Multiscale Semantic Feature Optimization and Fusion Network for Building Extraction Using High-Resolution Aerial Images and LiDAR Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
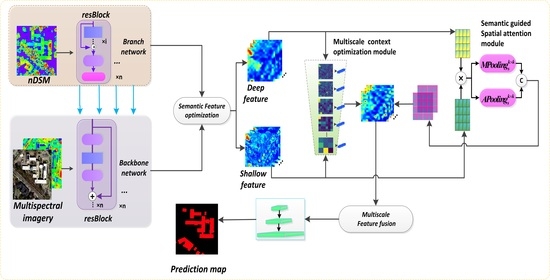
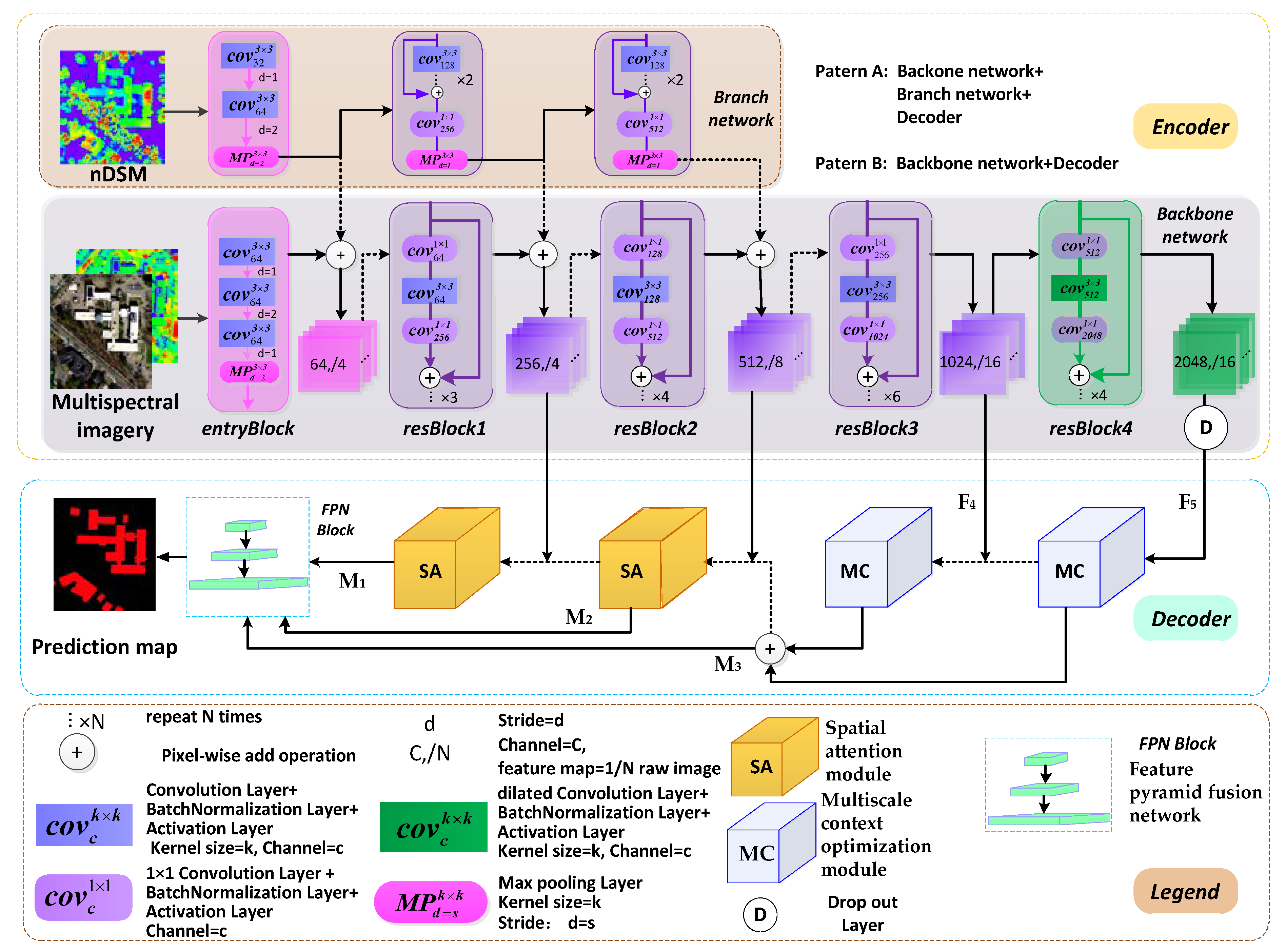
- We redesigned the FCN architecture using modified residual networks (ResNet50) as the backbone encoder network to extract features and obtain a large receptive field. The residual branch network assists the backbone network to convert features and enhance multi-modal data fusion. Feature pyramid structures with the proposed decoder modules effectively optimize and fuse across-level multiscale features.
