The Quantile-Matching Approach to Improving Radar Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in South China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
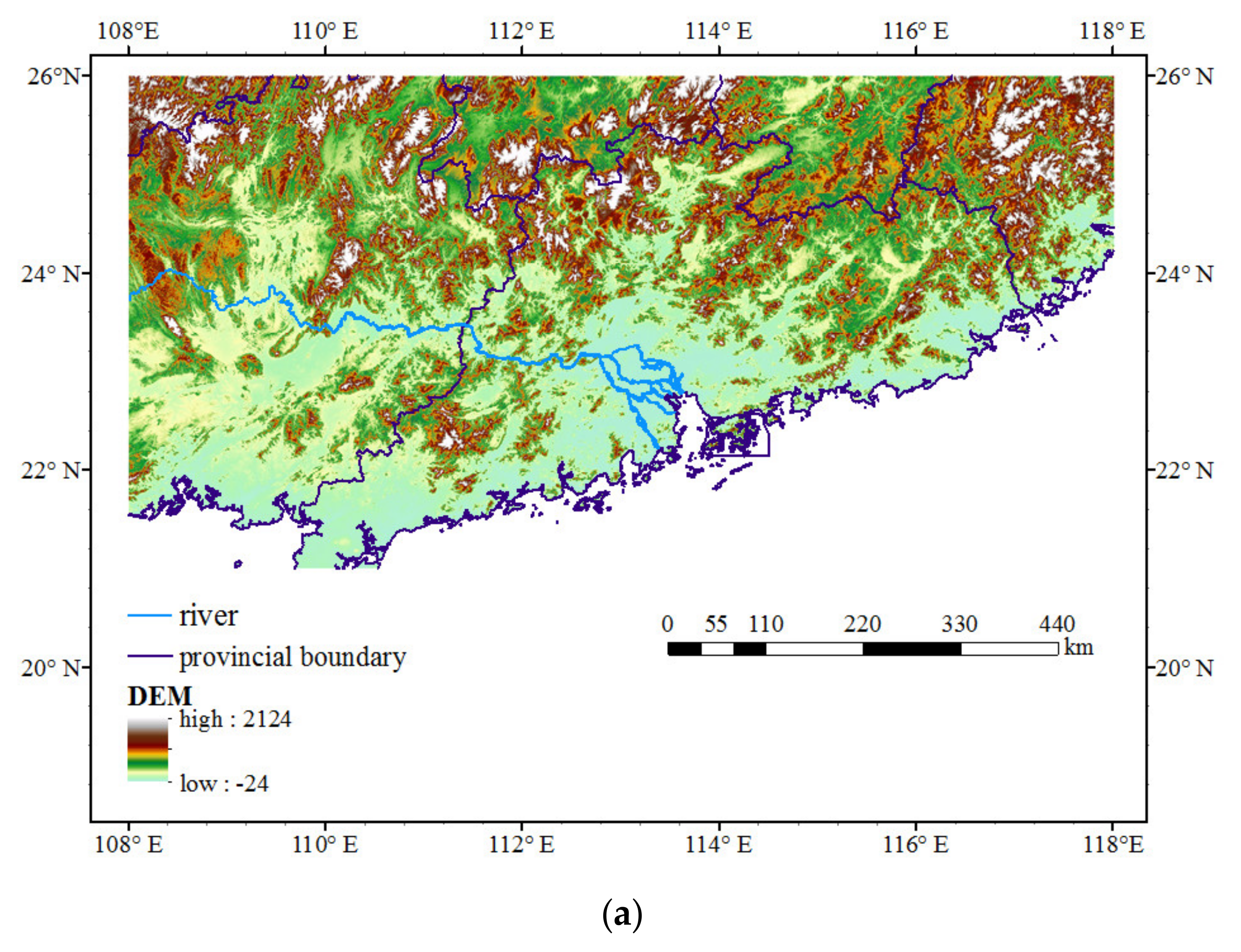
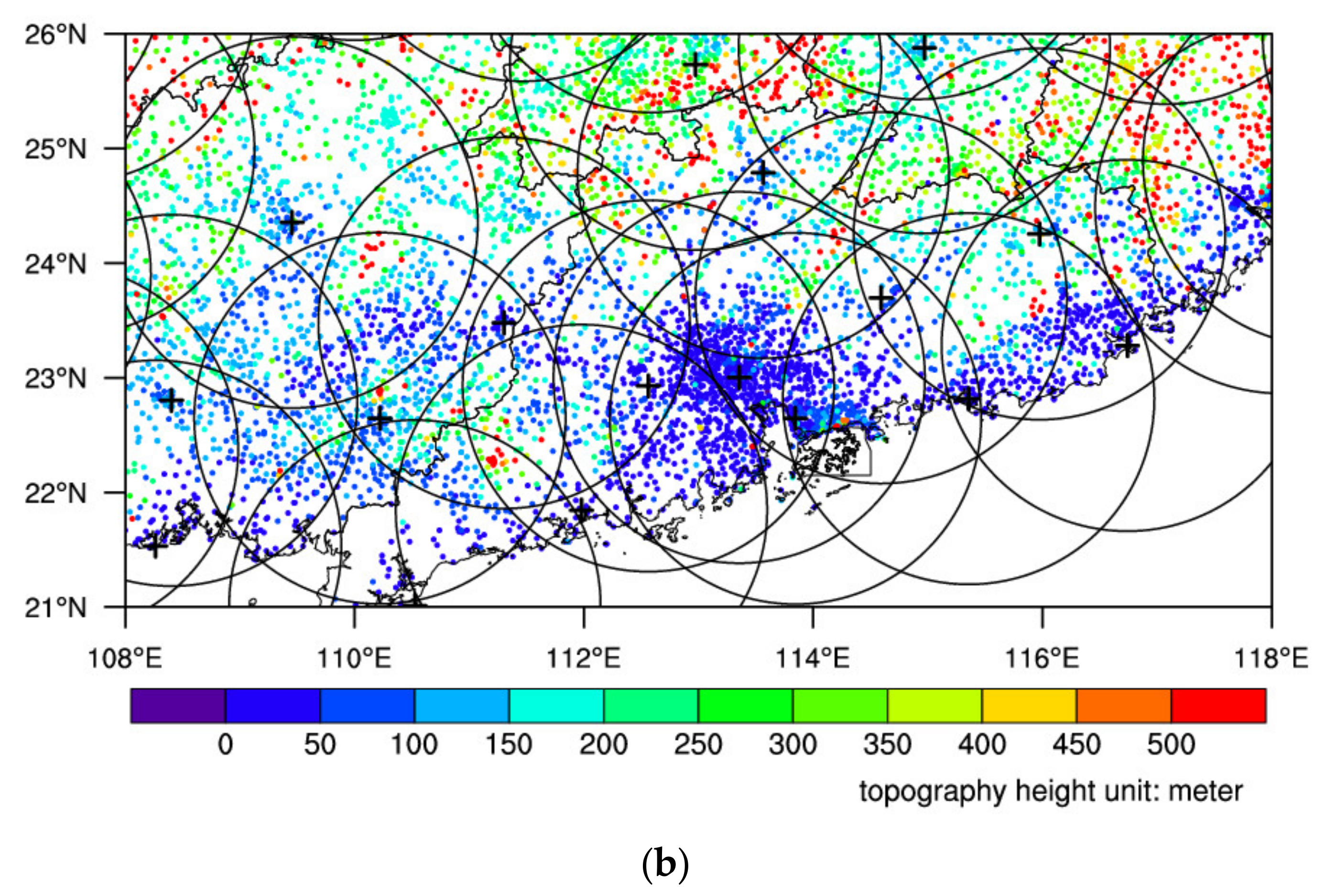
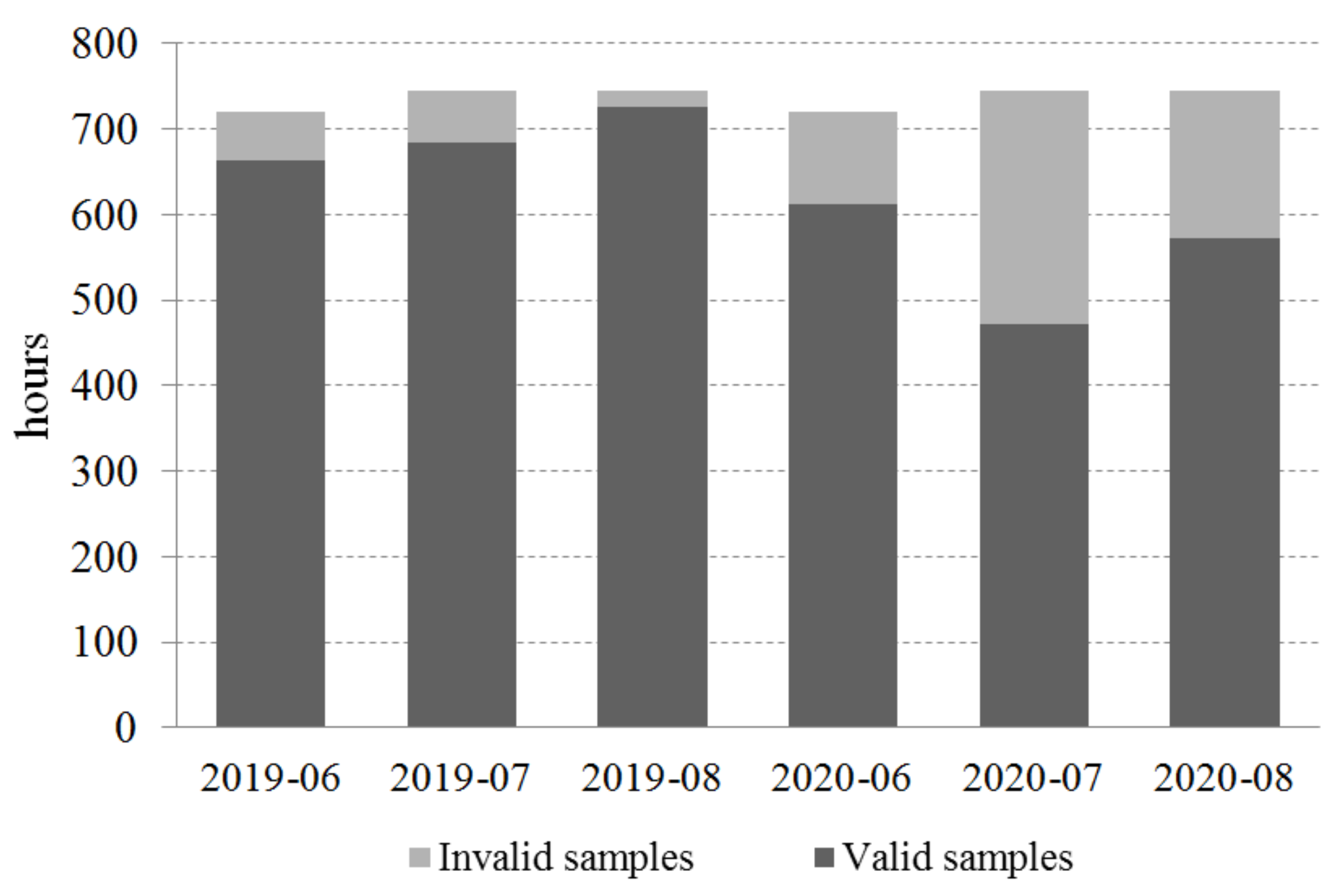
2. Data and Methods
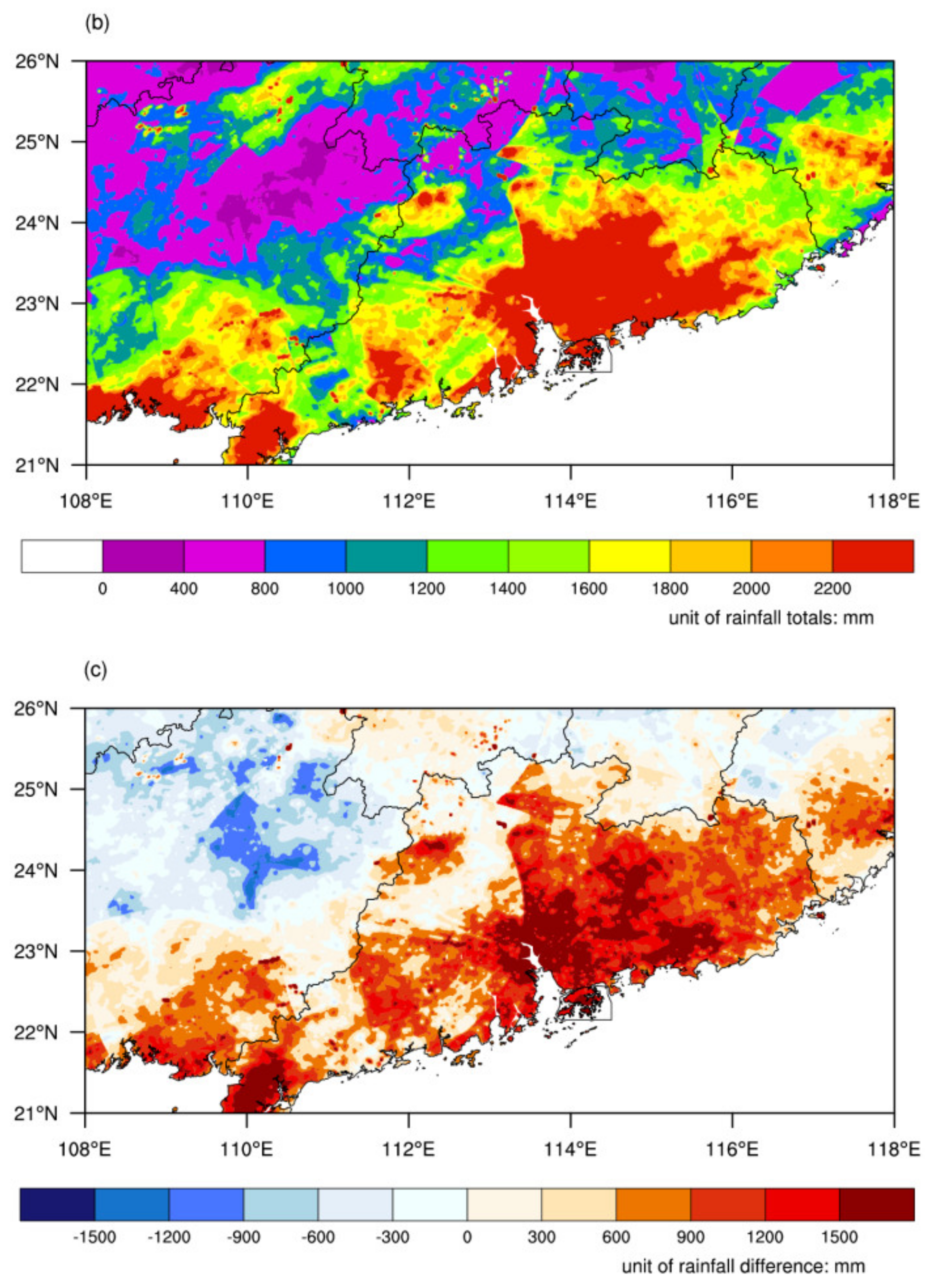
3. Results
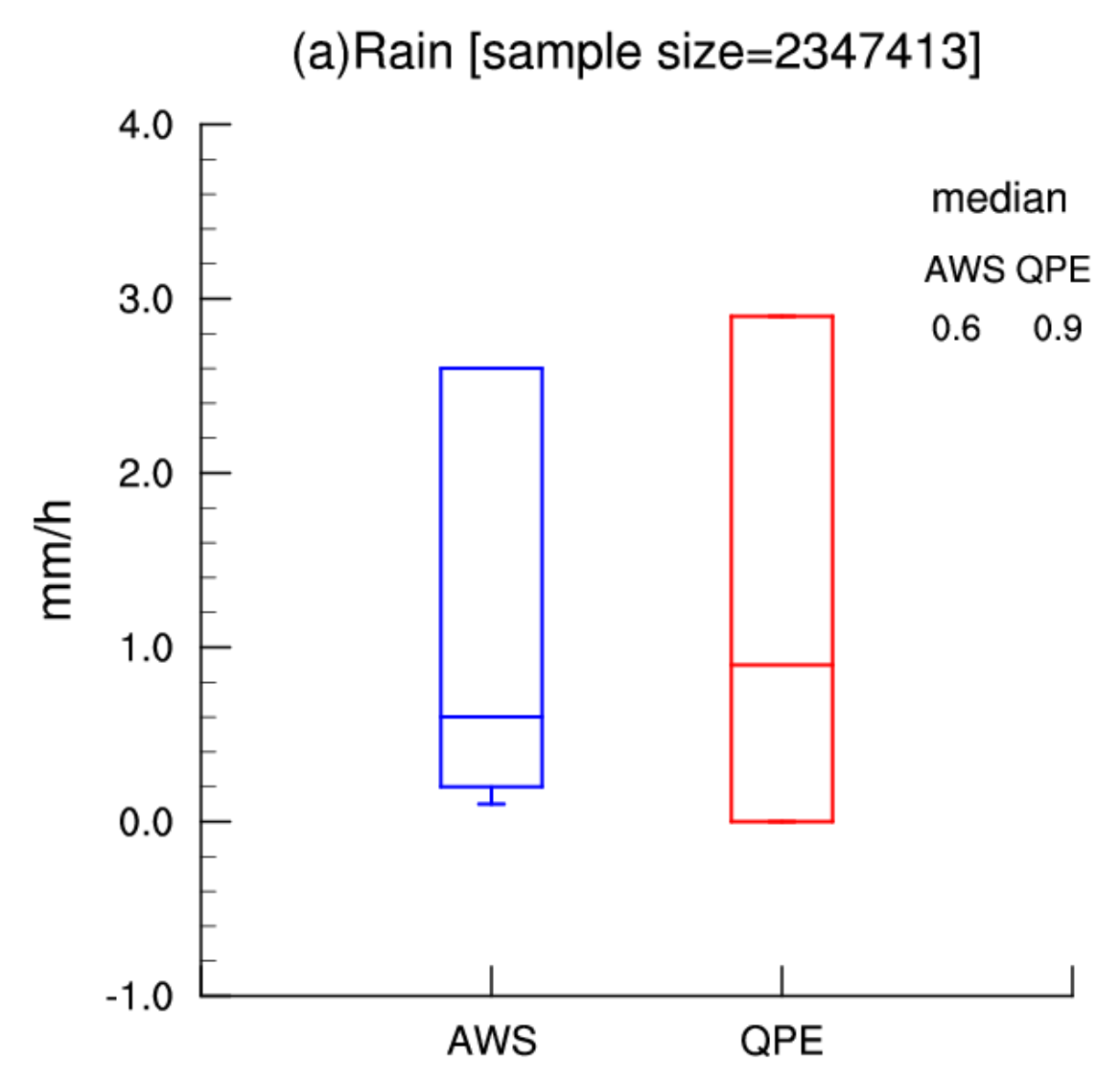
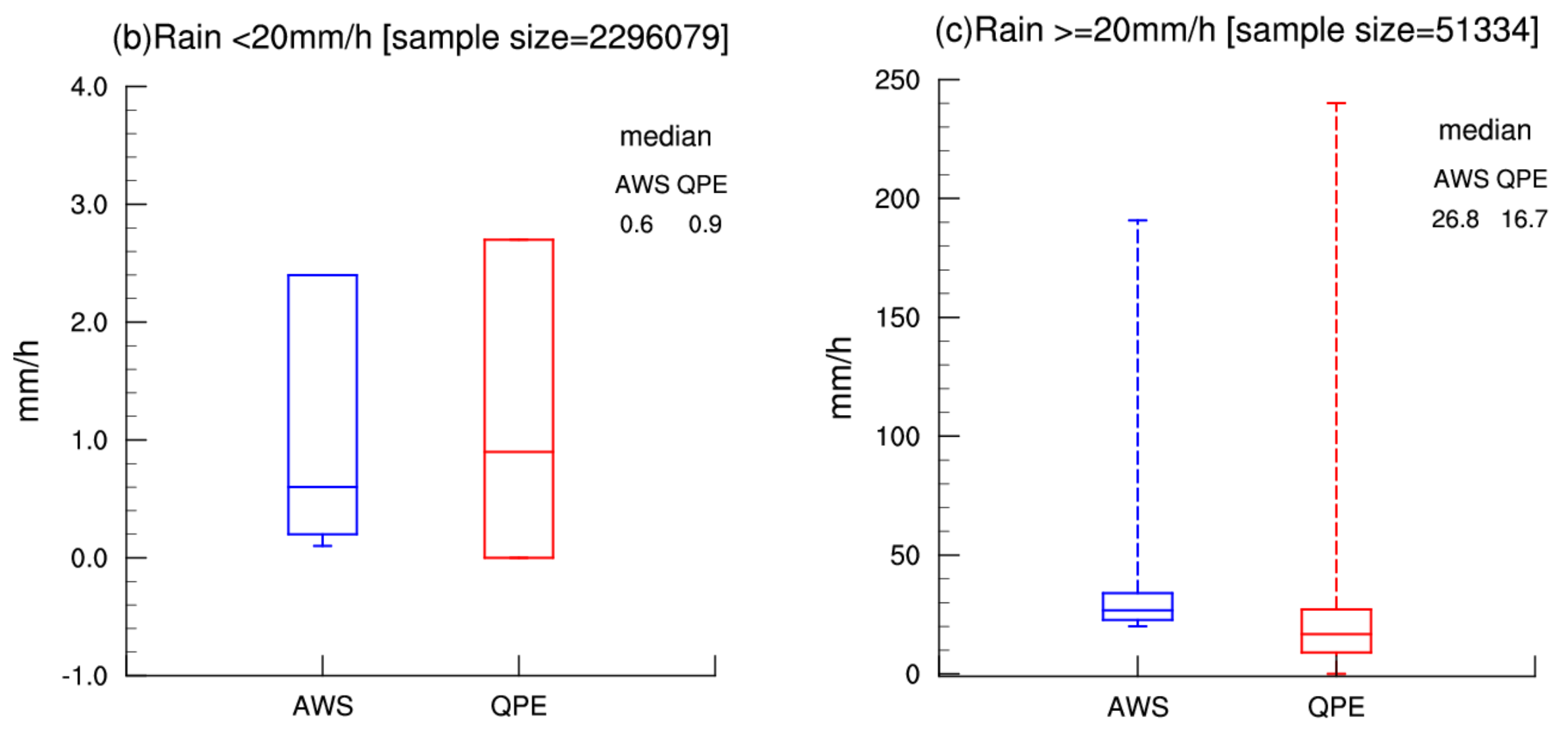
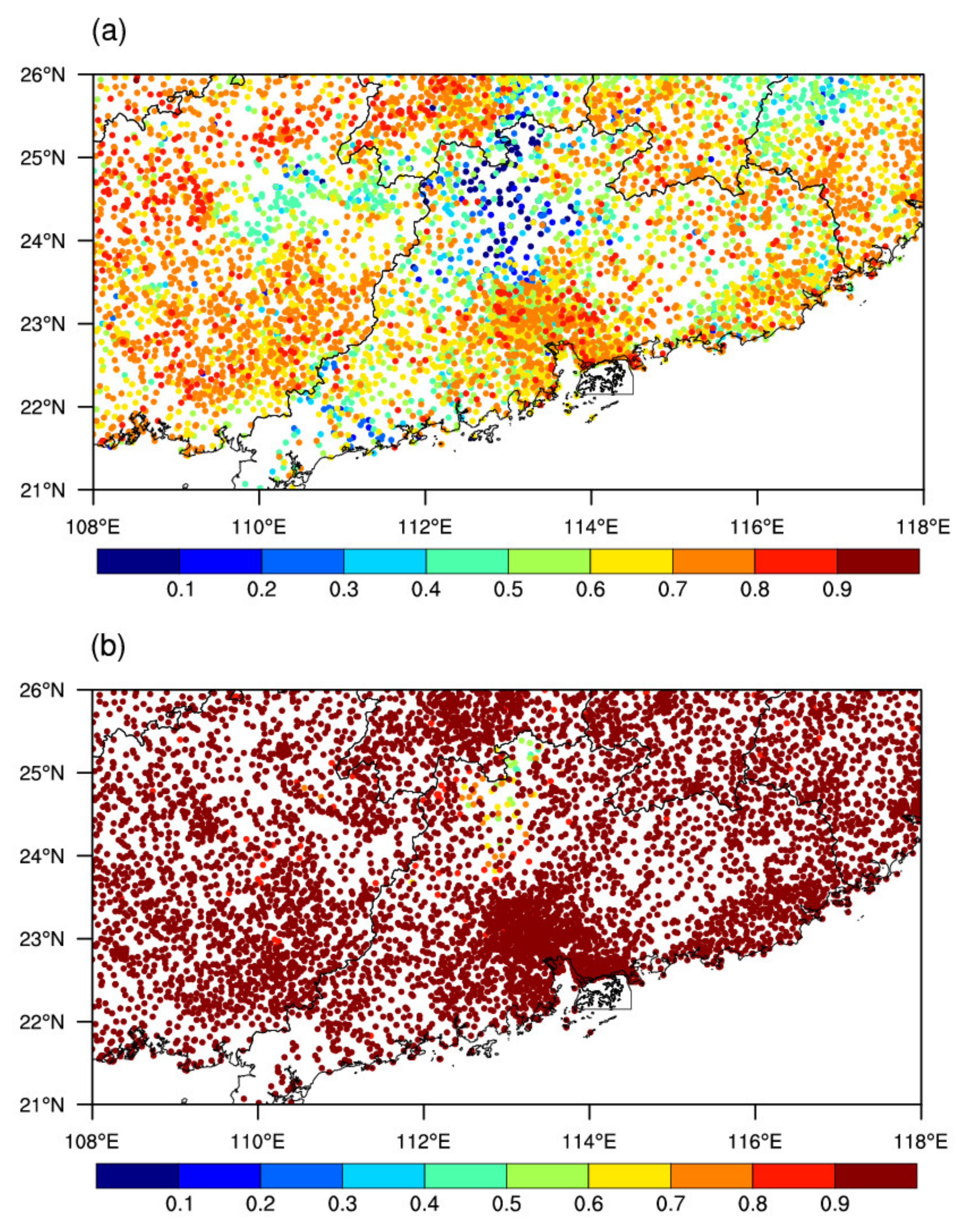
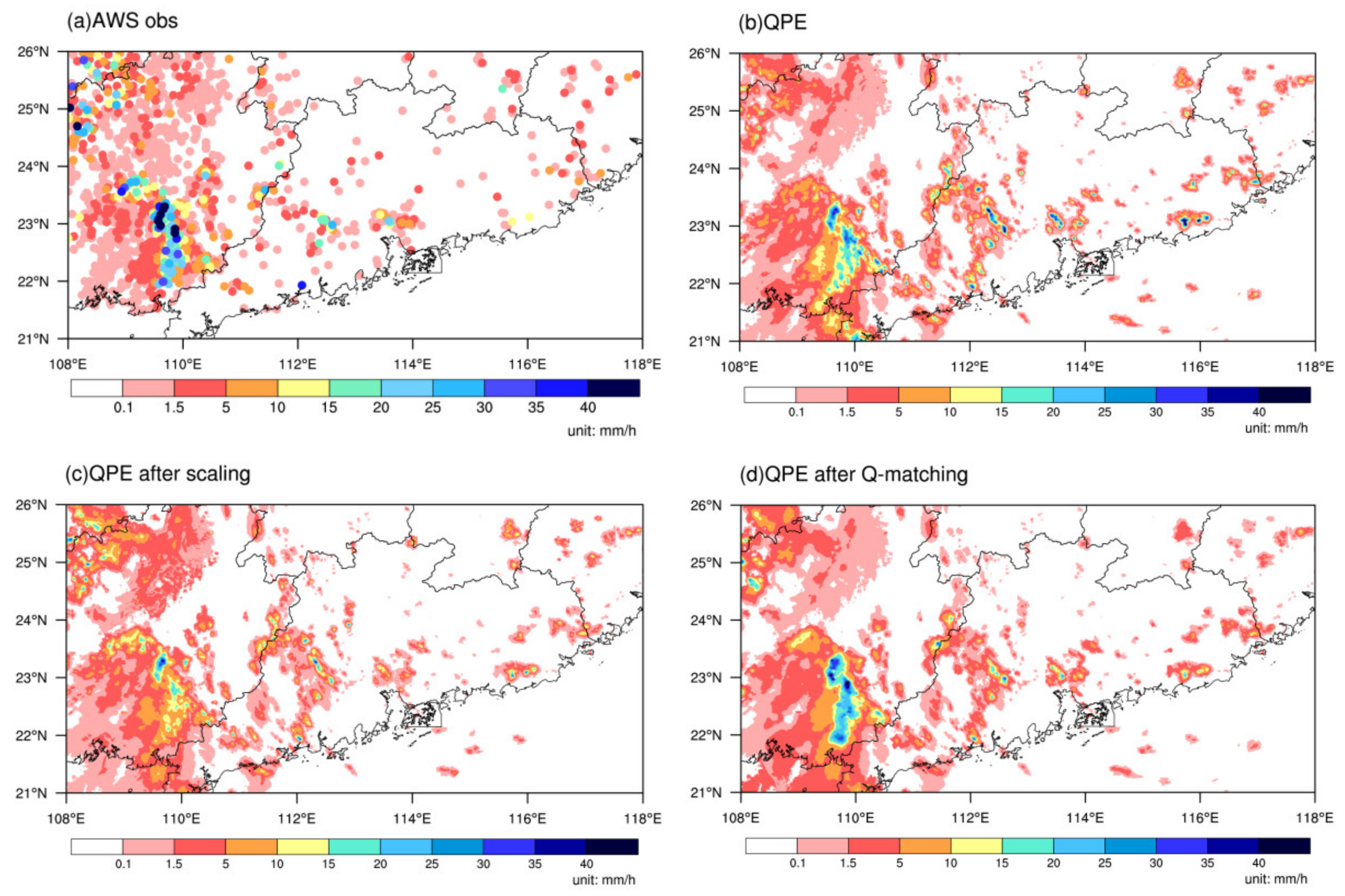
3.1. QPE Errors
3.2. Comparison of the Climatological Correction Scaling Algorithm and Q-matching Methods
4. Conclusions
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pellarin, T.G.; Delrieu, G.M.; Saulnier, H.A. Hydrologic visibility of weather radars operating in mountainous regions: Case study for the Ardeche catchment (France). J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, V.; Massari, C. On the performance of satellite precipitation products in riverine flood modeling: A review. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.C.; Guo, W.L.; Li, N.J.; Xie, Y.Y. Numerical simulation of urban ponding in Beijing. Meteorol. Mon. 2012, 41, 1111–1118. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, W.; Yao, S.; Nath, D.; Yu, B. Interannual variations of the rainy season withdrawal of the monsoon transitional zone in China. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 2031–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, S.N. Global Perspectives on Loss of Human Life Caused by Floods. Nat. Hazards 2005, 34, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.D. Detection and Warnings of Severe Convection with Doppler Weather Radar. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 31–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Wang, H.Q. Statistical characteristics of convective initiation in the Beijing-Tianjin region revealed by six-year radar data. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabella, M.; Speirs, P.; Hamann, U.; Germann, U.; Berne, A. Measurement of Precipitation in the Alps Using Dual-Polarization C-Band Ground-Based Radars, the GPM Spaceborne Ku-Band Radar, and Rain Gauges. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Germann, U.; Galli, G.; Boscacci, M.; Bolliger, M. Radar precipitation measurement in a mountainous region. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 132, 1669–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, A.; Krajewski, W.F. Radar for hydrology: Unfulfilled promise or unrecognized potential? Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W. Key Method Research on Radar Precipitation Estimation of Complex Terrain over the Tibet Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing, China, 2013; p. 128. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, L.P.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, D.; Feng, L.I. Development of a-real time quality control method for automatic rainfall gauge data using radar quantitative precipitation estimation. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 39, 59–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, M.; Smith, J.A. Use of Three-Dimensional reflectivity structure for automated detection and removal of nonpre-cipitating echoes in radar data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabella, M. Improving Operational Measurement of Precipitation Using Radar in Mountainous Terrain—Part II: Verification and Applications. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.D.; Knievel, J.C. Do Meteorologists Suppress Thunderstorms?: Radar-Derived Statistics and the Behavior of Moist Convection. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prat, O.P.; Barros, A.P. Exploring the transient behavior of Z-R relationships: Implications for radar rainfall estimation. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 48, 2127–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, W.F.; Villarini, G.; Smith, J.A. Radar-Rainfall Uncertainties: Where are we after thirty years of effort? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.M.; Ro, Y.; Kim, K.; Yoo, C. Analysis on Characteristics of Orographic Effect about the Rainfall Using Radar Data: A Case Study on Chungju Dam Basin. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 48, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, S.; Heistermann, M. Benchmarking attenuation correction procedures for six years of single-polarized C-band weather radar observations in South-West Germany. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 1785–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cong, F.; Liu, L. A comprehensive analysis of data from the CINRAD and the ground rainfall station. Meteorol. Monogr. 2011, 37, 532–539. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Byun, H.; Kim, H.; Jun, H. Evaluation of a rain gauge network considering the spatial distribution characteristics and entropy: A case study of Imha dam basin. J. Korean Soc. Hazard. Mitig. 2013, 13, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochoa-Rodriguez, S.; Wang, L.-P.; Willems, P.; Onof, C. A Review of Radar-Rain Gauge Data Merging Methods and Their Potential for Urban Hydrological Applications. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6356–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W.M.K. The distribution of raindrops with size. J. Meteorol. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Gao, F.; Kong, R.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Q. Introduction of auto-nowcasting system for convective storm and its performance in Beijing Olympics meteorological service. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2010, 21, 395–404. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.L.; Liu, L.P.; Ding, Y.Y. Improvement of radar quantitative precipitation estimation based on real-time adjustments to Z-R relationships and inverse distance weighting correction schemes. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.B.; Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Zhong, L.; Chen, C. Evaluation and analysis of the Z-R storm-grouping relationships fitting scheme based on storm identification. Torrential Rain Disasters 2015, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.W.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B.; Qi, Y.; Tang, L.; Grams, H.; Wang, Y.; Cocks, S.; Martinaitis, S.M.; et al. Multi-Radar Multi-Sensor (MRMS) Quantitative Precipitation Estimation: Initial Operating Capabilities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudenhoofdt, E.; Delobbe, L. Evaluation of radar-gauge merging methods for quantitative precipitation estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.P.; Ochoa-Rodriguez, S.; Simões, N.; Onof, C.; Maksimovic, Č. Radar-rain gauge data combination techniques: A revision and analysis of their suitability for urban hydrology. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Li, B.; Yang, H.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, L. A study of regional rainfall estimation by using radar and rain gauge: Proposal of model integration method. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2014, 42, 556–562. [Google Scholar]
- Berndt, C.; Rabiei, E.; Haberlandt, U. Geostatistical merging of rain gauge and radar data for high temporal resolutions and various station density scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Sharma, A.; Mariethoz, G.; Johnson, F.; Seed, A. Improving radar rainfall estimation by merging point rainfall measurements within a model combination framework. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 97, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.J.; Breidenbach, J.P.; Johnson, E.R. Real-time estimation of mean field bias in radar rainfall data. J. Hydrol. 1999, 223, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei, E.; Haberlandt, U. Applying bias correction for merging rain gauge and radar data. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringard, J.; Seyler, F.; Linguet, L. A Quantile Mapping Bias Correction Method Based on Hydroclimatic Classification of the Guiana Shield. Sensors 2017, 17, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chumchean, S.; Seed, A.; Sharma, A. Correcting of real-time radar rainfall bias using a Kalman filtering approach. J. Hydrol. 2006, 317, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoo, C. Using Extended Kalman Filter for Real-time Decision of Parameters of Z-R Relationship. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 47, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Yoo, C. Use of a dual Kalman filter for real-time correction of mean field bias of radar rain rate. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2785–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, V.H.; Aznar, M. An efficient approach to optimal interpolation of experimental data. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2010, 41, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.R.; Liang, J.Y.; Li, C.H. Radar quantitative precipitation estimation techniques and effect evaluation. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2012, 28, 77–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, D.S.; Dai, T.P. Application of the variational method in the calibration of regional rainfall measurement by weather radar. J. Nanjing Inst. Meteorol. 1990, 13, 598–603. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.C.; Dai, T.P.; Fu, D.S.; Wu, Z.F. Principle and accuracy of adjusting the area precipitation from digital weather radar through variational method. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 1992, 16, 248–256. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.J.; Huang, H.H.; Wu, D. Application of variational method for the calibration radar quantitative estimates of precip-itation. Q. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 11, 255–256. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, B.; van Leeuwen, P.J.; Hogan, R.; Berne, A. A Variational Approach to Retrieve Rain Rate by Combining Information from Rain Gauges, Radars, and Microwave Links. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, W.F. Cokriging radar-rainfall and rain gage data. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1987, 92, 9571–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideris, I.V.; Gabella, M.; Erdin, R.; Germann, U. Real-time radar–rain gauge merging using spatio-temporal co-kriging with external drift in the alpine terrain of Switzerland. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantet, P. Mapping the mean monthly precipitation of a small island using kriging with external drifts. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2015, 127, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinclair, S.; Pegram, G. Combining radar and rain gauge rainfall estimates using conditional merging. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2005, 6, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y. Precipitation Calibration Based on the Frequency-Matching Method. Weather. Forecast. 2015, 30, 1109–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Lin, G.F.; Hwang, L.R.; Chen, D.Y.C.; Chiang, C.C.; Wang, Y.C. Optimal Integration of the Ensemble Forecasts from an Ensemble Quantitative Precipitation Forecast Experiment. Procedia Eng. 2016, 154, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z. Geographically weighted regression based methods for merging satellite and gauge precipitation. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Fu, A.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J.; Wu, J. Improving quantitative precipitation estimates by radar-rain gauge merging and an inte-gration algorithm in the Yishu River catchment, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 144, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.Y.; Chen, M.X.; Cheng, C.L.; Gao, F.; Chen, M. Characteristics of summer QPE error and a climatological correction method over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2019, 77, 497–515. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Panofsky, H.A.; Brier, G.W. Some Applications of Statistics to Meteorology; Penn State University Press: University Park, PA, USA, 1958; p. 234. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, Z.S.; Rosenfeld, D. Optimality of empirical Z-R relations. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 123, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D. Bias Correction, Quantile Mapping, and Downscaling: Revisiting the Inflation Issue. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vrac, M.; Ayar, P.V. Influence of Bias Correcting Predictors on Statistical Downscaling Models. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2017, 56, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthias, J.; Themeßl, M.; Gobiet, A.; Leuprecht, A. Empirical–statistical downscaling and error correction of daily precip-itation from regional climate models. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 31, 1530–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Chaumont, D.; Braun, M. Finding appropriate bias correction methods in downscaling precipitation for hydrologic impact studies over North America. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4187–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.Y.; Duan, W.S.; Li, Y.; Mao, J.Y. A timescale decomposed threshold regression downscaling approach to forecasting South China early summer rainfall. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Huang, R. Interannual variability and triggers of the South China Sea summer monsoon withdrawal. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 4355–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, R. Extremely Early Summer Monsoon Onset in the South China Sea in 2019 Following an El Niño Event. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2020, 148, 1877–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Wo, W.F. Design and Implementation of SWAN2.0 Platform. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2018, 29, 25–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Liu, L.P.; Zhang, C.A.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, S. Operational evaluation of radar data quality control for ground clutter and electromagnetic interference. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2016, 36, 789–799. [Google Scholar]
- Haiden, T.; Kann, A.; Pistotnik, G.; Stadlbacher, K.; Wittmann, C. Integrated Nowcasting through Comprehensive Analysis (INCA)—System description. ZAMG Rep. 2010, 59. Available online: http://www.zamg.ac.at/fix/INCA_system.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- Michelangeli, P.-A.; Vrac, M.; Loukos, H. Probabilistic Downscaling Approaches: Application to Wind Cumulative Dis-tribution Functions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoben, W.J.M.; Freer, J.E.; Woods, R.A. Inherent benchmark or not? Comparing Nash–Sutcliffe and Kling–Gupta efficiency scores. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


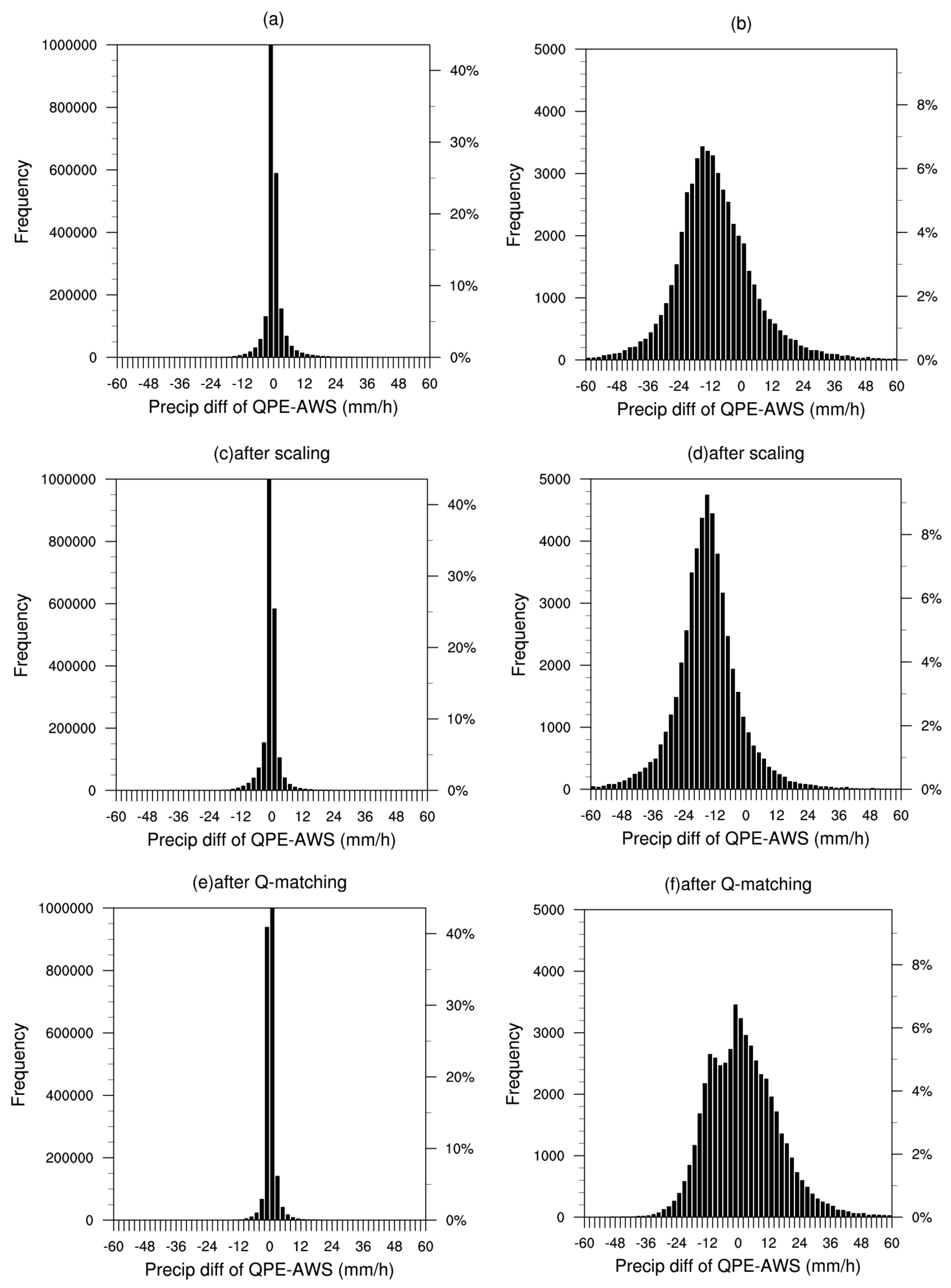
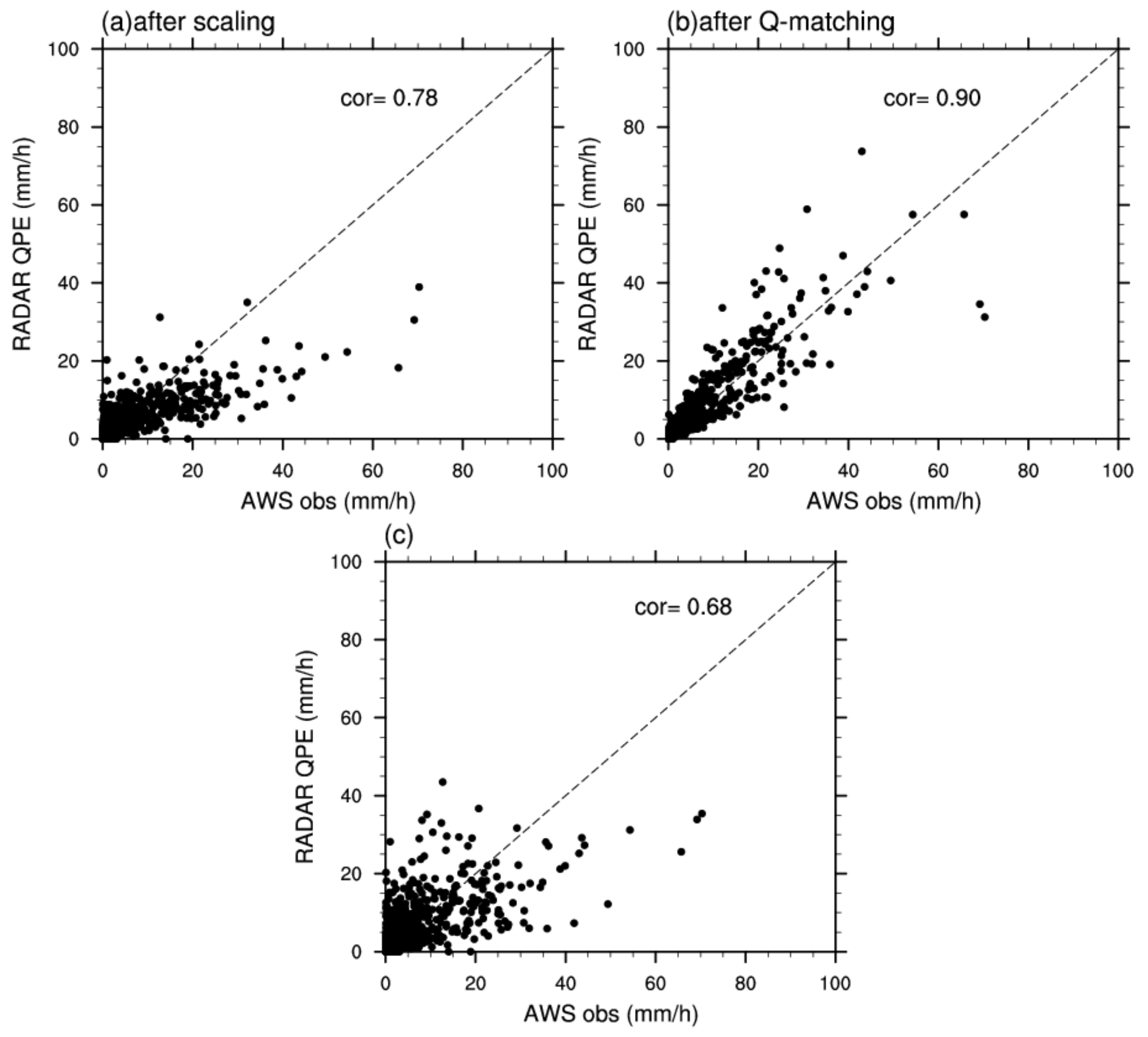
| Original QPE | QPE after Scaling | QPE after Q-Matching | Improvement by Scaling | Improvement by Q-Matching | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 2.237 | 1.947 | 1.257 | 12.96% | 43.81% |
