Abstract
Training a deep learning model requires highly variable data to permit reasonable generalization. If the variability in the data about to be processed is low, the interest in obtaining this generalization seems limited. Yet, it could prove interesting to specialize the model with respect to a particular theme. The use of enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks (ERSGAN), a specific type of deep learning architecture, allows the spatial resolution of remote sensing images to be increased by “hallucinating” non-existent details. In this study, we show that ESRGAN create better quality images when trained on thematically classified images than when trained on a wide variety of examples. All things being equal, we further show that the algorithm performs better on some themes than it does on others. Texture analysis shows that these performances are correlated with the inverse difference moment and entropy of the images.
1. Introduction
Images of high (HR, ~1–5 m per pixel) and very high (VHR, <1 m per pixel) spatial resolution are of particular importance for several Earth observation (EO) applications, such as for both visual and automatic information extraction [1,2,3]. However, currently, most high-resolution and all very high-resolution images acquired by orbital sensors need to be purchased at a high price. On the other hand, there is abundant medium-resolution imagery currently available for free (e.g., the multispectral instrument onboard Sentinel-2 and the operational land imager onboard Landsat-8). Improving the spatial resolution of medium-resolution imagery to the spatial resolution of high- and very high-resolution imagery would thus be highly useful in a variety of applications.
Image resolution enhancement is called super-resolution (SR) and is currently a very active research topic in EO image analysis [4,5,6] and computer vision in general, as shown in [7]. However, SR is inherently an ill-posed problem [8]. Multi-frame super-resolution (MFSR) uses multiple low-resolution (LR) images to constrain the reconstruction of a high-resolution (HR) image. However, this approach cannot be used when a single image is available. Single image super-resolution (SISR) is a particular type of SR that involves increasing the resolution of a low-resolution (LR) image to create a high-resolution (HR) image. SISR can be achieved by (1) the “external example-based” approach, where the algorithm learns from dictionaries [9], or by using (2) convolutional neural networks (CNNs), where the algorithm “learns” the relevant features of the image that would be useful for improving its resolution [10,11]. SISR can also be achieved by using (3) generative adversarial neural networks (GANs) [12]. GANs oppose two networks (a generator and a discriminator), one against the other, in an adversarial way. The generator is trained to produce new images to trick the discriminator into trying to distinguish whether it is a real image or a fake image. In this type of network, the generator and the discriminator act as adversaries. GANs provide a powerful framework for generating real-looking images with high quality, as is the case in [13], through enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks (ESRGAN). This architecture is now used in different applications, such as satellite imagery [14,15] or the improvement of the predictive resolution of some models [16,17].
In general, training a neural network model requires separating the dataset into the following three parts: (1) a training dataset; (2) a validation dataset; and (3) a test dataset. The training dataset is used to adjust the model parameters and biases. The validation dataset is used to estimate the model’s skill while tuning its hyperparameters, including the number of epochs, among others. As only the number of epochs will be relevant for the reader, its definition is given here. One “epoch” is defined as one forward pass and one backward pass through the entire training dataset. The test dataset is then used to verify the capability of the model to generalize its predictions based upon new data. If the model yields good predictions, then its ability to generalize is good. Otherwise, the model exhibits overfitting and is susceptible to overlearning, i.e., no further improvement in performance can be achieved and, indeed, further “tinkering” (experimentation or adjustment) may possibly result in its subsequent deterioration. Indeed, neural network models can be over-parameterized, yet can still correctly predict labels, even if these were assigned randomly [7,8,9]. Overfitting is a known problem in neural network models and deep learning in general, but different methods can allow us to avoid the problem, such as data augmentation by flipping or rotating the images [18,19], the use of a dropout layer that forces the model to work with part of its parameters turned “off” [20], or early stopping of the training phase [21,22]. Hence, the sample’s variability in the training dataset is key to minimize the possibility of overfitting.
In the particular case of SISR, is it relevant to try to maximize the variety of examples if the model is to be applied to a specific theme or topic? In this study, we use the ESRGAN method to increase the spatial resolution of different types of imagery and address this question. ESRGAN were chosen because they outperform, in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), other SISR methods, such as SRCNN, EDSR, RCAN, EnhanceNet or SRGAN [13], and are publicly available. We used airborne and satellite images to construct different datasets of different themes, as follows: (1) “daily life”; (2) agricultural; (3) forests; (4) urban areas; (5) rocky outcrops; (6) the planet Mars; and (7) a mixture of different themes. These groups of data have been used for training with different numbers of epochs (150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800). We demonstrated that training a model for a specific task is more interesting than maximizing the variability in the data during training. The results indicate that the number of epochs is not strictly correlated with the PSNR value; rather, it depends upon the topic being trained. Furthermore, this work highlights a correlation between the quality of the results and the textural homogeneity of the image, i.e., the inverse difference moment (IDM), together with entropy indices that are taken from the Haralick co-occurrence matrix [23].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ESRGAN Architecture
The ESRGAN architecture we used is inspired by the SRGAN or super-resolution generative adversarial network [24]. The architecture is described in [13], and we invite the reader to refer to it for more details. The models are trained to reconstruct images for which the resolution has been degraded by a factor of 4 using MATLAB bicubic kernel function. The use of other convolution methods to degrade the resolution is not recommended, given that they could generate artefacts. The codes that are used here are those provided by the authors of [13] on their GitHub (https://github.com/xinntao/ESRGAN) (accessed on 14 July 2021).
2.2. Datasets
Images that were used in this study originated from different sources. Each theme contains 650 images. The choice of themes was guided by the following two main criteria: (1) constructing themes that presented a large variability in environments (forests, regolith, and urban areas, among others); and (2) data availability. Table 1 lists the datasets used in this study, and the following section describes the different themes that were used in this study.

Table 1.
Datasets used in this study with their spatial resolution and location when relevant.
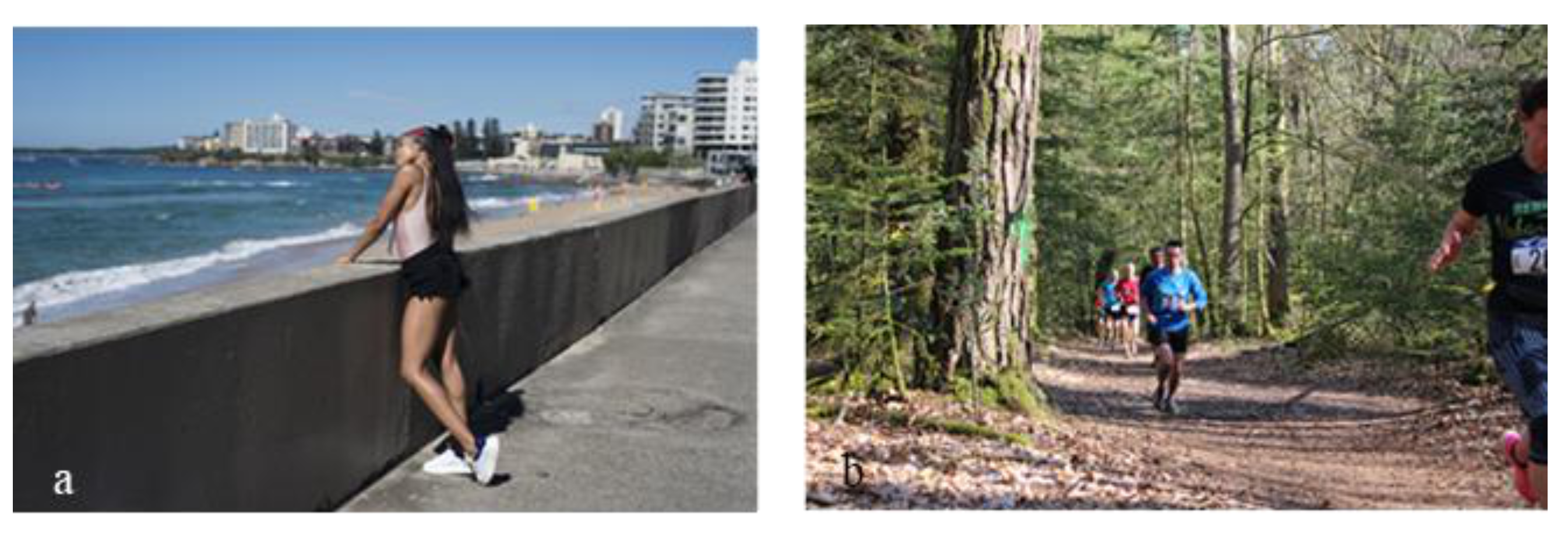
“Daily life” (Figure 1). The DIVerse 2K (DIV2K) resolution high-quality images dataset is commonly used in the literature to train and then to measure the performance of super-resolution algorithms [25]. The images are common scenes from daily life. This dataset possesses no spatial resolution that is associated with pixel size of the images.

