Effects of Variable Eruption Source Parameters on Volcanic Plume Transport: Example of the 23 November 2013 Paroxysm of Etna
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
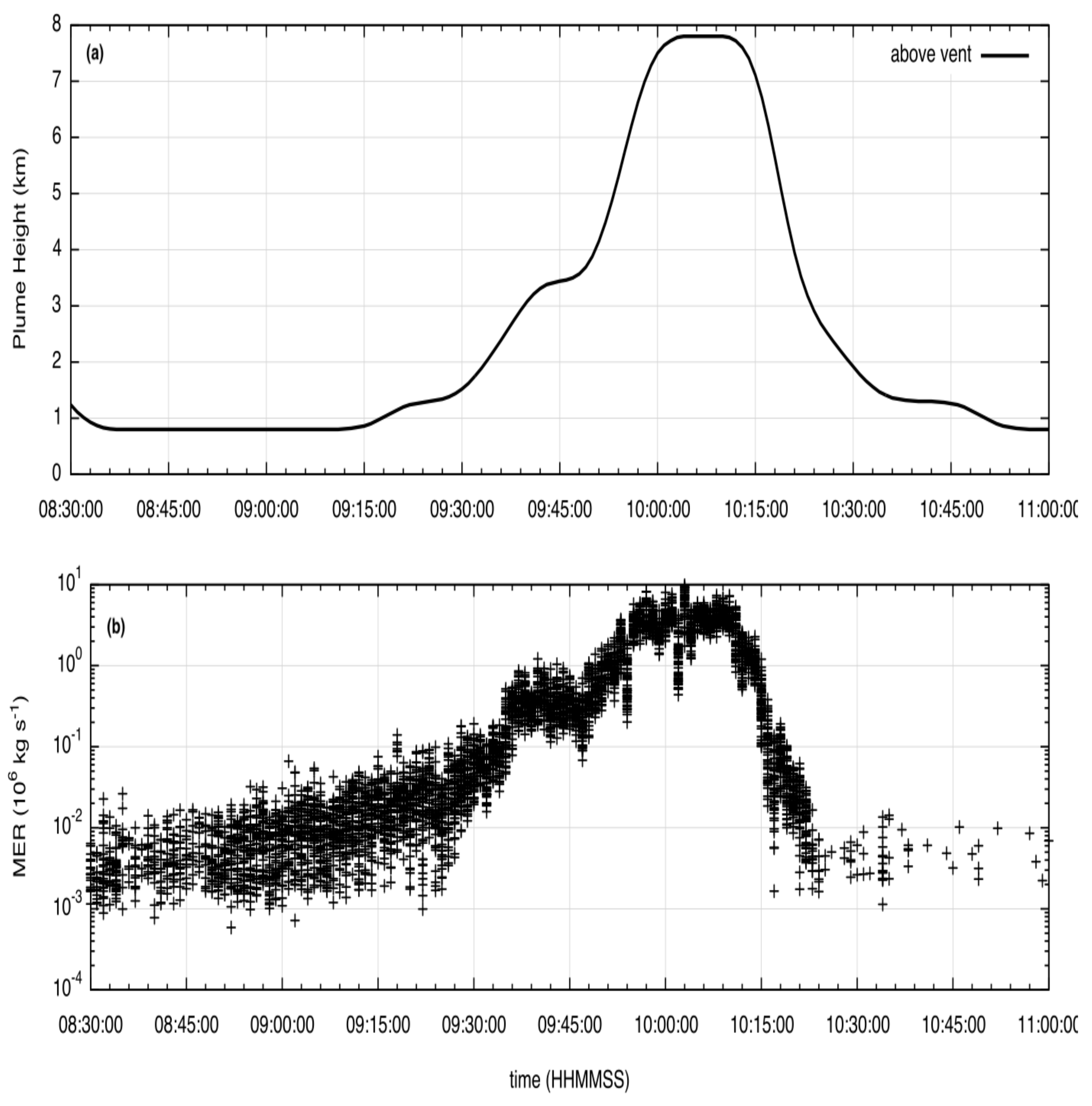
2.1. The 23 November 2013 Etna Paroxysm: Eruption Timeline and Synoptic Conditions
2.2. Remote-Sensing Data
2.2.1. VOLDORAD-2B Doppler Radar System
2.2.2. Suomi NPP (OMPS/VIIRS) Data
2.2.3. MSG SEVIRI Images Data
2.2.4. Multi-Satellite Volcanic Sulfur Dioxide Long-Term Global Database
2.3. Model Setup
2.3.1. Numerical Setup
2.3.2. Eruption Source Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
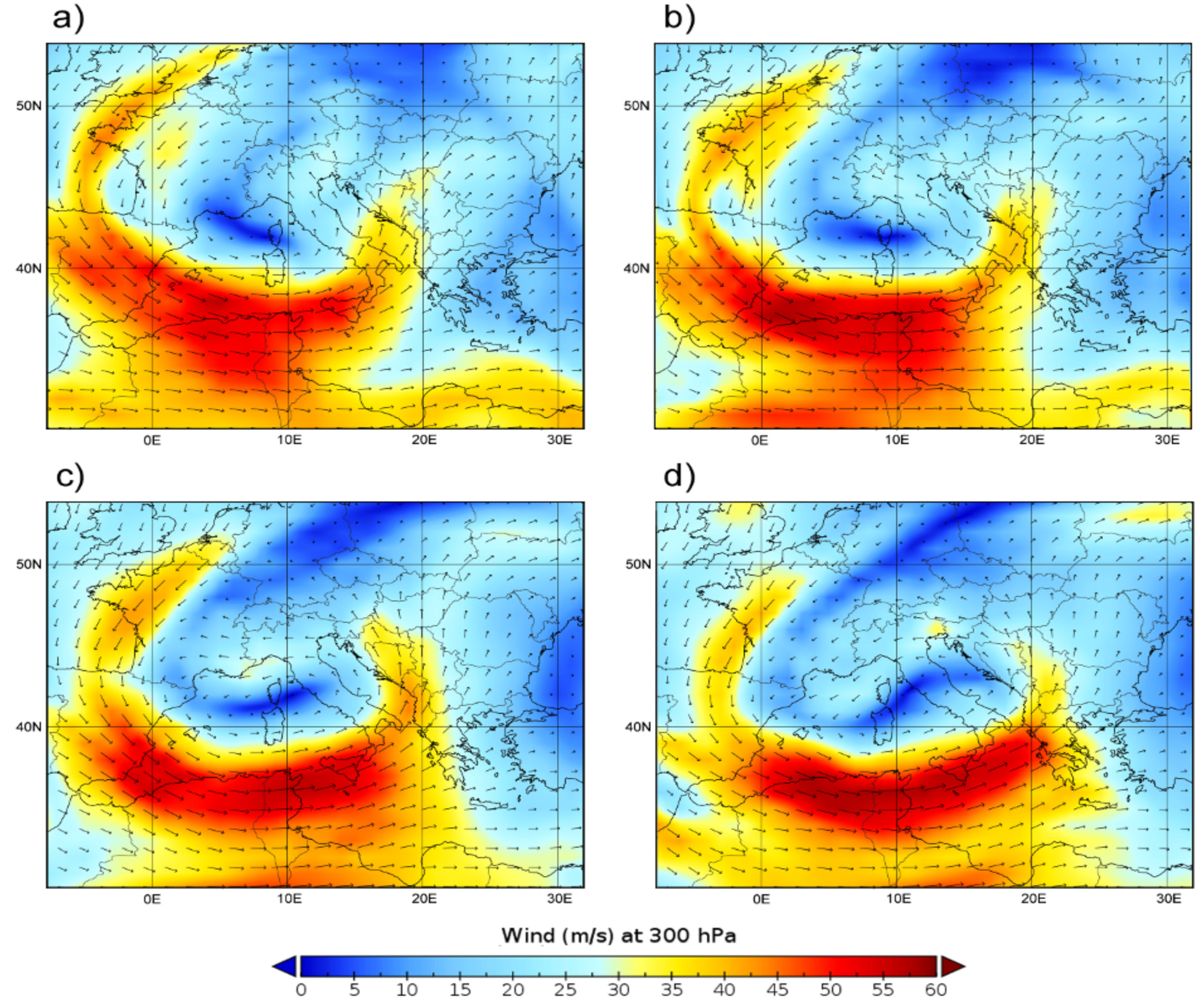
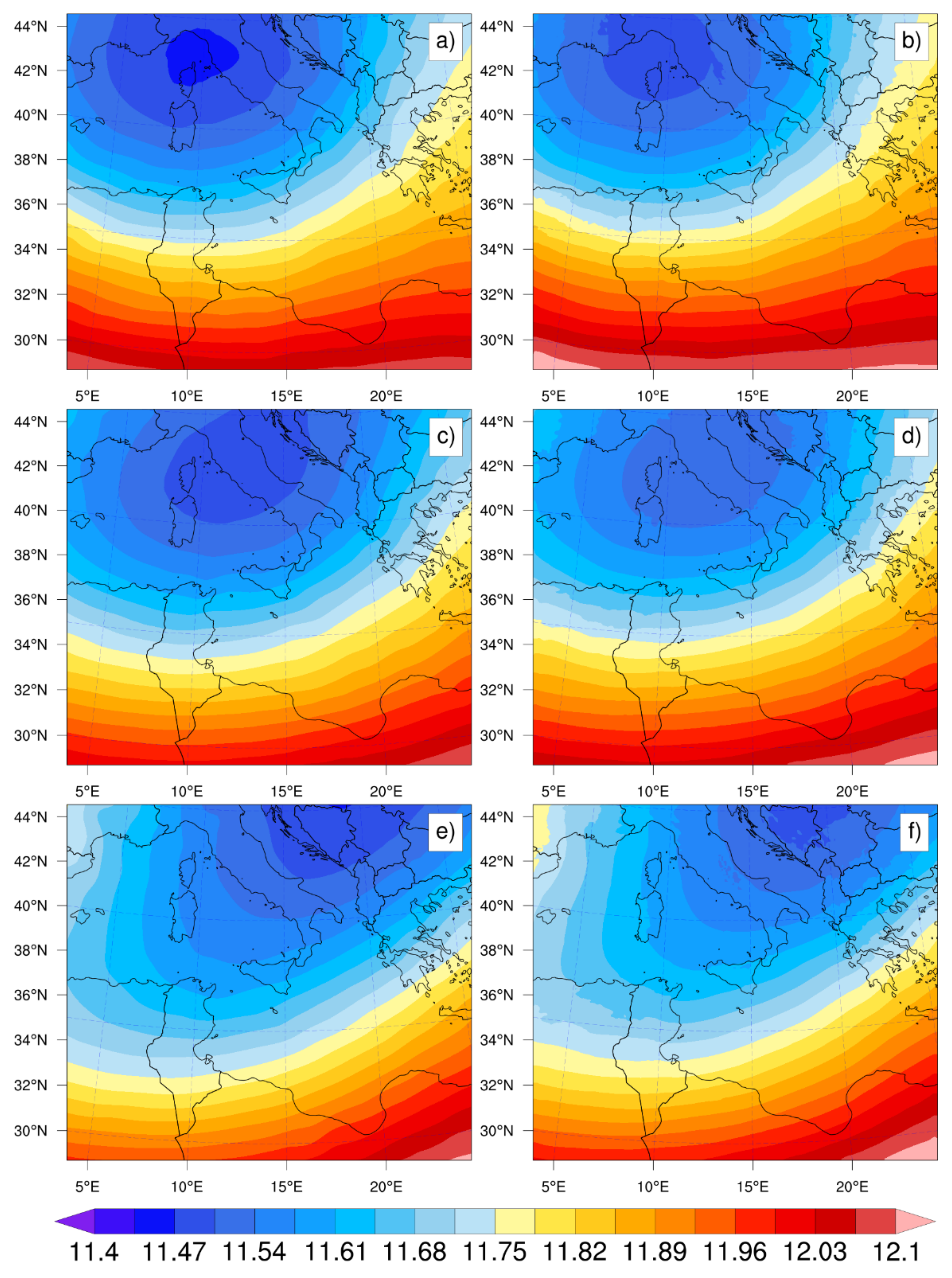
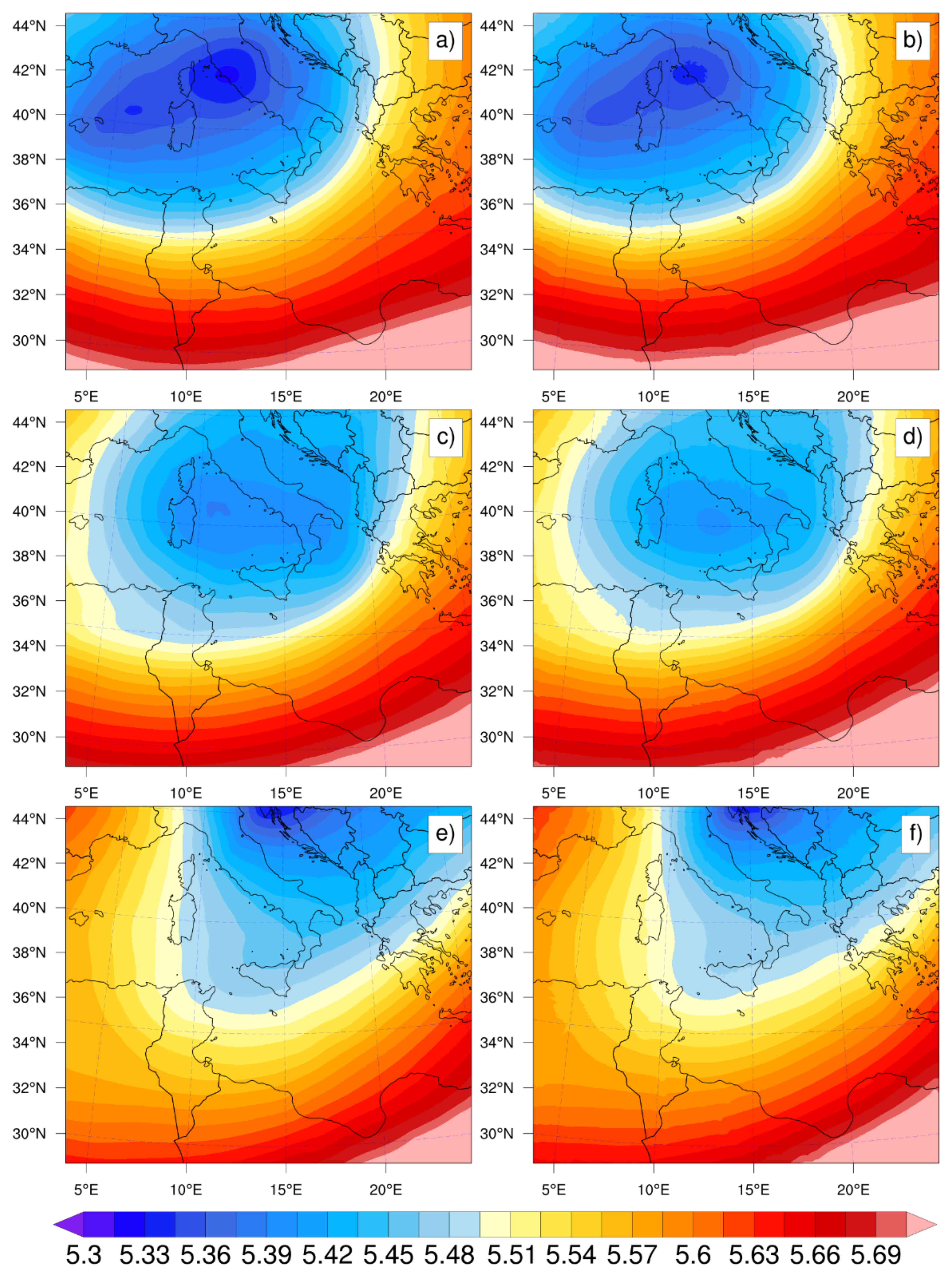
3.1. Geopotential ERA5 vs. WRF
3.2. Comparison for SO2
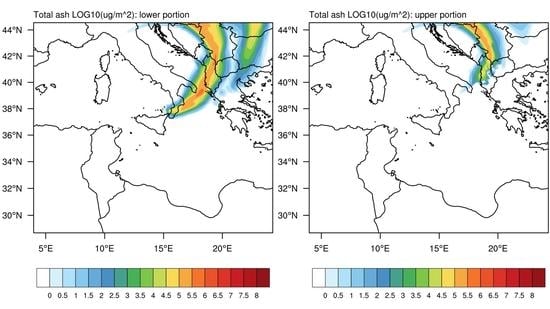
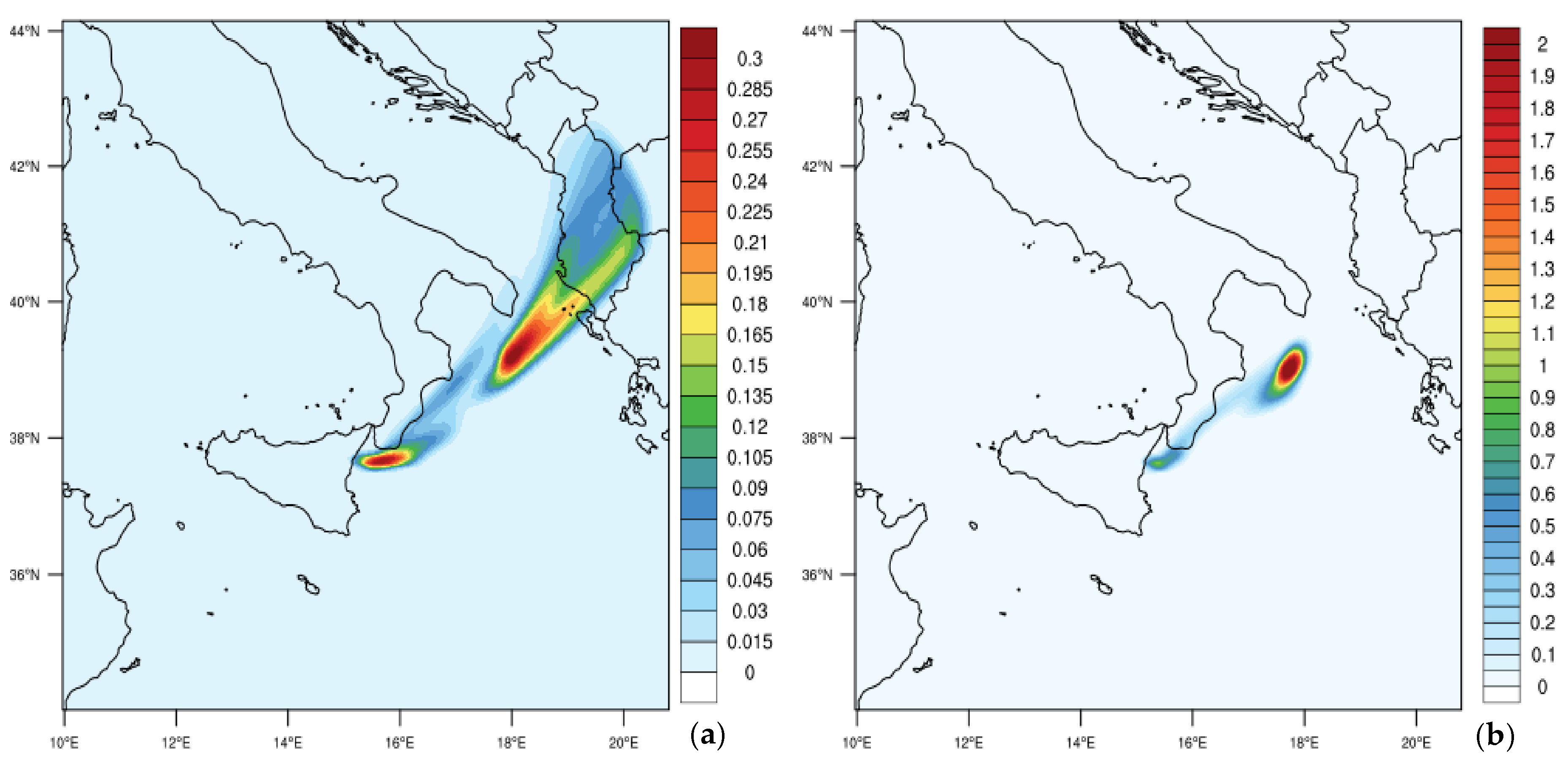
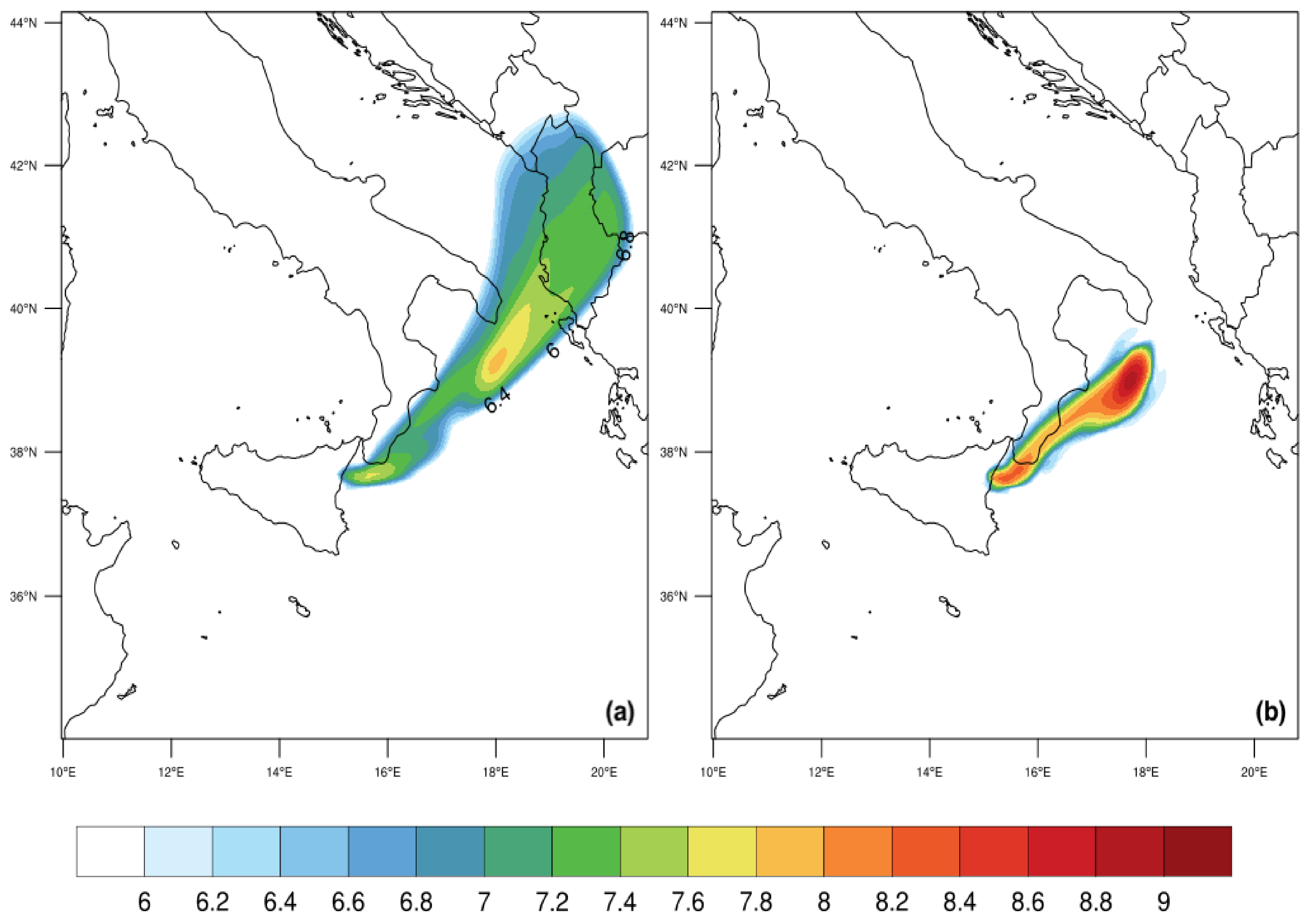
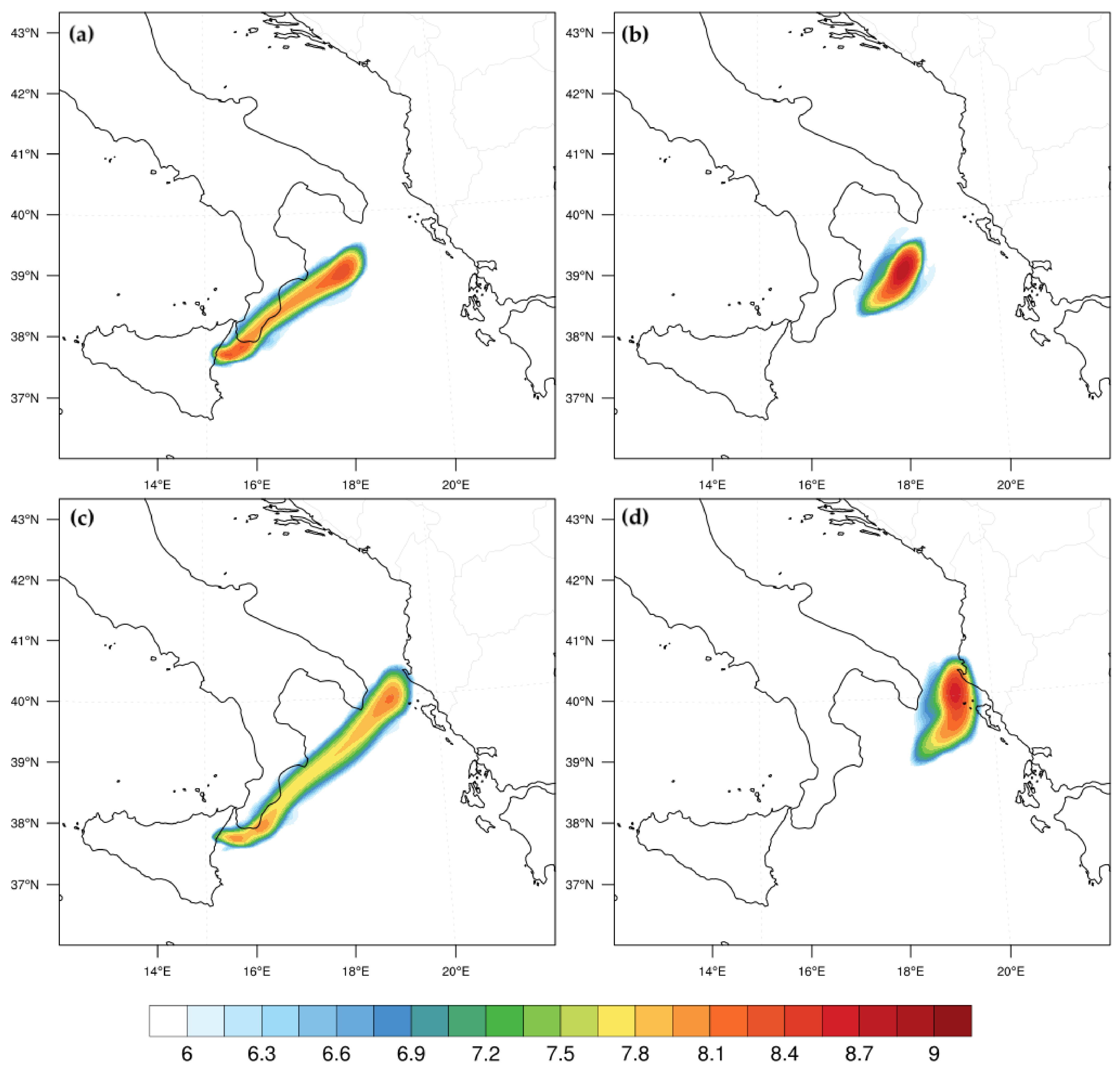
3.3. Comparison for Volcanic Ash
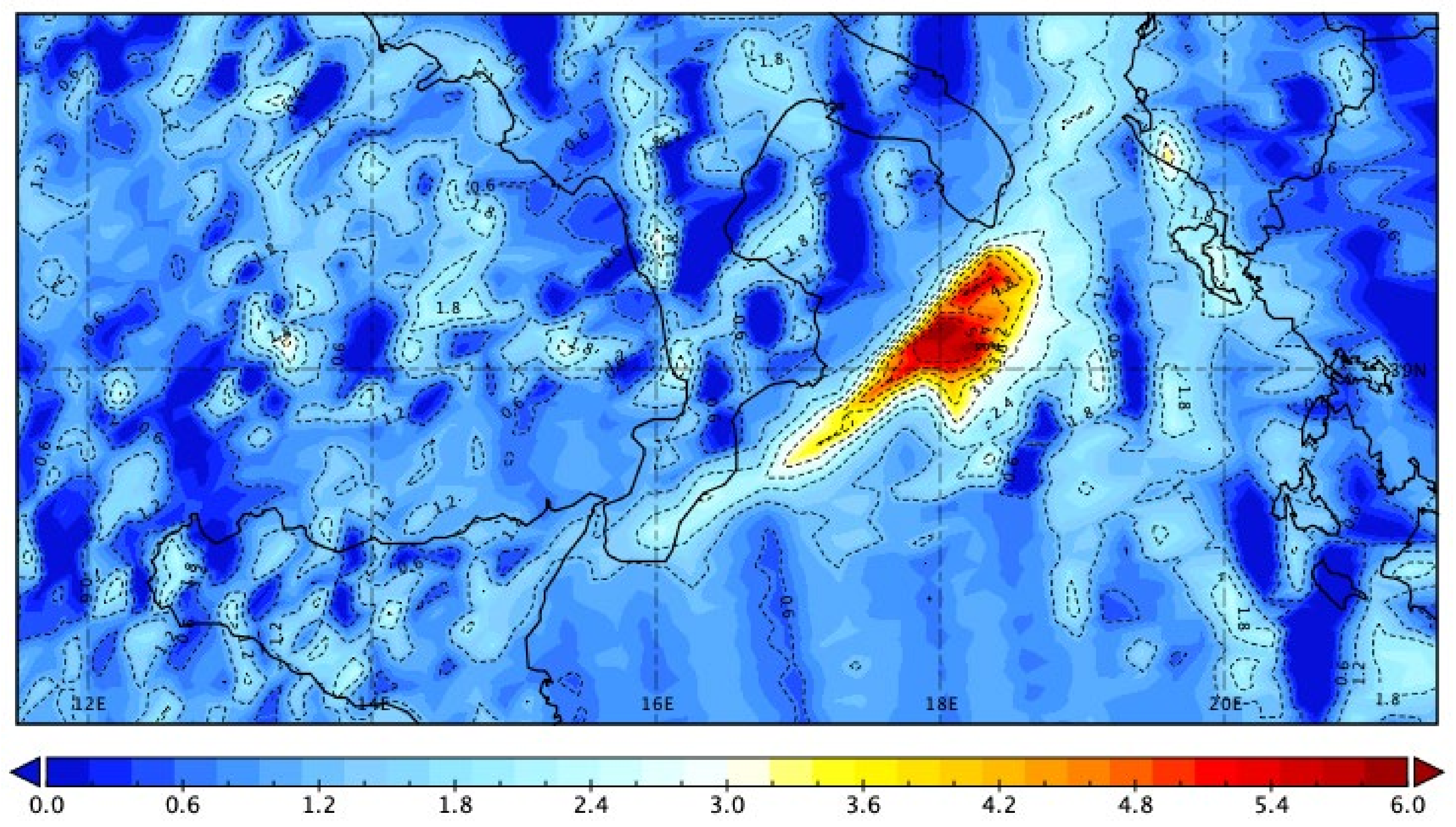
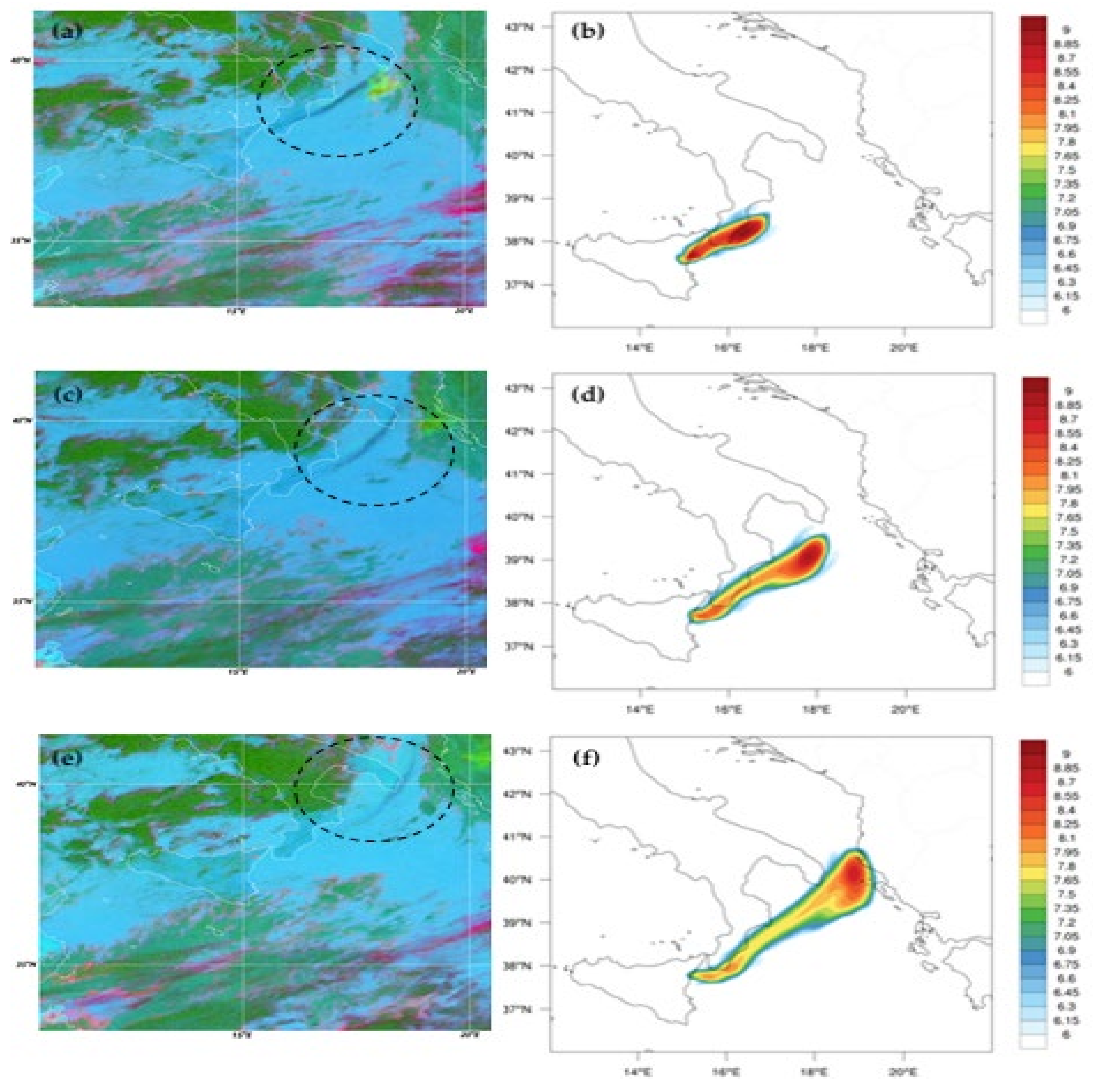
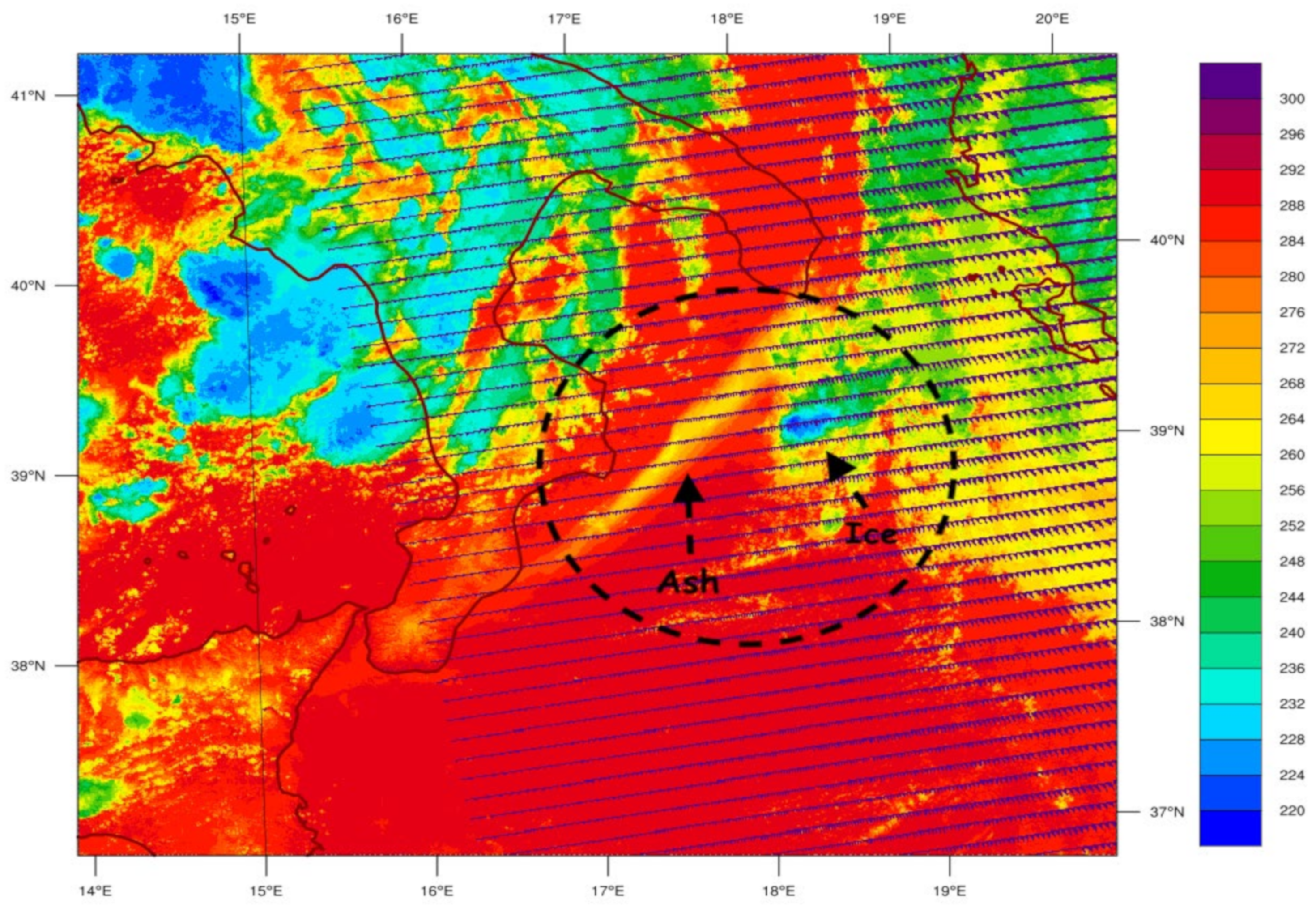
3.4. Comparison with MSG-SEVIRI Data
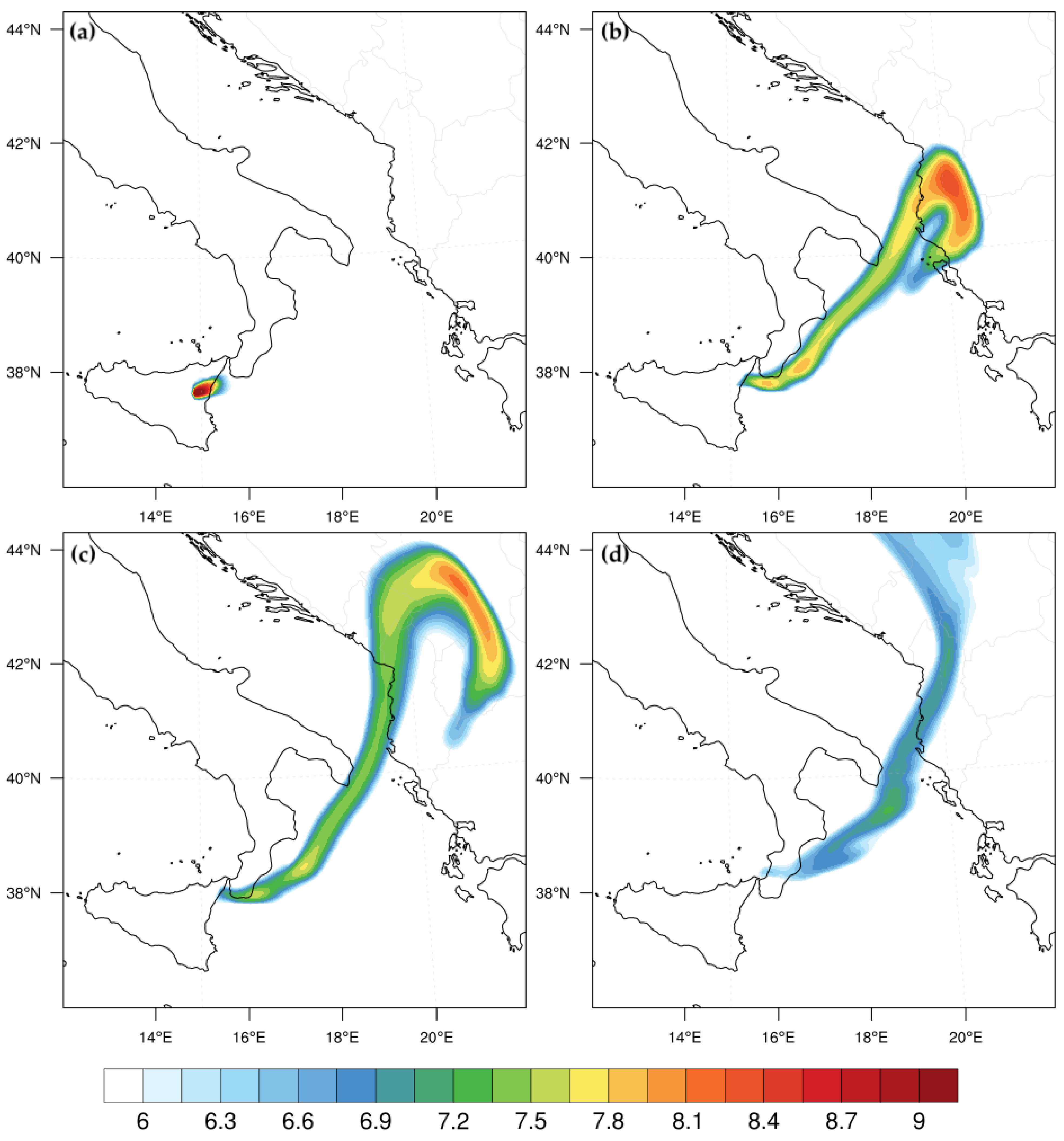
3.5. Ash Transport at Vertical Layers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B

Appendix C

References
- Robock, A. Volcanic eruptions and climate. Rev. Geophys. 2000, 38, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, A.J.; Bonadonna, C.; Horwell, C. Atmospheric and Environmental Impacts of Volcanic Particulates. Elements 2010, 6, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guffanti, M.; Casadevall, T.; Budding, K. Encounters of Air-Craft with Volcanic Ash Clouds: A Compilation of Known Incidents, 1953–2009, US Geological Survey Data Series 545, 1.0, 1. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/545 (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Poret, M.; Corradini, S.; Merucci, L.; Costa, A.; Andronico, D.; Montopoli, M.; Vulpiani, G.; Freret-Lorgeril, V. Reconstructing volcanic plume evolution integrating satellite and ground-based data: Application to the 23 November 2013 Etna eruption. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 4695–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prata, A.T.; Dacre, H.F.; Irvine, E.A.; Mathieu, E.; Shine, K.P.; Clarkson, R.J. Calculating and communicating ensemble-based volcanic ash dosage and concentration risk for aviation. Meteorol. Appl. 2018, 26, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folch, A.; Costa, A.; Macedonio, G. FPLUME-1.0: An integral volcanic plume model accounting for ash aggregation. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitturi, M.D.M.; Pardini, F. PLUME-MoM-TSM 1.0.0: A volcanic column and umbrella cloud spreading model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuefer, M.; Freitas, S.R.; Grell, G.; Webley, P.; Peckham, S.; McKeen, S.A.; Egan, S.D. Inclusion of ash and SO2 emissions from volcanic eruptions in WRF-Chem: Development and some applications. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muser, L.O.; Hoshyaripour, G.A.; Bruckert, J.; Horváth, A.; Malinina, E.; Wallis, S.; Prata, F.J.; Rozanov, A.; von Savigny, C.; Vogel, H.; et al. Particle aging and aerosol–radiation interaction affect volcanic plume dispersion: Evidence from the Raikoke 2019 eruption. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 15015–15036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carn, S. Multi-Satellite Volcanic Sulfur Dioxide L4 Long-Term Global Database V4, Greenbelt, MD, USA, Goddard Earth Science Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC). Available online: https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/MSVOLSO2L4_4/summary (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Branca, S.; Del Carlo, P. Types of eruptions of Etna volcano AD 1670–2003: Implications for short-term eruptive behaviour. Bull. Volcanol. 2005, 67, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollo, S.; Coltelli, M.; Bonadonna, C.; Del Carlo, P. Tephra hazard assessment at Mt. Etna (Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 3221–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andronico, D.; Scollo, S.; Caruso, S.; Cristaldi, A. The 2002–03 Etna explosive activity: Tephra dispersal and features of the deposits. