Automated Mosaicking of Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
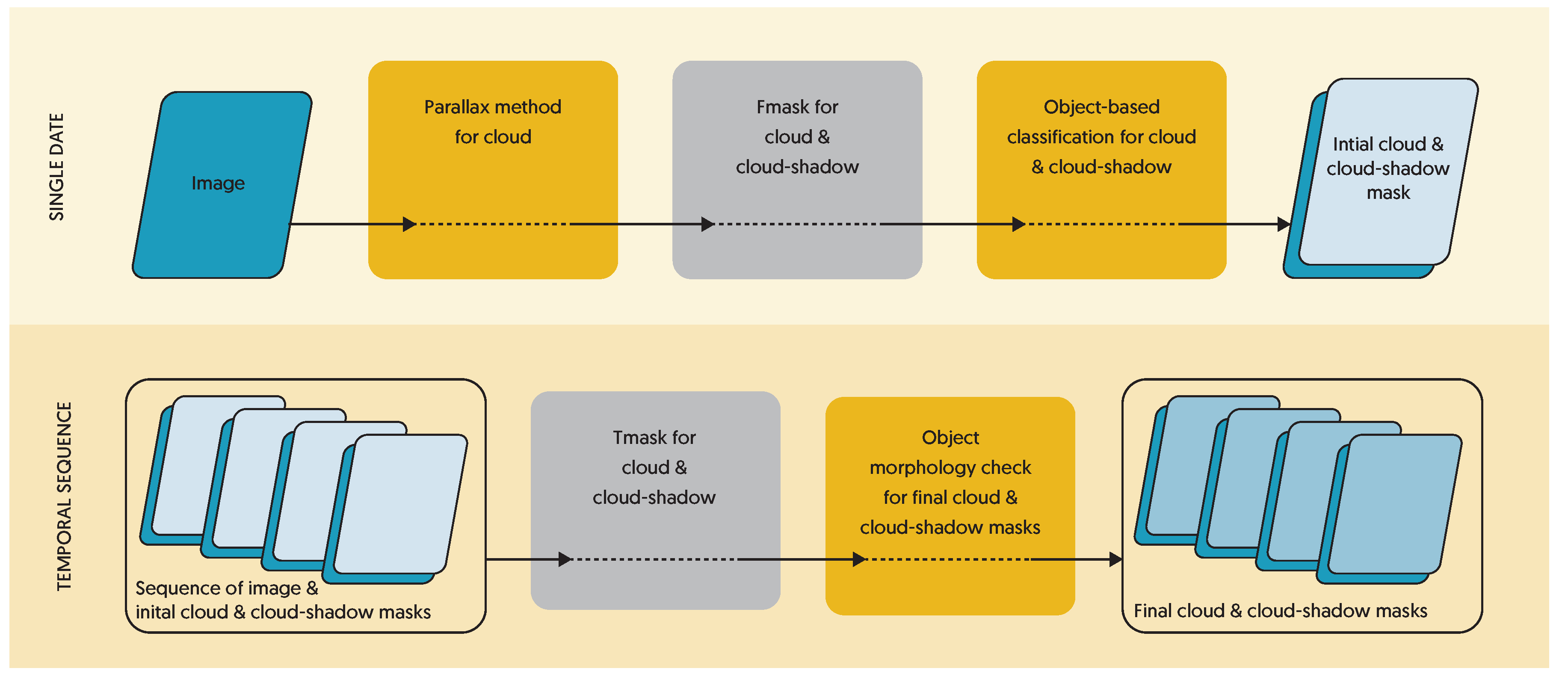
2. Methods
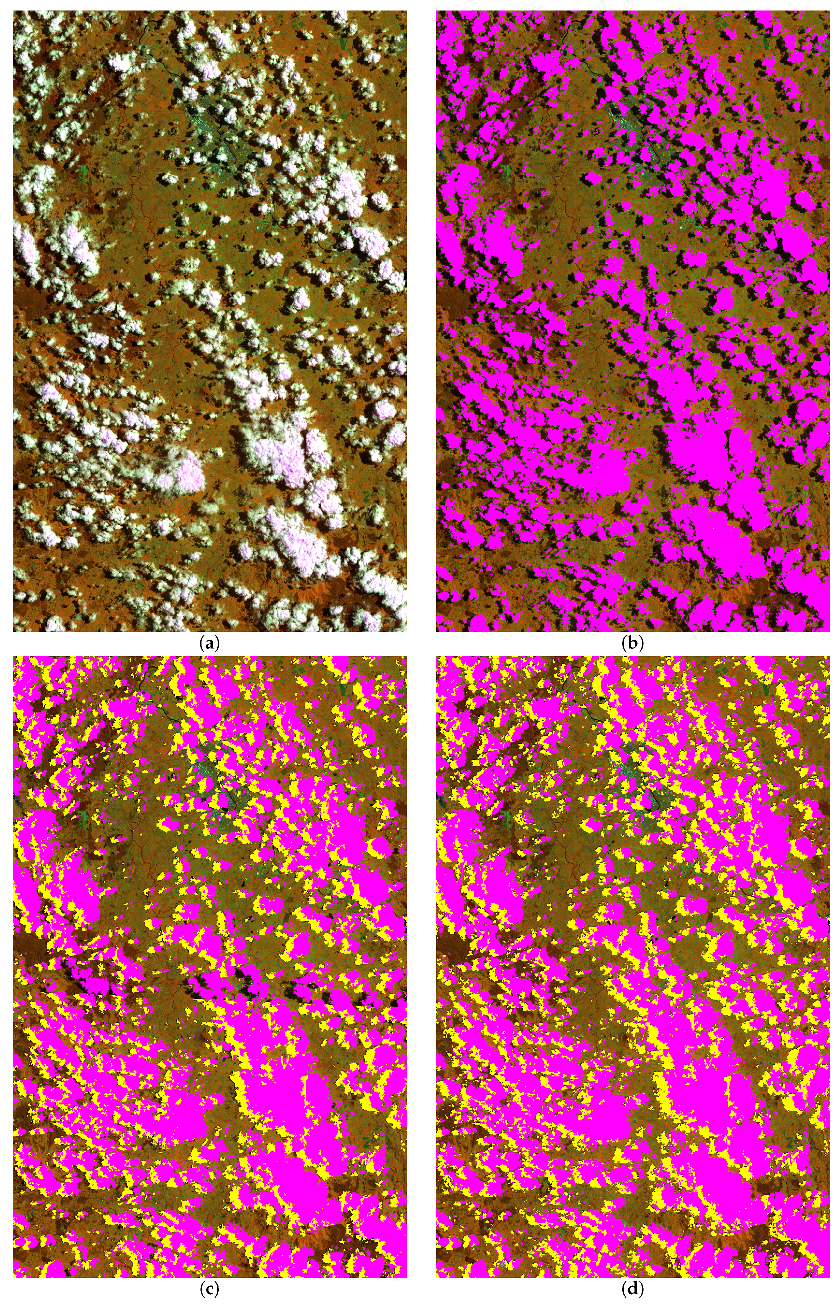
2.1. Parallax-Based Cloud Identification
2.2. Tmask Implementation
- d is the julian date,
- T is the number of days per year (365),
- N is the number of years (integer, rounded up),
- is the mean value for Sentinel band i TOA reflectance,
- are coefficients that describe the intra-annual change of Sentinel band i TOA reflectance,
- are coefficients that describe the inter-annual change of Sentinel band i TOA reflectance.
2.3. Object-Based Morphology Checking
2.4. Priority-Based Mosaicking
2.4.1. Best Mosaic over a Date Range (Prioritise for Quality)
2.4.2. Closest Mosaic to a Given Date (Prioritise for Date)
2.5. Mosaic Types
2.5.1. Manual Interpretation
2.5.2. Automatic Classification
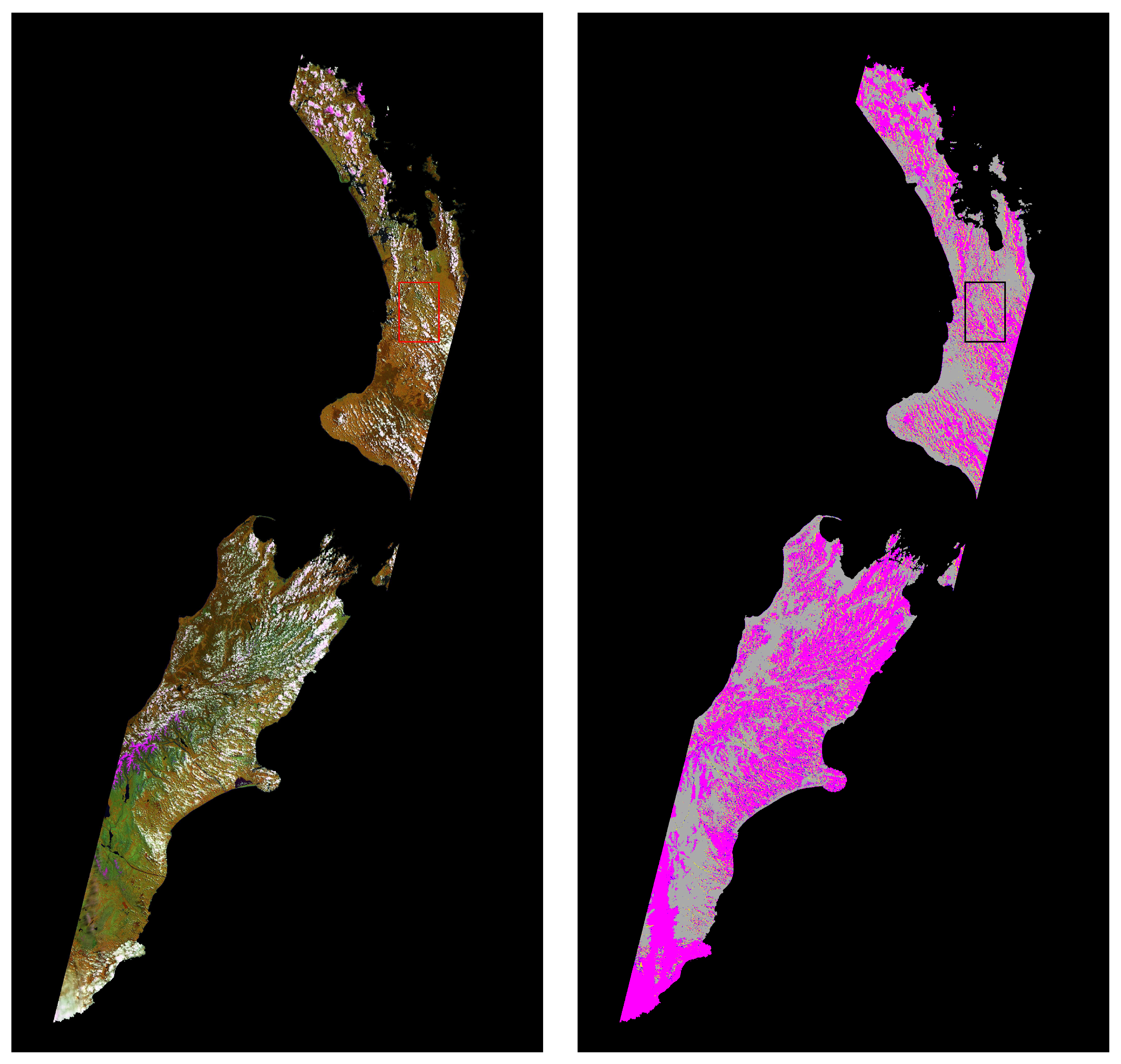
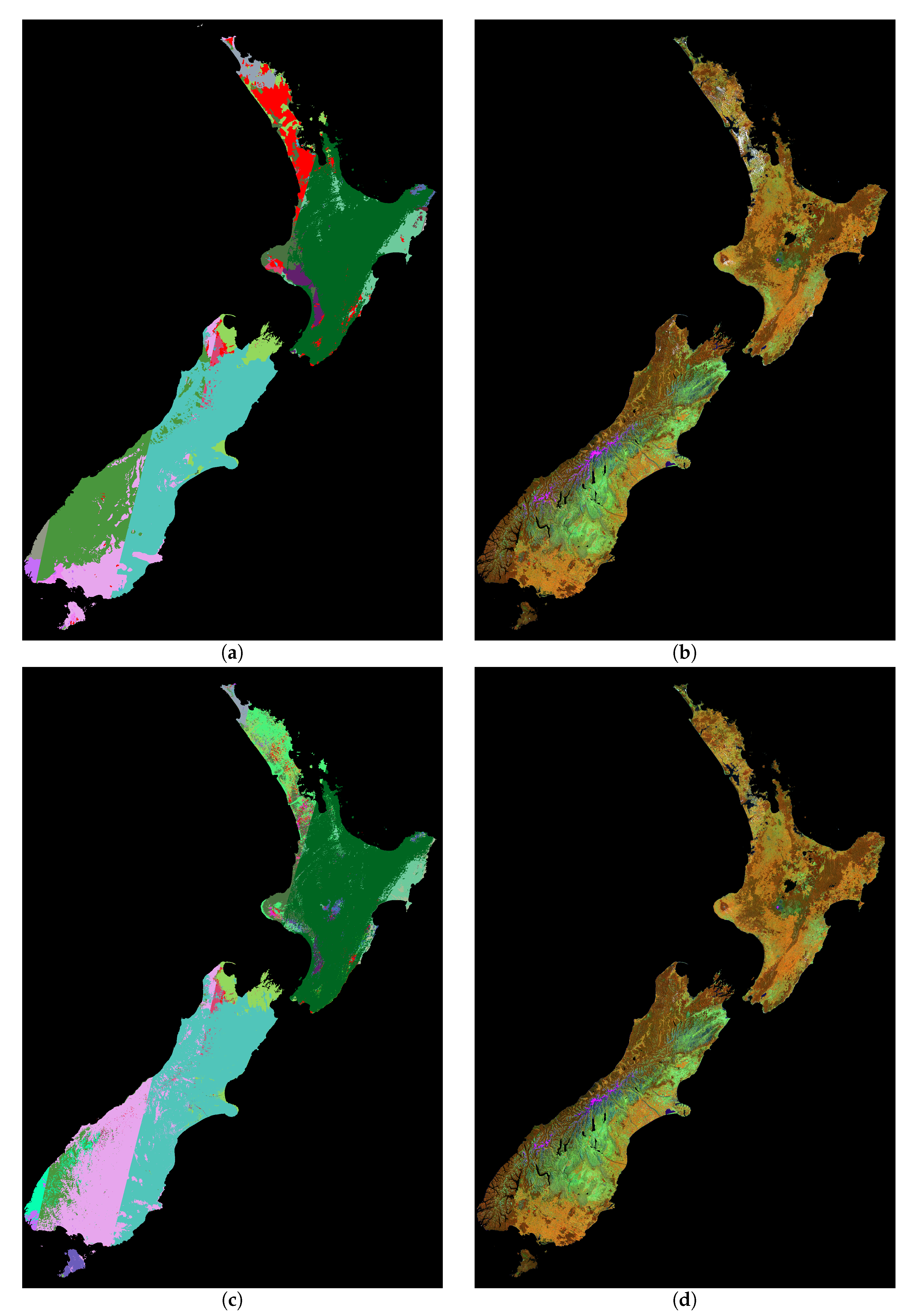
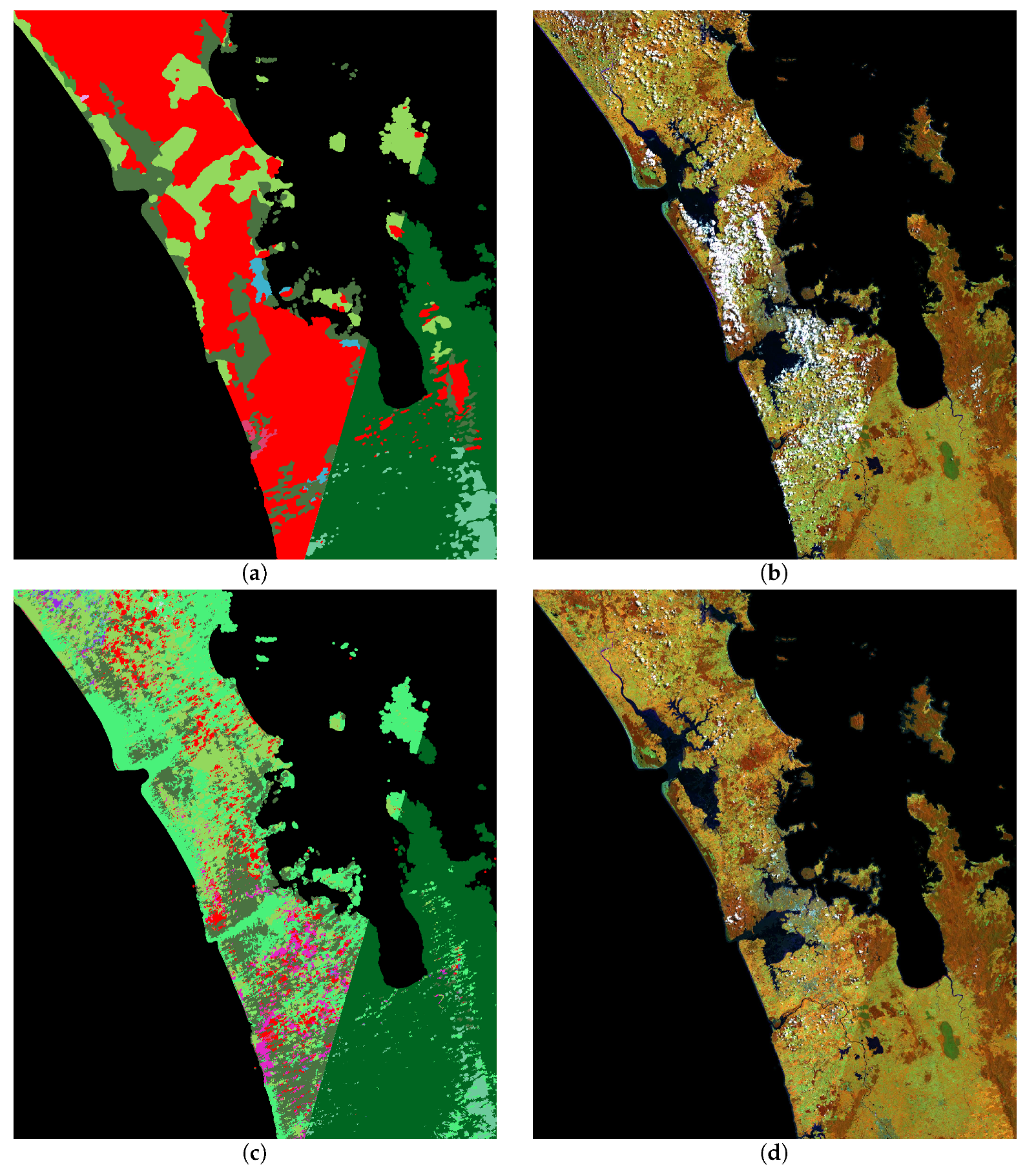
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wulder, M.; White, J.; Loveland, T.; Woodcock, C.; Belward, A.; Cohen, W.; Fosnight, E.; Shaw, J.; Masek, J.; Roy, D. The global Landsat archive: Status, consolidation, and direction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Ju, J.; Kline, K.; Scaramuzza, P.; Kovalskyy, V.; Hansen, M.; Loveland, T.; Vermote, E.; Zhang, C. Web-enabled Landsat data (WELD): Landsat ETM+ composited mosaics of the conterminous United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Nendel, C.; Hoster, P. Intra-annual reflectance composites from Sentinel-2 and Landsat for national-scale crop and land cover mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Loveland, T. A review of large area monitoring of land cover change using Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, J.; Puig, H.; Palacio, J.; Sosa-Lopez, A. Modelling deforestation using GIS and artificial neural networks. Environ. Model. Softw. 2004, 19, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Guo, X. Remote sensing of ecosystem health: Opportunities, challenges, and future perspectives. Sensors 2014, 14, 21117–21139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montzka, C.; Canty, M.; Kreins, P.; Kunkel, R.; Menz, G.; Vereecken, H.; Wendland, F. Multispectral remotely sensed data in modelling the annual variability of nitrate concentration in the leachate. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascon, F.; Bouzinac, C.; Thépaut, O.; Jung, M.; Francesconi, B.; Louis, J.; Lonjou, V.; Lafrance, B.; Massera, S.; Gaudel-Vacaresse, A.; et al. Copernicus Sentinel-2A calibration and products validation status. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; van der Linden, S.; Kuemmerle, T.; Hostert, P. A Pixel-Based Landsat Compositing Algorithm for Large Area Land Cover Mapping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 2088–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z. Change detection using landsat time series: A review of frequencies, preprocessing, algorithms, and applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.; Gao, X.; Ferriera, L. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, P.; Turbanova, S.; Hansen, M.; Adusei, B.; Broich, M.; Altstatt, A.; Mane, L.; Justice, C. Quantifying forest cover loss in Democratic Republic of the Congo, 2000–2010, with Landsat ETM+ data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Wulder, M.; Hobart, G.; Luther, J.; Hermosilla, T.; Griffiths, P.; Coops, N.; Hall, R.; Hostert, P.; Dyk, A.; et al. Pixel-based image compositing for large-area dense time series applications and science. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 40, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagolle, O.; Morin, D.; Kadiri, M. Detailed Processing Model for the Weighted Average Synthesis Processor (WASP) for Sentinel-2. Zenodo 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancutsen, C.; Pekel, J.; Bogaert, P.; Defourny, P. Mean compositing, an alternative strategy for producing temporal syntheses. Concepts and performance assessment for SPOT VEGETATION time series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 5123–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.; Holden, C.; Yang, Z. Generating synthetic Landsat images based on all available Landsat data: Predicting Landsat surface reflectance at any given time. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuolo, F.; Ng, W.T.; Atzberger, C. Smoothing and gap-filling of high resolution multi-spectral time series: Example of Landsat data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 57, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymond, J.R.; Shepherd, J.D.; Newsome, P.F.; Gapare, N.; Burgess, D.W.; Watt, P. Remote sensing of land-use change for Kyoto Protocol reporting: The New Zealand case. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, D.; Haß, E.; Uhl, A.; Stoffels, J.; Hill, J. Improvement of the Fmask algorithm for Sentinel-2 images: Separating clouds from bright surfaces based on parallax effects. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, D. FORCE—Landsat + Sentinel-2 Analysis Ready Data and Beyond. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Python Fmask. Available online: http://www.pythonfmask.org (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.D.; Bunting, P.; Dymond, J.R. Operational Large-Scale Segmentation of Imagery Based on Iterative Elimination. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 658–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Zealand Land Cover Database (LCDB). Available online: https://lris.scinfo.org.nz/layer/104400-lcdb-v50-land-cover-database-version-50-mainland-new-zealand (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- New Zealand Land Cover Database Version 2—Illustrated Guide to Target Classes. Available online: https://lris.scinfo.org.nz/document/22464-lcdb-v2-classes-illustratedpdf (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Automated cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection in multitemporal Landsat data: An algorithm designed specifically for monitoring land cover change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MultiSpectral Instrument (MSI) Overview. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/web/sentinel/technical-guides/sentinel-2-msi/msi-instrument (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Galassi, M.; Davies, J.; Theiler, J.; Gough, B.; Jungman, G.; Alken, P.; Booth, M.; Rossi, F.; Ulerich, R. GNU Scientific Library. Available online: https://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/doc/latex/gsl-ref.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Dymond, J.R.; Shepherd, J.D. The spatial distribution of indigenous forest and its composition in the Wellington region, New Zealand, from ETM+ satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.D.; Dymond, J.R. Correcting satellite imagery for the variance of reflectance and illumination with topography. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 3503–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.J.; Allen, R.B.; Whitehead, D.; Carswell, F.E.; Ruscoe, W.A.; Platt, K.H. Climate and Net Carbon Availability Determine Temporal Patterns of Seed Production by Nothofagus. Ecology 2005, 86, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schauber, E.M.; Kelly, D.; Turchin, P.; Simon, C.; Lee, W.G.; Allen, R.B.; Payton, I.J.; Wilson, P.R.; Cowan, P.E.; Brockie, R.E. Masting by Eighteen New Zealand Plant Species: The Role of Temperature as a Synchronizing Cue. Ecology 2002, 83, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müllerová, J.; Brůna, J.; Bartaloš, T.; Dvořák, P.; Vítková, M.; Pyšek, P. Timing Is Important: Unmanned Aircraft vs. Satellite Imagery in Plant Invasion Monitoring. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, B.A. Remote detection of invasive plants: A review of spectral, textural and phenological approaches. Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 1411–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.; Lee, W. Satellite mapping of gorse at regional scales. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2002, 55, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.; Dymond, J.; Cuff, J. Monitoring scrub weed change in the Canterbury region using satellite imagery. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2007, 60, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Zealand Land Use Map (LUM). Available online: https://www.mfe.govt.nz/more/data/available-datasets/land-use-map (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS). Available online: https://www.mfe.govt.nz/ets (accessed on 8 September 2020).

| Automatic Cloud Classification | Manual Cloud Clearing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer Mosaic | Remaining Cloud | Contributing Overpasses | Remaining Cloud | Contributing Overpasses | Available Overpasses |
| 2015/16 | % | 49 | % | 19 | 53 |
| 2016/17 | % | 64 | % | 15 | 119 |
| 2017/18 | % | 84 | - | - | 251 |
| 2018/19 | % | 90 | - | - | 253 |
| 2019/20 | % | 103 | - | - | 253 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shepherd, J.D.; Schindler, J.; Dymond, J.R. Automated Mosaicking of Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3680. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223680
Shepherd JD, Schindler J, Dymond JR. Automated Mosaicking of Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(22):3680. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223680
Chicago/Turabian StyleShepherd, James D., Jan Schindler, and John R. Dymond. 2020. "Automated Mosaicking of Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery" Remote Sensing 12, no. 22: 3680. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223680
APA StyleShepherd, J. D., Schindler, J., & Dymond, J. R. (2020). Automated Mosaicking of Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing, 12(22), 3680. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223680






