A Review of Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Satellite Resources, Institutions and Policies for Environmental Monitoring in China
2.1. Remote Sensing Satellite and Sensor Resources for Environmental Monitoring
2.2. Major Research and Education Institutions Involved in Remote Sensing of the Environment
2.3. Major Remotely-Sensed Environmental Monitoring Policies
3. Advances in Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring
3.1. Remote Sensing Retrieval of Ecological Indexes
3.1.1. Vegetation Index
3.1.2. Soil and Vegetation Moisture
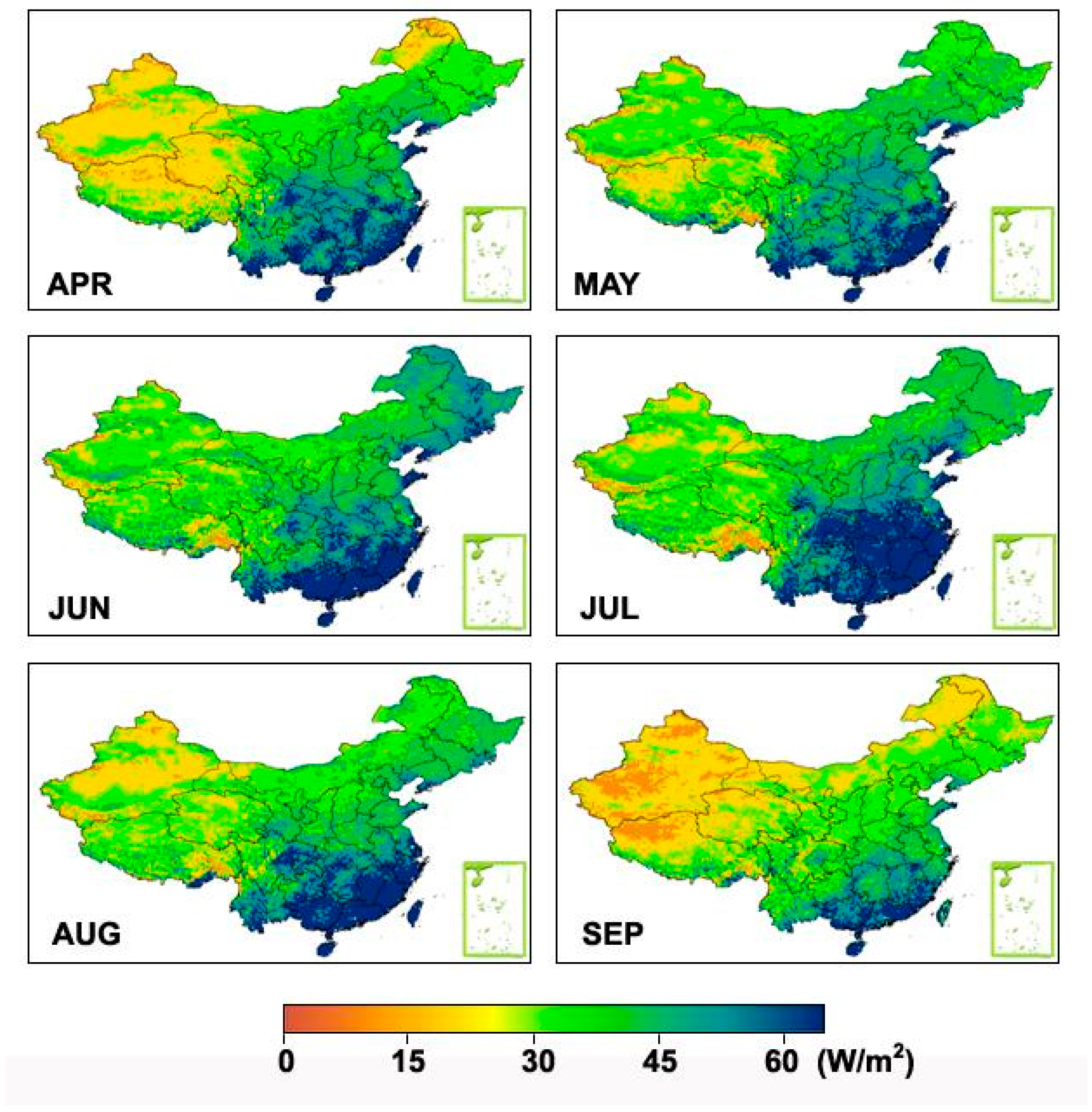
3.1.3. Evapotranspiration
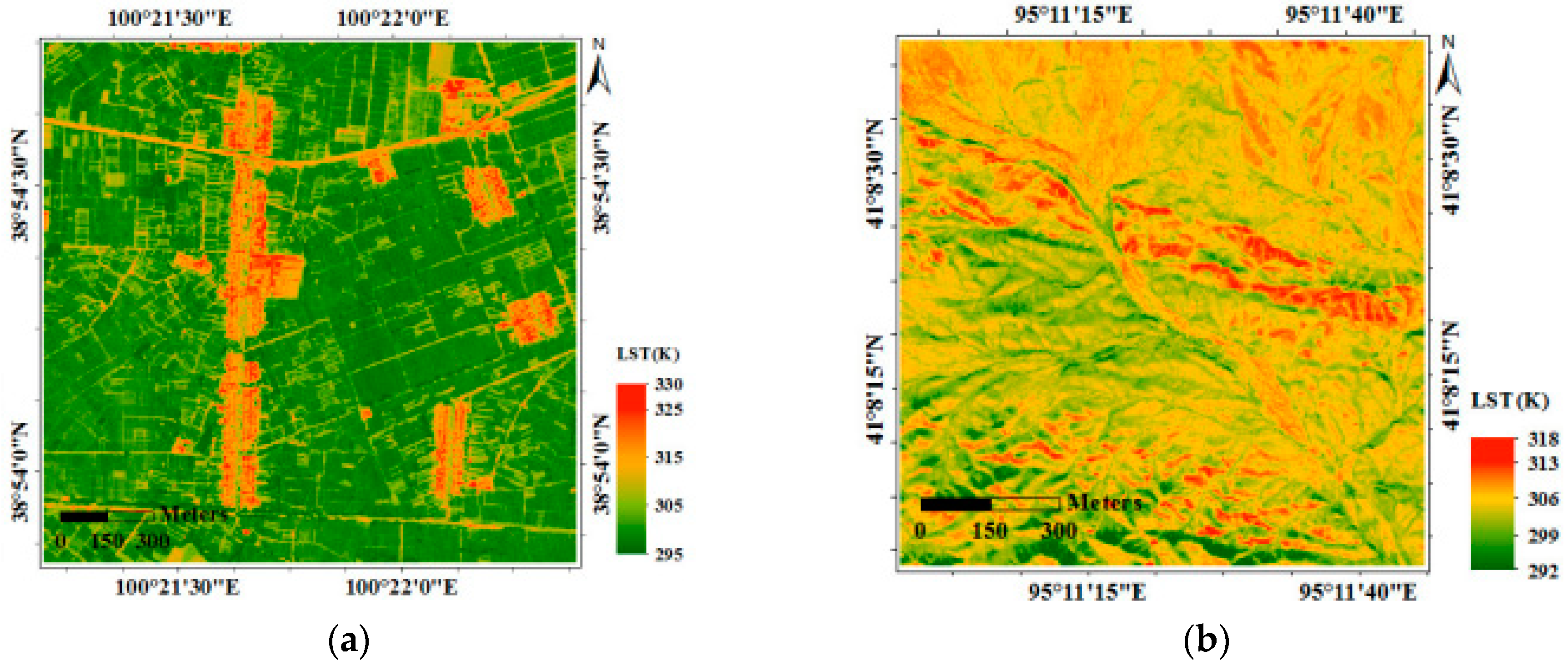
3.1.4. Land Surface Temperature
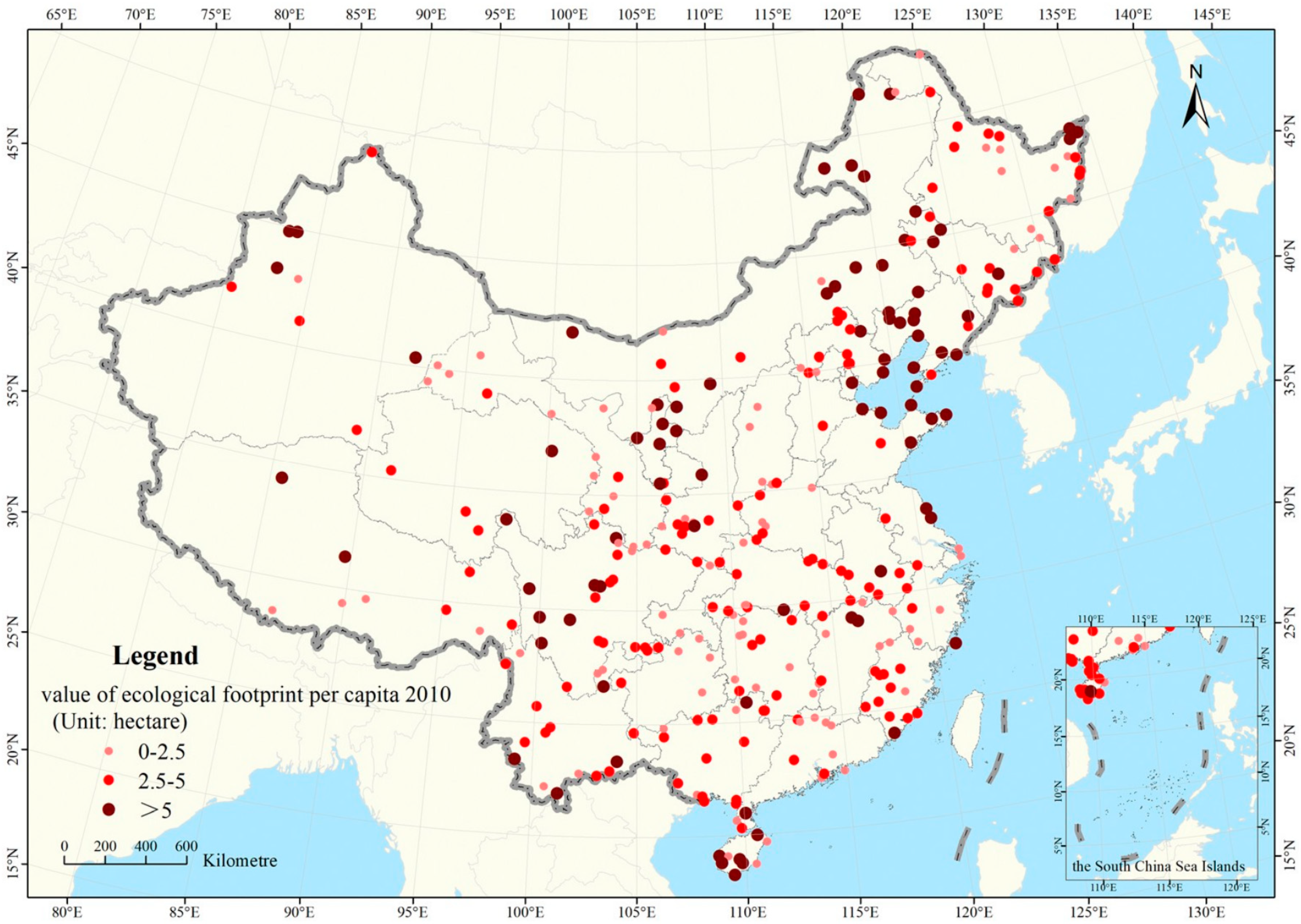
3.2. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Protected Areas
3.2.1. Nature Reserves
3.2.2. Biodiversity Conservation Priority Areas
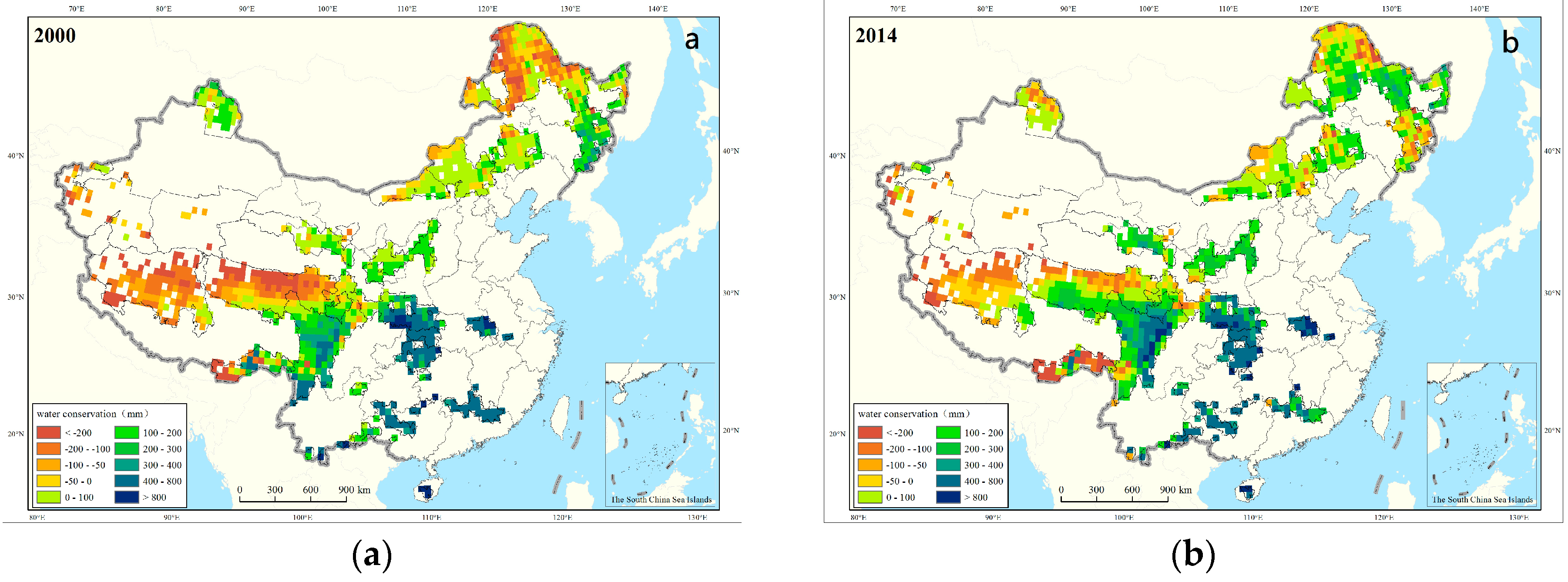
3.2.3. National Key Ecological Functional Region
3.3. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Rural Areas
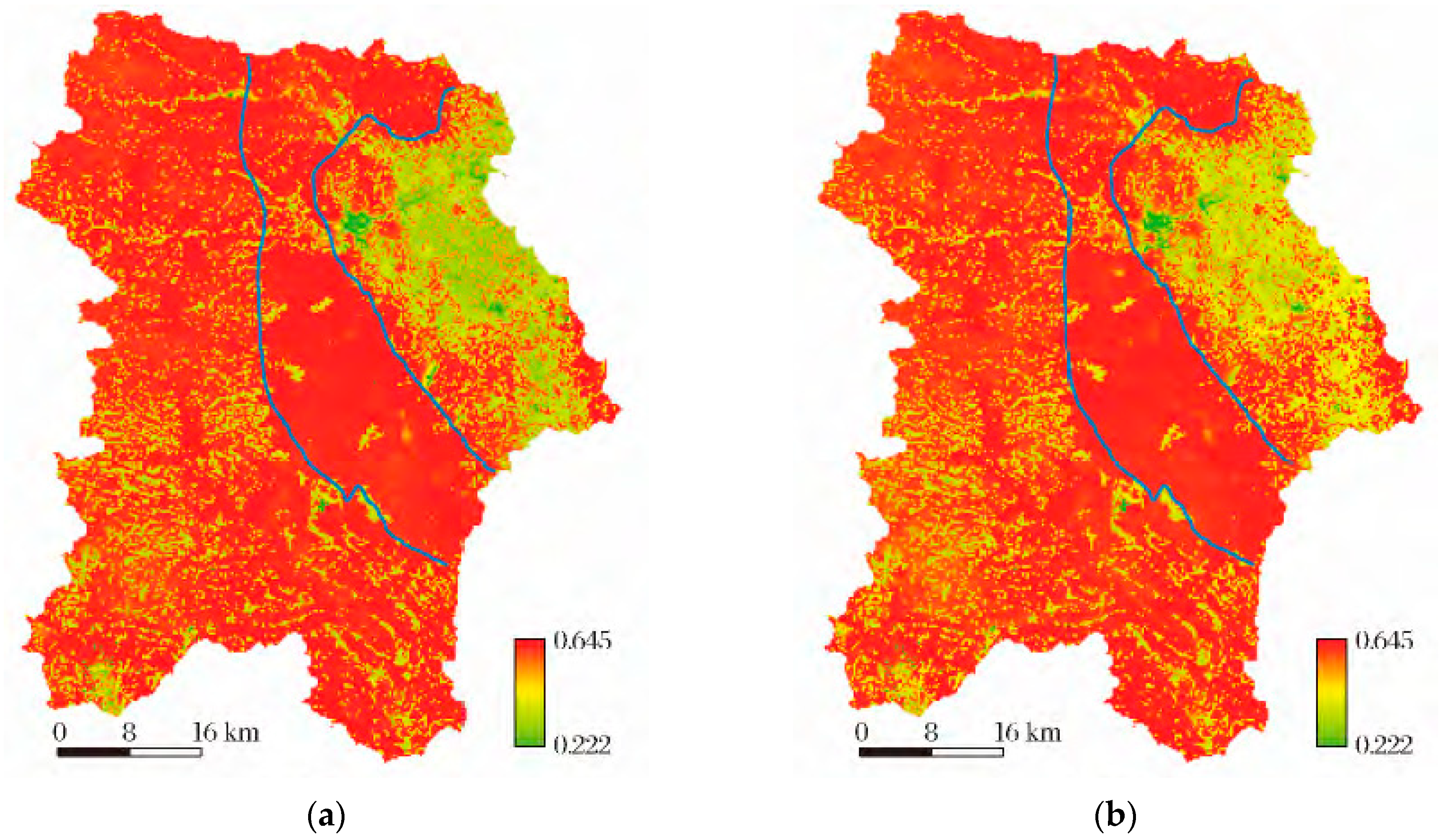
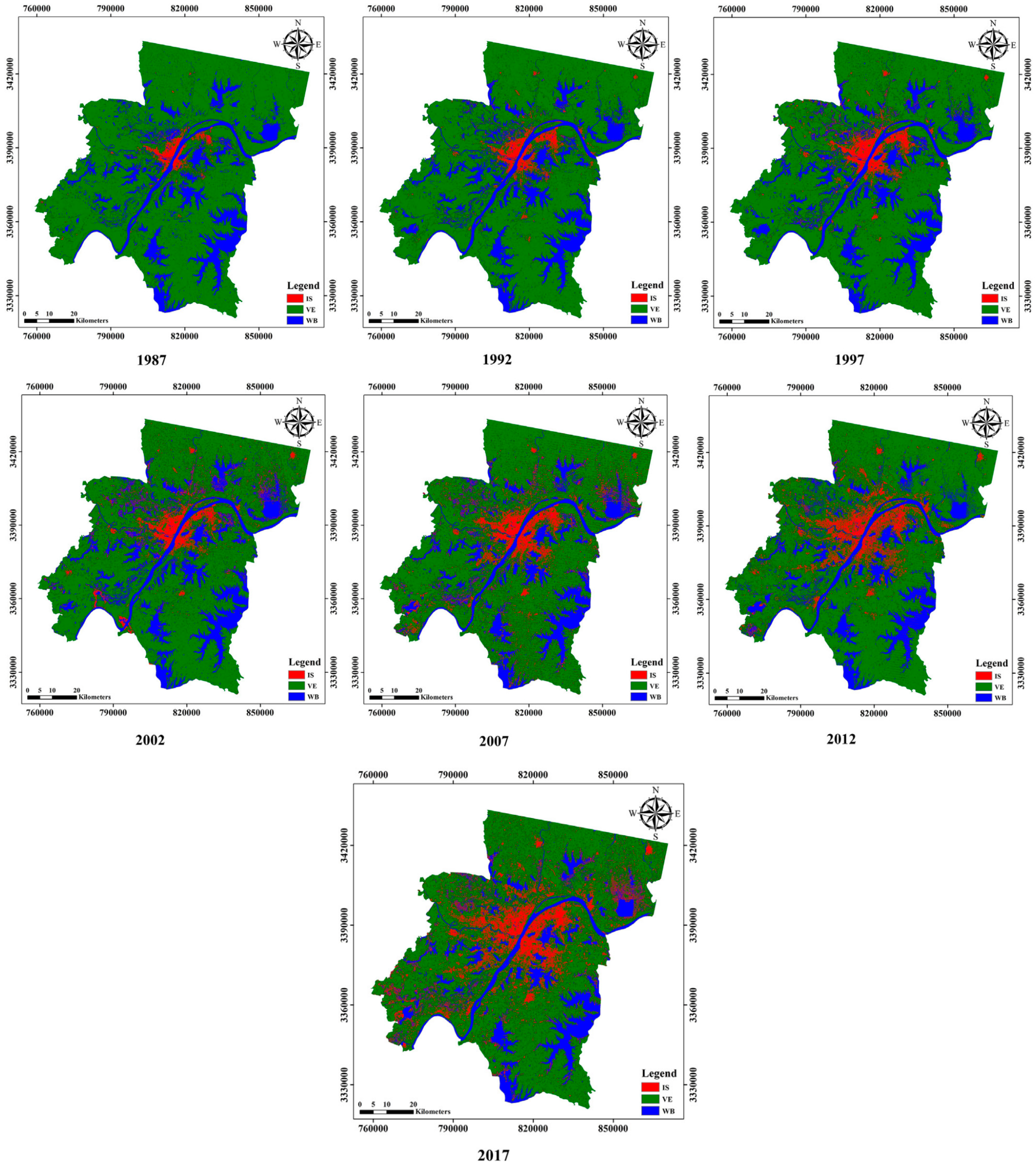
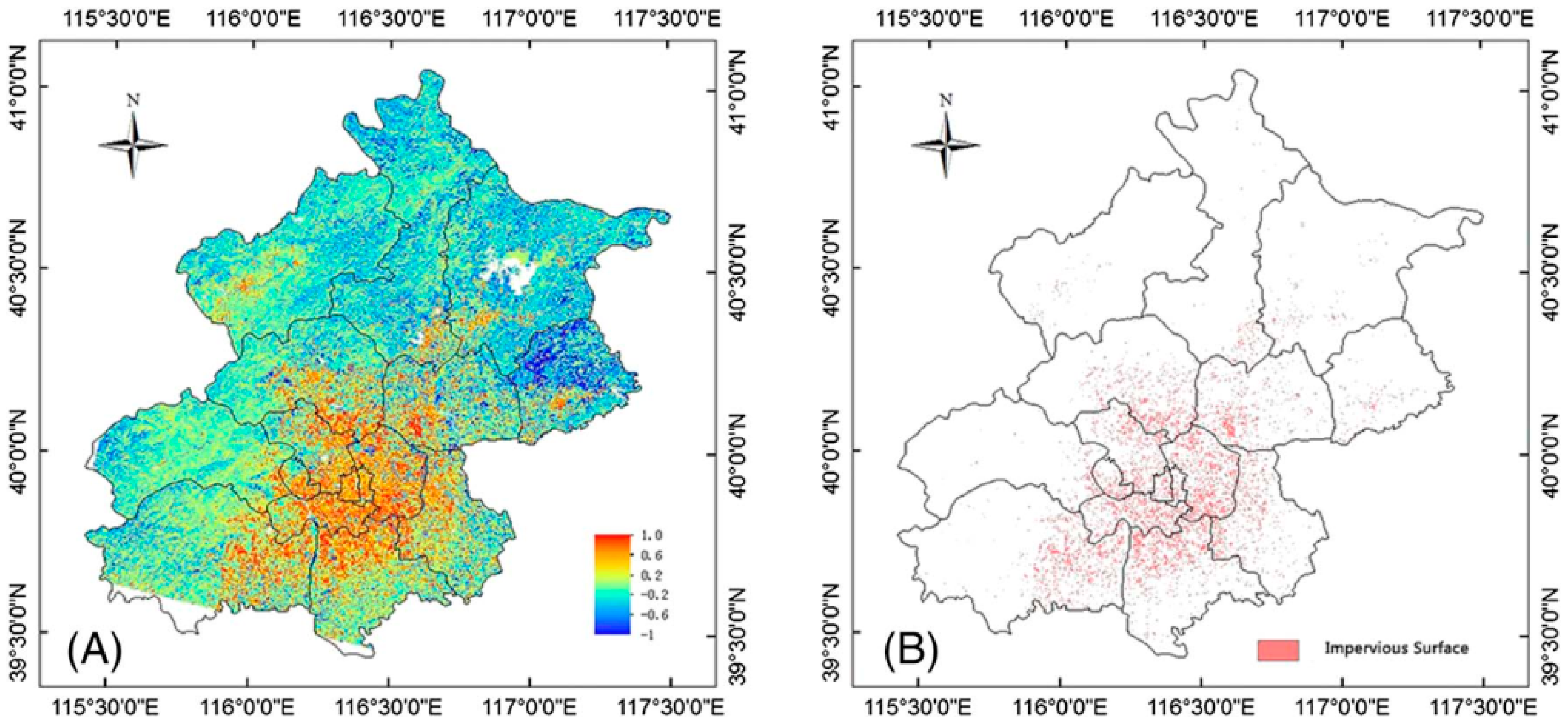
3.4. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Urban Areas
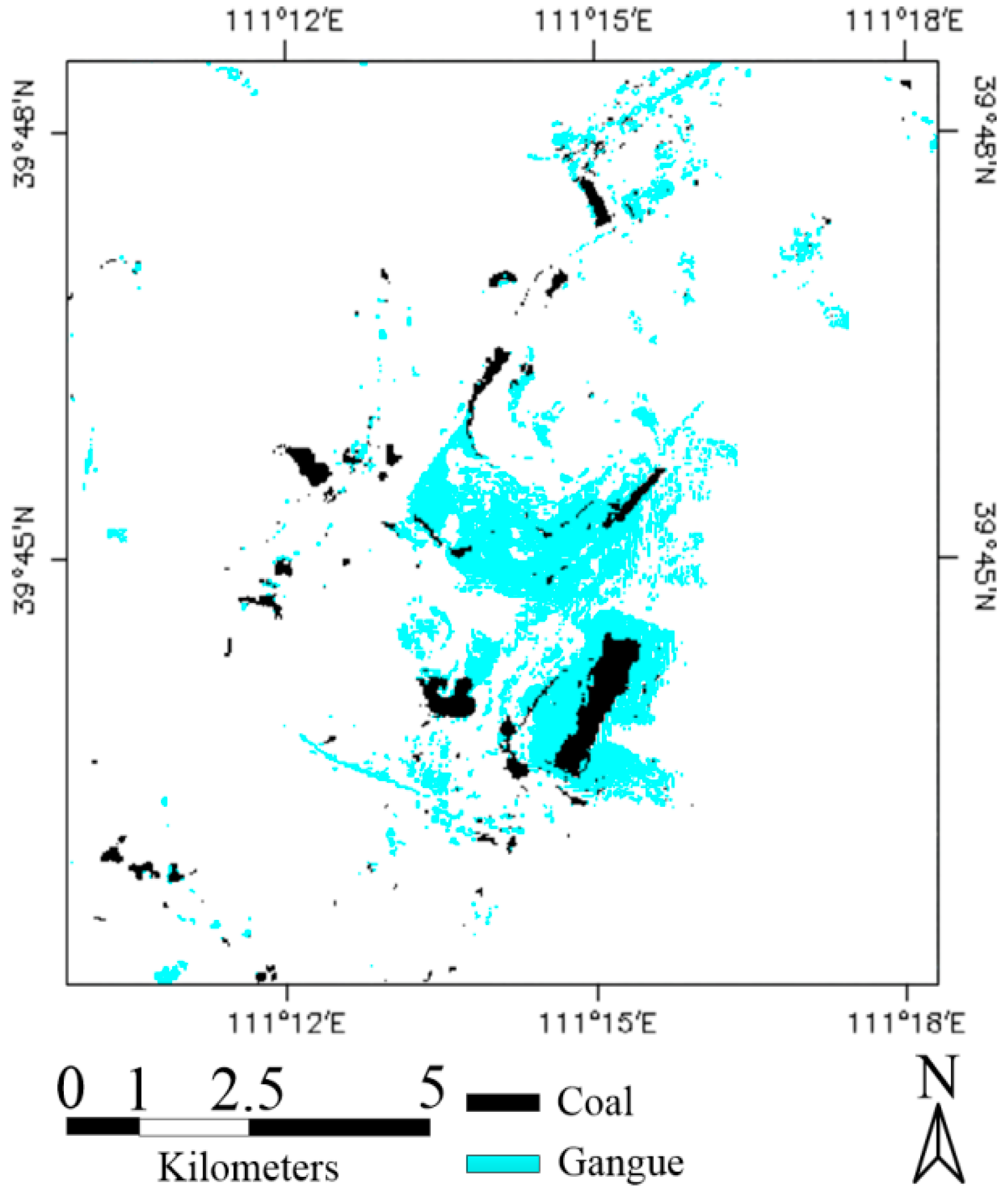
3.5. Remote Sensing Monitoring of MiningAreas
4. Discussion
4.1. Major Challenges of Remote Sensing of Environment in China
4.2. Outlook of Remote Sensing of Environment in China
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Yan, Y. Investigating the Impact of Human Activity on Land Use/Cover Change in China’s Lijiang River Basin from the Perspective of Flow and Type of Population. Sustainability 2017, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, H.; Ishii, R.; Nagai, S.; Suzuki, R.; Motohka, T.; Noda, H.M.; Hirota, M.; Nasahara, K.N.; Oguma, H.; Muramatsu, K. Linking Remote Sensing and In Situ Ecosystem/Biodiversity Observations by “Satellite Ecology”; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2012; pp. 277–308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z. An overview of satellite remote sensing technology used in China’s environmental protection. Earth Sci. Inform. 2017, 10, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Q.; Yao, Y.; You, L.; Jiang, H.; Cui, R. Research on Using a Mono-Window Algorithm for Land Surface Temperature Retrieval from Chinese Satellite for Environment and Natural Disaster Monitoring(HJ-1B) Data. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2011, 31, 1552–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Huang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, W. Evapotranspiration estimation for oasis transect in middle reach of Heihe river basin based on remote sensing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Yang, J.; Han, X.; Tang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Gao, C. Retrieving land surface temperature based on deep dynamic learning NN algorithm and radiation transmission model. China Agric. Inform. 2018, 30, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Xu, J.; Xu, L. An analysis on eco-environmental effect of urban land use based on remote sensing images: A case study of urban thermal environment and NDVI. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q. Trajectory and Driving Forces of Change in Farmland in Nanjing During the Period From 1985 to 2010. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2013, 29, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Liao, X.; Wang, T. Cultivated Land Use Changes in Hunan Based on Remote Sensing. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2014, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Meng, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. Characterizing spatial and temporal trends of surface urban heat island effect in an urban main built-up area: A 12-year case study in Beijing, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wu, D. Progress of Urban Ecological Environment Monitoring by Remote Sensing in China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J. Monitoring Glacier Change Based on Remote Sensing in the Mt. Qomolangma National Nature Preserve,1976-2006. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2010, 65, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zhu, B.; Tong, X.; Yue, Y.; Gan, H.; Wan, S. Change analysis in Hainan Dongzhai Wetland Reserve based on remote sensing data obtained during 2002-2013. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2017, 29, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; De, S.; Bao, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhao, C.