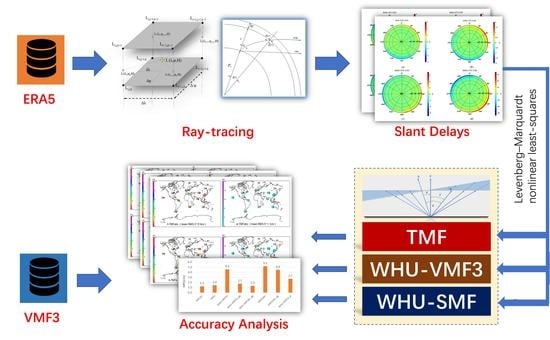
TMF: A GNSS Tropospheric Mapping Function for the Asymmetrical Neutral Atmosphere
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Ray-Tracing
2.1.1. Refractivity
2.1.2. Tropospheric Delay
2.1.3. ERA5 and Appropriate Land Cover Radius
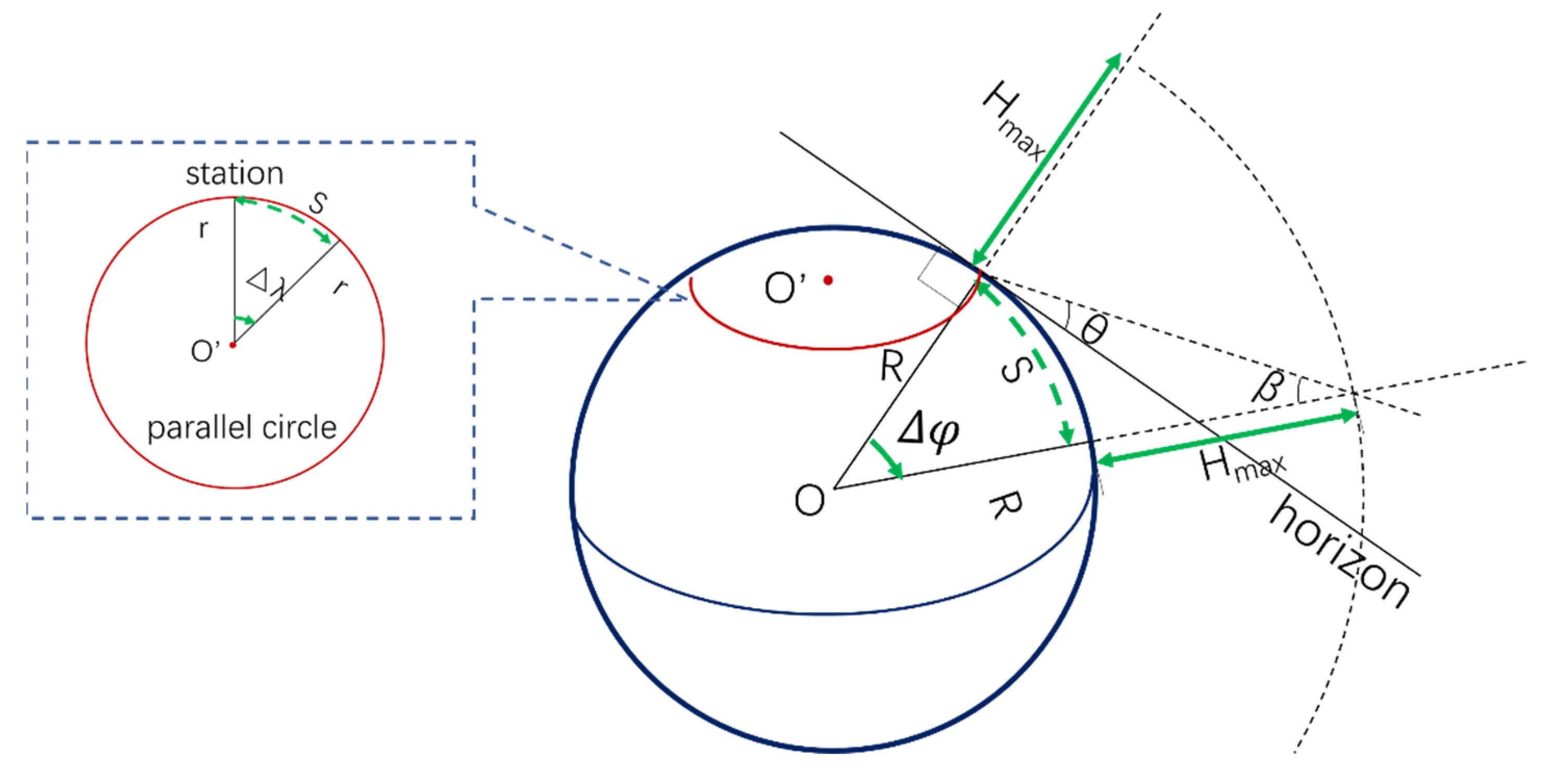
2.1.4. Eikonal Equation and 3D Ray-Tracing
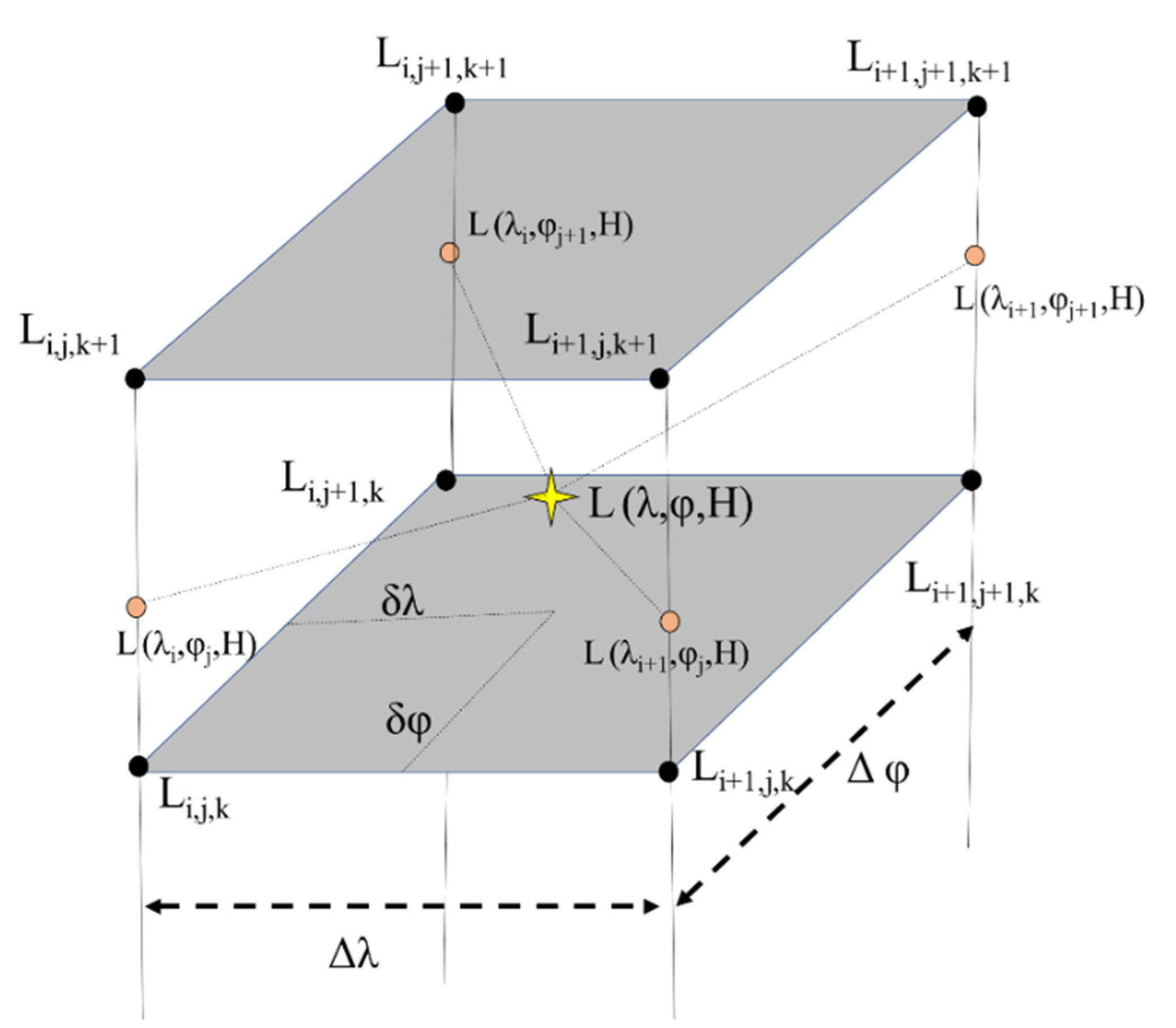
2.1.5. Interpolation of Meteorological Parameters
2.1.6. Height Transformation
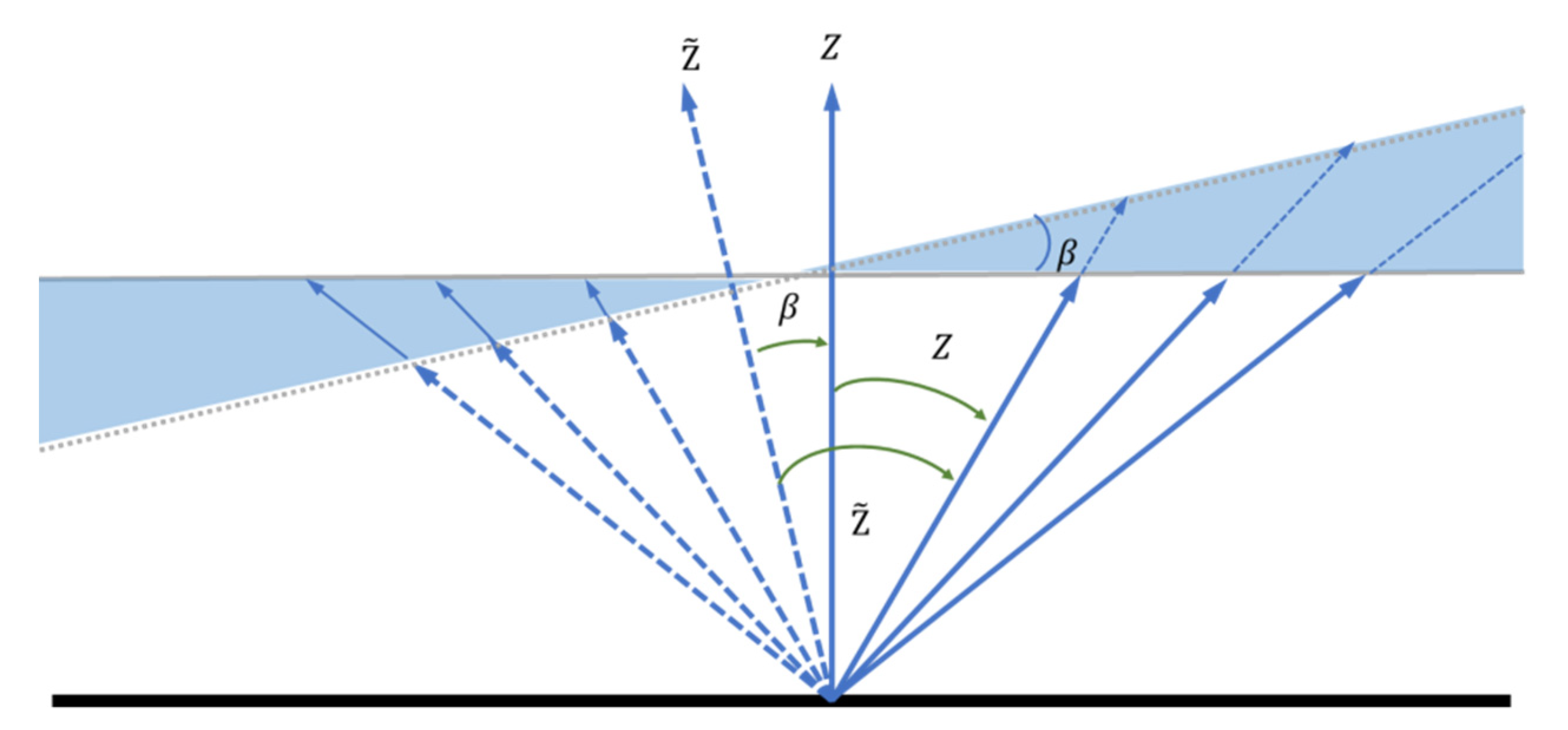
2.1.7. Asymmetsry Demonstration of Slant Delays
2.2. Construction of TMF
2.2.1. Tropospheric Mapping Function
2.2.2. The Definition of TMF
2.2.3. Fitting of TMF
2.3. Performance Test of TMF
3. Results
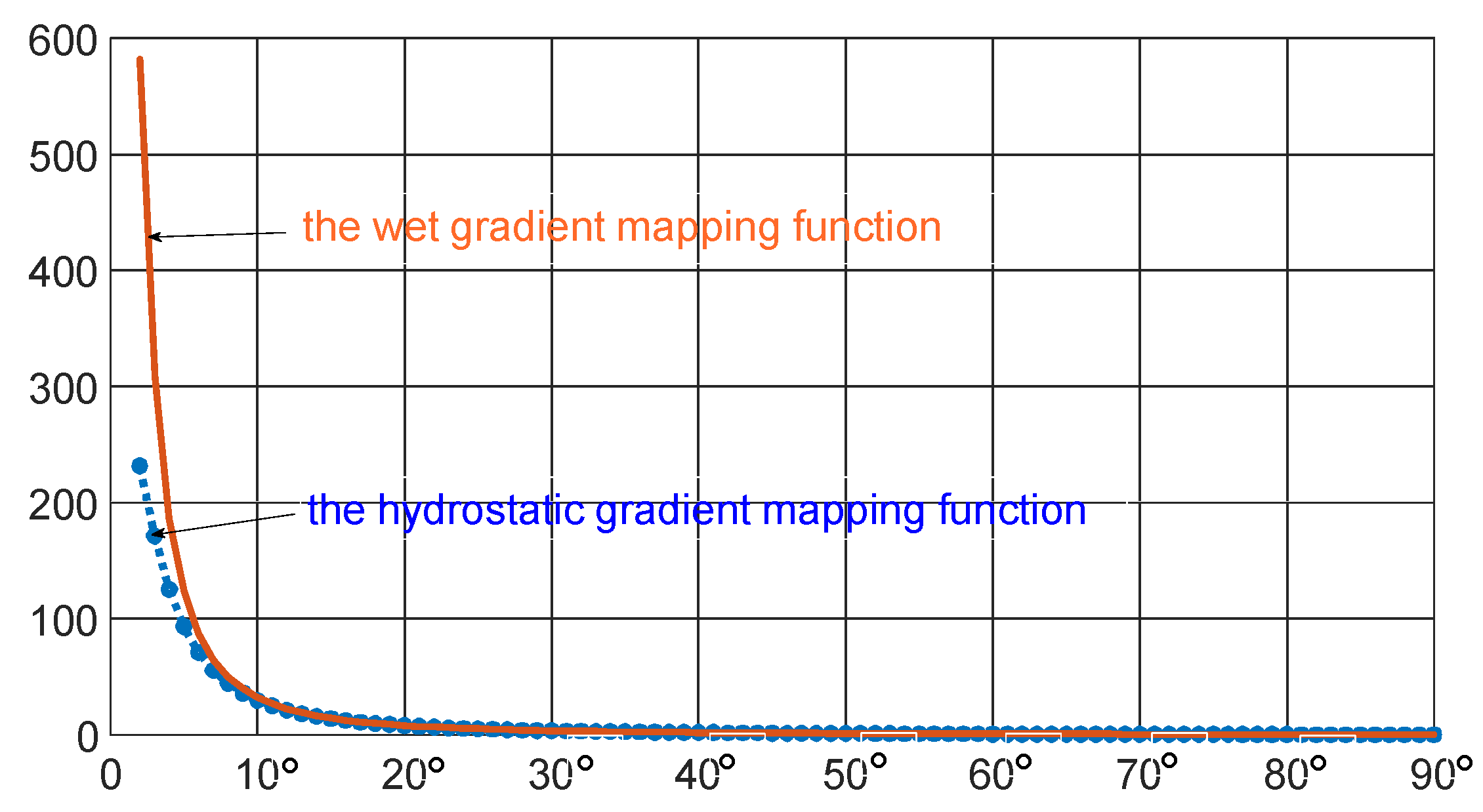
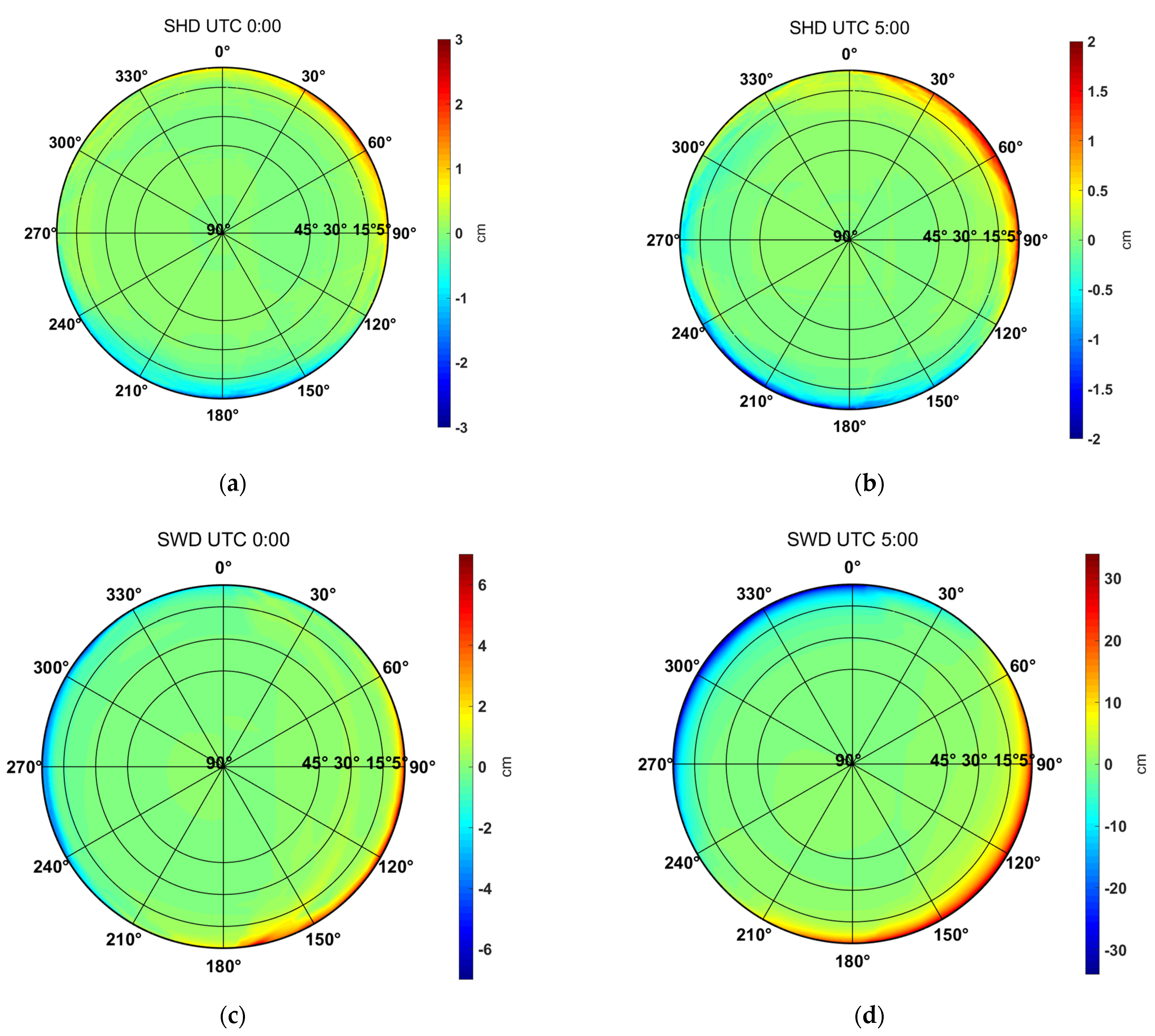
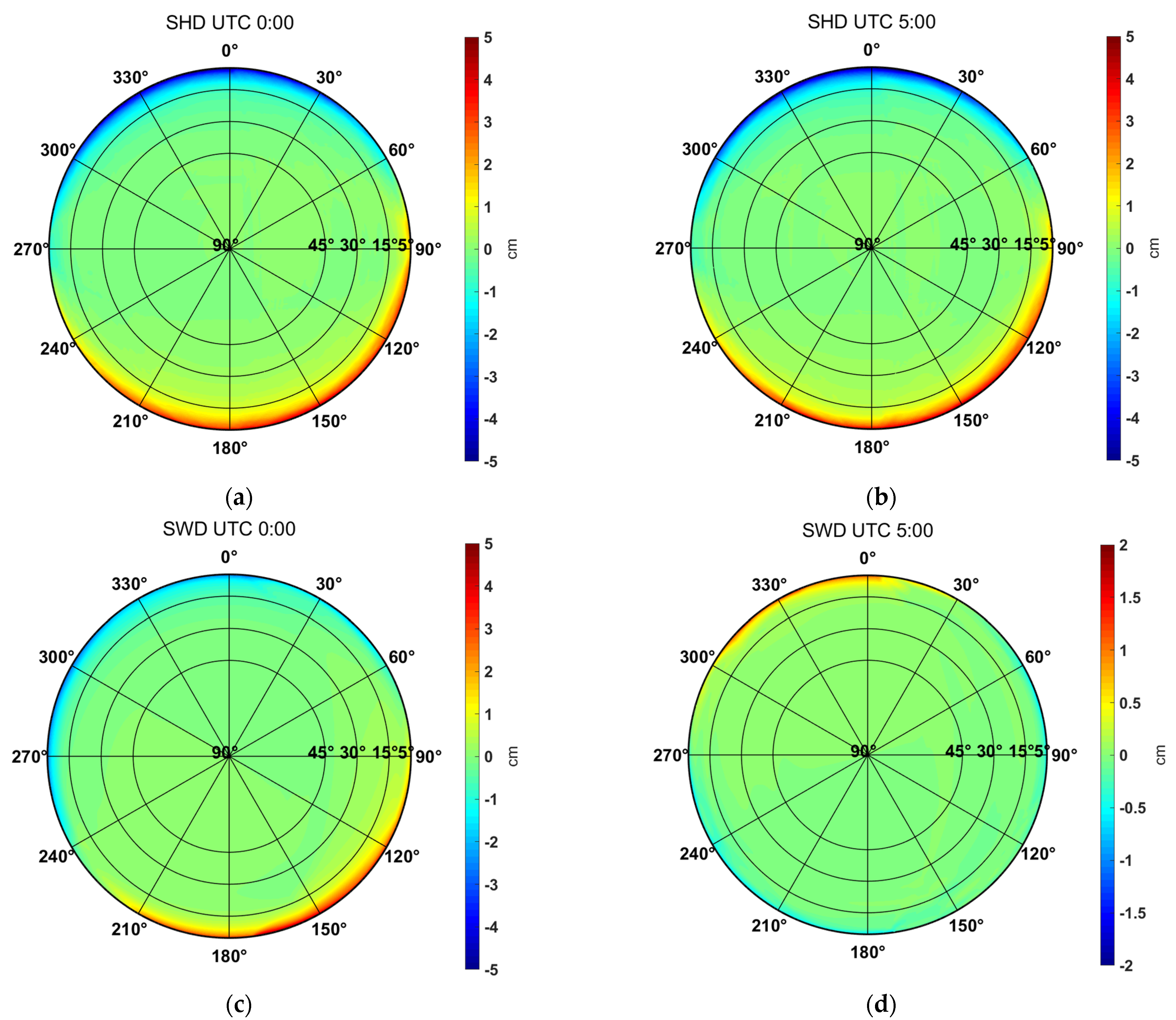
3.1. Tropospheric Delay Asymmetry
3.2. TMF Fitting
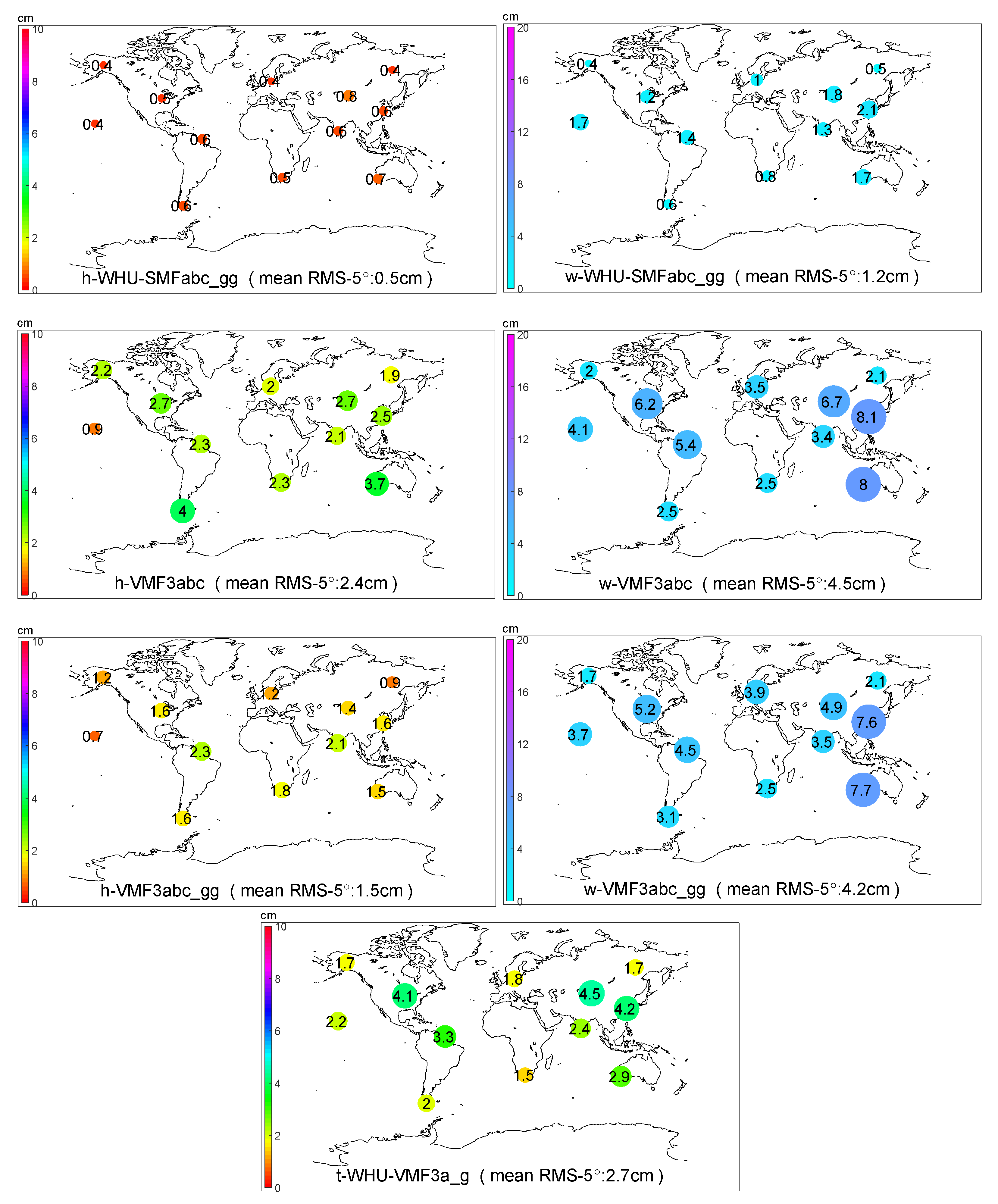
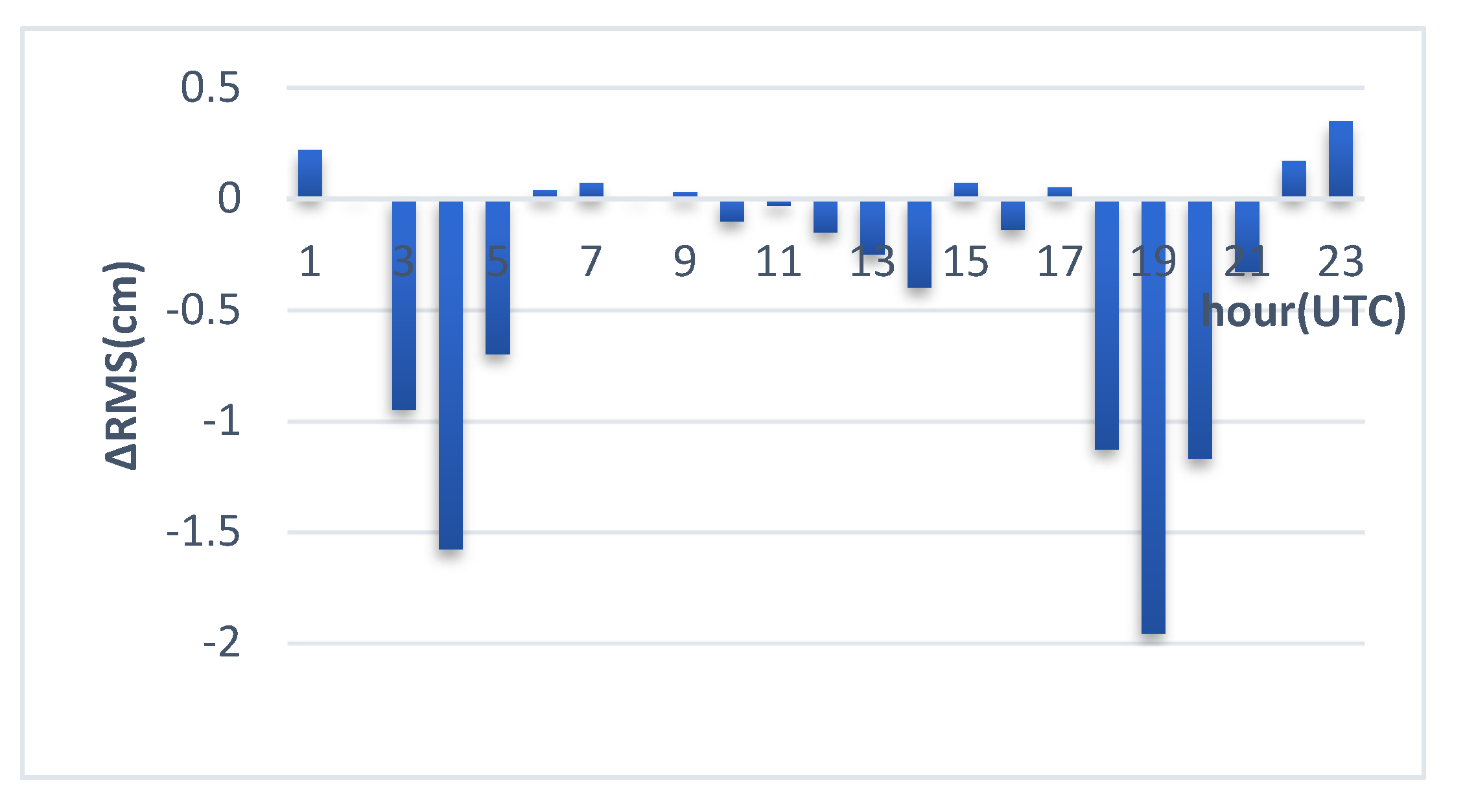
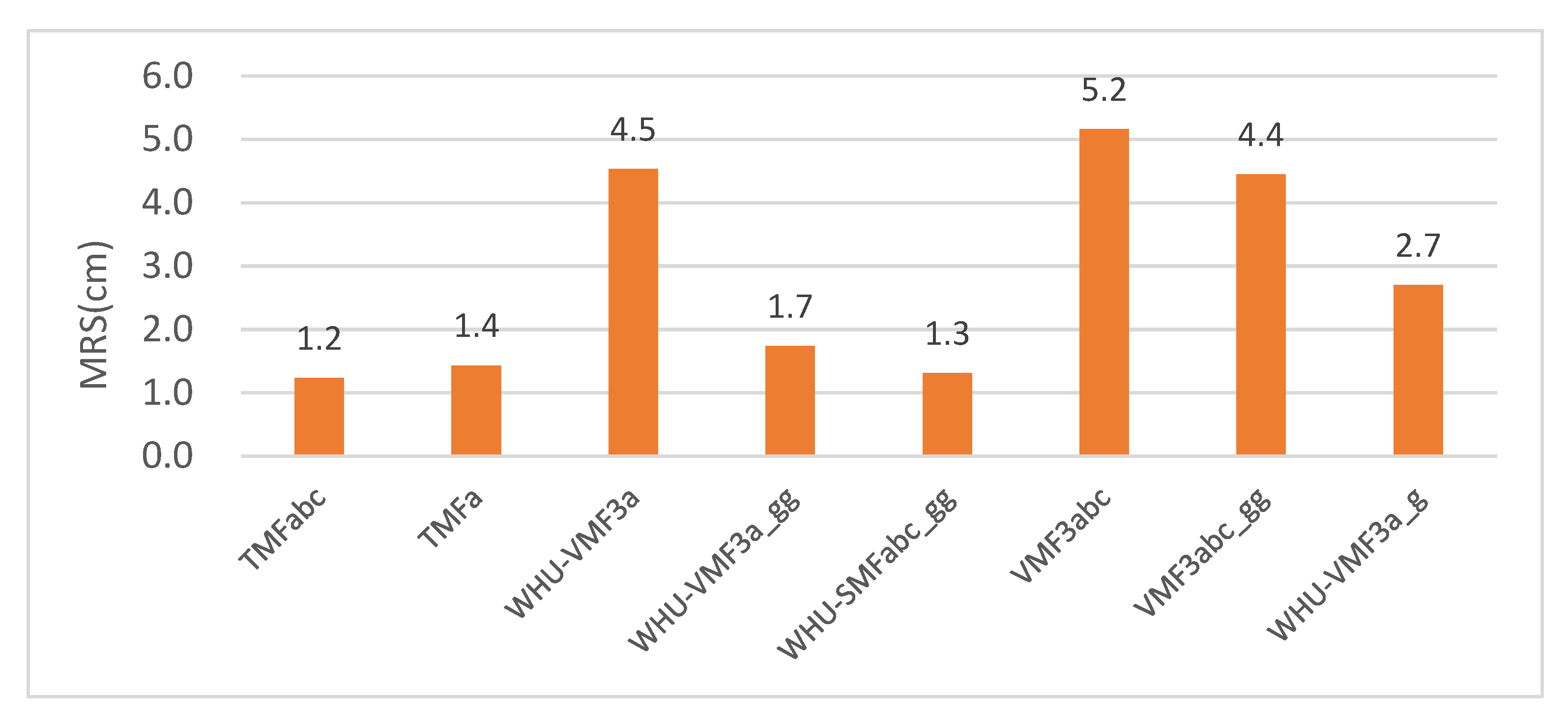
3.3. TMF Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, F.; Guo, J.; Meng, X.; Shi, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, D. Determination of Weighted Mean Temperature (Tm) Lapse Rate and Assessment of Its Impact on Tm Calculation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 155028–155037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D. The Study of the GNSS Tropospheric Zenith Delay Model and Mapping Function. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield, H. Two-quartic tropospheric refractivity profile for correcting satellite data. J. Geophys. Res. 1969, 74, 4487–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Atmospheric correction for the troposphere and stratosphere in radio ranging satellites. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 1972, 15, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.; Herring, T.; Shapiro, I.; Rogers, A.; Elgered, G. Geodesy by radio interferometry: Effects of atmospheric modeling errors on estimates of baseline length. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrada Baby, H.; Gole, P.; Lavergnat, J. A model for the tropospheric excess path length of radio waves from surface meteorological measurements. Radio Sci. 1988, 23, 1023–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifadis, I.I. The Atmospheric Delay of Radio Waves: Modeling the Elevation Dependence on a Global Scale; Technical Report 38L; Chalmers University of Technology: GÄoteborg, Sweden, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Askne, J.; Nordius, H. Estimation of tropospheric delay for microwaves from surface weather data. Radio Sci. 1987, 22, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Guo, J.; Chen, M.; Shi, J.; Zhou, L. Quantitative assessment of meteorological and tropospheric Zenith Hydrostatic Delay models. Adv. Space Res. 2016, 58, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COESA. U.S. Standard Atmosphere Supplements, 1966; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1966; pp. 101–102.
- Kirchengast, G.; Hafner, J.; Poetzi, W. The CIRA86aQ_UoG Model: An Extension of the CIRA-86 Monthly Tables Including Humidity Tables and a Fortran95 Global Moist Air Climatology Model; Institute for Meteorology and Geophysics, University of Graz: Graz, Austria, 1999; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Picone, J.; Hedin, A.; Drob, D.P.; Aikin, A. NRLMSISE-00 empirical model of the atmosphere: Statistical comparisons and scientific issues. JGR Space Phys. (1978–2012) 2002, 107, SIA 15-1–SIA 15-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, R.; Santos, M.; Langley, R.B. UNB neutral atmosphere models: Development and performance. In Proceedings of the ION NTM, Monterey, CA, USA, 18–20 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, A. Standard Temperature and Pressure. Ind. Heat. 2012, 80, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, J.; Möller, G.; Schindelegger, M.; Pain, G.; Weber, R. Development of an improved empirical model for slant delays in the troposphere (GPT2w). GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leandro, R.F.; Santos, M.C.; Langley, R.B. A North America wide area neutral atmosphere model for GNSS applications. Navigation 2009, 56, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RTCA. Minimum Operational Performance Standards for Global Positioning System/Wide Area Augmentation System Airborne Equipment; DO-229D; RTCA, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 13 December 2006; p. 564. [Google Scholar]
