Abstract
The use of topographic airborne LiDAR data has become an essential part of archaeological prospection, particularly as a tool for detecting archaeological features in the landscape. However, its use for landscape reconstruction and understanding archaeological sites in their environmental context is still underutilised. To this end, we took an innovative approach to using LiDAR data as a means of discovering, documenting, and interpreting agricultural land use systems by looking for significant environmental variation within a microregion. We combined information from LiDAR-derived DEM derivatives with archaeological, geological, and soil data. We introduced two methodological innovations. The first is the modified wetness index, which combines the LiDAR-derived precision with the accuracy of the effective field capacity of the soil to obtain a very realistic predictor of soil quality. The second is the modified landform classification, a combination of topographic position index and visual geomorphological analysis, which amalgamates two of the most important predictive variables for the distribution of plant species. Our approach is demonstrated by a case study focusing on early medieval settlements in the context of agricultural land use in the subalpine microregion of Bled (Slovenia). It revealed that early medieval settlers were drawn to light soils with high water retention capacity. Such soils were particularly suitable for the cultivation of barley, which is known to have been one of the most important staple crops of the period, especially in colder climate such as subalpine. Soils with lower water retention capacity were not colonized until the eleventh century, which may signify the transition at that time to a higher level of agricultural organisation and wheat as a staple cereal food.
1. Introduction
Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) or airborne Light Detection and Ranging data (hereafter LiDAR) are used in archaeology for visualization and detailed morphological analysis of the archaeological landscape. First and foremost, LiDAR has become an essential part of archaeological prospection as a tool for detecting archaeological features [,,,,,,,,,]. The free availability of LiDAR data in Slovenia since 2015 [], for example, has led to the discovery of numerous archaeological sites and features—such as prehistoric settlements, prehistoric and Roman field systems, Roman military camps, and Late Antique settlements [,,,,,,]—particularly in densely forested areas. Moreover, LiDAR data allows each site or feature to be observed at different scales [,,]. From the large “human” scale that provides overwhelming layout detail at the intra-site level to the small landscape scale where patterns of site distribution can be readily observed, it has broadened our understanding of archaeological and historical landscapes. LiDAR data, however, are only suitable for the detection of those archaeological features that are recognizable in the terrain morphology (either embedded, partially embedded, or standing features or standing objects []). Thus, the impact of LiDAR data on archaeology as a discipline was uneven. One area of low impact was the detection of early medieval settlements in Eastern Alpine region (hereafter EMS). EMS are preserved almost exclusively as scarce remains of wooden structures and square pit huts [,,,], while the remains of larger buildings, stone architecture, and sizeable earthworks are almost non-existent []. Therefore, EMS are not discernible in the terrain morphology and therefore cannot be directly detected with LiDAR data or any other type of archaeological prospection.
However, in addition to the archaeological prospection, LiDAR data can be utilized for landscape reconstruction [,,] in a process referred to as deep interpretation [,]. A host of research opportunities and approaches arise through such applications, for instance the reconstruction of historical geographical elements, paleogeographical analysis [,], and archaeology of agricultural land use. We are taking this approach and our particular interest lies in understanding archaeological sites in their land use context. This is possible as LiDAR provides landscape configuration in the form of a high-resolution digital elevation model (hereafter DEM). DEM allows us to provide measurable parameters and qualitative and quantitative characterizations of landscape configuration and thus objectively define physiographic regions. When these are correlated with other environmental factors such as soil type, hydrology, and geological data, site locations can be precisely characterized.
The focus of this paper is on agricultural land use and its direct or indirect influence on settlement location choice. Landscape configuration undoubtedly had an impact on the potential for agricultural land use in the archaeological past, and LiDAR data have recently been applied to this end, e.g., [,,]. In addition, under conditions of agricultural subsistence economy, agricultural land use in turn has an important influence on settlement location choice, e.g., [,,,]. This is not to say that there are not many other factors that can significantly influence settlement patterns in different areas and at different times (for example, cultural [], historical [], social [,,,], and climate [,]). However, like most of the studies cited, we focus on one that we believe to be the most important in this particular context.
We present an innovative approach to using LiDAR data as a means of discovering, documenting, and interpreting agricultural land use systems. We search for variables—significant environmental differences within the landscape—that have influenced land use. In doing so, we combine information from LiDAR DEM with archaeological, geological, and soil data. The aim of this paper is to develop and demonstrate a methodological approach to qualitatively and quantitatively describe and explain the settlement location choice model in the context of agricultural land use.
Our approach is showcased in a case study focused on EMS and the early medieval land use system in the Bled (Slovenia) microregion (Figure 1). The Bled microregion is uniquely suited due to the simultaneous availability of high quality archaeological and historical records for the early medieval period as well as LiDAR data, which are rare in the region.
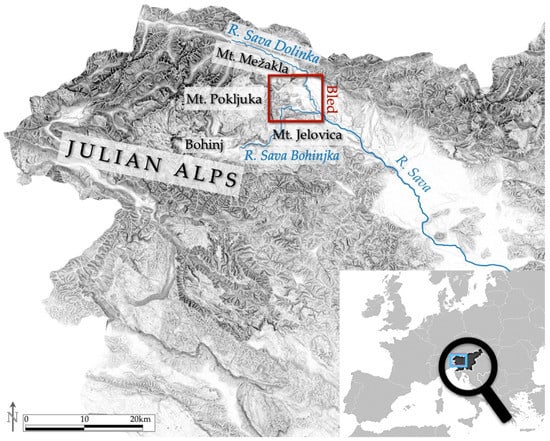
Figure 1.
Location of the study area with the most relevant topographic features mentioned in the text (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 14.1949; 46.1168).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Archaeological Context
To introduce the case study, a brief overview of the relevant archaeological context is required. The settlement of the early medieval Slavs is a controversial topic in European archaeology [,,,], for there are no first-hand, written sources before the end of the ninth century and archaeological evidence is sparse compared to many other early medieval peoples. As a result, there is a propensity for sweeping explanations on, for example, how could large parts of eastern Europe have been Slavicized in a relatively short period of time between the sixth and seventh centuries AD []. A small but by no means insignificant piece of this puzzle is the settlement of the Slavs in the Eastern Alpine region. Given the technical nature of this paper, we use the term “Slavs” hereafter as a terminus technicus describing a particular archaeological record and material culture typical of the Eastern Alpine region from the 6th century AD to the eleventh century AD, for example, typical pottery, pit huts, burial rites; we understand these as regional features and consider ethnic identities and habitus as complex research questions to be addressed in specialized studies [,].
Previous attempts to understand the landscape context of EMS in the Eastern Alpine region often reduced observations to height above sea level and soil type. One early analysis found that Slavs in Slovenia settled mainly in upland areas with dry soils and tended to avoid plains, narrow valleys, and wet soils []. In a preceding analysis of the Bled microregion, the reconstruction of the field system located the most suitable areas for early medieval agriculture and concluded that local topography had a direct influence on the EMS location choice model [,,]. A similar attempt to define the landscape type and soil type in which EMS occurs was made in Lower Austria. Under the term mesoregion, 36 EMS were analysed within their respective 5 km radii. Soil type and geomorphological context, which provided a description of the predominant landform types, were considered. The results showed that the EMS occur in two landscape types: (flood) plains and mountainous regions. Approximately half of EMS were located on alluvial river terraces, at least some of them within coeval floodplains on naturally elevated land. The other half of EMS was located in upland and hilly areas above 300 m a.s.l. In these areas, loess and brown earth soils were clearly preferred [].
In the archaeologically relevant neighbourhood, river terraces and hills were also recognized as the predominant locations for EMS in Bohemia []. Similar conclusions regarding landscape preference, habitat description, and soil conditions were also drawn for Great Moravia in Czech Republic [] and Slovakia [] and for several microregions in Slovenia (Krško polje [], Prekmurje and Podravje [,], and Bled [,]). A somewhat different situation was detected for the sixth-century Slavs in the Northern Danube region (present-day Slovakia, Moravia, Czech Republic, and Upper Austria), who settled the lowlands in strategic locations along roads and at river fords, while mountainous terrain was avoided [] (Figure 2).
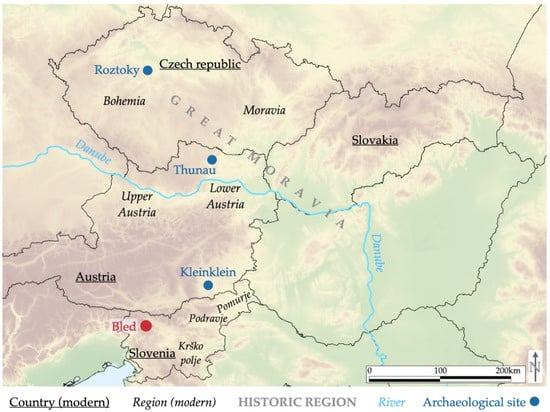
Figure 2.
Regional map of locations and sites mentioned in the comparative studies (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 17.8173; 47.8235).
As a note, it should be mentioned that EMS within floodplains would have severely restricted access to agricultural land. This suggests that the exploitation of riparian vegetation and other resources must have played an important and hitherto neglected role in early medieval economic life. The riparian zone was able to provide for fish, freshwater crabs, various edible plants; wild vines and similar could be gathered without having to invest in cultivation. Reeds for covering houses, but possibly also for making vessels, and willow twigs for building wattle walls in house construction could be gathered in the floodplain forests, as well as wood for timber construction [,].
Our particular interest in this paper is EMS in the Bled microregion in the context of agricultural land use. The Bled microregion (80 km2) is located in the northwest of Slovenia, in the subalpine area of Julian Alps. The microregion is bounded by the confluence of the rivers Sava Bohinjka and Sava Dolinka in the east, and by the high mountain plateaus of Pokljuka and Mežakla in the west and north (Figure 3). The area is notable for its intensive fluvio-glacial geomorphology. The archaeological significance of this microregion lies in the fact that it encompasses the entire territory of župa, which was the smallest administrative entity of the early medieval Slavs [,]. Bled has long been the focus of both archaeological and historical research, and from the point of view of early medieval archaeology, it is the best researched microregion in Slovenia. Since the 1880s, and most intensively in the 1970s and 1980s, 17 noteworthy early medieval archaeological sites have been documented by archaeological excavations [,,,,,,,,,] (Table 1; Figure 1).