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y. Dynamic Monitoring of Fractional Vegetation Cover of Eco-Function Area of Grassland on Northern Foot of Yinshan Mountains through Remote Sensing Technology. Res. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, D.; Ren, W. Comparison of Vegetation Coverage Extracting Based on MODIS Data. J. Atmos. Environ. Opt. 2010, 05, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Jin, G.; Deng, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Study of vegetation information extraction method based on Landsat8 satellite images. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2016, 41, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y. Study on Vegetation Information Extraction Method Based on Landsat-8 OLI Images. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2018, 41, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Ju, W.; Chen, J. Evaluation of topographic effects on four commonly used vegetation indices. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 17, 210–234. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Yang, B.; Wang, L.; Cheng, L.; Li, D. Comparison of methods for extracting vegetation information from GF-1. Agric. Technol. 2017, 37, 46–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Niu, S.; Ma, L.; He, H. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Vegetation Cover in Shule River Valley During 2000-2014. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2016, 32, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tian, M.; Liang, H.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C.; Qu, K.; Qian, J. Spatial and Temporal Changes of Vegetation Coverage and Influencing Factors in Hulun Buir Grassland During 2000-2016. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2018, 34, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, G.; Qin, Q.; Yao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, C. Remote detection of bare soil moisture using a surface-temperature-based soil evaporation transfer coefficient. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, S.; Shen, X.; Sui, X. New Index for Soil Moisture Monitoring Based on ∆Ts-Albedo Spectral Information. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2011, 31, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H. Soil moisture retrieval based on GA-BP neural networks algorithm. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2012, 31, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Qin, Q.; Ren, H.; Gao, Z.; Wu, L.; Meng, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Bare Soil Moisture Inversion Model Based on Visible-Shortwave Infrared Reflectance. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2015, 35, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Qin, Q. Soil Moisture Monitoring Based on Angle Dryness Index. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2016, 36, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, H.; Wang, X.; You, L. Reconstructing missing data in soil moisture content derived from remote sensing based on optimum interpolation. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2018, 30, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhao, Y. A new semi-empirical model for soil moisture content retrieval by ASAR and TM data in vegetation-covered areas. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, Y.; Xiong, W.; You, D.; Li, Y. Soil Moisture Mapping Using two Scenes SAR Imagery Without Knowing Information on Surface Parameters. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xuan, J. Retrieval method of soil moisture based on polarized information. Infrared Laser Eng. 2018, 47, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ji, W.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Z. Soil bidirectional reflectance characteristics as affected by soil moisture. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2011, 48, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Tong, L.; Jian, J.; Gu, X. Remote Sensing Quantitative Monitoring and Analysis Fuel Moisture Content Based on Spectral Index. Acta Opt. Sin. 2009, 29, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Yang, W.; Jian, J.; Dai, X. Remote Sensing Retrieval Model of Vegetation Moisture Content Based on Spectral Index: A Case Study in Maoergai of Mibjiang River’ Upstream. Remote Sens. Inf. 2013, 28, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Huang, C.; Lu, L.; Gu, J. Theretrieval of Vegetation Water Content based on ASTER Images in Middle of Heihe River Basin. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2015, 30, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Q.; Yao, Y.; Du, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, J. Estimating and Validating Wheat Leaf Water Content with Three MODIS Spectral Indexes: A Case Study in Ningxia Plain, China. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2016, 18, 387–398. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Leng, P.; Zhou, F.; Li, S. Estimation of vegetation canopy water content using Hyperion hyperspectral data. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2013, 33, 2833–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL): 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ji, R.; Xu, D.; Jia, Q.; Feng, R.; Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y. Daily evapotranspiration estimation of Panjin wetland based on SEBAL model and its distribution characteristics. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 15, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Remote Sensing Estimation of Land Surface Evapotranspiration Based on HJ-1B Data and SEBAL Model. Geospat. Inf. 2013, 11, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, H. Modelling evapotranspiration in provincial regions based on FY-3/VIRR remote sensing data. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for Estimation of Turbulent Heat Fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 1988, 6, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhou, J. Evapotranspiration in Heihe River Basin based on SEBS model. J. Lanzhou Univ. 2008, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J. Estimation and Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Evapotranspiration in Small-Scaled Catchments in Subtropics of China Based on Landsat 8 Data. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2016, 32, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y. Evapotranspiration and the Factors Affecting It in Chakou Basin Studied with the SEBS Model. J. Irrig. Drain. 2018, 37, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-Based Energy Balance for Mapping Evapotranspiration with Internalized Calibration (METRIC)—Model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 4, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Sun, L. Estimating latent heat flux over farmland from Landsat images using the improved METRIC model. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2018, 30, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, Y.; Bie, Q.; Fang, J.; Zhao, C. Estimation of field evapotranspiration in the middle reaches of Heihe River basin based on SEBS-METRIC Method. J. Lanzhou Univ. 2013, 49, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Qin, Q.; Fadhil, A.M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S.; Sui, X.; Dong, H. Evaluation of EDI derived from the exponential evapotranspiration model for monitoring China’s surface drought. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Karnieli, A.; Berliner, P. A mono-window algorithm for retrieving land surface temperature from Landsat TM data and its application to the Israel-Egypt border region. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3719–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, H.; Du, Y.; Cao, B.; Liu, Q.; Li, B. Retrieval and validation of the land surface temperature derived from Landsat 8 data: A case study of the Heihe River Basin. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 22, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Cheng, P.; Gui, X.; Teng, Y.; Tong, C. Overview of Surface Temperature Inversion Algorithm. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2016, 39, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, P.; Ye, Q. A Split-window Algorithm for Retrieving Land Surface Temperature from ASTER Data. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2012, 27, 728–734. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Ren, H.; Liu, R.; Qin, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J. Land Surface Temperature Estimate from Chinese Gaofen-5 Satellite Data Using Split-Window Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5877–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, A.; Wang, X.; Gao, Z.; LI, G. Vegetation spatio-temporal changes and driving factors in the Mt. Qomolangma Nature Reserve in 2000-2007. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, G.; Huang, C.; Zong, X. Using Remote Sensing Data to Monitor Dynamic Changes of Nature Reserve of the Yellow River Delta. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2010, 26, 376–381. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Su, D.; Xie, R. Research on the impact of land use activities on nature reserves: Heilongjiang Province as a case. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 38, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wen, R. Method for supervising and assessing of human activities in nature reserve based on sky and earth. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 3135–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Qin, W.; Liu, X.; Xia, X.; Zhou, D.; Fan, L.; Jiang, M. Status Quo of Distribution of Human Activities in the National Nature Reserves. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2015, 31, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xinghua, W.U.; Yang, S. The monitoring and evaluation of protective effectiveness in Shibalichangxia Nature Reserve of Hubei based on Remote Sensing technology. J. Cent. China Norm. Univ. 2015, 49, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fu, J.; Jiang, D.; Luo, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, H.; Wen, R.; Wang, X. Improvement of Ecological Footprint Model in National Nature Reserve Based on Net Primary Production (NPP). Sustainability 2018, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Xu, X. Human Disturbance Monitoring and Assessment in the Biodiversity Conservation Priority Area China. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2017, 19, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Qiao, W.; Jing, L.; Liu, X. Monitoring an invasive plant using hyperspectral remote sensing data. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, H. Biodiversity Monitoring and Assessment Using Remote Sensing Technology at County’s Scale. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2015, 30, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiong, K.; Huang, D. Analysis on the Spatiotemporal Change and Influence Factors of Vegetation Cover in Fanjingshan Mountain over the Last 30 Years. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yang, H.; Ding, F.; LI, Z. Spatial distribution and aggregation analysis of human activity in national key ecological function regions in China. Resour. Sci. 2016, 38, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Yuping, L.; Peng, H.; Tong, X.; Cao, G. Water Conservation Service Assessment and Its Spatiotemporal Features in National Key Ecological Function Zones. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Ecological Function Evaluation of Changbai Mountain Ecological Function Area. Master’s Thesis, Yanbian University, Yanbian, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, P. The Ecological Environment Change Monitoring in Earthquake Disaster Area Based on Remote Sensing. Surv. Mapp. 2018, 41, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wei, C.; Wang, A.; Zhou, H.; Chi, Y. Study on monitoring of informal open-air solid waste dumps based on Beijing-1 images. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 13, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, S.; Meng, B.; Ma, W.; Zhu, L.; Wu, C. Analysis of the non-regular garbage sites in the region of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei using remote sensing monitoring images. Chin. High Technol. Lett. 2016, 26, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, W.; Wen, J. Application of Satellite Image and Digital Elevation Model in Rural Environmental Quality Monitoring. Environ. Monit. China 2014, 30, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Cao, X. Mapping plastic greenhouse with medium spatial resolution satellite data: Development of a new spectral index. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Lou, Q.; Teng, J. Study on Extraction of Plasticulture Basing on GF-1 of High Resolution Image of China. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 43, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, L. A predictive model for the hyperspectral character of saltmarsh soil to its heavy metal content at Chongming Dongtan. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 08, 3427–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Wu, Q.; Cao, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L. Quantitative Retrieval of Soil Heavy Metal Content in Longkou Wastewater Irrigation Area Based on HJ1A-HSI Images. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2015, 22, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Wang, X.; Shen, R.