Abstract
Currently, satellite ocean color imageries play an important role in monitoring of water properties in various oceanic, coastal, and inland ecosystems. Although there is a long-time and global archive of such valuable data, no study has comprehensively used these data to assess the changes in the Caspian Sea. Hence, this study assessed the variability of bio-optical properties of the upper-water column in the Southern Caspian Sea (SCS) using the archive of the Sea-Viewing Wide Field-of-View Sensor (SeaWiFS) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). The images acquired from SeaWiFS (January 1998 to December 2002) and MODIS Aqua (January 2003 to December 2015) satellites were used to investigate the spatial–temporal variability of bio-optical properties including Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), attenuation coefficient, and remote sensing reflectance, and environmental parameters such as sea surface temperature (SST), wind stress and the El Nino-southern oscillation (ENSO) phenomena at different time lags in the study area. The trend analysis demonstrated an overall increase of 0.3358 mg m−3 in the Chl-a concentration during 1998–2015 (annual increase rate of 0.018 mg m−3 year−1) and four algal blooms and in turn an abnormal increase in Chl-a concentration were occurred in August 2001, September 2005, 2009, and August 2010. The linear model revealed that Chl-a in the northern and middle part of the study area had been influenced by the attenuation coefficient after a one-month lag time. The analysis revealed a sharp decline in Chl-a concentration during 2011–2015 and showed a high correlation with the turbidity and attenuation coefficient in the southern region, while Kd_490nm and remote sensing reflectance did a low one. Generally, Chl-a concentration exhibited a positive correlation with the attenuation coefficient (r = 0.63) and with remote sensing reflectance at the 555 nm (r = 0.111). This study can be used as the basis for predictive modeling to evaluate the changes of water quality and bio-optical indices in the Southern Caspian Sea (SCS).
1. Introduction
The Caspian Sea (CS) is the largest enclosed water body in the world and of high geo-ecological importance in Eurasia []. Hence, its natural environmental health status needs to be comprehensively monitored through taking an increasingly ecological approach by which the structure and dynamics (i.e., physiochemical parameters such as the sea level, water currents, surface water temperature, and wind) could be assessed. During the last two decades, the Caspian Sea has severely suffered biological and ecological changes because of increasing greenhouse gas emission and in turn global warming, receiving huge amounts of pollutants, and introducing invasive species []. Therefore, due to possessing abundant natural resources, the sea requires a conscious ecological policy concerning structure and dynamism of marine variations.
Given insufficient oceanographic information on the Caspian Sea after the fall of the Soviet Union, it is necessary to apply satellite data and to develop computational technology and numerical modeling []. Optical remote sensing data offer an effective means of monitoring biogeochemical variables in aquatic ecosystems, such as near-surface concentrations of chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) [] and suspended particulate matter (SPM). The information about these critical variables can be retrieved via inverting the spectral remote sensing reflectance (Rrs; 1/sr), defined as the ratio of water-leaving radiance to the total downwelling irradiance. Moreover, the accurate assessment of spatio-temporal variability in the biogeophysical phenomena, such as occasional coastal eutrophication and upwelling events, can be conducted using consistent and long-term records of satellite-derived Chl-a products [].
Thus far, few research have applied satellite data to assess spatio-temporal variability of bio-optical properties in the Caspian Sea. These studies have primarily focused on fluctuations in satellite-derived Chl-a product and its correlation with environmental drivers such as the sea surface temperature (SST), wind stress, and invasion of Mnemiopsis leidyi [,]. The highest concentration of Chl-a in the northern parts of the Caspian Sea has been ascribed to the Volga River discharge, but in the central and southern areas to wind stress and surface temperature []. The SeaWiFS data were analyzed to study the spatial and temporal variability of the bio-optical characteristics in the Barents, Black, and Caspian Seas in 1998–2001 []. The algorithms demonstrated that phytoplankton blooms in the north of the Caspian Sea were stemmed from river runoffs and shallow bathymetry. Due to the influence of the Volga River on the northern and middle regions of the Caspian Sea, some similarities were found in the 555 nm (Rrs_555 nm) SeaWiFS spectral band, whereas no such relationship was observed for ag and Chl-a, the maximum amounts of Chl-a at the 555 nm spectral band in the South China Sea from July to August (largely due to Mnemiopsis) but in the middle of the Caspian Sea in September. Another study (1998–2005) showed that a sharp increase of chl-a concentration in the Caspian Sea in July–August 2001 was attributed to a consequence of invasion Mnepiopsis leidyi [].
The moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard Aqua (MODISA) and the sea-viewing wide field-of-view sensor (SeaWiFS) were compared in four areas in South-East China from July 2002 and October 2004. The SeaWiFS and MODIS data showed similar spatial and temporal patterns and nearly identical concentrations for Chl (0.1–4 mg.m−3). The root mean square (RMS) error between the two data sets for monthly mean Chl was generally <11% in several sub-regions and <24% for the costal area, and spatiotemporal patterns derived by the two measurements were very similar and showed no significant relationship from July to October 2004 [].
A review of related literature in the world’s aquatic ecosystems shows that Krishna and Rao [] revealed that the seasonal and annual variation of phytoplankton population and, in turn, Chl-a concentration in the Arabian Sea was highly influenced by climate changes such as the El Nino-southern oscillation (ENSO), not wind stress. The ocean color sensors from 1996 to 2011 were integrated and showed a close correlation among algorithmic coefficient of SeaWiFS, MODIS Aqua, OCTs (ocean color temperature scanner), medium-spectral resolution, and imaging spectrometer (MERIS) []. In a time series monitoring, these measurements were applied to monitor Chl-a level in the coastal zone of California and revealed that the concentration could be altered with El Nino, though with a small correlation coefficient []. A further research analyzed near-surface Chl-a in the Bay of Bengal and China Sea over a 20-year period and exhibited a significant correlation between SST, winds tress, and Chl-a; the cooling and warming SST, respectively, raised and reduced the concentration of Chl-a in the China Sea and in the Bay of Bengal []. The authors stated that strong wind generally induced the growth of phytoplankton, not an increase of chlorophyll, although wind stress changed the Chl-a trend [,,]. Liu et al. [] analyzed a time series image of anomalies for a decade (2002–2012) in the northern part of the South China Sea. The findings illustrated that algal bloom and monsoons caused maximum Chl-a concentration in winter but a minimum one in spring, summer, and autumn. Algal bloom in the Persian Gulf was investigated using a total of 12, 6, and 4 images from MODIS, SeaWiFS, and MERIS, respectively, the observed anomalous patterns were speculated to be associated with harmful algal blooms []. Seasonal Chl-a variation in the Gulf of Mexico was analyzed using the time series data, and the findings indicated that the variations were related to anthropogenic and natural processes such as SST, wind stress, and El Nino []. The data also showed that low temperature and strong wind increased Chl-a concentration in the basin []. Baliarsingh et al. [] found the spatiotemporal distribution of Chl-a in the Bay of Bengal, which was caused by pre- and post-monsoon seasons trigging algal bloom events. Colella et al. [] applied the Mann–Kendall test to assess the concentration Chl-a in Mediterranean Sea over a decade (1998–2009) and observed the highest alterations following introducing excessive nutrients by runoffs in different seasons.
Limited information is available concerning large-scale bio-optical and biogeochemical variabilities of the Southern Caspian Sea (SCS). Therefore, the present study aims to analyze historic ocean color products (1998–2015) derived from the SeaWiFS and Aqua-MODIS to better understand the variability. The causes of regional variabilities spur future developments of region-specific algorithms to be evaluated. To identify seasonal patterns and to decipher the root caused through statistical analyses, a total of 648 ocean color products including Chl-a and the diffuse attenuation coefficients (Kd_490nm) were assessed.