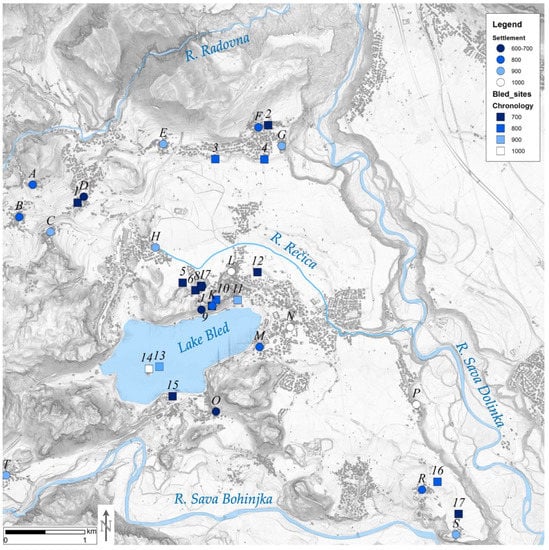
Figure 3.
Bled microregion (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 14.1139; 46.3752), early medieval sites (numbers refer to Table 1) and settlements (letters refer to Table 2) in the Bled microregion. The colours refer to the century of foundation (labelled as year AD in the legend).

Table 1.
Early medieval sites in the Bled microregion; No. refers to Figure 1 (source: []).
Only one settlement in Bled area has been fully excavated (Pristava at Bled) and further two (Grad, Zasip) have been confirmed by excavations, but the chronology of several others could be inferred from their respective cemeteries. Remaining settlements were dated by terminus ante quem, provided in written sources or inferred indirectly from the landscape analysis and retrograde analysis of the historical cadastre (Table 2; Figure 3). However, no detailed and systematic archaeobotanical research has been carried out in the Bled microregion to date, and there are no published palynological results dealing with the early medieval vegetation in this area yet. Similarly, extensive underwater archaeological investigations of the Lake Bled yielded minor early medieval finds [] but as yet no significant findings of relevance to this study.

Table 2.
Early medieval settlements in Bled microregion; ID refers to Figure 1 (source []).
Three decades have passed since the last comprehensive analysis of the Bled microregion, in which A. Pleterski combined archaeology, written sources, and retrograde analysis of historical cadastres [,]. He reconstructed the arable areas, which occurred in small patches scattered in the valley plains (Appendix A: Figure A1). His key conclusions were that most settlements were continuously inhabited from the early medieval period to the present time; the economic model was dominated by agriculture, with little developed crafts []. Therefore, each settlement was located adjacent to soils suitable for agriculture. Moreover, most, if not each, settlements had a cemetery nearby. The validity of the original study was subsequently confirmed with archaeological excavations on three separate locations in Žale near Zasip [], Zasip, and Došca []. He was therefore able to infer where and when the settlement took place with great level of confidence, but not why and how.
These conclusions confirmed the theory of central land cores put forward for the medieval settlement of present-day Slovenia by Ilešič in the 1950s []. He noted that each medieval settlement initially had relatively little cultivated land on particularly favourable soils in the immediate vicinity of the settlement. As the settlement grew, the existing fields were divided up and new ones further from the village were asserted. Thus, the central land core became increasingly fragmented and the total area of cultivated land increased.
The theory of central land cores has good parallels with the site-catchment analysis proposed in the 1970s []. The similarities are not coincidental, as both are based on mid 20th century human geography. The site catchment is defined as an area within which the exploitation of natural resources is economically justified. The area was defined as 5 km or an hour’s walk for sedentary farming communities and the share of arable land was estimated to be between 5% and 10%. Flannery [], Rossman [], and Zarky [] empirically tested the model on Mesoamerican villages and found that the site catchment area was at least half and the share of arable land up to ten times smaller than in the original theoretical estimates. They concluded that the distance between villages was determined by social rather than ecological factors. Similar conclusion was reached for the early medieval Bled microregion, where the site catchment for the field was estimated to be 7 min walking distance []. Modern studies of the site catchment reinforce the distinction between the exploitation area and its social status, i.e., direct exploitation is not the same as the area that is claimed to define the political status of a settlement []. The key advantage of modern studies is that the catchment area is no longer forcefully simplified into circles but is much more realistically estimated in terms of time of walking or energy expended. This is achieved in GIS by computing the time distance based on DEM and realistic formulas obtained through experiments [,,,,].
2.2. LiDAR Data
The airborne LiDAR data used in this study was acquired in 2014. These data have a nominal density of 5 points/m2 and an estimated horizontal and vertical root mean square error of 0.09 m and are distributed via the eVode webservice [,] (for correlation between point cloud density and DEM quality see, e.g., []). The data were processed using an algorithm developed specifically for archaeology []. The relevant metadata and paradata have been presented elsewhere []. The main product used in this study is 0.5 m DEM with archaeology-specific off-terrain features included [].
As already mentioned, in archaeology, processed LiDAR data are mostly used for interpretative mapping of archaeological features, i.e., feature detection. In this case study, however, we have used the data for what is termed integrated multi-scale ‘deep’ interpretation, which aims to deepen the understanding of archaeological features in their landscape context []. In this case, the digital terrain model is treated not just as a set of elevation values, but as an important habitat descriptor. The specific tools to achieve this are described below in more detail.
2.3. Geological Data
The Bled area can be divided broadly in four geomorphological areas: (i) the high alpine karst plateaus, (ii) the intramountain area, (iii) the till plain, and (iv) the marshy area. (i) The high alpine karst plateaus of Pokljuka (852–1630 m), Mežakla (776–1593 m), and Jelovica (900–1411 m) were formed by glaciers in the Pleistocene (Appendix A: Figure A2). The area is composed of Middle Triassic dolomites and limestones. (ii) Sedimentary deposits on the Quaternary slope cover the intramountain area between Poljšica and Podhom, which slopes gently towards the alpine Radovna River valley and the glacial Lake Bled (lithostratigraphic unit al.-alluvium). (iii) The Bohinj and Radovna glaciers had a particularly strong influence on the geomorphology and postglacial fluvial processes, with strong glacial activity leading to the deposition of a till plain with up to several 10 m of Quaternary sediments and with a small marsh basin in the northeast part of Lake Bled (lithostratigraphic unit, pr.—till; b—marsh deposits). (iv) During glaciation, the marshy area between Lake Bled and River Rečica was formed.
A characteristic feature of the Bled landform is the frontal moraine on the northeast edge of the lake and the dome-shaped monadnocks rising above the general level of glacial deposits [,,]. Bled Castle is located on one such cliff-like dome-shaped monadnocks []. The Pleistocene fluvioglacial sediments formed the terraces of Sava Dolinka and Sava Bohinjka Rivers (lithostratigraphic unit al.—alluvium and pr.—till). An important aftereffect of the underlying geological conditions in the study area is the lack of perennial water and permanent water streams (see Figure 1 and Figure 3 for the locations mentioned in the text).
Of particular relevance to our case study is the overall glacial nature of the area, which is clear evidence that the geomorphology has not changed significantly since the Pleistocene, let alone since the beginning of the early medieval period.
2.4. Soil Conditions
The underlying lithology (bedrock) described above is one of the diagnostic criteria for the variety of soil types in the study area, which are briefly summarized here. Rendzinas formed on limestone, dolomite, moraines, and talus deposits. Dystric brown soils formed on carbonate and siliciclastic rocks. All are mostly suitable for forest and alpine pastures. Eutric brown soils formed on moraine and talus deposits and on fluvioglacial sandy gravel sediments. Small patches of rendzinas formed on limestone mostly support forests and meadows. Brown soils on fluvioglacial sandy gravel sediments are among the most fertile soils in subalpine areas. They occur in the plains, are well drained, sufficiently deep, and have favourable physical and chemical properties for intensive cropland. However, the brown soils formed on moraine and talus deposits are of limited use as arable land for modern agriculture, as the soil skeleton consists of moraine loam and stones. A notable depression with hydromorphic soils (hypogley) formed on a Pleistocene clay and loam northeast of Lake Bled; it is mostly suitable for grassland. The areas adjacent to the riverbeds of Sava Bohinjka and Sava Dolinka are dominated by undeveloped soils on alluvial river deposits that have been frequently flooded in the past. Suitable land uses here are riparian forests and grassland [] (Appendix A: Figure A3).
2.5. Effective Field Capacity of Soil
For agricultural use, arguably the most important soil property is its ability to retain water. This quality is defined as the soil’s effective field capacity (hereafter FC). FC depends on soil texture, depth, and organic matter content and is measured as the water content of a soil after gravity has drained as much water from the soil as possible []. The higher the FC value of a soil, the more water it is able to retain and the less susceptible it is to drought.
For mapping purposes, soil types are defined as discrete pedocartographic units, and FC is one of the criteria used. In the Soil map of Slovenia [], which holds the best available data for the Bled microregion, FC is part of the description of pedocartographic units and is presented in 5 classes (Table 3; Appendix A: Figure A4). From the perspective of archaeology, the problem with soil maps is that they are produced on a small or medium scale. This is also the case with the soil map of Slovenia, which is designed for use at 1:25,000 scale, which is somewhat coarse for our purposes. To improve this, further analyses can be undertaken, such as the wetness index described below.

Table 3.
Classes of soil’s effective field capacity (FC) used in the soil map of Slovenia.
2.6. Modified Landform Classification Method
The landform or morphological classification of DEM, also termed geomorphology or morphometry, provides an objective and quantitative description of landform shapes, defined as specific geomorphic features, for example, plains, mountain ranges, hills, and valleys. The available methods have mostly been developed for geomorphological analysis of the terrain and are based on advanced spatial statistics [,,]. We applied an automated landform classification method, topographic position index-based landform classification (hereafter TPI), implemented as a module in SAGA GIS (Hamburg, Germany) [,,]. TPI provides a simple and powerful means of classifying the landscape into morphological classes. It is calculated as the difference between the elevation of a cell and the average elevation in large- and small-scale neighbourhoods. Positive values indicate that the cell is higher than its neighbours, while negative values indicate that the cell is lower (Figure 4) [,,].
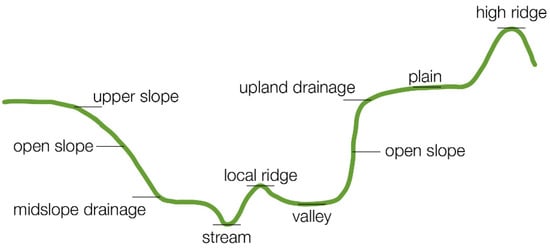
Figure 4.
