A Model-Downscaling Method for Fine-Resolution LAI Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Field LAI
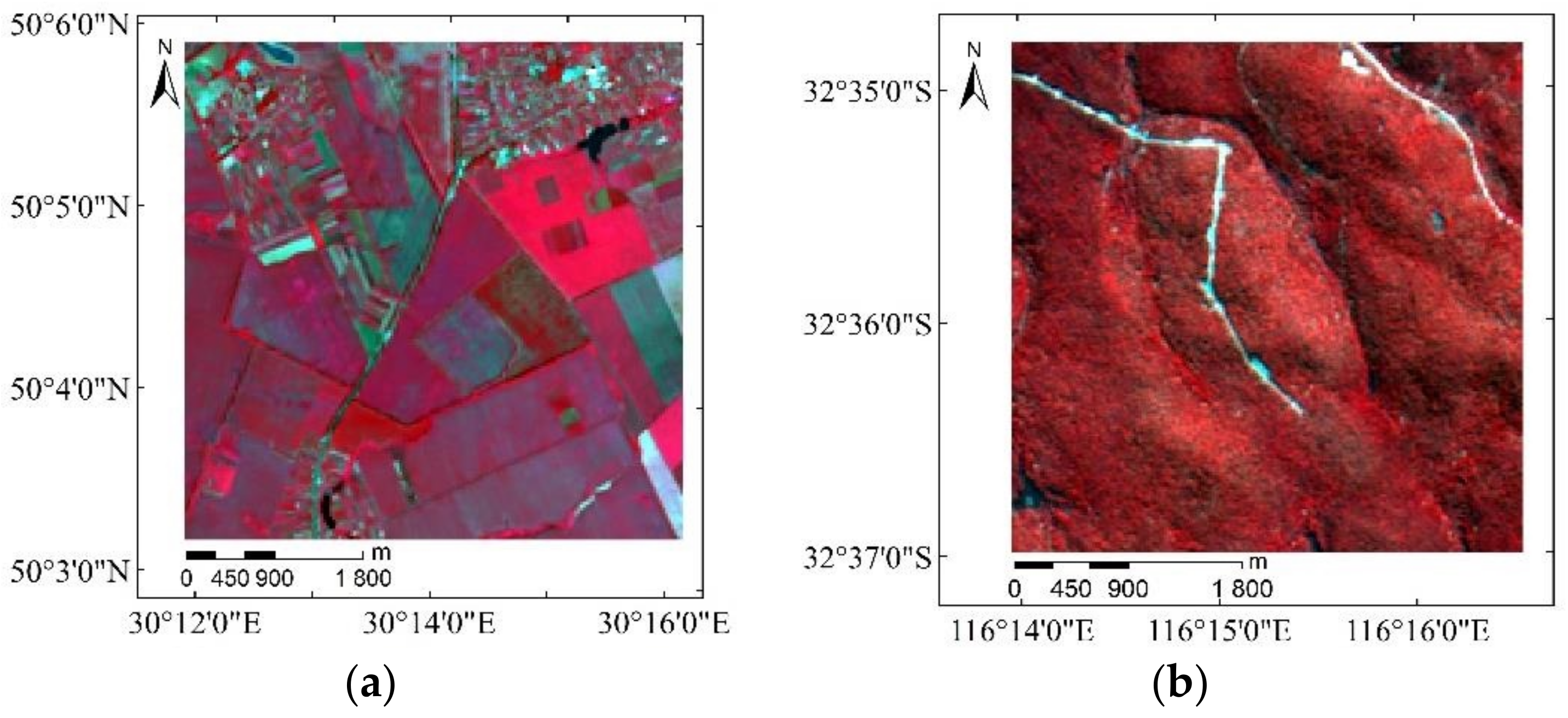
2.2. Satellite Imageries
2.3. Validation Data
3. Method
3.1. SEMP Construction Method
3.1.1. NDVI-LAI Model Construction
3.1.2. SEMP Generation
3.2. Model Downscaling Based on SEMPs
3.3. Fine-Resolution LAI Estimation
4. Results
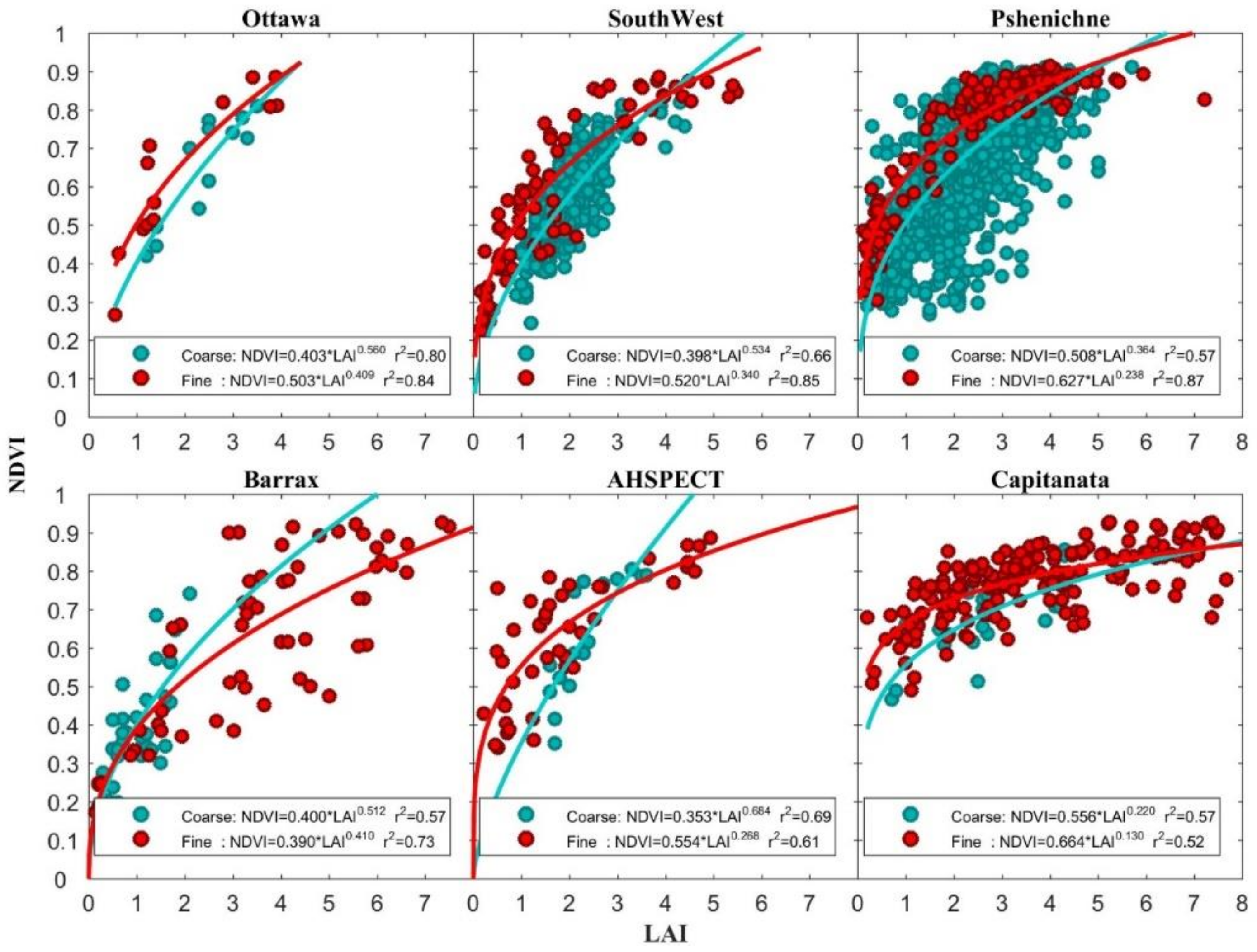
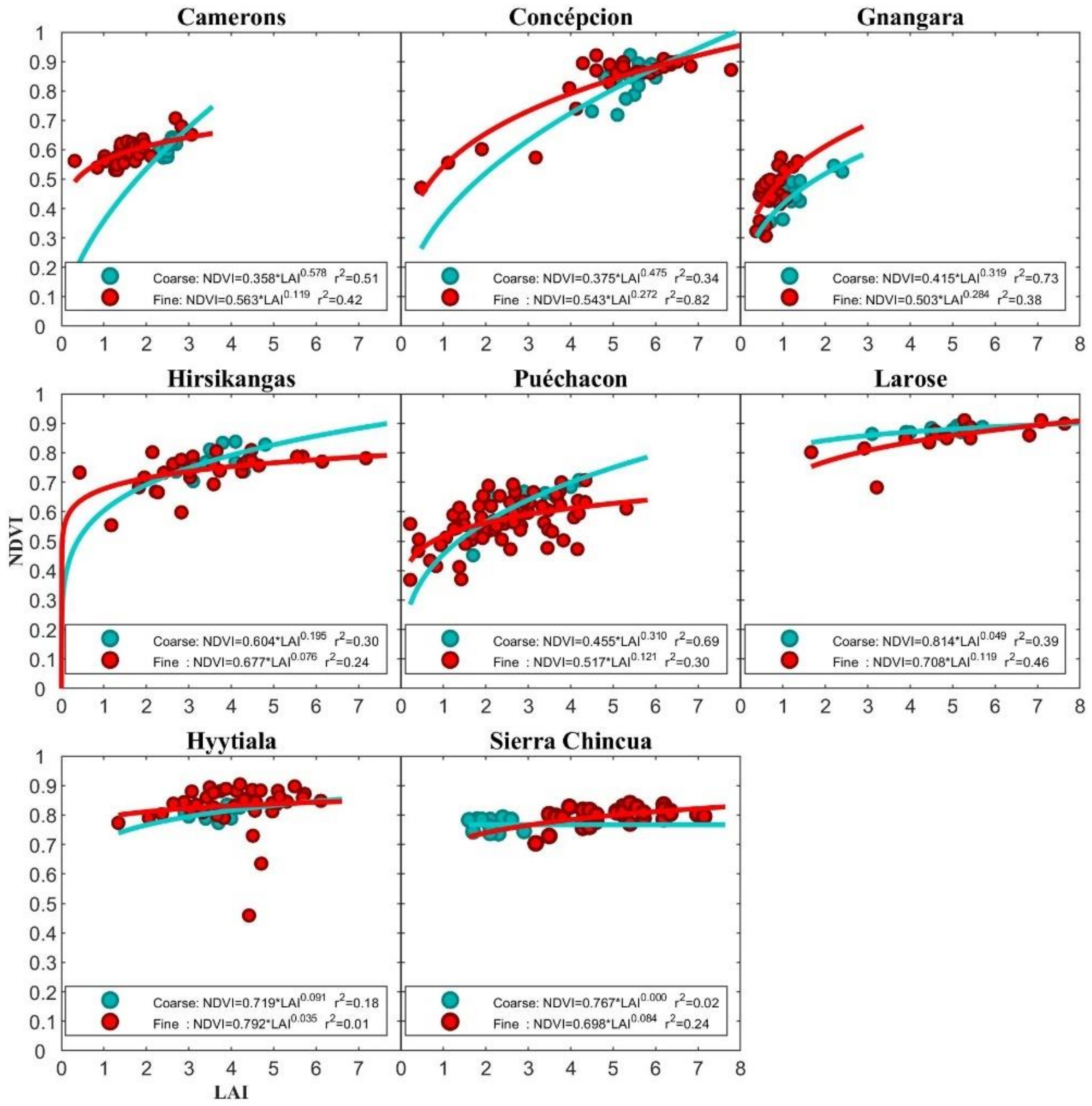
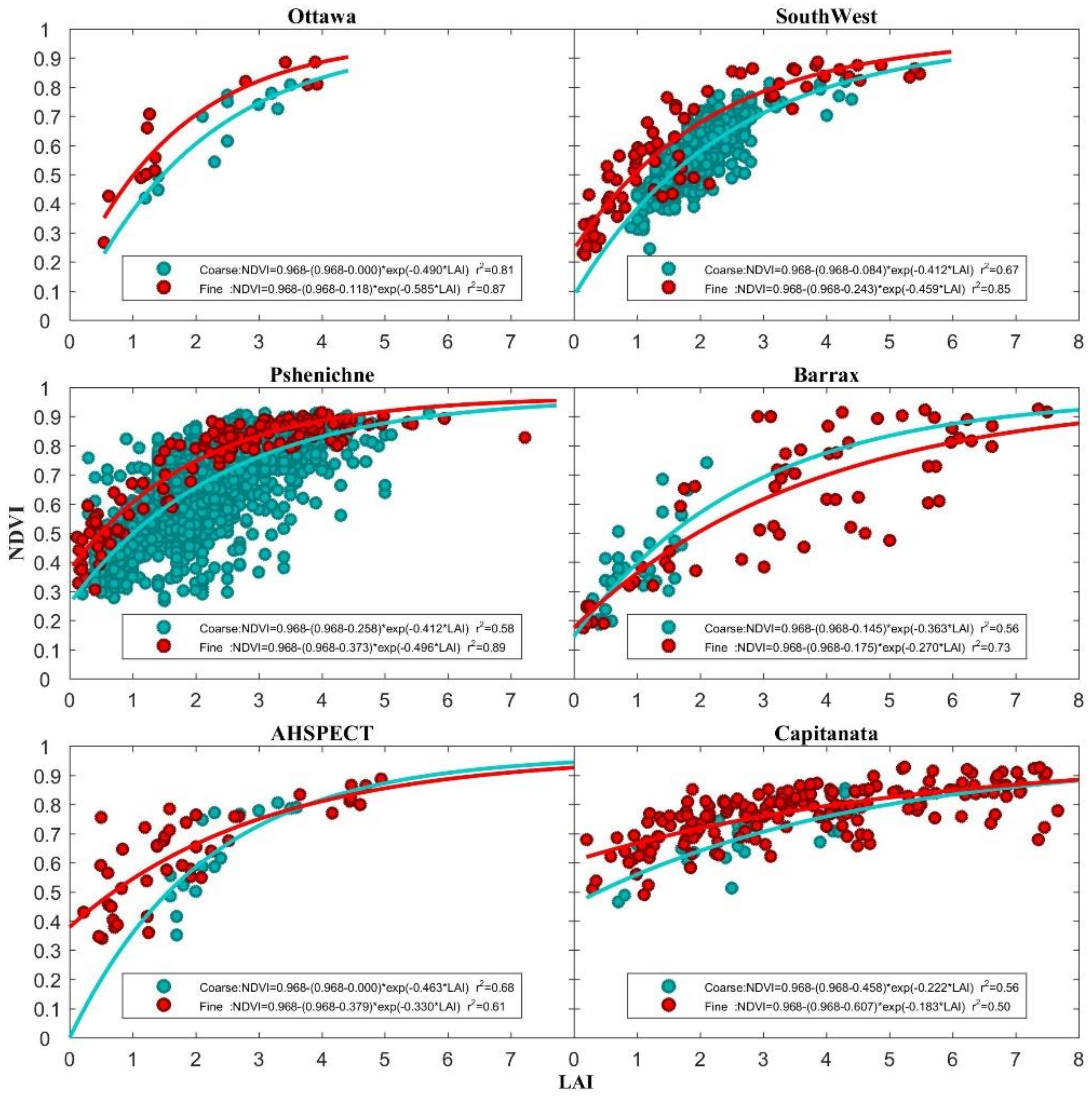
4.1. Accuracy of NDVI-LAI Statistical Models
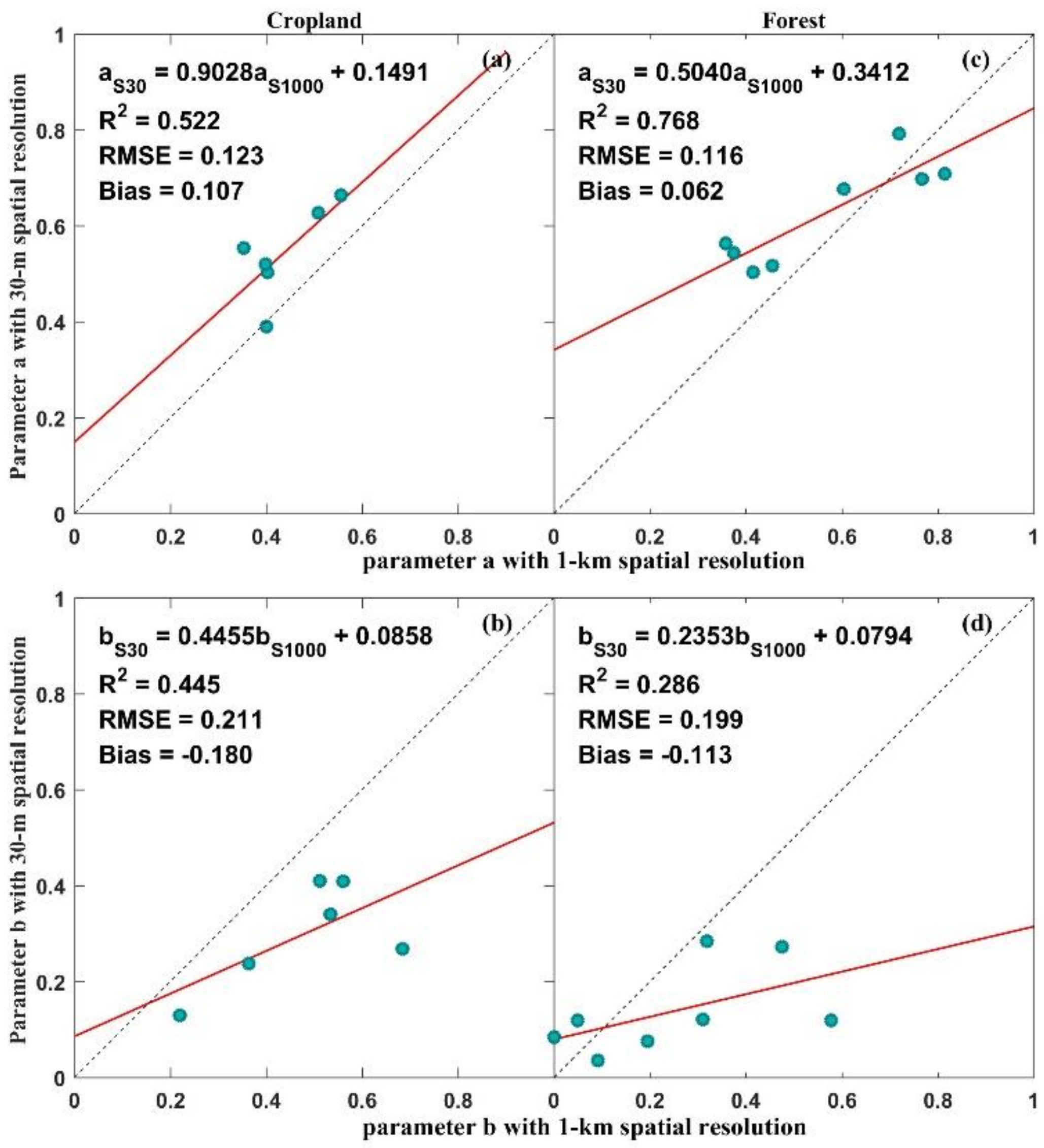
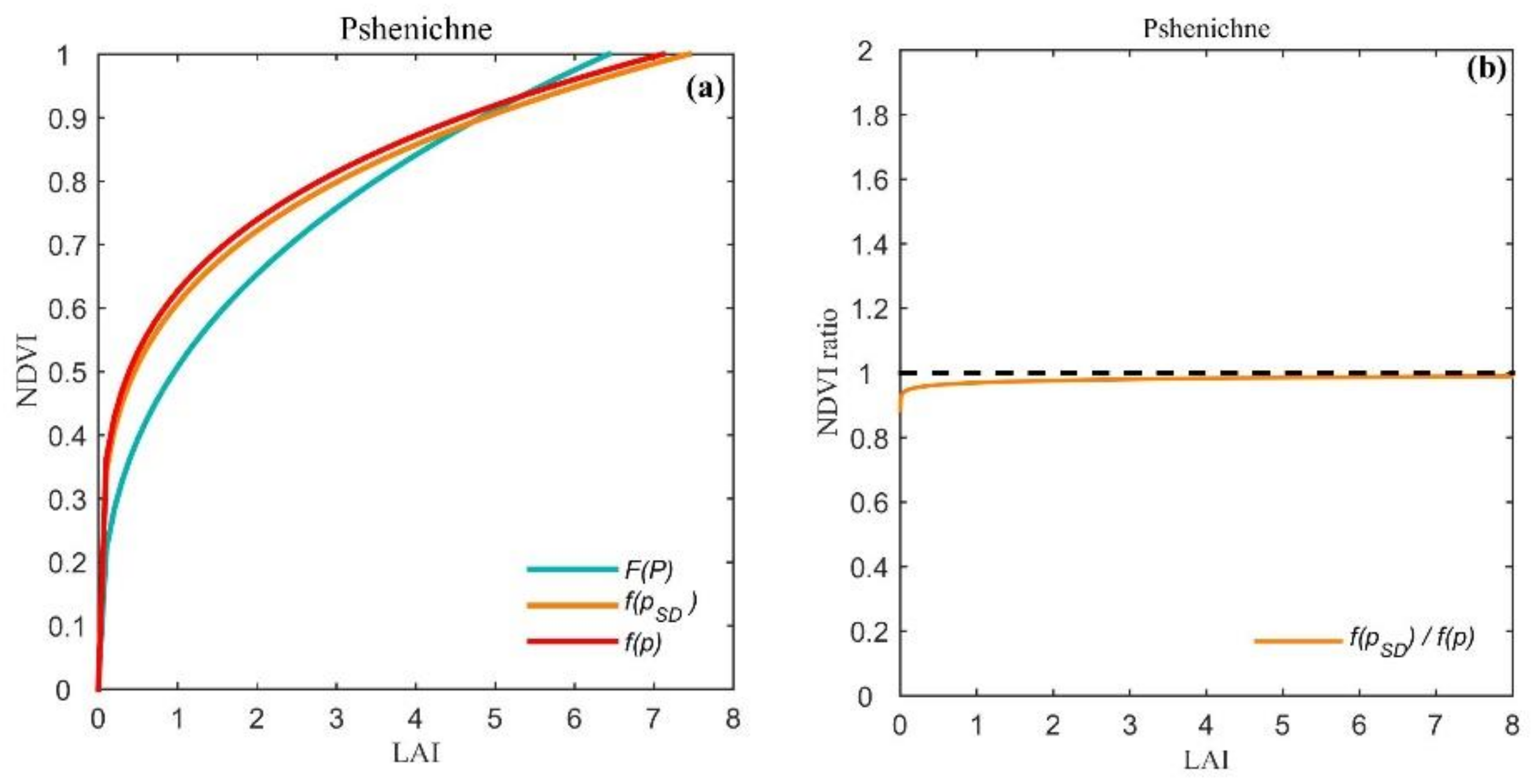
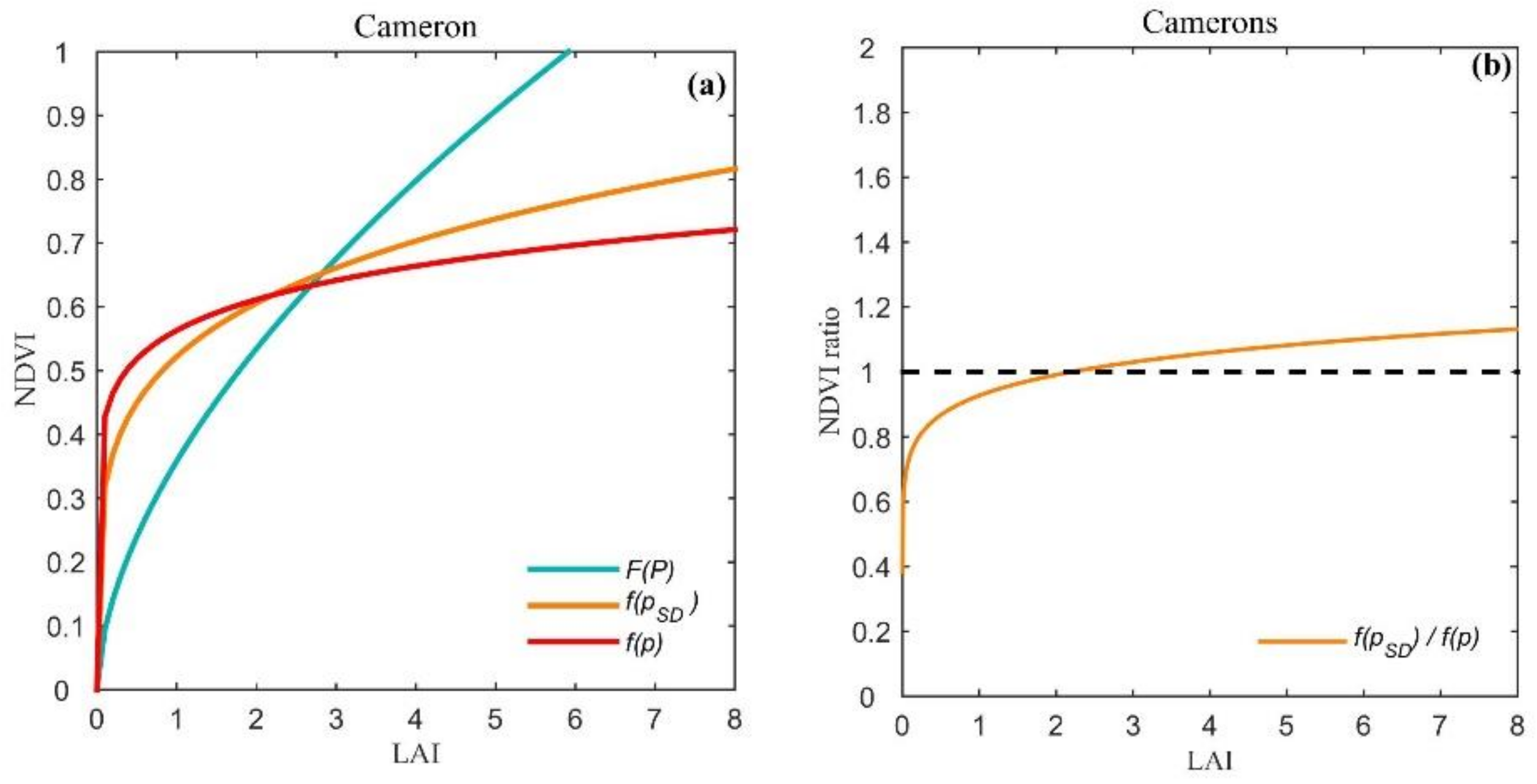
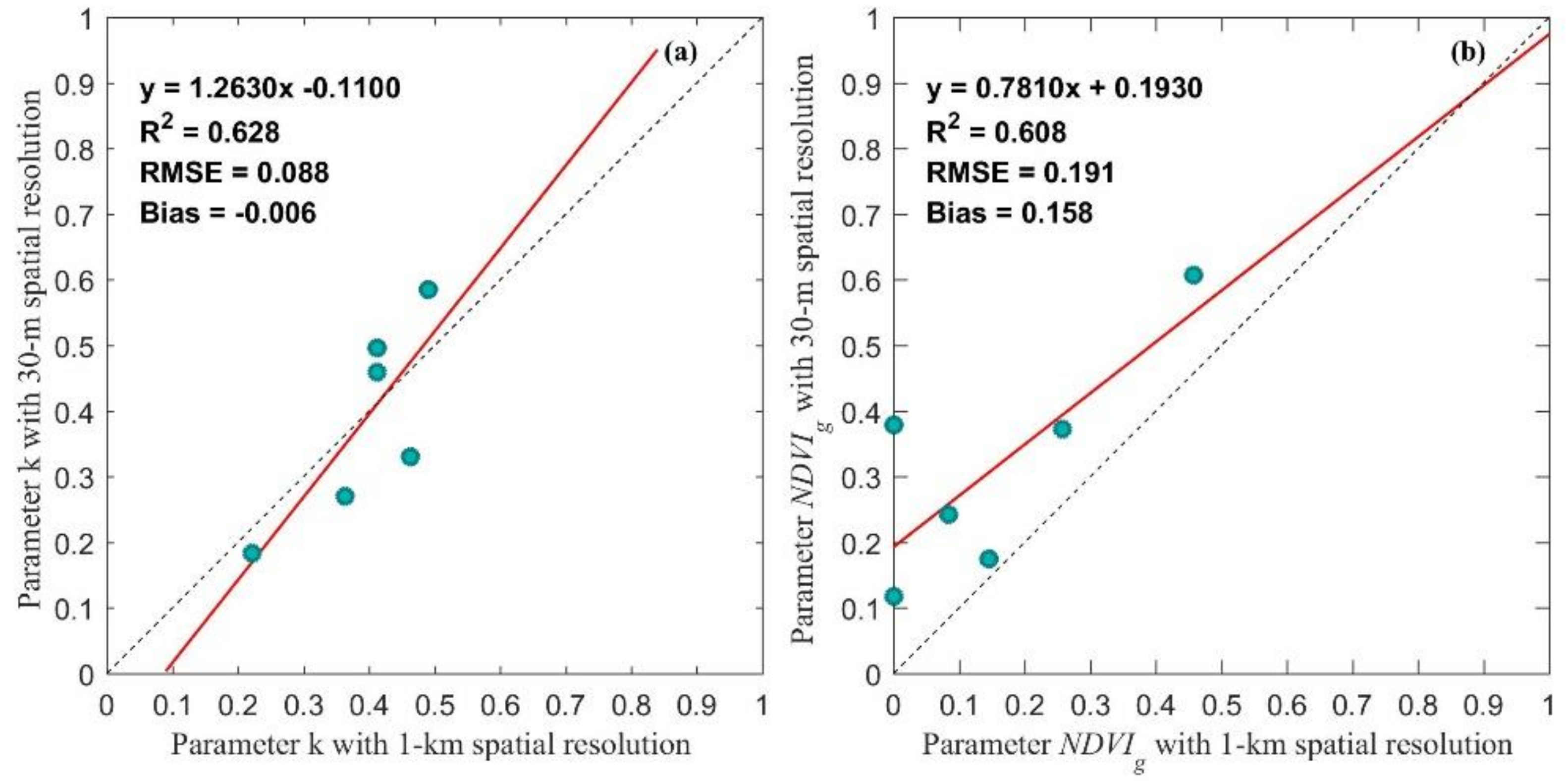
4.2. Accuracy of the Scaling Equations of Model Parameters
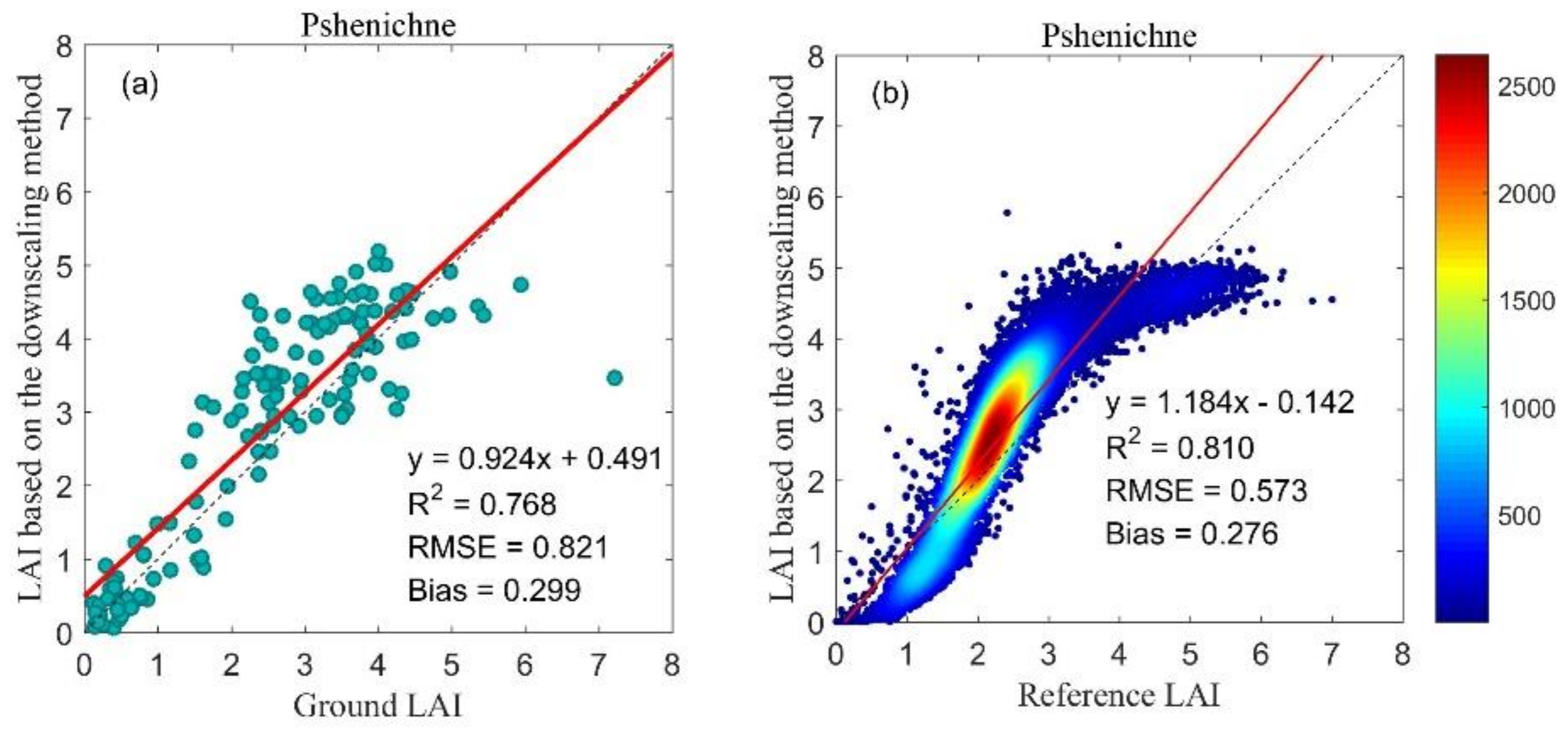
4.3. Accuracy of the Downscaled NDVI-LAI Statistical Model
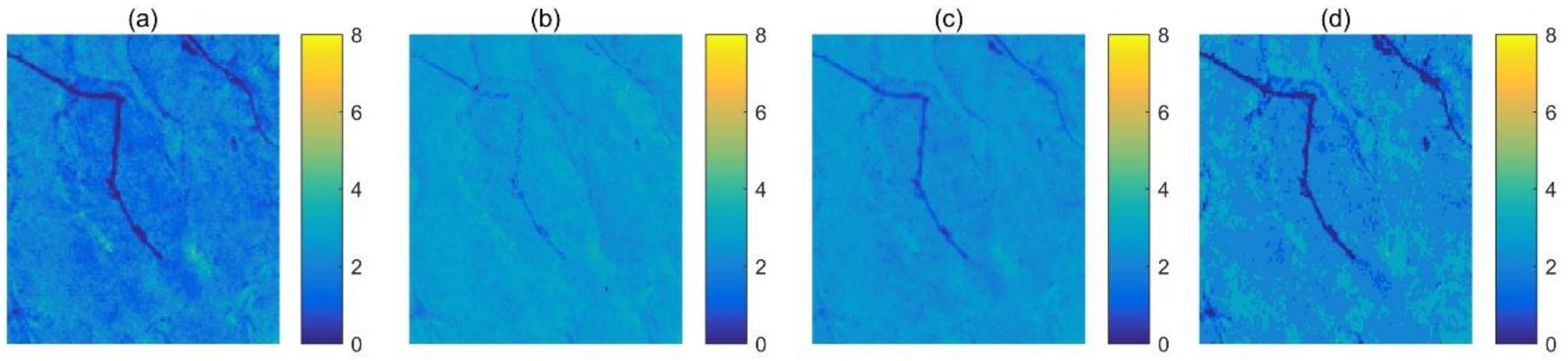
4.3.1. Cropland
4.3.2. Forest
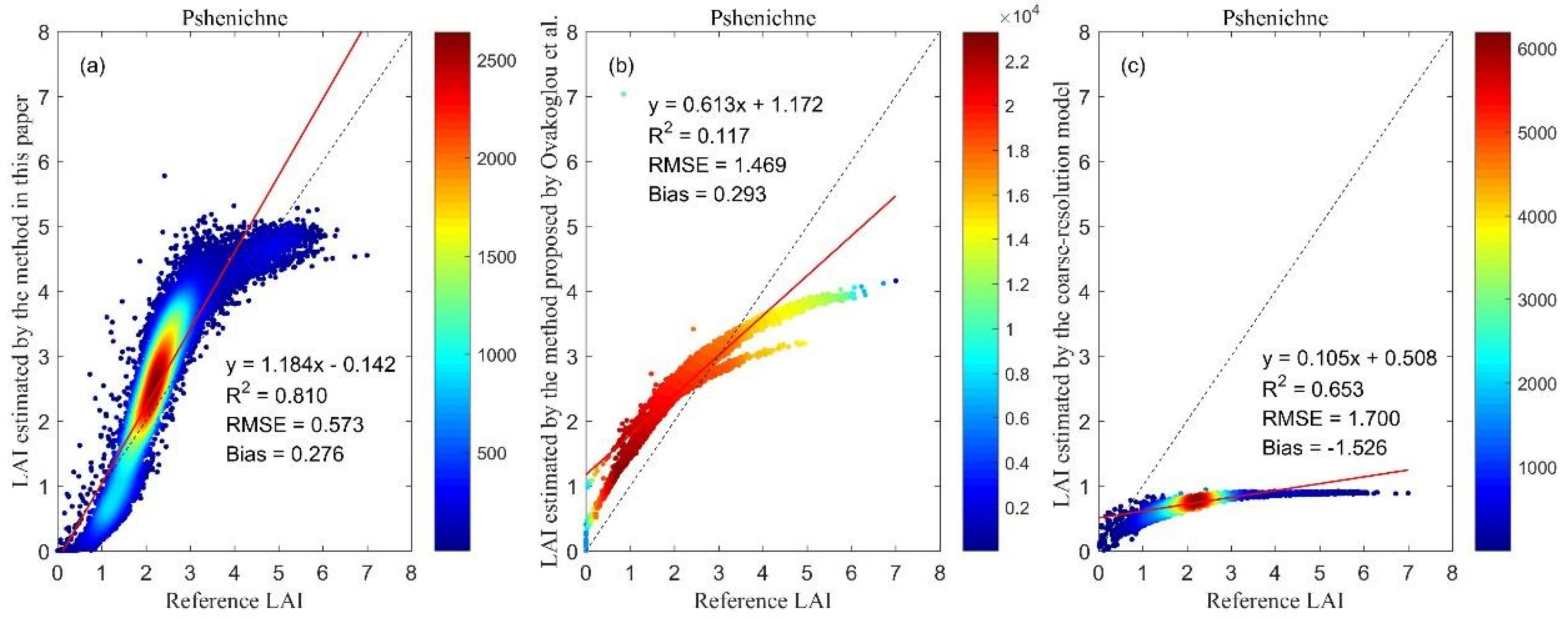
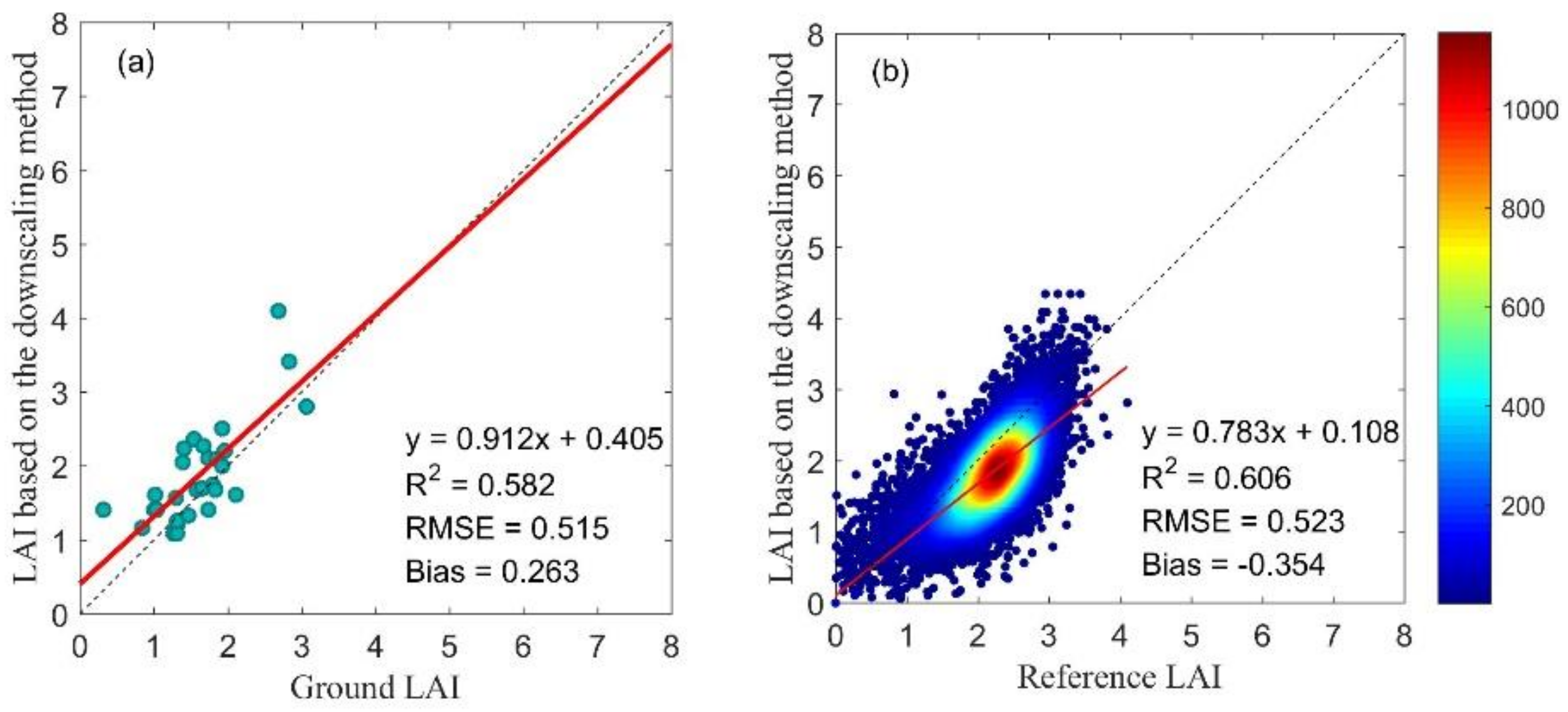
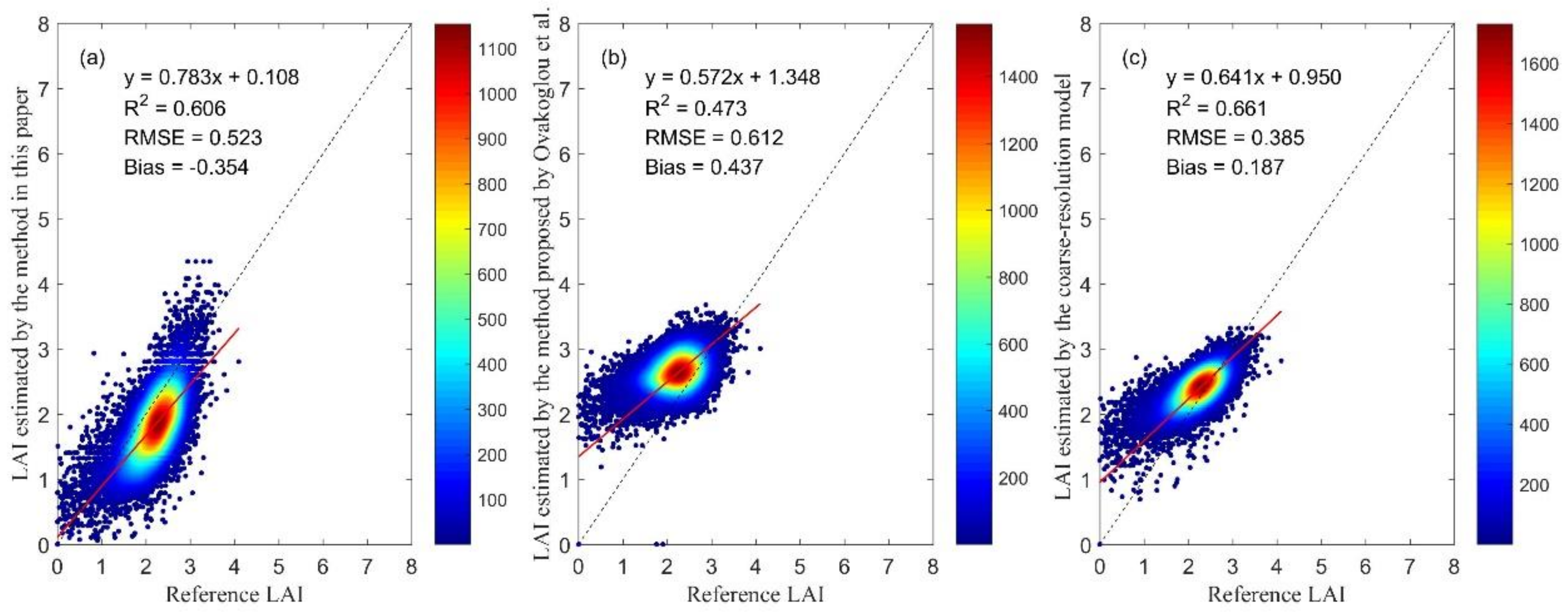
4.4. Accuracy of the Estimated Fine-resolution LAI
4.4.1. Crop
4.4.2. Forest
5. Discussion
5.1. Feasibility of the Model-Downscaling Method
5.2. The Amount of Data Needed for the Statistical Model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.M.; Black, T.A. Defining leaf area index for non-flat leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganopolski, A.; Kubatzki, C.; Claussen, M.; Brovkin, V.; Petoukhov, V. The influence of vegetation-atmosphere-ocean interaction on climate during the mid-Holocene. Science 1998, 280, 1916–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, R.B.; Hoffman, S.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Privette, J.L.; Glassy, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Smith, G.R.; et al. Global products of vegetation leaf area and fraction absorbed PAR from year one of MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verger, A.