2. Materials and Methods
To make it easier to report the results, the National Cartographic Center’s standard delineation procedure was adopted to divide the SCS into regional blocks with 1:250,000 scale and 14,300 km2 area (Figure 1).
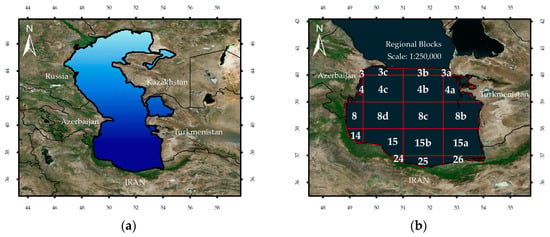
Figure 1.
(a) Spatial position of the Caspian Sea (CS) and (b) The spatial subsetting of the Southern Caspian Sea (SCS) based on Iran’s National Cartographic Center guidelines. The temporal variability in bio-optical properties is communicated for each block.
2.1. Database and Preprocessing
A database was prepared from the concurrent monthly 4-km MODIS and SeaWiFS level-3 data. The satellite data (from January 1998 to December 2015) was downloaded from the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center ocean color website (http://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov). The Chl-a data is the level 3 standard mapped image (SMI) product of monthly temporal resolution and 4.6 km (at the equator) spatial resolution. The current implementation for the default chlorophyll-a algorithm (Chla) employs the standard OC3/OC4 (OCx) band ratio algorithm. Currently, Chl-a algorithm products are based on the OC4 algorithm [], a valuable source of data on the spatial and temporal distribution of Chl-a in water ecosystems. The algorithm used for Kd_490nm hereafter mentioned as Kd [].
To preprocess and detect an anomaly among the data, the main step is to remove seasonal effects and then subtract the long term average from each month through the series [].
Generally, autocorrelation is a common complication in time-series data []. This restriction could be eliminated by reducing effective sample size, adjusting variance, and prewhitening []. Due to being greatly influencing factors on the analysis outputs, the last two methods may be useless especially when dealing with very small sizes []. Thus, prewhitening was carried out as a safe method for the present study.
The Durbin–Watson (DW) test is applied for autocorrelation and always has a value between 0 and 4. No serial autocorrelation is indicated by a value of 2, whereas the values of < 2 and > 2 indicate positive and negative serial autocorrelation, respectively. Critical values for the DW statistic can be found in standard statistical texts, and the following equation is applied to determine the DW statistic []:
The prewhitening process estimates p-values of the time series. The p-values of <0.05 can be directly determined []; for trend analysis by other methods, however, it is necessary to perform prewhitening.
Impurity is a common problem in time-series analyses. The problem can be solved by using regional geographical information on the impurities, and this method is a nonparametric test, which is on the basis of spatial autocorrelation []. The prewhitened time-series are analyzed in depth, but the incorporation of adjacent pixels leads to higher variance scores, a situation that is susceptible to reject the null hypothesis (i.e., no trend).
The spatial cross-correlation model can be corrected through adding regional data. The impact of the model is considered besides variance adjustment in the significance test, which is defined as the degree of relation between two-time series at a time lapse of ≥0 []. In more time lapses, this occurs in single series because of serial correlation. Therefore, it is necessity to correct the time lapse of 0 before prewhitening. Adjusting the variance of cross-correlation is determined in the significance test by determination of spatial cross-correlation as follows [].
Figure 2 illustrates only the areas with a significant trend in pixel. To evaluate the contextual Mann–Kendall (CMK) test, the results were compared to the Mann–Kendall (MK) test in which the contextual information is unconsidered.
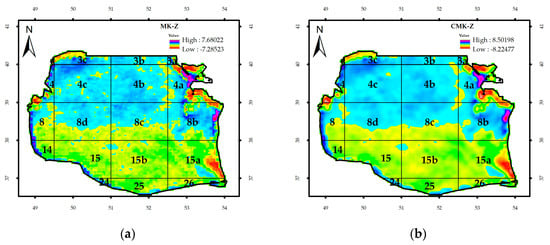
Figure 2.
The Southern Caspian Sea (SCS) basin and impact of contextual information on significant trends before (a) and after (b) inclusion of contextual information.
The software used for data analysis and processing were Arc GIS and TerrSet. TerrSet is an integrated geospatial software system for monitoring and modeling the Earth system for sustainable development. TerrSet is an object-oriented system designed for professional-level use and incorporates the GIS Analysis and Image Processing tools along with a constellation of vertical applications that one of them is the Earth trends modeler (ETM). The Earth trends modeler (ETM) is an integrated suite of tools within TerrSet for the analysis of image time series data associated with Earth observation remotely sensed imagery.
2.2. Series Trend Analysis
To analyze the time series, both parametric and non-parametric methods were used [].
2.2.1. Theil-Sen Median Trend Estimator
Theil–Sen median trend estimator, a powerful nonparametric statistical operator, is appropriate for assessing short-term variations and noisy data sets. This operator computes the median trend through analyzing the pixels of the time series. The results of longer time-series are similar to those of the ordinary least square (OLS), whereas the data of short time-series are more reliable because the variations do not interfere with the results when putting the breakdown point in the range of 29% [].
2.2.2. Mann–Kendall Trend Test
The MK test, a nonlinear method, computes the trend of a steadily increasing or decreasing process and varies from −1 to +1; the negative and positive values imply steady decreasing and increasing trends, respectively, yet zero indicates no trend []. The significance of the test is shown by Z values and the probability of a random event in trend, which is computed by the p value. The MK test was applied to assess H0. A trend was considered significant if the absolute value of Z was higher than Zα/2; where α stands for the lowest significance level (i.e., 5% and Z0.025 = 1.96) and the proof of the zero hypothesis [].
2.3. Linear Modeling
The relationships between series can be assessed using different monthly time lags. Time lag 0 shows that the dependent and independent series are compared simultaneously. In this study, the relationship among variables was analyzed according to the values of correlation coefficient R and R2 by introducing positive and negative time lags. The concept of correlation was used to evaluate the effects of variables on each other; the negative and positive time delays were called lead and lag, respectively.
Like other statistical tests, such as linear regression and correlation coefficient, the significance test of linear modeling is very important. However, serial correlation in residuals can cause error and consequent exaggeration of correlation coefficient after linear modeling. As such, it is necessary to conduct the significance test before evaluating the results. Generally the significance test should be conducted for p-values of more than 0.05 []. The obtained t-values and degrees of freedom (effect size; Figure 3) were compared with the t-standard to demonstrate the significance degree. The t-value was computed in three basic steps as follows: (1) computing and assessing the serial correlation degree of residuals (prediction errors) using the model, (2) computing the serial correlation using the image, and (3) determining the degree of serial correlation at pixel level. The same series were selected as the dependent variable with a time lag of 1, and then the effect size was computed via the following equation (Equation (1)) []. Moreover, the t-score statistic was estimated to determine the correlation significance, as shown in Figure 4, (Equation (2)) []. The effect size and T-score were determined individually in pixels.
where r stands for the correlation between the bio-optical characteristics. The numerator shows the degree of freedom, and k stands for partial regression, which is 0 in case of bio-optical parameters (Kd_490 nm and Rrs_555nm).