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113, B04209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donnadieu, F.; Freville, P.; Hervier, C.; Coltelli, M.; Scollo, S.; Prestifilippo, M.; Valade, S.; Rivet, S.; Cacault, P. Near-source Doppler radar monitoring of tephra plumes at Etna. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2016, 312, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freret-Lorgeril, V.; Donnadieu, F.; Scollo, S.; Provost, A.; Fréville, P.; Guéhenneux, Y.; Hervier, C.; Prestifilippo, M.; Coltelli, M. Mass Eruption Rates of Tephra Plumes during the 2011–2015 Lava Fountain Paroxysms at Mt. Etna From Doppler Radar Retrievals. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, F.S.; Mereu, L.; Scollo, S.; Donnadieu, F.; Bonadonna, C. Tephra Mass Eruption Rate from X-Band and L-Band Microwave Radars during the 2013 Etna Explosive Lava Fountain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3314–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.A.; Dean, K.G. Forecasting exposure to volcanic ash based on ash dispersion modeling. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2008, 170, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, A.; Costa, A.; Macedonio, G. FALL3D: A computational model for transport and deposition of volcanic ash. Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.; Klemp, J.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.; Barker, D.; Wang, W. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 2; No. NCAR/TN-468+STR; NCAR Scientific Divisions, University Corporation of Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3; NCAR Scientific Divisions: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008; NCAR Technical note-475 + STR.
- Collini, E.; Osores, M.S.; Folch, A.; Viramonte, J.G.; Villarosa, G.; Salmuni, G. Volcanic ash forecast during the June 2011 Cordón Caulle eruption. Nat. Hazards 2012, 66, 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modeling system of trajectories, dispersion, and deposition. Aust. Meteor. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.R.; Thomson, D.J.; Hort, M.; Devenish, B. The U.K. Met Office’s next-generation atmospheric dispersion model, NAME III’. In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application XVII., Proceedings of the 27 NATO/CCMS International Technical Meeting on Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application, Banff, Canada, 24–29 October 2004; Borrego, C., Norman, A.-L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searcy, C.; Dean, K.G.; Stringer, B. PUFF: A volcanic ash tracking and prediction model. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1998, 80, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plu, M.; Bigeard, G.; Sič, B.; Emili, E.; Bugliaro, L.; El Amraoui, L.; Guth, J.; Josse, B.; Mona, L.; Piontek, D. Modelling the volcanic ash plume from Eyjafjallajökull eruption (May 2010) over Europe: Evaluation of the benefit of source term improvements and of the assimilation of aerosol measurements. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devenish, B.J.; Francis, P.; Johnson, B.T.; Sparks, R.S.J.; Thomson, D.J. Sensitivity analysis of dispersion modeling of volcanic ash from Eyjafjallajökull in May 2010. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, H.N.; Thomson, D.J.; Johnson, B.T.; Heard, I.P.C.; Turnbull, K.; Marenco, F.; Kristiansen, N.I.; Dorsey, J.; Minikin, A.; Weinzierl, B.; et al. Operational prediction of ash concentrations in the distal volcanic cloud from the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folch, A.; Costa, A.; Basart, S. Validation of the FALL3D ash dispersion model using observations of the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull volcanic ash clouds. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 48, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailler, S.; Menut, L.; Khvorostyanov, D.; Valari, M.; Couvidat, F.; Siour, G.; Turquety, S.; Briant, R.; Tuccella, P.; Bessagnet, B.; et al. CHIMERE-2017: From urban to hemispheric chemistry-transport modeling. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 2397–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lachatre, M.; Mailler, S.; Menut, L.; Turquety, S.; Sellitto, P.; Guermazi, H.; Salerno, G.; Caltabiano, T.; Carboni, E. New strategies for vertical transport in chemistry transport models: Application to the case of the Mount Etna eruption on 18 March 2012 with CHIMERE v2017r4. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 5707–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R.; McKeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, U.; Brega, E.; Caccamo, M.; Castorina, G.; Morichetti, M.; Munaò, G.; Passerini, G.; Magazù, S. Analysis of the ETNA 2015 Eruption Using WRF–Chem Model and Satellite Observations. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.D.; Stuefer, M.; Webley, P.W.; Lopez, T.; Cahill, C.F.; Hirtl, M. Modeling volcanic ash aggregation processes and related impacts on the April–May 2010 eruptions of Eyjafjallajökull volcano with WRF-Chem. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 2721–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maters, E.C.; Dingwell, D.B.; Cimarelli, C.; Müller, D.; Whale, T.F.; Murray, B.J. The importance of crystalline phases in ice nucleation by volcanic ash. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 5451–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corradini, S.; Montopoli, M.; Guerrieri, L.; Ricci, M.; Scollo, S.; Merucci, L.; Marzano, F.S.; Pugnaghi, S.; Prestifilippo, M.; Ventress, L.J.; et al. A Multi-Sensor Approach for Volcanic Ash Cloud Retrieval and Eruption Characterization: The 23 November 2013 Etna Lava Fountain. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonaccorso, A.; Calvari, S.; Linde, A.; Sacks, S. Eruptive processes leading to the most explosive lava fountain at Etna volcano: The 23 November 2013 episode. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4912–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnadieu, F.; Freville, P.; Rivet, S.; Hervier, C.; Cacault, P. The Volcano Doppler Radar Data Base of Etna (VOLDORAD-2B); Université Clermont Auvergne CNRS: Clermont-Ferrand, France, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freret-Lorgeril, V.; Bonadonna, C.; Corradini, S.; Donnadieu, F.; Guerrieri, L.; Lacanna, G.; Marzano, F.; Mereu, L.; Merucci, L.; Ripepe, M.; et al. Examples of Multi-Sensor Determination of Eruptive Source Parameters of Explosive Events at Mount Etna. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degruyter, W.; Bonadonna, C. Improving on mass flow rate estimates of volcanic eruptions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, B.; Jia, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhou, T. An overview of passive and active dust detection methods using satellite measurements. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.J. Infrared radiative transfer calculations for volcanic ash clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1989, 16, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouhier, M.; Guéhenneux, Y.; Labazuy, P.; Cacault, P.; Decriem, J.; Rivet, S. HOTVOLC: A web-based monitoring system for volcanic hot spots. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2016, 426, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Niino, H. Development of an Improved Turbulence Closure Model for the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 895–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamin, S.G.; Grell, G.A.; Brown, J.M.; Smirnova, T.G.; Bleck, R. Mesoscale weather prediction with the RUC hybrid isentropic terrain- following coordinate model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 473–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmosphere: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison, H.; Thompson, G.; Tatarskii, V. Impact of Cloud Microphysics on the Development of Trailing Stratiform Precipitation in a Simulated Squall Line: Comparison of One- and Two-Moment Schemes. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2009, 137, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizza, U.; Mancinelli, E.; Canepa, E.; Piazzola, J.; Missamou, T.; Yohia, C.; Morichetti, M.; Virgili, S.; Passerini, G.; Miglietta, M.M. WRF Sensitivity Analysis in Wind and Temperature Fields Simulation for the Northern Sahara and the Mediterranean Basin. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montopoli, M. Velocity profiles inside volcanic clouds from three-dimensional scanning microwave dual-polarization Doppler radars. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 7881–7900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scollo, S.; Prestifilippo, M.; Pecora, E.; Corradini, S.; Merucci, L.; Spata, G.; Coltelli, M. Eruption column height estimation of the 2011–2013 Etna lava fountains. Ann. Geophys. 2014, 57, S0214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freret-Lorgeril, V. The Source Term of Tephra Plumes: Radar Applications at Etna and Stromboli Volcanoes (Italy). Ph.D. Thesis, Université Clermont Auvergne, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, R.S.J.; Bursik, M.I.; Carey, S.N.; Gilbert, J.S.; Glaze, L.S.; Sigurdsson, H.; Woods, A.W. Volcanic Plumes; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 1997; p. 574. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Horányi, A.; Sabater, J.M.; Nicolas, J.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; Soci, C.; et al. Global reanalysis: Goodbye ERA-Interim, hello ERA5. ECMWF Newsl. 2019, 159, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ukhov, A.; Ahmadov, R.; Grell, G.; Stenchikov, G. Improving dust simulations in WRF-Chem v4.1.3 coupled with the GOCART aerosol module. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Eidhammer, T. A Study of Aerosol Impacts on Clouds and Precipitation Development in a Large Winter Cyclone. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 3636–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Fung, J.C.H. Investigating the role of dust in ice nucleation within clouds and further effects on the regional weather system over East Asia—Part 1: Model development and validation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 8707–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. Available online: https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/bams/96/12/bams-d-14-00110.1.xml (accessed on 16 June 2021). [CrossRef]



| Var | Diameter [m] | E1 [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vash_1 | (1–2) 10−3 | −1:0 | 16.7 |
| vash_2 | (0.5–1) 10−3 | 0:1 | 8.35 |
| vash_3 | (0.25–0.5) 10−3 | 1:2 | 10.4 |
| vash_4 | (125–250) 10−6 | 2:3 | 12.5 |
| vash_5 | (62.5–125) 10−6 | 3:4 | 6.25 |