Figure 1.
Examples (a,b) of daily life images in the DIV2K dataset.
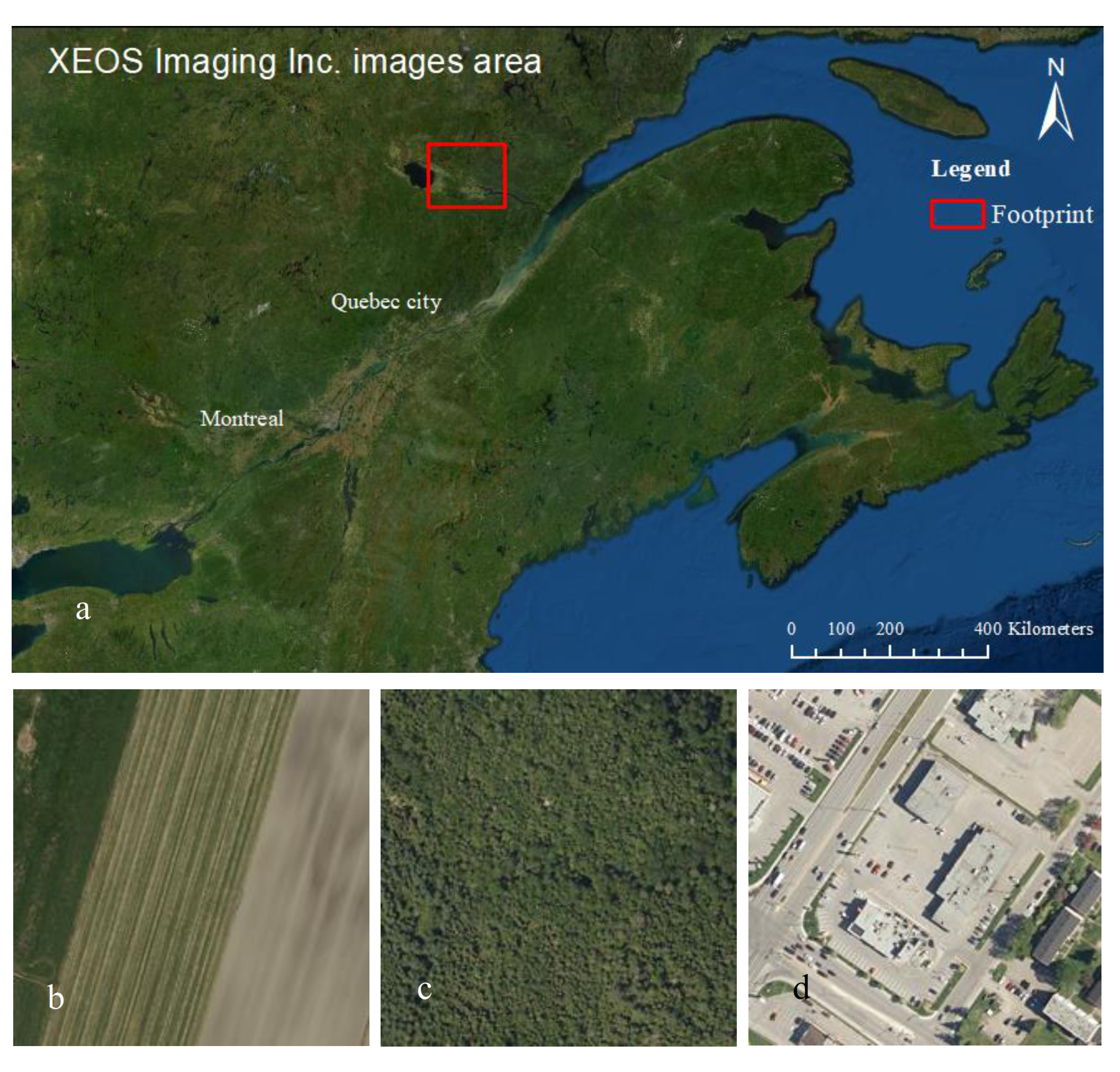
“Airborne imagery” (Figure 2). These images were acquired at 20 cm spatial resolution and have been kindly provided by XEOS Imaging Inc. (Quebec, QC, Canada). They cover different areas, randomly chosen, of the province of Quebec (Canada), between 70°29′02″W and 71°53′05″W, and between 40°12′31″N and 48°58′26″N. These images were visually classified into categories according to land use (agricultural, forest and urban).
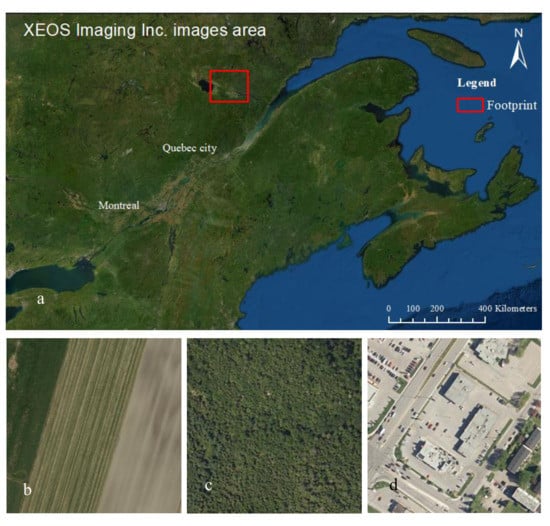
Figure 2.
Map (a) and examples of airborne imagery. Agriculture (b), forest (c), urban (d). Service Layer Credits: Esri, Maxar, GeoEye, Earth star Geographics, CNES/Airbus DS, USDA, USGS, AeroGRID, IGN, and the GIS User Community.
