Evaluating the Relationships of Inter-Annual Farmland Vegetation Dynamics with Biodiversity Using Multi-Spatial and Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Linear Trend Analysis
2.2.2. Biodiversity Modeling
3. Results
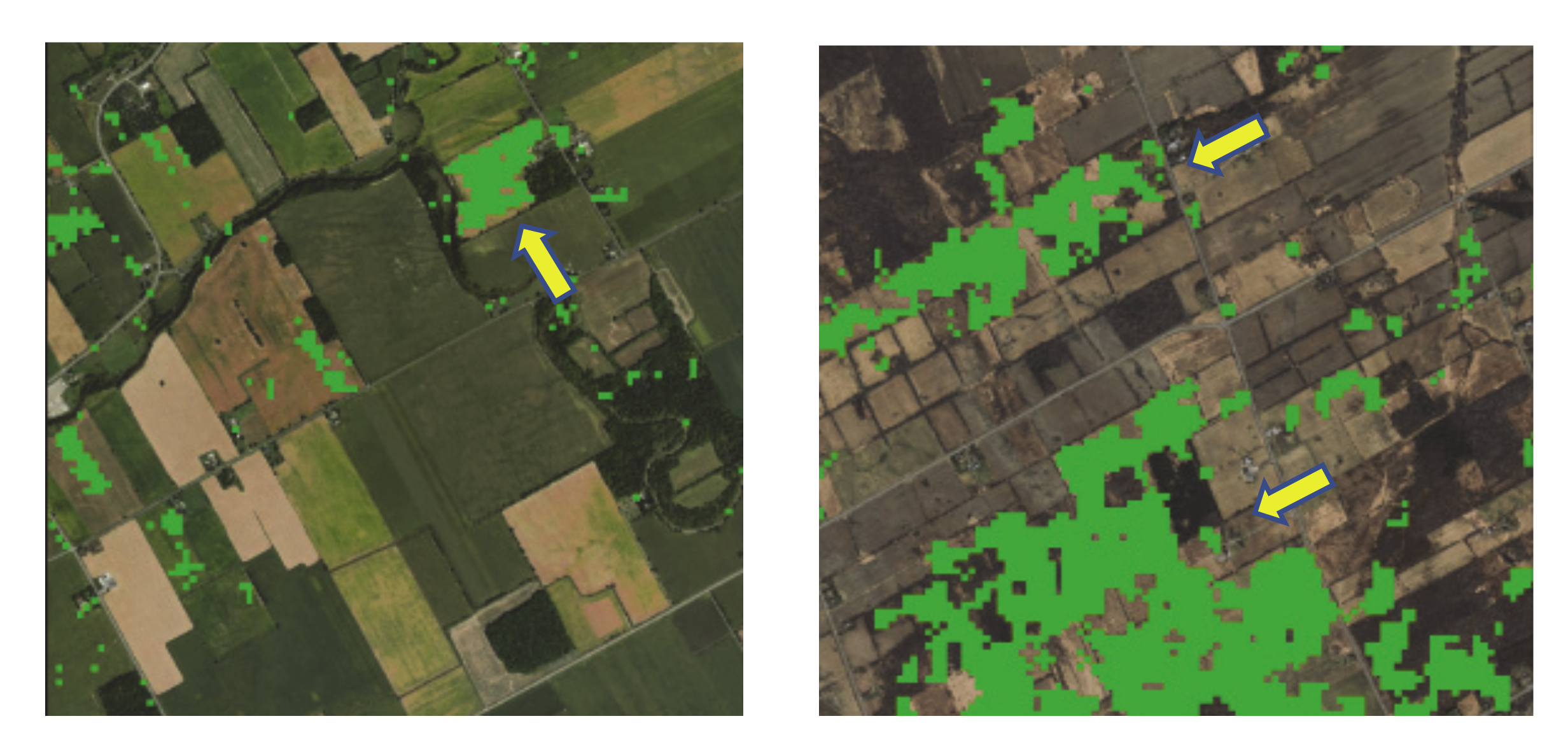
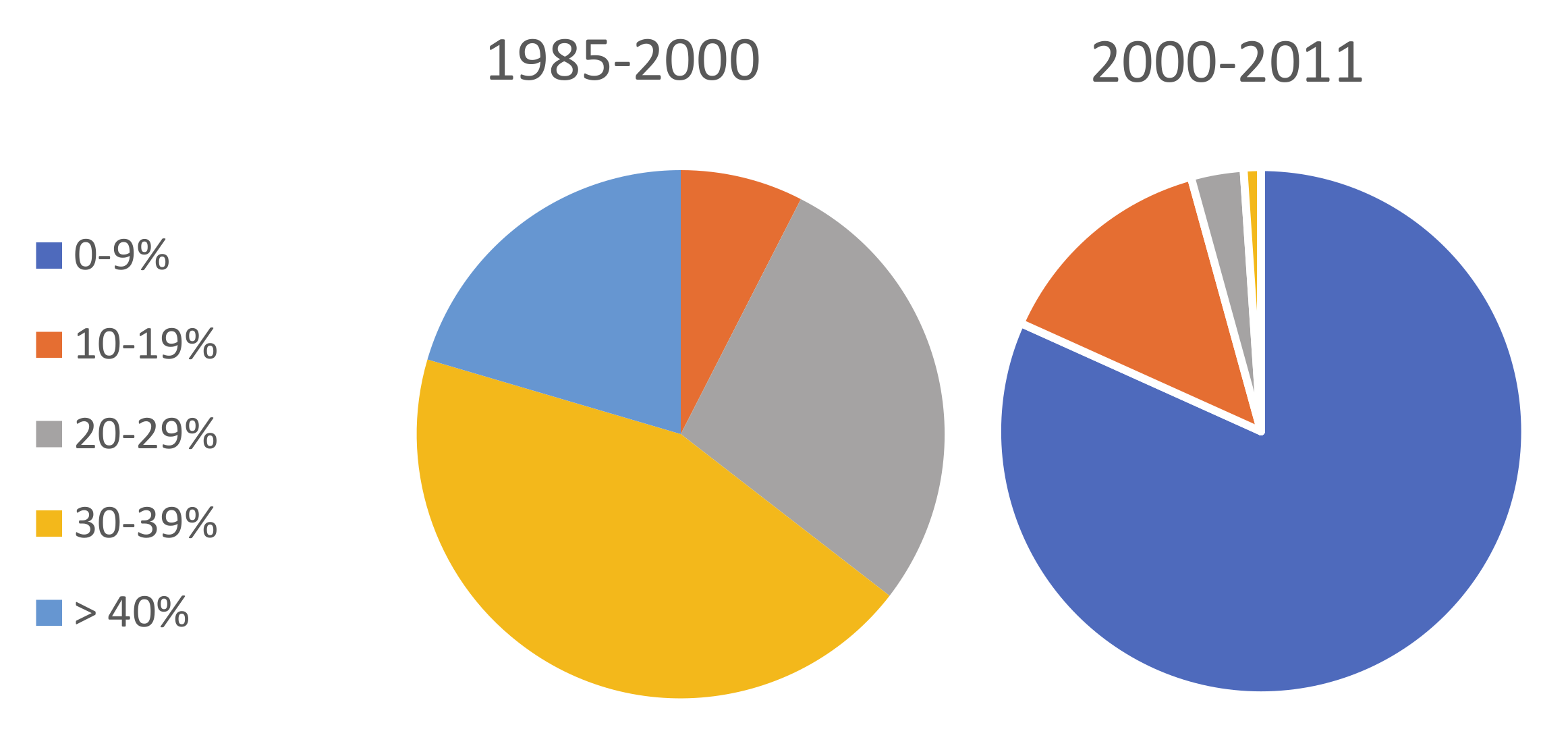
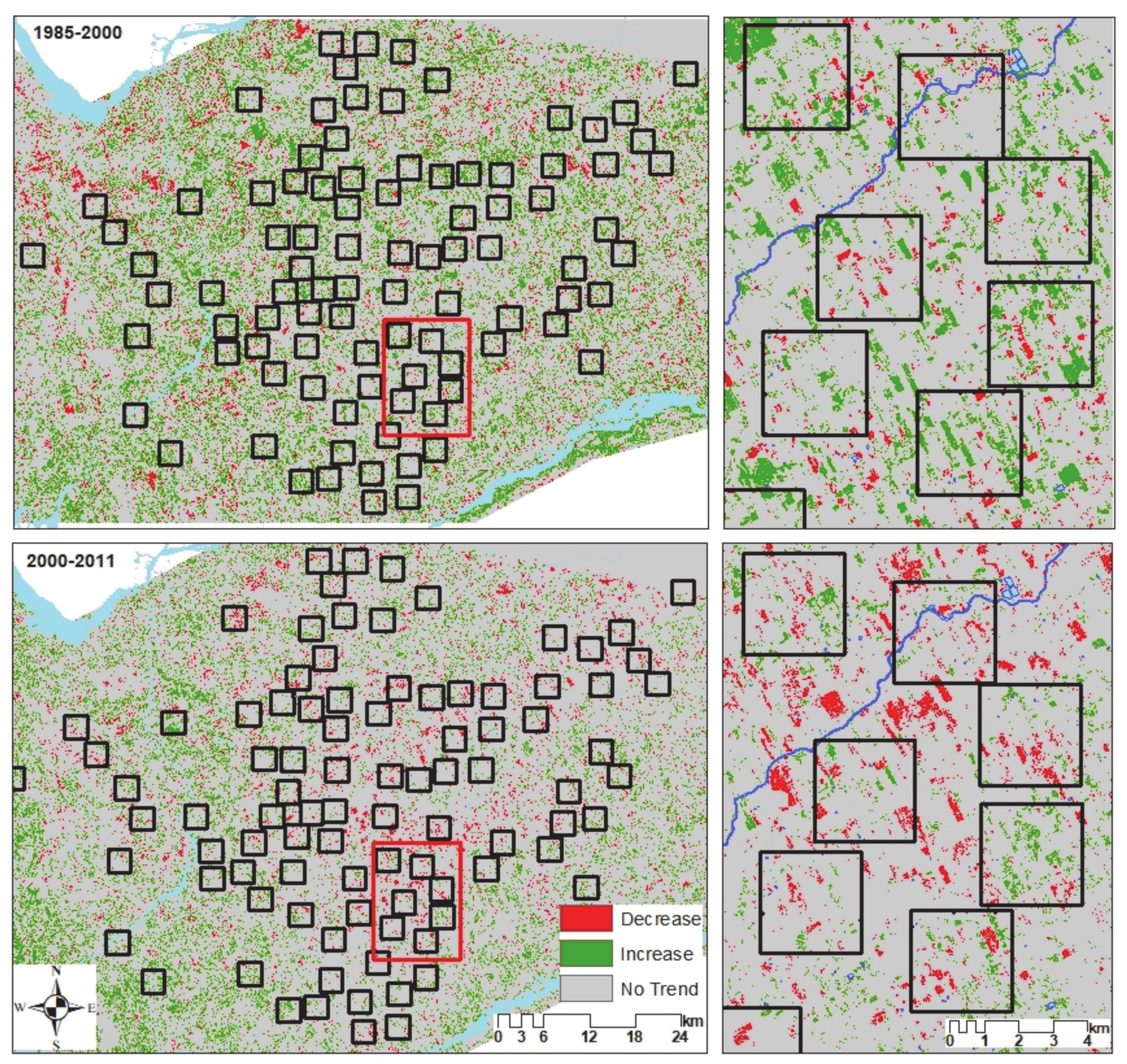
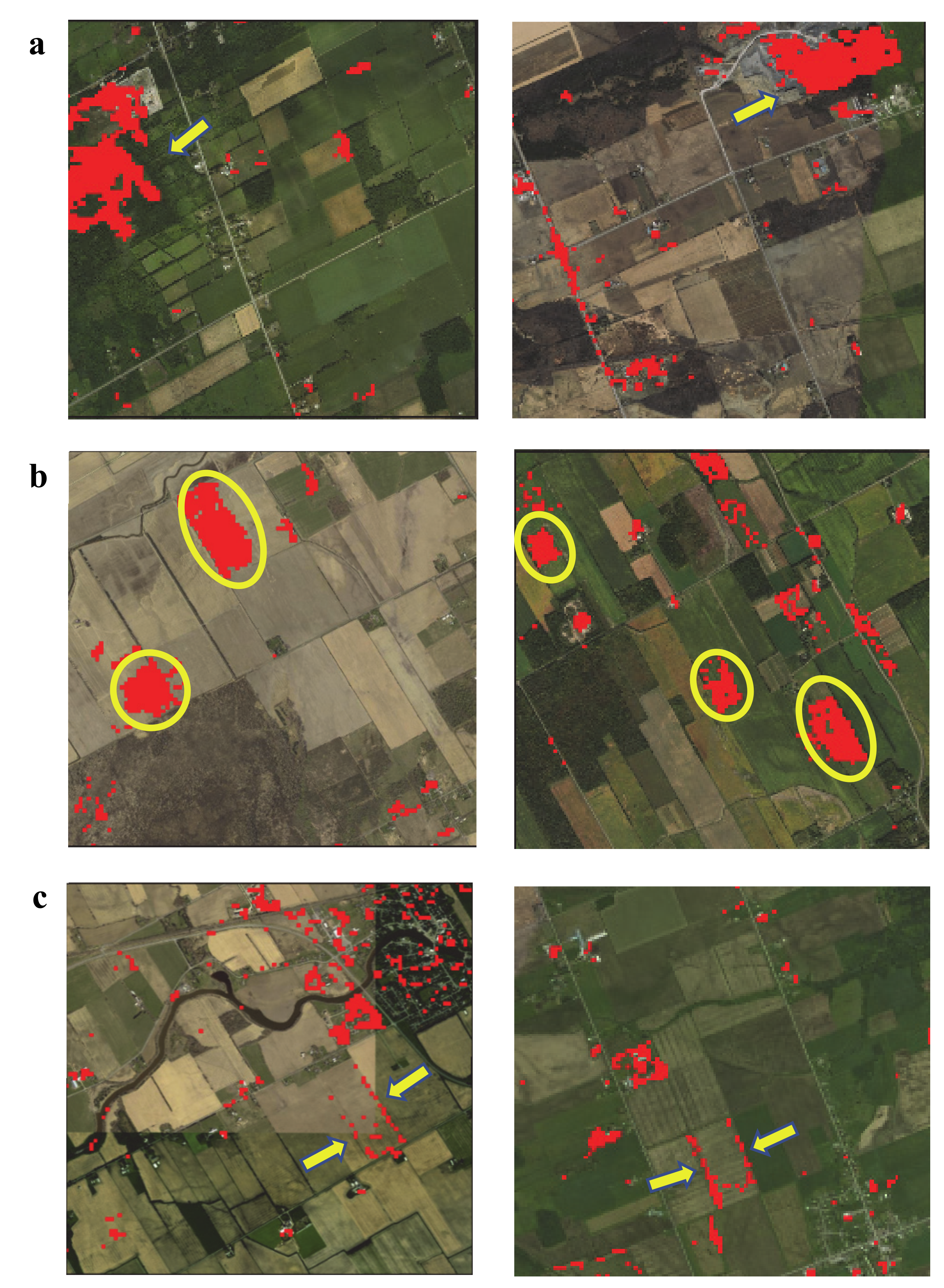
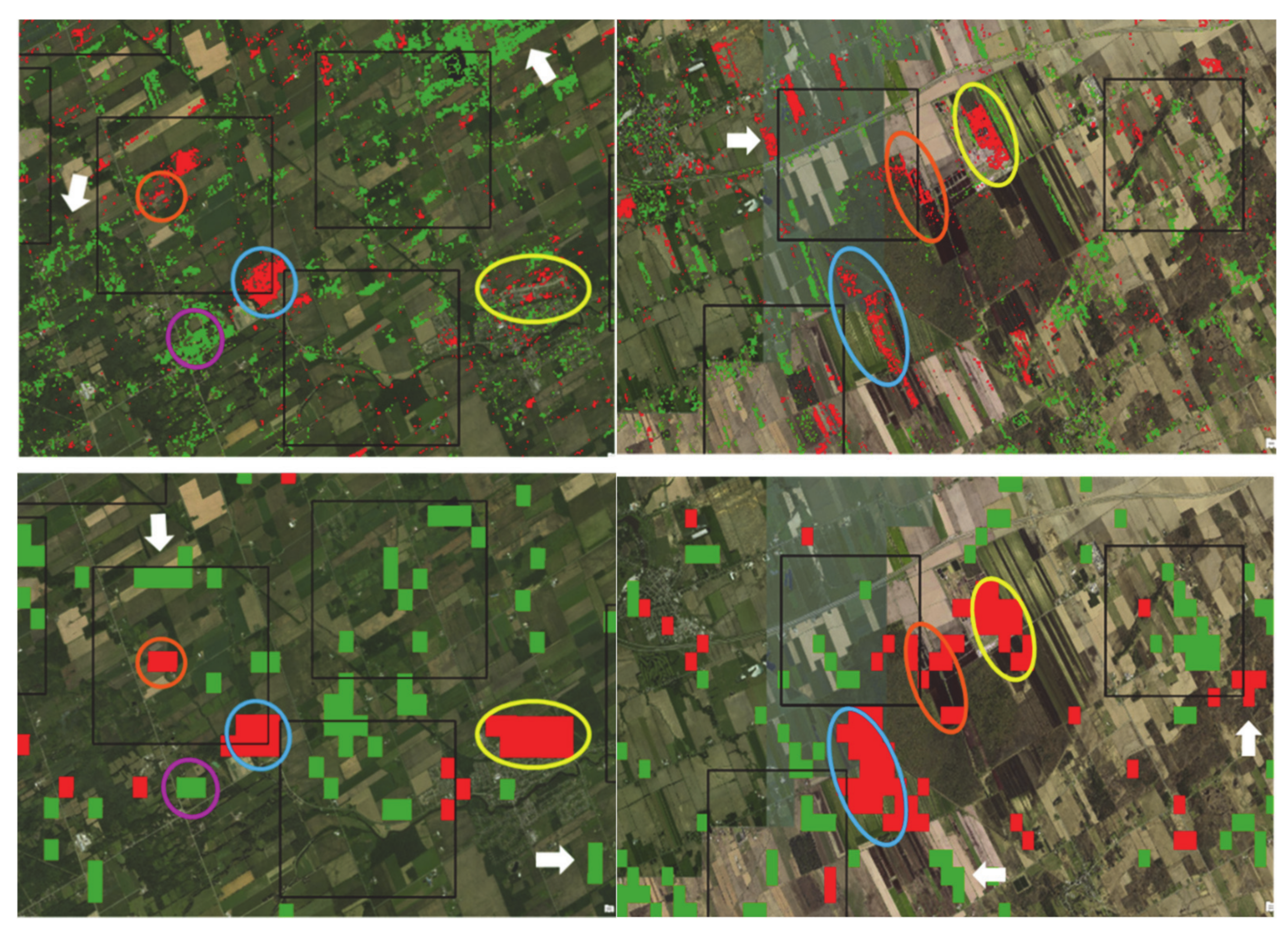
3.1. MODIS and Landsat Midsummer NDVI Inter-Annual Trends
3.2. Detection of a Change in Trend Slope for Subperiods in the Landsat Time Series
