Testing Side-Scan Sonar and Multibeam Echosounder to Study Black Coral Gardens: A Case Study from Macaronesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
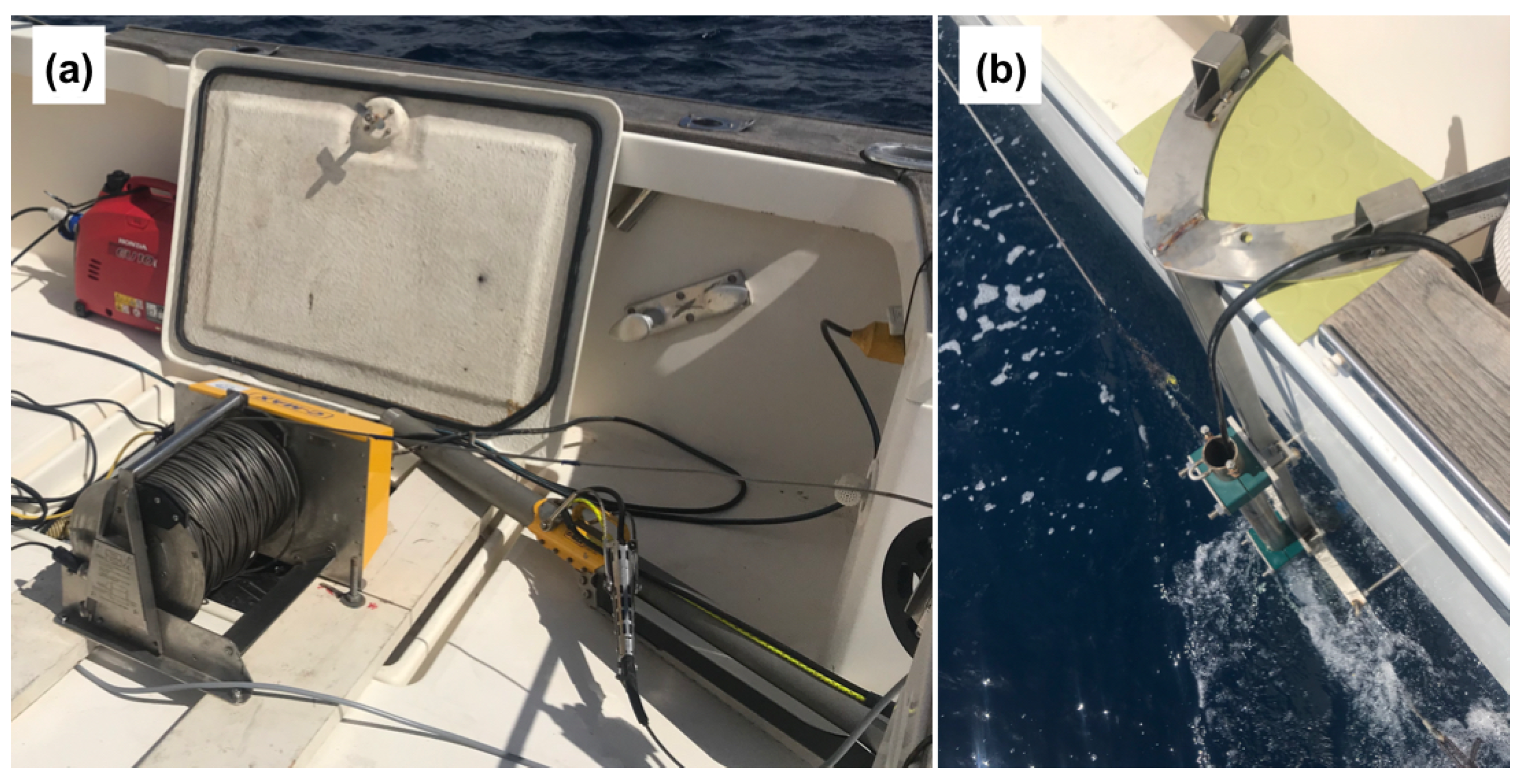
2.2. Hydroacoustic Data Acquisition
2.3. Acoustic Data Analysis
2.4. Ground-Truth Sampling and Analysis
3. Results
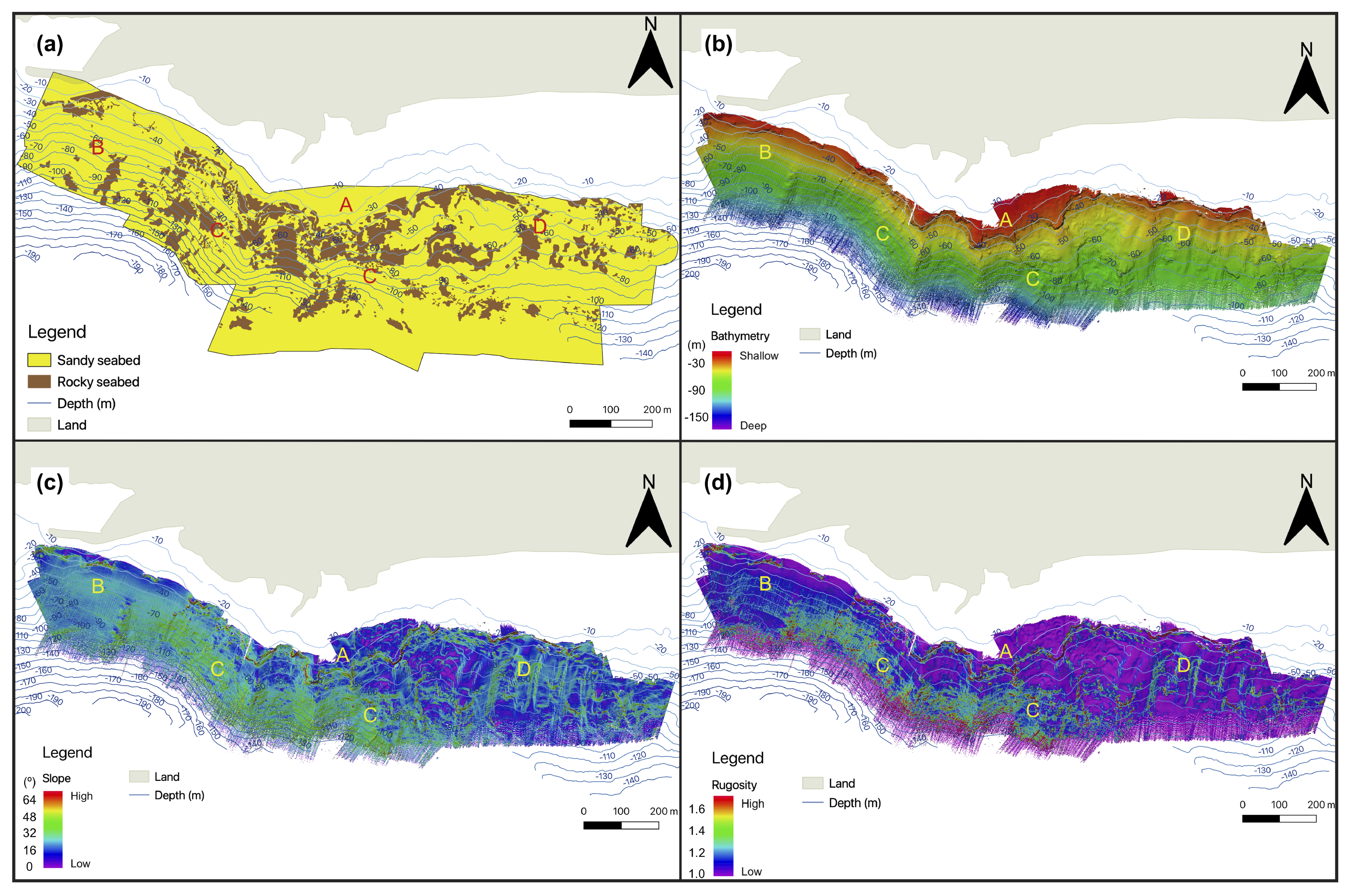
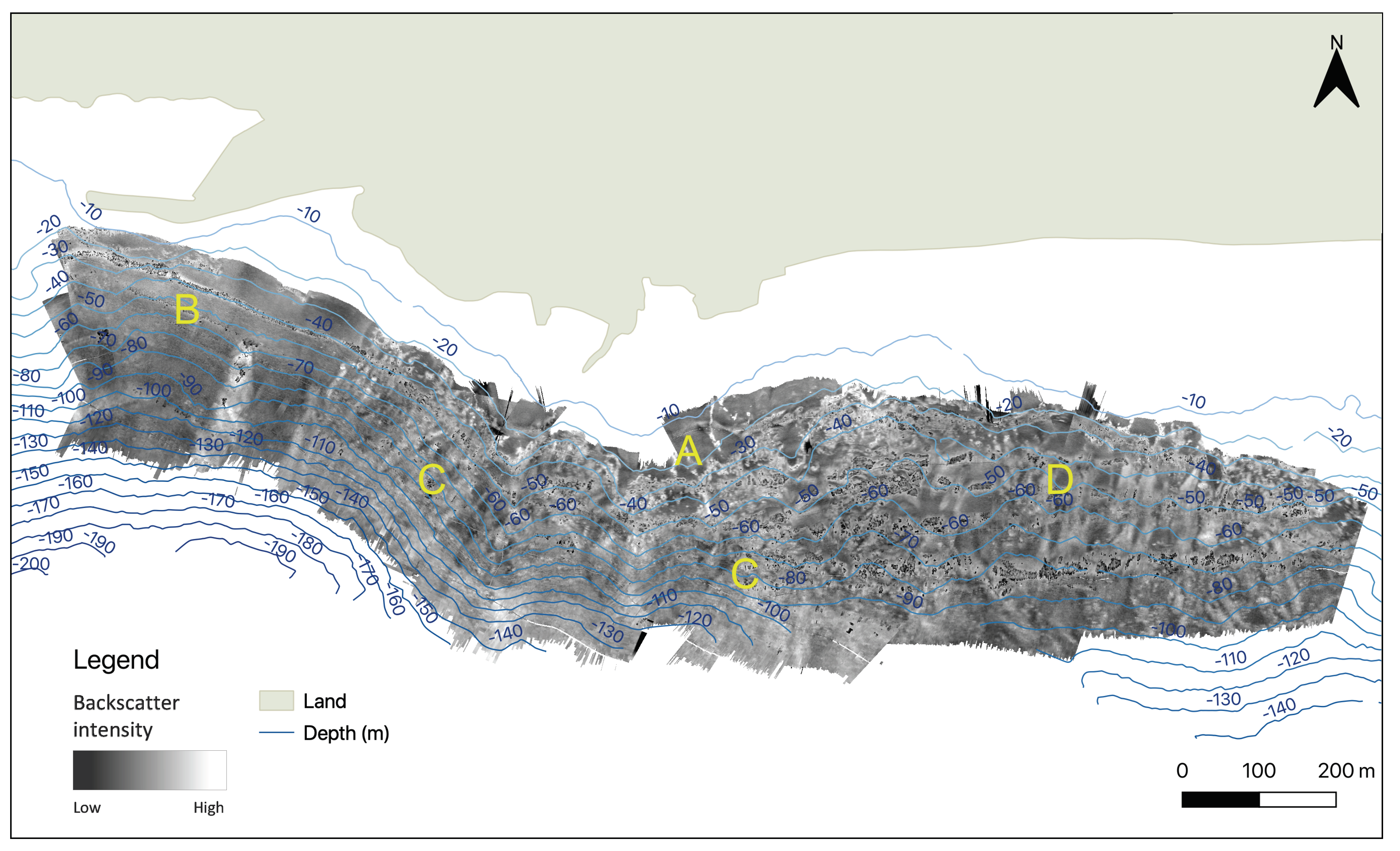
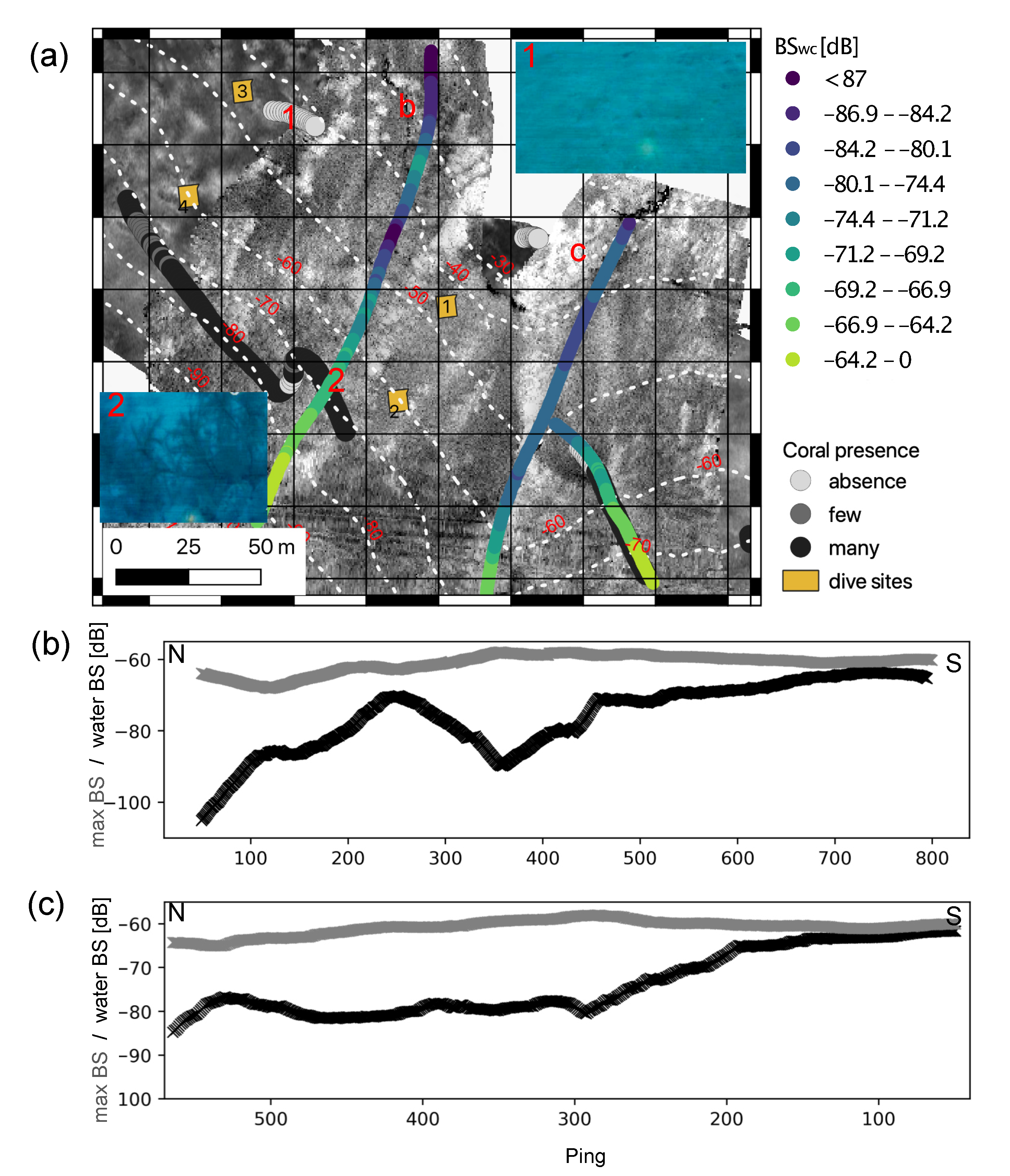
3.1. Seafloor Characteristics
3.1.1. Bathymetry and Derivative Parameters
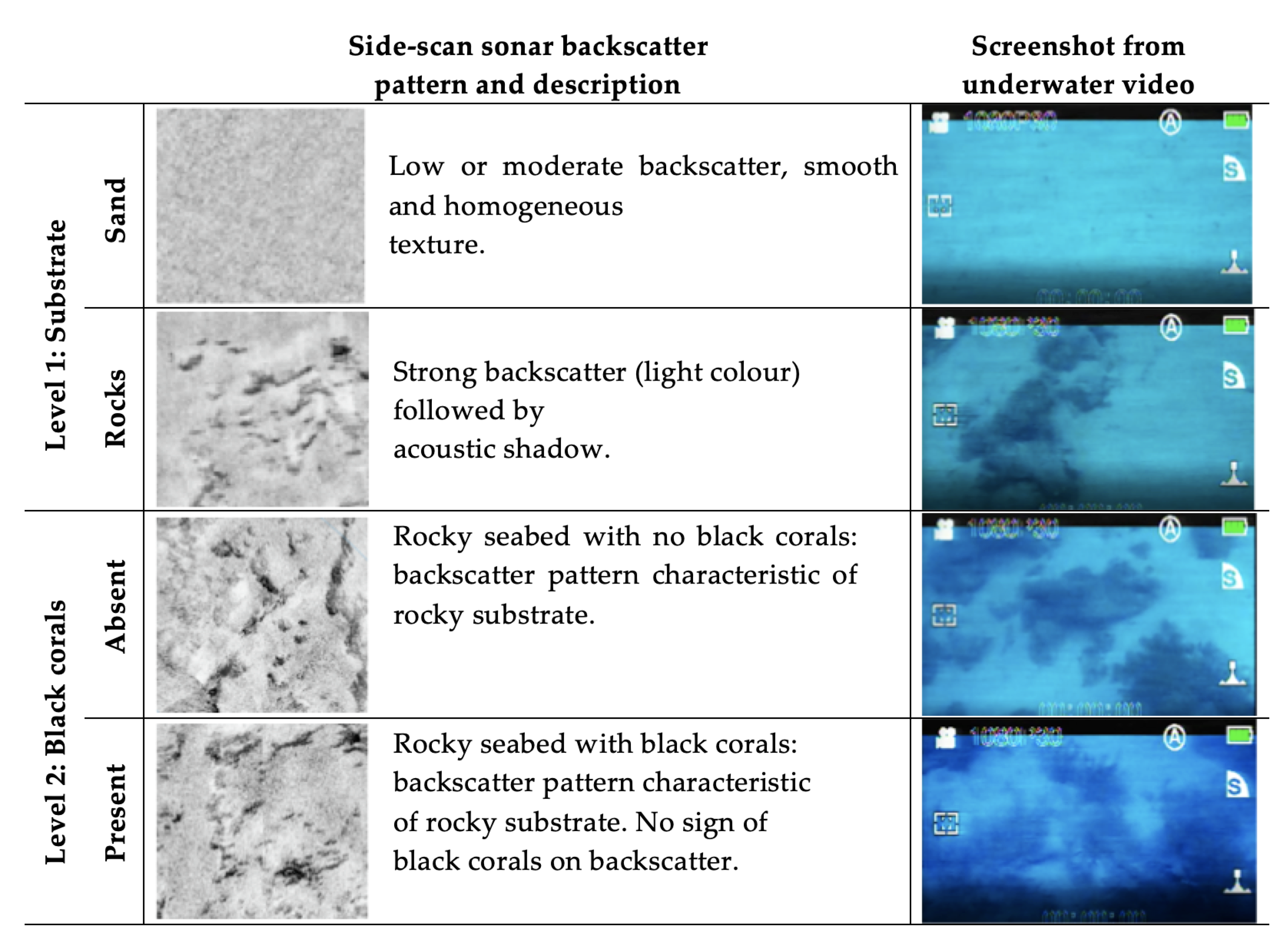
3.1.2. Backscatter
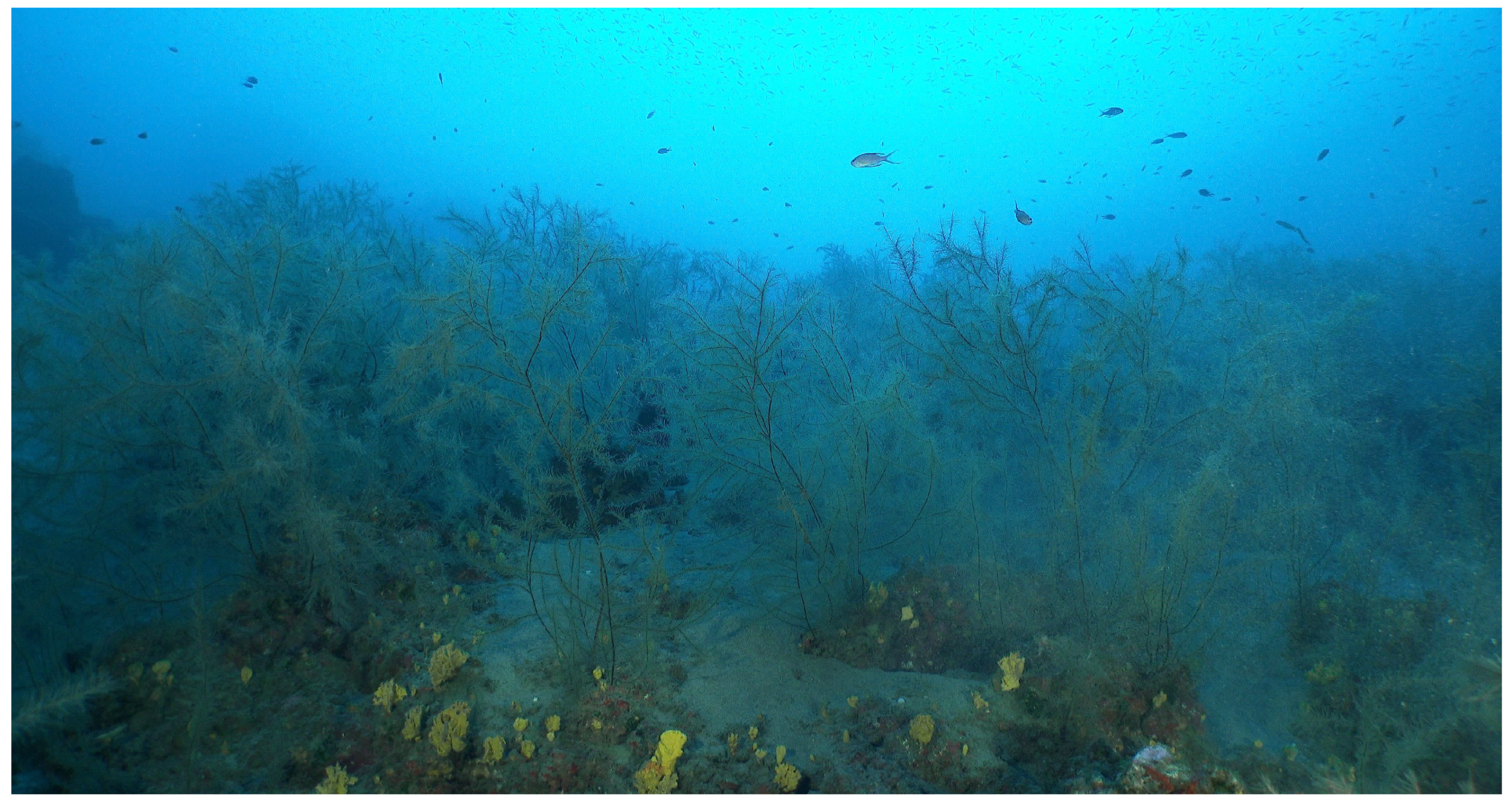
3.2. Underwater Video and Diving
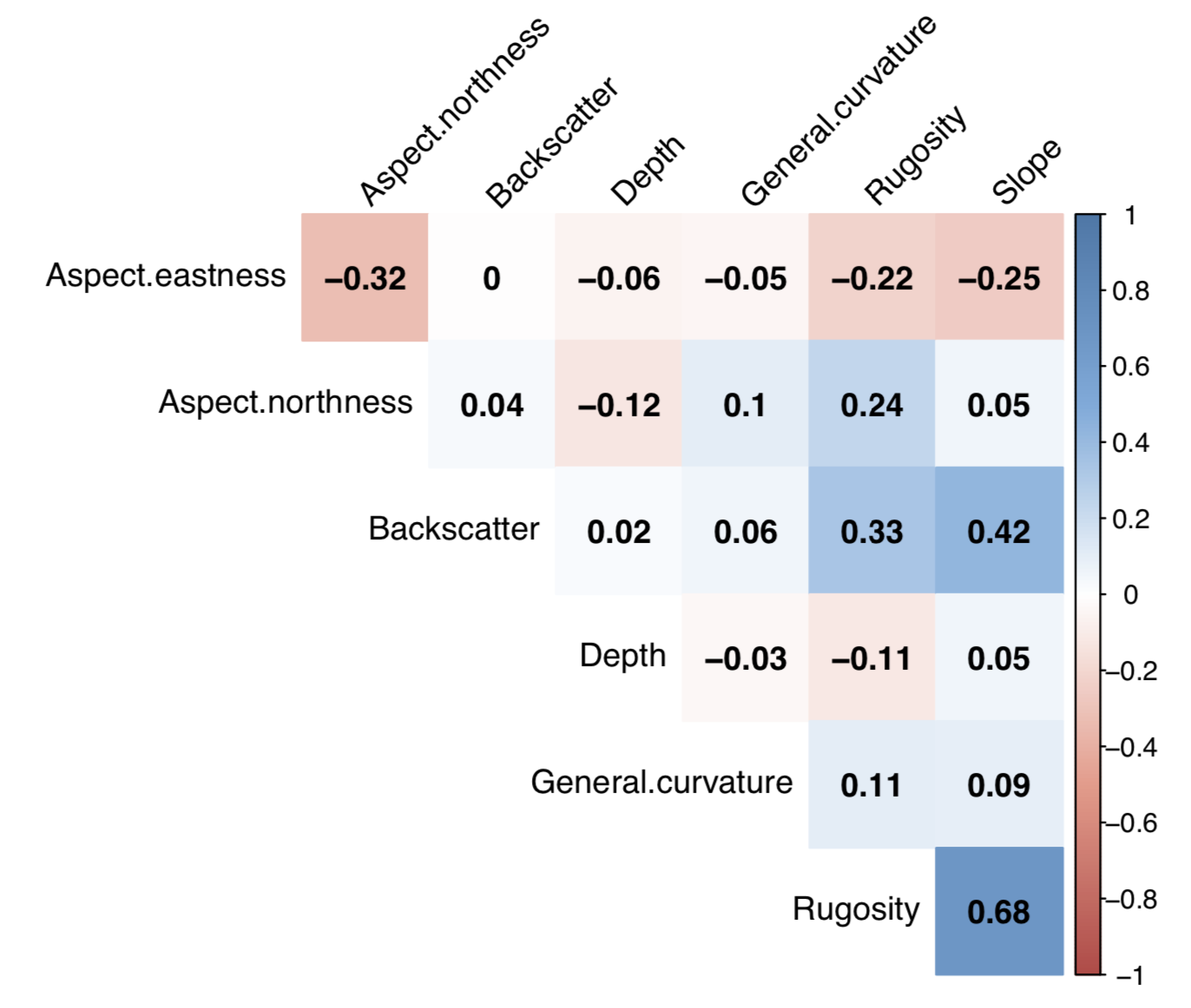
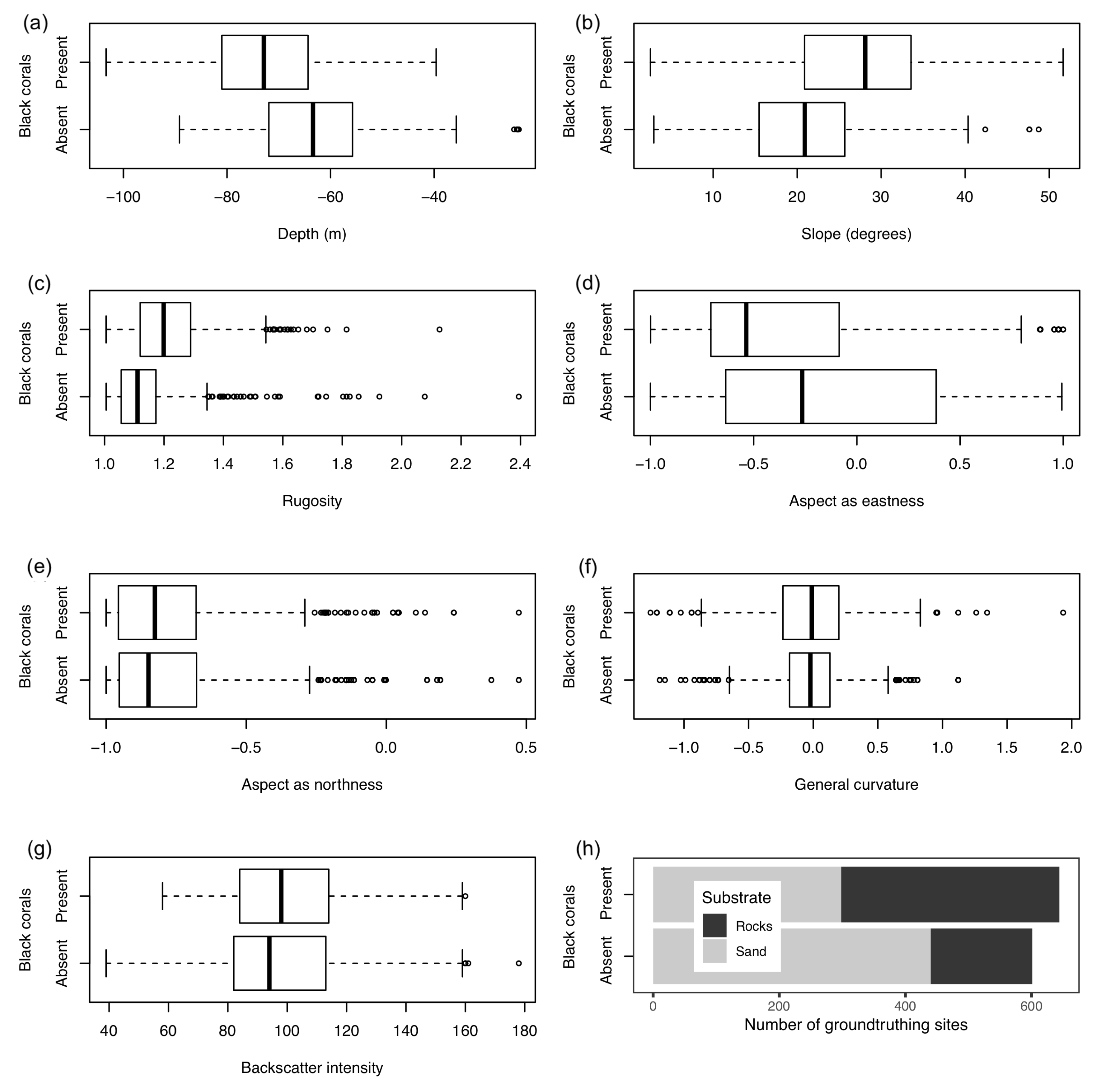
3.3. Statistical Analysis
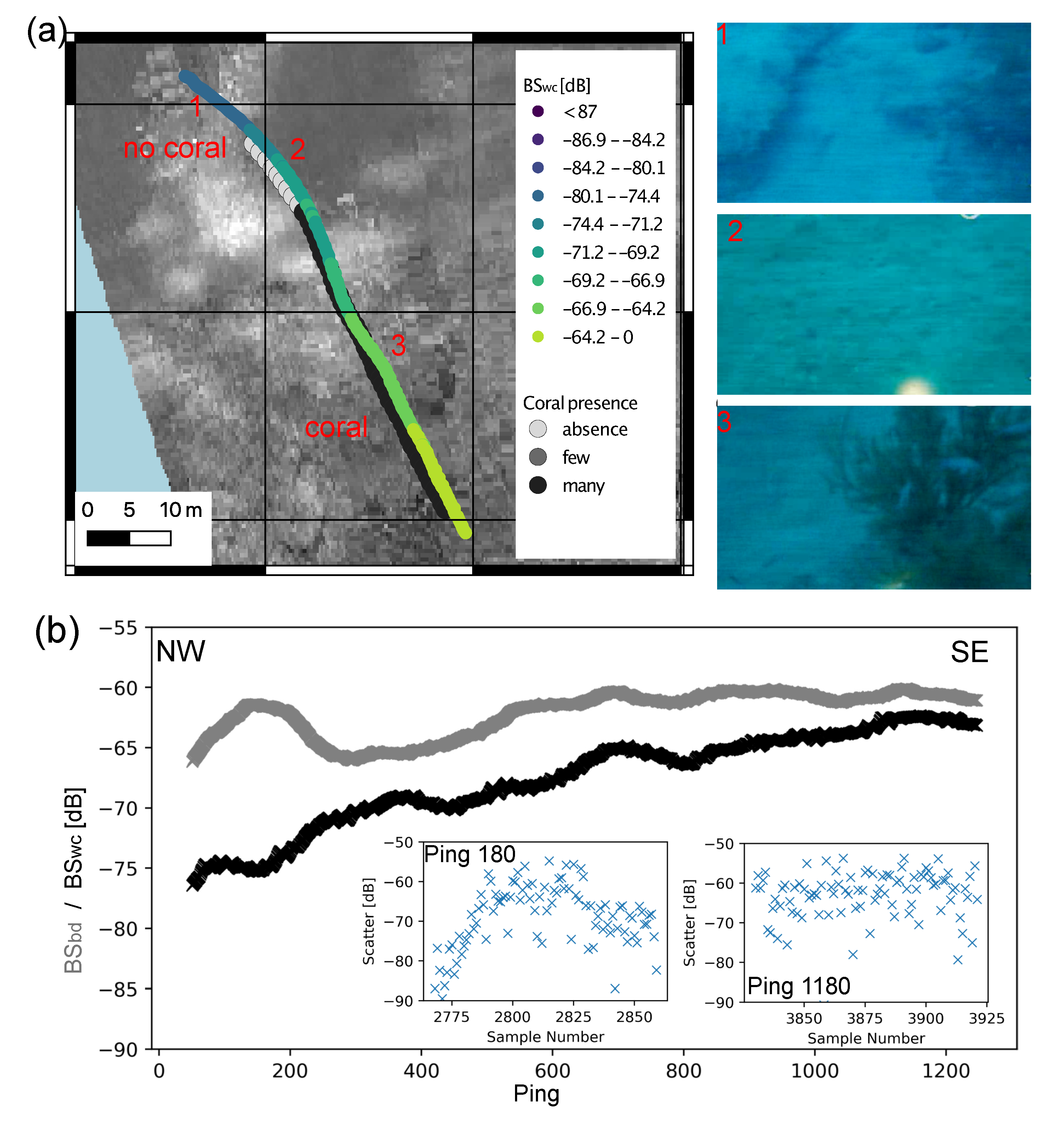
3.4. Water Column Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Detection of Black Corals in Acoustic Data
4.2. Implications for Black Coral Habitats Offshore Lanzarote
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Factor | z-Value | p-Value | Reduction in Deviance |
|---|---|---|---|
| full dataset: all depths (25 m–100 m) | |||
| Depth | −12.570 | <2 × 10−16 | 202.40 |
| Slope | 11.350 | <2 × 10−16 | 149.60 |
| Rugosity | 8.130 | 4.3 × 10−16 | 80.50 |
| Aspect eastness | −7.432 | 1.07 × 10−13 | 58.30 |
| Aspect northness | 1.122 | 0.262 | 1.30 |
| General curvature | 1.207 | 0.228 | 1.50 |
| Backscatter | 1.310 | 0.190 | 1.80 |
| Substrate: sand | −8.231 | <2 × 10−16 | 98.00 |
| Data subset: 45 m–70 m depth | |||
| Depth | −5.005 | 5.58 × 10−7 | 26.71 |
| Slope | 7.312 | 2.64 × 10−13 | 62.27 |
| Rugosity | 3.632 | 2.81 × 10−4 | 14.44 |
| Aspect eastness | −5.898 | 3.68 × 10−9 | 37.46 |
| Aspect northness | 1.539 | 0.124 | 2.38 |
| General curvature | 1.747 | 0.081 | 3.08 |
| Backscatter | −0.365 | 0.715 | 0.13 |
| Substrate: sand | −2.486 | 0.013 | 14.41 |
References
- EC. Directive of the European Parliament and the Council Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Marine Environmental Policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive); Directive 2008/56/ EC, OJ L 164; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- EEC. Habitats Directive 92/43/EEC; OJ L 206; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- UN. Convention on Biological Diversity; art. 1, 31 I.L.M. 818; United Nations: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Buhl-Mortensen, L.; Buhl-Mortensen, P.; Dolan, M.; Gonzalez-Mirelis, G. Habitat