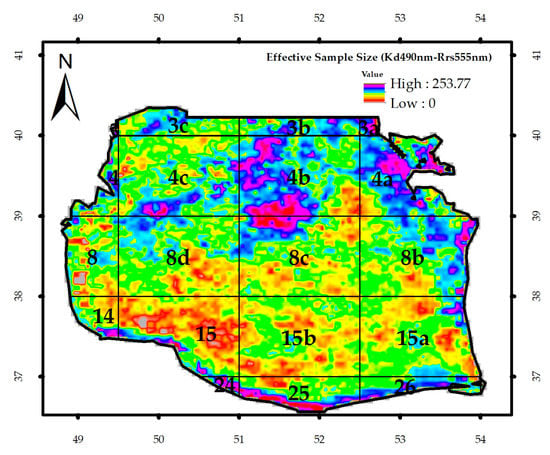
Figure 3.
The image of the effective sample size (ne).
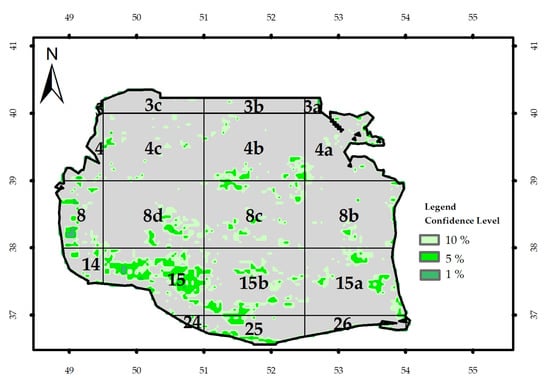
Figure 4.
T-score for three confidence levels (99%, 95%, and 90%) in relation to Kd_490nm and Rrs_555nm in different blocks of the Southern Caspian Sea (SCS).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Durbin–Watson and Prewhitening Statistics
The Durbin–Watson statistic, respectively, showed bio-optical anomaly and attenuation coefficient of 1.12 and 1.23 for both Chl-a and Rrs_555nm (Figure A1). The three bio-optical parameters showed values lower than 2, indicating a positive serial correlation (Figure A1). The bio-optical parameter of Chl-a exhibited serial correlation in different blocks of each SCS regions: 4b, 4c, 8d, and 8c, the central region; 3c and 3b, the northern region; and 15a and 4a, the eastern regions. In regards to the attenuation coefficient, the pixels displayed serial autocorrelation in most of the SCS. Furthermore, Durbin–Watson statistics demonstrated serial autocorrelation for Rrs_555nm in the western (3C, 4, 8, and 14), southern (26), and eastern blocks (15a and 8b, 3b, 4c, and 15). Figure A1 shows the trend of variations in bio-optical parameter attenuation coefficient. The results indicated that the anomalies in this factor are similar to those found in bio-optical parameter Chl-a: four unusual peaks during the years 2001, 2005, 2009, and 2010. There is also a general upward trend concerning this parameter.
Before the prewhitening process, the values of Durbin–Watson statistics for Chl-a, the attenuation coefficient, and remote sensing Rrs_555nm were 2.03, 2.04, and 1.93, respectively (Figure A2). These values are acceptable in terms of serial autocorrelations []. Moreover, this method showed a possibility to be used to eliminate serial correlation after prewhitening. These findings are consistent with those reported by [].
3.2. Temporal Profile (Chl-a, Attenuation Coefficient, and Rrs_555nm)
Figure 5 displays the time series of monthly anomalies of Chl-a concentration in the SCS. Four algal blooms and in turn abnormal increase in Chl-a concentration were occurred in August 2001, September 2005, 2009, and August 2010. From 2011 onwards, the situation of the study area reverted to previous conditions (prior to invasion of Mnemiopsis).
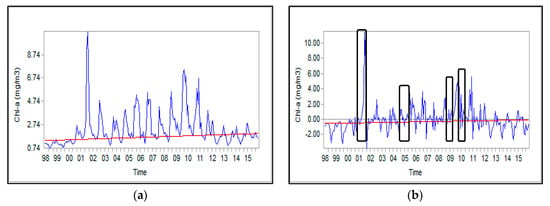
Figure 5.
Time series for Chl-a concentration in the SCS: (a) absolute values and (b) anomalies.
To identify the common and sudden variations across the study area in the time series, it is necessary to analyze the maps of Chl-a anomalies []. The values lower and higher than zero shown in the graph, respectively, represent an increase and decrease of Chl-a concentrations in a month when compared to the mid-month values.
The Theil-Sen slope estimator represents the concentration of Chl-a at the end of the trend relative to the beginning. The observed positive anomalies in time series might be ascribed to unexpected events such as harmful algal bloom; the results are consistent with those reported by []. As shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, the concurrent unusual increase in Chl-a concentration could be justified the observed positive correlation between Chl-a concentration and attenuation coefficient.
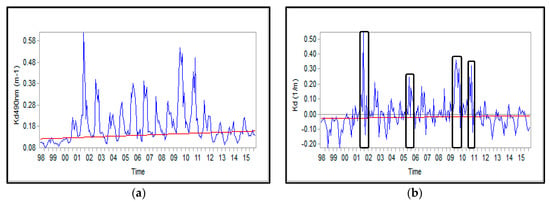
Figure 6.
Time series of attenuation coefficient in the SCS; (a) absolute values and (b) anomalies.
Turbidity in water bodies is mainly caused by phytoplankton []. Earlier studies conducted over the southern regions of the SCS and Chesapeake Bay illustrated a significant correlation between Chl-a and turbidity. The observed turbidity in the second lake was attributed to allochthonous nutrients (i.e., phosphorus and nitrate) from the surrounding lands, which increased phytoplankton population and in turn Chl-a concentration [].
Absolute values and anomalies of Rrs_555nm in the SCS are shown in Figure 7. Rrs_555nm decreased in the time series; that is, the suspended matter during the analyzed period reduced, so that the values of the peaks in later phases were smaller than those in the beginning ones. The years of 2001, 2009, 2012, and 2015 exhibited higher values than other years.
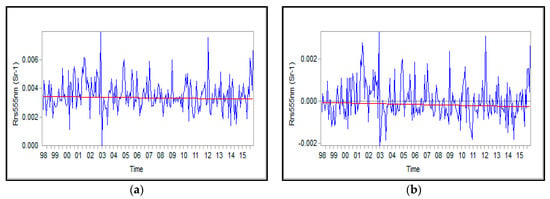
Figure 7.
Time series of Rrs_555nm in the (SCS): absolute values (a) and anomalies (b).
3.2.1. Median Trend Analysis of Bio-Optical Parameters
Figure 8 shows the mean values for median trend analysis of Chl-a. Apart from blocks 3 and 15a, other blocks indicate an upward trend; the highest variation rate was observed in 4B, 4c and 8d (0.002), 8, 8b and 8c, 15b, and 25 (0.001). Overall, the annual variation rate for the Chl-a in the SCS displayed an upward trend (0.018 mg m−3 year−1 during 1998–2015) while the variation rate for the entire time series was 0.3358 mg m−3 (Figure 11a). During the 1998–2015 time period, the highest downward rate of changes was observed in the block 4a (7 mg.m−3) in the eastern part and block 3C (5.61 mg m−3) and 4 (4.44 mg.m−3) in the western part. A possible explanation for this might be the anti- and cyclonic gyres, which occur in the south and middle of the SCS, respectively.
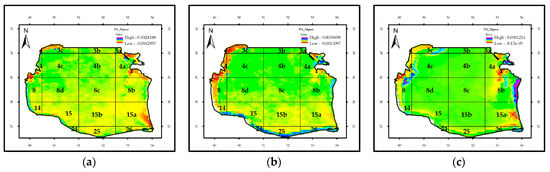
Figure 8.
