Contribution of Changes in Snow Cover Extent to Shortwave Radiation Perturbations at the Top of the Atmosphere over the Northern Hemisphere during 2000–2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
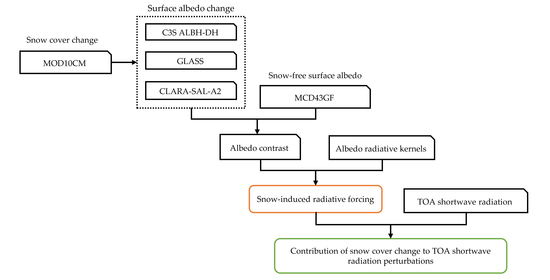
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Snow Cover Extent Dataset
NHSCE Snow Charts
MOD10CM
2.1.2. Land Surface Albedo Dataset
C3S ALBH-DH Surface Albedo Dataset
GLASS Land Surface Albedo Dataset
CLARA-SAL-A2 Land Surface Albedo Dataset
MCD43GF Snow-Free Surface Albedo Dataset
2.1.3. Albedo Radiative Kernels Datasets
2.1.4. TOA Radiation Budget Dataset
2.1.5. Data Preparation
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Z-Score Normalization
2.2.2. Linear Slope
2.2.3. Pearson Correlation Coefficient
2.2.4. Relative Contribution Calculation
3. Results
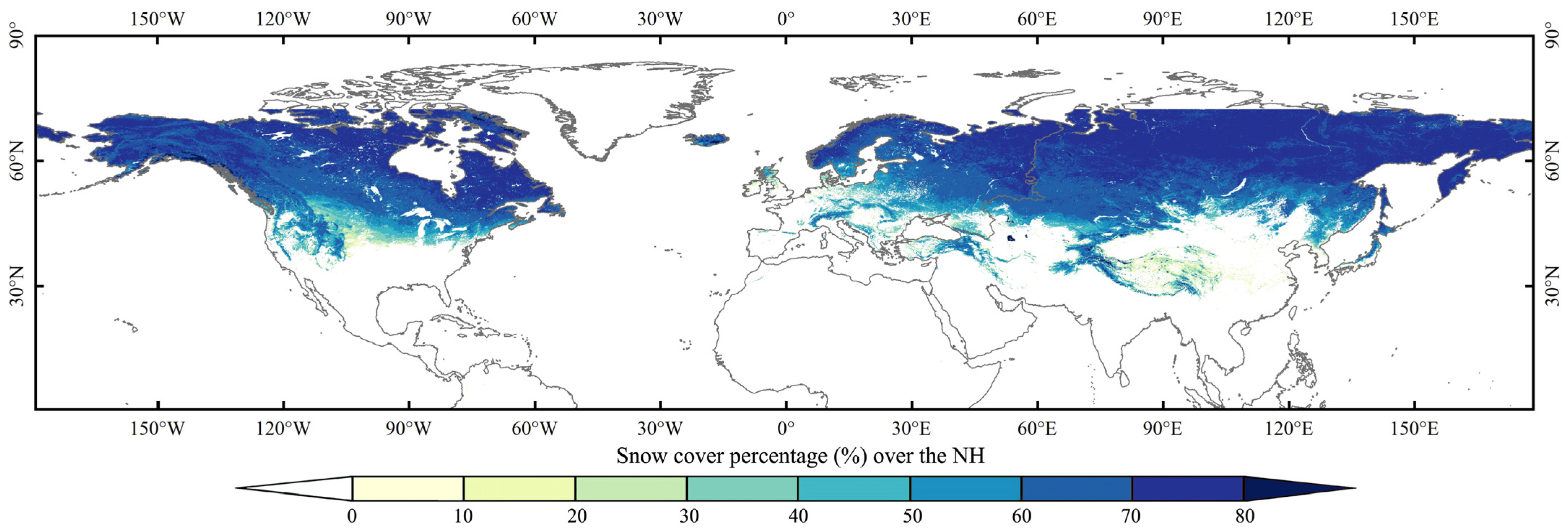
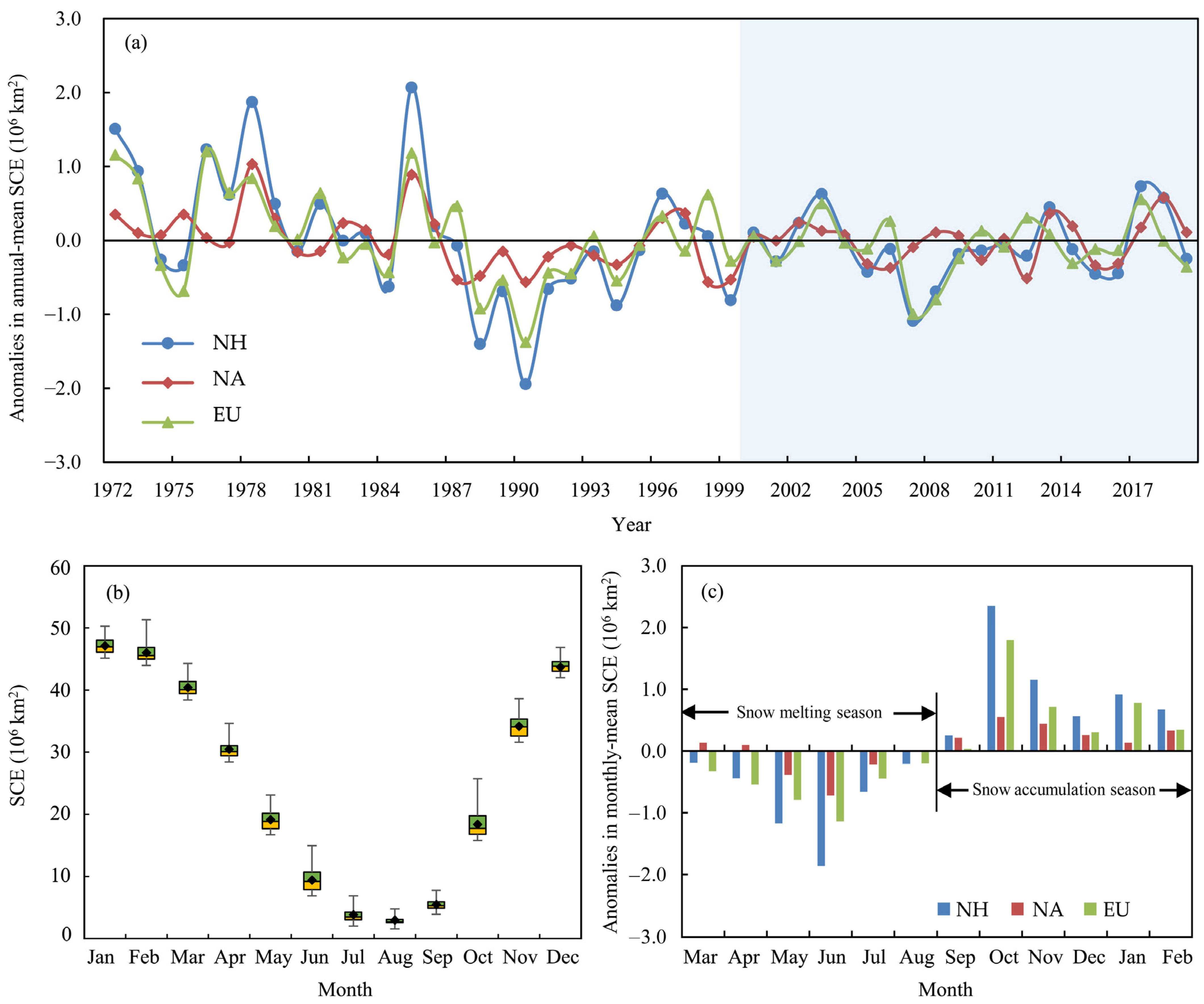
3.1. Characteristic of SCE Variability in the NH during 2000–2019
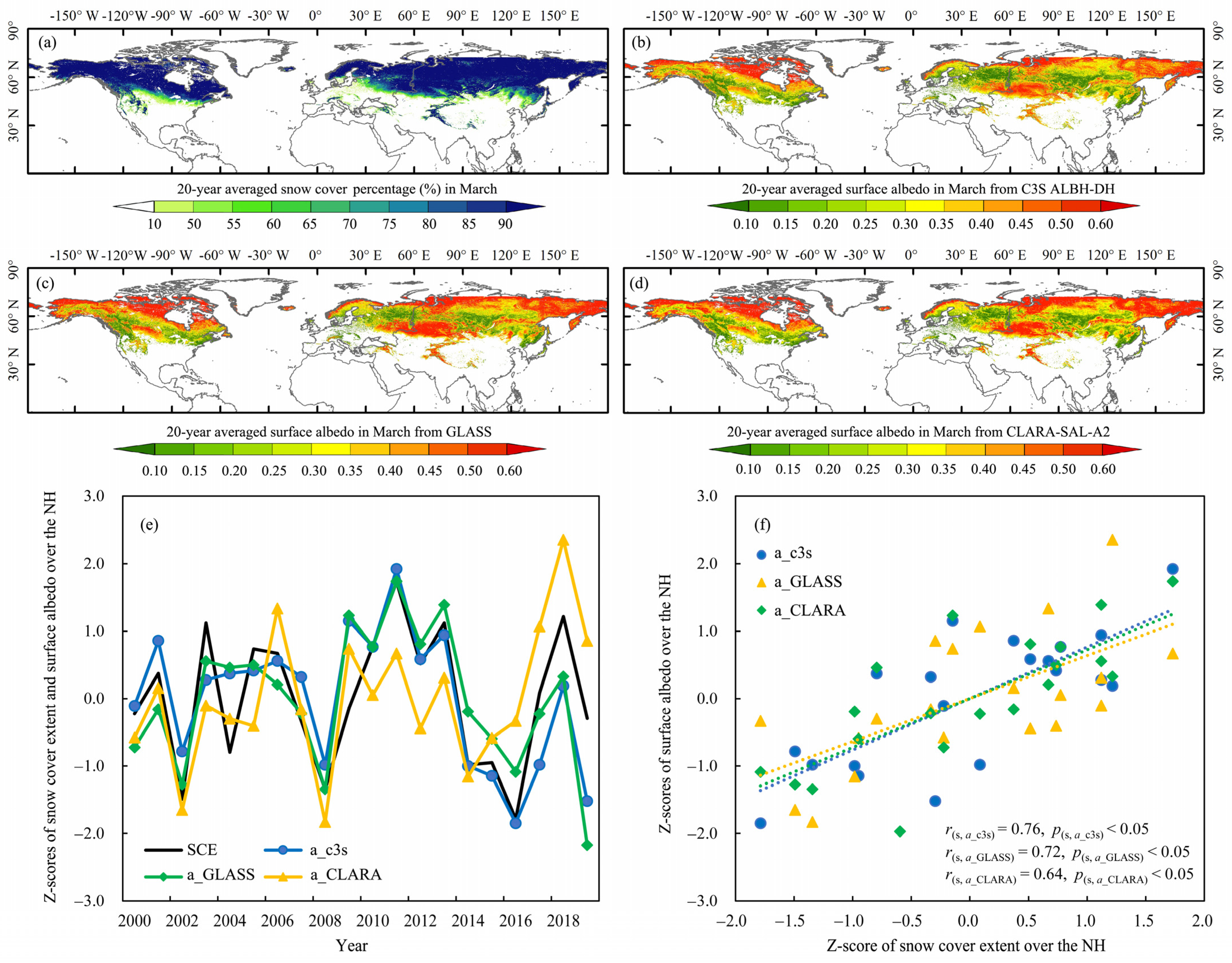
3.2. Validation of C3S Surface Albedo Dataset in SnRF Calculation
3.2.1. Performance of C3S ALBH-DH in March during 2000–2019
3.2.2. Performance of C3S-ALBH-DH in June during 2000–2019
3.3. Estimation of SnRF over the NH
3.3.1. Estimated SnRF over the NH during 2000–2019
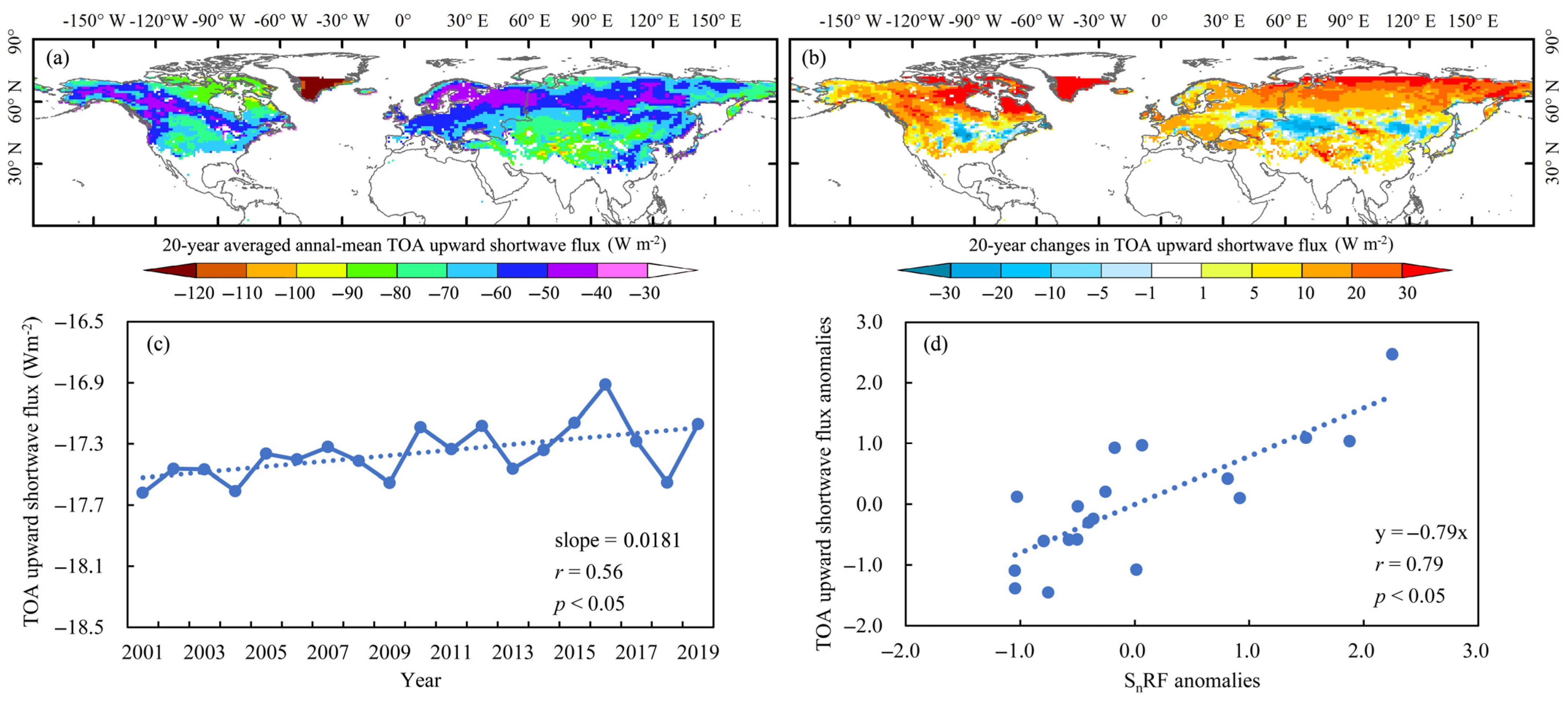
3.3.2. Direct Estimates of TOA Shortwave Flux Anomalies
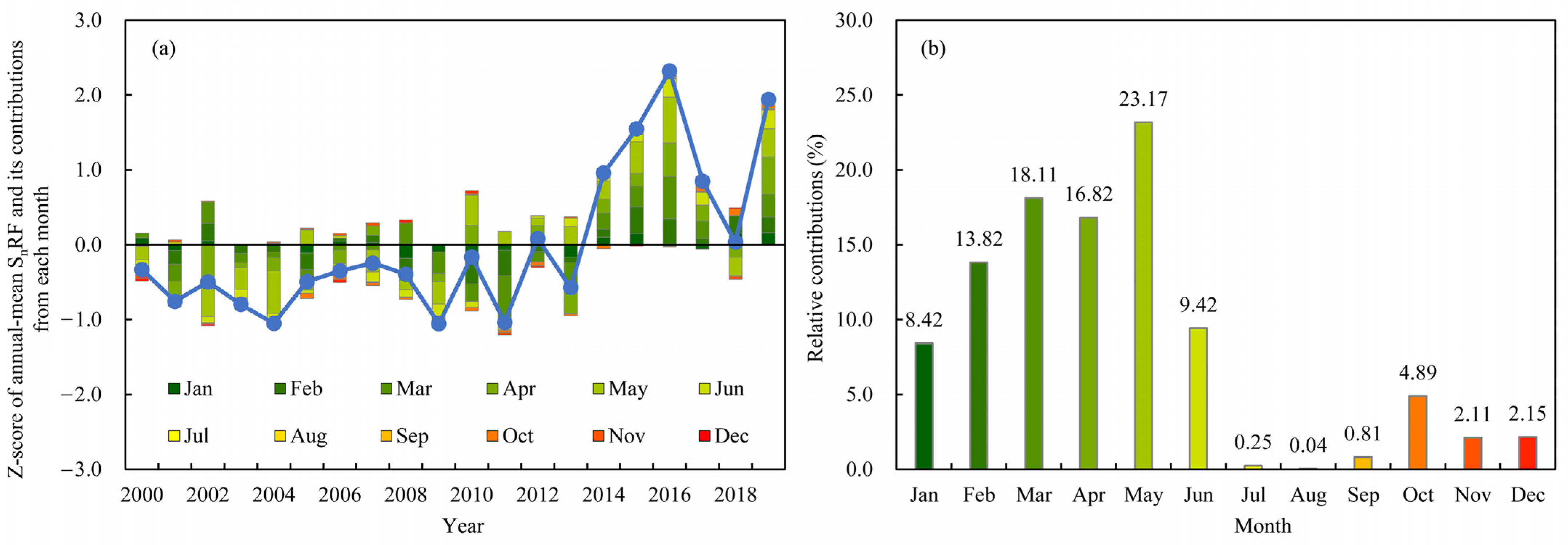
3.3.3. Attribution of SnRF Anomalies over the NH during 2000–2019
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GCOS. Snow: Essential Climate Variable (ECV) Factsheet. 2019. Available online: https://gcos.wmo.int/en/essential-climate-variables/snow/ (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Flanner, M.G.; Shell, K.M.; Barlage, M.; Perovich, D.K.; Tschudi, M.A. Radiative forcing and albedo feedback from the Northern Hemisphere cryosphere between 1979 and 2008. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, S.; Cao, Y. Satellite observed changes in the Northern Hemisphere snow cover phenology and the associated radiative forcing and feedback between 1982 and 2013. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 084002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, C.W.; Fletcher, C.G. Snow albedo feedback: Current knowledge, importance, outstanding issues and future directions. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 40, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, S.; Cao, Y.; He, T.; Wang, D. Observed contrast changes in snow cover phenology in northern middle and high latitudes from 2001–2014. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Liang, S.; Yang, Y. Differences in snow-induced radiative forcing estimated from satellite and reanalysis surface albedo datasets over the Northern Hemisphere landmass for the overlapping period of 1982–2012. Environ. Res. Commun. 2020, 2, 091001. [Google Scholar]
- Perket, J.; Flanner, M.G.; Kay, J.E. Diagnosing shortwave cryosphere radiative effect and its 21st century evolution in CESM. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, D.; Flanner, M.G.; Perket, J. The global land shortwave cryosphere radiative effect during the MODIS era. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 2057–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, X.; Hall, A. On the persistent spread in snow-albedo feedback. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, M.; Dutra, E.; Jacobi, H.-W.; Zolina, O. Spring snow albedo feedback over northern Eurasia: Comparing in situ measurements with reanalysis products. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Long, D.; Hong, Y.; Liang, S.; Hou, A. Observed radiative cooling over the Tibetan Plateau for the past three decades driven by snow-cover-induced surface albedo anomaly. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 6170–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSIDC. State of the Cryosphere: Northern Hemisphere Snow. 2019. Available online: https://nsidc.org/cryosphere/sotc/snow_extent.html (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, H. Distribution and Attribution of Terrestrial Snow Cover Phenology Changes over the Northern Hemisphere during 2001–2020. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Key, J.; Qu, X.; Hall, A. Controls on Northern Hemisphere snow albedo feedback quantified using satellite Earth observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L21702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estilow, T.W.; Young, A.H.; Robinson, D.A. A long-term Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent data record for climate studies and monitoring. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2015, 7, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, D.K.G.; Riggs, G.A. MODIS/Terra Snow Cover Monthly L3 Global 0.05 Deg CMG, Version 6. NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center. 2015. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5067/MODIS/MOD10CM.006 (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Riggs, G.A.; Hall, D.K. MODIS Snow Products Collection 6 User Guide. 2015. Available online: https://modis-snow-ice.gsfc.nasa.gov/uploads/C6_MODIS_Snow_User_Guide.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Frei, A.; Tedesco, M.; Lee, S.; Foster, J.; Hall, D.K.; Kelly, R.; Robinson, D.A. A review of global satellite-derived snow products. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 50, 1007–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groisman, P.Y.; Karl, T.R.; Knight, R.W. Observed Impact of Snow Cover on the Heat Balance and the Rise of Continental Spring Temperatures. Science 1994, 14, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GCOS. Albedo: Essential Climate Variable (ECV) Factsheet. 2019. Available online: https://gcos.wmo.int/en/essential-climate-variables/albedo (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- C3S. Surface albedo 10-daily gridded data from 1981 to present. In Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS); The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, UK, 2021; Available online: https://www.copernicus.eu/en/access-data/copernicus-services-catalogue/surface-albedo-10-daily-gridded-data-1981-present (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Schaaf, C.B. MODIS/Terra+Aqua BRDF/Albedo Gap-Filled Snow-Free Daily L3 Global 30ArcSec CMG V006. 