Satellite Retrieval of Air Pollution Changes in Central and Eastern China during COVID-19 Lockdown Based on a Machine Learning Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
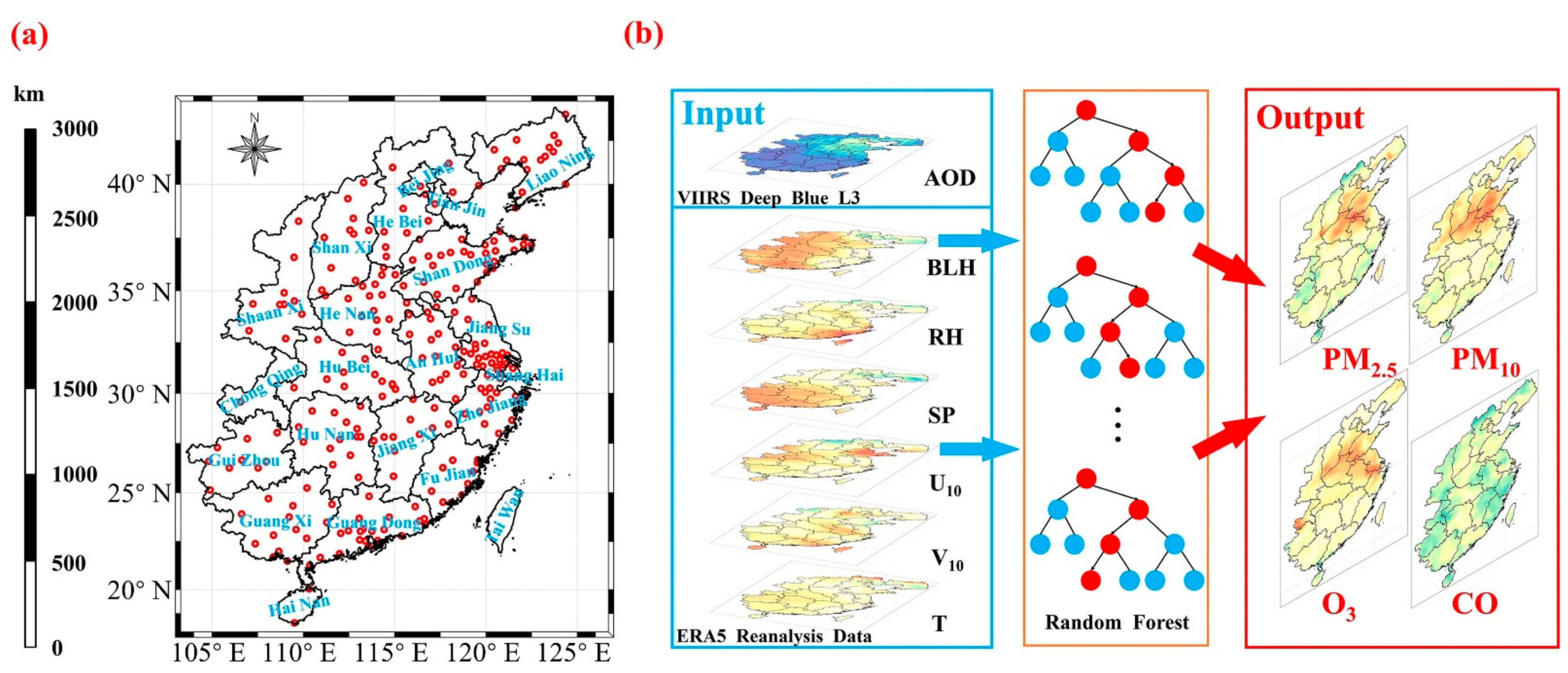
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Description
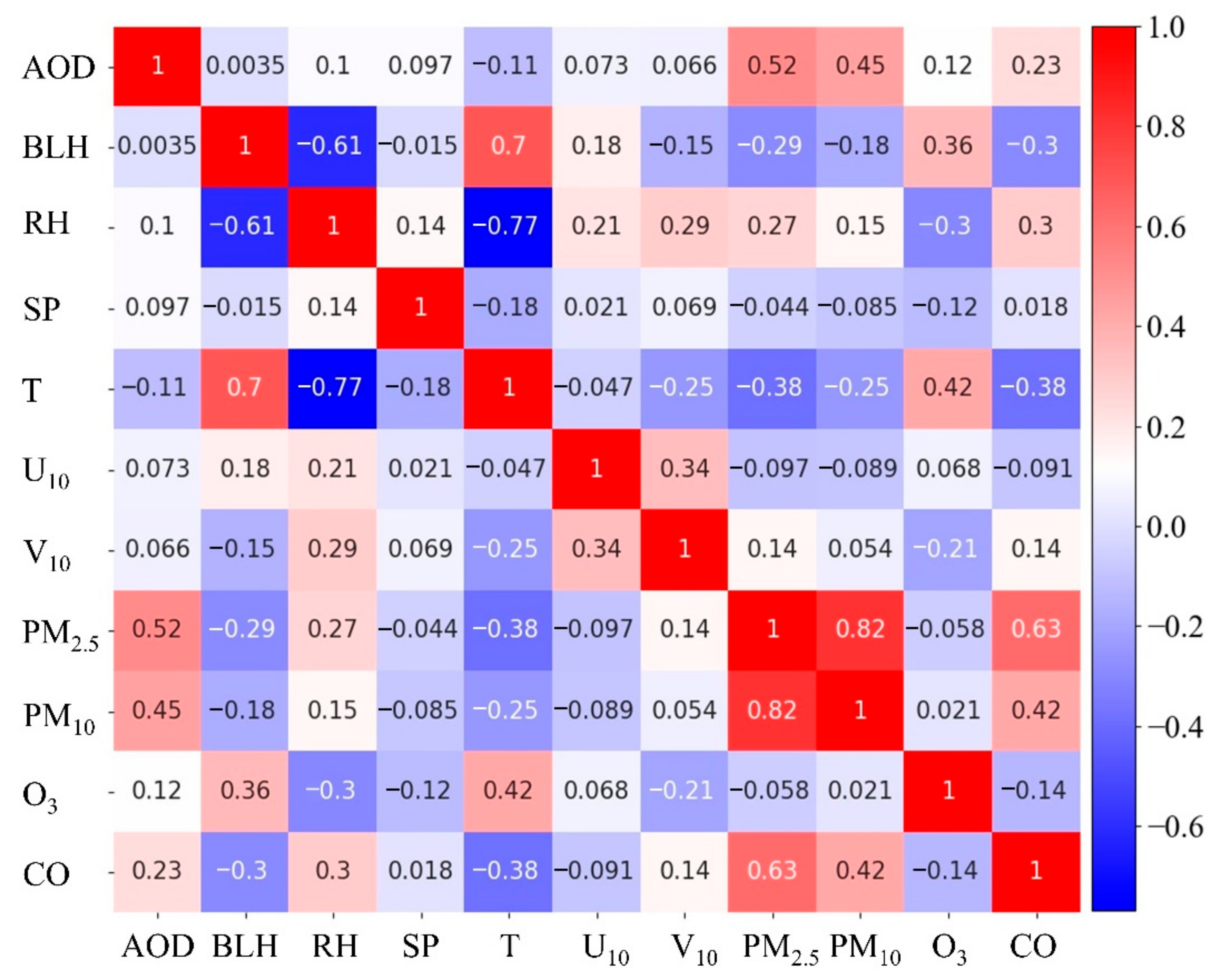
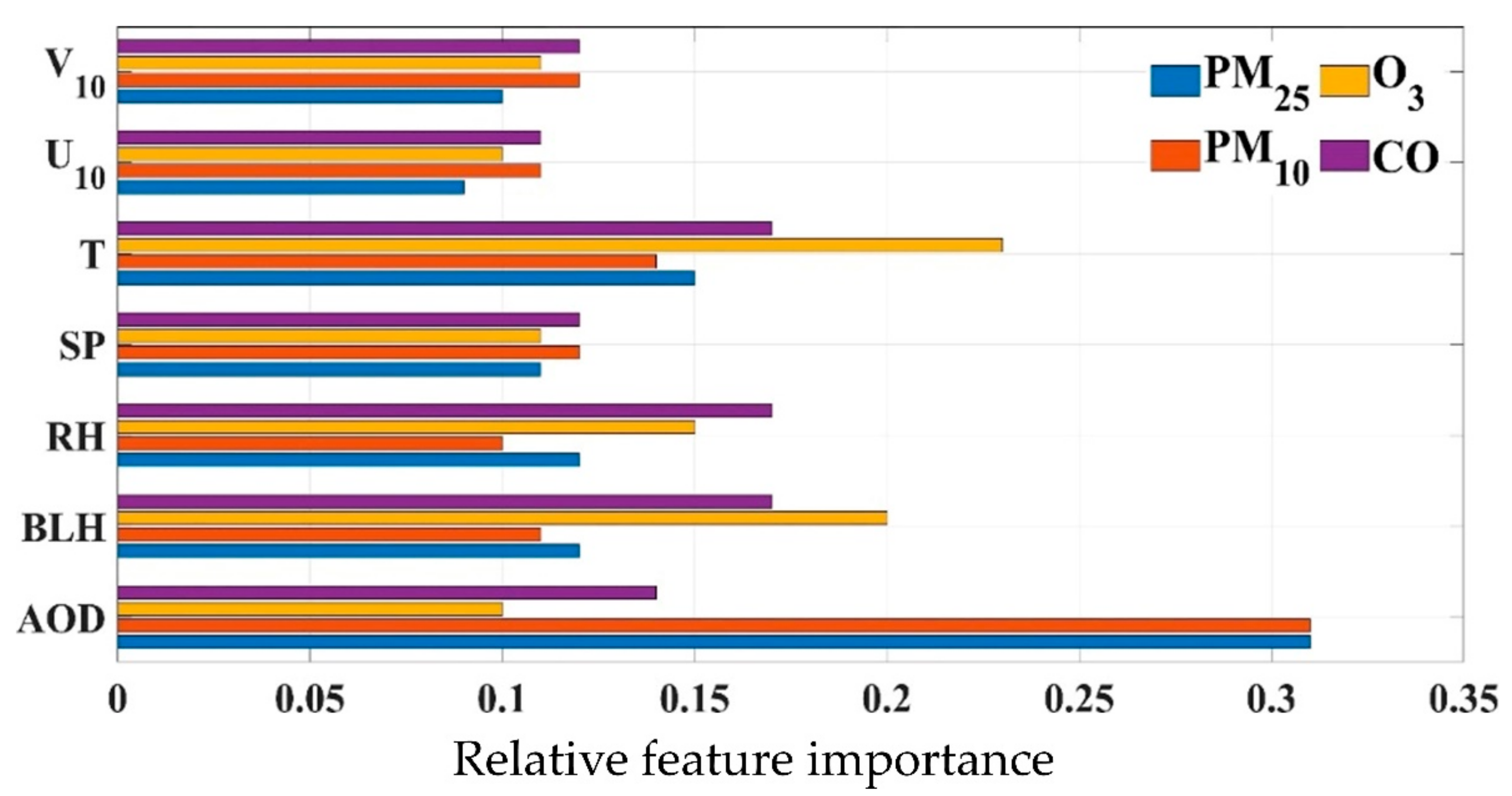
2.3. ML Algorithm
3. Results and Discussion
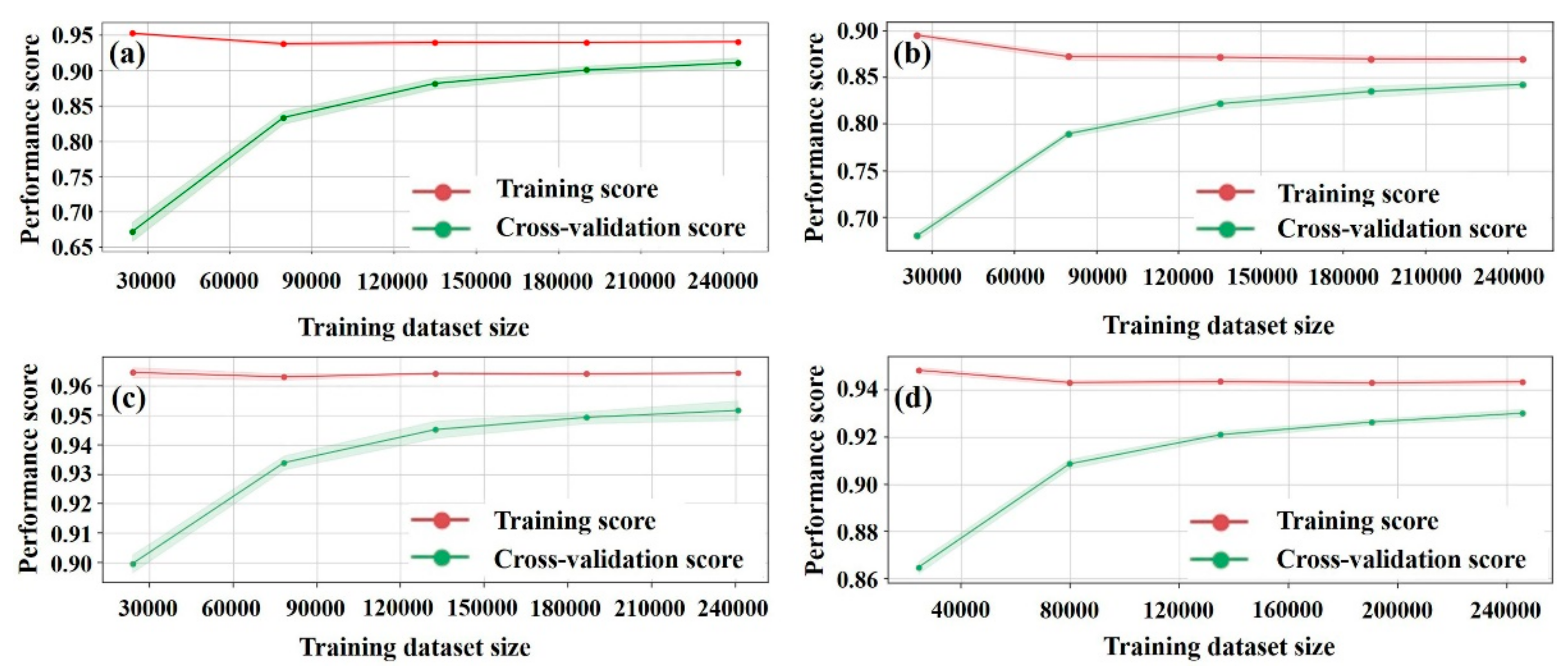
3.1. Evaluation of Model Performance
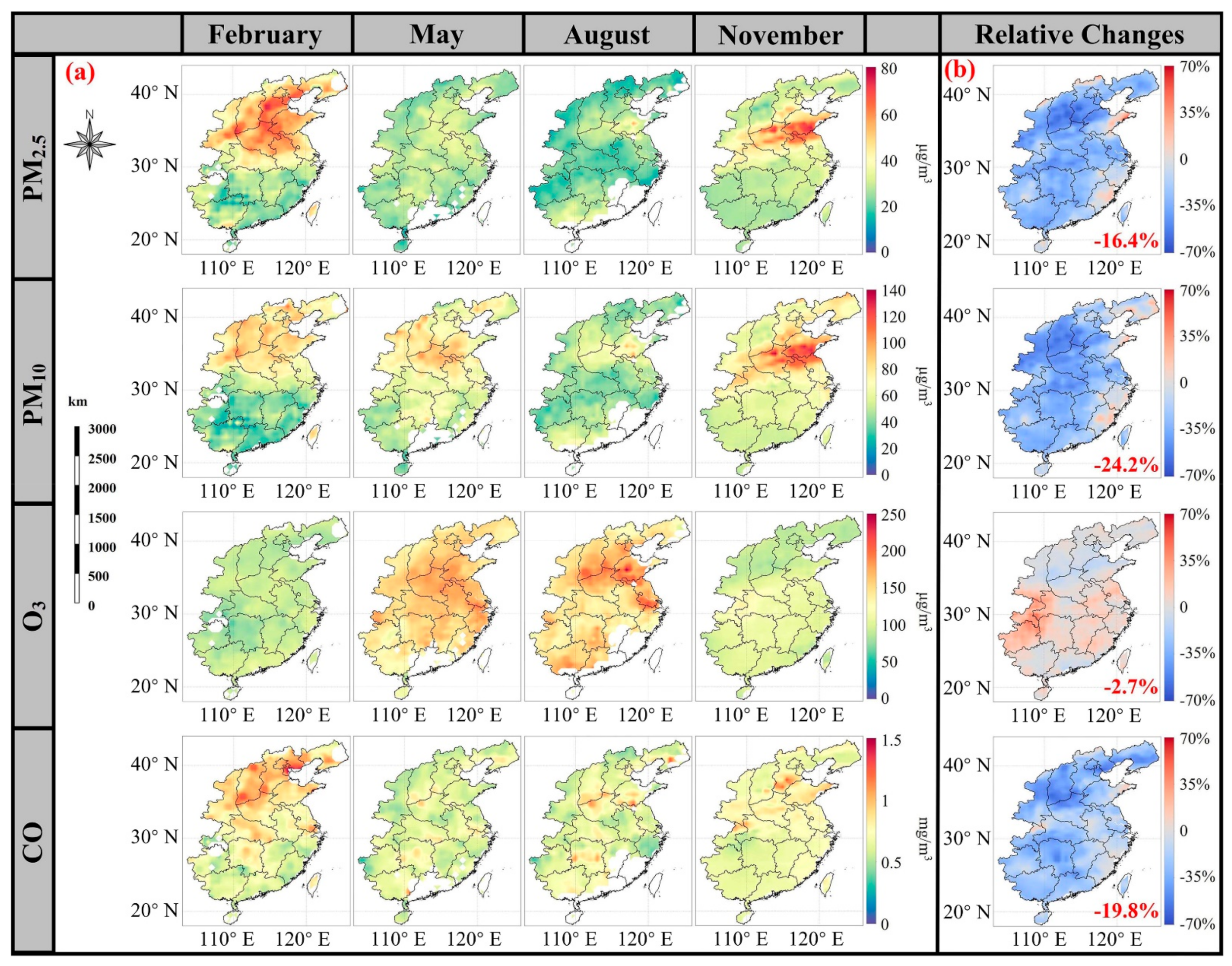
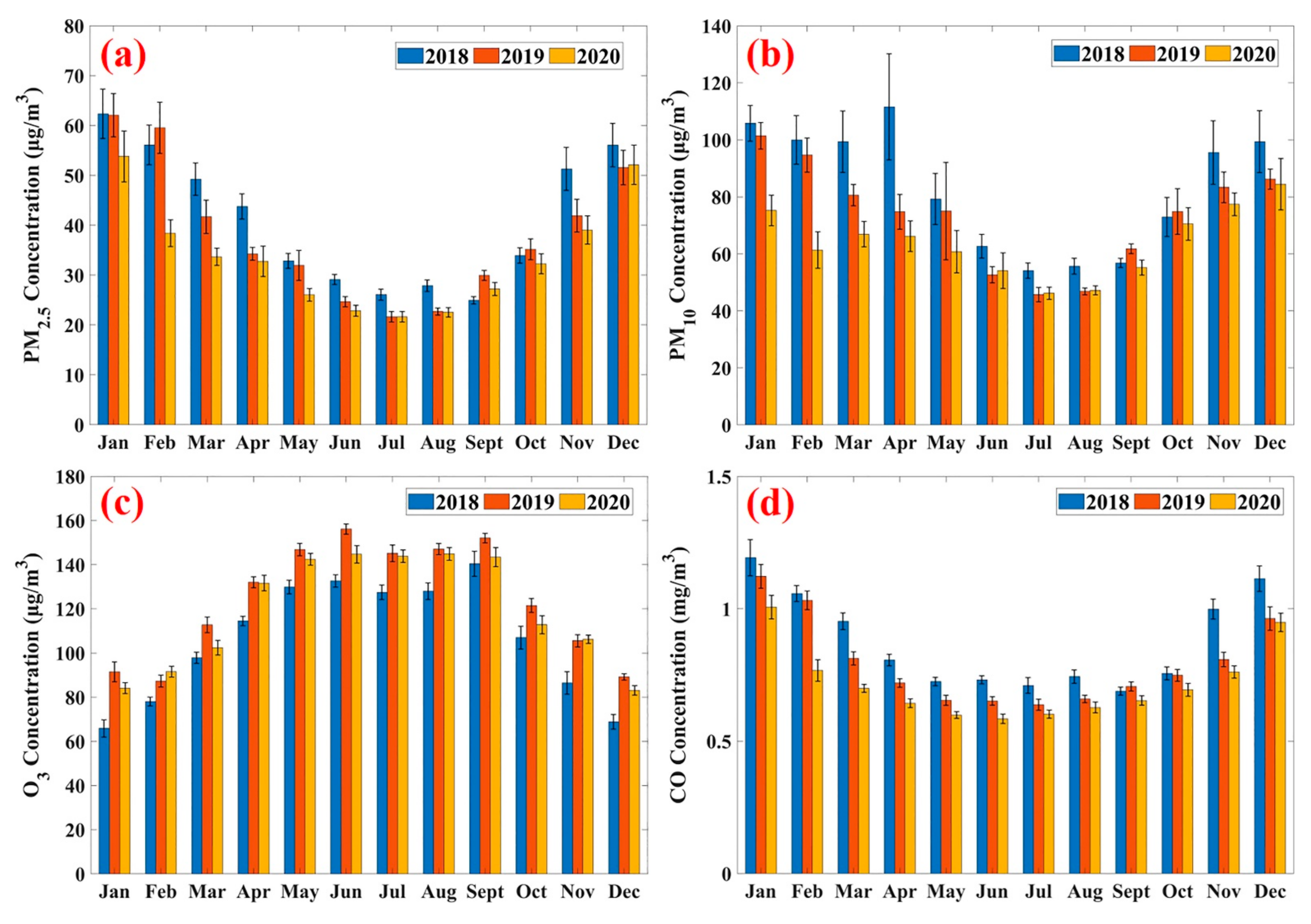
3.2. Annual Changes in Air Pollutants in 2020 Compared to 2018 and 2019
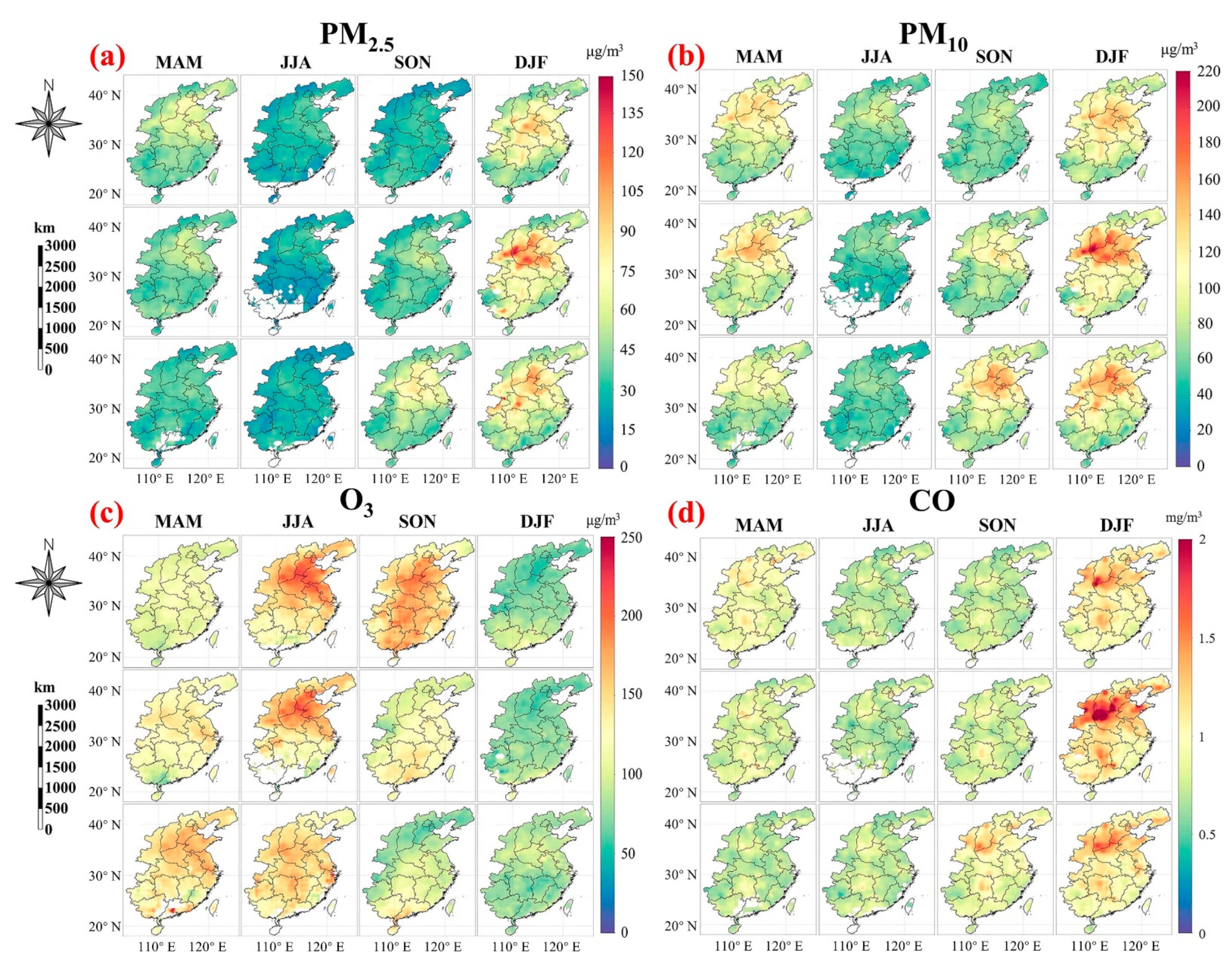
3.3. Seasonal Changes in Air Pollutants in 2020 Compared to 2018 and 2019
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, R.; Mao, H.; Wu, L.; He, J.; Ren, P.; Li, X. The evaluation of emission control to PM concentration during Beijing APEC in 2014. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.; Jin, T.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.; et al. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese State Council. Action Plan on Air Pollution Prevention and Control 2013. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2013-09/12/content_2486773.htm (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, W. The influence of multiple environmental regulations on haze pollution: Evidence from China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yin, D.; Yu, Y.; Kang, S.; Qin, D.; Dong, L. PM2.5 and O3 pollution during 2015–2019 over 367 Chinese cities: Spatiotemporal variations, meteorological and topographical impacts. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Zhu, J.; Shah, V.; Shen, L.; Bates, K.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, S. A two-pollutant strategy for improving ozone and particulate air quality in China. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, J.; Liao, H.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X. Meteorological influences on PM2.5 and O3 trends and associated health burden since China’s clean air actions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese State Council. Three-Year Action Plan on Defending the Blue Sky. 2018. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2018-07/03/content_5303158.htm (accessed on 10 May 2021). (In Chinese)
- Bauwens, M.; Compernolle, S.; Stavrakou, T.; Müller, J.; van Gent, J.; Eskes, H.; Levelt, P.F.; van der A., R.; Veefkind, J.P.; Vlietinck, J.; et al. Impact of coronavirus outbreak on NO2 pollution assessed using TROPOMI and OMI observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; van der A., R.J.; Eskes, H.J.; Mijling, B.; Stavrakou, T.; van Geffen, J.H.G.M.; Veefkind, J.P. NOx emissions reduction and rebound in China due to the COVID-19 crisis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, S.M.; Huang, W.-S.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chang, K.-E.; Lin, T.-H.; Wang, S.-H.; Lin, N.-H. Long-range air pollution transport in East Asia during the first week of the COVID-19 lockdown in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Gao, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, D.; Qi, X.; Tang, R.; Wang, J.; Ren, C.; Nie, W.; et al. Enhanced secondary pollution offset reduction of primary emissions during COVID-19 lockdown in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Du, R.; Teng, X.; Hu, R.; Yuan, Q.; Tang, S.; Ren, C.; Huang, X.; Xu, L.; et al. Chemistry of Atmospheric Fine Particles During the COVID-19 pandemic in a megacity of eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.; Zhang, A. Does