A schematic depiction of the morphological classes detected by the SAGA GIS module Topographic position index-based landform classification.
TPI has proven to be one of the most important predictive variables for vegetation species distribution. For example, in a study of plant distribution in the Spring Mountains of Nevada (USA), TPI was second only to elevation as the most important predictive variable []. In other words, in a typical landscape, TPI classes are informative not only of landform classes but indirectly also of plant communities. This demonstrates the importance of TPI for all landscape-aware human decisions, including the choice of EMS location.
In our application to archaeology, the results of TPI have presented significant challenges to analysis (Figure 5). The areas of moderately steep slopes and till plain were clearly defined, but the mountainous plateau and river terraces were not. Therefore, an additional visual geomorphological analysis was carried out. For this purpose, hypsometric tinting of DEM, transparently (60%) superimposed on a hillshade visualisation of the same DEM, was used to improve terrain classification and visualise relief differences more clearly. The most important criterion was the height above sea level. Applying this additional analytical step, we were able to precisely describe the mountainous plateau and the Holocene river terraces (Appendix A: Figure A5).
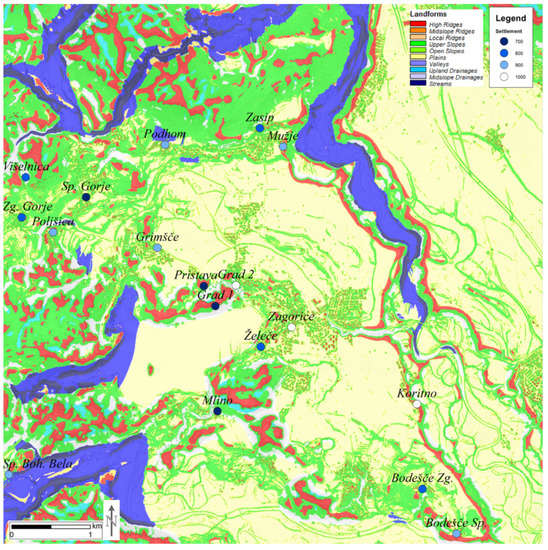
Figure 5.
Bled microregion (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 14.1139; 46.3752), topographic position index-based landform classification.
Our modified landform classification is thus a combination of TPI and visual geomorphological analysis that incorporates height above sea level. It allowed us to define quantified catchment descriptors of landscape morphology, which we termed Zones. Defined in this way, Zones represent two of the most important predictive variables of plant species distribution: TPI and height above sea level [].
2.7. Modified Wetness Index Method
Topographic modelling of soil moisture conditions can help alleviate the scale limitations of standard soil maps. Such modelling based on DEM is possible as water tends to flow and accumulate in response to gradients in gravitational potential energy []. The algorithms, commonly referred to as topographic wetness index, describe how susceptible specific areas in a study region are to become saturated [,]. They calculate for each cell of the grid the relationship between the specific upstream catchment area and the slope [,]. The first defines the potential of water intake (rainfall) and the latter the ability to discharge the water downslope (runoff; Formula: TWI = ln [Catchment Area/Slope]). One can think of these as a rainfall-runoff model (Figure 6a–c).
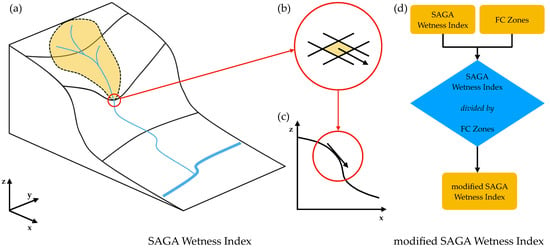
Figure 6.
Topographic wetness index: (a) flow accumulation area; (b) flow direction, and the corresponding flow width for a DEM cell; (c) tangent of slope angle; (d) custom algorithm for modified SAGA wetness index ((a–c) adopted from [], Figure 1, published under CC-BY 4.0 licence).
Methods differ primarily in the way the upslope contributing area is calculated []. We used the SAGA wetness index (hereafter SWI) because it does not think of the flow as a very thin film and hence it predicts more realistic (higher) potential soil moisture for valley floors []. The field tests demonstrated that SWI in combination with LiDAR derived DEM is the best existing predictor of soil wetness [,,].
Another advantage of the SWI is that it can be refined by setting the suction index []. Unfortunately, the suction index function is poorly documented in the SAGA GIS software used, and the best available description is in the source code []. In addition, the suction cannot be adjusted locally. Therefore, we developed custom modified SWI (hereafter mSWI) by using the FC value extracted from the Soil map of Slovenia [] as weighting index (Figure 6d). mSWI was calculated with map algebra using SWI and FC classes as an input.
In this way, we obtained mSWI (Appendix A: Figure A6) which combines the accuracy of the FC with the precision of the fine relief resolution of the SWI and is a very realistic predictor of soil quality.
2.8. General Methodological Remarks
There are two general methodological remarks to be made. First, our method of combining soil data with TPI and mSWI analysis is based on the premise that soil conditions in the Early Medieval period were similar to those of the modern period. This is justified in this particular case study by the fact that hydrological and surface conditions were subject to similar geomorphological processes throughout the Holocene and that the relationship between land surface properties (e.g., soil, vegetation, and lithology) was not very different in the early medieval period. In this particular case study, the stability is the result of the underlying lithology described above. Consequently, this method is only suitable for areas where either soil conditions have not changed significantly between the archaeological period under investigation and the time of soil data collection, or relevant soil data have been obtained through palaeoenvironmental analysis. In our case study, such example are urban areas where soil properties changed significantly (Figure 1: Zagorice, Želeče, Sp. Bohinjska Bela, Pristava), but those are relatively small and did not have significant influence on the results.
Second, the selection of methods used in this case study is indicative but by no means exhaustive. For example, slope and aspect can also be used as predictor variables for plant species distribution. In addition, climate (temperature, precipitation) and human impact are also very important for the distribution of plant species, as are many other factors. Alternative types of similar predictor variables include airborne LiDAR-derived feature detection used to identify landslides [], spectral parameters of airborne LiDAR data applied for detection of glacial landforms [], and object-based image analysis applied for volcanic and glacial landforms mapping []. TPI and mSWI methods in no way intend to compete with verified and established methods of environmental archaeology, such as archaeopalynology, archaeobotany, or archaeozoology, e.g., [,,,,,]. Rather, the aim is to introduce and test additional methods and, perhaps more importantly, to add LiDAR as a new data source for the archaeological analysis of past human land use. The suggested good practice would be to use TPI and mSWI in combination with other methods. However, in this case study, on the one hand, LiDAR and soil data are the only data currently available to the author, and on the other hand, TPI and mSWI were sufficient to provide new insights into the archaeological landscape in general and EMS in the context of agricultural land use in particular.
3. Results
Our modified landform classification is, as mentioned, the combination of TPI and visual geomorphological analysis, which resulted in the definition of four Zones. Below, each Zone is described (Figure 7; Table 4).
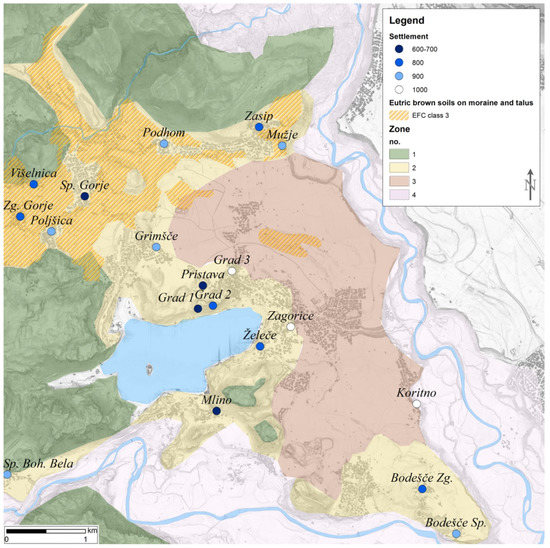
Figure 7.
Bled microregion (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 14.1139; 46.3752), brown soils with high capacity to retain water (marked with dashed lines) and physiographic zones. The areas most suitable for early medieval agriculture are located at the intersection of the dashed lines and yellow Zone 2.

Table 4.
A habitat descriptor for the defined zones within the Bled case study area.
Zone 1 is defined as a mountainous plateau with steep and very steep slopes (TPI classes: High Ridges, Midslope Ridges, Local Ridges; 931–580 m a.s.l.). Middle Triassic dolomite and limestone bedrock prevail (Table 4: T2/1; T2/2) and two soil types occur. The first are rendzinas and the second dystric brown soils. The latter have a higher FC (FC index 3; mSWI index: 0, −5). Nowadays the area is forested and suitable for alpine pasture. There are no EMS in Zone 1.
Zone 2 consists of gently sloping terrain at the foothills. It occurs mostly in the western part of the study area, on the low hills surrounding the Lake Bled and above the river terraces (TPI classes: Upper Slopes, Open Slope; 580–510 m a.s.l.). The bedrock are mostly Holocene alluvial fan deposits. Prevailing eutric brown soils were formed on talus slopes mixed with moraine material and deposited directly on inactive alluvial fans []. These soils have high FC (FC index 3; mSWI index: 0, −5). The area is mostly suitable for arable land and meadows. 16 out of 19 EMS are located within Zone 2.
Zone 3 represents a large till plain formed in postglacial fluvial processes that deposited up to several tens of metres of Quaternary sediments. It is limited by the riverbeds of Sava Dolinka and Sava Bohinjka (TPI class Plains; 510–480 m a.s.l). Over the glaciofluvial sand gravel deposits (Table 4: pr), fertile deposits of brown soils developed. However, due to the high porosity of Holocene sediments, the FC is low (FC index 2; mSWI: 0.7), which means that the entire area is exposed to drought. This is exacerbated by the absence of permanent surface water. Nevertheless, there are small patches of hydromorphic soils (Alluvial soils, Hypogley, Amphigley) with high FC (FC index 4; mSWI: 0, −5). Their formation was possible due the glacial activity and postglacial fluvial processes, which have resulted in deposition of clayed sediments north of the Bled lake []. The brown soils in the Zone 3 are the most suitable soils for modern agriculture in the area [], providing that drought effect can be mitigated (for example, by irrigation or drought-resistant crops). Only three EMS, all established only in the eleventh century, are located in Zone 3.
