Gap-Filling of a MODIS Normalized Difference Snow Index Product Based on the Similar Pixel Selecting Algorithm: A Case Study on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. MODIS NDSI Products
2.2.2. Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Data
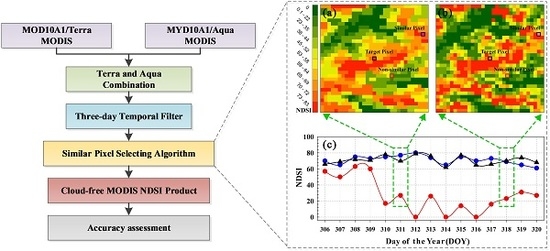
3. Methodology
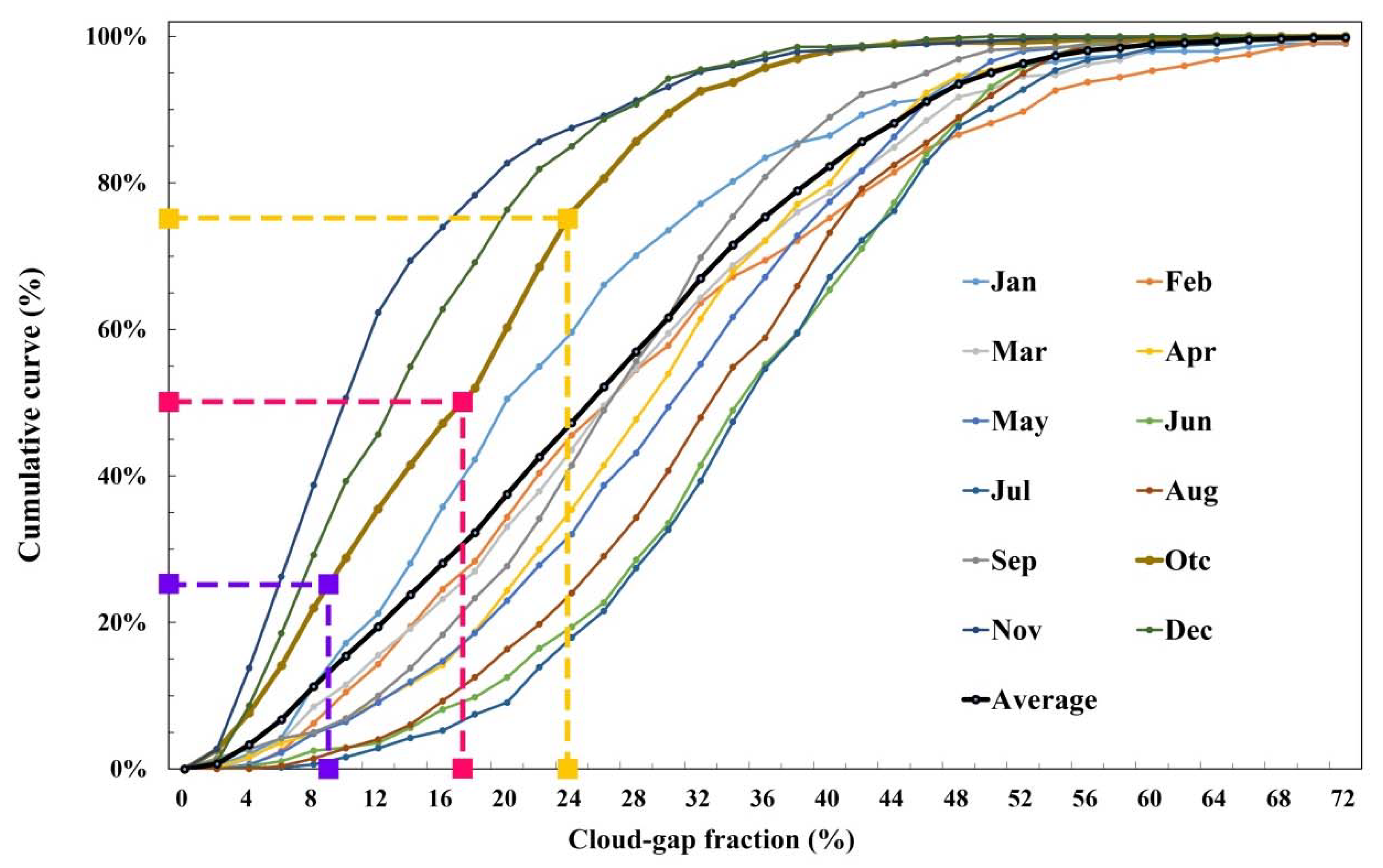
3.1. Analysis of Cloud Gaps in MODIS NDSI Products
3.2. Gap-Filling Procedure
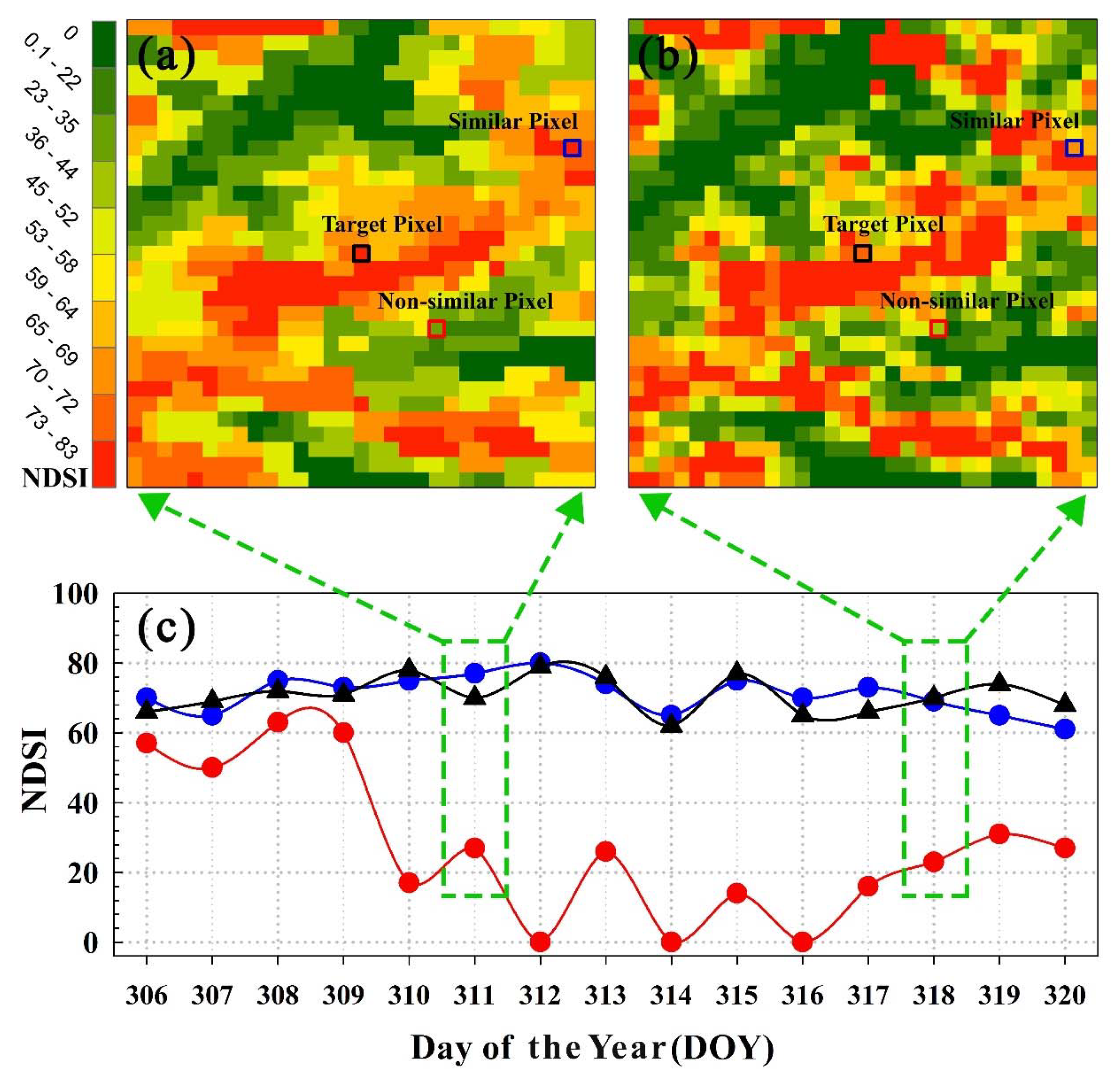
3.2.1. Theoretical Basis
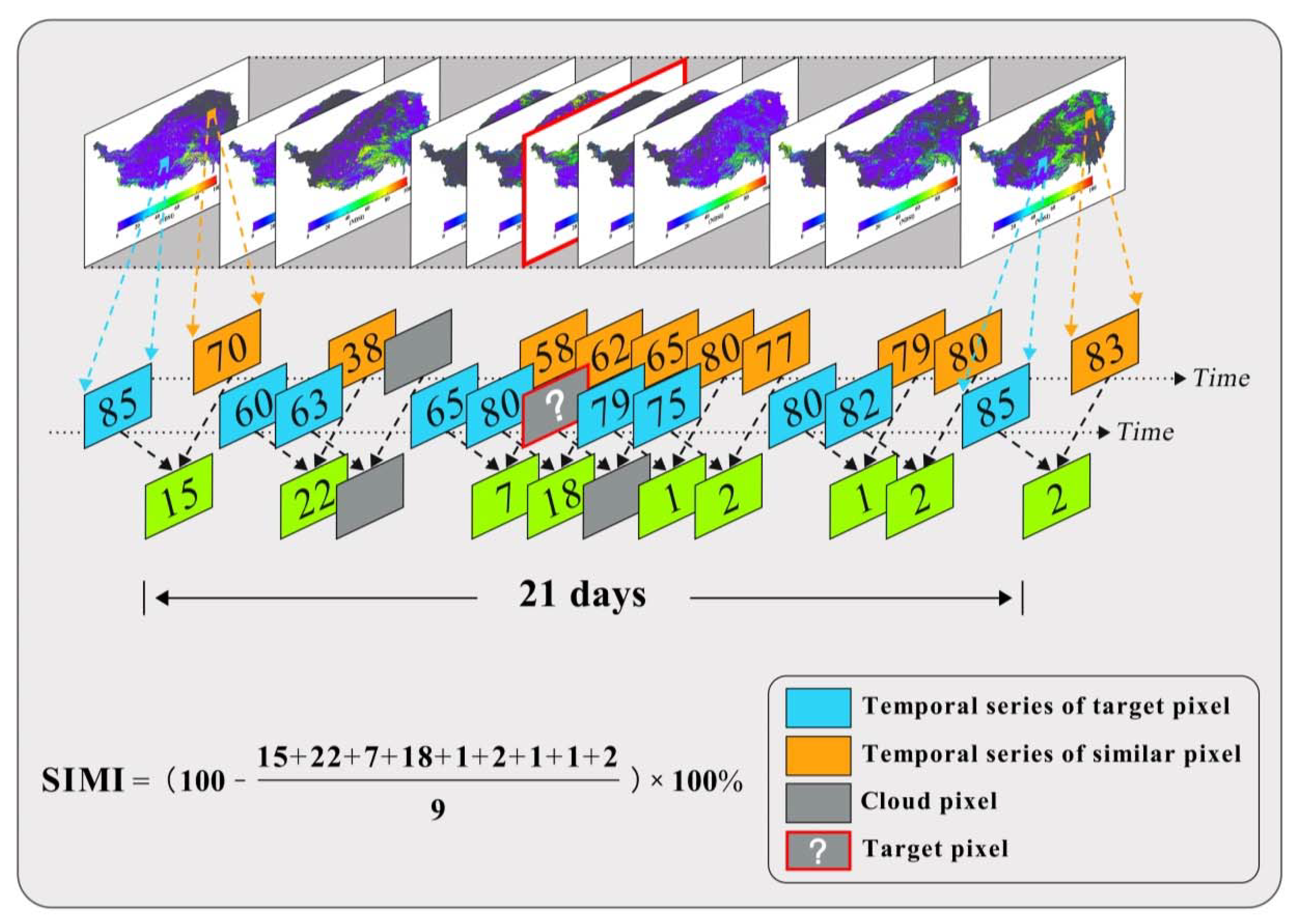
3.2.2. Gap-Filling Method
3.3. Validation
3.3.1. Validation Method Based on a “Cloud Mask Assumption”
- (A)
- For the TAC method: cloud-free pixels with NDSI values ranging from 0 to 100, both in the MOD10A1 and MYD10A1, were selected as test samples from 2003–2018. Pixels from MOD10A1 were taken as the true values, while the corresponding pixels from the MYD (at the same location) were taken as the predicted value. Equations (7)–(11) express the evaluation indicators.
- (B)
- For the 3DTF method: from 2003 to 2018, the cloud-free pixels with an NDSI value ranging from 0 to 100 within three consecutive days were selected as test samples, while the observed value of the middle day (date T) was taken as the true value. The arithmetic mean of the previous day’s (date T − 1) NDSI and the latter day’s (date T + 1) NDSI was taken as the predicted value. Equations (7)–(11) express the evaluation index.It should be noted that the evaluation of these two cloud removal methods (TAC and 3DTF) was performed day-by-day from 2003 to 2018. Each day, all pixels that satisfied these conditions were selected as verification samples. Thus, the accuracy indexes were available for each day.
- (C)
- For the SPSA method: a one-day cloud mask assumption was employed for validation. The specific details are outlined below.