3.3. Comparing 2000–2011 MODIS and Landsat Mid-Summer NDVI Trends
3.4. Modeling the Relationships of Biodiversity and Inter-Annual Landscape Dynamics
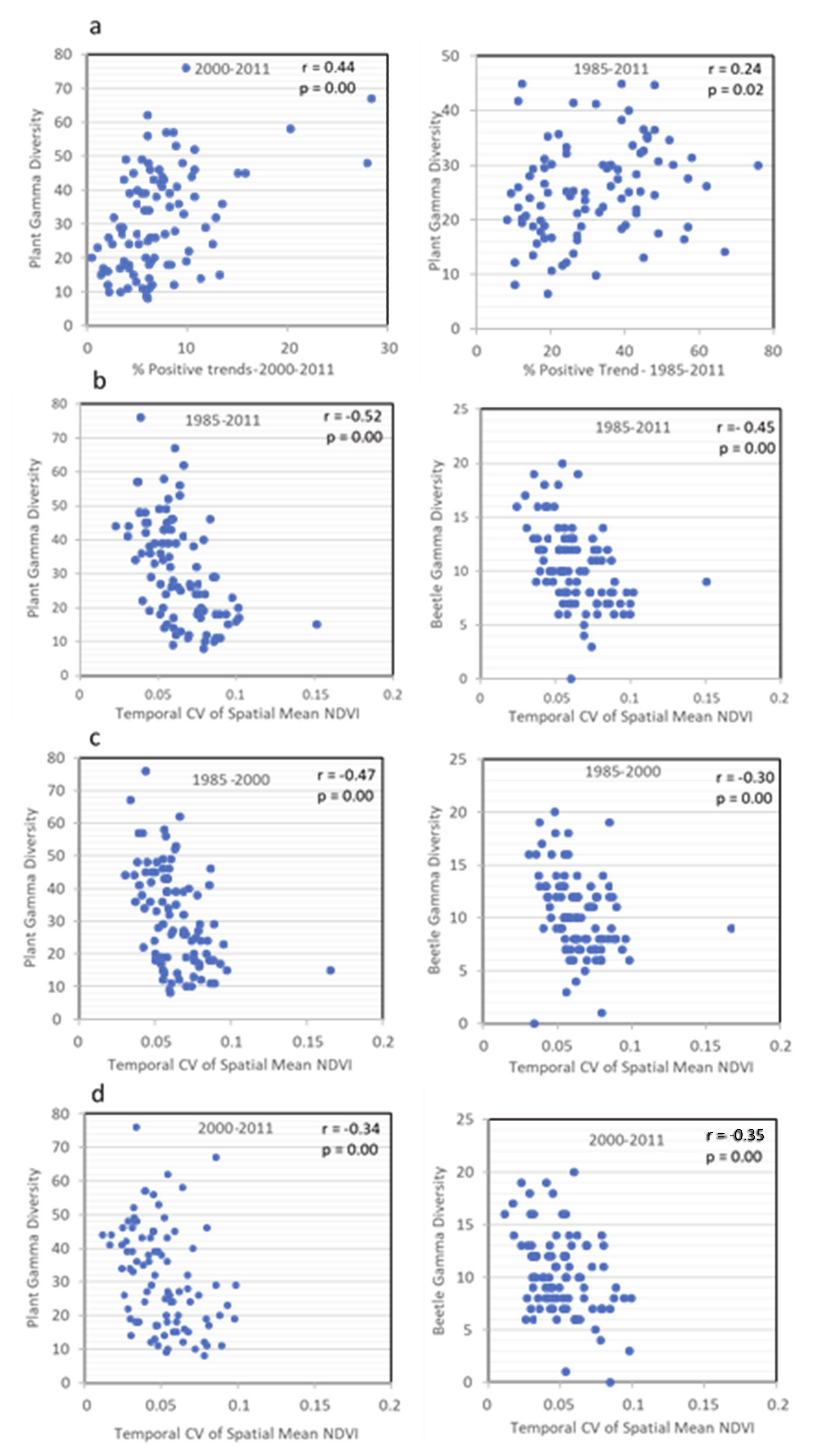
3.4.1. Relationships between Biodiversity and the Percentage of Sample Landscape Pixels with Significant Positive or Negative Trends in Vegetation Productivity
3.4.2. Relationships between Biodiversity and Inter-Annual Variability in Vegetation Productivity
3.4.3. Multiple Regression of Plant Gamma Diversity vs. Landscape Temporal Dynamics Metrics
4. Discussion
4.1. Trends in Vegetation Productivity
4.2. Relationships of Biodiversity with Inter-Annual Landscape Vegetation Dynamics
4.3. Limitations and Recommendations for Future Research
4.4. Implications of This Study for Policy and Monitoring of Biodiversity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahrig, L. Rethinking patch size and isolation effects: the habitat amount hypothesis. J. Biogeogr. 2013, 40, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2016 Census of Agriculture. Available online: https://www.statcan.gc.ca/eng/ca2016 (accessed on 4 November 2018).
- Norris, K. Agriculture and biodiversity conservation: opportunity knocks. Conserv. Lett. 2008, 1, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, N.; Acs, S.; Dallimer, M.; Gaston, K.J.; Graves, A.; Morris, J.; Armsworth, P.R. Farm-scale ecological and economic impacts of agricultural change in the uplands. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental sustainability of Canadian Agriculture: Agri-Environmental Indicator Report Series-Report #4. Available online: http://www.agr.gc.ca/eng/agriculture-and-climate/agricultural-practices/environmental-sustainability-of-canadian-agriculture-agri-environmental-indicator-report-series-report-4/?id=1467307820931 (accessed on 25 December 2018).