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M. GEOV2/VGT: Near real time estimation of global biophysical variables from VEGETATION-P data. In Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on the Analysis of Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Images, Banff, AB, Canada, 25–27 June 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Lacaze, R.; Camacho, F.; Makhmara, H.; Pacholcyzk, P.; Smets, B. GEOV1: LAI and FAPAR essential climate variables and FCOVER global time series capitalizing over existing products. Part1: Principles of development and production. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.Q.; Liang, S.L.; Wang, J.D.; Chen, P.; Yin, X.J.; Zhang, L.Q.; Song, J.L. Use of General Regression Neural Networks for Generating the GLASS Leaf Area Index Product From Time-Series MODIS Surface Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Park, T.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.D.; Song, W.J.; Yang, B.; Zeng, Y.L.; Liu, Z.; Yan, G.J.; Knyazikhin, Y.; et al. Generating Global Products of LAI and FPAR From SNPP-VIIRS Data: Theoretical Background and Implementation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2119–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Haro, F.J.; Campos-Taberner, M.; Munoz-Mari, J.; Laparra, V.; Camacho, F.; Sanchez-Zapero, J.; Camps-Valls, G. Derivation of global vegetation biophysical parameters from EUMETSAT Polar System. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wei, S.S.; Li, W.J.; Ye, Y.C.; Sun, T.; Liu, W.W. Validation of global moderate resolution leaf area index (LAI) products over croplands in northeastern China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xue, H.Z. Retrieval of 30-m-Resolution