| RMSE | 4.948 | 4.323 | 3.011 | 14.46% | 39.15% |
| CC | 0.629 | 0.650 | 0.893 | 3.34% | 41.97% |
| 1 mm/h | 5 mm/h | 10 mm/h | 15 mm/h | 20 mm/h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| original QPE | 0.756 | 0.609 | 0.523 | 0.460 | 0.411 |
| QPE after scaling | 0.702 | 0.512 | 0.393 | 0.314 | 0.257 |
| QPE after Q-matching | 0.914 | 0.840 | 0.786 | 0.756 | 0.741 |
| Improvement by scaling | −7.14% | −15.93% | −24.86% | −31.74% | −37.47% |
| Improvement by Q-matching | 20.90% | 37.93% | 50.29% | 64.35% | 80.29% |
| 1 mm/h | 5 mm/h | 10 mm/h | 15 mm/h | 20 mm/h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| original QPE | 0.323 | 0.438 | 0.497 | 0.559 | 0.612 |
| QPE after scaling | 0.262 | 0.354 | 0.398 | 0.448 | 0.495 |
| QPE after Q-matching | 0.188 | 0.241 | 0.280 | 0.337 | 0.398 |
| Improvement by scaling | 18.89% | 19.18% | 19.92% | 19.86% | 19.12% |
| Improvement by Q-matching | 41.80% | 44.98% | 43.66% | 39.71% | 34.97% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, L.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Qi, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, M.; Cao, W. The Quantile-Matching Approach to Improving Radar Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in South China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234956
Song L, Chen S, Li Y, Qi D, Wu J, Chen M, Cao W. The Quantile-Matching Approach to Improving Radar Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in South China. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(23):4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234956
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Linye, Shangfeng Chen, Yun Li, Duo Qi, Jiankun Wu, Mingxuan Chen, and Weihua Cao. 2021. "The Quantile-Matching Approach to Improving Radar Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in South China" Remote Sensing 13, no. 23: 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234956
APA StyleSong, L., Chen, S., Li, Y., Qi, D., Wu, J., Chen, M., & Cao, W. (2021). The Quantile-Matching Approach to Improving Radar Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in South China. Remote Sensing, 13(23), 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234956