mapping as a tool for conservation and sustainable use of marine resources: Some perspectives from the MAREANO Programme, Norway. J. Sea Res. 2015, 100, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.; Baker, E. (Eds.) Seafloor Geomorphology As Benthic Habitat. GeoHab Atlas of Seafloor Geomorphic Features and Benthic Habitats; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; p. 1030. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, A.; Lawler, M.; Halley, V.; Barrett, N. Seabed habitat mapping in the Kent Group of islands and its role in marine protected area planning. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2005, 15, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumby, P.; Green, E.; Edwards, A.; Clark, C. The cost-effectiveness of remote sensing for tropical coastal resources assessment and management. J. Environ. Manag. 1999, 55, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, M.; Katsanevakis, S.; Koukourouvli, N.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Dailianis, T.; Buhl-Mortensen, L.; Damalas, D.; Dendrinos, P.; Dimas, X.; Frantzis, A. Assembling ecological pieces to reconstruct the conservation puzzle of the Aegean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J.; Smith, S.J.; Lawton, P.; Anderson, J.T. Benthic habitat mapping: A review of progress towards improved understanding of the spatial ecology of the seafloor using acoustic techniques. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collings, S.; Campbell, N.A.; Keesing, J.K. Quantifying the discriminatory power of remote sensing technologies for benthic habitat mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2717–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavazzi, G.M.; Madricardo, F.; Janowski, L.; Kruss, A.; Blondel, P.; Sigovini, M.; Foglini, F. Evaluation of seabed mapping methods for fine-scale classification of extremely shallow benthic habitats–application to the Venice Lagoon, Italy. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 170, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Battista, T.; Pittman, S. Comparative evaluation of airborne LiDAR and ship-based multibeam SoNAR bathymetry and intensity for mapping coral reef ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1082–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, T.; Igararashi, C.; Tatsukawa, K.I.; Nakaoka, M.; Hiraishi, T.; Taira, A. Mapping of seagrass and seaweed beds using hydro-acoustic methods. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cosme, M.; Otero-Ferrer, F.; Tuya, F.; Espino, F.; Abreu, A.D.; Haroun, R. Mapping Subtropical and Tropical Rhodolith Seabeds Using Side Scan Sonar Technology. In Proceedings of the 6th International Rhodolith Workshop, Roscoff, France, 25–29 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Freiwald, A. Reef-forming cold-water corals. In Ocean Margin Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.; Brown, C.; Long, D.; Bates, C. Acoustic mapping using a multibeam echosounder reveals cold-water coral reefs and surrounding habitats. Coral Reefs 2005, 24, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glogowski, S.; Dullo, W.C.; Feldens, P.; Liebetrau, V.; von Reumont, J.; Hühnerbach, V.; Krastel, S.; Wynn, R.B.; Flögel, S. The Eugen Seibold coral mounds offshore western Morocco: Oceanographic and bathymetric boundary conditions of a newly discovered cold-water coral province. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2015, 35, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, A. An overview of seabed-mapping technologies in the context of marine habitat classification. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 60, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, P. The Handbook of Sidescan Sonar; Springer: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA; Praxis Pub: Chichester, UK, 2009; p. 316. [Google Scholar]
- Cobra, D.; Oppenheim, A.; Jaffe, J. Geometric distortions in side-scan sonar images: A procedure for their estimation and correction. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1992, 17, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervenka, P.; Moustier, C.D.; Lonsdale, P.F. Geometric corrections on sidescan sonar images based on bathymetry. Application with SeaMARC II and Sea Beam data. Mar. Geophys. Res. 1994, 16, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H. Obtaining High-Resolution Seabed Topography and Surface Details by Co-Registration of Side-Scan Sonar and Multibeam Echo Sounder Images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakiris, E.; Blondel, P.; Papatheodorou, G.; Christodoulou, D.; Dimas, X.; Georgiou, N.; Kordella, S.; Dimitriadis, C.; Rzhanov, Y.; Geraga, M.; et al. Multi-Frequency, Multi-Sonar Mapping of Shallow Habitats—Efficacy and Management Implications in the National Marine Park of Zakynthos, Greece. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Luck, D.; Toonen, R. The biology and ecology of black corals (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Hexacorallia: Antipatharia). Adv. Mar. Biol. 2012, 63, 67–132. [Google Scholar]