Leaf Area Index From China HJ-1 CCD Data and MODIS Products Through a Dynamic Bayesian Network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.A.; Li, A.N.; Yin, G.F.; Xiao, Z.Q.; Bian, J.H.; Nan, X.; Jing, J.C. A Multiscale Assimilation Approach to Improve Fine-Resolution Leaf Area Index Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8153–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.F.; Li, A.N.; Zeng, Y.L.; Xu, B.D.; Zhao, W.; Nan, X.; Jin, H.A.; Bian, J.H. A Cost-Constrained Sampling Strategy in Support of LAI Product Validation in Mountainous Areas. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Huang, F.; Qi, H. Generating High Resolution LAI Based on a Modified FSDAF Model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Quantitative Remote Sensing of Land Surfaces; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2012; p. 326. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, P.M. Downscaling in remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 22, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M. Spatial scaling of a remotely sensed surface parameter by contexture. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 69, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.L.; Islam, S. A framework for analyzing and designing scale invariant remote sensing algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Numerical experiments on the spatial scaling of land surface albedo and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Rev. 2000, 19, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tang, B.H.; Li, Z.L. Impact of nonlinearity and discontinuity on the spatial scaling effects of the leaf area index retrieved from remotely sensed data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 3503–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Z.L. Scale Issues in Remote Sensing: A Review on Analysis, Processing and Modeling. Sensors 2009, 9, 1768–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.L.; Ji, X.S.; Yao, X.; Tian, Y.C.