lockdown reduce air pollution? Evidence from 44 cities in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lei, L.; Zhou, W.; Chen, C.; He, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Ji, D.; et al. A chemical cocktail during the COVID-19 outbreak in Beijing, China: Insights from six-year aerosol particle composition measurements during the Chinese New Year holiday. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.; Bilal, M.; Ali, A.; Qiu, Z. Air pollution scenario over China during COVID-19. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Ge, J.; Chu, X.; Wang, J. Regional differences in spatial spillover and hysteresis effects: A theoretical and empirical study of environmental regulations on haze pollution in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Huang, R.; Ge, X.; Huang, X.; Hu, J.; Duan, Y.; Zou, Z.; Liu, X.; Lehmann, M.F. Puzzling haze events in China during the coronavirus (COVID-19) shutdown. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hites, R.A.; Lehman, D.C.; Salamova, A.; Venier, M. Temporal environmental hysteresis: A definition and implications for polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Tani, H.; Zhong, G.; Sun, Z. Study on spatial distribution of crop residue burning and PM2.5 change in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, I.-C.; Lee, C.-L.; Huang, H.-C. A new conceptual model for quantifying transboundary contribution of atmospheric pollutants in the East Asian Pacific rim region. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Ho, C.-H.; Lee, Y.G.; Choi, H.-J.; Song, C.-K. Influence of transboundary air pollutants from China on the high-PM10 episode in Seoul, Korea for the period October 16–20, 2008. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lary, D.; Alavi, A.H.; Gandomi, A.; Walker, A.L. Machine learning in geosciences and remote sensing. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y.C.; Zhao, W.; Bi, J. Spatiotemporal distributions of surface ozone levels in China from 2005 to 2017: A machine learning approach. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L.; Cribb, M. Estimating 1-km-resolution PM2.5 concentrations across China using the space-time random forest approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Shen, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, M. Spatiotemporal prediction of continuous daily PM2.5 concentrations across China using a spatially explicit machine learning algorithm. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 155, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2019. 2019. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2019/indexeh.htm (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Chen, G.; Li, S.; Knibbs, L.; Hamm, N.; Cao, W.; Li, T.; Guo, J.; Ren, H.; Abramson, M.J.; Guo, Y. A machine learning method to estimate PM2.5 concentrations across China with remote sensing, meteorological and land use information. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Cao, W.; Ren, H.; Knibbs, L.; Abramson, M.J.; Guo, Y. Spatiotemporal patterns of PM10 concentrations over China during 2005–2016: A satellite-based estimation using the random forests approach. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, Z.M.; Linder, F.J. edarf: Exploratory data analysis using random forests. J. Open Source Softw. 2016, 1, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vu, T.V.; Shi, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Wang, S.; Harrison, R.M. Assessing the impact of clean air action on air quality trends in Beijing using a machine learning technique. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11303–11314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Weng, F.; Li, Z. Satellite-based PM2.5 estimation directly from reflectance at the top of the atmosphere using a machine learning algorithm. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 208, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, C.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Y. Atmospheric inverse estimates of CO emissions from Zhengzhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Li, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Luan, Q.; Guo, J. Abnormally shallow boundary layer associated with severe air pollution during the COVID-19 lockdown in China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL090041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Air Pollutant Type | Rate of Change (2018–2019) Unit: μg/m3/day | Rate of Change (2019–2020) Unit: μg/m3/day | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site Measurement | Model Prediction | Site Measurement | Model Prediction | |
| PM2.5 | −0.0145 | −0.0153 | −0.0209 | −0.0215 |
| PM10 | −0.0276 | −0.0393 | −0.0324 | −0.0439 |
| O3 | 0.0235 | 0.0349 | −0.0364 | −0.0337 |
| CO | −0.2551 | −0.2653 | −0.3082 | −0.3038 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Bai, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, T.; He, X. Satellite Retrieval of Air Pollution Changes in Central and Eastern China during COVID-19 Lockdown Based on a Machine Learning Model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132525
Song Z, Bai Y, Wang D, Li T, He X. Satellite Retrieval of Air Pollution Changes in Central and Eastern China during COVID-19 Lockdown Based on a Machine Learning Model. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(13):2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132525
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zigeng, Yan Bai, Difeng Wang, Teng Li, and Xianqiang He. 2021. "Satellite Retrieval of Air Pollution Changes in Central and Eastern China during COVID-19 Lockdown Based on a Machine Learning Model" Remote Sensing 13, no. 13: 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132525
APA StyleSong, Z., Bai, Y., Wang, D., Li, T., & He, X. (2021). Satellite Retrieval of Air Pollution Changes in Central and Eastern China during COVID-19 Lockdown Based on a Machine Learning Model. Remote Sensing, 13(13), 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132525