The change rate of bio-optical parameters in the SCS: (a) Chl-a (mg.m−3), (b) attenuation coefficient (m−1), and (c) Rrs_555nm (Sr−1) during 1998–2015 time period.
The attenuation coefficient increased and decreased in the SCS (Figure 8b). The rate of changes in southern (24, 25 and 26) and south-eastern (14 and 15) blocks and in blocks of 3C, 4C, and 4a were relatively higher than the other blocks, with an average of 0.011 (1/m). In regards to the attenuation coefficient, it displayed an increase by a factor of 2.34.
Furthermore, the middle trend analysis of Rrs_555nm revealed that RSR underwent smaller variation rates in central blocks than in the eastern blocks. In eastern parts, the maximum variation rate of RSR was related to block 15a, with being a negative value (Figure 8c).
3.2.2. Mann–Kendall Analysis of Bio-Optical Parameters
Figure A3 presents the trend significance for monthly Chl-a concentrations using MK and Regional MK tests. A little variation was observed in the regions with a ρ-value < 0.005. The white, red, and green colors, respectively, represent no change, significant trends in different significance levels, and positive variations in different significance levels. Generally, a large part of the study area showed a certain trend.
The significance of the trend was similar for p-values smaller than 0.001 and 0.01 when the comparison was conducted between the MK and regional MK tests (Table A1). However, significance level increased (p < 0.05) when the Regional MK test applied the adjacent pixels.
The pixels with no significance in the MK test became significant when taking into account the adjacent pixels, with a significance level 0.05 (Figure A4). Most of these pixels belong to blocks 25 and 26 and 14 and 15 (the southwestern region), 15a (the western region), and 15b (the eastern region). The MK and regional MK tests were different concerning the attenuation coefficient and p values smaller than 0.001.
After applying the two tests, negative trends were found in some blocks in the southern part (15b), in parts far away from the southern coasts (15, 25, and 26), in western coasts (3, 3c, 4, 8 and 14), and also at the mouth of the Gorganrud River (Figure A5). Block 3C and 15a in the northern and eastern parts, respectively, exhibited more influence. Unlike Chl-a and attenuation coefficient, Rrs_555nm displayed higher significance levels. An upward trend with a significance level of 0.001 was observed in southern coasts. Overall, these findings obtained by MK and regional MK tests are in accordance with those reported by []. Spatial autocorrelation displayed a significant impact during the time series. Thus, the significance level for admitting or rejecting the statistical hypotheses was increased when the adjacent pixels considered. Taken all together, the values for Chl-a concentrations displayed a rate of change (ROC) in different parts of the study area: 0.058, 0.22, and 0.29 mg m−3, respectively, for the eastern, western, and central parts in the time series of 1998–2015. The values for attenuation coefficient in eastern, western, and central parts were 0.011, 0.007, and 0.02, respectively. In addition, Rrs_555nm presented negative value (−0.00033) in the central parts, whereas positive values in the eastern (0.00016) and western (0.00012) parts.
3.3. Linear Modeling
3.3.1. Relationships between Driving Factors in Variations of Chl-a
In various regions in the CS, the driving factors in variations of Chl-a, presented in Table 1, revealed correlation with different time lags: time series of North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) and El Nino-southern oscillation (Figure A6), monthly anomalies of wind stress (Figure A7), SST (Figure A8), attenuation coefficient (Figure A9), Rrs_555nm (Figure A10), and Chl-a concentration (Figure A11). According to attenuation coefficient data (Figure A9), each of the El Nino and La Niña phenomena occurred six times in the studied time series: El Nino (six times in 1998–2015; two average in 2002–2003 and 2009–2010; and one week during the years 2004–2005 and 2006–2007) and La Niña (four average in 1998–1999, 2007–2008, and 2010–2011, and two weak in 2000–2001 and 2011–2012).

Table 1.
Correlation coefficient and time lags of maximum correlations (in parentheses) for the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), El Nino-southern oscillation (ENSO), and sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies (SST-1, SST-2 and SST-3), Chl-a concentration (Ch-1, Ch-2 and Ch-3), wind stress (τ−1, τ−2, and τ−3), attenuation coefficient (Kd_490nm −1, Kd_490nm −2 and Kd_490nm −3), remote sensing reflectance (Rrs_555nm −1, Rrs_555nm −2 and Rrs_555nm −3) for 3 regions of the Caspian Sea (CS).
Monthly correlations of anomalies in Chl-a concentrations in the Northern Caspian Sea were relatively lower than in the Middle and Southern Caspian. This bio-optical index exhibited a mutual dependence (r = 0.4) in the last two parts, and the variations in the middle region led to variations in a one-month lag (Table 1). Lack of or insignificant relationship between shallow regions in the northern and middle and the deep parts of the SCS could be justified by significant differences in environmental conditions among these regions that like other deep open oceans around the world, phytoplankton assemblages occur due to the vertical stratifications in the SCS []. A deep refractive stratum in the surface of water acts as a natural barrier and separates deeper layers with nutrients from the upper ones, which are dominated by phytoplankton, reducing the necessary nutrients for phytoplankton growth. Wind pressure and cold surface layers eliminate the barrier and transfer the nutrients to upper layers, enhancing the growth of phytoplankton populations in the SCS. These results match those reported about The Caspian Sea Environment [].
In a time lag of seven to eight months, SSTs in the southern, middle, and northern parts of the study area (CS), respectively, revealed a positive and negative correlation with ENSO and NAO indices (Table 1). The positive phase of the NAO index shows a high-pressure and unusual strong subtropical area in the North Atlantic Ocean and a strong deeper center of low atmospheric pressure in the Iceland region. Besides the wind flow directions over the Northern Atlantic Ocean, which explain humid warm winters in Europe [], a great difference in pressure leads to the emergence of heavier winter storms. This phenomenon leads to cold flows over the Caspian Sea and declines its temperature, and more raining on the SCS.
The El Ninos happened during the analyzed time series led to an increase in SSTs []. Northern Hemisphere usually is faced with the reduction of atmospheric cyclones in the western regions and the southern line of longitude, mostly in warm seasons. These cyclones are heavily influenced by the intensity of northern line of longitude, especially during the cold seasons []. The present findings illustrated that the NAO index was generally positive, and the regional currents increased whenever warm winds dwindled in the Central and Southern Europe [,]. This is a complex phenomenon that reduces the warming rates of the Caspian Sea, which was already approved by [].
In three studied regions of the Caspian Sea, Chl-a concentration exhibited a negative correlation with the NAO index with a time lag of 5–8 months. The greatest impact of NAO was found in the southern regions of CS (SCS; Table 1). Between the ENSO index and Chl-a level in the northern regions, however, a positive and weak negative correlation was observed within a time lag of 11–12 and 5–6 months, respectively. Similar results have been reported by [] who found that the anomalies in Chl-a concentration in deep regions of the Caspian Sea are negatively correlated with NAO and positively with ENSO []. The ENSO index caused a greater impact on central regions than the other ones (Table 1). El Nino or wetter-than-normal years induced destructive rainfalls and ferocious floods, which changed Chl-a concentrations and turbidity in southern regions with time lags of 5–6 and 4–6 months, respectively.
