Probabilistic River Water Mapping from Landsat-8 Using the Support Vector Machine Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
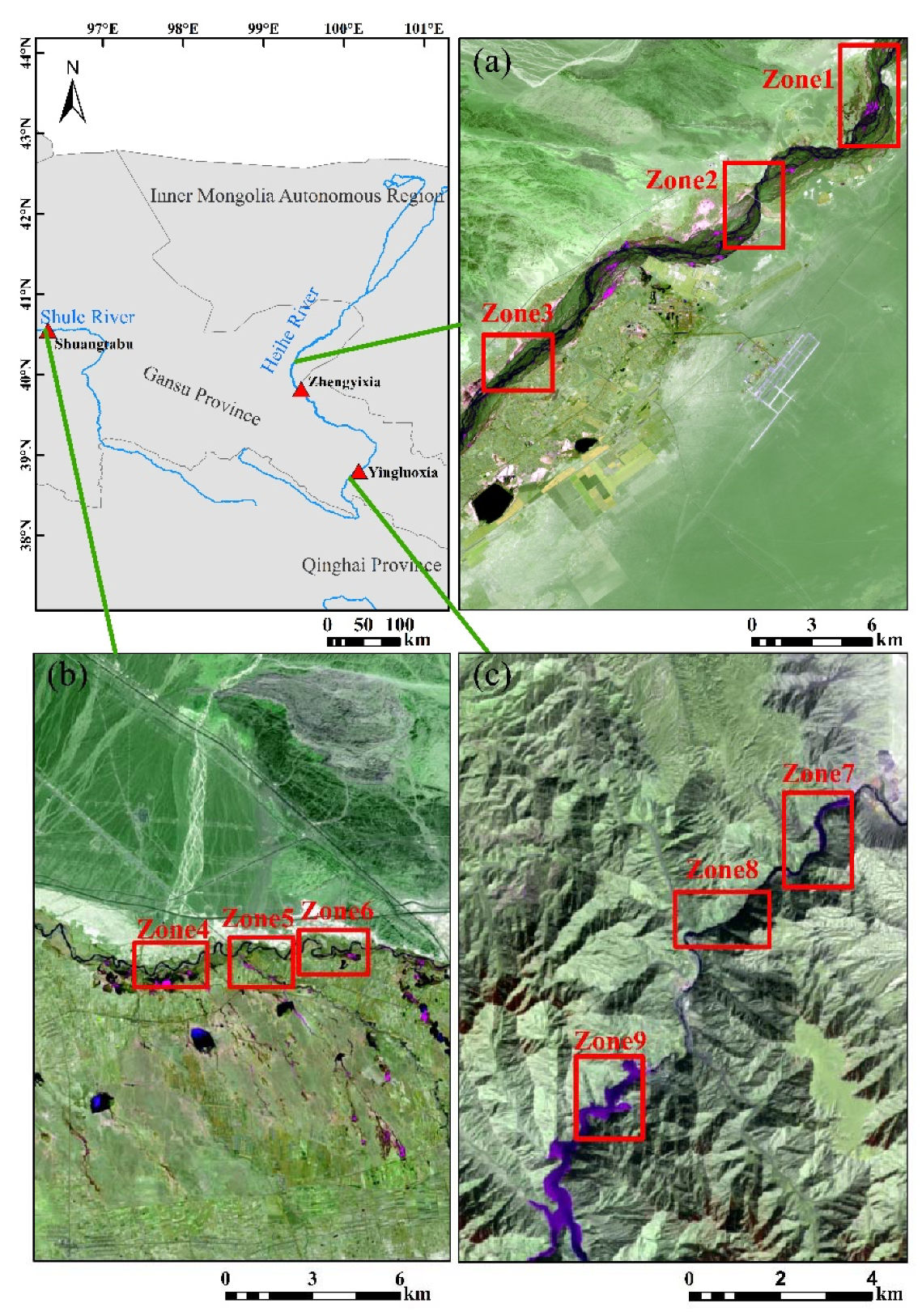
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methods
3.1. FMask Algorithm
3.2. Feature Set Construction
3.3. Posterior Probability Support Vector Machine (SVM)
3.4. Water Mapping Using Traditional Water Index Methods
3.5. Accuracy Assessment
3.5.1. Accuracy Assessment on Posterior Probability Images
3.5.2. Accuracy Assessment on Binary Water Maps
4. Result and Discussion
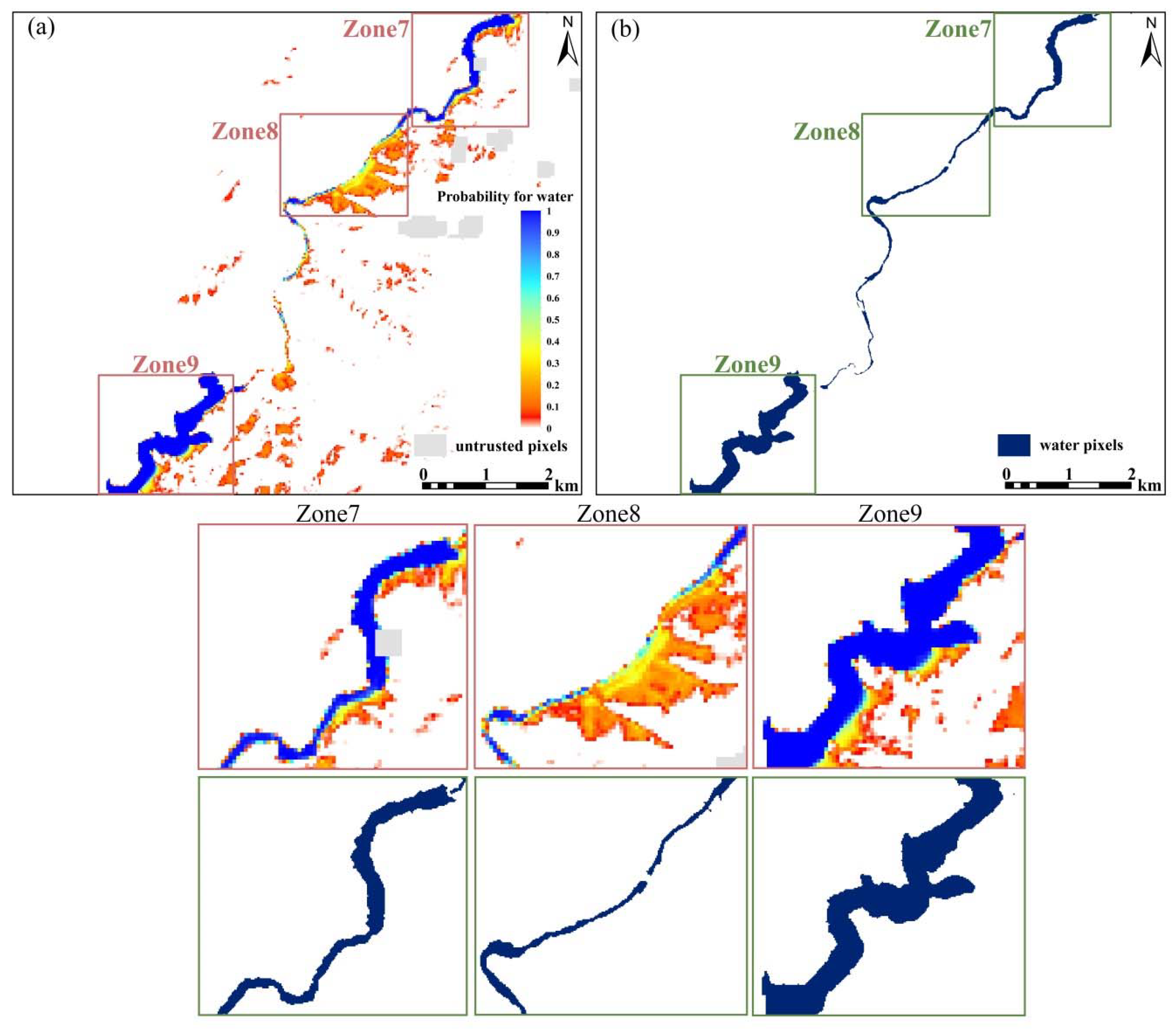
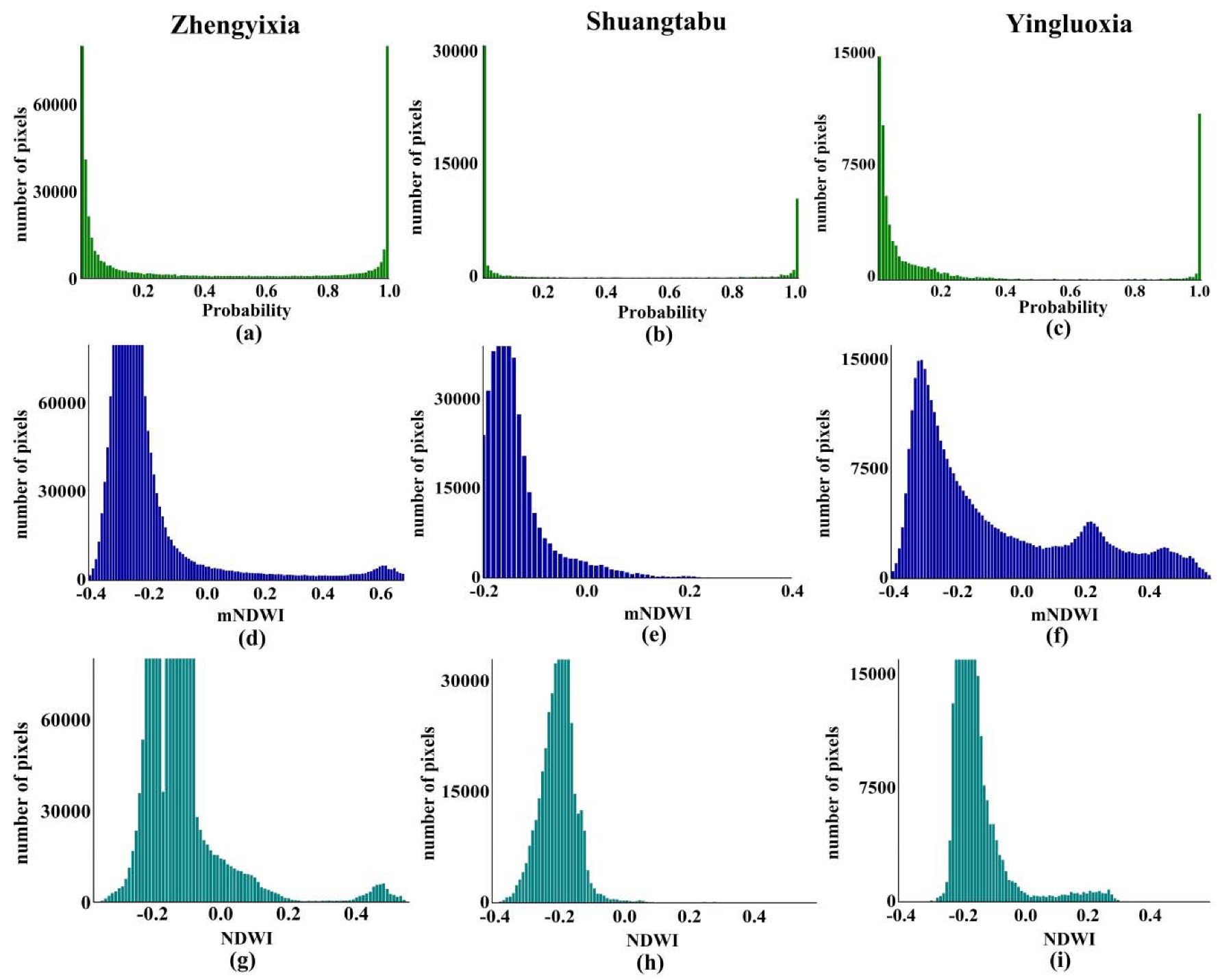
4.1. Posterior Probability Results
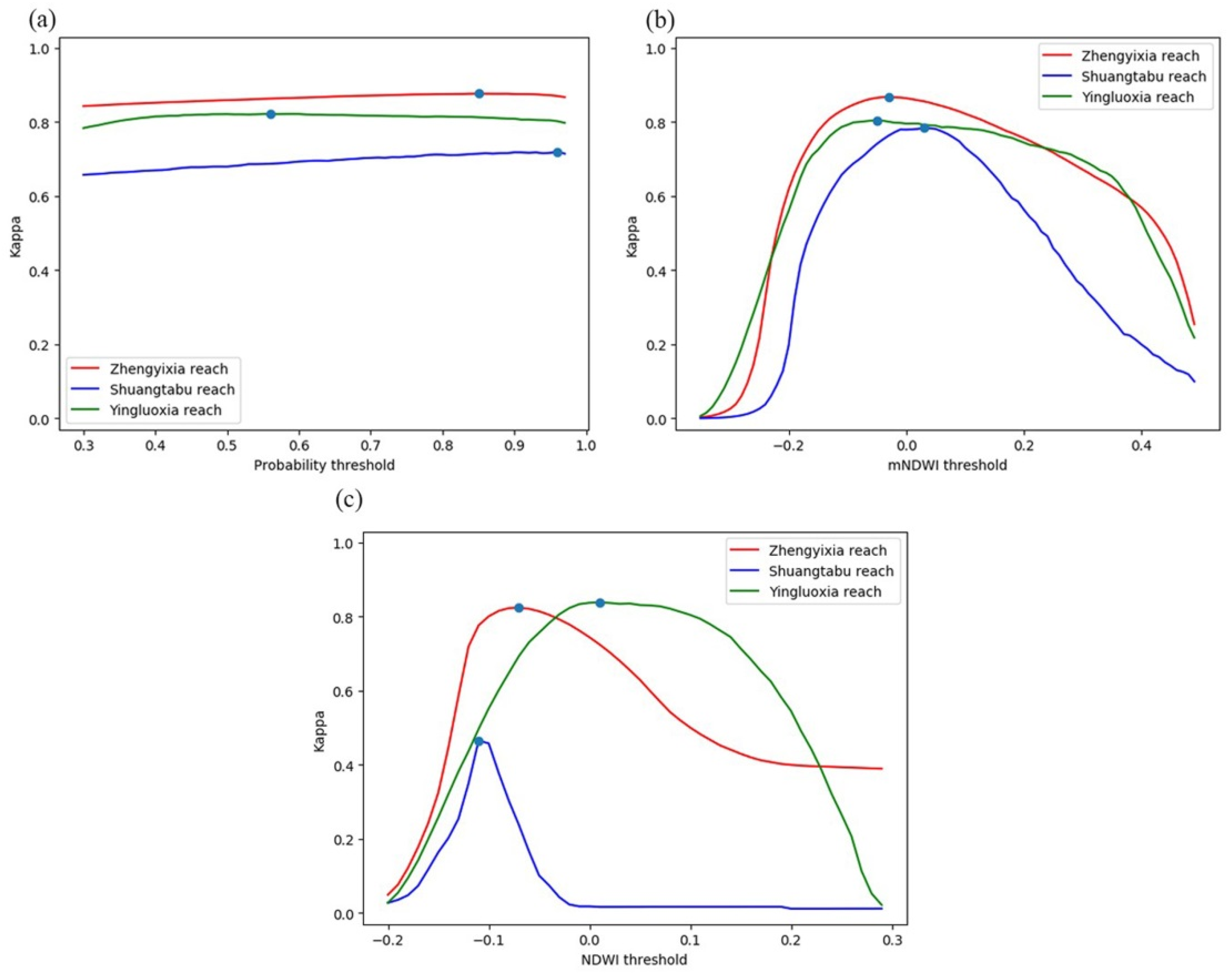
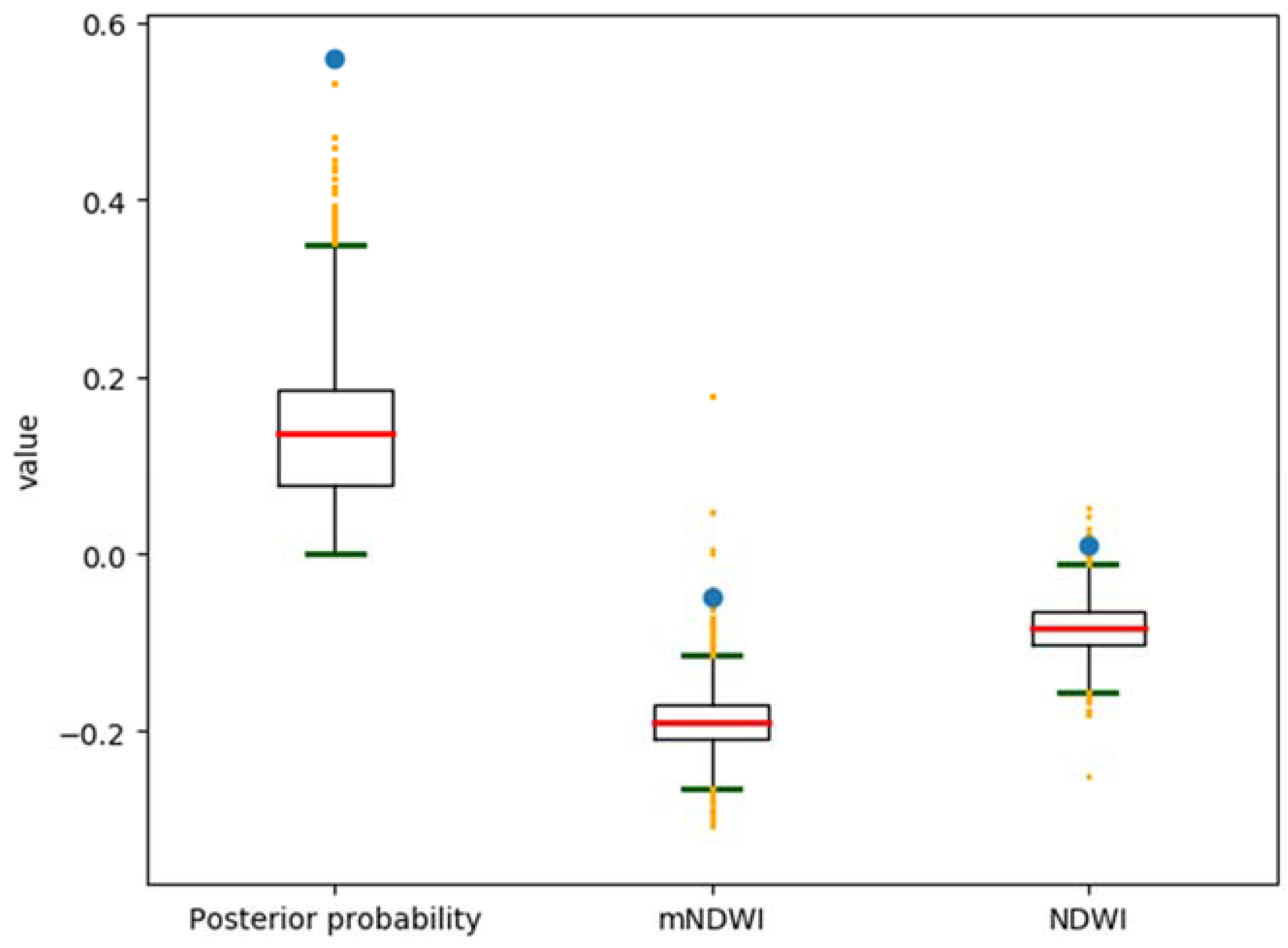
4.2. Histogram-Based Thresholding
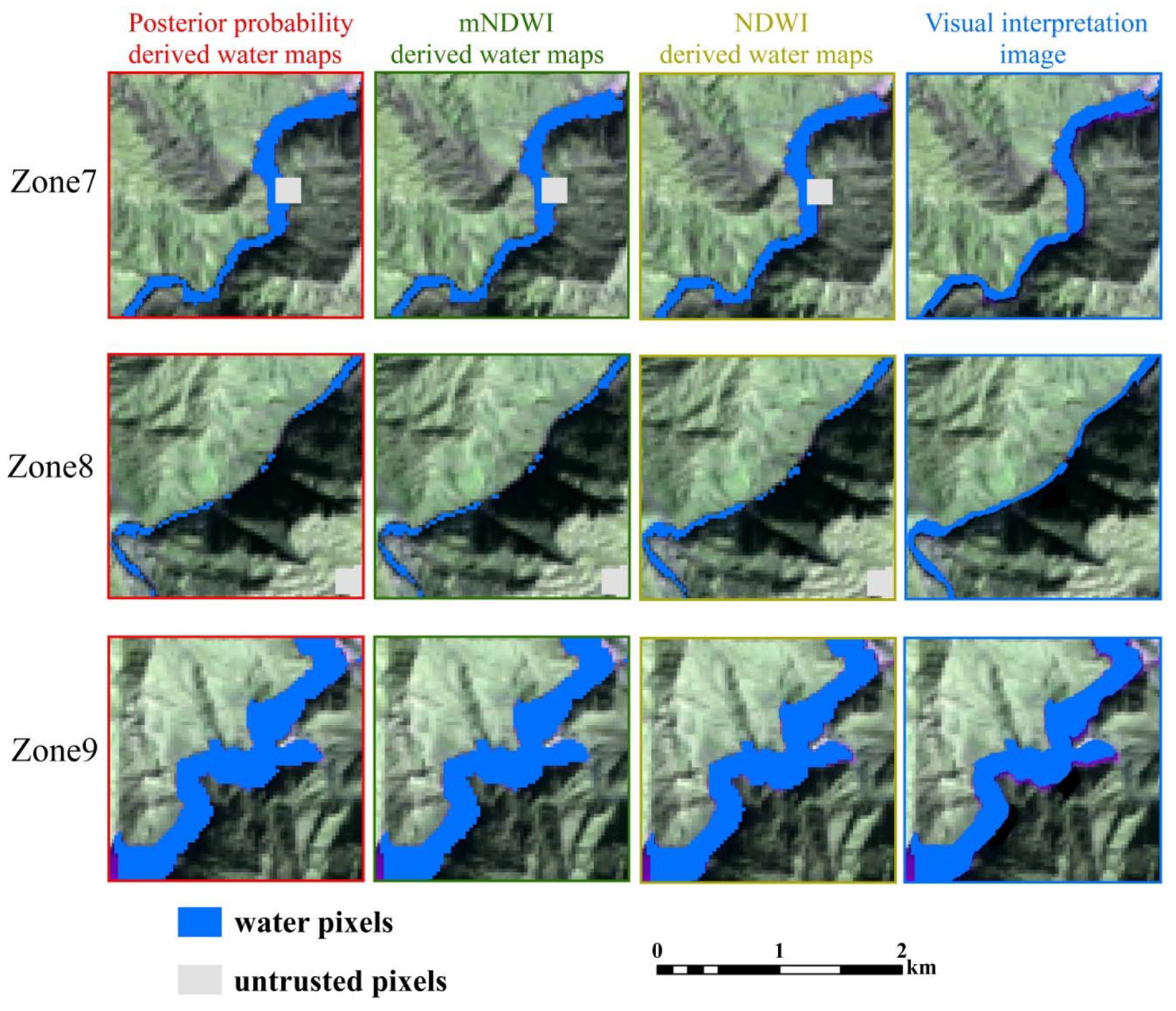
4.3. Binary Water Maps
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamazaki, D.; O’Loughlin, F.; Trigg, M.; Miller, Z.F.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Bates, P.D. Development of the Global Width Database for Large Rivers. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 3467–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing Landsat water index methods for automated water classification in eastern Australia. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Fatoyinbo, T.L.; Policelli, F. Flood extent mapping for Namibia using change detection and thresholding with SAR. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, P.S.; Page, K.J. Water Body Detection and Delineation with Landsat TM Data. Photogr. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Detecting, Extracting, and Monitoring Surface Water From Space Using Optical Sensors: A Review. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, D.; Trigg, M.; Ikeshima, D. Development of a global ~90 m water body map using multi-temporal Landsat images. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J. DEM-based modification of pixel-swapping algorithm for enhancing floodplain inundation mapping. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2013, 35, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, L.; Liu, R. An evaluation of Suomi NPP-VIIRS data for surface water detection. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Vernieuwe, H.; Verwaeren, J.; Chini, M.; Hostache, R.; Matgen, P.; Verhoest, N.; De Baets, B. Accounting for image uncertainty in SAR-based flood mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 34, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refice, A.; Capolongo, D.; Lepera, A.; Pasquariello, G.; Pietranera, L.; Volpec, F.; D’Addabbo, A.; Bovenga, F. SAR and InSAR for flood monitoring: Examples with COSMO/SkyMed data. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, R.; Kleuskens, M.P.H.; Winsemius, H.H.C.; Huizinga, H.J.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Bishop, C. Automated global water mapping based on wide-swath orbital synthetic-aperture radar. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Hostache, R.; Kavetski, D.; Chini, M.; Corato, G.; Schlaffer, S.; Matgen, P. Probabilistic Flood Mapping Using Synthetic Aperture Radar Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2016, 54, 6958–6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Tang, Z. Spectral matching based on discrete particle swarm optimization: A new method for terrestrial water body extraction using multi-temporal Landsat 8 images. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennó, C.; Nobre, A.D.; Cuartas, L.A.; Soares, J.V.; Hodnett, M.G.; Tomasella, J.; Waterloo, M.J. HAND, a new terrain descriptor using SRTM-DEM: Mapping terra-firme rainforest environments in Amazonia. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3469–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, A.D.; Cuartas, L.; Hodnett, M.; Rennó, C.; Rodrigues, G.; Silveira, A.; Waterloo, M.; Saleska, S. Height Above the Nearest Drainage – a hydrologically relevant new terrain model. J. Hydrol. 2011, 404, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Nguyen, D.; Zhang, S.; Cao, S.; Wagner, W. A Comparison of Terrain Indices toward Their Ability in Assisting Surface Water Mapping from Sentinel-1 Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Information 2017, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, U.; Choudhury, R.D. Soil texture classification using multi class support vector machine. Inf. Process. Agric. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.-Y.; Wu, X.-P. Posterior Probability Support Vector Machine Applied in Motor Imagery Classification. In Proceedings of the 2011 5th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Wuhan, China, 10–12 May 2011; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, J. Probabilities for support vector machines. In Advances in Large Margin Classifiers; Smola, A., Bartlett, P., Scholkopf, B., Schuurmans, D., Eds.; MIT Press: Boston, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Warrens, M.J.; Pratiwi, B.C. Kappa Coefficients for Circular Classifications. J. Classif. 2016, 33, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Site | Path/Row of Landsat-8 Image | Date of Landsat-8 Image | Date of Sentinel-2 Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zhengyixia | 134/32 | 2019-3-23 | 2019-3-22 |
| Shuangtabu | 136/32 | 2019-3-21 | 2019-3-18 |
| Yingluoxia | 134/33 | 2019-3-23 | 2019-3-22 |
| Name | Wavelength (μm) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| U-BLUE | 0.435–0.451 | Band 1 (ultra blue) surface reflectance |
| BLUE | 0.452–0.512 | Band 2 (blue) surface reflectance |
