Long-Term Discharge Estimation for the Lower Mississippi River Using Satellite Altimetry and Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
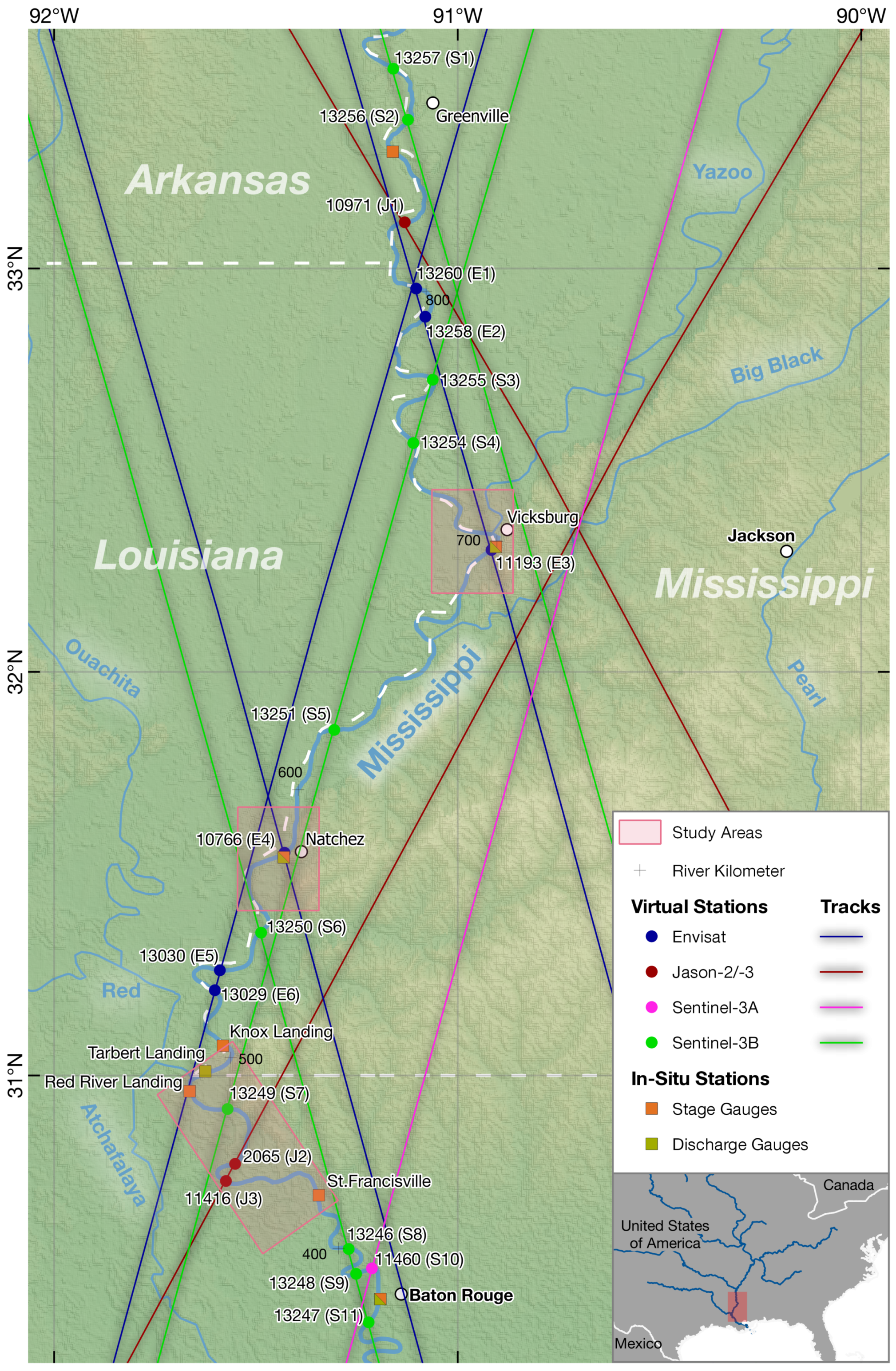
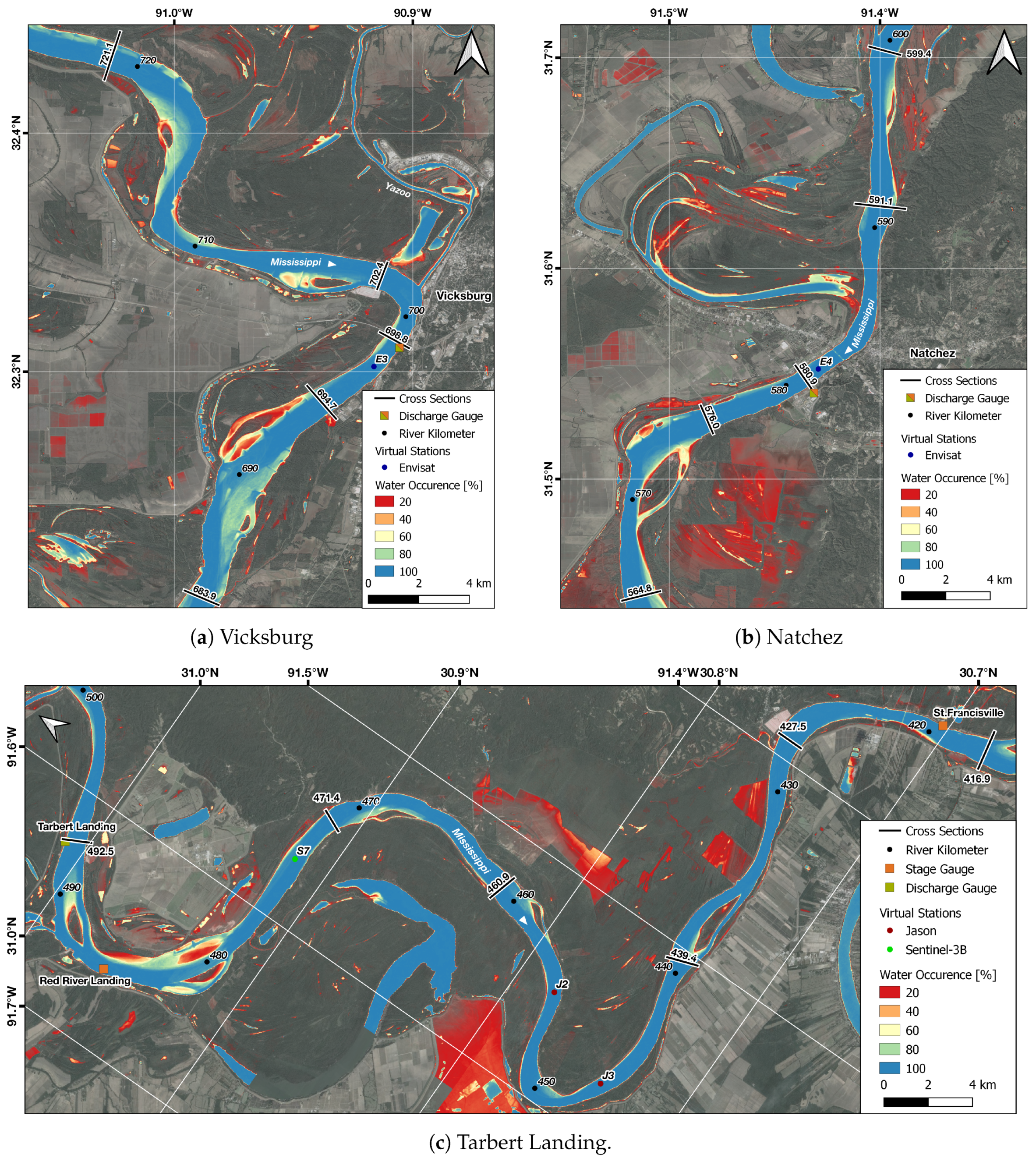
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. In-Situ Validation Data
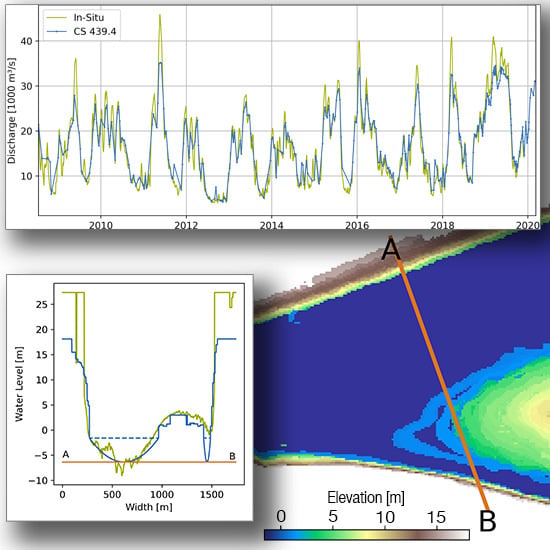
2.2.1. Water Levels and Discharge
2.2.2. River Bathymetry
2.3. Remote Sensing Data
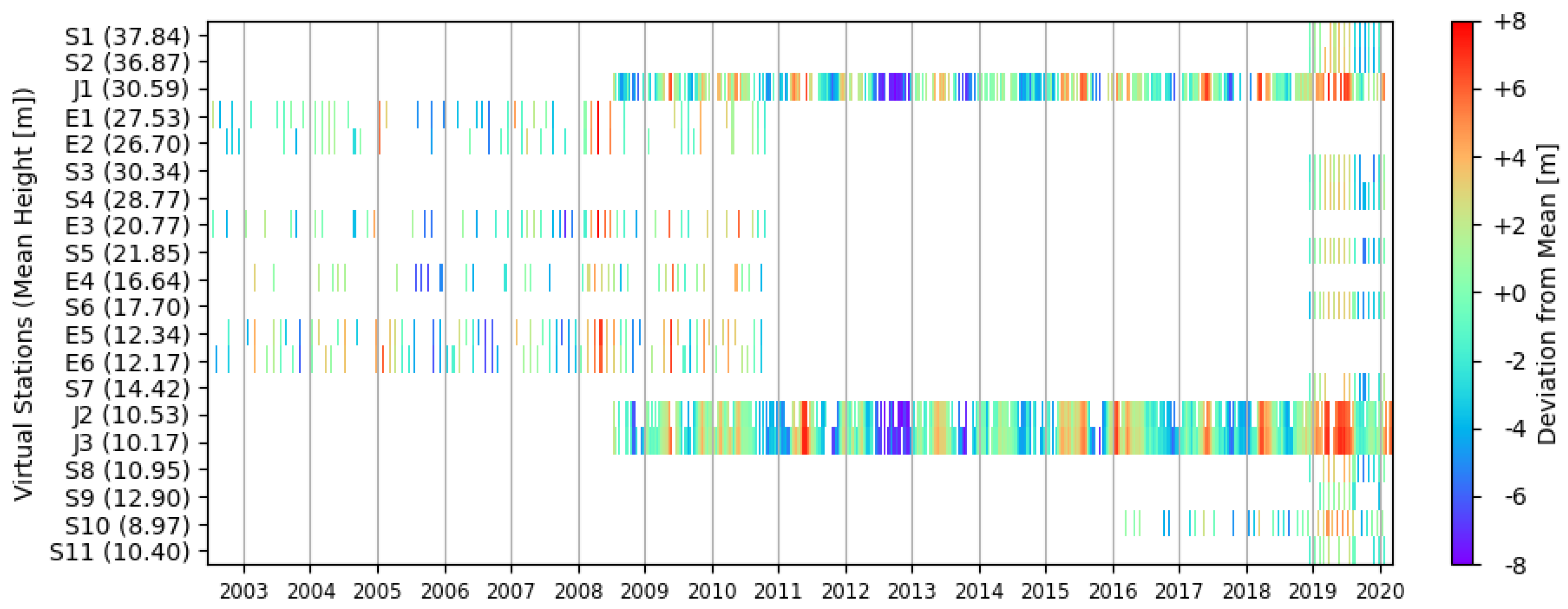
2.3.1. Satellite Altimetry
2.3.2. Water Surface Extent
2.4. River Centerline
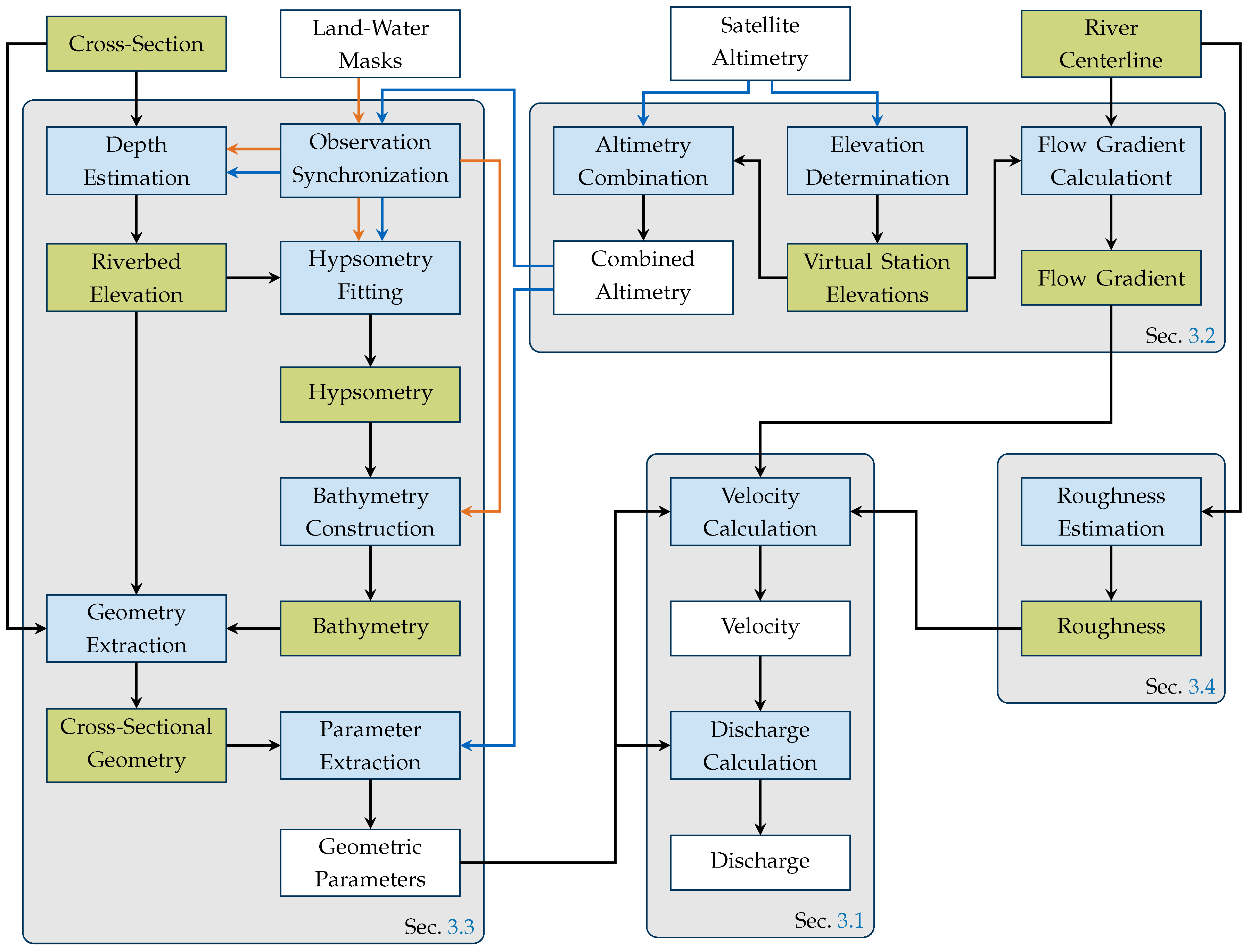
3. Methodology
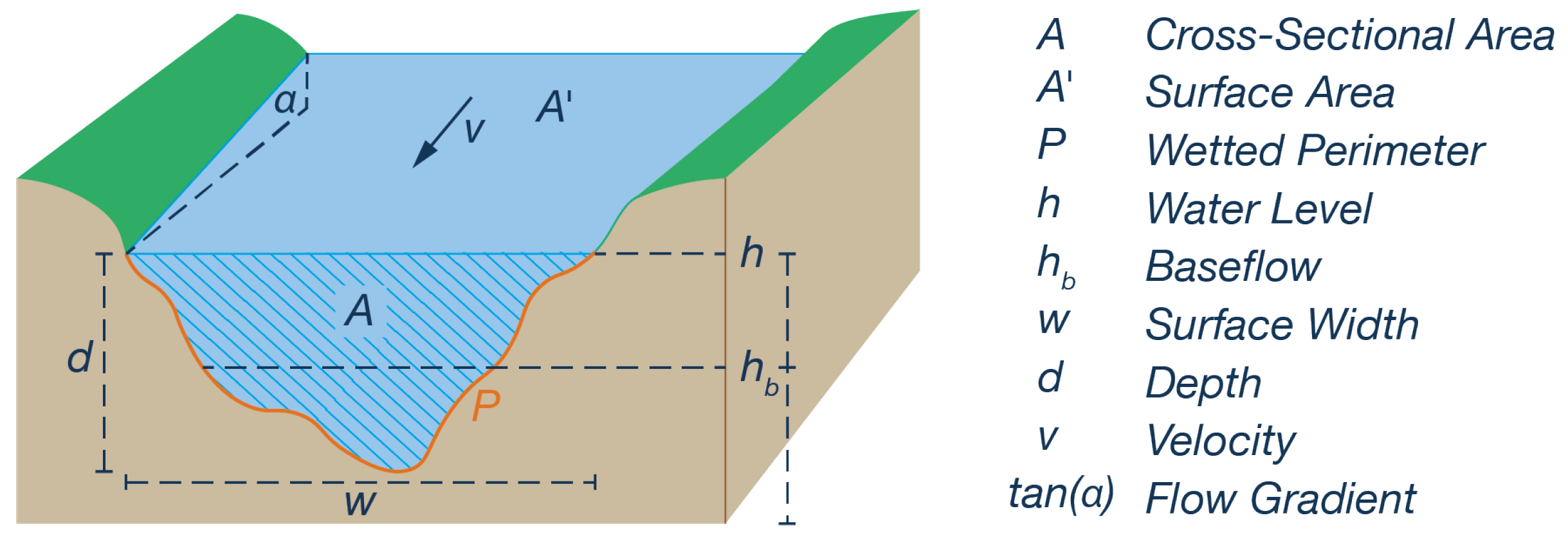
3.1. Discharge and Velocity Calculation
3.2. Elevation Determination
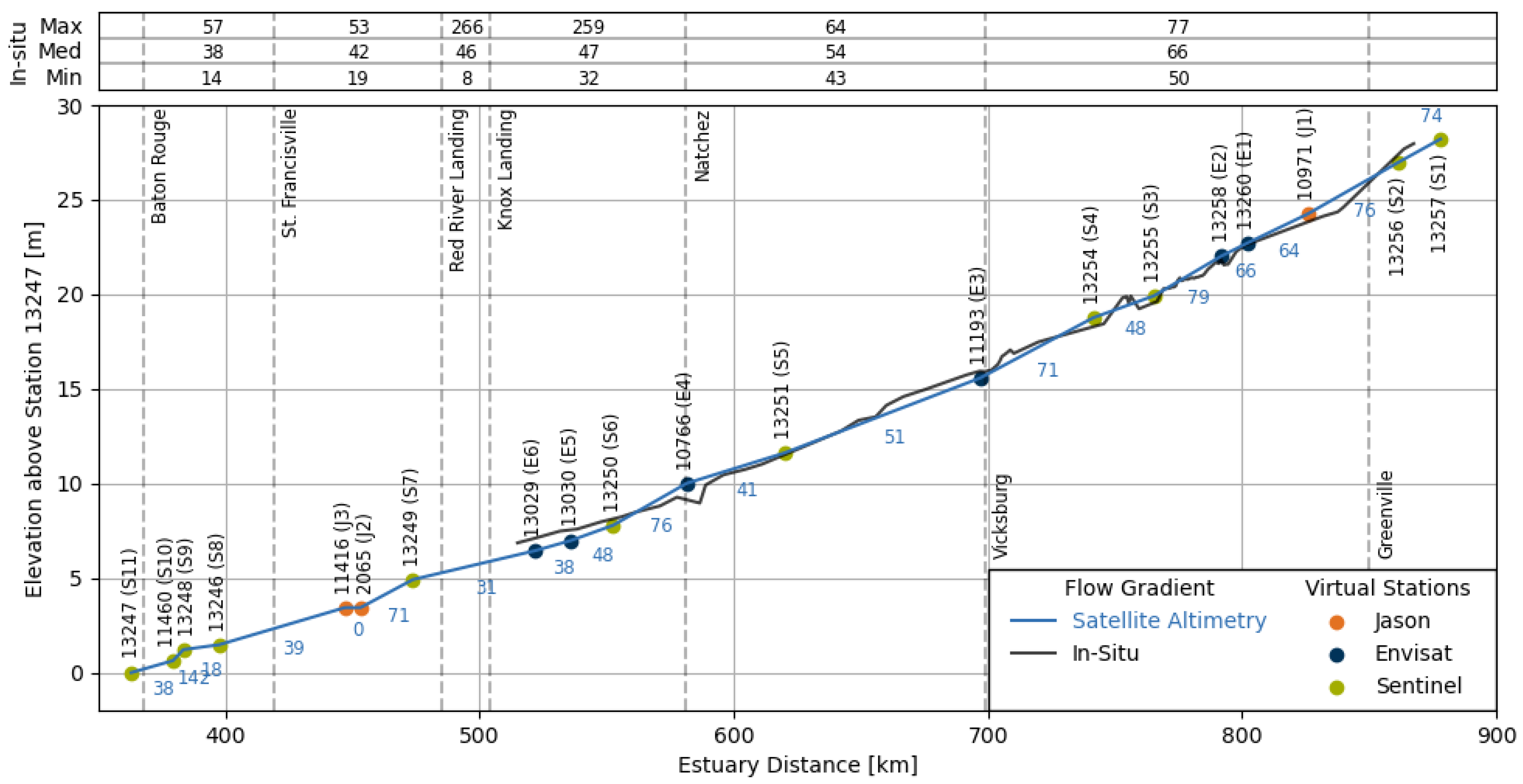
3.2.1. Flow Gradient Calculation
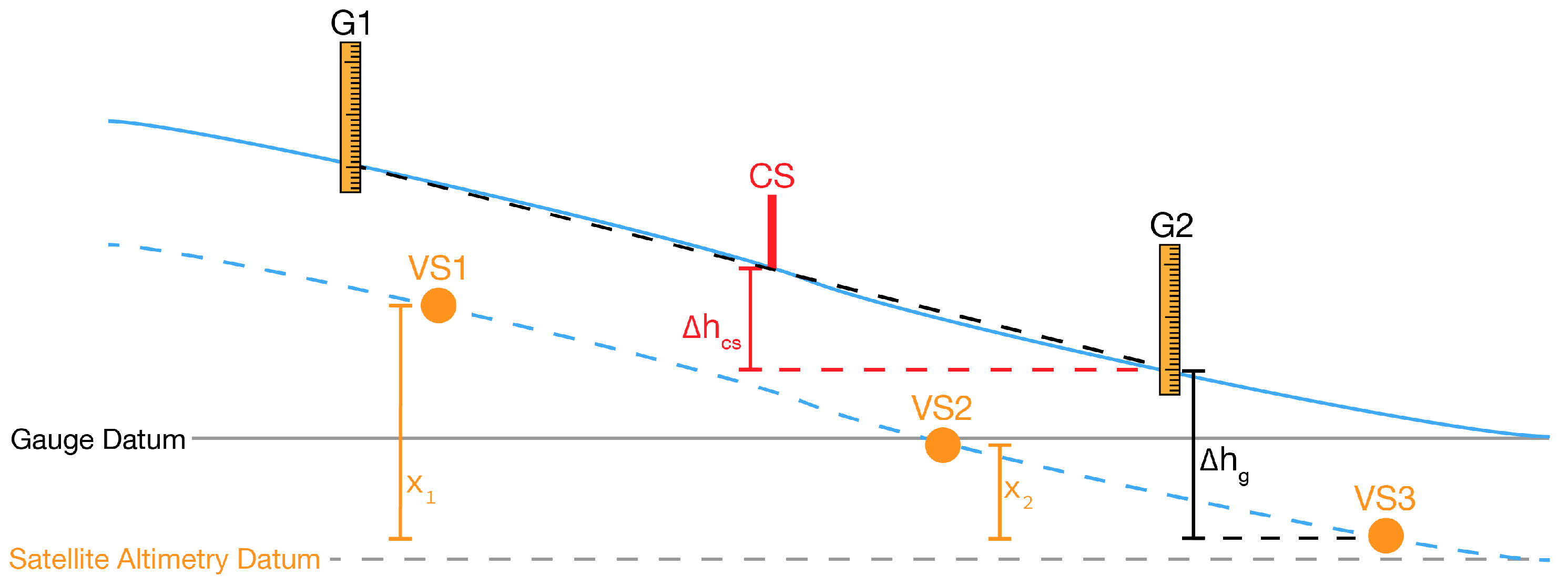
3.2.2. Altimetry Combination
3.3. Geometric Parameters
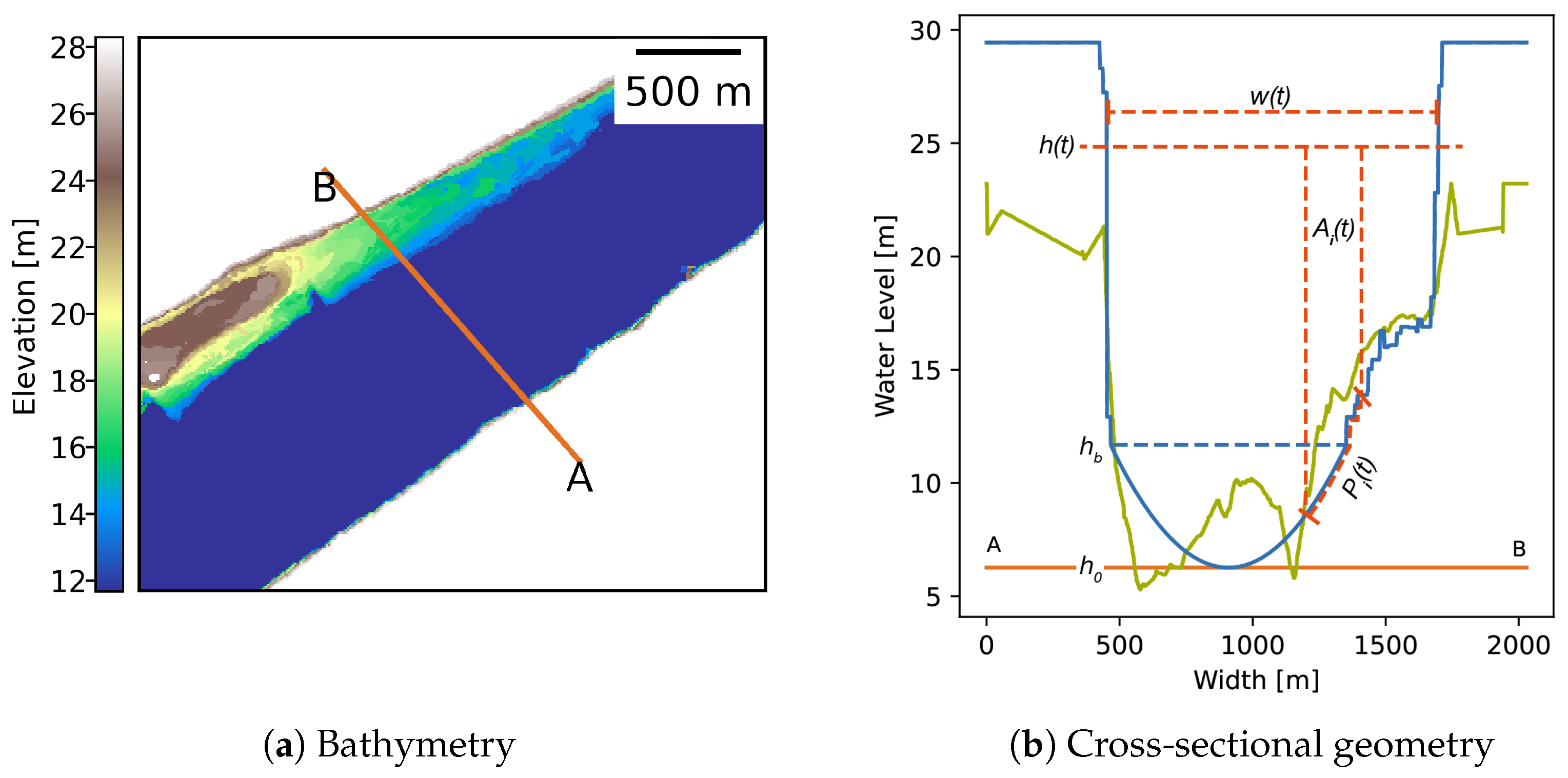
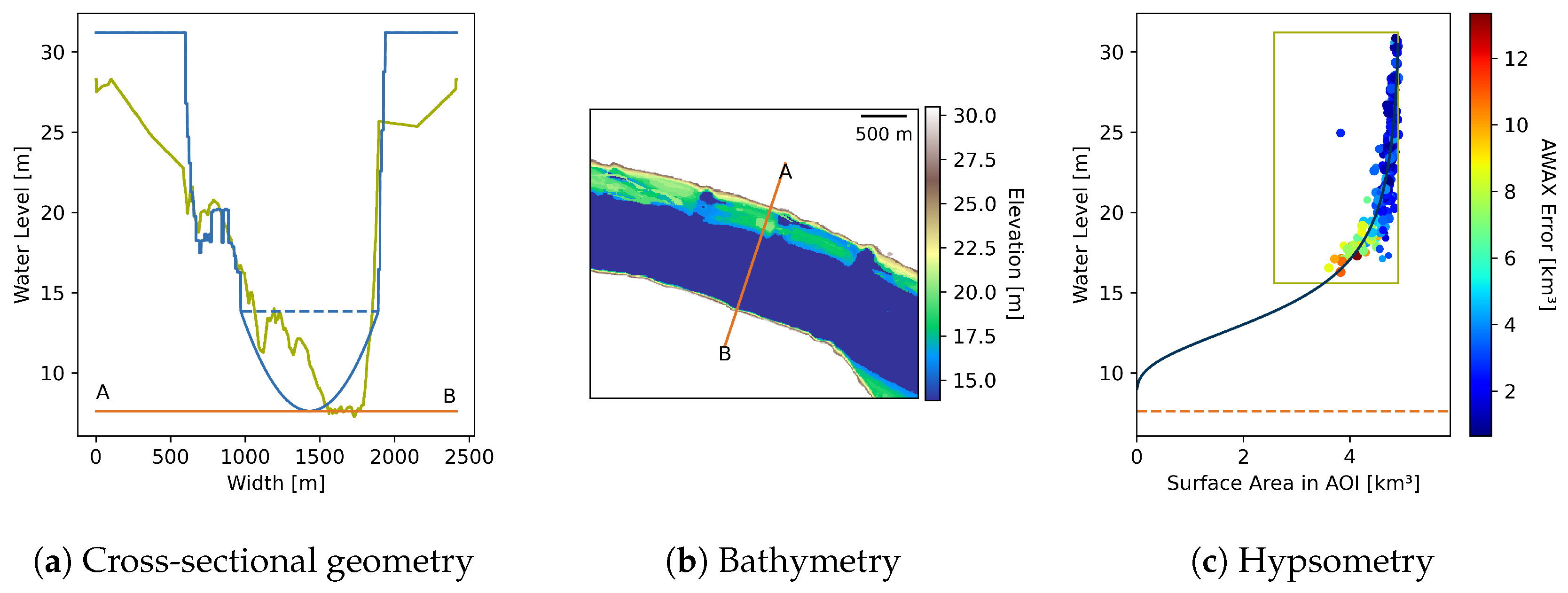
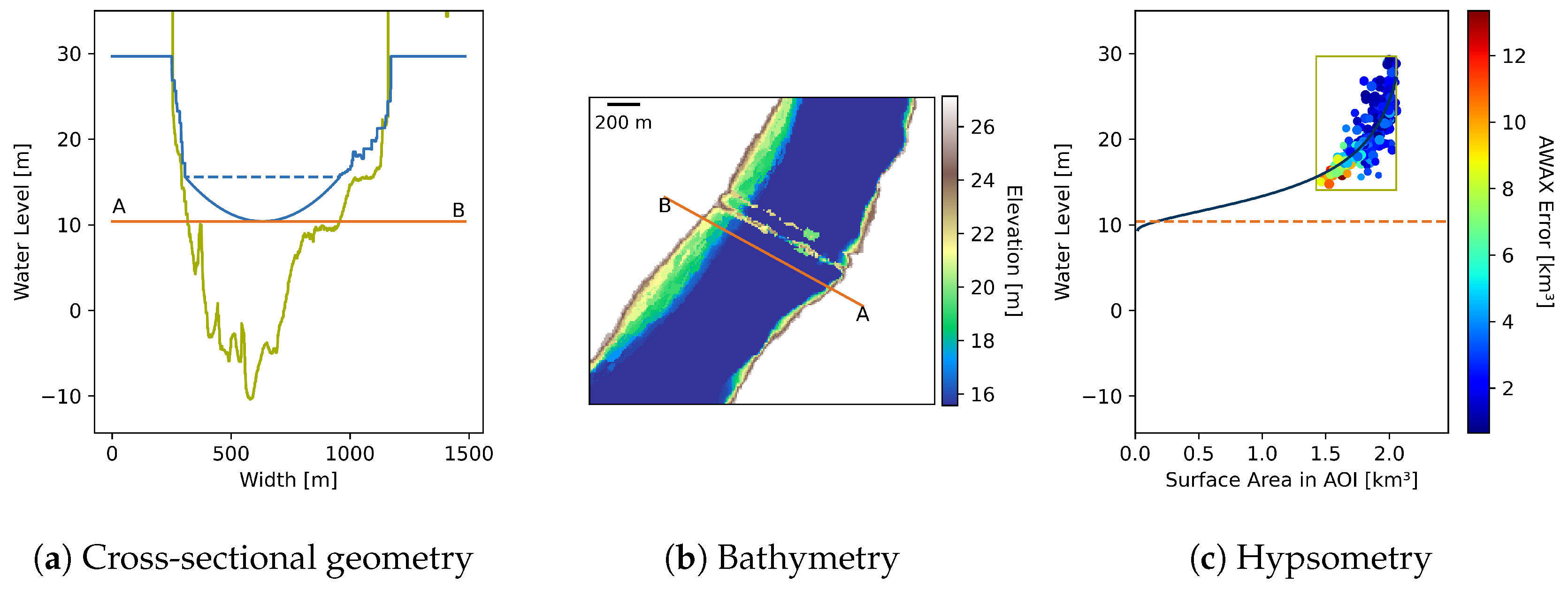
3.3.1. Bathymetry
Observation Synchronization
Depth Estimation
Hypsometry Fitting
Bathymetry Construction
3.3.2. Cross-Sectional Geometry
3.3.3. Geometric Parameter Extraction
3.4. Roughness Estimation
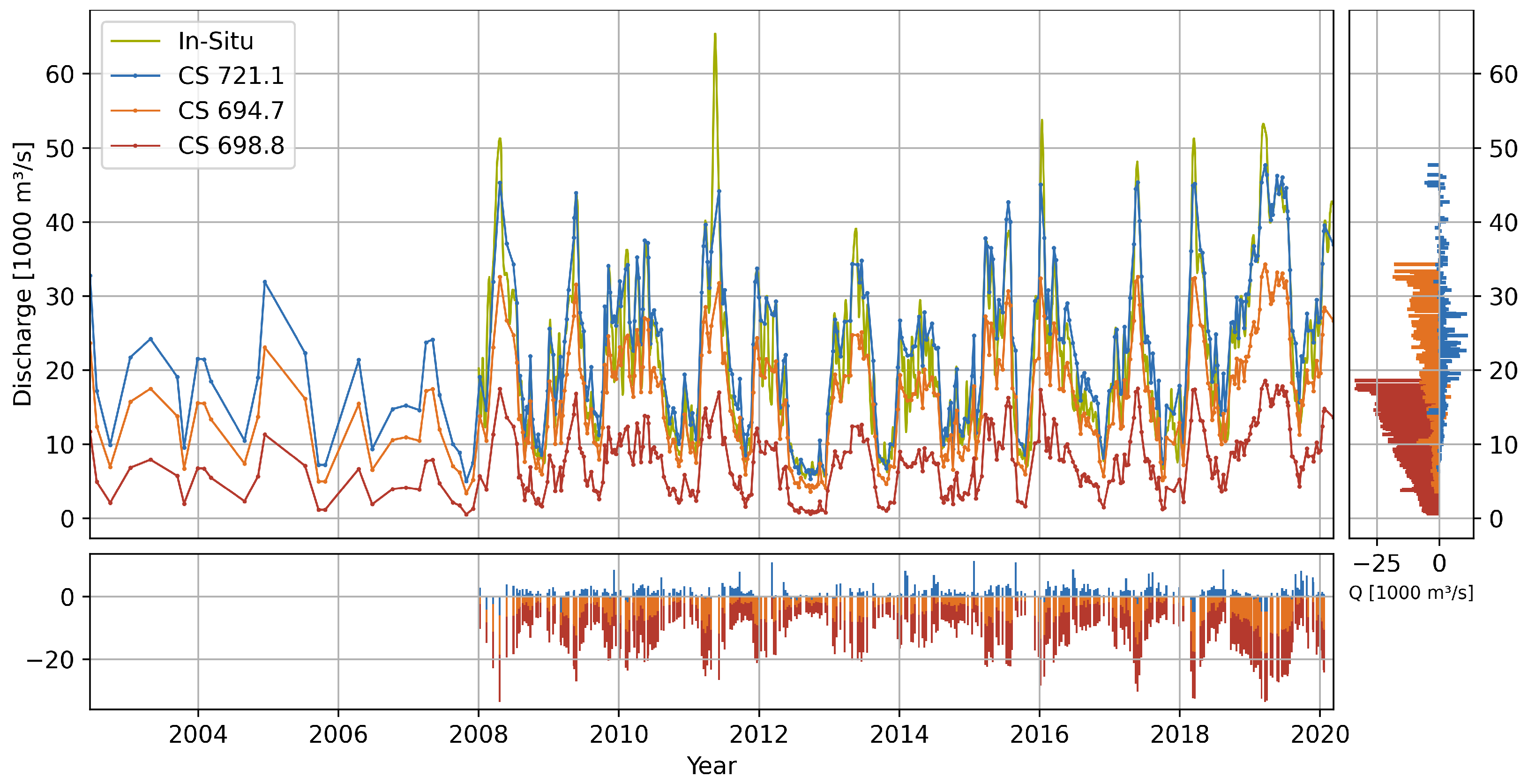
4. Results and Validation
4.1. Flow Gradient
4.2. Geometry and Discharge
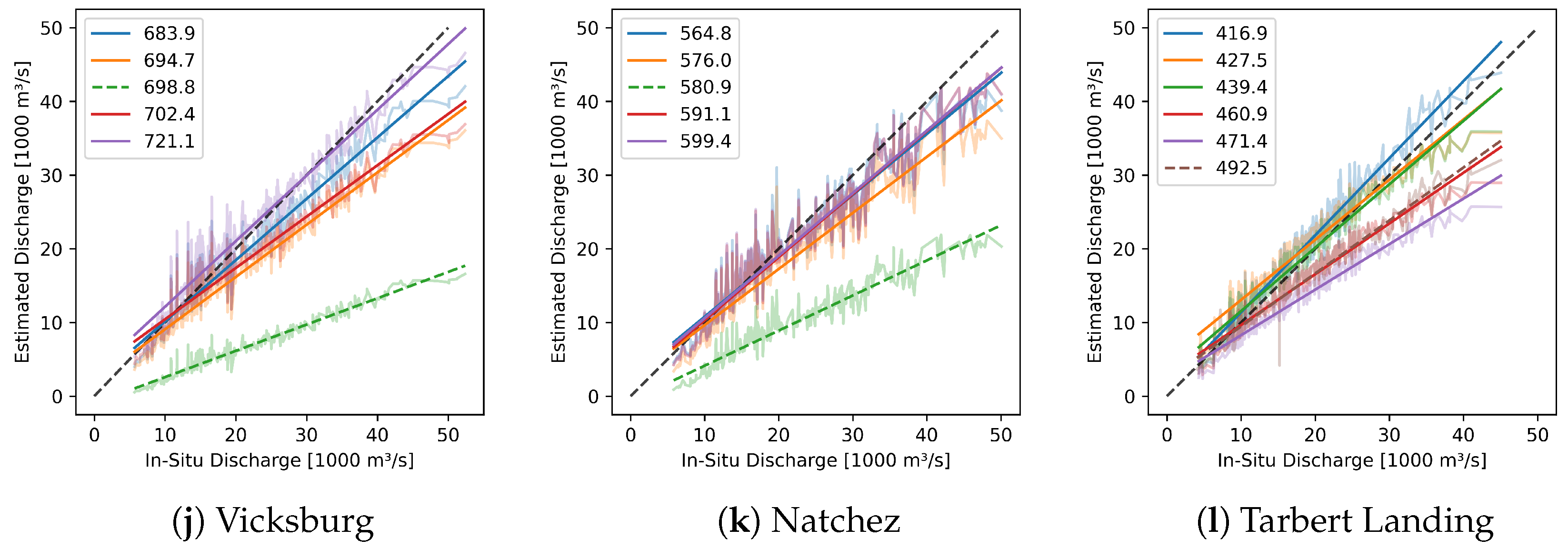
4.2.1. Vicksburg
4.2.2. Natchez
4.2.3. Tarbert Landing
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Gleick, P.H. Water resources. In Encyclopedia of Climate and Weather, 2nd ed.; Schneider, S.H., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 817–823. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, T.J. Capitalising on river flow data to meet changing national needs—A UK perspective. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2002, 13, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, M.; Döll, P. Value of river discharge data for global-scale hydrological modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 841–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahine, M.T. The hydrological cycle and its influence on climate. Nature 1992, 359, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, M.C. Streamflow Measurement. In Handbook of Applied Hydrology; Chow, V.T., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1964; Chapter 15. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, R.R. Streamflow Rating. In Handbook of Applied Hydrology, 2nd ed.; Singh, V.P., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, R.R. Streamflow Data. In Handbook of Applied Hydrology, 2nd ed.; Singh, V.P., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Hannah, D.M.; Demuth, S.; van Lanen, H.A.J.; Looser, U.; Prudhomme, C.; Rees, G.; Stahl, K.; Tallaksen, L.M. Large-scale river flow archives: Importance, current status and future needs. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, C.J.; Smith, L.C. Toward global mapping of river discharge using satellite images and at-many-stations hydraulic geometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4788–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, I.; Gessner, U.; Dietz, A.J.; Kuenzer, C. Global WaterPack—A 250 m resolution dataset revealing the daily dynamics of global inland water bodies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwatke, C.; Scherer, D.; Dettmering, D. Automated Extraction of Consistent Time-Variable Water Surfaces of Lakes and Reservoirs Based on Landsat and Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelsky, T.M.; Smith, L.C. RivWidth: A Software Tool for the Calculation of River Widths From Remotely Sensed Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.H.; Pavelsky, T. Global extent of rivers and streams. Science 2018, 361, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Allen, G.H.; Donchyts, G. RivWidthCloud: An Automated Google Earth Engine Algorithm for River Width Extraction From Remotely Sensed Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Rodríguez, E.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Measuring surface water from space. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, I.E.; Nearing, G.S.; Bolten, J.D.; Lakshmi, V. Remote Sensing Techniques and Data Assimilation for Hydrologic Modeling. In Handbook of Applied Hydrology, 2nd ed.; Singh, V.P., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar]
- Kugler, Z.; Nghiem, S.; Brakenridge, G. L-Band Passive Microwave Data from SMOS for River Gauging Observations in Tropical Climates. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, C.M. The contribution of TOPEX/POSEIDON to the global monitoring of climatically sensitive lakes. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 25179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, P.A.M. Global inland water monitoring from multi-mission altimetry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L16401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwatke, C.; Dettmering, D.; Bosch, W.; Seitz, F. DAHITI—An innovative approach for estimating water level time series over inland waters using multi-mission satellite altimetry. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4345–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancamaria, S.; Frappart, F.; Leleu, A.S.; Marieu, V.; Blumstein, D.; Desjonquères, J.D.; Boy, F.; Sottolichio, A.; Valle-Levinson, A. Satellite radar altimetry water elevations performance over a 200 m wide river: Evaluation over the Garonne River. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Schwartz, F.; Tseng, K.H.; Shum, C.K.; Lee, S. Satellite altimetry for measuring river stages in remote regions. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boergens, E.; Buhl, S.; Dettmering, D.; Klüppelberg, C.; Seitz, F. Combination of multi-mission altimetry data along the Mekong River with spatio-temporal kriging. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getirana, A.; Jung, H.C.; Tseng, K.H. Deriving three dimensional reservoir bathymetry from multi-satellite datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwatke, C.; Dettmering, D.; Seitz, F. Volume Variations of Small Inland Water Bodies from a Combination of Satellite Altimetry and Optical Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouraev, A.V.; Zakharova, E.A.; Samain, O.; Mognard, N.M.; Cazenave, A. Ob’ river discharge from TOPEX/Poseidon satellite altimetry (1992–2002). Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourian, M.J.; Sneeuw, N.; Bárdossy, A. A quantile function approach to discharge estimation from satellite altimetry (ENVISAT). Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4174–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourian, M.J.; Schwatke, C.; Sneeuw, N. River discharge estimation at daily resolution from satellite altimetry over an entire river basin. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, D.M.; Weijun, H.; Zaiyi, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhengwei, H.; Min, A. Mapping Monthly Water Scarcity in Global Transboundary Basins at Country-Basin Mesh Based Spatial Resolution. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oki, T.; Quiocho, R.E. Economically challenged and water scarce: Identification of global populations most vulnerable to water crises. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2020, 36, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancamaria, S.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Pavelsky, T.M. The SWOT Mission and Its Capabilities for Land Hydrology. Surv. Geophys. 2016, 37, 307–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, R. On the flow of water in open channels and pipes. Trans. Inst. Civ. Eng. Irel. 1891, 20, 161–207. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, C.J.; Smith, L.C.; Lee, J. Retrieval of river discharge solely from satellite imagery and at-many-stations hydraulic geometry: Sensitivity to river form and optimization parameters. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 9604–9619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, P.Y. River Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, M.; Neal, J.; Rodríguez, E.; Andreadis, K.M.; Smith, L.C.; Yoon, Y. Estimating reach-averaged discharge for the River Severn from measurements of river water surface elevation and slope. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Alsdorf, D.E.; Trigg, M. Estimating River Depth From Remote Sensing Swath Interferometry Measurements of River Height, Slope, and Width. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2010, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, E.; Nielsen, K.; Kamenev, G.; Kouraev, A. River discharge estimation from radar altimetry: Assessment of satellite performance, river scales and methods. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerklie, D.M.; Lawrence Dingman, S.; Vorosmarty, C.J.; Bolster, C.H.; Congalton, R.G. Evaluating the potential for measuring river discharge from space. J. Hydrol. 2003, 278, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garambois, P.A.; Monnier, J. Inference of effective river properties from remotely sensed observations of water surface. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 79, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerklie, D.M.; Birkett, C.M.; Jones, J.W.; Carabajal, C.; Rover, J.A.; Fulton, J.W.; Garambois, P.A. Satellite remote sensing estimation of river discharge: Application to the Yukon River Alaska. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 1000–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerklie, D.M. Estimating the bankfull velocity and discharge for rivers using remotely sensed river morphology information. J. Hydrol. 2007, 341, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, M.G.; Wang, L.; Yang, K.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Zeng, T.; Hu, Z. Discharge Estimates for Ungauged Rivers Flowing over Complex High-Mountainous Regions based Solely on Remote Sensing-Derived Datasets. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.; Gleason, C.J.; Garambois, P.A.; Bjerklie, D.; Smith, L.C.; Roux, H.; Rodriguez, E.; Bates, P.D.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Monnier, J.; et al. An intercomparison of remote sensing river discharge estimation algorithms from measurements of river height, width, and slope. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 4527–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichangi, A.W.; Wang, L.; Yang, K.; Chen, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Kuria, D. Estimating continental river basin discharges using multiple remote sensing data sets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 179, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moramarco, T.; Barbetta, S.; Bjerklie, D.M.; Fulton, J.W.; Tarpanelli, A. River Bathymetry Estimate and Discharge Assessment from Remote Sensing. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6692–6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichangi, A.; Wang, L.; Hu, Z. Estimation of River Discharge Solely from Remote-Sensing Derived Data: An Initial Study Over the Yangtze River. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J.C. The Mississippi River System. In Large Rivers; Gupta, A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Chichester, UK, 2007; pp. 145–182. [Google Scholar]
- Little, C.D.; Biedenharn, D.S. Mississippi River Hydrodynamic and Delta Management Study (MRHDM)—Geomorphic Assessment; Technical Report 14-5; US Army Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC): Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wohl, E.E. Hydrology and Discharge. In Large Rivers; Gupta, A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Chichester, UK, 2007; pp. 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- The Global Runoff Data Centre, 56068 Koblenz, Germany. GRDC Data Download Portal. 2020. Available online: https://portal.grdc.bafg.de/ (accessed on 5 August 2020).
- Lewis, J.; Brown, G.; Ayers, S. Investigation of Discharge Measurements of the Lower Mississippi River below Natchez, MS; Technical Report 3; US Army Corps of Engineering: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. USGS Water Data for the Nation. 2016. Available online: https://waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- US Army Corps of Engineers. Rivergages.com. 2019. Available online: http://rivergages.mvr.usace.army.mil (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- US Army Corps of Engineers. USACE Hydrographic Surveys Powered by eHydro. 2019. Available online: https://geospatial-usace.opendata.arcgis.com/datasets/4b8f2ba307684cf597617bf1b6d2f85d (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- US Army Corps of Engineers, N.O.D. Multibeam Bathymetric Data for the Lower Mississippi River. 