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. Study on Heavy Metal Element Content in the Coastal Saline Soil by Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2010, 25, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W. Study on Soil Cd Monitoring in Sewage Irrigation Area by Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. South North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 11, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wen, Q.; Liu, F.; Li, N. Remote Sensing Monitoring and Temporal Variation Analysis of Coastal Aquaculture in Shandong Province in the Recent Three Decades. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2014, 16, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, S. Estimation on pollution load and analysis on spatial characteristics of mariculture in Zhelin Bay. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2017, 44, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liu, M. Application analysis on the urban heat environment monitoring of Chongqing using HJ-1B satellite remotely sensed data. Sci. Sin. 2011, 41, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Li, L.; Fan, Y. Analysis of the Relationship between Urban Heat Island Effect and Urban Expansion in Chengdu, China. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2014, 16, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Ding, F.; Li, Q. Remote Sensing Analysis of Changes of Urban Thermal Environment of Fuzhou City in China in the Past 20 Years. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 20, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, X. A Study of Remote Sensing Monitoring of Urban Thermal Environment Based on ASTER Data. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2011, 19, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, C.; Yin, J.; Zhao, J. Monitoring of Urban Thermal Environment in Shanghai Area from 1995 to 2012 Using Thermal Satellite Remote Sensing. Infrared Technol. 2016, 38, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, L. Spatiotemporal changes of thermal environment landscape pattern in Changsha. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 3743–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, L. Study on Dynamic Monitoring Method of Urban Greening Land. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; Wang, J. Monitoring of urban ecological land use based on Gaofen-1 data. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2016, 41, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, H.; Gong, P.; Ju, W. Relationship Between Land Brightness Temperature and Vegetation Abundance in Wuhan City. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2009, 29, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Ren, Z.; Cui, M.; He, X. Spatial and temporal changes to urban surface thermal landscape patterns: A case study of Changchun City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 3264–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiong, C. Vegetation Coverage Based on Landsat8 Images in Guangzhou. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 38, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Y. Study on the thermal environment and its relationship with impervious surface in Beijing city using TM image. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013, 22, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Xu, H. Quantitative Relationship Between Impervious Surface and Land Surface Temperature Based on Remote Sensing Technology. J. Jilin Univ. 2013, 43, 1987–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MaiMaiTiJiang, M.; Kasimu, A. Study on Land Surface Characteristics and Its Relationship with Land Surface Thermal Environment of Typical City in Arid Region. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 24, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, R.; He, Z. An Analysis on Urban Impervious Surface and Its Relation with Thermal Environments Based on Landsat 8. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2015, 38, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, B.; Chen, D. Surface Parameters Analysis of Shenyang Urban Heat Island Based on Landsat. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2018, 41, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Fu, H.; Li, D.; Altan, O.; Cheng, T. Remote sensing monitoring of multi-scale watersheds impermeability for urban hydrological evaluation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, X. Advances in urban information extraction from high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, C.; Tong, X.; Liu, S. A New Fusion Approach for Extracting Urban Built-up Areas from Multisource Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xue, L. Dynamic monitoring and analysis of ecological environment in Weinan City, Northwest China based on RSEI model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3913–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, M.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Shi, W.; Xie, B. Quantitative Assess the Dynamic Change of Urban Ecological Environment Based on Remote Sensing-A Case Study in Yixing City, Jiangsu Province. J. Ningxia Univ. 2017, 38, 294–301. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Ma, B.; Liu, S. Analysis to vegetation coverage change in Shendong mining area with SPOT NDVI data. J. China Coal Soc. 2009, 34, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Guli, J.; Bao, A.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, J. Damage assessment of the vegetable types based on remote sensing in the open coalmine of arid desert area. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 707–713. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, D.; Shen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liao, B.; Wang, W. Changes of ecological environment in the Dexing copper mine based on TM images. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2015, 27, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yu, J.; Lu, Y. Investigation and Assessment of Artificial Influencing Factors of Land Degradation in Shendong Coal Mining Area Based on ZY-3 Satellite Data. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2016, 32, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Fu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, X. Remote Sensing Inversion of Soil Zinc Pollution in Gejiu Mining Area of Yunnan. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2018, 33, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Le, B.; Xiao, D.; Mao, Y.; Shan, F.; Ha, T. Coal mine area monitoring method by machine learning and multispectral remote sensing images. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, H.; Yin, P.; Wu, L.; Li, G. Landscape ecological quality assessment and its dynamic change in coal mining area: A case study of Peixian. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Gao, J. Aanlysis on Dynamic Change of Eco-Environmental Quality in Kailuan Mining Subsidence Area. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 433–440, 1433–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X. Monitoring of Vegetation Coverage Variation Based on Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data in Shendong Centre. Environ. Monit. China 2014, 30, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, E.; Yue, H. Dynamic monitoring and trend analysis of vegetation change in Shendong mining area based on MODIS. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2017, 29, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qiu, K. Dynamic Monitoring of Vegetation Coverage in Huainan Mining Area Based on MODIS NDVI. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2018, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J. How China will protect one-quarter of its land. Nature 2019, 569, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Satellite | Sensor | Spectral Range (μm) | Spatial Resolution (m) | Revisit Time (day) | Swath Width (km) | Launch Time | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOS-Terra/Aqua | MODIS | 0.62–14.38 | 250/500/1000 | 0.5 | 2330 | 1999/2002 | USA |
| Aster | 0.52–11.65 | 15/30/90 | 16 | 60 | 1999 | Japan | |
| NOAA-TIROS-N NOAA-7–19 | AVHRR | 0.55–12.5 | 1100 | 6 | 2800 | 1978.10–2009.2 | USA |
| Landsat (1–8) | MSS | 0.5–1.1 | 80 | 18 | 185 | 1972.7–1984.3 | USA |
| TM | 0.45~2.35 | 30/60/120 | 16 | 185 | 1982.7–1984.3 | USA | |
| ETM+ | 0.45~0.90 | 15/30/60 | 16d | 185*170 | 1999.4 | USA | |
| OLI | 0.433–1.39 | 15/30/60 | 16d | 170*180 | 2013.2 | USA | |
| TIRS | 10.6–11.2 11.5–12.5 | 100 | 16d | 170*180 | 2013.2 | USA | |
| IKONOS-2 | OSA | 0.45–0.9 | 0.82/3.28 | 1–3 | 11.3 | 1999.9 | USA |
| Quickbird | BGIS | 0.45–0.9 | 0.61/2.44 | 1–6 | 16.5 | 2001.10 | USA |
| GeoEye | GIS | 0.45–0.92 | 0.41/1.65 | 3 | 15.2 | 2008.9 | USA |
| Envisat | ASAR | C band | 10/30/150/1000 | 35 | 5/100/400 | 2002.3 | Europe |
| Sentinel-1 | SAR | C band | 5*20/ 5*5/ 5*5/20*40 | 12 | 20/80/250/400 | 2014.4 | Europe |
| Sentinel-2 | MSI | 0.4~2.4 | 10/20/60 | 10d | 290 | 2016.6 2017.3 | Europe |