3.3.2. Performance Metrics for NDSI
3.3.3. Classification Accuracy
4. Results
4.1. Cloud Gaps in MODIS NDSI Products across the TP
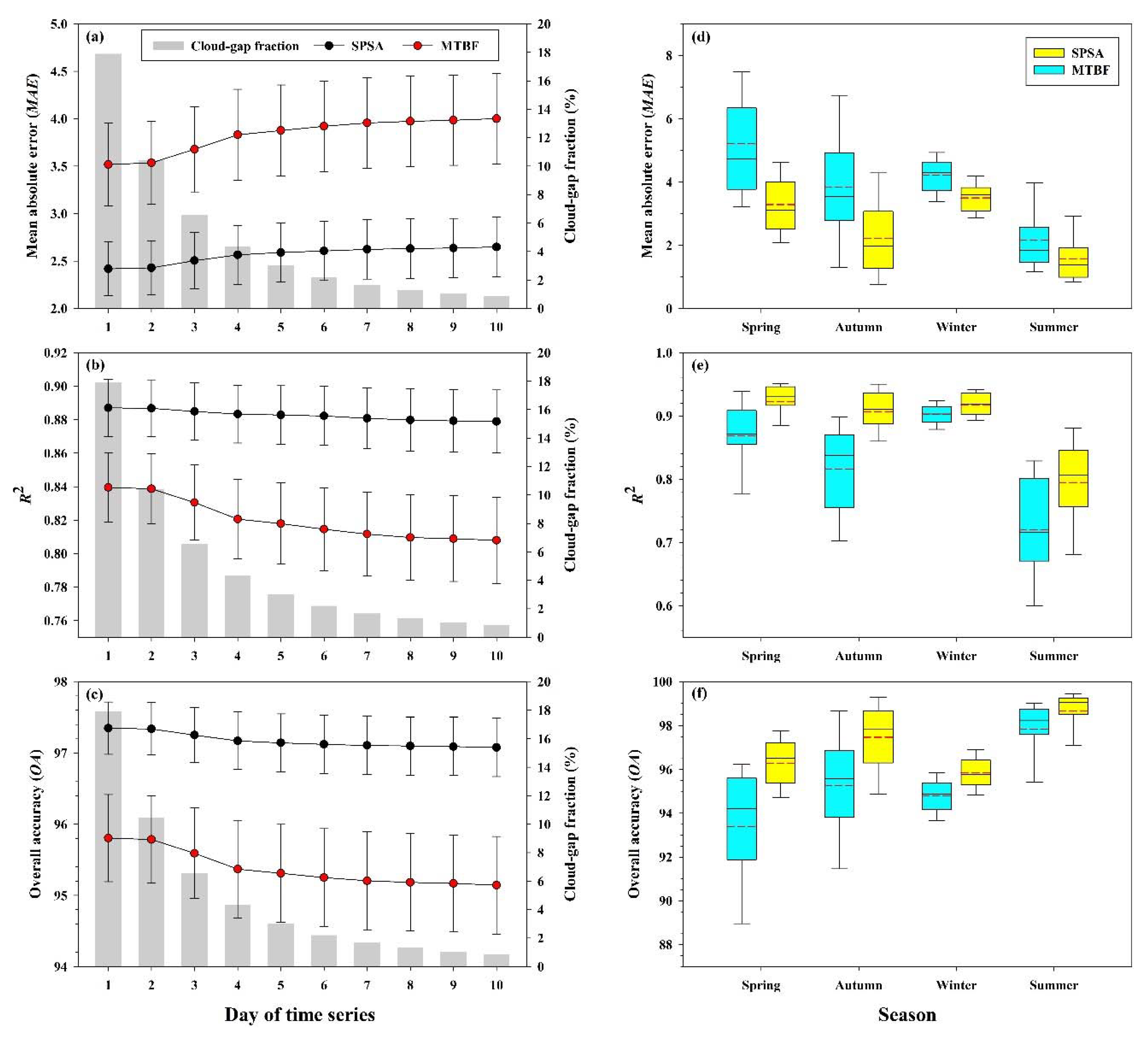
4.2. Effectiveness of the Gap-Filling Methodology
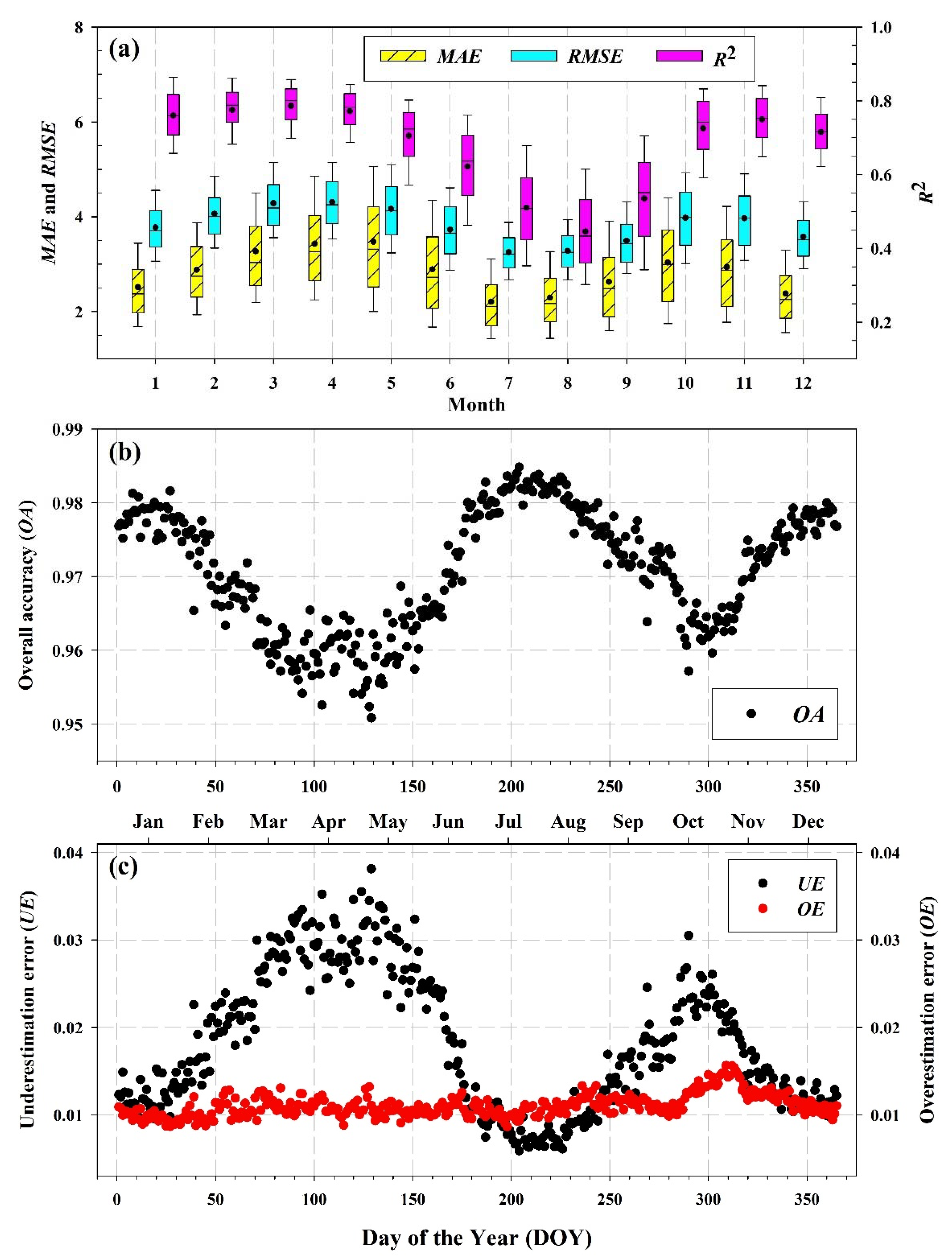
4.3. Accuracy Assessment
4.3.1. Accuracy Assessment of the Terra and Aqua Combination (TAC) Method
4.3.2. Accuracy Assessment of the Three-Day Temporal Filter (3DTF) Method
4.3.3. Accuracy Assessment of the Similar Pixel Selecting Algorithm (SPSA)
5. Discussion
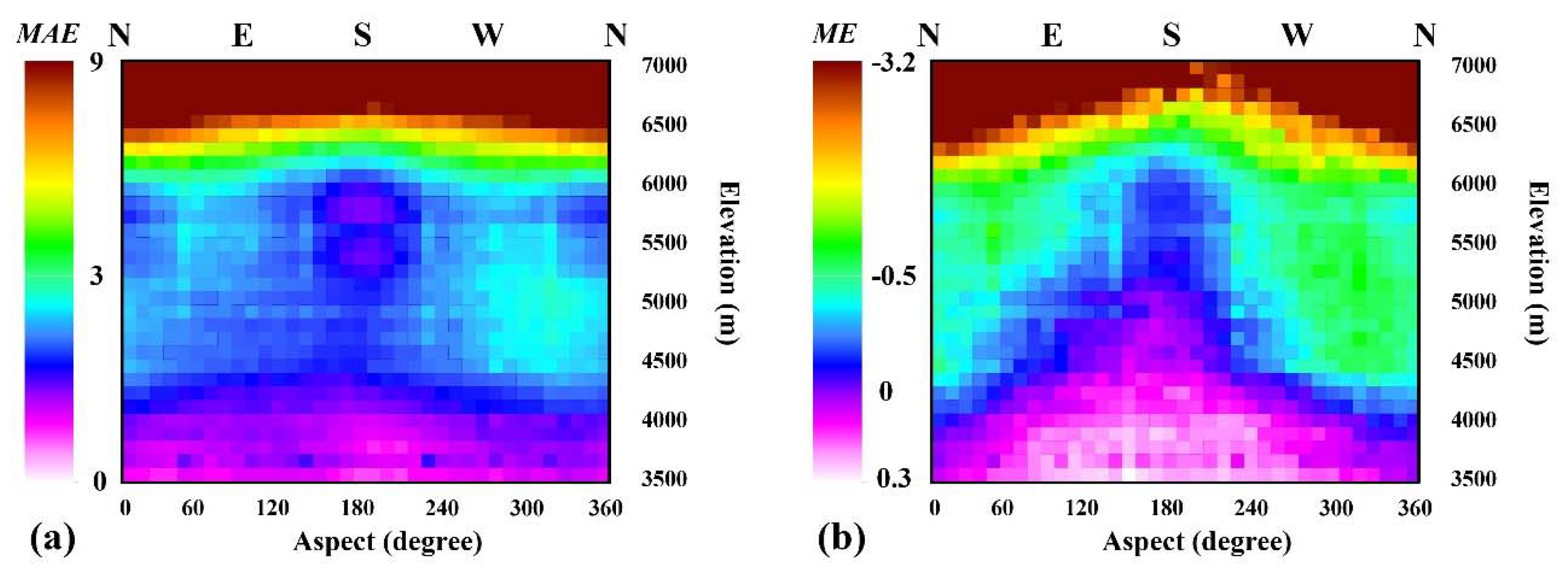
5.1. Impact Factor Analysis of the SPSA Algorithm
5.2. Comparison between TAC, 3DTF, and SPSA
5.3. Comparison between SPSA and the Multi-Temporal Backward Filter
5.4. Advantages and Limitations of the SPSA
6. Conclusions
Data Availability
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, D.A.; Dewey, K.F.; Heim, R.R. Global snow cover monitoring—An update. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 74, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, R.D. Northern hemisphere snow cover variability and change, 1915-97. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 2339–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Thorne, R.; Woo, M.-K. Using satellite imagery to validate snow distribution simulated by a hydrological model in large northern basins. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 2777–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Shafiq, M.; Ahmed, P.; Ul Islam, Z.; Joshi, P.K.; Bhat, W.A. Snow cover area change and its relations with climatic variability in Kashmir Himalayas, India. Geocarto Int. 2019, 34, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q. MODIS observed snow cover variations in the Aksu River Basin, Northwest China. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2019, 11, 208–217. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Menzel, L. Recent snow cover changes over central European low mountain ranges. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 34, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Yao, N.; Hu, W.; Yang, D.; Chen, C. Spatiotemporal variations of snow characteristics in Xinjiang, China over 1961–2013. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 1578–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Deng, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Hao, X.; Liang, T. Spatiotemporal dynamics of snow cover based on multi-source remote sensing data in China. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 2453–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- She, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Feng, X. Spatial and temporal characteristics of snow cover in the Tizinafu Watershed of the Western Kunlun Mountains. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3426–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K.; Rathore, B.P.; Bahaguna, I.M. Snow cover variability in the Himalayan-Tibetan region. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, Q.; Xie, H.; Zhang, H.; Lu, P.; Zhou, C. Spatiotemporal variations of snow cover in northeast China based on flexible multiday combinations of moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer snow cover products. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 084685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, A.J.; Kuenzer, C.; Conrad, C. Snow-cover variability in central Asia between 2000 and 2011 derived from improved MODIS daily snow-cover products. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 3879–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jing, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The recent developments in cloud removal approaches of MODIS snow cover product. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 2401–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Liang, H.; Sun, Y.; Feng, Q.; Liang, T. Tracking snow variations in the Northern Hemisphere using multi-source remote sensing data (2000–2015). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Y.; Lu, J.; Shi, J.; Xie, P.; Liang, W.; Wang, X. Passive microwave remote sensing data of snow water equivalent in High Asia. China Sci. Data 2019, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, N. Impacts of snow cover duration on vegetation spring phenology over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Plant Ecol. 2019, 12, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gregorio, L.; Callegari, M.; Marin, C.; Zebisch, M.; Bruzzone, L.; Demir, B.; Strasser, U.; Marke, T.; Günther, D.; Nadalet, R.; et al. A novel data fusion technique for snow cover retrieval. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 2873–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagler, T.; Rott, H.; Ossowska, J.; Schwaizer, G.; Small, D.; Malnes, E.; Luojus, K.; Metsämäki, S.; Pinnock, S. Snow cover monitoring by synergistic use of Sentinel-3 Slstr and Sentinel-L Sar data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 8727–8730. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Kan, X.; Ren, W.; Cao, T.; Tian, W.; Wang, J. Snow cover monitoring in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau based on Chinese Fengyun-3/VIRR data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2017, 45, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dariane, A.B.; Khoramian, A.; Santi, E. Investigating spatiotemporal snow cover variability via cloud-free MODIS snow cover product in Central Alborz Region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascoin, S.; Hagolle, O.; Huc, M.; Jarlan, L.; Dejoux, J.-F.; Szczypta, C.; Marti, R.; Sánchez, R. A snow cover climatology for the Pyrenees from MODIS snow products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2337–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, A.G.; Barnett, A.C. Validation of daily MODIS snow cover maps of the Upper Rio Grande River Basin for the 2000-2001 snow year. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liang, T.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z. Validation of MODIS snow cover products using Landsat and ground measurements during the 2001-2005 snow seasons over northern Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Yan, L. Spatiotemporal changes of snow cover over the Tibetan plateau based on cloud-removed moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer fractional snow cover product from 2001 to 2011. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 073582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, L.; Ménard, C.B.; Luojus, K.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Pulliainen, J. Evaluation of snow products over the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3247–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, A.; Fernandes, R.; Brown, R.; Romanov, P.; Park, W. Validation of VEGETATION, MODIS, and GOES plus SSM/I snow-cover products over Canada based on surface snow depth observations. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajka, J.; Blöschl, G. Validation of MODIS snow cover images over Austria. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. Developing daily cloud-free snow composite products from MODIS and IMS for the Tienshan Mountains. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Gu, J. Gap-Filling of MODIS fractional snow cover products via non-local spatio-temporal filtering based on machine learning techniques. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, T.; Nguyen, P.; Ombadi, M.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Qing, X. A cloud-free MODIS snow cover dataset for the contiguous United States from 2000 to 2017. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 180300. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, B.; Wu, J.; Kang, E.L.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Klein, A.; Chen, Y. Improving MODIS snow products with a HMRF-based spatio-temporal modeling technique in the Upper Rio Grande Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 568–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chu, D.