Rainfall lixiviates nutrients from the coastal lands into the SCS and enhances the concentration of Chl-a, thereby increasing turbidity and reducing remote sensing reflectance []. Given being negatively correlated with the NAO index, remote sensing reflectance needs further analysis in the study area. Shallow waters of the northern CS are muddy; hence, higher SSTs increased vertical stratifications and prevented phytoplankton growth in well-lit upper layers.
A positive correlation was observed between wind stress and Chl-a concentration in the SCS with a time lag of 3 months. It is speculated that winds can fertilize the water column through perturbing the sediments and stimulate the growth and reproduction of phytoplankton. Support for these findings have come from a study conducted by Nezlin (2005), and the difference in time lags could be explained by the differences in time series. For the SCS regions, the acquired negative values for remote sensing reflectance during an 11-month time lag might be a consequence of backscattering of sunlight by shallow water sediments [].
A positive correlation was found between SST anomalies in the Caspian Sea and Chl-a concentrations in deep waters of the middle region and the SCS (Table 1). Low SST means greater upwelling or tumultuous mixing, which is responsible for greater amounts of nutrients moved up to upper layers and higher growth of phytoplankton and in turn greater phytoplankton biomass. A 1-, 7-, and 12-month delay was indicated between the signal and response (i.e., low SST and high Chl-a concentration, respectively) in the Southern and Middle CS. However, it is assumed that stronger convective flows throughout the water column during winter can induce larger phytoplankton biomass in late summer (August to September). A similar relationship was reported in the Western Mediterranean area []. Another research demonstrated a close relationship between remote sensing Chl-a concentration and wind stress in the Middle Caspian Sea []. Stronger winds cause greater tumultuous mixing of phytoplankton biomass in deep areas of the Southern (time lag of 11 months) and the Middle Caspian Sea (time lag of 1 month).
3.3.2. Relationships between the Bio-Optical Indices
Values for correlation coefficients in terms of time lags were determined for different regions of the Caspian Sea (Table 1). In addition, Figure A12, Figure A13 and Figure A14 illustrate the variation anomalies of the bio-optical parameters in the studied regions. In the Northern and Middle Caspian Sea, Chl-a concentration is affected by light attenuation coefficient with a time lag of 1 month. These phenomena simultaneously occur in the SCS; however, the attenuation coefficient in the Northern Caspian Sea exhibited a weak correlation with that of in the middle and southern of the sea, and this finding could be ascribed to the differences in the physical geographical conditions and the seabed features. This index exhibited high effectiveness (r = +0.47) in the middle and southern areas, and in the late area showed a positive correlation (r = +0.63) with Chl-a concentration. In addition, the analysis showed a positive correlation between attenuation coefficient and Rrs_555nm in the SCS with time lags of 1–3 months, but a negative one in the Northern Caspian Sea with time lags of 12 months (Table 1).
3.3.3. Significance Test of Linear Modeling
Linear modeling of the analyzed time period demonstrated that Chl-a concentration had a positive correlation with an attenuation coefficient (r = + 0.63) and Rrs_555nm (r = +0.12) in the SCS with time lags of 0, 4, or 12 months, respectively (Table 1). However, these parameters displayed a negative correlation in blocks of 26, 4, and 3c.
Figure 9 depicts the image of ne and the t-test output for Kd_490nm and Chl-a concentration. The mean value of the t-test for the SCS was 1.16. Student’s t-test was more than 1.65 with 191 degrees of freedom and significance levels of 91, 95, and 99.99; therefore, these two parameters could not be significantly and simultaneously in correlation with each other (Table 1). In contrast, they showed a significant correlation at the significant levels of 90% and 95% for about 11% of the SCS surface and 99% for 4% of the area.
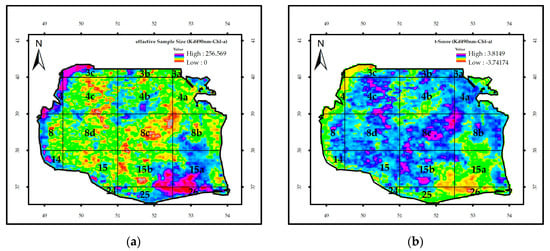
Figure 9.
(a) The image of effective sample size (ne), and (b) the value of t-test for the regression of Kd_490nm and Chl-a concentration in the SCS from 1998 to 2015.
The values of the effective sample size and Student’s t-test for Chl-a and Rrs_555nm are presented in Figure 10; the mean ne and p-values for the Southern Caspian Sea were 181 and 0.89, respectively. Since t value (1.65) was lower than all significance levels, no simultaneous correlation was found between Rrs_555nm and Chl-a concentration; however, the parameters showed a remarkable correlation (95–99%) in the coastal regions, block 3C in northern regions, and blocks 4a and 15a in the eastern regions. Moreover, a significant correlation was obtained at confidence levels of 90%, 95%, and 19%, respectively, in 5%, 4%, and 1% of the SCS surface area.
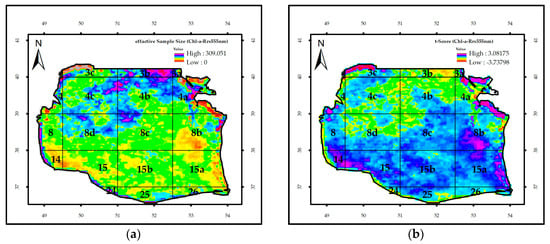
Figure 10.
The image of the effective sample size (ne) (a) and the value of t for the regression of Chl-a and Rrs_555nm (b) in the SCS.
The effective sample size index demonstrated values of 205 (p-value = 0.51) and 200 (p-value = 0.66) in the time lags of 4 and 10 months, respectively. The significance level test demonstrated a strong correlation between these two parameters, with simultaneous time lags of 4 and 12 months, albeit a high proportion of the correlation was related to the Eastern SCS (blocks 4a, 15a, 4, and 8).
Figure 11 illustrates the effective sample size for the attenuation coefficient and Rrs_555nm using the Student’s t-test. For these two parameters, the maximum correlation was found with time lags of 1 and 3 months (Table 1). A mean effective sample size of 196 was determined for the southern regions of the SCS, indicating no significant correlation between the regions with a t-value of 0.99. According to the t-test analysis, maximum correlations could be identified in block 15 and 25 in and block 15A in the eastern one. Strong correlations with a time lag of 1 month and significance levels of 90% and 95% were observed, respectively, in 10% and 7% of the study area, including blocks 15, 15A, and 15b and block 25 of the eastern region. An effective sample size of 179 and a t-value of 0.82 were measured for these two factors at a time lag of 3 months, indicating no significant correlation at any confidence level in the SCS. Moreover, these indices revealed a high correlation with confidence levels of 90% and 95% in 5% and 3% of the whole regions, mainly in the block 8, 15a (mouth of Gorganrud River), 15b, and 8C.
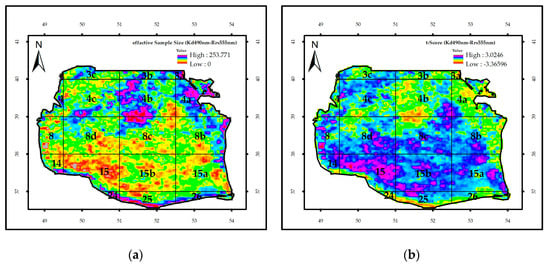
Figure 11.
The image of effective sample size (ne) (a) and the value of t-test for the regression of Kd_490nm and Rrs_555nm (b) in the SCS.
4. Conclusions
Chl-a, the attenuation coefficient (Kd_490nm), and remote sensing reflectance at the 555 nm band (Rrs_555nm) are among the most common remote sensing parameters to assess physicochemical parameters of water bodies. The amount and variation of these parameters over time determine the possibility of life and the reproduction of plants and animal species in marine environments.