| SPOT(1–3) | HRV | 0.50–0.89 | 10/20 | 26 | 60 | 1986.2 | France |
| SPOT 4 | HRVIR | 0.50–1.75 | 10/20 | 26 | 60 | 1998.3 | France |
| VGT | 0.45–1.75 | 1150 | 26 | 2250 | 1998.3 | France | |
| SPOT 5 | HRG | 0.48–1.75 | 2.5/5/10/20 | 26 | 60 | 2002.5 | France |
| VGT | 0.45–1.75 | 1150 | 26 | 2250 | 2002.5 | France | |
| SPOT 6 | NAOMI | 0.45–0.89 | 1.5/6 | 26 | 60×60 | 2012.9 | France |
| SPOT 7 | NAOMI | 0.45–0.89 | 1.5/6 | 26 | 60 | 2014.6 | France |
| Rapid Eye | MSI | 0.4–0.85 | 5 | 1 | 77 | 2008.8 | Germany |
| RADARSAT 1 | SAR | C band | 8–100 | 1–3 | 20/50/75/100/ 150/170/300/500 | 1995.11 | Canada |
| RADARSAT 2 | SAR | C band | 1–100 | 1–3 | 18/20/50/75/100/ 150/170/300/500 | 2007.12 | Canada |
| ALOS-1 | PRISM | 0.52–0.77 | 2.5 | 2 | 70 | 2006.1 | Japan |
| AVNIR-2 | 0.42–0.89 | 10 | 2 | 70 | 2006.1 | Japan | |
| PALSAR | L band | 7–100 | 2 | 20–350 | 2006.1 | Japan | |
| ALOS-2 | PALSAR-2 | L band | 1–100 | 14 | 25/50–70/350/490 | 2014.5 | Japan |
| HJ-A | CCD | 0.43–0.90 | 30 | 4 | 360 | 2008.9 | China |
| HSI | 0.43–0.52 | 100 | 4 | 50 | 2008.9 | China | |
| HJ-B | CCD | 0.43–0.90 | 30 | 4 | 360 | 2008.9 | China |
| IRS | 0.43–0.52 | 150/300 | 4 | 720 | 2008.9 | China | |
| HJ-C | SAR | S band | 5/20 | 31 | 40/100 | 2012.11 | China |
| ZY-1-02C | HRC/PMS | 0.50–0.89 | 2.36/5/10 | 3–5 | 54/60 | 2011.11 | China |
| ZY-3-01/02 | PMS/MUX | 0.45–0.89 | 2.1/5.8 | 3–5 | 51 | 2012.1 2016.5 | China |
| Gaofen-1 | PMS/WFV | 0.45–0.9 | 2/8/16 | 2–4 | 60/800 | 2013.4 | China |
| Gaofen -2 | PMS/MSS | 0.45–0.9 | 1/4 | 5 | 45 | 2014.8 | China |
| Gaofen -3 | SAR | C band | 1–500 | 1.5–3 | 10–650 | 2016.8 | China |
| Gaofen -4 | PMI | 0.45–0.9 3.5–4.1 | 50/400 | 20 seconds | 400 | 2015.12 | China |
| Gaofen -5 | AHSI | 0.45–2.5 | 30 | 51 | 60 | 2018.5 | China |
| VIMI | 0.45–12.5 | 20/40 | 51 | 60 | |||
| Gaofen -6 | PMS/WFV | 0.45–0.9 | 2/8/16 | 2–4 | 60/800 | 2018.6 | China |
| Institutions | City | Fields |
|---|---|---|
| National Remote Sensing Center of China | Beijing | Remote sensing technology management |
| Satellite Environment Center, Ministry of Ecology and Environment | Beijing | Remote sensing of ecology and environment |
| Land Satellite Remote Sensing Application Center, Ministry of Natural Resource | Beijing | Remote sensing of land resource |
| National Satellite Ocean Application Service, Ministry of Natural Resource | Beijing | Remote sensing of ocean |
| National Satellite Meteorological Centre, China Meteorological Administration | Beijing | Remote sensing of meteorology |
| National Disaster Reduction Center, Ministry of Emergency Management | Beijing | Application of remote sensing in disaster reduction |
| China Center for Resources Satellite Date and Application | Beijing | Remote sensing data acquisition and management |
| Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences | Beijing | Comprehensive research in remote sensing |
| Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences | Beijing | Remote sensing of environment and ecosystem |
| Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences | Beijing | Application of remote sensing in natural resource |
| Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences | Beijing | Remote sensing of environment and geology |
| Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences | Beijing | Remote sensing of atmosphere |
| Chinese Academy of Forestry | Beijing | Remote sensing of forestry |
| Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences | Beijing | Remote sensing of agriculture |
| Nanjing Institute of Geography & Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences | Nanjing | Remote sensing of environment |
| Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences | Nanjing | Application of remote sensing in soil science |
| Peking University | Beijing | Education |
| Tsinghua University | Beijing | Education |
| Beijing Normal University | Beijing | Education |
| University of Chinese Academy of Sciences | Beijing | Education |
| China University of Mining and Technology | Beijing and Xuzhou | Education |
| China University of Geosciences | Beijing and Wuhan | Education |
| Beihang University | Beijing | Education |
| Capital Normal Univeristy | Beijing | Education |
| Wuhan University | Wuhan | Education |
| Central South University | Changsha | Education |
| Tongji University | Shanghai | Education |
| Sun Yat-sen University | Guangzhou | Education |
| Nanjing University | Nanjing | Education |
| Chang’an University | Xi’an | Education |
