Attention-Guided Multi-Scale Segmentation Neural Network for Interactive Extraction of Region Objects from High-Resolution Satellite Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To effectively and simply simulate the user-provided interactions of selecting the region object, our algorithm not only adopts the click-based interaction but also supports the scribble-based interaction. We provide a more flexible and suitable interactive mechanism for the users to select the appropriate way of interactions based on a certain scene.
- To take the image context and appearance into consideration, we propose an effective transformation of user-provided interactions to obtain the guidance maps. We combine the modified Euclidean distance transformation, sampling transformation, and geodesic distance transformation to avoid the rich information loss, which is caused by using only the simple Euclidean distance transformation adopted by existing methods.
- We present a novel way to incorporate user-interactions and convolutional neural networks, using the guidance maps as extra channels of the input of the segmentation network. It is the first work to adopt this special mechanism to the interactive extraction of region objects from satellite imagery.
- With our proposed attention-guided multi-scale segmentation network that can focus the special channels and take multi-scale information into account, we achieve higher segmentation accuracy with fewer user interactions compared with other interactive methods.
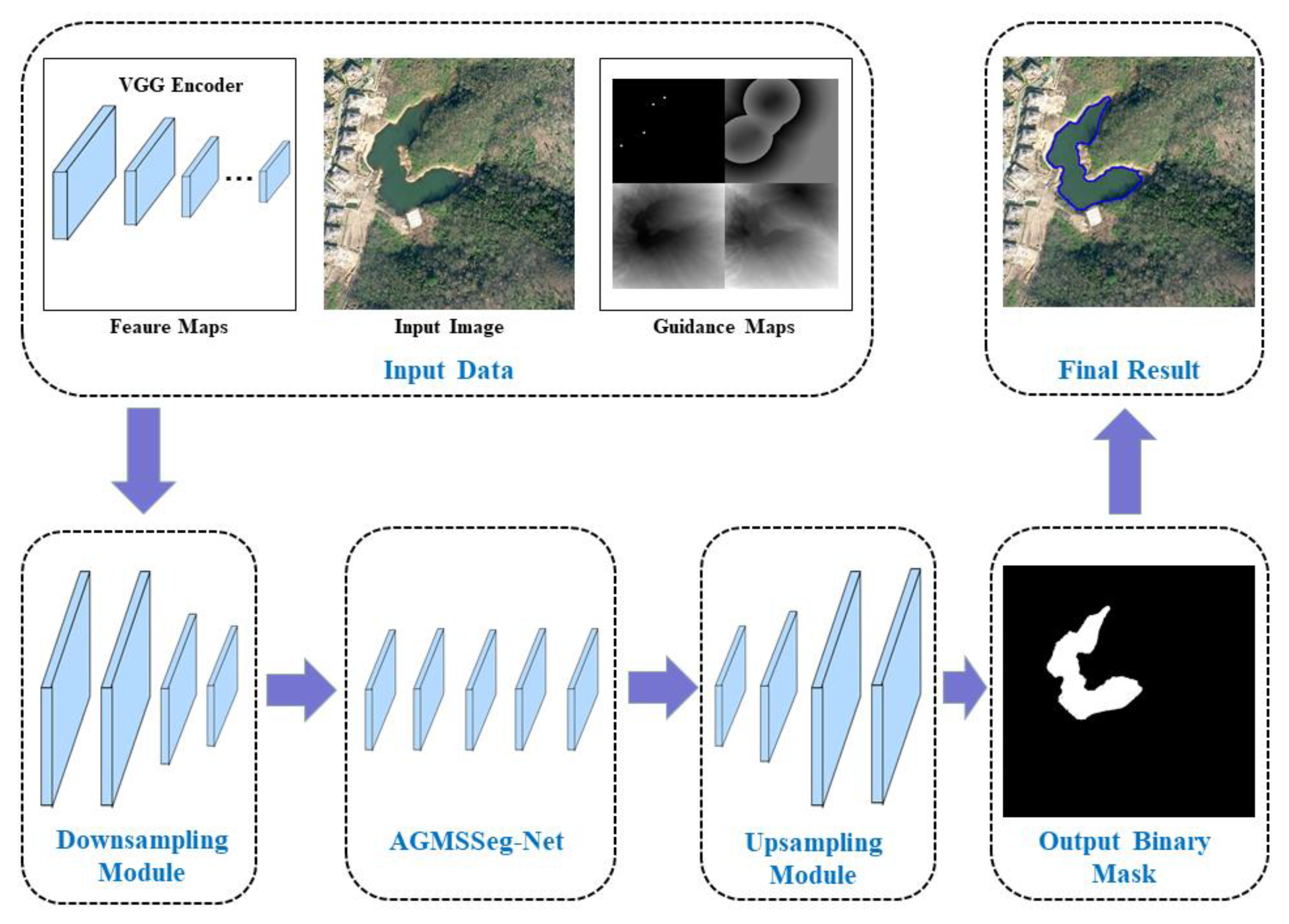
2. Methodology
2.1. Generation of Guidance Maps
2.1.1. Simulating User Sampling
2.1.2. Transformation from Interactions to Guidance Maps
2.2. Attention-Guided Multi-Scale Segmentation Network
2.2.1. Attention-Guided Convolution (AGC) Module
2.2.2. AGC Enhanced Segmentation Network
2.3. Post-Processing for Final Region Object Extraction
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Implementation Details
3.3. Evaluation Indexes
3.4. Comparison with Related Works
3.5. Ablation Study
3.5.1. Without the Proposed Interaction Transformation
3.5.2. Without the Pre-Trained Feature Maps
3.5.3. Without the AGC Module
4. Discussion
4.1. Interactions Transformation
4.2. Comparison with Existing Networks
4.3. Difference between Artificial and Non-Artificial Objects
4.4. Human-in-the-Loop
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mobley, C.D.; Sundman, L.K.; Davis, C.O.; Bowles, J.H.; Gleason, A. Interpretation of hyperspectral remote-sensing imagery by spectrum matching and look-up tables. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 3576–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, V.; Luo, F. Automatic interpretation of digital maps. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Tian, J. Semi-Automatic Building Extraction from Very High Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery Via Energy Minimization Model. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 657–660. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.; Hu, Y. A method of Interactively Extracting Region Objects from high-resolution remote sensing image based on full connection CRF. In Proceedings of the 10th IAPR Workshop on Pattern Recognition in Remote Sensing (PRRS), Beijing, China, 19–20 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fazan, A.J.; Dal, P.; Aluir, P. Rectilinear building roof contour extraction based on snakes and dynamic programming. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, J.; Inglada, J.; Christophe, E. Interactive object segmentation in high resolution satellite images. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 5, pp. 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Washington, DC, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2015; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Boston, MA, USA, 14–18 September 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipoll, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Yamashita, T.; Aoki, Y. Multiple Object Extraction from Aerial Imagery with Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 2016, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussul, N.; Lavreniuk, M.; Skakun, S.; Shelestov, A. Deep Learning Classification of Land Cover and Crop Types Using Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemker, R.; Salvaggio, C.; Kanan, C. Algorithms for semantic segmentation of multispectral remote sensing imagery using deep learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Price, B.; Cohen, S.; Yang, J.; Huang, T. Deep Interactive Object Selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 373–381. [Google Scholar]
- Rajchl, M.; Lee, M.; Oktay, O.; Kamnitsas, K.; Passerat-Palmbach, J.; Bai, W.; Rutherford, M.; Hajnal, J.; Kainz, B.; Rueckert, D. DeepCut: Object Segmentation from Bounding Box Annotations using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 36, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zuluaga, M.A.; Li, W.; Pratt, R.; Patel, P.A.; Aertsen, M.; Doel, T.; David, A.L.; Deprest, J.; Ourselin, S.; et al. DeepIGeoS: A Deep Interactive Geodesic Framework for Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 41, 1559–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Koltun, V. Interactive image segmentation with latent diversity. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 577–585. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Qi, H.; Rong, Z.; Rong, Z.; Liu, L.; Su, H. Scribble-Supervised Segmentation of Aerial Building Footprints Using Adversarial Learning. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 58898–58911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; He, G.; Zhang, Z.; Long, T.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z. Visual attention model based mining area recognition on massive high-resolution remote sensing images. Clust. Comput. 2015, 2, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, A.; Sultani, W.; Ali, M. Deep built-structure counting in satellite imagery using attention based re-weighting. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tao, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhong, Z. Attention-mechanism-containing neural networks for high-resolution remote sensing image classification. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maninis, K.K.; Caelles, S.; Pont-Tuset, J.; Luc, V.G. Deep extreme cut: From extreme points to object segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 616–625. [Google Scholar]
- Majumder, S.; Yao, A. Content-Aware Multi-Level Guidance for Interactive Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 11602–11611. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, H.; Gao, J.; Kar, A.; Chen, W.; Fidler, S. Fast interactive object annotation with curve-gcn. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5257–5266. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.C.; Kashyap, R.L.; Chu, C.N. Building skeleton models via 3-D medial surface axis thinning algorithms. Graph. Models Image Process. 1994, 56, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criminisi, A.; Sharp, T.; Blake, A. GeoS: Geodesic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Marseille, France, 11–14 October 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, Y.; Vladlen, K. Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Residual Attention Network for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, H.; Li, S.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Zheng, H.; Mei, T. Look Closer to See Better: Recurrent Attention Convolutional Neural Network for Fine-grained Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4438–4446. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courcille, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Krähenbühl, P.; Koltun, V. Efficient Inference in Fully Connected CRFs with Gaussian Edge Potentials. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1210.5644. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; Zhao, L.; Lv, Y.; Luo, M.; Pang, S. Learning dual multi-scale manifold ranking for semantic segmentation of high-resolution images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boykov, Y.; Veksler, O.; Zabih, R. Fast approximate energy minimization via graph cuts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 1222–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, T. Relevance feedback in image retrieval: A comprehensive review. Multimed. Syst. 2003, 8, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Dataset | Size | GSD | Images | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset 1 | 0.5m | 60 | None | |
| Dataset 2 | 0.5m | 12 | China |
| Method | IoU | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graph cut [46] | 66.52% | 79.47% | 81.59% | 76.54% |
| DIOS [25] | 73.67% | 76.65% | 93.63% | 84.25% |
| LD [28] | 76.07% | 78.96% | 95.80% | 85.79% |
| AGMSSeg-Net | 81.09% | 83.81% | 96.03% | 88.62% |
| Method | IoU | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graph cut [46] | 75.22% | 86.40% | 84.15% | 85.23% |
| DIOS [25] | 78.27% | 88.24% | 82.94% | 86.42% |
| LD [28] | 81.29% | 83.46% | 97.27% | 89.11% |
| AGMSSeg-Net | 85.87% | 94.79% | 90.51% | 91.98% |
| Method | Dataset 1 | Dataset 2 |
|---|---|---|
| DIOS [25] | 11.31 | 10.34 |
| LD [28] | 8.79 | 8.02 |
| AGMSSeg-Net | 7.32 | 6.57 |
| Method | Subset 1 | Time(ms) |
|---|---|---|
| DIOS [25] | 8.69 | 532 |
| LD [28] | 6.45 | 257 |
| AGMSSeg-Net | 5.76 | 479 |
| Method | Dataset 1 | Dataset 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Without PIT | 76.93 | 78.63 |
| Without PFM | 78.74 | 80.06 |
| Without AGC | 79.94 | 83.32 |
| AGMSSeg-Net | 81.09 | 85.87 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Hu, X.; Jiang, H.; Shu, Z.; Zhang, M. Attention-Guided Multi-Scale Segmentation Neural Network for Interactive Extraction of Region Objects from High-Resolution Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050789
Li K, Hu X, Jiang H, Shu Z, Zhang M. Attention-Guided Multi-Scale Segmentation Neural Network for Interactive Extraction of Region Objects from High-Resolution Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(5):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050789
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kun, Xiangyun Hu, Huiwei Jiang, Zhen Shu, and Mi Zhang. 2020. "Attention-Guided Multi-Scale Segmentation Neural Network for Interactive Extraction of Region Objects from High-Resolution Satellite Imagery" Remote Sensing 12, no. 5: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050789
APA StyleLi, K., Hu, X., Jiang, H., Shu, Z., & Zhang, M. (2020). Attention-Guided Multi-Scale Segmentation Neural Network for Interactive Extraction of Region Objects from High-Resolution Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing, 12(5), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050789