- Yeates, G.W.; Bardgett, R.D.; Cook, R.; Hobbs, P.; Bowling, P.; Potter, F. Faunal and microbial diversity in three Welsh grassland soils under conventional and organic management regimes. J. Appl. Ecol. 1997, 34, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.; Fjelsted, H.; Kristensn, S. Approaches to assess the environmental impact of organic farming with particular regard to Denmark. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 83, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald, A.B. Weed vegetation (wild flora) of long established organic versus conventional cereal fields in Denmark. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1999, 134, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, T.; Vickery, J.A.; Wilson, J.D. Farmland biodiversity: Is habitat heterogeneity the key? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhig, L.; Baudry, J.; Brotons, L.; Burel, F.G.; Crist, T.O.; Fuller, R.J.; Sirami, C.; Siriwardena, G.M.; Martin, J.L. Functional landscape heterogeneity and animal biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Freemark, K.; Boutin, C.; Keddy, C. Importance of farmland habitats for conservation of plant species. Conserv. Biol. 2002, 16, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flick, T.; Feagan, S.; Fahrig, L. Effects of landscape structure on butterfly species richness and abundance in agricultural landscapes in eastern Ontario, Canada. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 156, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, J.; Verdu, J.R.; Eduardo, G. Species richness in Mediterranean agroecosystems: Spatial and temporal analysis for biodiversity conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 134, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijn, D.; Kohler, F.; Baldi, A.; Batary, P.; Concepcion, E.D.; Clough, Y.; Dıaz, M.; Gabriel, D.; Holzschuh, A.; Knop, E.; et al. On the relationship between farmland biodiversity and land-use intensity in Europe. In Proceedings of the Royal Society B: biological sciences; Royal Society B: London, UK, 2009; Volume 276, pp. 903–909. [Google Scholar]
- Krauss, J.; Bommarco, R.; Guardiola, M.; Heikkinen, R.K.; Helm, A.; Kuussaari, M.; Lindborg, R.; Öckinger, E.; Pärtel, M.; Pino, J.; et al. Habitat fragmentation causes immediate and time-delayed biodiversity loss at different trophic levels. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H.; Wildi, O.; Ewald, L. Additive partitioning of plant species diversity in an agricultural mosaic landscape. Landsc. Ecol. 2000, 15, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, S.; Bunce, R.; Firbank, L.; Coward, P. Do field boundaries act as refugia for grassland plant species diversity in intensively managed agricultural landscapes in Britain? Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, M.; Peter, D.; Christine, M.; David, K.; Bernhard, S. The Swiss agri-environment scheme enhances pollinator diversity and plant reproductive success in nearby intensively managed farmland. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 44, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brose, U. Relative importance of isolation, area and habitat heterogeneity for vascular plant species richness of temporary wetlands in east-German farmland. Ecography 2001, 24, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrig, L.; Girard, J.; Duro, D.; Pasher, J.; Smith, A.; Javorek, S.; King, D.; Freemark Lindsay, K.; Mitchell, S.; Tischendorf, L. Farmlands with smaller crop fields have higher within-field biodiversity. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 200, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Kang, M.; Gao, Q.; He, L.; Xiong, M.; Jia, Z.; Jin, Z. Impact of land use on plant biodiversity and measures for biodiversity conservation in the Loess Plateau in China – a case study in a hilly-gully region of the Northern Loess Plateau. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 12, 2121–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidsma, P.; Tekelenburg, T.; van den Berg, M.; Alkemade, R. Impacts of land-use change on biodiversity: An assessment of agricultural biodiversity in the European Union. Agr. Ecosyst. and Environ. 2006, 114, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapathi, D.; Carvalheiro, L.G.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Dodson, C.A.; Evans, R.L.; McKerchar, M.; Morton, R.D.; Moss, E.D.; Stuart, P.M.; Kunin, W.E.; et al. The impact of over 80 years of land cover changes on bee and wasp pollinator communities in England. In Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences; Royal Society B: London, UK, 2015; Volume 282, p. 20150294. [Google Scholar]
- Nagendra, H. Review article: Using remote sensing to assess biodiversity. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 2377–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagendra, H.; Lucas, R.; Honradoc, J.P.; Adamo, M.; Mairota, P. Remote sensing for conservation monitoring: Assessing protected areas, habitat extent, habitat condition, species diversity, and threats. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 33, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, W.; Spector, S.; Gardiner, N.; Fladeland, M.; Sterling, E.; Steininger, M. Remote sensing for biodiversity science and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.E. Remote Sensing for Biodiversity and Wildlife Management: Synthesis and Applications; McGraw-Hill Education: Whitby, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rocchini, D.; Balkenhol, N.; Carter, G.A.; Foody, G.M.; Gillespie, T.W.; He, K.S.; Kark, S.; Levin, N.; Lucas, K.; Nagendra, H. Remotely sensed spectral heterogeneity as a proxy of species diversity: Recent advances and open challenges. Ecol. Inform. 2010, 5, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Ottinger, M.; Wegmann, G.H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Dech, S.; Wikelski, M. Review Article: Earth observation satellite sensors for biodiversity monitoring: potentials and bottlenecks. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6599–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Mitchell, G.W.; Pasher, J.; McGovern, M.; Hudson, M.A.R.; Fahrig, L. Influence of crop type, heterogeneity and woody structure on avian biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.W.; Wohlgemuth, T.; Earls, P.G.; Arévalo, J.R.; Thompson, S. Opportunities for Long-Term Ecological Research at the Tallgrass Prairie Preserve, Oklahoma. In Proceedings of the ILTER Regional Workshop: Cooperation in Long Term Ecological Research in Central and Eastern Europe, Budapest, Hungary, 22 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, T.; Foody, G.M.; Rocchini, D. Measuring and modelling biodiversity from space. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2008, 32, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duro, D.; Girard, J.; King, D.; Fahrig, L.; Mitchell, S.; Lindsay, K.; Tischendorf, L. Predicting species diversity in agricultural environments using Landsat TM imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Louis, V.; Pidgeon, A.M.; Kuemmerle, T.; Sonnenschein, R.; Radeloff, V.C.; Clayton, M.K.; Locke, B.A.; Bash, D.; Hostert, P. Modelling avian biodiversity using raw, unclassified satellite imagery. Philos. Transl. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontario Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs. Available online: http://www.omafra.gov.on.ca/english/crops/index (accessed on 18 October 2011).