2013. Available online: mvn.usace.army.mil/Missions/Engineering/Channel-Improvement-and-Stabilization-Program/2013MBMR/ (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Girardeau-Montaut, D. CloudCompare (version 2.9.1). 2019. Available online: http://www.cloudcompare.org/ (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Bosch, W.; Dettmering, D.; Schwatke, C. Multi-Mission Cross-Calibration of Satellite Altimeters: Constructing a Long-Term Data Record for Global and Regional Sea Level Change Studies. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2255–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovmöller, E. The Trough-and-Ridge diagram. Tellus 1949, 1, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenStreetMap Contributors. Planet Dump. 2017. Available online: https://planet.osm.org (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Einstein, H.A. Der hydraulische oder Profil-Radius. Schweiz. Bauztg. 1934, 103/104, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Niemeier, W. Ausgleichungsrechnung; De Gruyter: Tubingen, Germany, 2008; p. 512. [Google Scholar]
- Spearman, C. The Proof and Measurement of Association between Two Things. Am. J. Psychol. 1987, 100, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, J.A.; Troutman, B.M. Characterization of the spatial variability of channel morphology. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2002, 27, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.N. Hypsometric (Area-Altitude) Analysis of Erosional Topography. GSA Bull. 1952, 63, 1117–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, W. Estimating hydraulic roughness coefficients. Agric. Eng. 1956, 37, 473–475. [Google Scholar]
- Arcement, G.J.; Schneider, V.R. Guide for Selecting Manning’s Roughness Coefficients for Natural Channels and Flood Plains; Technical Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Fitzpatrick, F.A.; Waite, I.R. Revised Methods for Characterizing Stream Habitat in the National Water-Quality Assessment Program; Technical Report; Geological Survey (U.S.): Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Leopold, L.B.; Wolman, M.G.; Miller, J.P. Fluvial Processes in Geomorphology; Dover Publications, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, N.D.; McMahon, T.A.; Finlayson, B.L.; Gippel, C.J.; Nathan, R.J. Stream Hydrology: An Introduction for Ecologists, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gaines, R.A.; Priestas, A.M. Particle Size Distribution of Bed Sediments along the Mississippi River, Grafton, Illinois, to Head of Passes, Louisiana, November 2013; Technical Report 7; US Army Corps of Engineers: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lecher, K. (Ed.) Taschenbuch der Wasserwirtschaft, 9th ed.; Springer-Vieweg: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.; Sutcliffe, J. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.E. A Method of Determining the Daily Discharge of Rivers if Variable Slope; Technical Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1916.
- Perumal, M.; Shrestha, K.B.; Chaube, U.C. Reproduction of Hysteresis in Rating Curves. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 130, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakwan, M. Spreadsheet-based modelling of hysteresis-affected curves. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
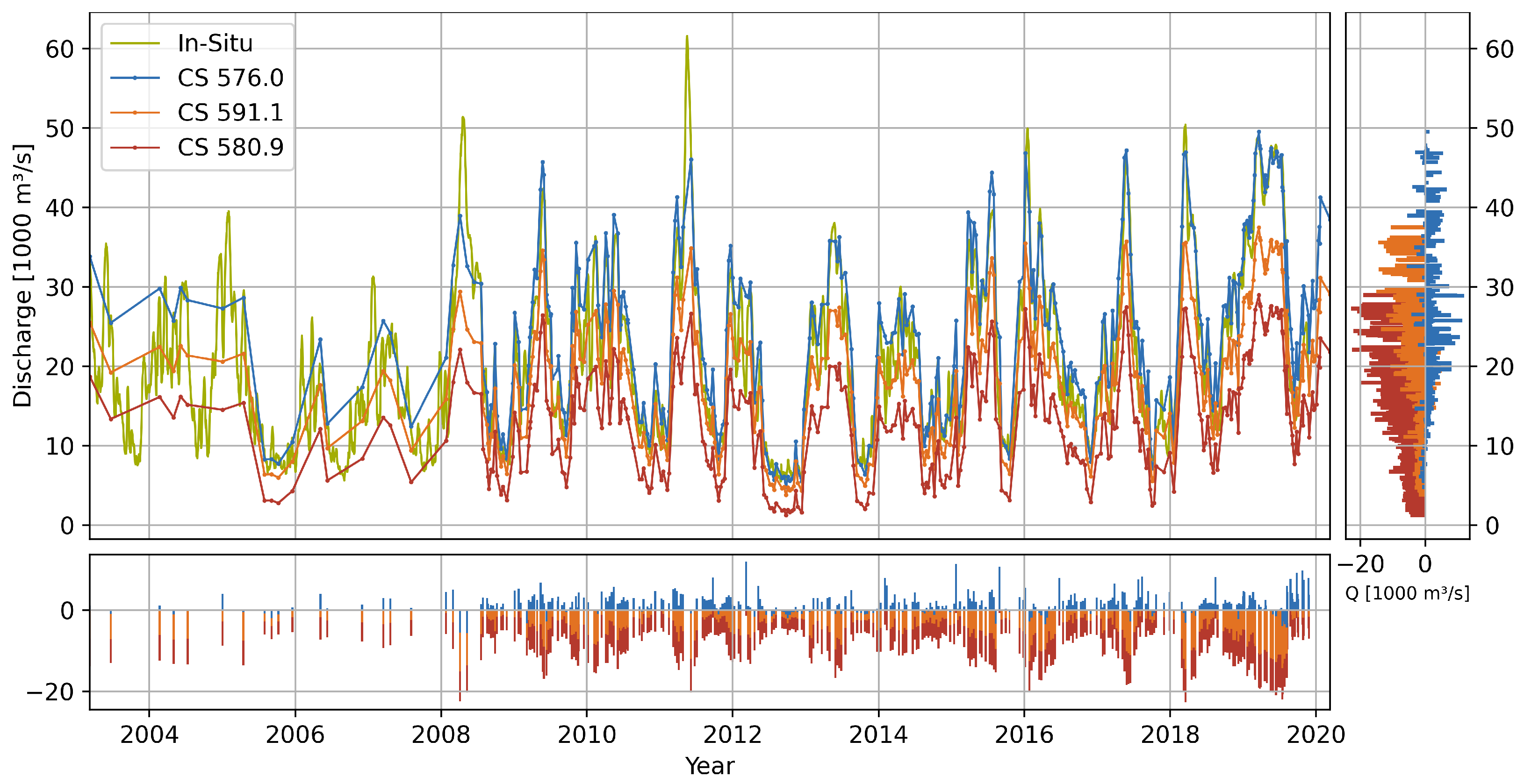
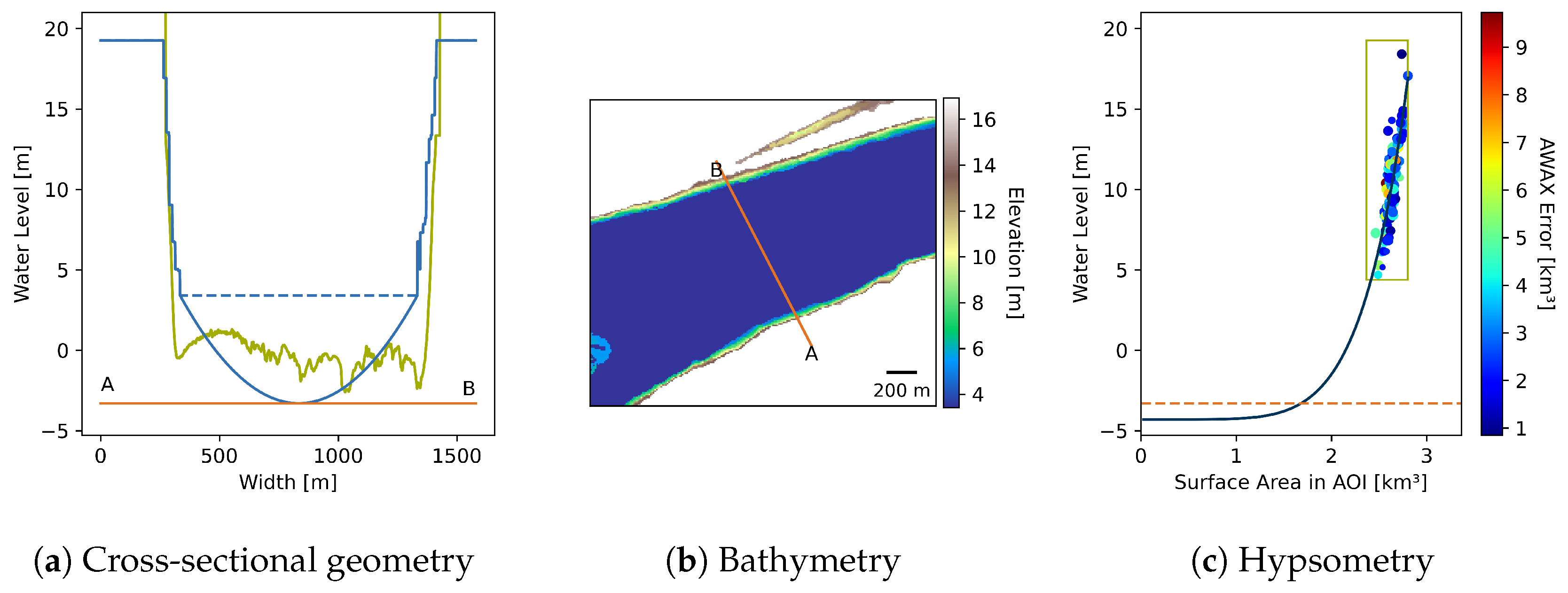
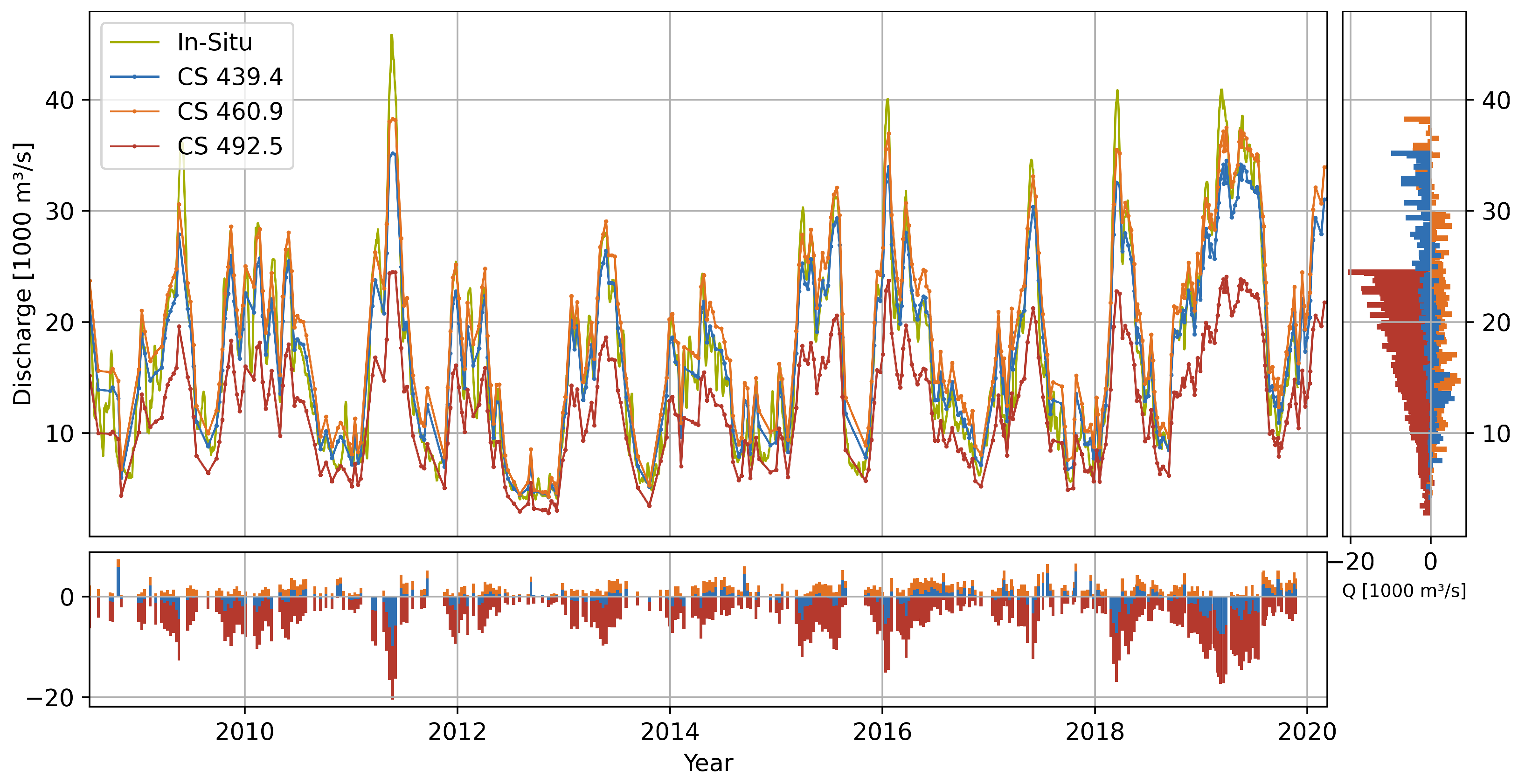
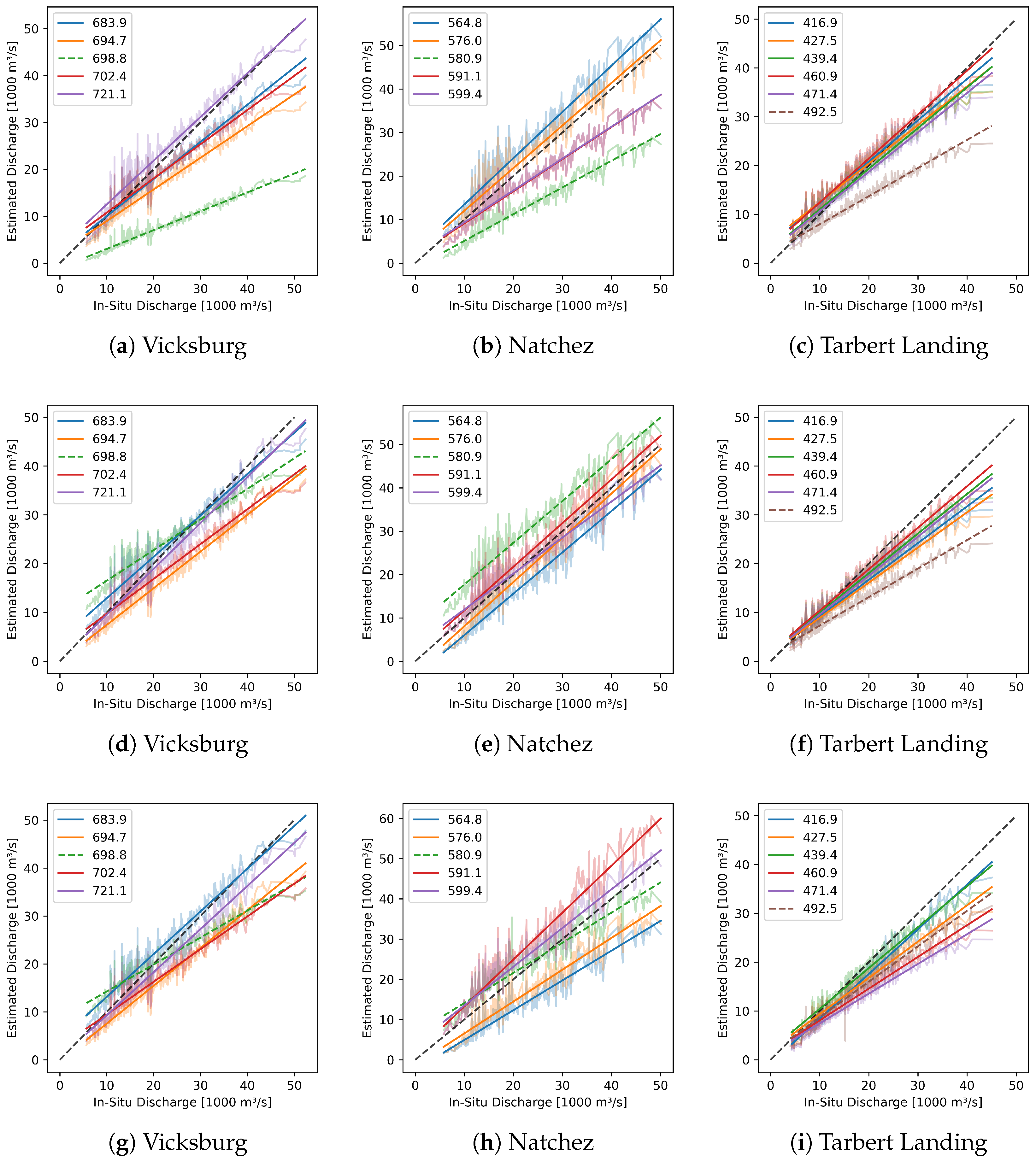
| Station | Gauge | Distance | # | Offset | RMSE | NRMSE | Outliers | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (DAHITI ID) | [km] | [m] | [%] | ||||||
| S1 (13257) | Greenville • | 28.08 | ↓ | 13 | 2.35 | 0.35 | 0.99 | 0.994 | 40 |
| S2 (13256) | 11.69 | ↓ | 14 | 1.04 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.999 | 40 | |
| J1 (10971) | 24.29 | ↑ | 282 | −1.85 | 0.68 | 2.11 | 0.965 | 40 | |
| E1 (13260) | 47.97 | ↑ | 42 | −3.68 | 0.73 | 2.34 | 0.951 | 40 | |
| E2 (13258) | 58.16 | ↑ | 36 | −4.37 | 0.39 | 1.24 | 0.985 | 40 | |
| S3 (13255) | Vicksburg ∘ | 66.64 | ↓ | 12 | 3.89 | 0.37 | 1.38 | 0.991 | 28 |
| S4 (13254) | 42.86 | ↓ | 14 | 2.67 | 0.53 | 2.01 | 0.969 | 28 | |
| E3 (11193) | 1.70 | ↑ | 46 | −0.17 | 1.13 | 5.44 | 0.901 | 28 | |
| S5 (13251) | Natchez ∘ | 39.08 | ↓ | 13 | 2.07 | 0.43 | 2.13 | 0.976 | 24 |
| E4 (10766) | 0.70 | ↓ | 34 | 0.19 | 0.47 | 2.86 | 0.978 | 24 | |
| S6 (13250) | 28.28 | ↑ | 14 | −1.66 | 0.51 | 2.60 | 0.976 | 24 | |
| E5 (13030) | Knox Landing • | 31.57 | ↓ | 50 | 1.18 | 0.44 | 3.98 | 0.986 | 50 |
| E6 (13029) | 17.38 | ↓ | 53 | 0.67 | 0.79 | 7.03 | 0.948 | 50 | |
| S7 (13249) | Red River Landing • | 11.40 | ↑ | 10 | −0.29 | 0.22 | 1.49 | 0.995 | 42 |
| J2 (2065) | 31.99 | ↑ | 299 | −1.50 | 0.50 | 4.23 | 0.981 | 42 | |
| J3 (11416) | St. Francisville • | 27.67 | ↓ | 347 | 1.32 | 0.49 | 5.48 | 0.979 | 9 |
| S8 (13246) | 21.77 | ↑ | 11 | −0.78 | 0.20 | 1.71 | 0.997 | 9 | |
| S9 (13248) | Baton Rouge ∘ | 15.39 | ↓ | 7 | 1.22 | 0.21 | 1.78 | 0.989 | 39 |
| S10 (11460) | 11.29 | ↓ | 29 | 0.73 | 0.14 | 1.80 | 0.998 | 39 | |