- Appeltans, W.; Ahyong, S.; Anderson, G.; Angel, M.; Artois, T.T. The Magnitude of Global Marine Species Diversity. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2189–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.; Wheeler, A.; Freiwald, A.; Cairns, S. Cold-Water Corals: The Biology and Geology of Deep-Sea Coral Habitats; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; p. 334. [Google Scholar]
- Brook, G. Report on the Antipatharia collected by HMS Challenger during the years 1873–1876. Chall. Rep. Zool. 1889, 32, 1–222. [Google Scholar]
- ICES. Report of the Working Group on Deep-Water Ecology (WGDEC); ICES Advisory Committee on Ecosystems; ICES Document CM 2007/ACE:01; ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- De Clippele, L.; Huvenne, V.; Molodtsova, T.; Roberts, J.M. The diversity and ecological role of non-scleractinian corals (Antipatharia and Alcyonacea) on scleractinian cold-water coral mounds. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiwald, A.; Fossa, J.; Grehan, A.; Koslow, T.; Roberts, J. Cold-Water Coral Reefs: Out of Sight-No Longer out of Mind; UNEP-WCMC: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Krieger, K.; Wing, B. Megafauna associations with deepwater corals (Primnoa spp.) in the Gulf of Alaska. Hydrobiologia 2002, 471, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazioli, S.; Bo, M.; Boyer, M.; Rotinsulu, H.; Bavestrello, G. Ecological observations of some common antipatharian corals in the marine park of Bunaken (North Sulawesi, Indonesia). Zool. Stud. 2007, 46, 227–241. [Google Scholar]
- Herler, J. Microhabitats and ecomorphology of coral-and coral rock-associated gobiid fish (Teleostei: Gobiidae) in the northern Red Sea. Mar. Ecol. 2007, 28, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, B.N.; Yoklavich, M.M.; Love, M.S.; York, K.; Amend, M. Benthic invertebrates that form habitat on deep banks off southern California, with special reference to deep sea coral. Fish. Bull. 2006, 104, 167–181. [Google Scholar]