2019. Available online: https://10.5067/MODIS/MCD43GF.006 (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Liang, S.; Cheng, J.; Jia, K.; Jiang, B.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; et al. The Global Land Surface Satellite (GLASS) Product Suite. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 102, E323–E337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, K.-G.; Anttila, K.; Trentmann, J.; Stengel, M.; Fokke Meirink, J.; Devasthale, A.; Hanschmann, T.; Kothe, S.; Jääskeläinen, E.; Sedlar, J.; et al. CLARA-A2: The second edition of the CM SAF cloud and radiation data record from 34 years of global AVHRR data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5809–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, K.-G.; Anttila, K.; Trentmann, J.; Stengel, M.; Fokke Meirink, J.; Devasthale, A.; Hanschmann, T.; Kothe, S.; Jääskeläinen, E.; Sedlar, J.; et al. CLARA-A2.1: CM SAF cLoud, Albedo And surface RAdiation Dataset from AVHRR Data—Edition 2.1. Satellite Application Facility on Climate Monitoring. 2020. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5676/eum_saf_cm/clara_avhrr/v002_01 (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- He, T.; Liang, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, F.; Liu, Q. Greenland surface albedo changes in July 1981–2012 from satellite observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shell, K.M.; Kiehl, J.T.; Shields, C.A. Using the Radiative Kernel Technique to Calculate Climate Feedbacks in NCAR’s Community Atmospheric Model. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 2269–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soden, B.J.; Held, I.M.; Colman, R.; Shell, K.M.; Kiehl, J.T.; Shields, C.A. Quantifying Climate Feedbacks Using Radiative Kernels. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 3504–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauritsen, T.; Graversen, R.G.; Klocke, D.; Langen, P.L.; Stevens, B.; Tomassini, L. Climate feedback efficiency and synergy. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 41, 2539–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wielicki, B.A.; Barkstorm, B.R.; Harrison, E.F.; Lee, R.B.; Smith, G.L.; Cooper, J.E. Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES): An Earth observing system experiment. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1996, 77, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loeb, N.G.; Wielicki, B.A.; Doelling, D.R.; Smith, G.L.; Keyes, D.F.; Kato, S.; Manalo-Smith, N.; Wong, T. Toward Optimal Closure of the Earth’s Top-of-Atmosphere Radiation Budget. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 748–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreyszig, E. Advanced Engineering Mathematics; Wiley: Jefferson City, MO, USA, 1979; pp. 1014–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, E.; Birch, J.B. Influence Measures in Ridge Regression. Technometrics 1988, 30, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Mo, X.; Hu, S.; Liu, S. Contributions of climate change, elevated atmospheric CO2 and human activities to ET and GPP trends in the Three-North Region of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 295, 108183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, T.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, F.; Ma, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C. Seasonal divergence in the sensitivity of evapotranspiration to climate and vegetation growth in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Derksen, C.; Wang, L. A multi-data set analysis of variability and change in Arctic spring snow cover extent, 1967–2008. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D16111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.D.; Robinson, D.A. Northern Hemisphere spring snow cover variability and change over 1922–2010 including an assessment of uncertainty. Cryosphere 2011, 5, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derksen, C.; Brown, R. Spring snow cover extent reductions in the 2008–2012 period exceeding climate model projections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L19504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hock, R.; Rasul, G.; Adler, C.; Cáceres, B.; Gruber, S.