Zone 4 is an area of multiple alluvial terraces covered by Quaternary sediment (till, fluvio-glacial sediment, and slope sediment) deposits rising above adjacent active floodplains (TPI class Upland Drainage, Midslope Drainage, Streams; 480–450 m a.s.l). The area is characterized by undeveloped soils formed on alluvial deposits with very low FC (FC index 1; mSWI: 0, −11). It is overgrown with riparian vegetation. There are no EMS in Zone 4.
It can be concluded that the preferred landscape type for EMS was moderately steep slopes and brown soils with high FC, defined here as Zone 2 (Figure 7). This is the case for most EMS in our case study (Figure 1: Višelnica, Zgornje in Spodnje Gorje, Poljšica, Grmišče, Zasip, and Mužje). The location of two other EMS (Figure 1: Zg. in Sp. Bodešče) fits the landform classification criteria but not the soil conditions as depicted on the pedological map. We explain this by the fact that the existing soil map is not detailed enough to show the microlevel differences. Indeed, the area is full of glacial moraines and micro valleys, and under such conditions, water-rich and marshy soils tend to develop. Their presence in this particular area is confirmed by the historical field names (“V blateh”, “Curkovca”, “Pretaka”, “Nad potokam”, which means “In the mud”, “Stream”, Flow”, “Above the stream”) [].
The only other landscape context where three EMS exist is large till plain with fertile brown soils with low FC, defined here as Zone 3. However, all three (Figure 1: Zagorice, Grad 3, Koritno) have only been established in the eleventh century.
The above presented focus of EMS on a landscape characterised by moderately steep slopes and brown soils with high FC is consistent with previous research on EMS in similar landscape conditions by Wawruschka. Her mountainous or hilly areas fit well with the description of our Zone 2, although some of the data (e.g., m a.s.l.) cannot be directly compared [].
The most important result of this analysis is the definition of the ecological niche that was preferred by the EMS and is based on the agricultural land use. The importance of this lies in the scalability, i.e., this result can be directly applied to regional studies of the early medieval settlement in Eastern Alpine region and possibly other regions with subalpine climate.
The results also enable new insights into the early medieval Bled microregion by characterizing the individual EMS. Exclusive preference for Zone 2 prior to the eleventh century strongly suggests two things. First, these are primarily agricultural settlements. There are two exceptions (Figure 1: Grad 2, Mlino) where the landscape morphology does not allow for the presence of significant arable land and non-agricultural function seems probable []. Second, the relatively narrow scope of agricultural land use, as can be inferred from the exclusive occupancy of Zone 2, suggests a not overly diversified agricultural land use system, possibly based on a single staple crop.
4. Discussion
The significance of these results goes beyond the case study area and is important for the EMS of the entire subalpine area settled by the Slavs. To fully appreciate the advantages of the proposed method, however, a brief discussion of the archaeological context must be introduced.
Brown soils with high FC (Zone 2) in the vicinity of which most of the EMS are located are not particularly suitable for agriculture by high- and late medieval or post-medieval standards because they contain abundant moraine loam enriched with stones. This is particularly conspicuous because often more fertile soils which are easier to work but have low FC (Zone 3) are adjacent (Figure 5). The late expansion into “the area in the plain where the soil was good” (our Zone 3) was already observed by Pleterski; based on historical and archaeological analysis he concluded that the area was covered with forest but could not explain why []. Then, why were areas of high FC (Zone 2) the main attractor of EMS? The land use characteristics presented above suggest that the key factor in the EMS location choice model was the proximity of the specific soil type that minimizes the risk of exposing crops to water stress. This conclusion is noteworthy for two reasons. First, it helps to elucidate the agricultural characteristics of EMS. Second, it can be used to predict the location of landscape contexts suitable for EMS throughout the Eastern Alpine region.
While the latter is the subject of ongoing research, the former can be discussed here. A brief overview reveals that the early medieval Slavs had a limited choice of the principal field crops available. Rye (Secale cereale), wheat (Triticum sp.), oats (Avena sp.), barley (Hordeum sp.), and millet (Panicum miliaceum) were the main cereals in the western Slavic settlement area (present-day eastern Germany) []. In Southern Russia we know of wheat and barley []. The first Slavic settlers in north-western Russia brought with them a great variety of cereals and legumes, but only the crops that guaranteed agricultural success in the colder north were kept in cultivation: barley and rye []. Closer to the Bled microregion, wheat, barley, and rye were the most common crops at Roztoky (Czech Republic) []. In Thunau (Austria), both in the settlement and in one of the graves, the most common cereal remains were wheat, millet, barley, and rye []. In Kleinklein (Austria), the contents of a settlement pit revealed barley, millet, and rye []. On Bled Island, the central location of the Bled microregion, charred barley and millet grains were recovered but are dated to a later period in the mid-13th century []. Therefore, the early medieval Slavs, like other contemporary Europeans, relied mainly on wheat, barley, rye, and millet as staple cereal foods. Of these, barley has the greatest ecological amplitude and is able to cope with extreme ecological conditions []. It was grown, for example, in Highland Britain [], in Scandinavian north-western Europe [], and even in the Faroe Islands []. Regardless of climate, barley was the dominant crop in western Europe and Britain at the beginning of the early Middle Ages [], where it was important enough to warrant a special barley tax []. Wheat in western and rye in north-western Europe had replaced barley as the dominant cereal by the end of the early Middle Ages [] (Figure 8).
Figure 8.
Early medieval cultivation of Barley in Europe (heights above 1000 m a.s.l. are darker), locations mentioned in text (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 19.8237; 54.8443). For inset with sites Roztoky, Thunau, and Kleinklein, see Figure 2.
There are many differences between wheat, millet, barley, and rye. Most pertinent to this case study is that while millet and rye have exceptional drought tolerance, wheat and barley under rainfed conditions may suffer from drought resulting in significant yield loss [,]. Consequently, it is barley and wheat that require soils with high FC. Between the two, barley matures earlier, has greater tillering capacity, and competes better with weeds, but generally yields less []. Wheat requires more labour in terms of cultivation and manuring to achieve potentially high yields. An increase in wheat cultivation thus implies a higher degree of agricultural organization [,].
Therefore, we infer that barley was most likely the principal field crop in the Bled microregion until the eleventh century. There are three pieces of evidence to support this. First, barley is best suited to a society with a lower level of agricultural organization [,], such as the colonist society that was establishing EMS in the Bled microregion between the 7th and 9th centuries (cf., []; also see below). Second, barley was the cereal of choice for the Slavs when they settled in what they perceived as colder climates, such as the above-mentioned colonization of north-western Russia []; due to its height above sea level close to 500 m the subalpine climate of the Bled microregion is colder (under any climatic conditions) than the areas from which the Slavs were arriving [], for example, from the western edges of the Pannonian plain that they settled already in the 6th century []. Third, under rain-fed conditions, barley prefers high FC to all other soil properties [,].
To explain the expansion of EMS in the eleventh century into areas of soil with lower FC (Zone 3), another evidence must be introduced. Namely, in 1004 AD, parts of the Bled microregion were bestowed to the bishops of Brixen by a royal charter [,]. In addition to the small estate, they received all the lands in the Bled microregion that were not directly worked by existing owners, including the then forested Zone 3 []. This deed was more than just an exchange of ownership, as it signified the assertion of direct control over the Bled microregion by the Kingdom of Germany for the first time after more than a century (for historical context see, e.g., [,]). The new owners undoubtedly imposed their own agricultural organization on their newly acquired property. It was based on the complex manorial system, which was a subsistence economy oriented towards stability and based on strategies of risk avoidance through diversification of resources and redistribution by means of storage and transport []. In the early eleventh century (i.e., at the end of early medieval period), wheat was the main staple crop in this system []. Subsequent institutional and social changes in the Bled microregion that reflected a higher degree of agricultural organization have been chronicled as extensive property changes in the following centuries [,,,]. This was a marked difference from the pre-eleventh-century system operated by the Slavs, which used similar technology [], but was far less diversified and almost exclusively embedded in the local community of a single Župa [,], which in this case is the Bled microregion.
The political and social changes of the early 11th century thus introduced a higher degree of agricultural organization that is necessary, among other things, for a successful wheat production [,]. More importantly, the EMS expansion into areas with low FC soils was possible since the diversified manorial system was designed to routinely cope with local crop failures by transporting supplies from distant estates []. In other words, the pre-eleventh-century agricultural system could not cope with occasional crop failures on low FC soils due to dry Summers. The post-eleventh-century manorial system could and was therefore able to take advantage of this otherwise fertile area, most likely to grow wheat. The fact that none of the eleventh century EMS were established directly by the bishops of Brixen [] does not change the fact that it was the newly introduced manorial agricultural system that enabled the colonisation of this area.
These conclusions are important not only for the understanding of the Bled microregion EMS but also to further our understanding (e.g., [,]) of regional agricultural dynamics during the transition from the early to the high medieval period in Eastern Alpine region.
5. Conclusions
The main objective of the paper was to present and test new methods that offer additional uses of LiDAR for archaeological analysis of past land use. This is important not only in terms of the specific method and research application presented but also because this is an underdeveloped area in archaeology that needs more attention.
This paper utilizes an existing corpus of open access archaeological database Zbiva [,], open access remote sensing data and environmental data (geological and soil data), as well as open-source software tools (e.g., QGIS, SAGA) to reassess existing knowledge on the early medieval archaeological landscapes, specifically on agricultural land use. While the importance of free and open-source software in science in general, e.g., [], and in the field of airborne LiDAR data for archaeology in particular, e.g., [], is well recognised, we believe that the importance of the increasingly abundant and easily accessible free environmental and archaeological data, e.g., [], is too often overlooked. Hopefully, this article is a step towards recognizing the importance that this data source can have for archaeology.
A novel objective method was presented and, perhaps more importantly, LiDAR as a new data source for the archaeological analysis of agricultural land use systems. The suggested good practice would be to use this method in combination with existing complementary methods, such as archaeobotanical analyses. However, in this case study, the presented method was sufficient to provide new insights into the archaeological landscape in general and EMS in the context of agricultural land use in particular.