- Angel, M.; Boxhal, G. Life in the benthic boundary layer: Connections to the mid-water and sea floor. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1990, 331, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, M.; Tazioli, S.; Spanò, N.; Bavestrello, G. Antipathella subpinnata (Antipatharia, Myriopathidae) in Italian seas. Ital. J. Zool. 2008, 75, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humes, A.; Goenaga, C. Calonastes imparipes, new genus, new species (Copepoda, Cyclopoida), associated with the antipatharian coral genus Stichopathes in Puerto Rico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1978, 28, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Baillon, S.; Hamel, J.; Wareham, V.; Mercier, A. Deep cold-water corals as nurseries for fish larvae. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes-Pereira, J.; Carmo, V.; Catarino, D.; Jakobsen, J.; Alvarez, H.; Aguilar, R.; Hart, J.; Giacomello, E.; Menezes, G.; Stefanni, S.; et al. Cold-water corals and large hydrozoans provide essential fish habitat for Lappanella fasciata and Benthocometes robustus. Deep Sea Res. Part II Trop. Stud. Oceanogr. 2017, 145, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molodtsova, T.; Budaeva, N. Modifications of corallum morphology in black corals as an effect of associated fauna. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2007, 81, 469–479. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, A.; Stone, R.; Lundstrom, C.; DeVogelaere, A. Growth rate and age determination of bamboo corals from the northeastern Pacific Ocean using refined 210 Pb dating. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 397, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roark, E.; Guilderson, T.; Dunbar, R.; Fallon, S.; Mucciarone, D. Extreme longevity in proteinaceous deep-sea corals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5204–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.; Opresko, D. Description of a new species of Leiopathes (Antipatharia: Leiopathidae) from the Hawaiian Islands. Zootaxa 2015, 3974, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Rowden, A. Effect of deepwater trawling on the macro-invertebrate assemblages of seamounts on the Chatham Rise, New Zealand. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2009, 56, 1540–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todinanahary, G.; Terrana, L.; Lavitra, T.; Eeckhaut, I. First records of illegal harvesting and trading of black corals (Antipatharia) in Madagascar. Madag. Conserv. Dev. 