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Jackson, M.; Kääb, A.; Kang, S.; Kutuzov, S.; et al. High Mountain Areas. In IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate Cambridge; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Brutel-Vuilmet, C.; Ménégoz, M.; Krinner, G. An analysis of present and future seasonal Northern Hemisphere land snow cover simulated by CMIP5 coupled climate models. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J.; Foster, J.; Barlow, M.; Saito, K.; Jones, J. Winter 2009–2010: A case study of an extreme Arctic Oscillation event. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 2010GL044256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WMO. WMO Statement on the State of the Global Climate in 2018. 2019. Available online: https://public.wmo.int/en/resources/library/wmo-statement-state-of-global-climate-2018 (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Qu, X.; Hall, A. What Controls the Strength of Snow-Albedo Feedback. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 3971–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WMO. WMO Statement on the State of the Global Climate in 2019. 2020. Available online: https://public.wmo.int/en/resources/library/wmo-statement-state-of-global-climate-2019 (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Cohen, J. An observational analysis: Tropical relative to Arctic influence on midlatitude weather in the era of Arctic amplificatio. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 5287–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.A.; Vavrus, S.J.; Cohen, J. Amplified Arctic warming and mid-latitude weather: New perspectives on emerging connections. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2017, 8, e474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, S.; Cao, Y.; He, T. Distribution, attribution, and radiative forcing of snow cover changes over China from 1982 to 2013. Clim. Chang. 2016, 137, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Variable | Dataset | Horizontal Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Time Span | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snow cover | MOD10CM | 0.05° | Monthly | 2000–2019 | SCE change detection |