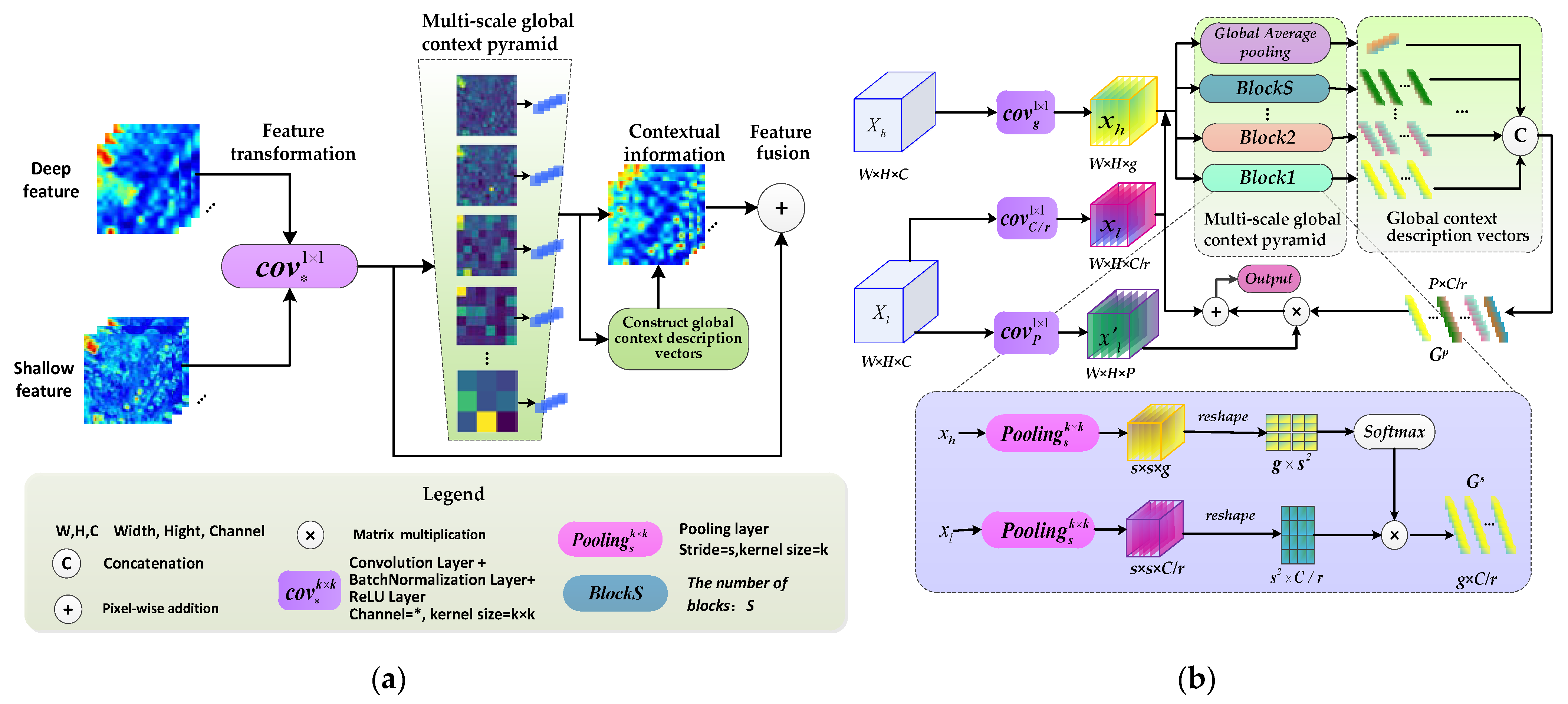
- The proposed multiscale context optimization module (MCOM) can obtain multiscale global semantic features and generate the contextual representations of different local regions to adaptively enhance the semantic consistency of intra-class and the discrepancy of inter-class for multiscale building regions.