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.; Gianni, M. The Implementation of UNGA Resolutions 61/105 and 64/72 in the Management of Deep-Sea Fisheries on the High Seas—A Report from the International Programme on the State of the Ocean; Report Prepared for the Deep-Sea Conservation Coalition; International Programme on the State of the Ocean: London, UK, 2011; 97p. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, S.; Murillo, F.; Wareham, V.; Kenchington, E. Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems Dominated by Deep-Water Corals and Sponges in the NAFO Convention Area; Serial No N5524; NAFO: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- De Matos, V.; Gomes-Pereira, J.N.; Tempera, F.; Ribeiro, P.A.; Braga-Henriques, A.; Porteiro, F. First record of Antipathella subpinnata (Anthozoa, Antipatharia) in the Azores (NE Atlantic), with description of the first monotypic garden for this species. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 99, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D. Synopsis of the families and genera of axiferous zoophytes or barked corals. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1857, 25, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.; Haroun, R.; Morri, C.; Wirtz, P. The subtidal epibenthic communities off Puerto del Carmen (Lanzarote, Canary Islands). Arquipélago 2000, 2, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-García, L.; Brito-Izquierdo, I.; Brito-Hernández, A. Changes in benthic communities due to submarine volcanic eruption: Black coral (Antipathella wollastoni) death in the Marine Reserve of El Hierro (Canary Islands). Rev. Acad. Canar. Cienc. 2015, 27, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez, L.; Ferrer, F. Aquaculture and marine biodiversity boost: Case examples from the Canary Islands. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 97, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Riera, R.; Becerro, M.; Stuart-Smith, R.; Delgado, J.; Edgar, G. Out of sight, out of mind: Threats to the marine biodiversity of the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-García, L.; Brito-Izquierdo, I.; Brito-Hernández, A. Bionomía bentónica de las Reservas Marinas de Canarias (España). Comunidades y hábitats bentónicos del infralitoral; Ministerio de Agricultura y Pesca, Alimentación y Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2016; p. 181. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, J.; Uchupi, E.; Muñoz, A.; Herranz, P.; Palomo, C.; Ballesteros, M.; Group, Z.W. Geologic evolution of the Canarian Islands of Lanzarote, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria and La Gomera and comparison of landslides at these islands with those at Tenerife, La Palma and El Hierro. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2003, 24, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bogaard, P. The origin of the Canary Island Seamount Province-New ages of old seamounts. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, K.; Lazier, J. Dynamics of Marine Ecosystems: Biological-Physical Interactions in the Oceans; Blackwell Scientific Publiations: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; p. 446. [Google Scholar]
- Guinotte, J.; Davies, A. Predicted Deep-Sea Coral Habitat Suitability for Alaskan Waters; Report to NOAA-NMFS; NOAA-NMFS: Seattle, WA, USA, 2013; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Yesson, C.; Bedford, F.; Rogers, A.; Taylor, M. The global distribution of deep-water Antipatharia habitat. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2017, 145, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnyder, J.; Eberli, G.; Kirby, J.; Shi, F.; Tehranirad, B.; Mulder, T.; Ducassou, E.; Hebbeln, D.; Wintersteller, P. Tsunamis caused by submarine slope failures along western Great Bahama Bank. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.; O’Connell, B.; Brown, C.; Guinan, J.; Grehan, A. Multiscale terrain analysis of multibeam bathymetry data for habitat mapping on the continental slope. Mar. Geod. 2007, 30, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevenbergen, L.; Thorne, C. Quantitative analysis of land surface topography. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1987, 12, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix, Version 0.84; CRAN: Wien, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Buscombe, D.; Grams, P.E.; Kaplinski, M.A. Compositional Signatures in Acoustic Backscatter Over Vegetated and Unvegetated Mixed Sand-Gravel Riverbeds. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 1771–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurton, X.; Lamarche, G.; Brown, C.; Lucieer, V.; Rice, G.; Schimel, A.; Weber, T. Backscatter Measurements by Seafloor-Mapping Sonars Guidelines and Recommendations. 2015, p. 200. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Backscatter-measurements-by-seafloor%E2%80%90mapping-and-Lurton-Lamarche/792763b9321fe1c0408fc260e8a3e57fd3d0192f (accessed on 11 September 2020).