We used the LiDAR data for what is termed integrated multi-scale ‘deep’ interpretation, which aims to deepen the understanding of archaeological features in their landscape context. It should be reiterated that, in our opinion, such a use of these data in archaeology remains underexploited despite some promising early studies, e.g., [,,]. The Bled case study illustrates such potential contribution of LiDAR data to explore landscape gradients that have influenced human activities. We have clearly demonstrated a preference of early medieval agriculture for terrain on moderately steep slopes with brown soils that have a high capacity to retain water. We have tentatively connected this to a society with a subsistence agricultural organization that is growing barley as a staple cereal food. It is highly likely that cultural and technological changes at the turn of the millennium brought, among other things, a higher level of agricultural organization and wheat as a staple cereal food.
One of the most important contributions is the discussion of scale issues. Since the scale of many soil maps is inadequate for archaeological analysis, a method to overcome this challenge is presented using various indices. The solution presented is scalable to other types of landscape and other archaeological periods, as well as to other types of soil data.
In the wider context of LiDAR methodology in archaeology, we have focused on the potential of LiDAR data to provide a source for very detailed landscape description and observe environmental components using GIS analysis, specifically modified landform classification and mSWI. This approach leads to a more detailed and objective analysis of the environment and spatial context of any observed archaeological phenomena. Given the rise of open access data and open access tools, there is huge potential for this and similar methods in geocomputational archaeology of the near future.
Funding
This research was funded by Austrian Science Fund (FWF) grant number I 3992 (Internationale Projekte, project title “Settlement of the south-eastern Alpine region in the Early Middle Ages”).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Airborne LiDAR data used are publicly available at http://gis.arso.gov.si/evode/profile.aspx?id=atlas_voda_Lidar@Arso (accessed on 8 July 2021). Geology data are publicly available at https://ogk100.geo-zs.si (accessed on 8 July 2021). Soil data are publicly available at http://gis.arso.gov.si/atlasokolja/profile.aspx?id=Atlas_Okolja_AXL@Arso (accessed on 8 July 2021).
Acknowledgments
I thank Mateja Belak for providing the raw data from the Zbiva database and Benjamin Štular and Jernej Rihter for discussion and suggested readings for the Discussion section. Open Access funding by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF).
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Additional Maps
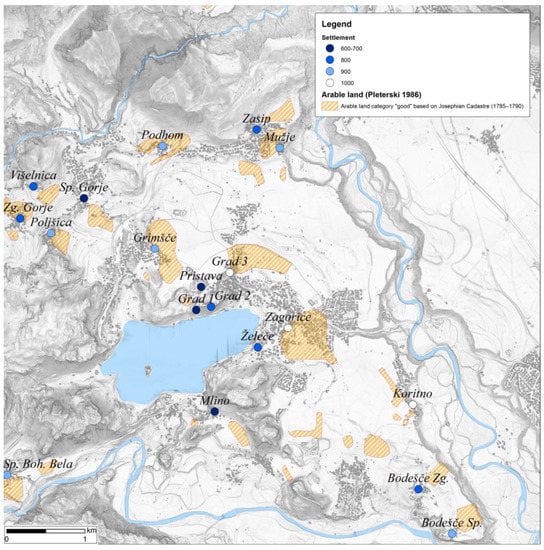
Figure A1.
Bled microregion (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 14.1139; 46.3752), early medieval settlements (letters refer to Table 2 in the text), and arable land category “good” based on the retrograde analysis of the 19th century Franciscan Cadastre (source data adopted from []; North at the top).
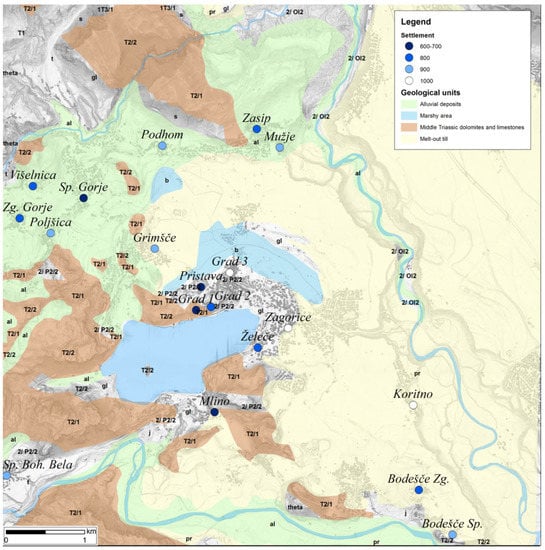
Figure A2.
Bled microregion (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 14.1139; 46.3752), geological background. The most main geological units prevailing in the study area are presented (source data adopted from [,,]; North at the top).

Figure A3.
Bled micro-region (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 14.1139; 46.3752), soil map (source data adopted from []; North at the top).

Figure A4.
Bled micro-region (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 14.1139; 46.3752), effective field soil capacity (FC) classes (source data adopted from []; North at the top).
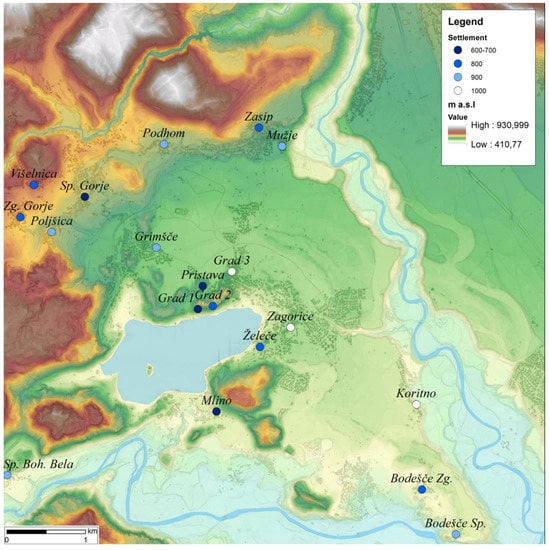
Figure A5.
Bled microregion (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 14.1139; 46.3752), visualisation created for visual geomorphological analysis (hypsometric tinting of high-resolution DEM, transparently (60%) superimposed over a hillshaded surface). The highest elevation zone is white, brown represents the mountainous plateau, a darker green for the upper slopes, and light green for the verdant valleys. EMS are represented with points. North at the top.

Figure A6.
Bled microregion (decimal longitude and latitude coordinates of the map centre: 14.1139; 46.3752), modified SAGA wetness index (mSWI). The area with modified values between 11 and 0 has a (very) low capacity to retain water (map in yellow and brown), and the area with high capacity to retain water (values 0 to −5, green). North at the top.
References
- Canuto, M.A.; Estrada-Belli, F.; Garrison, T.G.; Houston, S.D.; Acuña, M.J.; Kováč, M.; Marken, D.; Nondédéo, P.; Auld-Thomas, L.; Castanet, C.; et al. Ancient lowland Maya complexity as revealed by airborne laser scanning of northern Guatemala. Science 2018, 361, eaau0137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chase, A.F.; Chase, D.Z.; Weishampel, J.F.; Drake, J.B.; Shrestha, R.L.; Slatton, K.C.; Awe, J.J.; Carter, W.E. Airborne LiDAR, archaeology, and the ancient Maya landscape at Caracol, Belize. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devereux, B.J.; Amable, G.; Crow, P.; Cliff, A. The potential of airborne lidar for detection of archaeological features under woodland canopies. Antiquity 2005, 79, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.H.; Fletcher, R.J.; Pottier, C.; Chevance, J.-B.; Soutif, D.; Tan, B.S.; Im, S.; Ea, D.; Tin, T.; Kim, S.; et al. Uncovering archaeological landscapes at Angkor using lidar. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12595–12600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Schwerin, J.; Richards-Rissetto, H.; Remondino, F.; Spera, M.G.; Auer, M.; Billen, N.; Loos, L.; Stelson, L.; Reindel, M. Airborne LiDAR acquisition, post-processing and accuracy-checking for a 3D WebGIS of Copan, Honduras. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, T.; Triadan, D.; López, V.A.V.; Fernandez-Diaz, J.C.; Omori, T.; Bauer, M.B.M.; Hernández, M.G.; Beach, T.; Cagnato, C.; Aoyama, K.; et al. Monumental architecture at Aguada Fénix and the rise of Maya civilization. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 582, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menéndez Blanco, A.; García Sánchez, J.; Costa-García, J.M.; Fonte, J.; González-Álvarez, D.; Vicente García, V. Following the Roman Army between the Southern Foothills of the Cantabrian Mountains and the Northern Plains of Castile and León (North of Spain): Archaeological Applications of Remote Sensing and Geospatial Tools. Geosciences 2020, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, T.W.; Ardren, T.; Barth, N.C.; Fernandez-Diaz, J.C.; Rohrer, P.; Meyer, D.E.; Miller, S.J.; Magnoni, A.; Pérez, M. ‘Structure’ density, area, and volume as complementary tools to understand Maya Settlement: An analysis of lidar data along the great road between Coba and Yaxuna. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 29, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.E. Detecting Classic Maya Settlements with Lidar-Derived Relief Visualizations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swieder, A. Per Laserstrahl durchs Selketal. Landschaftsarchäologische Untersuchungen mittelalterlicher und frühneuzeitlicher Bodendenkmale im Ostharz anhand digitaler Geländedaten. Jahresschr. Mitteldtsch. Vorgesch. 2021, 98, 379–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triglav Čekada, M.; Bric, V. Končan Je Projekt Laserskega Skeniranj Slovenije. Geod. Vestn. 2015, 59, 586–592. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini, F.; Vinci, G.; Horvat, J.; De Min, A.; Forte, E.; Furlani, S.; Lenaz, D.; Pipan, M.; Zhao, W.; Sgambati, A.; et al. Early Roman military fortifications and the origin of Trieste, Italy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1520–E1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardini, F.; Vinci, G. Archaeological landscape in central northern Istria (Croatia) revealed by airborne LiDAR: From prehistoric sites to Roman centuriation. Archaeol. Anthr. Sci. 2020, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laharnar, B.; Lozić, E.; Štular, B. A structured Iron Age landscape in the hinterland of Knežak, Slovenia. In Rural Settlement. Relating Buildings, Landscape, and People in the European Iron Age; Cowley, D.C., Fernández-Götz, M., Romankiewicz, T., Wendling, H., Eds.; Sidestone Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 263–271. ISBN 978-90-8890-819-4. [Google Scholar]
- Laharnar, B.; Štular, B.; Mlinar, M. Gradič above Kobarid—A Late Republican fortified emporium?=Gradič nad Kobaridom, poznorepublikanski utrjeni emporij? In Evidence of the Roman Army in Slovenia = Sledovi Rimske Vojske Na Slovenskem; Istenič, J., Laharnar, B., Horvat, J., Eds.; Narodni Muzej Slovenije: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2015; Volume 41, pp. 243–256. ISBN 978-961-6169-97-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mlekuž, D. Skin Deep: LiDAR and Good Practice of Landscape Archaeology. In Good Practice in Archaeological Diagnostics: Non-invasive Survey of Complex Archaeological Sites; Corsi, C., Slapšak, B., Vermeulen, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 113–129. ISBN 978-3-319-01784-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mlekuž, D. Airborne Laser Scanning and Landscape Archaeology. Opusc. Archaeol. 2018, 39–40, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štular, B. The Use of Lidar-Derived Relief Models in Archaeological Topography the Kobarid Region (Slovenia) Case Study. Arheol. Vestn. 2011, 62, 393–432. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, P. Illuminating woodland heritage: The technical specifications and limitations of lidar. In Past Landscapes Beneath the Trees: Using lidar in Woodlands, Proceedings of the a One-Day Conference at The Park Campus, University of Gloucestershire, Cheltenham, UK, 11–23 September 2010; Gloucestershire County Council and the Forestry Commission: Gloucestershire, UK, 2010; pp. 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Crutchley, S. Ancient and modern: Combining different remote sensing techniques to interpret historic landscapes. J. Cult. Heritage 2009, 10, e65–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doneus, M.; Kühteiber, T. Airborne laser scanning and archaeological interpretation—bringing back the people. In Interpreting Archaeological Topography: Airborne Laser Scanning, 3D Data and Ground Observation; Opitz, R.S., Cowley, D.C., Eds.; Occasional Publication of the Aerial Archaeology Research Group, Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 32–50. ISBN 978-1-84217-516-3. [Google Scholar]