| NH SCE CDR v01r01 | – | Monthly | 1966–2019 | ||
| Surface albedo | GLASS | 0.05° | 8-day | 2000–2019 | Albedo contrast calculation |
| CLARA-SAL-A2 | 0.25° | 5-day | 2000–2019 | ||
| C3S-ALBH-DH | 1-km | 10-day | 2000–2019 | ||
| MCD43GF | 0.0083° | Daily | 2001–2017 | ||
| Albedo radiative kernels | CAM3 | 2.81° | Monthly | – | Radiative kernel calculation |
| AM2 | 2.50° | Monthly | – | ||
| ECHAM6 | 1.88° | Monthly | – | ||
| TOA shortwave flux | CERES EBAF | 1.88° | Monthly | 2000–2019 | Contribution analysis |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Yin, C. Contribution of Changes in Snow Cover Extent to Shortwave Radiation Perturbations at the Top of the Atmosphere over the Northern Hemisphere during 2000–2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4938. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234938
Chen X, Yang Y, Yin C. Contribution of Changes in Snow Cover Extent to Shortwave Radiation Perturbations at the Top of the Atmosphere over the Northern Hemisphere during 2000–2019. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(23):4938. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234938
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaona, Yaping Yang, and Cong Yin. 2021. "Contribution of Changes in Snow Cover Extent to Shortwave Radiation Perturbations at the Top of the Atmosphere over the Northern Hemisphere during 2000–2019" Remote Sensing 13, no. 23: 4938. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234938
APA StyleChen, X., Yang, Y., & Yin, C. (2021). Contribution of Changes in Snow Cover Extent to Shortwave Radiation Perturbations at the Top of the Atmosphere over the Northern Hemisphere during 2000–2019. Remote Sensing, 13(23), 4938. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234938