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.X.; Cheng, T. Evaluation of Three Techniques for Correcting the Spatial Scaling Bias of Leaf Area Index. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, S.; Allard, D.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M. Influence of landscape spatial heterogeneity on the non-linear estimation of leaf area index from moderate spatial resolution remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.L.; Liu, X.N.; Liu, C.H.; Wu, L.; Xia, X.P.; Liu, M.L.; Du, Z.H. Analyzing the Spatial Scaling Bias of Rice Leaf Area Index from Hyperspectral Data Using Wavelet-Fractal Technique. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3068–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Qin, Q.M.; Liu, X.N.; Ren, H.Z.; Wang, J.H.; Zheng, X.P.; Ye, X.; Sun, Y.J. Spatial Up-Scaling Correction for Leaf Area Index Based on the Fractal Theory. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Wang, Y.J. Simple method for retrieving leaf area index from Landsat using MODIS leaf area index products as reference. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Sun, R.; Xiao, Z.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.M.; Liu, G. Generation of High Resolution Vegetation Productivity from a Downscaling Method. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovakoglou, G.; Alexandridis, T.K.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Gitas, I.Z. Downscaling of MODIS leaf area index using landsat vegetation index. Geocarto Int. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Bogaert, J.; Myneni, R.B. Radiative transfer based scaling of LAI retrievals from reflectance data of different resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, G.