| Liaoning Technical University | Fuxin | Education |
| Xi‘an University of Science and Technology | Xi’an | Education |
| Shandong University of Science and Technology | Qingdao | Education |
| Hohai University | Nanjing | Education |
| Lanzhou Jiaotong University | Lanzhou | Education |
| Zhengzhou University | Zhengzhou | Education |
| Southwest Jiaotong University | Chengdu | Education |
| Field of Monitoring | Monitoring Element | Methods and Algorithms | Remote Sensing Datasets Used | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecological index retrieval | Vegetation index | Band combination method, principal component combination method, derivative band combination method etc. | Landsat TM/ETM+/OLI, Gaofen-1, MODIS | 78%–94.55% [15,16,17,18,19,20,21] |
| Soil moisture | Empirical models, semi-empirical models, physical models | MODIS, Landsat TM, Envisat-1 ASAR | MRE = 17.5%–32.8% [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31] | |
| Vegetation moisture | Regression model, vegetation moisture index | Landsat ETM+, ASTER, Hyperion, MODIS | RMSE < 0.794 kg/m2 [32,33,34,35,36] | |
| Evapotranspiration | SEBAL model, SEBS model, METRIC model, semi-empirical model | HJ-IB, FY-3, Landsat TM, MODIS | MRE ≤ 12% [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] | |
| Land surface temperature | Single-channel algorithm, split-window algorithm, neural network-based algorithms | HJ-1B, ASTER, Landsat TM/ETM+/TIRS, MODIS | RMSE ≤ 2K [6,49,50,51,52,53] | |
| Protected area monitoring | Land use/cover change | Automatic image classification, visual interpretation | Landsat TM/ETM+/OLI, HJ-1, SPOT, World View-2 CBERS, ALOS, Gaofen-1 | ≥80% [54,55] |
| Human activity | Human activity impact index, visual interpretation | [56,57,58,59,60,61] | ||
| Biodiversity level, biological species, vegetation et al. | Spectral angle classification method | HJ-1A, Landsat TM/ETM+ | [62,63,64,65,66,67,68] | |
| Rural area monitoring | Solid waste | Human-computer interaction interpretation | Beijing-1, Gaofen-1/2 | 90%–95% [69,70] |
| Greenhouse film | PGI index, support vector machine classification | Gaofen-1, Landsat ETM+, Quickbird-2 | ≥90% [71,72,73] | |
| Soil pollution | Partial least squares regression method | Hyperion, HJ-1A HSI | MRE < 15% [74,75,76,77] | |
| Aquaculture | Human-computer interaction interpretation, object-oriented analysis and spectral eigenvalue method | Landsat TM/ETM+/OLI, CBERS, HJ-1 CCD | ≥80% [78,79] | |
| Urban area monitoring | Urban heat island | Land surface temperature retrieval algorithms | HJ-1B, ASTER, Landsat TM/ETM+/TIRS, MODIS | RMSE ≤ 2K [80,81,82,83,84,85] |
| Urban green space information | Stepwise hierarchical method, pixel dichotomy model, mono-window algorithm | Landsat ETM+/OLI, Quickbird, ALOS, Gaofen-1 | >90% [86,87,88,89,90] | |
| Urban impervious surface | Linear spectral unmixture analysis, dynamic impermeability analysis | Landsat TM/ETM+, urban DEM | RMSE < 0.02 [91,92,93,94,95,96] | |
| Expansion of urban built-up areas | Object-oriented classification | Landsat 8, Quickbird, Gaofen-1 | Around 90% [10,97,98] | |
| Urban environment quality | Environment indicator | Landsat dataset | [99,100] | |
| Mining area monitoring | Ecological damage and impact | Image interpretation, linear regression | SPOT 4/5, Quickbird, Landsat TM/ETM+, ZY-3, ASTER | ≥85% [101,102,103,104,105,106] |
| Ecological restoration | Ecological index, pixel dichotomy model | Landsat TM/ETM+, HJ-1A CCD, MODIS | [107,108,109,110,111] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Pei, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xiao, R.; Sang, X.; Zhang, C. A Review of Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring in China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071130
Li J, Pei Y, Zhao S, Xiao R, Sang X, Zhang C. A Review of Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring in China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(7):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071130
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jun, Yanqiu Pei, Shaohua Zhao, Rulin Xiao, Xiao Sang, and Chengye Zhang. 2020. "A Review of Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring in China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 7: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071130
APA StyleLi, J., Pei, Y., Zhao, S., Xiao, R., Sang, X., & Zhang, C. (2020). A Review of Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring in China. Remote Sensing, 12(7), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071130