| vash_6 | (31.25–62.5 10−6 | 4:5 | 12.5 |
| vash_7 | (15.625–31.25) 10−6 | 5:6 | 14.6 |
| vash_8 | (7.8125–15.625) 10−6 | 6:7 | 8.3 |
| vash_9 | (3.9065–7.8125) 10−6 | 7:8 | 6.2 |
| vash_10 | <3.9065 10−6 | >8 | 4.2 |
| Case | Paroxysm Duration HHMM | wt% Distribution Ash | Column Height a.s.l. [km] | MER Ash [kg s−1] | MER SO2 [g h−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| run1 | 0700–1030 | E1 | 11 | 2.77 × 105 | 1.67 × 109 |
| run2 | 0700–1030 | E1 | ECV | V2B | V2B |
| run3 | 0700–1030 | E1 | 4-7-11-7 | 2.77 × 105 | V2B |
| run4 | 0955–1015 | E1 | 11 | 0.65 × 107 | V2B |
| run5 | 0700–1030 | E1 | 7 | 4.0 × 105 | V2B |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizza, U.; Donnadieu, F.; Magazu, S.; Passerini, G.; Castorina, G.; Semprebello, A.; Morichetti, M.; Virgili, S.; Mancinelli, E. Effects of Variable Eruption Source Parameters on Volcanic Plume Transport: Example of the 23 November 2013 Paroxysm of Etna. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204037
Rizza U, Donnadieu F, Magazu S, Passerini G, Castorina G, Semprebello A, Morichetti M, Virgili S, Mancinelli E. Effects of Variable Eruption Source Parameters on Volcanic Plume Transport: Example of the 23 November 2013 Paroxysm of Etna. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(20):4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204037
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizza, Umberto, Franck Donnadieu, Salvatore Magazu, Giorgio Passerini, Giuseppe Castorina, Agostino Semprebello, Mauro Morichetti, Simone Virgili, and Enrico Mancinelli. 2021. "Effects of Variable Eruption Source Parameters on Volcanic Plume Transport: Example of the 23 November 2013 Paroxysm of Etna" Remote Sensing 13, no. 20: 4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204037
APA StyleRizza, U., Donnadieu, F., Magazu, S., Passerini, G., Castorina, G., Semprebello, A., Morichetti, M., Virgili, S., & Mancinelli, E. (2021). Effects of Variable Eruption Source Parameters on Volcanic Plume Transport: Example of the 23 November 2013 Paroxysm of Etna. Remote Sensing, 13(20), 4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204037