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.L.; Wan, H.; Guo, L. Evaluating the fraction of vegetation cover based on NDVI spatial scale correction model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 5359–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Baret, F.; Andrieu, B.; Danson, F.M.; Jaggard, K. Extraction of vegetation biophysical parameters by inversion of the prospect plus sail models on sugar-beet canopy reflectance data—Application to tm and aviris sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 52, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Strahler, A.H. Geometric-Optical Bidirectional Reflectance Modeling of the Discrete Crown Vegetation Canopy—Effect of Crown Shape And Mutual Shadowing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Davis, F.W.; Michaelsen, J.; Moritz, M.A. Scaling and uncertainty in the relationship between the NDVI and land surface biophysical variables: An analysis using a scene simulation model and data from FIFE. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrar, G.; Myneni, R.B.; Choudhury, B.J. Spatial heterogeneity in vegetation canopies and remote sensing of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation: A modeling study. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Wang, J.D.; Strahler, A.H. Scale effect of Planck’s law over nonisothermal blackbody surface. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 1999, 42, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Allard, D.; Garrigue, S.; Leroy, M.; Jeanjean, H.; Fernandes, R.; Myneni, R.; Privette, J.; Bohbot, H.; et al. VALERI: A network of sites and methodology for the validation of medium spatial resolution land products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 76, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Pisek, J.; Chen, J.M.; Lacaze, R.; Sonnentag, O.; Alikas, K. Expanding global mapping of the foliage clumping index with multi-angular POLDER three measurements: Evaluation and topographic compensation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H.; Ozdogan, M.; Zipper, S.C.; Roman, M.O.; Walker, J.; Hong, S.Y.; Marshall, M.; Magliulo, V.; Moreno, J.; Alonso, L.; et al. How Universal Is the Relationship between Remotely Sensed Vegetation Indices and Crop Leaf Area Index? A Global Assessment. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.G.; Pattey, E.; Jego, G. Assessment of vegetation indices for regional crop green LAI estimation from Landsat images over multiple growing seasons. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, K.; Zhu, W.Q.; Xie, Z.Y.; Li, P.X. Estimating the Seasonal Dynamics of the Leaf Area Index Using Piecewise LAI-VI Relationships Based on Phenophases. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Suzuki, R.; Kobayashi, S. Reflectance seasonality and its relation to the canopy leaf area index in an eastern Siberian larch forest: Multi-satellite data and radiative transfer analyses. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birky, A.K. NDVI and a simple model of deciduous forest seasonal dynamics. Ecol. Model. 2001, 143, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Cihlar, J. Retrieving leaf area index of boreal conifer forests using landsat TM images. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 55, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.P.; Cohen, W.B.; Kennedy, R.E.; Fassnacht, K.S.; Briggs, J.M. Relationships between leaf area index and Landsat TM spectral vegetation indices across three temperate zone sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.C.; Wang, J.D.; Wang, J.; Qu, Y.H. A Prior Knowledge-Based Method to Derivate High-Resolution Leaf Area Index Maps with Limited Field Measurements. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ID | Site Name | Country | Location | DOY | Year | Land Cover | Instrument | Number of Ground Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Camerons | Australia | 32.598°S 116.254°E | 61–64 | 2004 | Broadleaf forest | DHP | 29 |
| 2 | Concépcion | Chile | 37.467°S 73.470°W | 7–10 | 2003 | Coniferous forest | DHP | 26 |
| 3 | Gnangara | Australia | 31.534°S 115.882°E | 58–63 | 2004 | Broadleaf forest | DHP | 31 |
| 4 | Hirskangas | Finland | 62.643°N 27.011°E | 219–232 | 2003 | Coniferous forest | LAI-2000 | 30 |
| 5 | Hyytiälä | Finland | 61.851°N 24.308°E | 170–206 | 2008 | Coniferous forest | DHP | 41 |
| 6 | Larose | Canada | 45.380°N 75.217°W | 217–220 | 2003 | Mixed forest | DHP | 28 |
| 7 | Puéchabon | France | 43.725°N 3.652°E | 162–166 | 2001 | Broadleaf forest | DHP | 60 |
| 8 | Sierra Chincua | Mexico | 19.675°N 100.282°W | 345–347 | 2001 | Coniferous forest | DHP | 17 |
| 9 | SouthWest | France | 43.504°N 1.171°E | 170–177 205–210 228–232 245–249 | 2013 | Mixed cropland | DHP | 71 |
| 10 | Ottawa | Canada | 45.035°N 75.767°W | 153 178 186 | 2014 | Mixed cropland | SDP/DHP | 13 |
| 11 | Pshenichne | Ukraine | 50.077°N 30.232°E | 134–137 163 212 174 204 | 2013 2014 2014 2015 2015 | Mixed cropland | DHP | 148 |
| 12 | Barrax | Spain | 39.054°N 2.101°W | 139–140 147 203 | 2014 2015 2015 | Mixed cropland | DHP/ LAI-2200 | 72 |
| 13 | AHSPECT | France | 43.573°N 1.375°E | 173–176 | 2015 | Mixed cropland | DHP/ LAI-2200/ Lp80 | 77 |
| 14 | Capitanata | Italy | 41.464°N 15.487°E | 76 113 | 2015 | Wheat | LAI-2000 | 182 |
| Site Name | Year | MOD13A2 NDVI (DOY) | GLASS LAI | Landsat NDVI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOY | Number of Ground Samples | DOY | Satellite | |||