- Simmonds, J. Survey design for acoustic seabed classification. In Acoustic Seabed Classification of Marine Physical and Biological Landscapes; Anderson, J., Ed.; International Council for the Exploration of the Sea: Copenhagen, Danmark, 2007; pp. 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Lurton, X. An Introduction to Underwater Acoustics: Principles and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Buscombe, D. Spatially explicit spectral analysis of point clouds and geospatial data. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 86, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, P.; von Schneider Deimling, J. New Feature Classes for Acoustic Habitat Mapping—A Multibeam Echosounder Point Cloud Analysis for Mapping Submerged Aquatic Vegetation (SAV). Geosciences 2019, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowski, L.; Tęgowski, J.; Nowak, J. Seafloor mapping based on multibeam echosounder bathymetry and backscatter data using Object-Based Image Analysis: A case study from the Rewal site, the Southern Baltic. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2018, 47, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tęgowski, J. Acoustical classification of the bottom sediments in the southern Baltic Sea. Quat. Int. 2005, 130, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, A.C.G.; Brown, C.J.; Ierodiaconou, D. Automated Filtering of Multibeam Water-Column Data to Detect Relative Abundance of Giant Kelp (Macrocystis pyrifera). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, K.; Niel, K.V.; Radford, B.; Kendrick, G.; Grove, S. Modelling distribution of marine benthos from hydroacoustics and underwater video. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinan, J.; Brown, C.; Dolan, M.; Grehan, A. Ecological niche modeling of the distribution of cold-water coral habitat using underwater remote sensing data. Ecol. Inform. 2009, 4, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengstorf, A.; Grehan, A.; Yesson, C.; Brown, C. Towards high-resolution habitat suitability modeling of vulnerable marine ecosystems in the deep-sea: Resolving terrain attribute dependencies. Mar. Geod. 2012, 35, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, R.; Opresko, D. Order Antipatharia, black corals. In Reef and Shore Fauna of Hawaii. Section 1: Protozoa through Ctenophora; Devaney, D., Eldredge, L., Eds.; Bishop Museum Press: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1977; pp. 242–261. [Google Scholar]
- Opresko, D.M. Review of the genus Schizopathes (Cnidaria: Antipatharia: Schizopathidae) with a description of a new species from the Indian Ocean. Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1998, 1, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrano, C.; Danovaro, R.; Gambi, C.; Pusceddu, A.; Riva, A.; Schiaparelli, S. Gold coral (Savalia savaglia) and gorgonian forests enhance benthic biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in the mesophotic zone. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J.; Beaudoin, J.; Brissette, M.; Gazzola, V. Multispectral Multibeam Echo Sounder Backscatter as a Tool for Improved Seafloor Characterization. Geosciences 2019, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldens, P.; Schulze, I.; Papenmeier, S.; Schönke, M.; Schneider von Deimling, J. Improved Interpretation of Marine Sedimentary Environments Using Multi-Frequency Multibeam Backscatter Data. Geosciences 2018, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, R. Ecological studies of black coral in Hawaii. Pac. Sci. 1965, 19, 244–260. [Google Scholar]
- Talley, L. Descriptive Physical Oceanography: An Introduction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; p. 564. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, A.; Ocaña, B. Corales de las Islas Canarias: Antozoos con Esqueleto de los Fondos Litorales y Profundos; Francisco Lemus: La Laguna, Spain, 2004; p. 477. [Google Scholar]

| Depth | Zone | Number of Colonies per 5 m | Average Density per m | Average Height of Colonies per Zone (cm) | Average Height (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| shallow | 1 | 32/38/11/13/23 | 0.94 ± 0.21 | 92.4/74.8/102.0/96.0/91.2 | 91.28 ± 4.53 |
| shallow | 3 | 12/12/25/9/10 | 0.54 ± 0.12 | 82.4/85.4/106.2/96.4/115.4 | 97.16 ± 6.21 |
| deep | 2 | 35/48/38/47/46 | 1.71 ± 0.11 | 100.4/117.4/126.6/102.8/92.6 | 107.96 ± 6.15 |
| deep | 4 | 33/50/21/22/47 | 1.38 ± 0.24 | 126.2/127.2/87.4/100.8/131.0 | 114.52 ± 8.64 |
| Estimate | SE | z-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −6.48 | 0.92 | −7.06 |
| Slope | 0.08 | 0.01 | 6.34 |
| Aspect Eastness | −0.80 | 0.17 | −4.65 |
| Depth | −0.08 | 0.01 | −5.53 |
| Substrate: Sand | −0.53 | 0.19 | −2.77 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czechowska, K.; Feldens, P.; Tuya, F.; Cosme de Esteban, M.; Espino, F.; Haroun, R.; Schönke, M.; Otero-Ferrer, F. Testing Side-Scan Sonar and Multibeam Echosounder to Study Black Coral Gardens: A Case Study from Macaronesia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193244
Czechowska K, Feldens P, Tuya F, Cosme de Esteban M, Espino F, Haroun R, Schönke M, Otero-Ferrer F. Testing Side-Scan Sonar and Multibeam Echosounder to Study Black Coral Gardens: A Case Study from Macaronesia. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(19):3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193244
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzechowska, Karolina, Peter Feldens, Fernando Tuya, Marcial Cosme de Esteban, Fernando Espino, Ricardo Haroun, Mischa Schönke, and Francisco Otero-Ferrer. 2020. "Testing Side-Scan Sonar and Multibeam Echosounder to Study Black Coral Gardens: A Case Study from Macaronesia" Remote Sensing 12, no. 19: 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193244
APA StyleCzechowska, K., Feldens, P., Tuya, F., Cosme de Esteban, M., Espino, F., Haroun, R., Schönke, M., & Otero-Ferrer, F. (2020). Testing Side-Scan Sonar and Multibeam Echosounder to Study Black Coral Gardens: A Case Study from Macaronesia. Remote Sensing, 12(19), 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193244