The results showed a significant difference between the blocks in the SCS only when the adjacent pixels at the confidence level of 0.05 were taken into account. The concentration of Chl-a in the western coasts was higher than the eastern ones and corroborates the in-situ observations for the increase of turbidity in an east–west bound direction []. In addition, the east–west gradient of the phytoplankton biomass can be attributed to the cyclonic circulations in the middle and southern parts of the SCS, which transfer nutrients and phytoplankton from the north of the CS to other areas [,].
Monthly average of Chl-a concentration, attenuation coefficient, and Rrs_555nm revealed maximum and minimum values, except for Rrs_555nm, in summer and spring, respectively. Generally, Chl-a concentration considerably decreased in all seasons during 2011–2015, when compared with previous years. A good correlation was observed between Chl-a, attenuation coefficient and Rrs_555nm in different time lags. Moreover, SST and other environmental parameters exhibited correlation with Chl-a concentration and altered its spatial–temporal distribution. The concentration of Chl-a displayed a positive correlation with attenuation coefficient and Rrs_555nm but did a negative one with wind stress (−0.11) at time lags of 2, 5, and 11 months and with SST at time lags of 1 and 12 months []. The thermal system of the SCS is an important factor that influences on Chl-a concentration; that is, phytoplankton growth is regulated and influenced by the vertical stratifications of the water column of this ecosystem.
This study revealed a high correlation between the attenuation coefficient and Chl-a concentration and between Kd_490nm and remote sensing reflectance. In the study area, the attenuation coefficient was mostly influenced by Chl-a concentration. The amount of primary oceanic production depends on Chl-a concentration; therefore, human activities in organizations such as marine protected areas (MPAs) and marine agriculture are directly related to this parameter.
The observed variation rates of Chl-a concentration, the attenuation coefficient, and Rrs_555nm indicated that Chl-a had had an upward trend, though with no significance, in all of the coastal regions and aquaculture sites of the SCS. However, the downward trends were significant at confidence levels of 95% and 99%. Concerning the attenuation coefficient, an upward trend at a confidence level of 99% was shown in the coastal areas of Middle SCS, whereas a downward trend at confidence levels of 95% and 99% was measured in eastern and western regions. In addition, variation rates for Rrs_555nm in the middle, western, and eastern regions demonstrated a downward trend with confidence levels of 95% and 99%.
According to the p value obtained from the MK and regional MK tests, Chl-a concentration showed no significant difference with the attenuation coefficient throughout the SCS (p < 0.05) but did with Rrs_555nm in many of the regions. In general, the Student’s t-value for the SCS was smaller (1.16) than that of that represented in Table 1 (1.65), with 191 degrees of freedom. However, their correlation showed confidence levels of about 90% and 95% for 11% (especially block 2) and 99% for 4% of the SCS. The SCS proved to be with and without significance for 26% and 74%, respectively. Hence, there was a significant correlation between Chl-a and attenuation coefficient for the evaluated time series in the SCS.
Overall, this study could be used as the basis for predictive modeling to evaluate the changes of water quality and bio-optical indices in the Southern Caspian Sea (SCS).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G.; Methodology, M.G.; Software, B.A. and M.G.; Validation, M.G. and T.K. and S.V. and A.K.; Formal Analysis, B.A; Investigation, B.A; Resources, B.A.; Data Curation, B.A.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, B.A.; Writing—Review & Editing, M.G. and T.K. and S.V. and A.K.; Visualization, B.A.; Supervision, M.G.; Project Administration, M.G.; Funding Acquisition, T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The study presented here is part of the thesis in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of M.Sc. in Tarbiat Modares University (T.M.U.) of Iran. The authors extend their appreciation for the support provided by the authorities of the Tarbiat Modares University in funding the study. We also thank Nima Pahlevan (NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, USA) for his constructive suggestions and comments. Tiit Kutser’s work was supported from the Estonian Research Council grant PRG302. Also, A.G. Kostianoy participated in this paper in the framework of the Russian Science Foundation Project N 19-77-20060 entitled assessing ecological variability of the Caspian Sea in the current century using satellite remote sensing data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
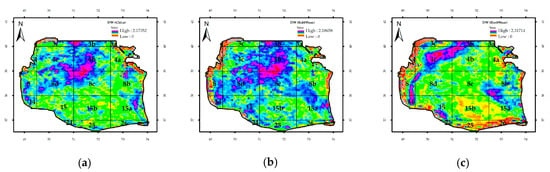
Figure A1.
Column Durbin–Watson statistics for bio-optical parameters in the Southern Caspian Sea: (a) Chl-a, (b) attenuation coefficient, and (c) Rrs_555nm.
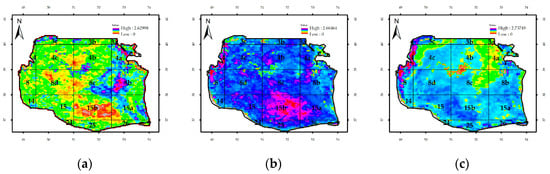
Figure A2.
Durbin–Watson statistics before the prewhitening process for bio-optical parameters; (a) Chl-a, (b) attenuation coefficient, and (c) Rrs_555nm.
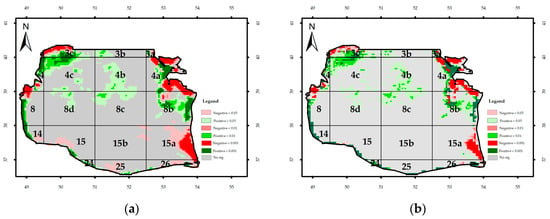
Figure A3.
Monthly significance trend of Chl-a concentration in the Southern Caspian Sea (SCS): (a) Regional Mann–Kendal and (b) Mann–Kendal.

Table A1.
The significance of bio-optical parameters in the study area. The Mann–Kendall and Regional Mann–Kendal statistics were used and the data are expressed in percentage (%).
Table A1.
The significance of bio-optical parameters in the study area. The Mann–Kendall and Regional Mann–Kendal statistics were used and the data are expressed in percentage (%).
| Significance Level. | Mann–Kendal. Chl-a | Regional Mann–Kendal. Chl-a | Mann–Kendal. Attenuation Coefficient | Regional Mann–Kendal. Attenuation Coefficient | Mann–Kendal (Rrs_555nm) | Regional Mann–Kendal. (Rrs_555nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.00 | 7.50 | 11.80 | 11.80 | 57.90 | 59.70 | |
| 12.00 | 12.00 | 15.90 | 16.40 | 73.90 | 77.20 | |
| 22.00 | 24.40 | 23.90 | 26.00 | 87.30 | 88.30 | |
| insignificant | 88.00 | 75.40 | 76.10 | 74.00 | 12.70 | 11.70 |
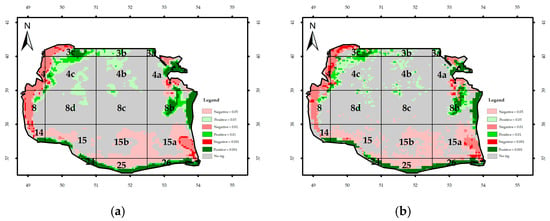
Figure A4.
Significance of the monthly trend of the attenuation coefficient: (a) regional Mann–Kendal and (b) Mann–Kendal.