| Camerons | 2004 | 049 | 057 | 20 | 62 | TM |
| Concépcion | 2003 | 001 | 009 | 20 | 10 | ETM+ |
| Gnangara | 2004 | 049 | 057 | 12 | 62 | TM |
| Hirskangas | 2003 | 225 | 225 | 9 | 231 | TM |
| Hyytiälä | 2008 | 177 | 177 | 12 | 212 | ETM+ |
| Larose | 2003 | 209 | 217 | 12 | 212 | ETM+ |
| Puéchabon | 2001 | 161 | 161 | 12 | 177 | ETM+ |
| Sierra Chincua | 2001 | 345 | 337 | 12 | 330 | TM |
| SouthWest | 2013 2013 2013 2013 | 161 193 225 241 | 161 193 225 241 | 560 | 177 193 232 248 | OLI OLI OLI OLI |
| Ottawa | 2014 | 145 177 177 | 145 177 185 | 12 | 153 178 186 | OLI OLI ETM+ |
| Pshenichne | 2013 2014 2014 2015 2015 | 129 161 209 161 193 | 129 161 209 161 193 | 2000 | 138 157 212 176 189 | OLI OLI OLI OLI OLI |
| Barrax | 2014 2015 2015 | 129 145 193 | 129 145 193 | 36 | 130 126 197 | OLI OLI OLI |
| AHSPECT | 2015 | 161 | 161 | 16 | 174 | OLI |
| Capitanata | 2015 2015 | 113 65 | 113 73 | 24 | 120 80 | OLI ETM+ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, R.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H. A Model-Downscaling Method for Fine-Resolution LAI Estimation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244147
Zhang J, Wang J, Sun R, Zhou H, Zhang H. A Model-Downscaling Method for Fine-Resolution LAI Estimation. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(24):4147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244147
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingyu, Jindi Wang, Rui Sun, Hongmin Zhou, and Helin Zhang. 2020. "A Model-Downscaling Method for Fine-Resolution LAI Estimation" Remote Sensing 12, no. 24: 4147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244147
APA StyleZhang, J., Wang, J., Sun, R., Zhou, H., & Zhang, H. (2020). A Model-Downscaling Method for Fine-Resolution LAI Estimation. Remote Sensing, 12(24), 4147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244147