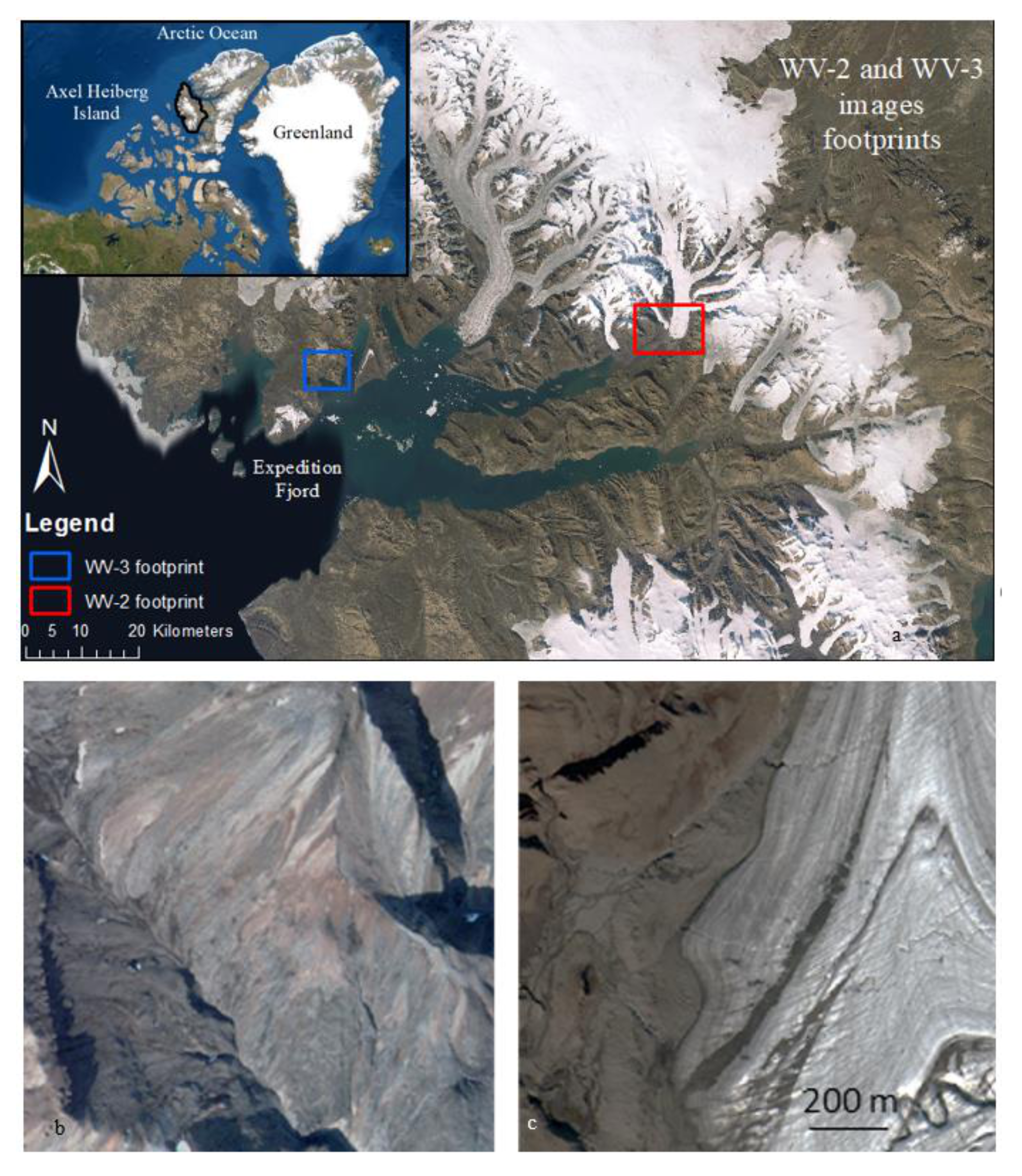
“WorldView satellite imagery” (Figure 3). The images were acquired by the sensors onboard the WorldView-2 (WV-2) and WorldView-3 (WV-3) satellites, which have a spatial resolution of 2 m. The images cover two geographical areas of Axel Heiberg Island (Nunavut) in the Canadian High Arctic. They include mostly regolith, rocks, and glaciers. To be compared with the other themes, only the RGB channels were kept, then converted to 8 bits images.
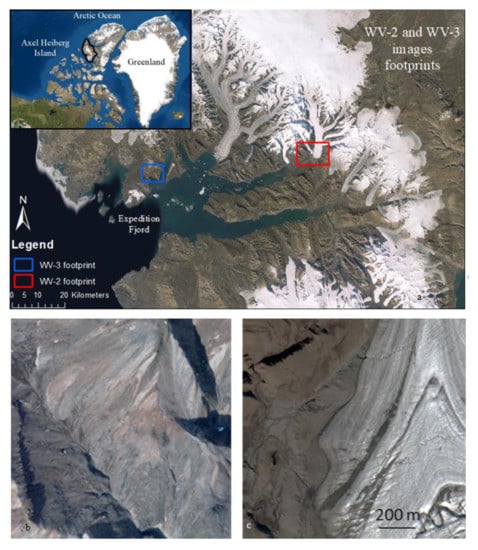
Figure 3.
Map (a) and examples of satellite imagery from WV-2 (b) and WV-3 (c). Service Layer Credits: Esri, Maxar, GeoEye, Earth star Geographics, CNES/Airbus DS, USDA, USGS, AeroGRID, IGN, and the GIS User Community.
“HiRISE satellite imagery” (Figure 4). Forty-nine images that were acquired by the HiRISE (high-resolution imaging experiment) instrument onboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter have been downloaded from the University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ, USA) website (https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu) (accessed on 15 April 2021). The images cover a wide range of geomorphological variability that is found on Mars (dunes, craters and canyons, among others). The spatial resolution of these images ranges between approximately 25 cm and 50 cm depending on the orbiter’s altitude.
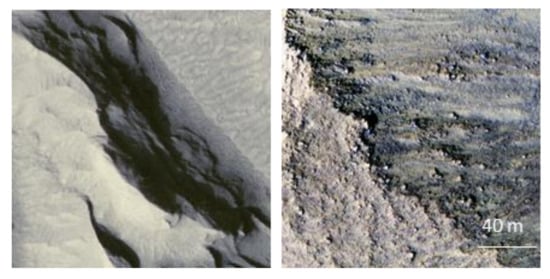
Figure 4.
Examples of HiRISE satellite imagery.
The “mixed” theme is an equiproportional mixture of images that have been randomly selected from each of the other six themes.
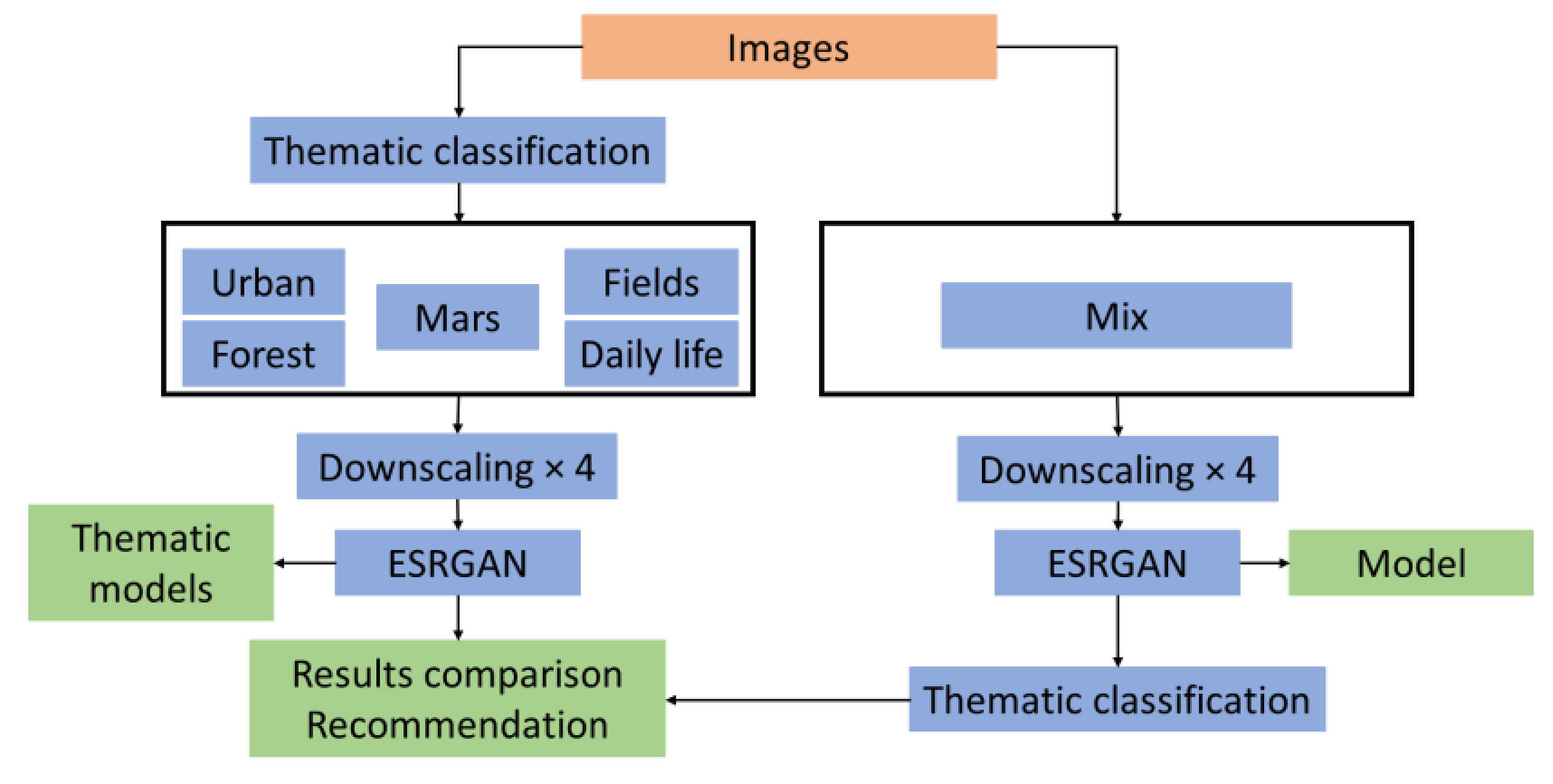
All of the images of the various themes have undergone bicubic convolution (by a factor of 4) to degrade their resolution. The data were separated into a training set (520 images), a validation set (65 images), and a test set (65 images). The different models were trained to reconstruct the images at their original resolution for 6 different epoch numbers (150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800), i.e., 42 models in total. Training took 19 days on an NVIDIA Quadro RTX 4000 graphics card. For each reconstruction, the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) was calculated to evaluate its quality. The model that was trained on the greatest variety of images was then used on each of the themes for 4800 epochs to test whether a) greater benefit was obtained by training a model on a wide array of examples or b) specializing on a single theme was a better option. The workflow that is depicted in Figure 5 summarizes the entire methodological approach.