- Pasher, J.; Mitchell, S.; King, D.; Fahrig, L.; Smith, A.; Lindsay, K. Optimizing landscape selection for estimating relative effects of landscape variables on ecological responses. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, N. Evaluating the Relationships of Phenological and Inter-Annual Landscape Dynamics with Farmland Biodiversity using Multi-Spatial and Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Carleton University, Ottawa, ON, Canada.
- Crist, E. A TM Tasseled Cap Equivalent Transformation for Reflectance Factor Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1985, 17, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, H. A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis. I, II, III. Nederl. Akad. Wetensch. Proc 1950, 53, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, B. Characterization of Land Transitions Patterns from Multivariate Time Series Using Seasonal Trend Analysis and Principal Component Analysis. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12639–12665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifovic, R.; Pouliot, D. Monitoring cumulative long-term vegetation changes over the Athabasca oil sand region. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1939–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeti, N.; Eastman, J.R. A Contextual Mann-Kendall Approach for the Assessment of Trend Significance in Image Time Series. Trans. GIS 2010, 15, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, C.; King, D.; Mitchell, S. Mapping Forest growth and decline in a temperature mixed forest using temporal trend analysis of Landsat imagery, 1978–2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlagel, J.D.; Newton, C.M. A GIS-based statistical method to analyze spatial change. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1996, 62, 839–844. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.G.R. Long-term temporal trends in agri-environment and agricultural land use in Ontario, Canada, Transformation, Transition and Significance. J. Geog. Geol. 2015, 7, 32–55. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, B.M.; Solvik, K.; Hogg, E.H.; Ju, J.; Masek, J.G.; Michaelian, M.; Berner, L.T.; Goetz, S.J. Detecting early warning signals of tree mortality in boreal North America using multiscale satellite data. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 2284–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baan, L.; Alkemade, R.; Koellner, T. Land use impacts on biodiversity in LCA: a global approach. Int. J. Life Cycle Ass. 2013, 18, 1216–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetz, W.; Wilcove, D.S.; Dobson, A.P. Projected Impacts of Climate and Land-Use Change on the Global Diversity of Birds. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naujokaitis-lewis, I. (Landscape Science and Technology Division, Environment and Climate Change Canada, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada). Personal communication. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- North American Breeding Bird Survey. Available online: https://www.pwrc.usgs.gov/bbs/ (accessed on 16 March 2018).
- Schmidt, M.; Udelhoven, T.; Roder, A.; Gill, T. Long term data fusion for a dense time series analysis with MODIS and Landsat imagery in an Australian Savana. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063512. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.J.; de Beurs, K.M.; Wynne, R.H.; Gao, F. Evaluation of Landsat and MODIS data fusion products for analysis of dryland forest phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.; Coops, N.; Linke, J.; McDermid, G.; Masek, J.; Gao, F.; White, J. A new data fusion model for high spatial and temporal resolution mapping of forest distribution based on Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agri-Environmental Indicator Report Series. Available online: http://www.agr.gc.ca/eng/agriculture-and-climate/agricultural-practices/environmental-sustainability-of-canadian-agriculture-agri-environmental-indicator-report-series-report-4/?id=1467307820931 (accessed on 16 March 2018).
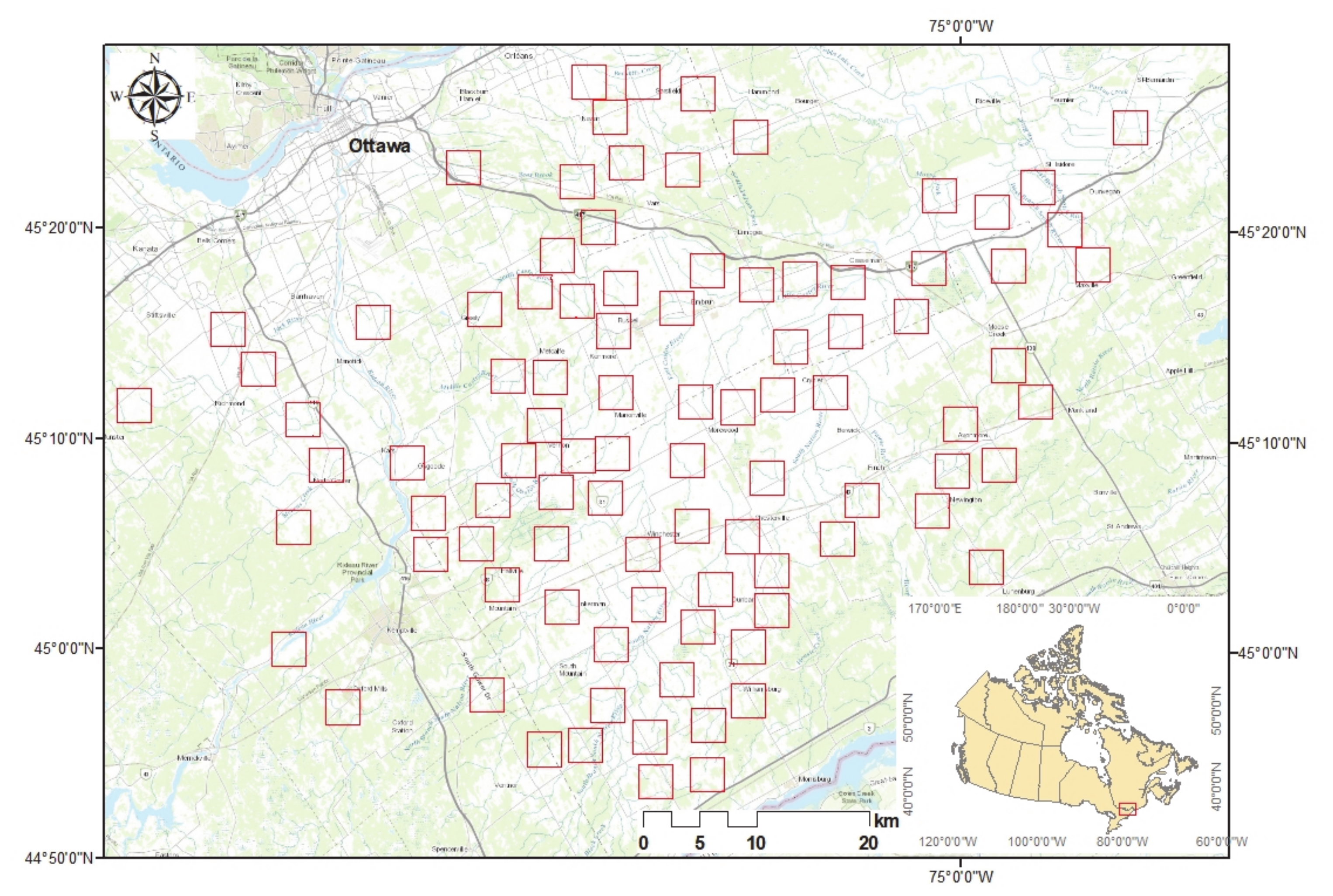

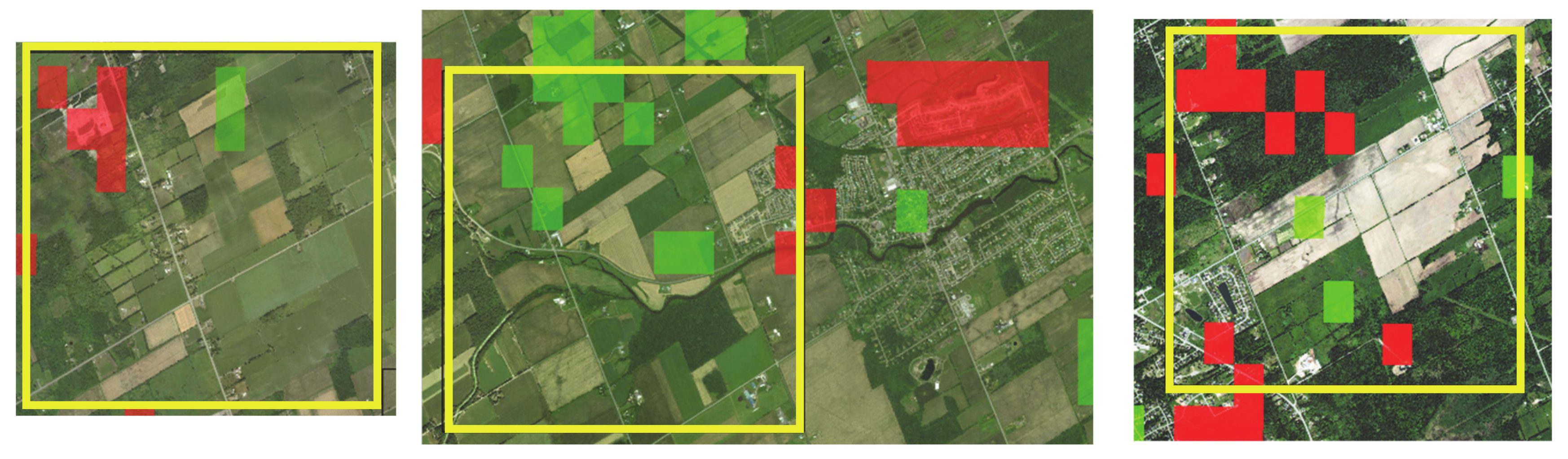
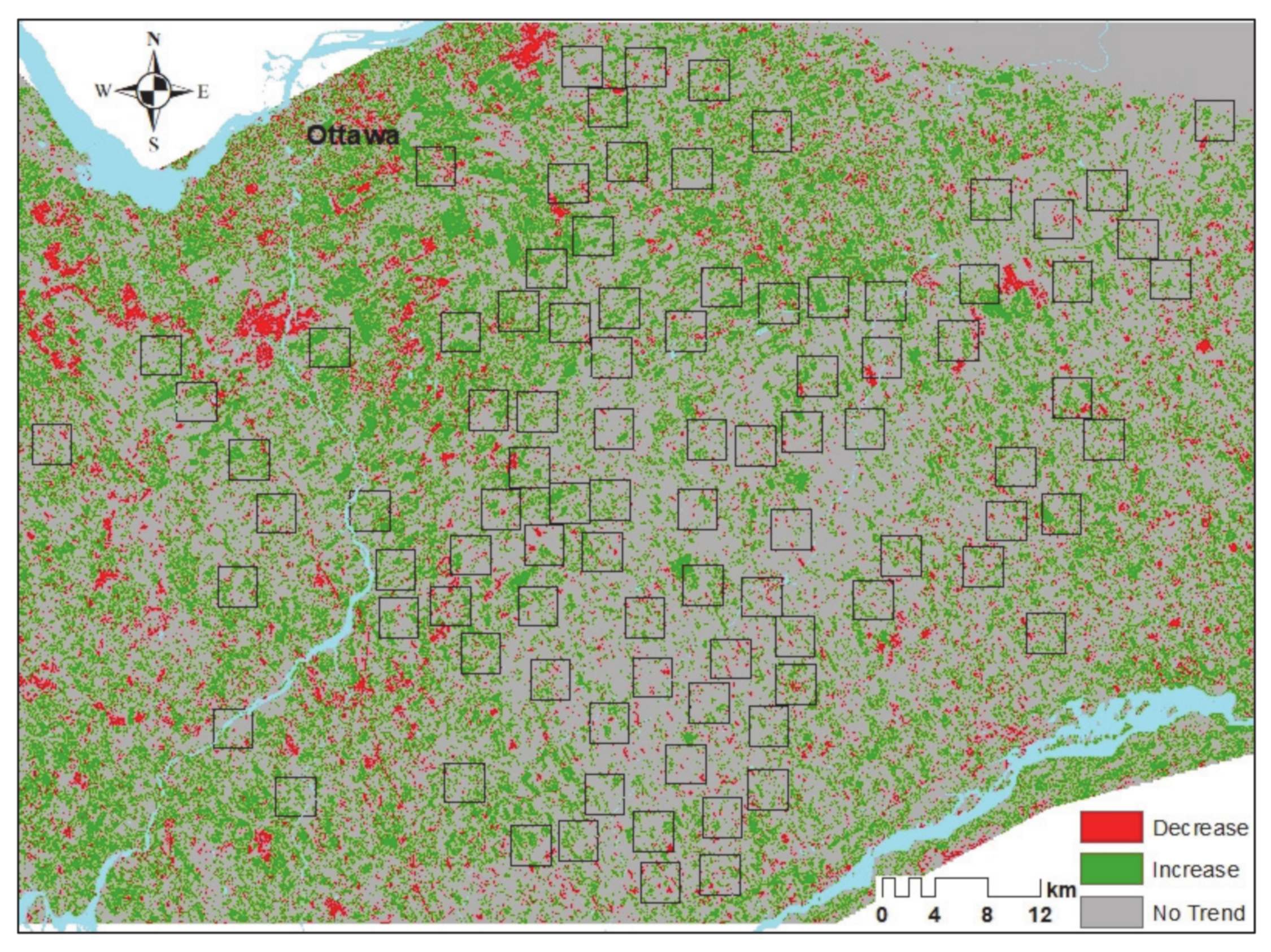
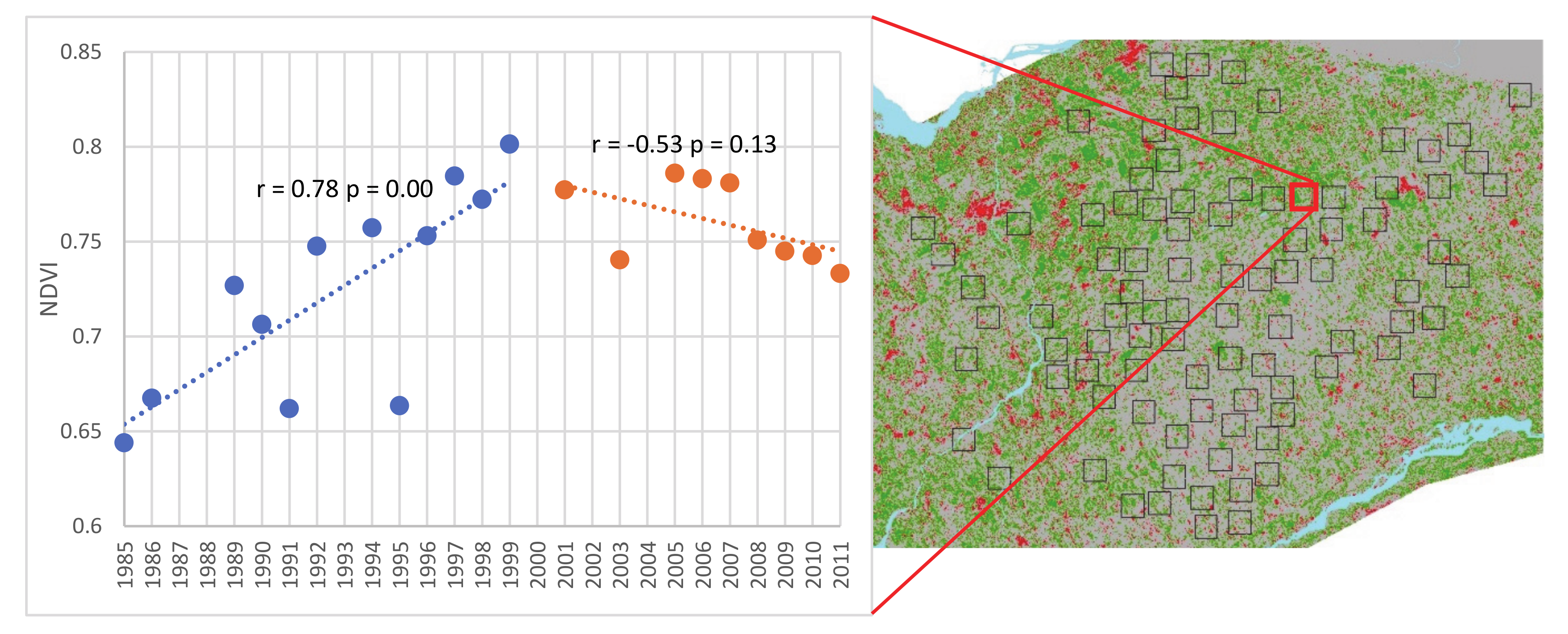

