008 | 10:24:30 | 11:59:02 |
| 10.06.2009 | 09:03:42 | 11:56:09 |
| 11.06.2009 | 09:03:42 | 11:59:12 |
| 14.07.2009 | 08:19:33 | 11:33:15 |
| 16.07.2009 | 08:47:30 | 10:06:26 |
| 17.07.2009 | 07:49:44 | 11:59:30 |
| 26.07.2009 | 08:00:29 | 11:59:22 |
| 30.07.2009 | 12:15:29 | 15:59:08 |
| 07.07.2010 | 00:00:30 | 21:59:27 |
| 08.07.2010 | 09:00:42 | 12:59:03 |
| 09.08.2015 | 00:00:26 | 01:59:26 |
| 10.08.2015 | 09:14:40 | 16:12:28 |
| 12.08.2015 | 20:04:40 | 23:59:28 |
| 13.08.2015 | 00:00:28 | 01:59:26 |
| 19.08.2015 | 00:00:28 | 01:59:26 |
| 20.08.2015 | 00:00:28 | 01:59:26 |
| Window Size | M 1 | M, Std 2 | M, Std, Sk 3 | M, Std, Sk, K 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 84.39 ± 1.96 | 92.58 ± 1.00 | 93.41 ± 2.05 | 93.71 ± 1.82 |
| 80 | 89.24 ± 1.88 | 97.50 ± 1.43 | 95.91 ± 1.20 | 95.23 ± 1.19 |
| 100 | 93.26 ± 1.87 | 97.05 ± 0.91 | 96.21 ± 0.87 | 97.05 ± 1.40 |
| 120 | 94.24 ± 2.82 | 96.14 ± 1.26 | 96.52 ± 1.25 | 97.50 ± 1.07 |
| 140 | 94.92 ± 1.68 | 95.83 ± 1.09 | 96.97 ± 1.29 | 97.80 ± 1.10 |
| 160 | 95.76 ± 1.20 | 94.85 ± 1.46 | 96.36 ± 1.55 | 98.18 ± 0.81 |
| 180 | 96.14 ± 1.61 | 94.62 ± 1.45 | 97.05 ± 1.69 | 96.67 ± 1.39 |
| 200 | 95.15 ± 1.14 | 92.65 ± 1.07 | 96.82 ± 1.63 | 95.76 ± 1.56 |
| Window Size | M 1 | M, Std 2 | M, Std, Sk 3 | M, Std, Sk, K 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 84.53 ± 0.88 | 93.00 ± 0.68 | 93.63 ± 0.71 | 94.23 ± 0.79 |
| 80 | 88.50 ± 0.79 | 96.47 ± 0.53 | 95.93 ± 0.52 | 95.57 ± 0.59 |
| 100 | 92.57 ± 0.82 | 96.93 ± 0.49 | 97.00 ± 0.75 | 97.20 ± 0.63 |
| 120 | 94.67 ± 0.63 | 96.63 ± 0.33 | 96.60 ± 0.56 | 97.87 ± 0.45 |
| 140 | 94.80 ± 1.21 | 96.33 ± 0.59 | 96,67 ± 0.72 | 98.13 ± 0.42 |
| 160 | 95.57 ± 0.55 | 96.00 ± 0.44 | 96.87 ± 0.83 | 98.07 ± 0.52 |
| 180 | 95.73 ± 0.54 | 95.50 ± 0.95 | 97.10 ± 0.72 | 97.53 ± 0.59 |
| 200 | 95.40 ± 0.86 | 93.33 ± 0.80 | 96.57 ± 0.55 | 97.33 ± 0.52 |
| Window Size | M 1 | M, Std 2 | M, Std, Sk 3 | M, Std, Sk, K 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 85.53 | 92.58 | 93.64 | 94.70 |
| 80 | 89.39 | 96.67 | 95.91 | 95.08 |
| 100 | 92.88 | 96.29 | 97.05 | 97.20 |
| 120 | 94.55 | 96.67 | 96.52 | 97.50 |
| 140 | 95.00 | 95.83 | 96.44 | 97.50 |
| 160 | 95.53 | 95.91 | 96.59 | 97.58 |
| 180 | 95.91 | 95.15 | 97.12 | 96.59 |
| 200 | 94.70 | 92.50 | 97.42 | 96.89 |
| Window Size | M 1 | M, Std 2 | M, Std, Sk 3 | M, Std, Sk, K 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 84.71 | 92.62 | 92.89 | 93.98 |
| 80 | 88.17 | 96.72 | 95.86 | 95.37 |
| 100 | 91.88 | 96.83 | 96.54 | 96.90 |
| 120 | 94.25 | 96.72 | 96.43 | 97.53 |
| 140 | 95.05 | 96.14 | 96.39 | 97.55 |
| 160 | 95.45 | 95.50 | 96.80 | 97.73 |
| 180 | 95.88 | 94.90 | 96.82 | 96.91 |
| 200 | 95.23 | 92.88 | 96.37 | 96.63 |
| Window Size | M 1 | M, Std 2 | M, Std, Sk 3 | M, Std, Sk, K 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 84.56 | 92.73 | 93.11 | 93.73 |
| 80 | 88.44 | 96.66 | 95.79 | 95.45 |
| 100 | 92.45 | 96.75 | 96.54 | 97.02 |
| 120 | 94.42 | 96.51 | 96.61 | 97.55 |
| 140 | 95.13 | 96.03 | 96.57 | 97.67 |
| 160 | 95.53 | 95.63 | 96.66 | 97.68 |
| 180 | 95.70 | 95.11 | 96.98 | 96.78 |
| 200 | 95.02 | 93.02 | 96.65 | 96.55 |
References