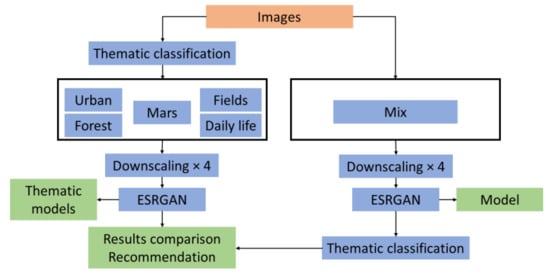
Figure 5.
Methodological flowchart.
3. Results
The results are presented in three sections. The first section provides examples of image resolution improvements. The second section presents the average PSNR values that were obtained for each of the themes. The third section provides several textural indices that highlight correlations between the texture of the images and the quality of the reconstruction.
3.1. Examples of Upscaling Results
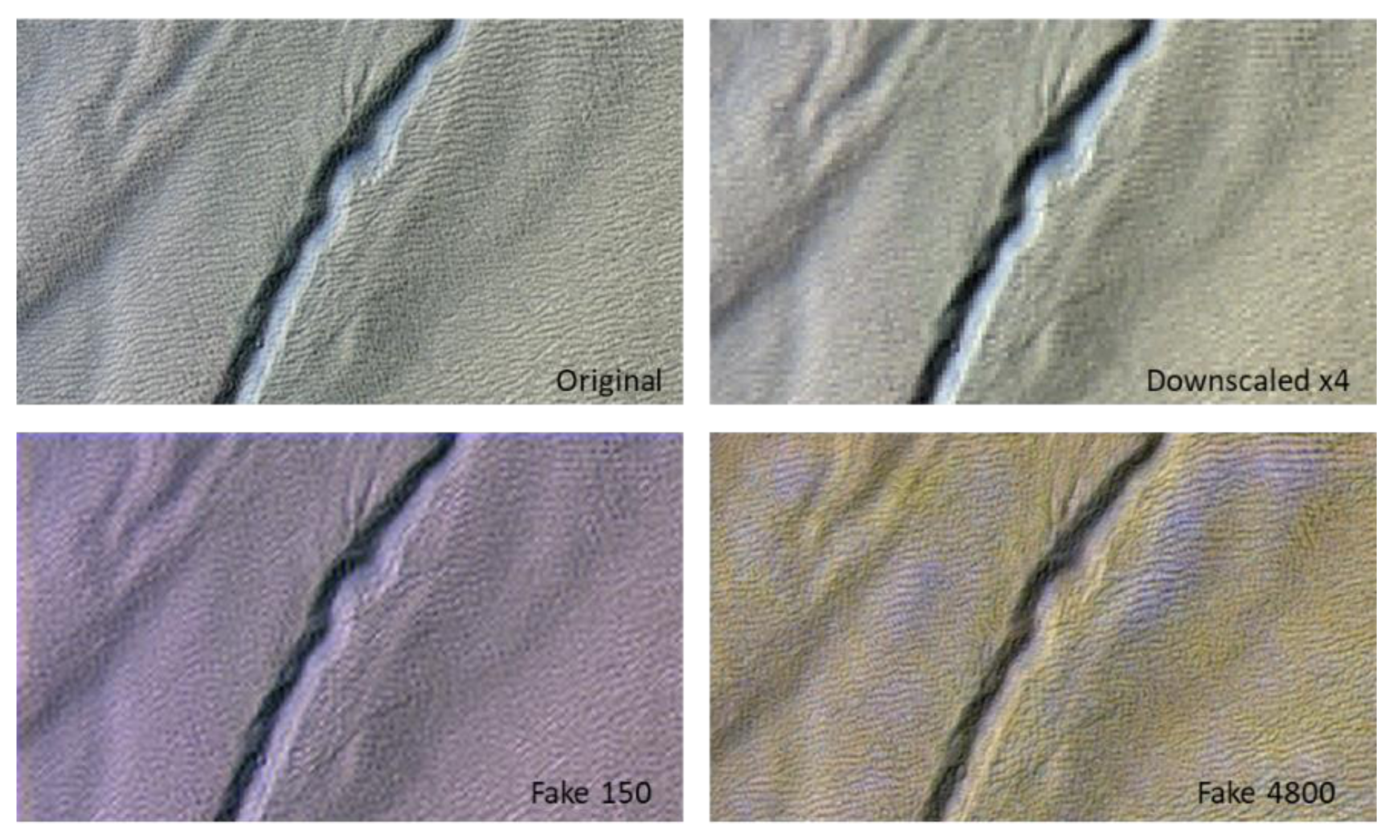
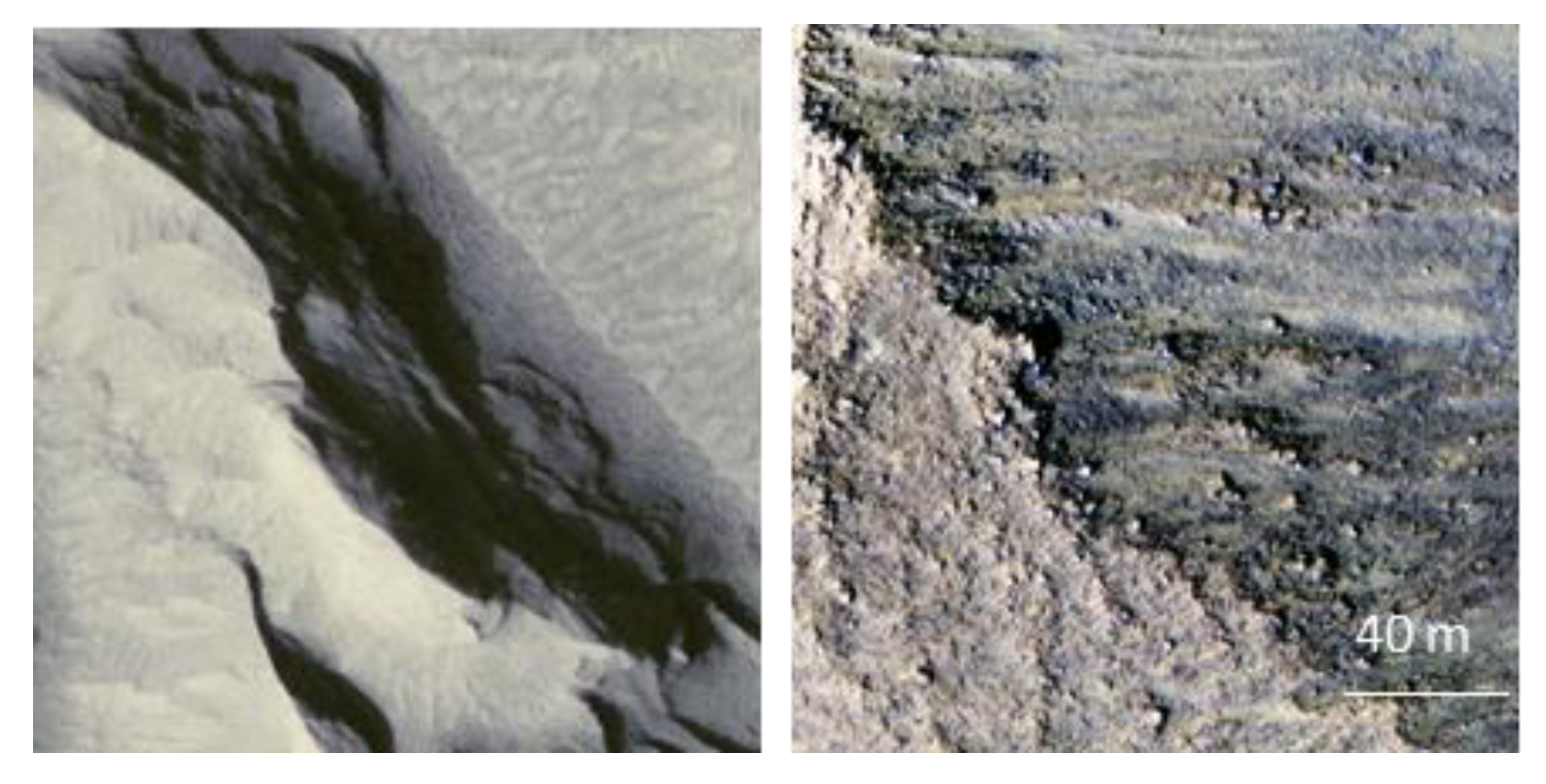