- Štular, B.; Lozić, E.; Eichert, S. Airborne LiDAR-Derived Digital Elevation Model for Archaeology. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, P. Haus, Hof Und Dorf in Mitteleuropa Vom 7. Bis 12. Jahrhunder: Archäologische Beiträge Zur Entwicklung Und Struktur Der Bäuerlichen Siedlun; Akademie Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Milo, P. Frühmittelalterliche Siedlungen in Mitteleuropa. Eine Vergleichende Strukturanalyse Durch Archäologie Und Geophysik; Studien zur Archäologie Europas; Verlag Dr. Rudolf Habelt GmbH: Bonn, Germany, 2014; Volume 21, pp. 26–153. ISBN 978-3-7749-3840-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovič, D. Začetki Zgodnjeslovanske Poselitve Prekmurja = Beginnings of the Early Slavic Settlement in the Prekmurje Region, Slovenia. Arheol. Vestn. 2017, 68, 349–386. [Google Scholar]
- Šalkovský, P. Häuser in der Frühmittelalterlichen Slawischen Welt; Archaeologica Slovaca Monographiae; Archeologický Ústav Slovenskej Akad. Vied: Nitra, Slovakia, 2001; ISBN 80-88709-52-0. [Google Scholar]
- Pleterski, A. Zgodnjesrednjeveška Naselbina Na Blejski Pristavi: Tafonomija, Predmeti in Čas (Frühmittelalterliche Siedlung Pristava in Bled: Taphonomie, Fundgegenstände Und Zeitliche Einordnung); Opera Instituti Archaeologici Sloveniae; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2010; Volume 19, ISBN 978-961-254-206-1. [Google Scholar]
- De Boer, A.G.; Laan, W.N.; Waldus, W.; Van Zijverden, W.K. LiDAR-based surface height measurements: Applications in archaeology. In Beyond Illustration: 2D and 3D Digital Technologies as Tools for Discovery in Archaeology; Frischer, B., Dakouri-Hild, A., Eds.; BAR International Series; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 76–84, 154–156. ISBN 978-1-4073-0292-8. [Google Scholar]
- Coluzzi, R.; Lanorte, A.; Lasaponara, R. On the LiDAR contribution for landscape archaeology and palaeoenvironmental studies: The case study of Bosco dell’Incoronata (Southern Italy). Adv. Geosci. 2010, 24, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prufer, K.; Thompson, A.E. Lidar-Based Analyses of Anthropogenic Landscape Alterations as a Component of the Built Environment. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2016, 4, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozić, E.; Štular, B. Documentation of Archaeology-Specific Workflow for Airborne LiDAR Data Processing. Geosciences 2021, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierik, H.J.; Van Lanen, R.J. Roman and early-medieval habitation patterns in a delta landscape: The link between settlement elevation and landscape dynamics. Quat. Int. 2019, 501, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishampel, J.F.; Hightower, J.; Chase, A.F.; Chase, D.Z. Remote Sensing of Below-Canopy Land Use Features from the Maya Polity of Caracol. In Understanding Landscapes: From Discovery through Land Their Spatial Organization; Djinjian, F., Robert, S., Eds.; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ringle, W.M.; Negrón, T.G.; Ciau, R.M.; Seligson, K.E.; Fernandez-Diaz, J.C.; Zapata, D.O. Lidar survey of ancient Maya settlement in the Puuc region of Yucatan, Mexico. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, W.; Murtha, T.; Broadbent, E.N.; Zambrano, A.M.A. A confluence of communities: Households and land use at the junction of the Upper Usumacinta and Lacantún Rivers, Chiapas, Mexico. World Archaeol. 2021, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, M. Kolonizacija in populacija v srednjem veku. In Gospodarska in Družbena Zgodovina Slovencev. Enciklopedična Obravnava Po Panogah. Zgodovina Agrarnih Panog. Zv. 1, Agrarno Gospodarstvo; Blaznik, P., Grafenauer, B., Vilfan, S., Eds.; Slovenska akademija znanosti in umetnosti, Institut za zgodovino-Sekcija za občo in narodno zgodovino; Državna založba Slovenije: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 1970; pp. 67–88. [Google Scholar]
- Pleterski, A. The Invisible Slavs: Župa Bled in the Prehistoric Early Middle Ages; Opera Instituti archaeologici Sloveniae; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2013; ISBN 978-961-254-440-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wawruschka, C. Frühmittelalterliche Siedlungsstrukturen in Niederösterreich (Mitteilungen der Prähistorischen Kommission); VÖAW: Wien, Austria, 2009; ISBN 978-3-7001-6060-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zeman, J. Nejstarší slovanské osídlení Čech (Die älteste slawische Besiedlung Böhmens). Památky Archeol. 1976, 67, 115–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, M.J.; Buchanan, B.; Walker, R.S. Scaling the Size, Structure, and Dynamics of Residentially Mobile Hunter-Gatherer Camps. Am. Antiq. 2018, 83, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casana, J. Structural Transformations in Settlement Systems of the Northern Levant. Am. J. Archaeol. 2007, 111, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, Y.F. Rootedness versus Sense of Place. Landscape 1980, 24, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, S.; Edwards, M. Approaching Late Antiquity. In Approaching Late Antiquity; Oxford University Press (OUP): Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 20–52. [Google Scholar]
- Carboni, F. Inspecting the transformation of Roman settlements in the Upper Potenza Valley (Marche region) across Late Antiquity and into the Early Medieval era. IL Cap. Cult. Stud. Value Cult. Herit. 2015, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensing, S.A.; Schoolman, E.; Tunno, I.; Noble, P.J.; Sagnotti, L.; Florindo, F.; Piovesan, G. Historical ecology reveals landscape transformation coincident with cultural development in central Italy since the Roman Period. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, S.R. Climate Change in the Breadbasket of the Roman Empire—Explaining the Decline of the Fayum Villages in the Third Century CE*. Stud. Late Antiq. 2020, 4, 486–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.; Palmisano, A.; De Gruchy, M.W. Collapse and continuity: A multi-proxy reconstruction of settlement organization and population trajectories in the Northern Fertile Crescent during the 4.2kya Rapid Climate Change event. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barford, P.M. The Early Slavs: Culture and Society in Early Medieval Eastern Europe; Cornell University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-8014-3977-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ivković, T.; Crnčević, D.; Bulić, D.; Petrović, V.; Cvijanović, I.; Radovanović, B. The World of the Slavs. Studies on the East, West and South Slavs: Civitas, Oppidas, Villas and Archeological Evidence (7th to 11th Centuries AD); The Institute of History: Belgrade, Serbia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Curta, F. The Making of the Slavs: History and Archaeology of the Lower Danube Region, c. 500–700; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; ISBN 978-0-511-49629-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fine, J.V.; Fine, J.V.A. The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century; University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1991; ISBN 0-472-08149-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, W. The Early Slavs: Culture and Society in Early Medieval Eastern Europe. P. M. Barford. Speculum 2004, 79, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brather, S. Ethnische Identitäten Als Konstrukte Der Frühgeschichtlichen Archäologie. Ger. Anz. Röm.-Ger. Komm. Dtsch. Archäol. Inst. 2000, 78, 139–177. [Google Scholar]
- Brather, S. Ethnizität Und Mittelalterarchäologie. Eine Antwort Auf Florin Curta. Z. Für Archäol. Mittelalt. 2011, 39, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Pleterski, A. Župa Bled. Nastanek, Razvoj, Prežitki; SAZU: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Pleterski, A. Sebenjski zaklad. Arheol. Vestn. 1987, 38, 237–330. [Google Scholar]
- Měřínský, Z. České Země Od Příchodu Slovanů Po Velkou Moravu I; Libri: Praha, Czech Republic, 2002; pp. 87–153. ISBN 80-7277-104-3. [Google Scholar]
- Fusek, F.G. Slovensko Vo Včasnoslovanskom Obdobi; Archaeologica Slovaca Monographiae; Archeologicky ustav AV ČR Brno: Nitra, Slovakia, 1994; pp. 143–149. ISBN 80-88709-17-2. [Google Scholar]
- Rihter, J. Poplavna ravnica reke Save na Krškem polju kot gospodarsko zaledje kmečkih gospodarstev v prvi polovici 20. stoletja. Studia Univ. Hered. Znan. Rev. Raziskave Teor. Kult. Dediščine 2019, 7, 9–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdič, A. Arheološka Interpretacija Dravske Ravni in Okoliških Vzpetin Med 6. in 12. Stoletjem. Ph.D. Thesis, Podiplomska šola ZRC SAZU, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Magdič, A. New Archaeological Research into the Middle Ages in the Slovenian Regions of Pomurje and Podravje. The Issue of Settlement Continuity and the Development of Agrarian Activities (Novejše arheološke raziskave srednjega veka na prostoru slovenskega Pomurja in Podravja. Vprašanje kontinuitete poselitve in razvoja agrarnih dejavnosti). In Srednjovjekovna Naselja U Svjetlu Arheoloških Izvora (Mediaeval Settlements in the Light of Archaeological Sources); Sekelj Ivančan, T., Tkalčec, T., Krznar, S., Belaj, J., Eds.; Zbornik Instituta za Arheologiju/Serta Instituti Archaeologici; Institut za Arheologiju Zagreb: Zagreb, Croatia, 2017; pp. 441–467. [Google Scholar]