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Zheng, Z. Cloud removing algorithm for the daily cloud free MODIS-based snow cover product over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2017, 39, 515–526. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Chang, L.; Shi, L. Daily fractional snow cover dataset over High Asia (2002–2016). China Sci. Data 2017, 2, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Xie, H.; Zhang, H.; Ke, C.; Yao, R. Developing daily cloud-free snow composite products from MODIS Terra-Aqua and IMS for the Tibetan Plateau. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Menzel, L. Producing cloud-free MODIS snow cover products with conditional probability interpolation and meteorological data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Huang, X.; Feng, Q.; Ma, X.; Liang, T. Toward improved daily cloud-free fractional snow cover mapping with multi-source remote sensing data in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6986–7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parajka, J.; Pepe, M.; Rampini, A.; Rossi, S.; Blöschl, G. A regional snow-line method for estimating snow cover from MODIS during cloud cover. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafurov, A.; Bárdossy, A. Cloud removal methodology from MODIS snow cover product. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parajka, J.; Blöschl, G. Spatio-temporal combination of MODIS images—Potential for snow cover mapping. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W03406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Wu, C.; Feng, Q.; Huang, X.; Chen, Q. Toward improved daily snow cover mapping with advanced combination of MODIS and AMSR-E measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3750–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J.; Painter, T.H.; Rittger, K.; Frew, J.E. Time—Space continuity of daily maps of fractional snow cover and albedo from MODIS. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Liang, T.; Huang, X. Comparison and validation of MODIS standard and new combination of Terra and Aqua snow cover products in northern Xinjiang, China. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wang, X.; Liang, T. Development and assessment of combined Terra and Aqua snow cover products in Colorado Plateau, USA and northern Xinjiang, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2009, 3, 033559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazari, N.; Tekeli, A.E.; Xie, H.; Sharif, H.I.; El Hassan, A.A. Assessment of ice mapping system and moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer snow cover maps over Colorado Plateau. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 073540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Burgos, V.; Gupta, H.V.; Clark, M. Reducing cloud obscuration of MODIS snow cover area products by combining spatio-temporal techniques with a probability of snow approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1809–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Xie, H.; Yao, T.; Xue, C. Integrated assessment on multi-temporal and multi-sensor combinations for reducing cloud obscuration of MODIS snow cover products of the Pacific Northwest USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1662–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, K.P.; Andersen, P. Monitoring snow cover variability in an agropastoral area in the Trans Himalayan region of Nepal using MODIS data with improved cloud removal methodology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, J.M.; Menounos, B.; Moore, R.D.; Tennant, C. An approach to derive regional snow lines and glacier mass change from MODIS imagery, western North America. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coll, J.; Li, X. Comprehensive accuracy assessment of MODIS daily snow cover products and gap filling methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V. MODIS Snow Products User Guide to Collection 5. 2006. Available online: http://modis-snow-ice.gsfc.nasa.gov/sug_c5.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2019).