- A semantic guided spatial attention module (SAM) is developed that leverages features from shallow and deep layers. This module can generate an attention map using across-level features to acquire long-distance correlation for pixel-wise spatial position and refine low-level features by filtering redundant information.
2. Related Work
2.1. Contextual Feature Aggregation
2.2. Attention Mechanism
2.3. Multiscale Feature Fusion
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Network Framework
3.2. Multiscale Context Optimization Model
3.2.1. Model Formulation
3.2.2. Global Context Description Vectors
3.2.3. Multiscale Global Context Pyramid
3.3. Semantic Guided Spatial Attention Module
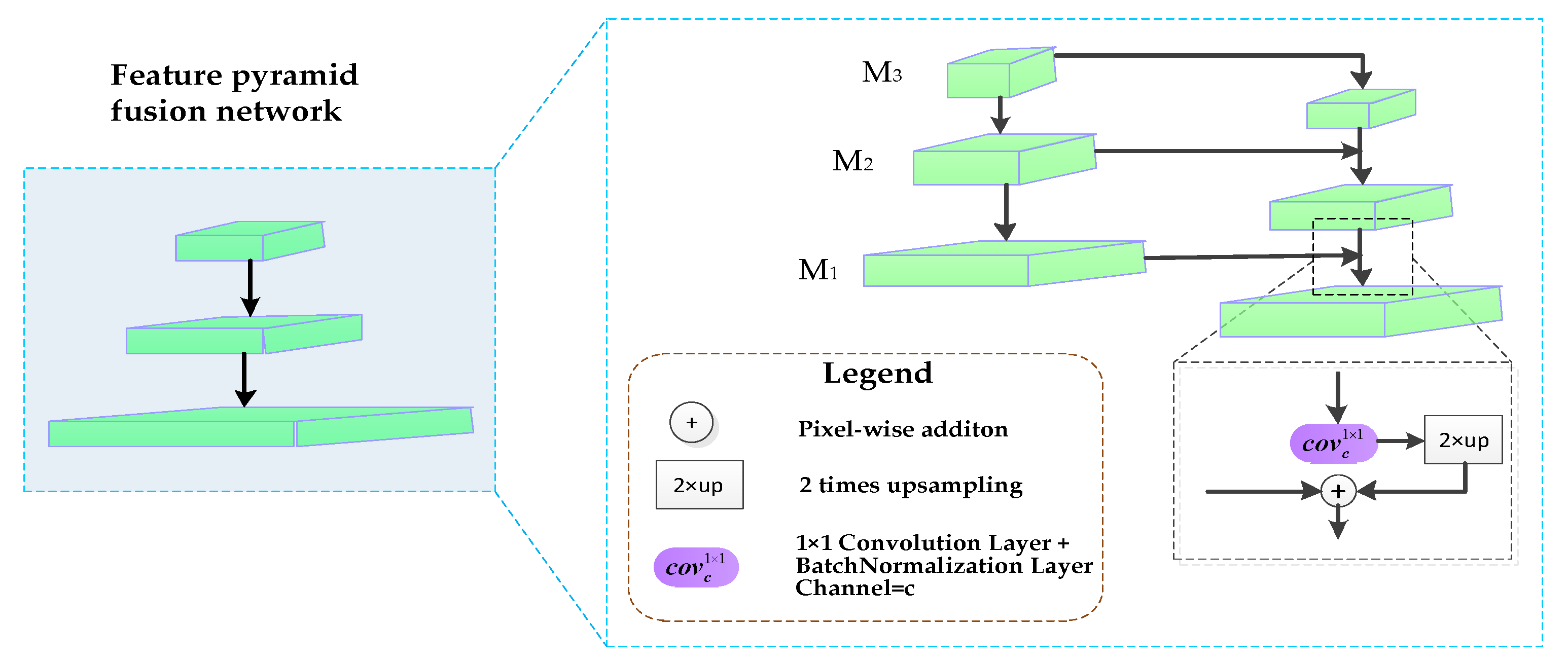
3.4. Feature Pyramid Fusion Network
4. Experiment Design
4.1. Dataset Description
4.2. Data Preprocessing
4.3. Experimental Setting
4.4. Accuracy Assessment
5. Experiment Results and Analysis
5.1. Ablation Experiments
5.1.1. Ablation on Multiscale Global Context Module
5.1.2. Ablation on Spatial Attention Decoder
5.1.3. Ablation on Different Data Inputs
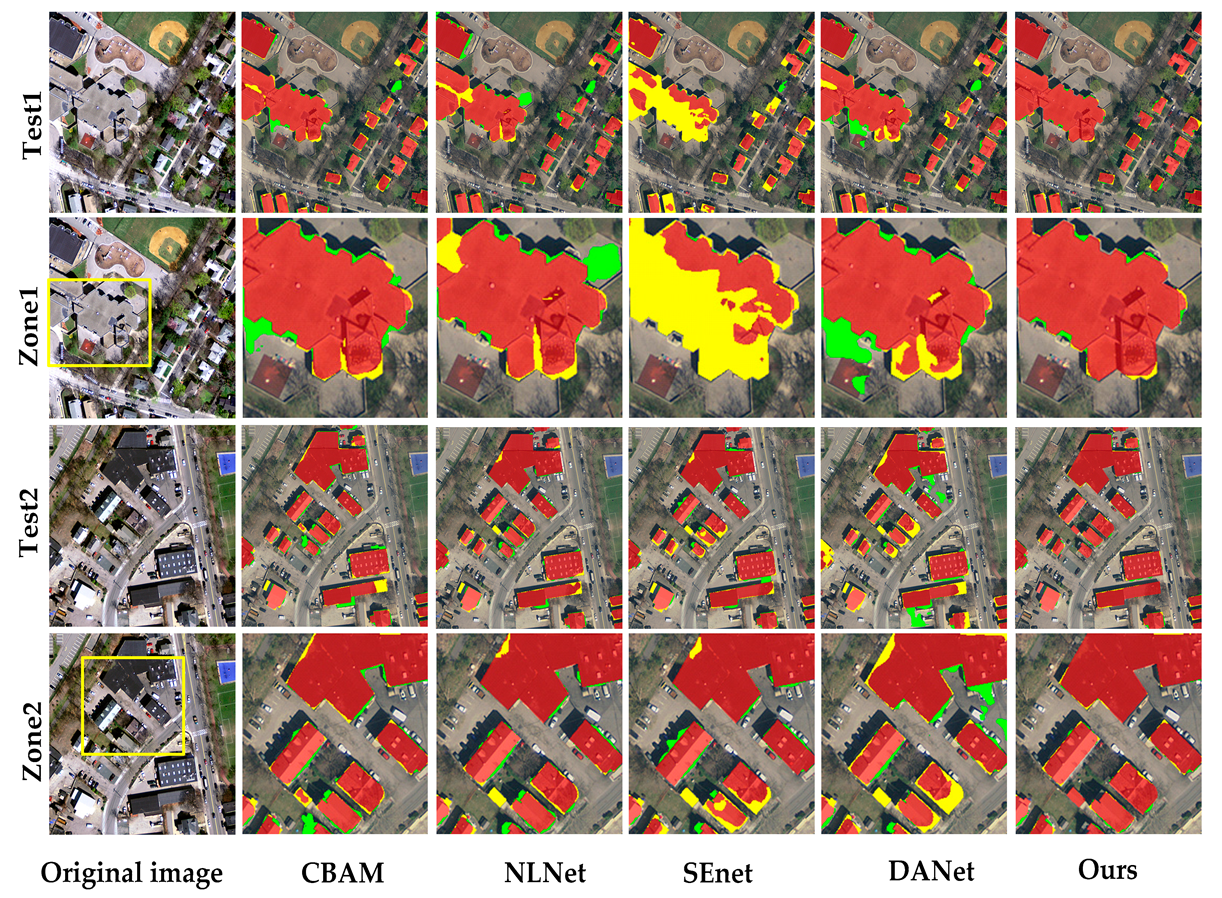
5.2. Comparison of Attention Mechanism
5.3. The Proposed Model with Different Network Frameworks
6. Discussions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Model | WHU Datset | Boston Datset | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter Size (MB) | GFLOPs | Parameter Size (MB) | GFLOPs | |
| SegNet | 112.33 | 2.64 | 127.8 | 2.34 |
| GRRNet | 100.34 | 4.57 | 116.5 | 3.35 |
| Senet | 95.74 | 3.87 | 105.67 | 2.77 |
| DANet | 119.76 | 2.37 | 134.38 | 3.47 |
| CBAM | 127.63 | 3.64 | 133.79 | 2.37 |
| NLNet | 137.84 | 2.45 | 157.36 | 2.87 |
| PSPnet | 178.84 | 1.28 | 217.35 | 1.78 |
| Deeplabv3+ | 158.39 | 5.32 | 167.87 | 4.62 |
| Fused-FCN4s | 93.14 | 2.79 | 100.2 | 2.14 |
| Ours | 138.47 | 4.73 | 148.96 | 3.72 |
References
- Jin, X.; Davis, C.H. Automated building extraction from high-resolution satellite imagery in urban areas using structural, contextual, and spectral information. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2005, 2005, 745309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Morphological Building/Shadow Index for Building Extraction from High-Resolution Imagery over Urban Areas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Gerhardinger, A.; Kayitakire, F. A robust built-up area presence index by anisotropic rotation-invariant textural measure. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2008, 1, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanea, M.; Moallem, P.; Momeni, M. Automatic building extraction in dense urban areas through geoeye multispectral imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 5094–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Feng, W.; Zou, X.; Huang, K. Real-time detection of surface deformation and strain in recycled aggregate concrete-filled steel tubular columns via four-ocular vision. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2019, 59, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.C.; Wang, C.; Luo, L.; Zou, X. Recognition and localization methods for vision-based fruit picking robots: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharibbafghi, Z.; Tian, J.; Reinartz, P. Modified super-pixel segmentation for digital surface model refinement and building extraction from satellite stereo imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirmacek, B.; Unsalan, C. A probabilistic framework to detect buildings in aerial and satellite images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 49, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liasis, G.; Stavrou, S. Building extraction in satellite images using active contours and color features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 1127–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongus, D.; Lukač, N.; Žalik, B. Ground and building extraction from LiDAR data based on differential morphological profiles and locally fitted surfaces. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Xu, S.; He, X.; Chen, S. Automatic building extraction from LiDAR data fusion of point and grid-based features. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Yang, B.; Liang, F.; Dai, W.; Li, J.; Tian, M.; Xu, W. A top-down strategy for buildings extraction from complex urban scenes using airborne LiDAR point clouds. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 92, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Wang, R. Extraction of residential building instances in suburban areas from mobile LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, M. A building extraction approach based on the fusion of LiDAR point cloud and elevation map texture features. Remote Sens. 2019, 14, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, M.; Lin, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, K.; He, Y.; Li, L. Vision-Based Three-Dimensional Reconstruction and Monitoring of Large-Scale Steel Tubular Structures. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, L.; Yang, X.; Bilal, M.; Li, Q. Object-based multi-modal convolution neural networks for building extraction using panchromatic and multispectral imagery. Neurocomputing 2020, 386, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.; Boehm, J. Improving public data for building segmentation from Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for fused airborne Lidar and image data using active contours. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shi, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, X. Building Footprint Generation by Integrating Convolution Neural Network with Feature Pairwise Conditional Random Field (FPCRF). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 7502–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, P.; Yao, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y. Building extraction in very high resolution imagery by dense-attention networks. Remote Sens. 2018, 24, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, Z.; Fu, Y.; Gan, M.; Deng, J.; Comber, A.; Wang, K. Building Extraction from Very High Resolution Aerial Imagery Using Joint Attention Deep Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, P. Automatic building extraction from high-resolution aerial images and LiDAR data using gated residual refinement network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Yang, F.; Gao, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Fan, H.; Ren, J. Building extraction from high-resolution aerial imagery using a generative adversarial network with spatial and channel attention mechanisms. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bittner, K.; Adam, F.; Cui, S.; Körner, M.; Reinartz, P. Building footprint extraction from VHR remote sensing images combined with normalized DSMs using fused fully convolutional networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2615–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X. Building segmentation through a gated graph convolutional neural network with deep structured feature embedding. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 12, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Milan, A.; Shen, C.; Reid, I. Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1925–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Rabinovich, A.; Berg, A.C. Parsenet: Looking wider to see better. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.04579. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, M.; Bai, S.; Huang, T.; Bai, X. Asymmetric non-local neural networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October 2019; pp. 593–602. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Peng, C.; Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, G.; Jiang, W. An end-to-end network for panoptic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15 June 2019; pp. 6172–6181. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, M. Fully Convolutional Networks for Multisource Building Extraction from an Open Aerial and Satellite Imagery dataset. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- NOAA. Available online: https://coast.noaa.gov/dataviewer/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Mnih, V. Machine Learning for Aerial Image Labeling. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- CloudCompare. Available online: http://www.cloudcompare.org/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Glorot, X.; Bengio, Y. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics; PMLR: Sardinia, Italy, May 2010; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]








| Usage | Data Groups | Resolution | Acquisition Time | Data Type | Number of Buildings | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training and validation | WHU | 0.15 m | 2011 | Aerial image | 79,018 | Christchurch |
| Boston | 0.30 m | 2015 | Aerial image+LiDAR | 15,667 | Boston | |
| Test | WHU test1 | 0.15 m | 2011 | Aerial image | 13,846 | Christchurch |
| WHU test2 | 0.15 m | 2011 | Aerial image | 10,828 | Christchurch | |
| Boston test1 | 0.30 m | 2014 | Aerial image+LiDAR | 2416 | Boston | |
| Boston test2 | 0.30 m | 2014 | Aerial image+LiDAR | 716 | Boston |
| Datasets | Method | Pooling Types | Pooling Rates | IoU (%) | OA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHU | Backbone network | - | - | 91.04 | 94.75 |
| Backbone network + MCOM | average | 2/3/6 | 92.08 | 97.64 | |
| max | 2/3/6 | 92.06 | 96.57 | ||
| average | 2/4/8 | 92.13 | 97.87 | ||
| max | 2/4/8 | 92.11 | 97.56 | ||
| average | 3/6/8 | 92.05 | 97.43 | ||
| max | 3/6/8 | 92.08 | 97.38 | ||
| average | 3/4/8 | 92.09 | 97.81 | ||
| max | 3/4/8 | 92.07 | 97.39 | ||
| Backbone network + SA | - | - | 93.41 | 96.63 | |
| Boston | Backbone + Branch network | - | - | 86.73 | 93.12 |
| Backbone + Branch network +MCOM | average | 2/3/6 | 88.44 | 96.37 | |
| max | 2/3/6 | 89.95 | 95.19 | ||
| average | 2/4/8 | 90.36 | 96.54 | ||
| max | 2/4/8 | 89.87 | 96.51 | ||
| average | 3/6/8 | 89.66 | 95.17 | ||
| max | 3/6/8 | 89.47 | 96.48 | ||
| average | 3/4/8 | 90.37 | 96.21 | ||
| max | 3/4/8 | 88.88 | 95.23 | ||