| # | Year | Date | # | Year | Date | # | Year | Date | # | Year | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1985 | 13-Jul | 5 | 1996 | 28-Aug | 9 | 2003 | 15-Jul | 13 | 2008 | 12-Jul |
| 2 | 1987 | 20 Aug | 6 | 1997 | 30-Jul | 10 | 2005 | 20-Jul | 14 | 2009 | 15-Jul |
| 3 | 1994 | 07-Aug | 7 | 1998 | 02-Aug | 11 | 2006 | 07-Jul | 15 | 2010 | 02-Jul |
| 4 | 1995 | 10-Aug | 8 | 2001 | 10-Aug | 12 | 2007 | 26-Jul | 16 | 2011 | 05-Jul |
| Negative Trend | Positive Trend | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0%–4% | 5%–9% | >10% | 0%–4% | 5%–9% | >10% | ||
| MODIS | 69 | 18 | 6 | 31 | 23 | 39 | |
| Landsat | 84 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 90 | |
| MODIS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | No trend | Sum | % Agreement | ||
| Landsat | Negative | 1190 | 2300 | 34,346 | 37,836 | 3.1 |
| Positive | 1440 | 4445 | 64,402 | 70,287 | 6.3 | |
| No trend | 16,294 | 48,537 | 749,849 | 814,680 | 92.0 | |
| Sum | 18,924 | 55,282 | 848,597 | 922,803 | ||
| % Agreement | 6.3 | 8.0 | 88.4 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alavi, N.; King, D. Evaluating the Relationships of Inter-Annual Farmland Vegetation Dynamics with Biodiversity Using Multi-Spatial and Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091479
Alavi N, King D. Evaluating the Relationships of Inter-Annual Farmland Vegetation Dynamics with Biodiversity Using Multi-Spatial and Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(9):1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091479
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlavi, Niloofar, and Douglas King. 2020. "Evaluating the Relationships of Inter-Annual Farmland Vegetation Dynamics with Biodiversity Using Multi-Spatial and Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data" Remote Sensing 12, no. 9: 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091479
APA StyleAlavi, N., & King, D. (2020). Evaluating the Relationships of Inter-Annual Farmland Vegetation Dynamics with Biodiversity Using Multi-Spatial and Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing, 12(9), 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091479