Two themes were selected to illustrate our work. All the images were visually displayed with the same “minimum–maximum” histogram stretch available in the ArcMap software. This manner of proceeding could show differences in coloration, due to differences in the pixel values recovered by the model. Figure 6 displays the results that were obtained for 150 epochs and 4800 epochs on a Martian talweg, the line of lowest elevation in a valley.

Figure 6.
Example of results that were obtained for 150 and 4800 epochs of the “Mars” theme.

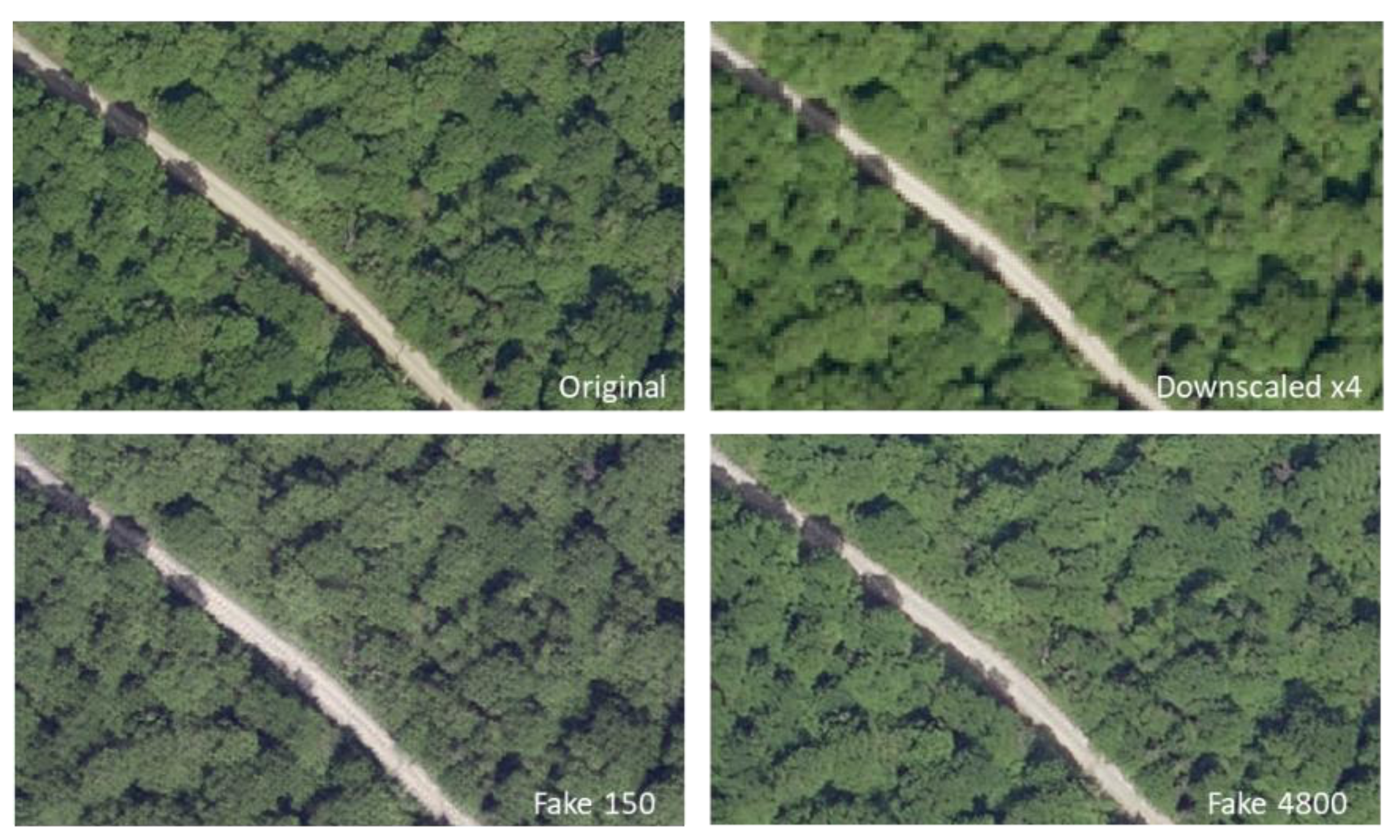
Figure 7.
Example of results that were obtained for 150 and 4800 epochs on an image belonging to the “forest” theme.