| Backbone + Branch network + SA | - | - | 89.37 | 96.67 |
| Datasets | Metrics | Different Data Inputs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGB | RGB+NDVI | RGB+NIR | RGB+NDVI+nDSM | ||
| Boston | IoU (%) | 91.02 | 91.09 | 90.94 | 94.72 |
| OA (%) | 95.34 | 96.51 | 96.47 | 97.84 | |
| Method | Datasets | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHU | Boston | |||||
| IoU (%) | OA (%) | F1-Score (%) | IoU (%) | OA (%) | F1-Score (%) | |
| DANet | 83.57 | 97.54 | 91.03 | 94.32 | 97.55 | 93.97 |
| CBAM | 92.16 | 97.52 | 94.21 | 89.44 | 97.50 | 92.16 |
| SEnet | 88.47 | 96.41 | 89.74 | 79.57 | 97.57 | 83.22 |
| NLNet | 81.78 | 97.38 | 90.47 | 92.87 | 97.14 | 92.81 |
| Ours | 93.19 | 97.56 | 95.83 | 94.72 | 97.84 | 96.67 |
| Method | Datasets | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHU | Boston | |||||
| IoU (%) | OA (%) | F1-Score (%) | IoU (%) | OA (%) | F1-Score (%) | |
| Deeplabv3+ | 87.37 | 97.55 | 93.27 | 86.13 | 97.17 | 89.46 |
| PSPNet | 73.87 | 94.11 | 85.73 | 92.72 | 96.89 | 95.53 |
| SegNet | 85.31 | 97.04 | 91.15 | 84.15 | 97.37 | 86.17 |
| Fused-FCN4s | 86.32 | 96.38 | 90.65 | 94.68 | 97.58 | 95.33 |
| GRRNet | 86.16 | 96.59 | 90.42 | 93.21 | 96.94 | 94.47 |
| Ours | 93.19 | 97.56 | 95.83 | 94.72 | 97.84 | 96.67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Q.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Alias, A.H.; Hashim, S.J.b. Multiscale Semantic Feature Optimization and Fusion Network for Building Extraction Using High-Resolution Aerial Images and LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132473
Yuan Q, Shafri HZM, Alias AH, Hashim SJb. Multiscale Semantic Feature Optimization and Fusion Network for Building Extraction Using High-Resolution Aerial Images and LiDAR Data. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(13):2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132473
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Qinglie, Helmi Zulhaidi Mohd Shafri, Aidi Hizami Alias, and Shaiful Jahari bin Hashim. 2021. "Multiscale Semantic Feature Optimization and Fusion Network for Building Extraction Using High-Resolution Aerial Images and LiDAR Data" Remote Sensing 13, no. 13: 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132473
APA StyleYuan, Q., Shafri, H. Z. M., Alias, A. H., & Hashim, S. J. b. (2021). Multiscale Semantic Feature Optimization and Fusion Network for Building Extraction Using High-Resolution Aerial Images and LiDAR Data. Remote Sensing, 13(13), 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132473