| GREEN | 0.533–0.590 | Band 3 (green) surface reflectance |
| RED | 0.636–0.673 | Band 4 (red) surface reflectance |
| NIR | 0.851–0.879 | Band 5 (near infrared) surface reflectance |
| SWIR1 | 1.566–1.651 | Band 6 (shortwave infrared 1) surface reflectance |
| SWIR2 | 2.107–2.294 | Band 7 (shortwave infrared 2) surface reflectance |
| Method | Overall Accuracy | Commission Error | Omission Error | Kappa | Critical Success Index (CSI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPSVM | 98.3% | 0.9% | 0.6% | 0.877 | 0.795 |
| mNDWI | 98.2% | 1.0% | 0.7% | 0.868 | 0.781 |
| NDWI | 97.7% | 1.1% | 1.2% | 0.824 | 0.723 |
| Method | Overall Accuracy | Commission Error | Omission Error | Kappa | Critical Success Index (CSI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPSVM | 98.9% | 0.6% | 0.5% | 0.719 | 0.574 |
| mNDWI | 99.1% | 0.5% | 0.3% | 0.784 | 0.650 |
| NDWI | 97.6% | 1.5% | 0.9% | 0.465 | 0.321 |
| Method | Overall Accuracy | Commission Error | Omission Error | Kappa | Critical Success Index (CSI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPSVM | 98.8% | 0.6% | 0.6% | 0.822 | 0.707 |
| mNDWI | 98.6% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.804 | 0.682 |
| NDWI | 98.9% | 0.5% | 0.6% | 0.839 | 0.730 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Huang, C.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S. Probabilistic River Water Mapping from Landsat-8 Using the Support Vector Machine Method. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091374
Liu Q, Huang C, Shi Z, Zhang S. Probabilistic River Water Mapping from Landsat-8 Using the Support Vector Machine Method. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(9):1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091374
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qihang, Chang Huang, Zhuolin Shi, and Shiqiang Zhang. 2020. "Probabilistic River Water Mapping from Landsat-8 Using the Support Vector Machine Method" Remote Sensing 12, no. 9: 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091374
APA StyleLiu, Q., Huang, C., Shi, Z., & Zhang, S. (2020). Probabilistic River Water Mapping from Landsat-8 Using the Support Vector Machine Method. Remote Sensing, 12(9), 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091374