- Knific, T. Arheološki Zemljevid Blejskega Kota v Zgodnjem Srednjem Veku. Kronika 1984, 32, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Pleterski, A.; Belak, M. ZBIVA. Cerkve v Vzhodnih Alpah Od 8. Do 10. Stoletja. ZBIVA (Archäologische Datenbank Für Den Ostalpenbereich. Die Kirchen in Den Ostalpen Vom 8. Bis 10. Jahrhundert). Zgod. Časopis 1995, 49, 19–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kazanski, M. Archaeology of the Slavic Migrations. In Encyclopedia of Slavic Languages and Linguistics Online; BRILL: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pleterski, A. Vprašanja o Preteklosti Zgodnjih Slovanov Ob Primeru Župe Bled. Arheol. Vestn. 2013, 64, 335–352. [Google Scholar]
- Kastelic, J.; Škerlj, B. Slovanska Nekropola Na Bledu. Arheološko in Antropološko Poročilo Za Leto 1948; Dela 1. Razreda SAZU Vol. 2; SAZU: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Kastelic, J. Slovanska Nekropola Na Bledu. Poročilo o Izkopavanjih Leta 1949 in 1951; Dela 1. razreda SAZU Vol. 13; SAZU: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Knific, T. Bled v Zgodnjem Srednjem Veku. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Knific, T. Na Stičišču Treh Svetov: Arheološki Podatki o Goriški v Zgodnjem Srednjem Veku. Goriški Letn. 2004, 29, 5–30. [Google Scholar]
- Knific, T. Arheološki sledovi blejskih prebivalcev iz pozne antike in zgodnjega srednjega veka. In Bled tisoč let. Blejski zbornik 2004; Dežman, J., Ed.; Didakta: Radovljica, Slovenia, 2004; pp. 93–117. ISBN 961-6463-87-X. [Google Scholar]
- Pleterski, A. Zgodnjesrednjevški žgani grobov v vzhodnih Alaph (Frühmittelalterliche Brandgräger im Ostalpenraum). In Frühmittelalterarchäologie in der Steiermark. Beiträge Eines Fachgesprächs Anlässlich des 65. Geburtstags von Diether Kramer; Steinklauber, U., Ed.; Schild von Steier, Beiheft: Graz, Austria, 2008; pp. 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Pleterski, A. Zgodnjesrednjeveška Naselbina Na Blejski Pristavi. Najdbe (Frühmittelalterliche Siedlung Pristava in Bled. Funde); Opera Instituti archaeologici Sloveniae; Inštitut za arheologijo ZRC SAZU Vol. 14; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2008; ISBN 978-961-254-072-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pleterski, A. Zbiva v3.08; Research Centre of Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Institute of Archeology: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2016. Available online: http://zbiva.zrc-sazu.si (accessed on 2 August 2021).
- Gaspari, A. (Ed.) Neznano Blejsko Jezero Podvodna Kulturna Dediščina in Rezultati Arheoloških Raziskav; Zavod za Varstvo Kulturne Dediščine Slovenije: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Knific, T.; Pleterski, A. Staroslovanski Grobišči v Spodnjih Gorjah in Zasipu. Arheol. Vestn. 1993, 44, 235–267. [Google Scholar]
- Modrijan, Z. Bodešče. In Srednjeveški Blejski otok v Arheoloških Virih = Medieval Archaeology of Bled Island; Štular, B., Ed.; Opera Instituti Archaeologici Sloveniae Vol. 42; Založba ZRC, ZRC SAZU: Ljubjana, Slovenia, 2020; pp. 279–286. ISBN 978-961-05-0260-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ilešič, S. Sistemi Poljske Razdelitve Na Slovenskem.-SAZU, Ljubljana; Dela 4. Razreda SAZU; SAZU: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Vita-Finzi, C.; Higgs, E.S. Prehistoric Economy in the Mount Carmel Area of Palestine: Site Catchment Analysis. Proc. Prehist. Soc. 1970, 36, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, K.V. Empirical Determination of Site Catchments in Oaxaca and Tehuacán. In The Early Mesoamerican Village; Flannery, K.V., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976; pp. 103–116. ISBN 0-12-259850-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann, D.L. The village and its catchment area. In The Early Mesoamerican Village; Flannery, K.V., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976; pp. 95–102. ISBN 0-12-259850-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zarky, A. Statistical analysis of site-catchment at Ocos, Guatemala. In The Early Mesoamerican Village; Flannery, K.V., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976; pp. 117–127. ISBN 0-12-259850-4. [Google Scholar]
- Perko, D.; Nared, J.; Čeh, M.; Hladnik, D.; Krevs, M.; Podobnikar, T.; Šumrada, R. Geografski Informacijski Sistemi v Sloveniji 2005–2006; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2006; ISBN 961-6568-55-8. [Google Scholar]
- Seubers, J. Many rivers to cross: Revisiting the territory of ancient Crustumerium with a cost surface based site catchment analysis. In Early States, Territories and Settlements in Protohistoric Central Italy, Proceedings of the Specialist Conference at the Groningen Institute of Archaeology of the University of Groningen, 2013; Attema, P., Seubers, J., Willemsen, S., Eds.; Corollaria Crustumina; Barkhuis Publishing: Groningen, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 51–65. ISBN 978-94-91431-99-9. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, E. Mountaincraft and Leadership; Cordee: Leicester, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, W. Three Presentations on Geographical Analysis and Modeling: Non-Isotropic Geographic Modeling; Speculations on the Geometry of Geography; and Global Spatial Analysis; Technical Report; National Center for Geographic Information and Analysis, University of California: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Štular, B. Analiza gospodarskega zaledja v arheologiji krajin (Site catchment analysis in landscape archaeology). In Geografski Informacijski Sistemi V Sloveniji 2005–2006; Perko, D., Nared, J., Čeh, M., Hladnik, D., Krevs, M., Podobnikar, T., Šumrada, R., Eds.; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2006; pp. 199–210. ISBN 961-6568-55-8. [Google Scholar]
- Field, S.; Heitman, C.; Richards-Rissetto, H. A Least Cost Analysis: Correlative Modeling of the Chaco Regional Road System. J. Comput. Appl. Archaeol. 2019, 2, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards-Rissetto, H.; Landau, K. Movement as a Means of Social (Re)Production: Using GIS to Measure Social Integration across Urban Landscapes. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 41, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Štular, B.; Lozić, E. Comparison of Filters for Archaeology-Specific Ground Extraction from Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavec, M.; Verbič, T. The extent of Quaternary glaciations in Slovenia. In Quaternary Glaciations-Extent and Chronology Europe; Ehlers, J., Gibbard, P.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 385–388. ISBN 978-0-444-51462-2. [Google Scholar]
- Serianz, L. Tri-dimensional Model of the Radovna Glacier from the Last Glacial Period. Geologija 2016, 59, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serianz, L.; Rman, N.; Brenčič, M. Hydrogeochemical Characterization of a Warm Spring System in a Carbonate Mountain Range of the Eastern Julian Alps, Slovenia. Water 2020, 12, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogorelec, B. Geological Setting of the Surroundings of Lakes Bled and Bohnij. Geology 1978, 21, 93–164. [Google Scholar]
- Lisec, A.; Montanarella, L.; Vrščaj, B.; Kralj, T.; Lobnik, F.; Suhadolc, M.; Prus, T.; Mihelič, R.; Rupreht, J.; Zupan, M.; et al. Soils of Slovenia = Tla Slovenije; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2015; ISBN 978-92-79-23063-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bleam, W.F. Soil and Environmental Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 40–69. ISBN 978-0-12-415797-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pike, R.J. The geometric signature: Quantifying landslide-terrain types from digital elevation models. Math. Geol. 1988, 20, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagil, S.; Jenness, J. GIS-Based Automated Landform Classification and Topographic, Landcover and Geo-logic Attributes of Landforms Around the Yazoren Polje, Turkey. J. Appl. Sci. 2008, 8, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.D. The Geomorphological Characterisation of Digital Elevation Models. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Böhner, J.; Selige, T. Spatial Prediction of Soil attributes using terrain Analysis and Climate Regionalisation. In SAGA—Analyses and Modelling Applications; Goltze: Göttingen, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gallant, J.C.; Wilson, J.P. Primary Topographic Attributes. In Terrain Analysis: Principles and Applications; Wilson, J.P., Gallant, J.C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 51–85. ISBN 0-471-32188-5. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, A.D. Topographic Position and Landforms Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2001 ESRI International User Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Guisan, A.; Weiss, S.B.; Weiss, A.D. GLM versus CCA spatial modeling of plant species distribution. Plant Ecol. 1999, 143, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.N.C.; Ogilvie, J.; Arp, P. Topographic modelling of soil moisture conditions: A comparison and verification of two models. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 60, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaya, V.; Conrad, O. Geomorphometry in SAGA. In Geomorphometry Concepts, Software, Applications, Developments in Soil Science; Hengl, T., Reuter, H.I., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Neatherlands, 2009; pp. 293–308. [Google Scholar]
- Bohner, J.; Koethe, R.; Conrad, O.; Gross, J.; Ringeler, A.; Selige, T. Soil Regionalisation by Means of Terrain Analysis and Process Parameterisation. In Soil Classification 2001. European Soil Bureau, Research Report No. 7; Micheli, E., Nachtergaele, F., Montanarella, L., Eds.; European Soil Bureau: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2002; pp. 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Mattivi, P.; Franci, F.; Lambertini, A.; Bitelli, G. TWI computation: A comparison of different open source GISs. Open Geospat. Data Softw. Stand. 2019, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, R.; Zinko, U.; Seibert, J. On the Calculation of the Topographic Wetness Index: Evaluation of Diðerent Methods Based on Field Observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2005, 2, 1807–1834. [Google Scholar]