3.2. PSNR Obtained for Each Model
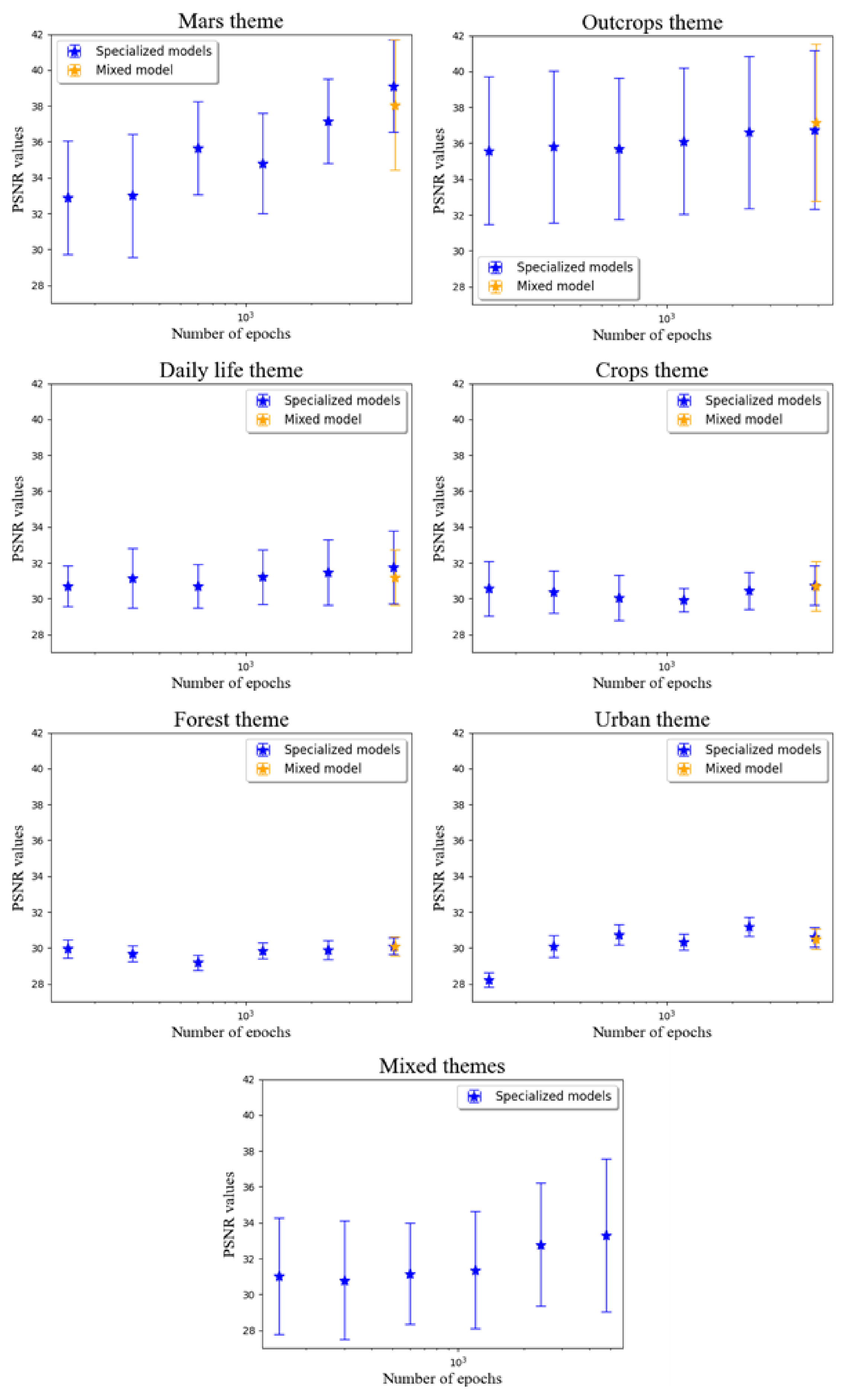
The PSNR was calculated for the 65 images of the test set, for each theme and for each number of epochs (150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800). The standard deviation was also calculated to characterize the dispersion of the quality of the results that were obtained. Each theme was also reconstructed with the model that was trained with 4800 epochs on the “mixed” theme, which is an equiproportional mixture of images from the other six themes (Figure 8). This highlights the influence of variability in the examples on the final quality of the reconstructed images.
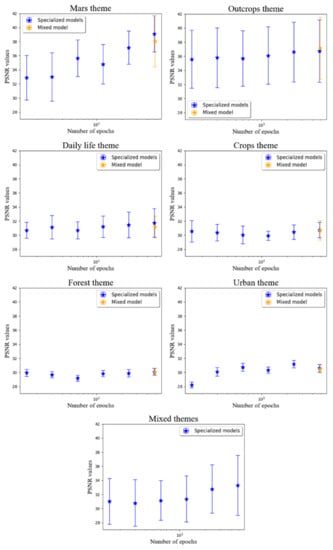
Figure 8.
Peak signal-to-noise ratios (PSNRs), with their associated standard deviations, for the different themes. For the highest number of epochs, the “mixed” model also tested whether increasing the variability in the samples was relevant.
3.3. Texture Indices
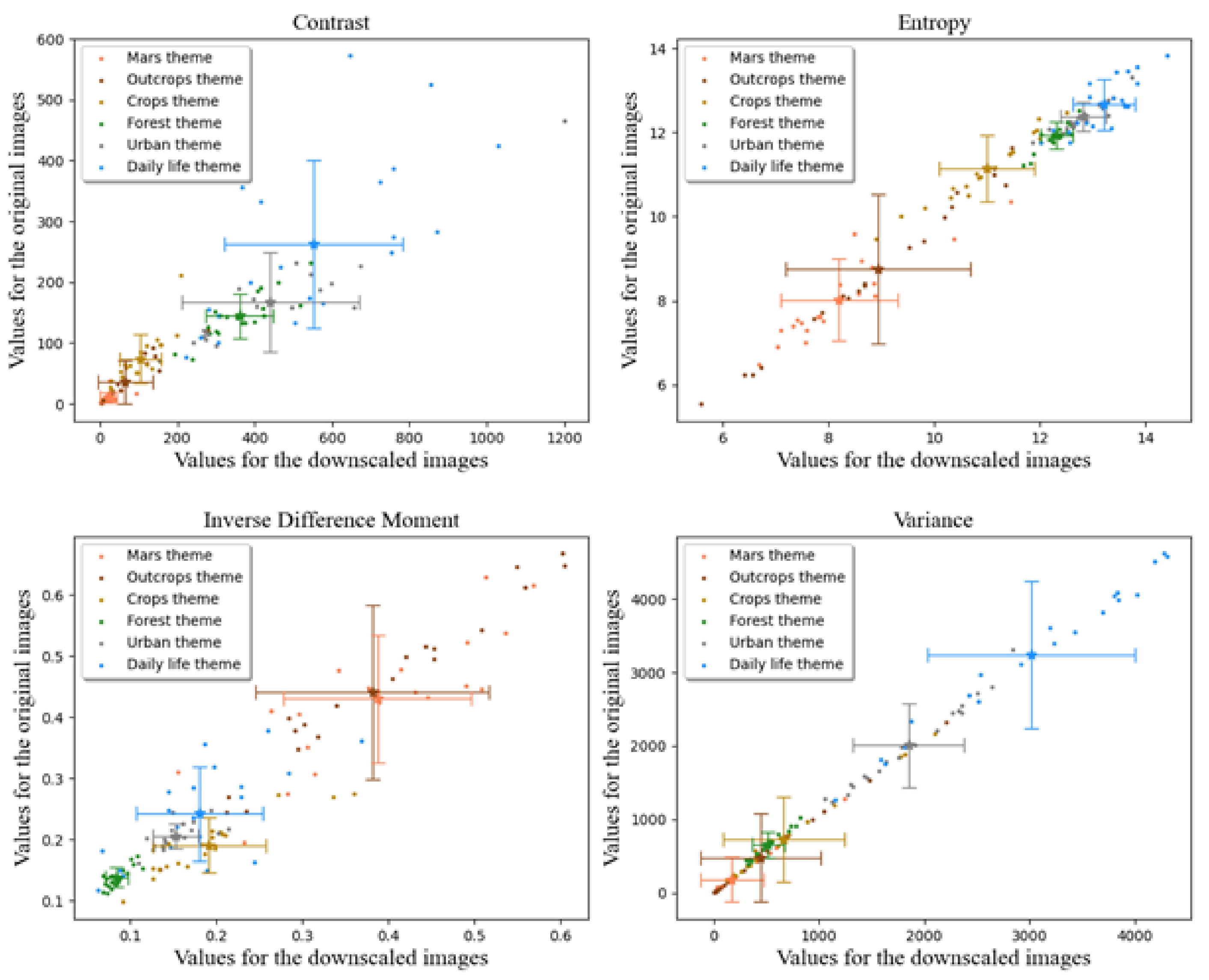
Since two themes have significantly higher PSNRs than the other five, an image-texture study was undertaken to try to understand the underlying phenomenon. Four Haralick texture indices, from the gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM), were selected to determine whether there was a correlation between the ability of the model to reconstruct the HR images and the intrinsic characteristics of the image’s textures.