- Riggs, G.A.; Hall, D.K.; Román, M.O. MODIS Snow Products User Guide for Collection 6 (C6). 2016. Available online: http://modis-snow-ice.gsfc.nasa.gov/?c=userguides (accessed on 20 November 2019).
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Bayr, K.J. MODIS snow-cover products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A. Accuracy assessment of the MODIS snow products. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 1534–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomonson, V.V.; Appel, I. Estimating fractional snow cover from MODIS using the normalized difference snow index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, G.A.; Hall, D.K.; Román, M.O. Overview of NASA’s MODIS and Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) snow-cover Earth System Data Records. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gafurov, A.; Vorogushyn, S.; Farinotti, D.; Duethmann, D.; Merkushkin, A.; Merz, B. Snow-cover reconstruction methodology for mountainous regions based on historic in situ observations and recent remote sensing data. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gafurov, A.; Lüdtke, S.; Unger-Shayesteh, K.; Vorogushyn, S.; Schöne, T.; Schmidt, S.; Kalashnikova, O.; Merz, B. MODSNOW-Tool: An operational tool for daily snow cover monitoring using MODIS data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gafurov, A.; Kriegel, D.; Vorogushyn, S.; Merz, B. Evaluation of remotely sensed snow cover product in Central Asia. Hydrol. Res. 2013, 44, 506–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Zeng, C. Cloud removal for remotely sensed images by similar pixel replacement guided with a spatio-temporal MRF model. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Ding, Y. Cryospheric Changes and Their Impacts: Present, Trends and Key Issues. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2009, 5, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Tong, K.; Meng, F.; Kan, B. Spatiotemporal variation of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau based on MODIS snow product, 2001–2014. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 708–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.F.; Graf, H.F. Recent land cover changes on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. Clim. Chang. 2009, 94, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rees, H.G.; Collins, D.N. Regional differences in response of flow in glacier-fed Himalayan rivers to climatic warming. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. Inpainting for remotely sensed images with a multichannel nonlocal total variation model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, G.; Osher, S. Nonlocal operators with applications to image processing. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2008, 7, 1005–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. Computer movie simulating urban growth in Detroit region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W. On the First Law of Geography: A Reply. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2004, 94, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, J. A new geostatistical approach for filling gaps in Landsat ETM+ SLC-off images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G.; Che, T.; Yan, W.; Ye, M.; Ma, N. Ground-based evaluation of MODIS snow cover product V6 across China: Implications for the selection of NDSI threshold. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2712–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Lu, G.; Liu, J.; Qin, C.Z.; Zhou, C. Spatial prediction based on Third Law of Geography. Ann. GIS 2018, 24, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevington, A.R.; Gleason, H.E.; Foord, V.N.; Floyd, W.C.; Griesbauer, H.P. Regional influence of ocean-atmosphere teleconnections on the timing and duration of MODIS-derived snow cover in British Columbia, Canada. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 2693–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krajči, P.; Holko, L.; Perdigāo, R.A.P.; Parajka, J. Estimation of regional snowline elevation (RSLE) from MODIS images for seasonally snow covered mountain basins. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ma, H.; Wu, D.; Yuan, W. Assessment of the daily cloud-free MODIS snow-cover product for monitoring the snow-cover phenology over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Fu, W.; Shen, H.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L. Monitoring snow cover variability (2000–2014) in the Hengduan Mountains based on cloud-removed MODIS products with an adaptive spatio-temporal weighted method. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Luo, S.; Che, T.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Dai, L.; Huang, X.; Feng, Q. Accuracy assessment of four cloud-free snow cover products over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillinger, T.; Roberts, D.A.; Collar, N.M.; Dozier, J. Cloud masking for Landsat 8 and MODIS Terra over snow-covered terrain: Error analysis and spectral similarity between snow and cloud. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6169–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, S.K.; Goswami, A.; Saraf, A.K. Role of elevation and aspect in snow distribution in Western Himalaya. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Peng, L.; Liang, C.; He, Y.; Mu, Z.; Zheng, S. Analysis of snow coverage in Yarkant River Basin based on MODIS Snow data. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2018, 50, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemifar, E.; Mohammadi, C.; Farajzadeh, M. Spatiotemporal analysis of snow cover in Iran based on topographic characteristics. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Meng, Z.; Jia, X.; Du, P.; Liang, Y. Distribution and trend of snow cover in Inner Mongolia from 2001 to 2016 based on MODIS data. Arid Zone Res. 2019, 36, 104–112. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Foster, J.L.; Kumar, S.V. Development and evaluation of a cloud-gap-filled MODIS daily snow-cover product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Román, M.O. Evaluation of MODIS and VIIRS cloud-gap-filled snow-cover products for production of an Earth science data record. Hydrol. Earth Sys. Sci. 2019, 23, 5227–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






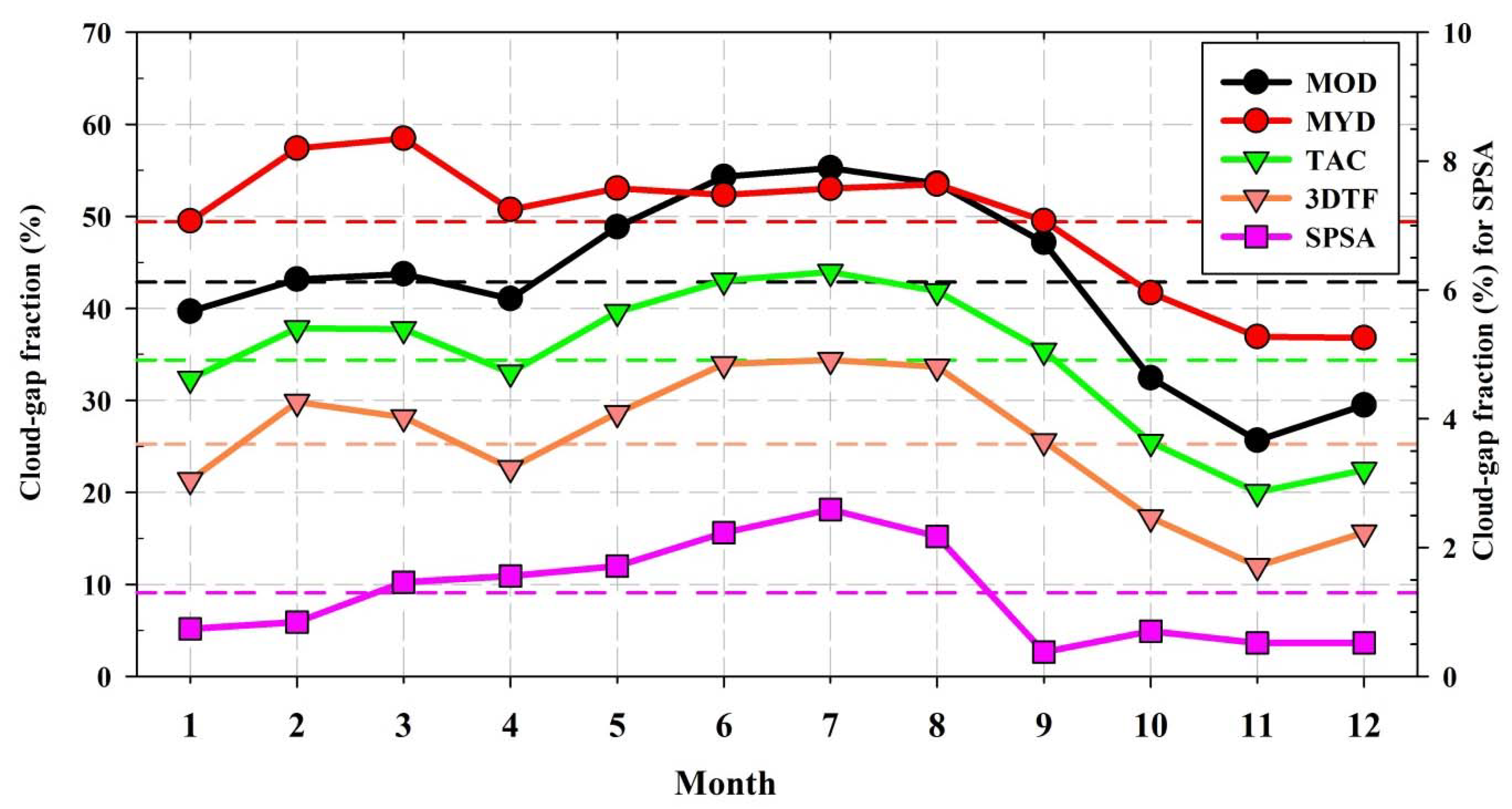
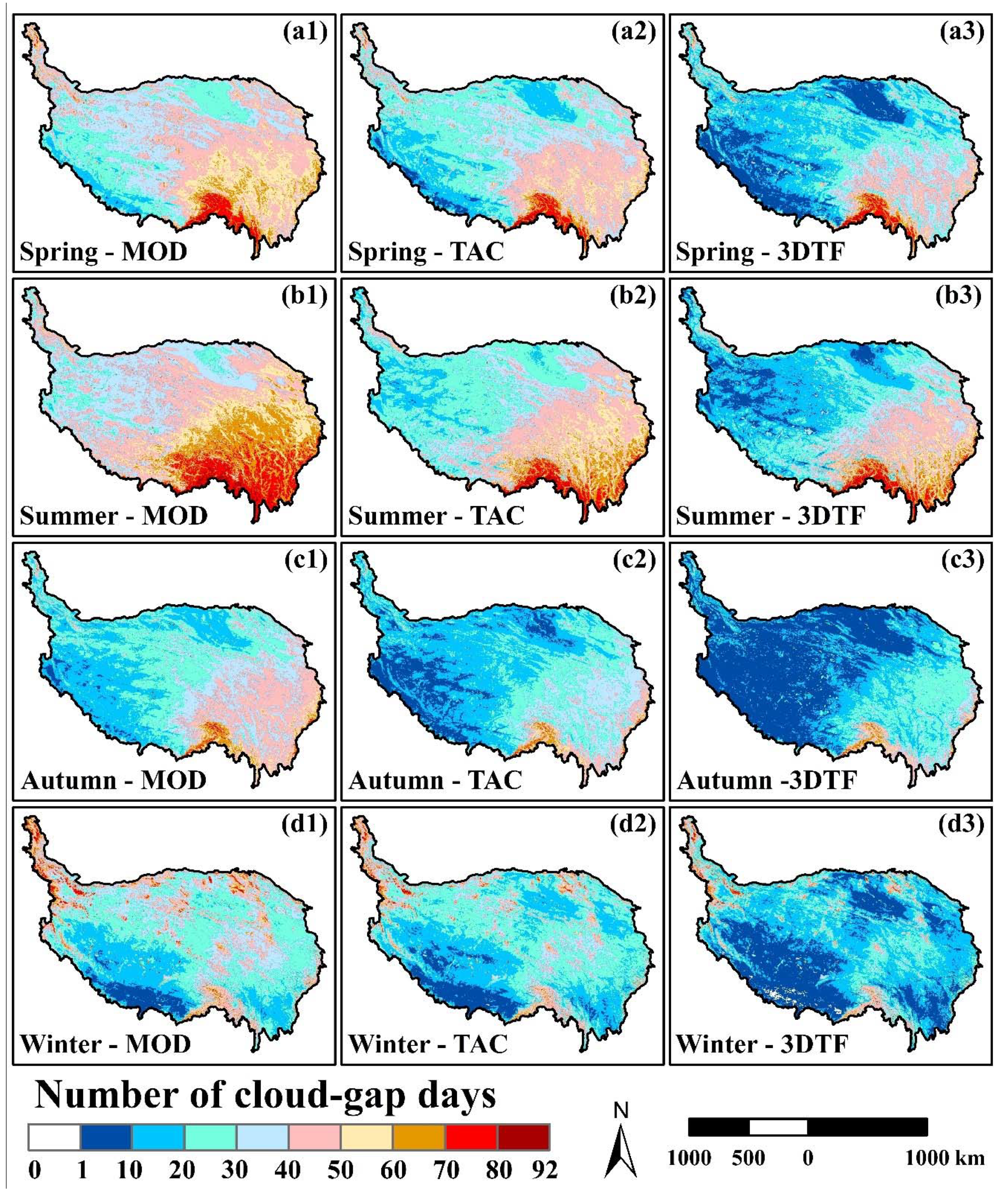
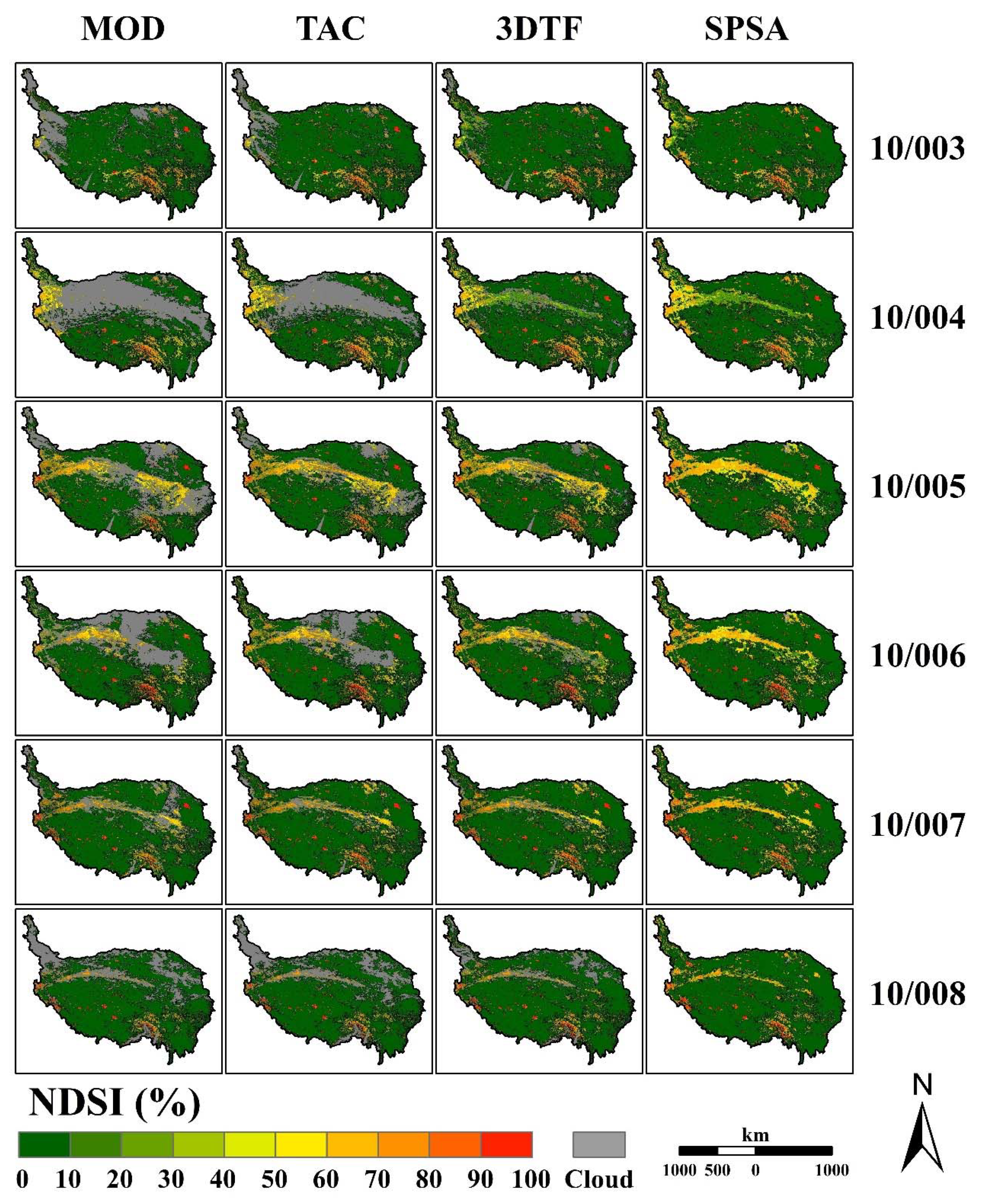




| Image | Month | P25 | P50 | P75 | |||
| Date | CGF(%) | Date | CGF(%) | Date | CGF(%) | ||
| True image | Jan | 18/022 | 1.52 | 03/020 | 1.75 | 07/028 | 3.26 |
| Feb | 09/039 | 3.22 | 14/032 | 3.42 | 10/053 | 4.40 | |
| Mar | 15/084 | 2.16 | 10/078 | 3.10 | 13/064 | 3.12 | |
| Apr | 07/107 | 1.09 | 12/092 | 2.26 | 06/119 | 3.17 | |
| May | 09/139 | 2.03 | 11/125 | 2.76 | 04/129 | 3.89 | |
| Jun | 13/161 | 2.09 | 16/155 | 4.83 | 13/163 | 5.05 | |
| Jul | 15/206 | 2.46 | 08/188 | 8.49 | 03/204 | 9.16 | |
| Aug | 11/239 | 4.62 | 13/215 | 6.24 | 10/219 | 9.18 | |
| Sep | 04/258 | 0.94 | 07/260 | 1.33 | 15/273 | 1.36 | |
| Oct | 13/282 | 0.01 | 16/276 | 1.08 | 17/292 | 1.17 | |
| Nov | 10/313 | 1.20 | 03/306 | 1.22 | 16/315 | 1.35 | |
| Dec | 16/342 | 1.70 | 05/349 | 1.85 | 17/344 | 2.51 | |
| P25 | P50 | P75 | |||||
| Cloud mask image | Date | CGF(%) | Date | CGF(%) | Date | CGF(%) | |
| Jan | 03/013 | 13.12 | 18/029 | 19.88 | 09/025 | 31.09 | |
| Feb | 13/040 | 16.51 | 04/054 | 26.31 | 14/040 | 39.92 | |
| Mar | 15/082 | 17.19 | 16/089 | 26.25 | 17/073 | 37.87 | |
| Apr | 08/120 | 20.09 | 09/119 | 28.46 | 06/104 | 37.18 | |
| May | 06/138 | 20.96 | 08/127 | 30.19 | 18/130 | 39.24 | |
| Jun | 12/170 | 26.79 | 03/177 | 34.20 | 14/181 | 43.19 | |