- Ecklund, W.L.; Balsley, B.B. Long-term observations of the Arctic mesosphere with the MST radar at Poker Flat, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1981, 86, 7775–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.N.; Röttger, J. An updated review of polar mesosphere summer echoes: Observation, theory, and their relationship to noctilucent clouds and subvisible aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 2001–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, M.; Lübken, F.J. Polar mesosphere summer echoes (PMSE): Review of observations and current understanding. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 2601–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latteck, R.; Strelnikova, I. Extended observations of polar mesosphere winter echoes over Andøya (69° N) using MAARSY. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 8216–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röttger, J.; La Hoz, C. Characteristics of polar mesosphere summer echoes (PMSE) observed with the EISCAT 224 MHz radar and possible explanations of their origin. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1990, 52, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Dalin, P.; Mann, I. Towards a Framework for Noctilucent Cloud Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrea, I.; Aikio, A.; Alfonsi, L.; Belova, E.; Buchert, S.; Clilverd, M.; Engler, N.; Gustavsson, B.; Heinselman, C.; Kero, J.; et al. The science case for the EISCAT_3D radar. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, I.; Häggström, I.; Tjulin, A.; Rostami, S.; Anyairo, C.C.; Dalin, P. First wind shear observation in PMSE with the tristatic EISCAT VHF radar. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 11271–11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A. The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Ann. Eugen. 1936, 7, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroumbas, K.; Theodoridis, S. Pattern Recognition, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bera, A.K.; Premaratne, G. Modeling Asymmetry and Excess Kurtosis in Stock Return Data; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Westfall, P.H. Kurtosis as Peakedness, 1905–2014. R.I.P. Am. Stat. 2014, 68, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtinen, M.S.; Huuskonen, A. General incoherent scatter analysis and GUISDAP. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1996, 58, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, W.E. Incoherent Scattering of Radio Waves by Free Electrons with Applications to Space Exploration by Radar. Proc. IRE 1958, 46, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, S.; Greenwald, R.A.; Meng, C.-I.; Sigillito, V.G.; Hutton, L.V. Neural networks for automated classification of ionospheric irregularities in HF radar backscattered signals. Radio Sci. 2003, 38, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
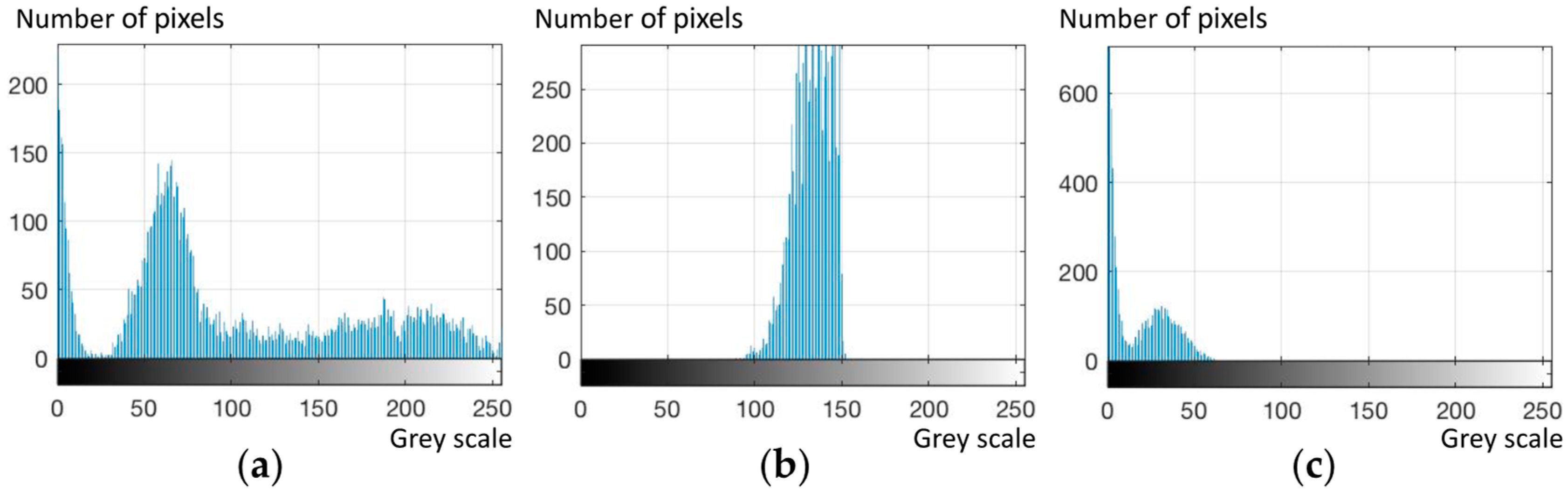



| Window Size | M | M, Std 1 | M, Std, Sk 2 | M, Std, Sk, K 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 93.26 ± 1.87 | 97.05 ± 0.91 | 96.21 ± 0.87 | 97.05 ± 1.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jozwicki, D.; Sharma, P.; Mann, I. Investigation of Polar Mesospheric Summer Echoes Using Linear Discriminant Analysis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030522
Jozwicki D, Sharma P, Mann I. Investigation of Polar Mesospheric Summer Echoes Using Linear Discriminant Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(3):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030522
Chicago/Turabian StyleJozwicki, Dorota, Puneet Sharma, and Ingrid Mann. 2021. "Investigation of Polar Mesospheric Summer Echoes Using Linear Discriminant Analysis" Remote Sensing 13, no. 3: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030522
APA StyleJozwicki, D., Sharma, P., & Mann, I. (2021). Investigation of Polar Mesospheric Summer Echoes Using Linear Discriminant Analysis. Remote Sensing, 13(3), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030522