- Schüler, T. The TropGrid2 standard tropospheric correction model. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, C.; Shi, J.; Cao, N.; Zhang, B.; Yang, J. ITG: A New Global GNSS Tropospheric Correction Model. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Ou, J.; Chai, Y.; Li, Z.; Liou, Y.-A.; Wang, N. New versions of the BDS/GNSS zenith tropospheric delay model IGGtrop. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Wang, J.G.; Wang, A.H.; Ding, J.S.; Zhang, Y.Z. SHAtropE-A Regional Gridded ZTD Model for China and the Surrounding Areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tralli, D.M.; Lichten, S.M. Stochastic estimation of tropospheric path delays in global positioning system geodetic measurements. Bull. Géodésique 1990, 64, 127–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.R. Kinematic GNSS Tropospheric Estimation and Mitigation over a Range of Altitudes. Ph.D. Thesis, Newcastle University, Newcastle, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mousa, A.E.L.K.; Aboualy, N.; Sharaf, M.; Zahra, H.; Darrag, M. Tropospheric wet delay estimation using GNSS: Case study of a permanent network in Egypt. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2016, 5, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dach, R.; Lutz, S.; Walser, P.; Fridez, P. Bernese GNSS Software Version 5.2; University of Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2015; p. 854. [Google Scholar]
- Herring, T.A.; King, R.W.; Floyd, M.A.; McClusky, S.C. GAMIT Reference Manual Release 10.7; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Yao, Y.; Yao, W.; Zhang, S. GNSS-derived PWV and comparison with radiosonde and ECMWF ERA-Interim data over mainland China. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2018, 182, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Shen, Z.; Wan, M.; Li, L. Precipitable Water Vapor Converted From GNSS-ZTD and ERA5 Datasets for the Monitoring of Tropical Cyclones. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 87275–87290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Guo, J.; Meng, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y. An improved weighted mean temperature (T-m) model based on GPT2w with T-m lapse rate. GPS Solut. 2020, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriot, J.-P.; Peng, F. Beyond Mapping Functions and Gradients; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, J.W. Correction of Satellite Tracking Data for an Arbitrary Tropospheric Profile. Radio Sci. 1972, 7, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, T.A. Modeling Atmospheric Delays in the Analysis of Space Geodetic Data. In Refraction of Transatmospheric Signals in Geodesy; De Munck, J.C., Spoelstra, T.A., Eds.; The Netherlands Commission on Geodesy: Delft, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Niell, A.E. Global mapping functions for the atmosphere delay at radio wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res. [Solid Earth] 1996, 101, 3227–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niell, A.E. Preliminary evaluation of atmospheric mapping functions based on numerical weather models. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A 2001, 26, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Langley, R.B. A New Tropospheric Propagation Delay Mapping Function for Elevation Angles Down to 2 degrees. In Proceedings of the ION GPS 2003, Portland, OR, USA, 9–12 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Boehm, J.; Schuh, H. Vienna mapping functions in VLBI analyses. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehm, J.; Werl, B.; Schuh, H. Troposphere mapping functions for GPS and very long baseline interferometry from European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts operational analysis data. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, B02406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagler, K.; Schindelegger, M.; Böhm, J.; Krásná, H.; Nilsson, T. GPT2: Empirical slant delay model for radio space geodetic techniques. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landskron, D.; Bohm, J. VMF3/GPT3: Refined discrete and empirical troposphere mapping functions. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zus, F.; Dick, G.; Dousa, J.; Wickert, J. Systematic errors of mapping functions which are based on the VMF1 concept. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.B.; Holden, L.; Kealy, A.; Choy, S.; Hordyniec, P. Assessment of forecast Vienna Mapping Function 1 for real-time tropospheric delay modeling in GNSS. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1501–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, X.M.; Li, Z.S.; Zhang, S.T.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, J.L.; Yuan, H. The Performance of Different Mapping Functions and Gradient Models in the Determination of Slant Tropospheric Delay. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Herring, T.A. Effects of atmospheric azimuthal asymmetry on the analysis of space geodetic data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 20489–20502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Urquhart, L.; Steigenberger, P.; Heinkelmann, R.; Nafisi, V.; Schuh, H. A Priori Gradients in the Analysis of Space Geodetic Observations. In Reference Frames for Applications in Geosciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Landskron, D.; Bohm, J. Refined discrete and empirical horizontal gradients in VLBI analysis. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bar-Sever, Y.E.; Kroger, P.M.; Borjesson, J.A. Estimating horizontal gradients of tropospheric path delay with a single GPS receiver. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 5019–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothacher, M.; Springer, T.A.; Schaer, S.; Beutler, G. Processing Strategies for Regional GPS Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Meindl, M.; Schaer, S.; Hugentobler, U.; Beutler, G. Tropospheric gradient estimation at CODE: Results from global solutions. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 82, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Heinkelmann, R.; Nilsson, T.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. GNSS tropospheric gradients with high temporal resolution and their effect on precise positioning. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwabuchi, T.; Miyazaki, S.i.; Heki, K.; Naito, I.; Hatanaka, Y. An impact of estimating tropospheric delay gradients on tropospheric delay estimations in the summer using the Japanese nationwide GPS array. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zus, F.; Douša, J.; Kačmařík, M.; Václavovic, P.; Balidakis, K.; Dick, G.; Wickert, J. Improving GNSS Zenith Wet Delay Interpolation by Utilizing Tropospheric Gradients: Experiments with a Dense Station Network in Central Europe in the Warm Season. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zus, F.; Lu, C.; Ning, T.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Retrieving high-resolution tropospheric gradients from multiconstellation GNSS observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 4173–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.L.; Elgered, G.; Niell, A.E.; Kuehn, C.E. Ground-based measurement of gradients in the “wet” radio refractivity of air. Radio Sci. 1993, 28, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Schuh, H. Troposphere gradients from the ECMWF in VLBI analysis. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Heise, S.; Wickert, J.; Bender, M. Real-time GPS sensing of atmospheric water vapor: Precise point positioning with orbit, clock and phase delay corrections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3615–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D. A building method for a troposphere mapping function model representing atmospheric anisotropy (patent of China). ZL201610831005.8, 19 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Barriot, J.P.; Xu, G.; Hopuare, M. Modeling the Slant Wet Delays From One GPS Receiver as a Series Expansion With Respect to Time and Space: Theory and an Example of Application for the Tahiti Island. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 7520–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, C.S. Correction of laser tracking data for the effects of horizontal refractivity gradients. Appl. Opt. 1977, 16, 2427–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, D.; Shi, J.; Zhou, M. Using Ray-Tracing to Analyse the Precision of Three Classical Tropospheric Mapping Functions in China. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Uni. 2015, 40, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Quart. J. R. Met. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.K.; Weintraub, S. The constants in the equation for atmospheric refractive index at radio frequencies. Proc. IRE 1953, 41, 1035–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nafisi, V.; Madzak, M.; Bohm, J.; Ardalan, A.A.; Schuh, H. Ray-traced tropospheric delays in VLBI analysis. Radio Sci. 2012, 47, RS2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, V.; Urquhart, L.; Santos, M.C.; Nievinski, F.G.; Bohm, J.; Wijaya, D.D.; Schuh, H.; Ardalan, A.A.; Hobiger, T.; Ichikawa, R. Comparison of ray-tracing packages for troposphere delays. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüeger, J.M. Refractive index formulae for radio waves. In Proceedings of the FIG XXII International Congress, Washington, DC, USA, 19–26 April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, J.M.; Hobbs, P.V. Atmospheric Science: An Introductory Survey; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; Volume 92. [Google Scholar]
- WMO. Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation, 7th ed.; Secretariat of the World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, P.; Li, F.; Yan, J.; Zhang, F.; Barriot, J.-P. Assessment of the Accuracy of the Saastamoinen Model and VMF1/VMF3 Mapping Functions with Respect to Ray-Tracing from Radiosonde Data in the Framework of GNSS Meteorology. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Met. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobiger, T.; Ichikawa, R.; Koyama, Y.; Kondo, T. Fast and accurate ray-tracing algorithms for real-time space geodetic applications using numerical weather models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, V. Modeling the Neutral-Atmospheric Propagation Delay in Radiometric Space Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton, NB, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, E.L.; Chandra, S.; Schoeberl, M.; Barnett, J.J. Monthly Mean Global Climatology of Temperature, Wind, Geopotential Height, and Pressure for 0–120 km; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1988.