| Jul | 07/212 | 27.22 | 18/198 | 34.63 | 16/206 | 43.56 | |
| Aug | 04/230 | 24.42 | 18/231 | 32.75 | 03/241 | 40.53 | |
| Sep | 11/263 | 18.60 | 04/245 | 26.32 | 04/248 | 33.54 | |
| Oct | 15/285 | 8.66 | 07/295 | 17.52 | 05/276 | 23.88 | |
| Nov | 07/331 | 5.78 | 09/325 | 9.86 | 09/315 | 16.30 | |
| Dec | 05/355 | 7.23 | 05/335 | 12.90 | 09/344 | 19.67 | |
| Observed NDSI | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| NDSI (≥) | NDSI (<) | ||
| Predicted NDSI | NDSI (≥) | ss | sn |
| NDSI (<) | ns | nn | |
| Category | Index | Autumn | Winter | Spring | Summer | Annual Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance metrics for NDSI | MAE | 2.25 | 3.63 | 3.49 | 1.69 | 2.77 |
| RMSE | 3.42 | 4.52 | 4.30 | 2.86 | 3.78 | |
| R2 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.62 | 0.78 | |
| MAPE | 37.84% | 31.39% | 29.25% | 71.12% | 42.40% | |
| Classification accuracy | OA | 97.45% | 95.65% | 96.04% | 98.54% | 96.92% |
| OE | 0.90% | 1.66% | 1.32% | 0.53% | 1.10% | |
| UE | 1.64% | 2.69% | 2.64% | 0.94% | 1.98% |
| Image | Date | CGF | Date | CGF | Date | CGF | Date | CGF | Date | CGF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | ||||||
| True | 08/313 [1] | 1.69 | 10/077 [2] | 2.18 | 12/092 [3] | 2.26 | 13/321 [4] | 2.86 | 16/318 [5] | 1.61 |
| Image | ||||||||||
| Cloud mask image | 18/092 [1] | 3.42 | 18/359 [9] | 13.4 | 12/265 [17] | 21.87 | 17/057 [25] | 30.16 | 08/265 [33] | 39.83 |
| 13/146 [2] | 5.01 | 17/127 [10] | 14.41 | 15/034 [18] | 22.92 | 11/002 [26] | 31.11 | 12/009 [34] | 41.32 | |
| 18/011 [3] | 6.34 | 18/135 [11] | 15.71 | 14/063 [19] | 24 | 18/002 [27] | 32.11 | 06/139 [35] | 43.13 | |
| 11/116 [4] | 7.49 | 15/131 [12] | 16.85 | 08/204 [20] | 25.05 | 08/237 [28] | 33.12 | 08/150 [36] | 44.98 | |
| 09/299 [5] | 8.62 | 05/326 [13] | 18.02 | 04/036 [21] | 26.02 | 11/168 [29] | 34.26 | 17/066 [37] | 46.66 | |
| 07/304 [6] | 9.75 | 13/033 [14] | 19.05 | 08/078 [22] | 27 | 14/080 [30] | 35.58 | 09/090 [38] | 49.41 | |
| 18/357 [7] | 10.93 | 05/285 [15] | 19.9 | 11/295 [23] | 28.08 | 13/149 [31] | 36.98 | 03/030 [39] | 53.21 | |
| 17/305 [8] | 12.19 | 18/263 [16] | 20.98 | 17/266 [24] | 29.23 | 14/224 [32] | 38.25 | 18/183 [40] | 64.68 |
| Index | Method | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | TAC | 96.09% | 97.71% | 96.95% | 97.58% | 97.08% |
| 3DTF | 97.90% | 98.60% | 98.30% | 98.71% | 98.38% | |
| SPSA | 96.04% | 98.54% | 97.45% | 95.65% | 96.92% | |
| MAE | TAC | 3.39 | 2.45 | 2.87 | 2.58 | 2.82 |
| 3DTF | 1.71 | 1.32 | 1.48 | 1.27 | 1.45 | |
| SPSA | 3.49 | 1.69 | 2.25 | 3.63 | 2.77 | |
| R2 | TAC | 0.75 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 0.75 | 0.67 |
| 3DTF | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.88 | |
| SPSA | 0.85 | 0.62 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.78 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Zhu, X.; Li, N.; Pan, Y. Gap-Filling of a MODIS Normalized Difference Snow Index Product Based on the Similar Pixel Selecting Algorithm: A Case Study on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071077
Li M, Zhu X, Li N, Pan Y. Gap-Filling of a MODIS Normalized Difference Snow Index Product Based on the Similar Pixel Selecting Algorithm: A Case Study on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(7):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071077
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Muyi, Xiufang Zhu, Nan Li, and Yaozhong Pan. 2020. "Gap-Filling of a MODIS Normalized Difference Snow Index Product Based on the Similar Pixel Selecting Algorithm: A Case Study on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau" Remote Sensing 12, no. 7: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071077
APA StyleLi, M., Zhu, X., Li, N., & Pan, Y. (2020). Gap-Filling of a MODIS Normalized Difference Snow Index Product Based on the Similar Pixel Selecting Algorithm: A Case Study on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 12(7), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071077