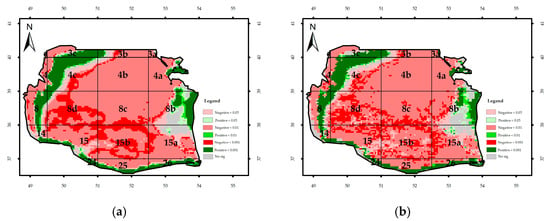
Figure A5.
Significance of monthly trend of Rrs_555nm: (a) Regional Mann–Kendal and (b) Mann–Kendal.
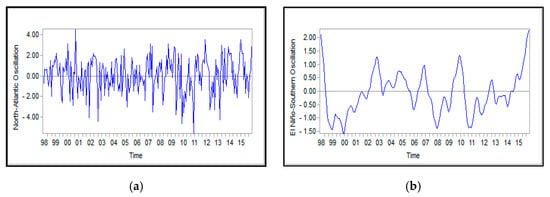
Figure A6.
Monthly mean values for the NAO index (a) and ENSO index (b) obtained from database Http://www.Esrl.Noaa.Gov/psd/data/correlation/oni. Data and Https://climatedataguide.Ucar.Edu/sites/default/files/nao_station_monthly.Txt during the years 1998–2015; (a) North-Atlantic Oscillation and (b) El Nino-southern oscillation.
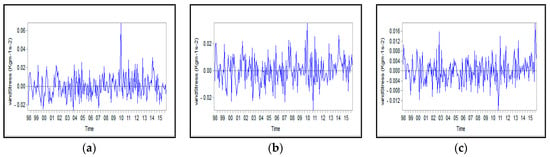
Figure A7.
Monthly anomalies of wind stress for: (a) Northern, (b) Middle, and (c) Southern Caspian Sea.
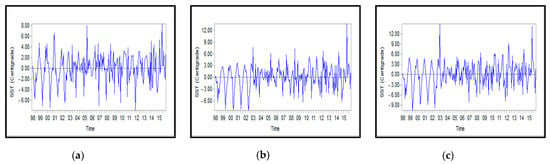
Figure A8.
Monthly anomalies of the surface temperature for: (a) Northern, (b) Middle, and (c) Southern Caspian Sea.
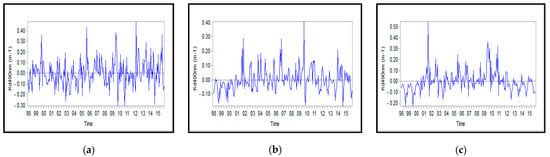
Figure A9.
Monthly anomalies of the attenuation coefficient for: (a) Northern, (b) Middle, and (c) Southern Caspian Sea.
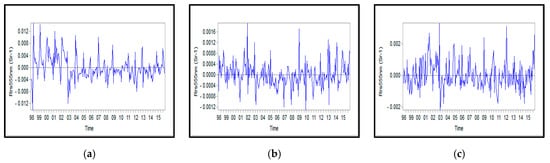
Figure A10.
Monthly anomalies of Rrs_555nm for: (a) Northern, (b) Middle, and (c) Southern Caspian Sea.
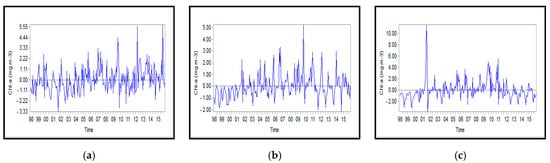
Figure A11.
Monthly anomalies of Chl-a concentration for: (a) Northern, (b) Middle, and (c) Southern Caspian Sea.
Appendix B
For seasonal analysis of the bio-optical parameters, the seasonal average was taken. Seasonal changes affected the bio-optical parameters in different parts of the SCS (Figure A12). The maximum and minimum levels of Chl-a were observed in summer and spring, respectively. The maximal level of Chl-a could stem from discharging nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrate from agricultural fields and other sources into coastal rivers, thereby leading to the eutrophication phenomenon [,]. A further reasoning for the obtained values could be attributed to other physicochemical characteristics such as SST and dissolved oxygen [].
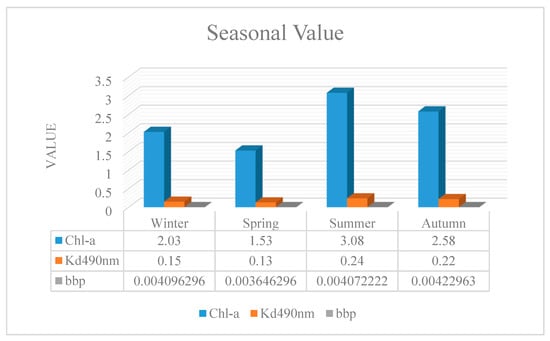
Figure A12.
Seasonal variability of bio-optical parameters in 1998–2015.
During the analyzed time series, the highest and lowest attenuation coefficient took place in summer and spring, respectively. In general, this index exhibited an order of summer > autumn > winter > spring. Furthermore, the seasonal maximum values were acquired in the winter of 2010, spring of 2001, summer of 2009, and autumn of 1999, whereas the lowest ones in the winter of 1998, spring of 1998, summer of 1999, and autumn of 2010.
Regarding Rrs_555nm, monthly variations revealed the maximum value in autumn but the minimum one in spring (Figure 8). The considerable amount of bbp in autumn could be explained by rainstorms and floods, which contribute to the increase in suspended matter.
Appendix C
MODIS and Sea-WiFS measurements:
Regarding Chl-a concentration in the study area from 2003 to 2007, the data derived from MODIS and SeaWiFS in three formats exhibited no significant difference with those obtained from the sensor (MODIS and SeaWiFS) about anomalies and the preprocessing step. Likewise, no difference was observed between MODIS and SeaWiFS sensors because of the low value of Z-score in the Chl-a measurements (Figure A13).
In terms of time, Pearson correlation coefficient displayed no difference between the outputs of MODIS and Sea-WiFS for the SCS regions (Figure A14).
The time series analysis of Chl-a concentration using the two sensors demonstrated correlation between two series (r = 0.65), in anomalies (r = 0.95), and after preprocessing (r = 0.93; Figure A14). The findings are in accordance with those reported by []. Given the high correlation coefficient, both sensors could be used together for these times series []. Therefore, the length of time series can be extended in order to enrich the data and also to have a better time coverage for precise identification of phenomena and trends in the southern part of the SCS [].
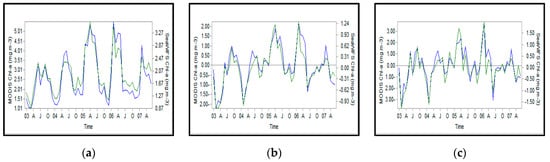
Figure A13.
Pearson correlation coefficient for the Chl-a index in the Southern Caspian Sea during 2003–2007: (a) satellite data (b) anomalies, and (c) data after the prewhitening process.
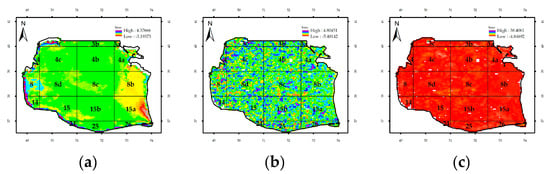
Figure A14.
Z-score statistics for the Chl-a concentration in the Southern Caspian Sea from 2003 to 2007: (a) satellite data, (b) anomalies, and (c) data after the prewhitening process.
References
- Mamedov, R.; Khoshravan, H. The Atlas of Caspian Sea Hydromorphology; Sophia Publishing Group: Richmond, BC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- The Caspian Sea Environment; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 5.