- Younes, S.A.M. Improved dry tropospheric propagation delay mapping function for GPS measurements in Egypt. J. Spat.Sci. 2014, 59, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Moritz, H. Physical Geodesy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, A.; Ruffini, G.; Rius, A. 4D tropospheric tomography using GPS slant wet delays. Ann. Geophys. Atmos. Hydrosph. Space Sci. 2000, 18, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, S.; McClusky, S.; Koulali, A.; Tregoning, P. A directional model of tropospheric horizontal gradients in Global Positioning System and its application for particular weather scenarios. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 4401–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Scheme | Resolution of ERA5 | Number of Data for Fitting | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Temporal | Pressure Levels | Elevations × Azimuths | |
| 1 | 0.25° × 0.25° | 1-hour1y | 137 | 87 × 360 |
| 2 | 0.25° × 0.25° | 1-hour1y | 137 | 18 × 24 |
| 3 | 1° × 1° | 1-hour1y | 137 | 87 × 360 |
| 4 | 1° × 1° | 1-hour1y | 137 | 18 × 24 |
| Code | Elevations | Azimuths | Determination of | Estimation of Gradient | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b, c | ||||
| TMFabc | 18 | 8 | LS | LS | no |
| TMFa | 18 | 8 | LS | VMF3 ① | no |
| WHU-VMF3a ② | 1 | 8 | mean | VMF3 ① | no |
| WHU-VMF3a_g ② | 1 (18) ③ | 8 | mean | VMF3 ① | total |
| WHU-VMF3a_gg ② | 1 (18) ③ | 8 | mean | VMF3 ① | h,w ④ |
| WHU-SMFabc_gg ② | 18 | 8 | LS | LS | h,w ④ |
| VMF3abc | 1 | 8 [40] | VMF3 ① | VMF3 ① | no |
| VMF3abc_gg | 1 | 16 [46] | VMF3 ① | VMF3 ① | VMF3 ① |
| UTC | Elevation Angle | SHD (m) | SWD (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Range | RMS | Mean | Range | RMS | ||
| 0:00 | 5° | 23.135 | 0.040 | 0.012 | 3.515 | 0.119 | 0.037 |
| 10° | 12.706 | 0.015 | 0.004 | 1.850 | 0.029 | 0.007 | |
| 15° | 8.703 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 1.255 | 0.018 | 0.004 | |
| 20° | 6.636 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.953 | 0.012 | 0.003 | |
| 5:00 | 5° | 23.102 | 0.039 | 0.011 | 3.894 | 0.678 | 0.245 |
| 10° | 12.689 | 0.015 | 0.004 | 2.078 | 0.245 | 0.080 | |
| 15° | 8.691 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 1.410 | 0.118 | 0.037 | |
| 20° | 6.627 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 1.071 | 0.066 | 0.021 | |
| UTC | Elevation Angle | SHD (m) | SWD (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Range | RMS | Mean | Range | RMS | ||
| 5° | 23.525 | 0.100 | 0.034 | 1.632 | 0.075 | 0.026 | |
| 0:00 | 10° | 12.896 | 0.035 | 0.012 | 0.858 | 0.024 | 0.008 |
| 15° | 8.828 | 0.017 | 0.006 | 0.581 | 0.012 | 0.004 | |
| 20° | 6.730 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.440 | 0.007 | 0.002 | |
| 5° | 23.492 | 0.100 | 0.035 | 1.540 | 0.022 | 0.007 | |
| 5:00 | 10° | 12.876 | 0.036 | 0.012 | 0.806 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
| 15° | 8.814 | 0.019 | 0.006 | 0.545 | 0.003 | 0.001 | |
| 20° | 6.719 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.414 | 0.002 | 0.000 | |
| Elevation Angle | ΔSHD (cm) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bias1 | RMS1 | bias2 | RMS2 | bias3 | RMS3 | bias4 | RMS4 | |
| 3°–15° | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.3 | −0.3 | 0.7 | −0.3 | 0.7 |
| 15°–89° | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | −0.2 | 0.3 | −0.2 | 0.3 |
| Elevation Angle | ΔSWD (cm) | |||||||
| bias1 | RMS1 | bias2 | RMS2 | bias3 | RMS3 | bias4 | RMS4 | |
| 3°–15° | 0.0 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 8.0 | 0.0 | 7.9 |
| 15°–89° | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 2.8 | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| Code | BIAS (cm) | RMS (cm) | BIAS at 5° (cm) | RMS at 5° (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMFabc | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.5 |
| TMFa | 0.0 | 0.2 | −0.1 | 0.6 |
| WHU-VMF3a | 0.0 | 0.6 | −0.2 | 2.0 |
| WHU-VMF3a_gg | 0.0 | 0.2 | −0.2 | 0.7 |
| WHU-SMFabc_gg | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| VMF3abc | −0.1 | 0.8 | −0.9 | 2.4 |
| VMF3abc_gg | −0.1 | 0.5 | −0.9 | 1.5 |
| Code | BIAS (cm) | RMS (cm) | BIAS at 5° (cm) | RMS at 5° (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMFabc | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| TMFa | 0.0 | 0.5 | −0.1 | 1.3 |
| WHU-VMF3a | 0.0 | 1.3 | −0.3 | 4.1 |
| WHU-VMF3a_gg | 0.0 | 0.6 | −0.3 | 1.6 |
| WHU-SMFabc_gg | 0.0 | 0.5 | −0.1 | 1.2 |
| VMF3abc | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 4.5 |
| VMF3abc_gg | 0.0 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 4.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Guo, J.; Fang, T.; Wei, N.; Mei, W.; Zhou, L.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y. TMF: A GNSS Tropospheric Mapping Function for the Asymmetrical Neutral Atmosphere. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132568
Zhang D, Guo J, Fang T, Wei N, Mei W, Zhou L, Yang F, Zhao Y. TMF: A GNSS Tropospheric Mapping Function for the Asymmetrical Neutral Atmosphere. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(13):2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132568
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Di, Jiming Guo, Tianye Fang, Na Wei, Wensheng Mei, Lv Zhou, Fei Yang, and Yinzhi Zhao. 2021. "TMF: A GNSS Tropospheric Mapping Function for the Asymmetrical Neutral Atmosphere" Remote Sensing 13, no. 13: 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132568
APA StyleZhang, D., Guo, J., Fang, T., Wei, N., Mei, W., Zhou, L., Yang, F., & Zhao, Y. (2021). TMF: A GNSS Tropospheric Mapping Function for the Asymmetrical Neutral Atmosphere. Remote Sensing, 13(13), 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132568