Figure 9 illustrates values that had been obtained for these four indices for 20 images that were randomly selected in each theme, except for the “mixed” scenario, which would not have added any new information. In each panel, the index values of the original images (y-axis) are plotted against values that were calculated for the degraded images (x-axis).
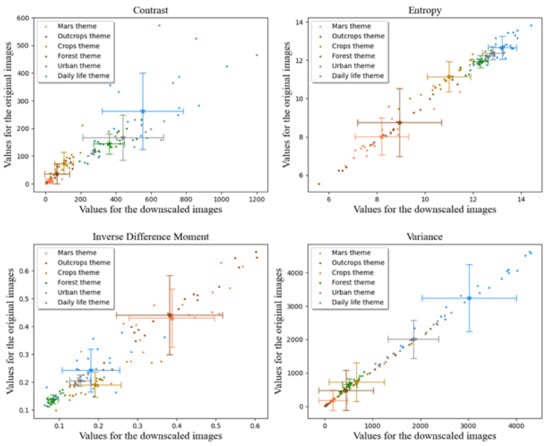
Figure 9.
Values that were obtained for four indices that were derived from the Haralick co-occurrence matrix for downscaled images and the original images.
4. Discussion
This section is organized into three parts. First, we acknowledge that the use of ESRGAN for the reconstruction of images (downscaled by a factor of four) does not correspond to a real-world application. We then discuss the PSNR values that were obtained for the different themes and epoch numbers to understand how variability among examples affects the quality of the results. Finally, we show that the image texture indices are positively correlated with the ability of ESRGAN to improve their resolution.
4.1. Image Resolution Improvement with ESRGAN
As explained in the Methods, the ESRGAN model is trained by “teaching” it to reconstruct an image, the resolution of which has been degraded. This allows the analyst to quantitatively evaluate the quality of the results by comparing the reconstructed version of the image to the original version. However, this approach does not allow the analyst to judge the real capacity of the model to create a new image that has not been degraded by bicubic convolution beforehand. Recent research has tried to overcome this difficulty [8,26,27]. However, these new architectures are beyond the scope of our study and should be the subject of further work.
4.2. Interest in the Specialization of Examples in Learning
Peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) is a measurement that is frequently used in super-resolution to express the quality of the image reconstruction. In the study that is presented here, PSNR provides a good idea of the quality of the results.
Figure 8 depicts the variability in the quality of reconstructions for high-resolution images; for example, the “Mars” theme attains a maximum PSNR of 39.10 dB for 4800 epochs, while the “forest” theme reaches 30.11 dB for an equivalent number of epochs. As a function of the number of epochs, the PSNR shows that the learning capacity of the model is not equivalent among the different themes. To illustrate the progression in learning as the number of epoch increases, we averaged the PSNRs that were obtained at 150 and 300 epochs. The same operation was performed for 2400 and 4800 epochs. This averaging mitigates the noise surrounding the measurement moving from one group of epochs to the next. The improvement between the two values is expressed as a percent-age of the first value. Table 2 summarizes these results.

Table 2.
Average PSNRs were obtained for 150 and 300 epochs, and then for 2400 and 4800 epochs. The increase in these average PSNRs is expressed as a percentage of the values in the first column. The colours highlight groups of values of the same order of magnitude.
Table 1 shows that increasing the number of epochs, even by a factor of 32 (=4800/150), offers improvements to PSNRs (<1%) for three of the seven themes that are treated here (i.e., agricultural, urban and forestry themes). In contrast, the “Mars” and “mixed” themes showed strong improvements, reaching 15.72% and 6.86%, respectively. The rock outcrop and "DIV2K" dataset themes remained below 3%.
The final PSNRs that were obtained for 2400 and 4800 epochs group the different themes in a similar manner. The “Mars”, “outcrop” and “mixed” themes had good PSNRs, while the “agriculture”, “urban” and “forest” themes did not reach a value of 31 dB. The "DIV2K" dataset has a PSNR that is intermediate between the two aforementioned groups.
Interestingly, the use of the widest variety of examples does not generally lead to better results. With the exception of the Axel Heiberg Island tests, the PSNRs that were obtained at 4800 epochs are similar to, or lower than, the values that were obtained on a dedicated training set. The exception of the rocky outcrops, however, should not be taken as significant, since the improvement is only 1.12% of the value obtained for 4800 epochs (0.41, in terms of the absolute value). This is all the more negligible, since it is the theme that offers the greatest standard deviation, with 4.38 or 11.8% of the mean value.
4.3. Texture Indices and Reconstruction of HR Images
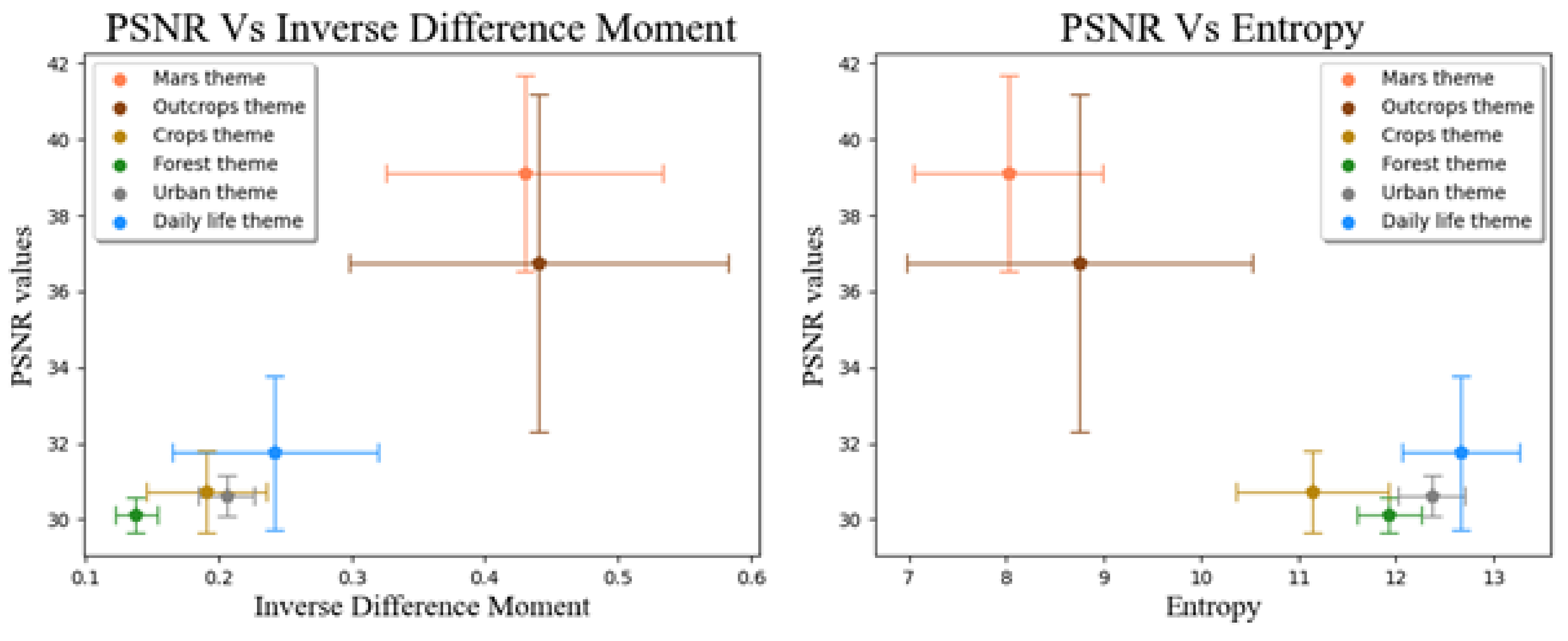
All the texture indices that are presented in Figure 9 show that HiRISE and WorldView data are comparable, as they plot in similar regions of the graphs. Indeed, these datasets have systematically obtained close values; in the cases of entropy and the inverse difference moment, they can be clearly distinguished from the other themes. Entropy and the inverse difference moment, therefore, would appear to be suitable textural indices for explaining the ability of ESRGAN to best reconstruct HR images. Figure 10 shows the PSNR values as a function of these indices.