- Kemppinen, J.; Niittynen, P.; Riihimäki, H.K.; Luoto, M. Modelling soil moisture in a high-latitude landscape using LiDAR and soil data. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 43, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienzle, S. The Effect of DEM Raster Resolution on First Order, Second Order and Compound Terrain Derivatives. Trans. GIS 2003, 8, 83–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, M.; Böhner, J.; Conrad, O.; Köthe, R.; Ringeler, A. Methods for creating functional soil databases and applying Digital Soil Mapping with SAGA GIS. In Status and Prospect of Soil Information in South-Eastern Europe: Soil Databases, Projects and Applications; Hengl, T., Panagos, P., Jones, A., Toth, G., Eds.; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2007; pp. 149–162. ISBN 978-92-79-04972-9. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Böhner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, G.; Liu, S. Identification of Forested Landslides Using LiDar Data, Object-based Image Analysis, and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9705–9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowski, L.; Tylmann, K.; Trzcinska, K.; Rudowski, S.; Tegowski, J. Exploration of Glacial Landforms by Object-Based Image Analysis and Spectral Parameters of Digital Elevation Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizizadeh, B.; Garajeh, M.K.; Blaschke, T.; Lakes, T. An object based image analysis applied for volcanic and glacial landforms mapping in Sahand Mountain, Iran. Catena 2021, 198, 105073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincauze, D. Environmental Archaeology. Principles and Practice; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; ISBN 978-0-521-31077-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.M. (Ed.) Environmental Archaeology: A Guide to the Theory and Practice of Methods, from Sampling and Recovery to Post-Excavation; English Heritage: Swindon, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.G. Environmental Archaeology and the Social Order; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 0-203-34581-9. [Google Scholar]
- Reitz, E.J.; Scarry, C.M.; Scudder, S.J. (Eds.) Case Studies in Environmental Archaeology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-387-71303-8. [Google Scholar]
- Reitz, E.; Shackley, M. Environmental Archaeology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Andrič, M.; Tolar, T.; Toškan, B. Okoljska Arheologija in Paleoekologija: Palinologija, Arheobotanika in Arheozoologija; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2016; ISBN 978-961-254-872-8. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, A.; Popit, T.; Šmuc, A. Sedimentological and geomorphological characteristics of Quaternary deposits in the Planica-Tamar Valley in the Julian Alps (NW Slovenia). J. Maps 2018, 14, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brather, S. Archäologie Der Westlichen Slawen. Siedlung, Wirtschaft Und Gesellschaft Im Früh-Und Hochmittelalterlichen Ostmitteleuropa; Ergänzungsbände zum Reallexikon der Germanischen Altertumskunde; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-3-11-020609-8. [Google Scholar]
- Korobov, D. Early Medieval Settlement in Southern Russia: Changing Directions. Mediev. Archaeol. 2012, 56, 34–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Archaeology of Medieval Novgorod in Context. In The Archaeology of Medieval Novgorod in Context; Policy Press: Bristol, UK, 2012; pp. 321–350.
- Profantová, N. Nové Objekty Kultury s Keramikou Pražského Typu z Roztok u Prahy (Neue Objekte Der Kultur Mit Keramik Des Prager Typus Aus Roztoky Bei Prag). Památky Archeol. 2005, 96, 127–164. [Google Scholar]
- Teschler-Nicola, M.; Novotny, F.; Spannagl-Steiner, M.; Haring, E.; Irrgeher, J.; Zitek, A.; Rumpelmayr, K.; Wild, E.M.; Tautscher, B.; Prohaska, T. Die frühmittelalterlichen Fundstellen von Thunau am Kamp (NÖ) und ihre bioanthropologischen Evidenzen-eine Zusammenfassung. In 50 Jahre Archäologie in Thunau am Kamp: Festschrift für Herwig Friesinger: Tagung “50 Jahre Archäologie in Thunau. Zur Situation Eines Österreichischen Langzeitprojektes” Mistelbach, 27–30 Oktober 2015"; Nowotny, E., Obenaus, M., Uzunoglu-Obenaus, S., Eds.; Universität Krems: Krems, Austria, 2018; pp. 219–239. ISBN 978-3-903150-25-6. [Google Scholar]
- Heiss, A.G.; Wiesinger, S. Archaeobotanical reports. Kurzbericht zur archäobotanischen Analyse zu Fundmaterial aus einer villa rustica bei Kleinklein (Gem. Großklein, Bez. Leibnitz) in der Steiermark (2018). In Plants–Animals–People. Lively Archaeological Landscapes of Styria and Northeastern Slovenia = Pflanzen–Tiere–Menschen. Lebendige Archäologische Landschaften der Steiermark Und Nordostsloweniens = Rastline–Živali–Ljudje. Žive Arheološke Krajine Avstrijske Štajerske in Severovzhodne Slovenije; Črešnar, M., Kiszter, S., Mele, M., Peitler, K., Vintar, A., Eds.; Schild von Steier; Universalmuseum Joanneum, Archäologie & Münzkabinett, Zavod za Varstvo Kulturne Dediščine Slovenije: Graz, Austria; Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019; pp. 291–292. ISBN 9-783903-179240. [Google Scholar]
- Bitenc, B.P.; Knific, T. Interpretacija grobišča in najdb = Interpretation of burial ground and finds. In Sred-Njeveški Blejski Otok V Arheoloških Virih = Medieval Archaeology of Bled Island; Štular, B., Ed.; Opera Instituti Archaeologici Sloveniae; Založba ZRC: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2020; pp. 45–91. ISBN 978-961-05-0191-6. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, W. Handbuch des Speziellen Pflanzenbaues: Band 1; Parey: Berlin/Hamburg, Germany, 1972; pp. 53–79. ISBN 978-3-489-65610-4. [Google Scholar]
- Gillingham, J.; Griffiths, R.A. Medieval Britain: A Very Short Introduction; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 68–69. ISBN 0-19-285402-X. [Google Scholar]
- Hamerow, H. Early Medieval Settlements: The Archaeology of Rural Communities in North-West Europe 400–900; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 125–155. ISBN 978-0-19-924697-7. [Google Scholar]
- Arge, S.V.; Sveinbjarnardóttir, G.; Edwards, K.J.; Buckland, P.C. Viking and Medieval Settlement in the Faroes: People, Place and Environment. Hum. Ecol. 2005, 33, 597–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, C. Framing the Early Middle Ages. Europe and the Mediterranean 400–800; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; p. 245. ISBN 0-19-926449-x. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, A.; Lozovskaya, M.V.; Zvolinsky, V.P.; Teixeira da Silva, J. Effect of Soil and Climatic Conditions on Yield-Related Components Performance of Spring Wheat (Triticum aestivum, L.) Varieties in the Northern Bangladesh. Nat. Sci. J. Fund Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sveinsson, S.; Hermannsson, J. A Project Report Deliverable T2.1.3 A Farmer’s Handbook for Cereal Cultivation in the Northern Periphery and Artic Region 2017; pp. 7–9. Available online: https://cereal.interreg-npa.eu/subsites/CEREAL/Cereal_cultivation-Farmers_handbook-Report-NPA-Cereal-DT213-Version2.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2021).
- Taylor, D.; Cormack, B. Choice of cereal and pulse species and varieties. In Organic Cereals and Pulses; Younie, D., Taylor, B.R., Welsh, J.P., Wilkinson, J.M., Eds.; Chalcombe Publications: Welton, UK, 2002; pp. 9–28. ISBN 978-0-948617-47-8. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, B.M.S. English Seigniorial Agriculture, 1250–1450; Cambridge Studies in Historical Geography, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 218–224, 292, 309–346. ISBN 978-0-521-30412-2. [Google Scholar]
- Grafenauer, B. Poljedelsko Orodje. In Gospodarska in Družbena Zgodovina; Blaznik, P., Grafenauer, B., Vilfan, S., Eds.; Slovenska Akademija Znanosti in Umetnosti, Institut za Zgodovino-Sekcija za Občo in Narodno Zgodovino; Državna Založba Slovenije: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 1970; pp. 201–218. [Google Scholar]
- Štih, P. Bled Tisoč Let. Blejski Zbornik 2004; Dežman, J., Ed.; Didakta: Radovljica, Slovenia, 2004; pp. 7–34. ISBN 961-6463-87-X. [Google Scholar]
- Štih, P. Tisoč let od prve omembe Blejskega gradu (1011–2011) in začetki blejskega gospostva škofov iz Brik-sna. In Blejski Grad -1000 Let Prve Omembe; Vidic, M., Ed.; Muzejsko društvo Bled, Narodni Muzej Slovenije, Zavod za Kulturo Bled: Bled, Slovenia, 2011; pp. 8–27. ISBN 978-961-269-539-2. [Google Scholar]
- Štih, P. The Middle Ages between the Eastern Alps and the Northern Adriatic. Select Papers on Slovene Historiography and Medieval History; Brill: Leiden, The Neatherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 233–255. ISBN 978 90 04 18591 3. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, B. Medieval Germany 500–1300; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, T. A farewell to the market! Constructing a Carolingian subsistence economy east of the Rhine. Ruralia 2011, 8, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornik, F. Zgodovina Blejske Župnije; Mohorjeva Založba: Celje, Slovenia, 1990; ISBN 86-7577-011-1. [Google Scholar]
- Blaznik, P. Kolonizacija Poljanske Doline. Glas. Muz. Druš. Za Slov. 1938, 19, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Blaznik, P. Škofja Loka in Loško Gospostvo; Muzejsko Društvo Škofja Loka: Škofja Loka, Slovenia, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Štular, B. The Zbiva Web Application: A tool for Early Medieval archaeology of the Eastern Alps. In The AR-IADNE Impact; Richards, J.D., Niccolucci, F., Eds.; Archaeolingua: Budapest, Hungary, 2019; pp. 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M. Building Research Equipment with Free, Open-Source Hardware. Science 2012, 337, 1303–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štular, B.; Eichert, S.; Lozić, E. Airborne LiDAR Point Cloud Processing for Archaeology. Pipeline and QGIS Toolbox. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.D.; Niccolucci, F. (Eds.) The ARIADNE Impact; Archaeolingua: Budapest, Hungary, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).