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; Mitchell, B.G.; Siegel, D.A.; Carder, K.L.; Garver, S.A.; Kahru, M.; McClain, C. Ocean color chlorophyll algorithms for SeaWiFS. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1998, 103, 24937–24953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezlin, N.P.; Li, B.-L. Time-series analysis of remote-sensed chlorophyll and environmental factors in the Santa Monica–San Pedro Basin off Southern California. J. Mar. Syst. 2003, 39, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavak, M.T. Long term investigation of SST regime variability and its relationship with phytoplankton in the Caspian Sea using remotely sensed AVHRR and SeaWiFS data. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 12, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopelevich, O.; Sheberstov, V.I.B.V. Application of SeaWiFS data for studying variability of bio-optical characteristics in the Barents, Black and Caspian Seas. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2004, 51, 1063–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezlin, N.P. Patterns of seasonal and interannual variability of remotely sensed chlorophyll. In The Caspian Sea Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 5, pp. 143–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kopelevich, O.; Burenkov, V.I.; Sheberstov, S.V. Case Studies of Optical Remote Sensing in the Barents Sea, Black Sea and Caspian Sea. Remote Sens. Eur. Seas 2008, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, C.; Shang, S.; Müller-Karger, F.E.; Li, Y.; Dai, M.; Huang, B.; Ning, X.; Hong, H. Bridging between SeaWiFS and MODIS for continuity of chlorophyll-a concentration assessments off Southeastern China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, K.M.; Rao, S.R. Seasonal and interannual variability of sea surface chlorophyll a concentration in the Arabian Sea. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 023501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahru, M.; Kudela, R.M.; Manzano-Sarabia, M.; Mitchell, B.G. Trends in the surface chlorophyll of the California Current: Merging data from multiple ocean color satellites. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2012, 77, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pan, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Wang, T. Are the trends in the surface chlorophyll opposite between the South China Sea and the Bay of Bengal? In Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions 2014; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, T.; Sun, L.; Yang, Y.; Fu, Y.-F. Monsoon and eddy forcing of chlorophyll-a variation in the northeast South China Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 7431–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, T.; Yang, Y.; Sun, L.; Fu, Y.-F. Spatiotemporal variability of satellite-derived colored dissolved and detrital organic materials in the South China Sea from 1997–2007. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2012, 15, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Ma, A.; Li, T.; Du, Z. Spatio-temporal stability and abnormality of chlorophyll-a in the Northern South China Sea during 2002–2012 from MODIS images using wavelet analysis. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 75, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ghedira, H. Monitoring red tide with satellite imagery and numerical models: A case study in the Arabian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Karger, F.E.; Smith, J.P.; Werner, S.; Chen, R.; A Roffer, M.; Liu, Y.; Muhling, B.; Lindo-Atichati, D.; Lamkin, J.T.; Cerdeira-Estrada, S.; et al. Natural variability of surface oceanographic conditions in the offshore Gulf of Mexico. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 134, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliarsingh, S.K.; Lotliker, A.A.; Sahu, K.C.; Kumar, T.S. Spatio-temporal distribution of chlorophyll-a in relation to physico-chemical parameters in coastal waters of the northwestern Bay of Bengal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colella, S.; Falcini, F.; Rinaldi, E.; Sammartino, M.; Santoleri, R. Mediterranean Ocean colour chlorophyll trends. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Franz, B. Chlorophyll aalgorithms for oligotrophic oceans: A novel approach based on three-band reflectance difference. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.R. TerrSet Help System. Accessed in TerrSet [18.10]; Clark University: Worcester, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Von Storch, H. Misuses of statistical analysis in climate research. In Analysis of Climate Variability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeti, N.; Eastman, J.R. A contextual mann-kendall approach for the assessment of trend significance in image time series. Trans. GIS 2011, 15, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Swail, V.R. Changes of extreme wave heights in northern hemisphere oceans and related atmospheric circulation regimes. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 2204–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.; Vogel, R.M.; Kroll, C.N. Trends in floods and low flows in the United States: Impact of spatial correlation. J. Hydrol. 2000, 240, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motiee, H.; McBean, E. An assessment of long-term trends in hydrologic components and implications for water levels in Lake Superior. Hydrol. Res. 2009, 40, 564–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nychka, D.; Buchberger, R.; Wigley, T.M.L.; Santer, B.D.; Taylor, K.E.; Jones, R. Confidence Intervals for Trend Estimates with Autocorrelated Observations; 2000; Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.33.6828&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- PSU. Available online: http://sites.stat.psu.edu/~ajw13/stat505/fa06/08_partcor/06_partcor_partial.html (accessed on 18 August 2013).
- Acker, J.G.; Harding, L.W.; Leptoukh, G.; Zhu, T.; Shen, S. Remotely-sensed chl a at the Chesapeake Bay mouth is correlated with annual freshwater flow to Chesapeake Bay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, N.; Ahmadi, M.R.; Babanezhad, M.; Seyfabadi, J. Environmental variables and their interaction effects on chlorophyll-a in coastal waters of the southern Caspian Sea: Assessment by multiple regression grey models. Aquat. Ecol. 2014, 48, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, S.N. Global and Regional Climate Interaction: The Caspian Sea Experience; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanghermeh, A.; Roshan, G.; Al-Yahyai, S. The influence of Atlantic-Eurasian teleconnection patterns on temperature regimes in South Caspian Sea coastal areas: a study of Golestan Province, North Iran. Pollution 2015, 1, 67–83. [Google Scholar]
- Byshev, V.I.; Neiman, V.G.; Romanov, Y.A. On the essential differences between the large-scale variations of the surface temperature over the oceans and continents. Oceanology 2006, 46, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, E. Low-frequency variability of atmospheric circulation and the Caspian Sea level in the second half of the 20th century. Meteorol. Gidrol. 2001, 11, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Stanev, E.; Peneva, E.L. Regional sea level response to global climatic change: Black Sea examples. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2001, 32, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostianoy, A.G.; Ginzburg, A.I.; Lavrova, O.Y.; Lebedev, S.A.; Mityagina, M.I.; Sheremet, N.A.; Soloviev, D.M. Comprehensive Satellite Monitoring of Caspian Sea Conditions; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 505–521. [Google Scholar]
- Cianca, A.; Rueda, M.J.; Neuer, S.; Marrero, F.J.P.; Godoy, J.M.; Martin, J.M.; Llinas, O. Interannual variability of chlorophyll and the influence of low-frequency climate modes in the North Atlantic subtropical gyre. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2012, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Harding, L.W., Jr.; Feldman, G.C.; McClain, C.R. Regional and seasonal variability of chlorophyll-a in Chesapeake Bay as observed by SeaWiFS and MODIS-Aqua. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kideys, A.; Moghim, M. Distribution of the alien ctenophore Mnemiopsisleidyi in the Caspian Sea in August 2001. Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosarev, A.N.; Tuzhilkin, V.S.; Kostianoy, A.G. Main features of the Caspian Sea hydrology. In Dying and Dead Seas Climatic Versus Anthropic Causes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 159–184. [Google Scholar]
- Sur, H.I.; Özsoy, E.; Ibrayev, R. Satellite-derived flow characteristics of the Caspian Sea. In Elsevier Oceanography Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nassar, M.Z.A.; El-Din, N.G.S.; Gharib, S.M. Phytoplankton variability in relation to some environmental factors in the eastern coast of Suez Gulf, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhurst, A. Seasonal cycles of pelagic production and consumption. Prog. Oceanogr. 1995, 36, 77–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).