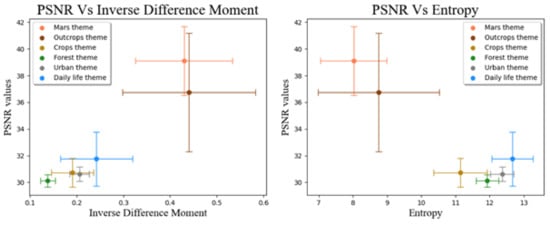
Figure 10.
Mean PSNR values (error bars are SDs) plotted as a function of mean (±SD) texture index values for the inverse difference moment and entropy.
The inverse difference moment measures the local homogeneity of the image. The greater the value, the greater the homogeneity is. Entropy measures the degree of disorder in the image. The lower the value, the greater the order in the texture is. Thus, it is not surprising that the best performances of ESRGAN are obtained for images with high homogeneity and low entropy; the reconstruction of the image at its original resolution is more predictable. The model is less perturbed by statistic variations, the randomness of which would prevent prediction. This explains why the best PSNRs were obtained for two similar themes, i.e., Martian and Arctic regolith, which are indeed much more homogeneous than other themes, despite having unfavourable signal-to-noise ratios.
5. Conclusions
For this study, ESRGAN were used to increase the spatial resolution of the following different themes: (1) “daily life”; (2) agricultural; (3) forests; (4) urban areas; (5) rocky outcrops; (6) the planet Mars; and (7) a mixture of different themes. Our aim was to verify whether it is advantageous to maximize the variability in the examples during the training phase, or if it is preferable to provide a specialized model. Moreover, training was performed for six different levels of epochs (150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, and 4800) to validate whether it is judicious to always maximize the learning time. Finally, texture indices were used to explain the variability in the quality of the results that were obtained. The conclusions of this work are as follows:
- It is more beneficial to create a specialized ESRGAN model for a specific task, rather than trying to maximize the variability in examples.
- The ability to learn depends upon the subject matter. No recommendations can be made a priori.
- ESRGAN perform better on images with a high inverse difference moment and low entropy indices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, É.C., M.L., M.G. and Y.B.; methodology, É.C.; validation, É.C., M.L., M.G., Y.B. and T.S.-P.; formal analysis, É.C.; investigation, É.C.; resources, É.C., M.L., M.G., Y.B. and T.S.-P.; data curation, É.C. and T.S.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, É.C.; writing—review and editing, É.C., M.L., M.G., Y.B. and T.S.-P.; visualization, É.C.; supervision, M.L., M.G. and Y.B.; project administration, M.L.; funding acquisition, M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was undertaken, in part, thanks to funding from the Canada Research Chair in Northern and Planetary Geological Remote Sensing (950-232175), an NSERC Discovery grant held by Myriam Lemelin and a Mitacs Accelerate grant (IT17517) held by Mickaël Germain.
Data Availability Statement
The codes used in this paper are available on Github at the following address: https://github.com/ettelephonne/ESRGAN-Haralick (accessed on 14 July 2021). Some of our data and results are available following this link: https://usherbrooke-my.sharepoint.com/:u:/g/personal/clae2101_usherbrooke_ca/ESpyvfn7rUlFilBMMTO9Q00Bhi6I-1M-yz1Z-PsSR8wi4Q?e=sOmml1 (accessed on 14 July 2021). The data provided by XEOS Imagery Inc. are not publicly available.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank XEOS Imaging Inc. for letting us use some of their data. We also thank the University of Arizona for allowing us to freely download images that were acquired by the HiRISE instrument. We finally would like to thank W.F.J. Parsons for language revisions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Transon, J.; d’Andrimont, R.; Maugnard, A.; Defourny, P. Survey of Hyperspectral Earth Observation Applications from Space in the Sentinel-2 Context. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collin, A.M.; Andel, M.; James, D.; Claudet, J. The Superspectral/Hyperspatial Worldview-3 as the Link Between Spaceborne Hyperspectral and Airborne Hyperspatial Sensors: The Case Study of the Complex Tropical Coast. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W13, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, P.C.; Koutsias, N.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Srivastava, P.K.; Ben Dor, E. Land Use/Land Cover in View of Earth Observation: Data Sources, Input Dimensions, and Classifiers—a Review of the State of the Art. Geocarto Int. 2021, 36, 957–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haut, J.M.; Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Paoletti, M.E.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A. Remote Sensing Image Superresolution Using Deep Residual Channel Attention. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9277–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Märtens, M.; Izzo, D.; Krzic, A.; Cox, D. Super-Resolution of PROBA-V Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Astrodyn 2019, 3, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deudon, M.; Kalaitzis, A.; Goytom, I.; Arefin, M.R.; Lin, Z.; Sankaran, K.; Michalski, V.; Kahou, S.E.; Cornebise, J.; Bengio, Y. HighRes-Net: Recursive Fusion for Multi-Frame Super-Resolution of Satellite Imagery. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.06460. [Google Scholar]
- Lugmayr, A.; Danelljan, M.; Timofte, R. NTIRE 2021 Learning the Super-Resolution Space Challenge. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 596–612. [Google Scholar]
- Lugmayr, A.; Danelljan, M.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. SRFlow: Learning the Super-Resolution Space with Normalizing Flow. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 715–732. [Google Scholar]
- Ayas, S. Single Image Super Resolution Using Dictionary Learning and Sparse Coding with Multi-Scale and Multi-Directional Gabor Feature Representation. Inf. Sci. 2020, 512, 1264–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Learning a Deep Convolutional Network for Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–14 September 2014; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, K.M. Accurate Image Super-Resolution Using Very Deep Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1646–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; Xue, J.-H.; Liao, Q. Deep Learning for Single Image Super-Resolution: A Brief Review. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2019, 21, 3106–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Qiao, Y.; Loy, C.C. ESRGAN: Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018 Workshops; Leal-Taixé, L., Roth, S., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11133, pp. 63–79. ISBN 978-3-030-11020-8. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, L.S.; Marcello, J.; Vilaplana, V. Super-Resolution of Sentinel-2 Imagery Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clabaut, É.; Lemelin, M.; Germain, M. Generation of Simulated “Ultra-High Resolution” HiRISE Imagery Using Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network Modeling. Online. 15 March 2021, p. 2. Available online: https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2021/pdf/1935.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- Watson, C.D.; Wang, C.; Lynar, T.; Weldemariam, K. Investigating Two Super-Resolution Methods for Downscaling Precipitation: ESRGAN and CAR. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.01233. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Ma, P. Esrgan-Based Dem Super-Resolution for Enhanced Slope Deformation Monitoring In Lantau Island Of Hong Kong. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIII-B3-2020, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, L.; Wang, J. The Effectiveness of Data Augmentation in Image Classification Using Deep Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.04621. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A Survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Raskutti, G.; Wainwright, M.J.; Yu, B. Early Stopping and Non-Parametric Regression: An Optimal Data-Dependent Stopping Rule. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 335–366. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Soltanolkotabi, M.; Oymak, S. Gradient Descent with Early Stopping Is Provably Robust to Label Noise for Overparameterized Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Palermo, Sicily, Italy, 3–5 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszar, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1609.04802. [Google Scholar]
- Agustsson, E.; Timofte, R. NTIRE 2017 Challenge on Single Image Super-Resolution: Dataset and Study. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1122–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Lugmayr, A.; Danelljan, M.; Timofte, R. Unsupervised Learning for Real-World Super-Resolution. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.09629. [Google Scholar]
- Umer, R.M.; Foresti, G.L.; Micheloni, C. Deep Generative Adversarial Residual Convolutional Networks for Real-World Super-Resolution. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.00953. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).