| S11 (13247) | 5.10 | ↑ | 8 | 0.07 | 0.53 | 5.08 | 0.970 | 39 |
| VS: | S1 | S2 | J1 | E1 | E2 | S3 | S4 | E3 | S5 | E4 | S6 | E5 | E6 | S7 | J2 | J3 | S8 | S9 | S10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [mm]: | 27 | 26 | 20 | 51 | 51 | 21 | 21 | 48 | 21 | 68 | 18 | 42 | 42 | 23 | 18 | 18 | 20 | 23 | 36 |
| Parameters | Discharge Validation | Synchronization | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | I | A | R | NSE | NRMSE | RMSE | Pairs | ||||||
| [] | [%] | [%] | [m] | [m/s] | [%] | [m/s] | [Days] | ||||||
| 683.9 | 51 | 50.00 | 92.72 | 109.31 | 2.70 | −2130.80 | 0.873 | 17.34 | 3827 | 0.974 | 239 | 0.681 | 5.00 |
| 694.7 | 51 | 43.48 | 98.14 | 104.40 | 0.97 | −4321.02 | 0.658 | 28.43 | 6275 | 0.976 | 239 | 0.704 | 5.00 |
| 698.8 | 71 | 38.46 | 60.72 | 60.96 | 20.78 | −13457.17 | −1.112 | 70.69 | 15604 | 0.960 | 239 | 0.634 | 5.00 |
| 702.4 | 71 | 38.46 | 102.47 | 105.63 | 3.84 | −1938.45 | 0.844 | 19.24 | 4246 | 0.978 | 239 | 0.748 | 5.00 |
| 721.1 | 71 | 50.00 | 97.38 | 161.45 | 0.37 | 1471.94 | 0.929 | 12.96 | 2861 | 0.975 | 239 | 0.720 | 5.00 |
| Parameters | Discharge Validation | Synchronization | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | I | A | R | NSE | NRMSE | RMSE | Pairs | ||||||
| [] | [%] | [%] | [m] | [m/s] | [%] | [m/s] | [Days] | ||||||
| 564.8 | 76 | 50.00 | 125.53 | 140.19 | −2.43 | 4094.80 | 0.785 | 21.92 | 5059 | 0.963 | 232 | 0.829 | 5.14 |
| 576.0 | 76 | 50.00 | 99.43 | 118.78 | −0.86 | 1625.15 | 0.921 | 13.26 | 3060 | 0.966 | 232 | 0.572 | 5.14 |
| 580.9 | 76 | 50.00 | 59.14 | 83.75 | 11.90 | −9632.32 | −0.002 | 47.27 | 10912 | 0.956 | 232 | 0.714 | 5.14 |
| 591.1 | 41 | 50.00 | 76.13 | 111.05 | 1.54 | −3714.84 | 0.745 | 23.83 | 5500 | 0.966 | 232 | 0.715 | 5.14 |
| 599.4 | 41 | 50.00 | 87.92 | 104.37 | 7.10 | −3516.56 | 0.754 | 23.42 | 5405 | 0.967 | 232 | 0.655 | 5.14 |
| Parameters | Discharge Validation | Synchronization | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | I | A | R | NSE | NRMSE | RMSE | Pairs | ||||||
| [] | [%] | [%] | [m] | [m/s] | [%] | [m/s] | [Days] | ||||||
| 416.9 | 39 | 50.00 | 115.52 | 117.83 | 6.41 | 1191.17 | 0.933 | 12.12 | 2226 | 0.981 | 148 | 0.899 | 4.12 |
| 427.5 | 39 | 43.48 | 116.25 | 117.48 | −0.71 | 1188.82 | 0.924 | 12.97 | 2381 | 0.982 | 148 | 0.847 | 4.12 |
| 439.4 | 39 | 50.00 | 103.66 | 100.79 | 2.69 | −109.32 | 0.946 | 10.95 | 2011 | 0.978 | 148 | 0.818 | 4.12 |
| 460.9 | 72 | 43.48 | 107.07 | 109.58 | 2.58 | 1541.46 | 0.925 | 12.86 | 2361 | 0.980 | 147 | 0.712 | 4.00 |
| 471.4 | 72 | 43.48 | 102.30 | 112.37 | 3.66 | −555.25 | 0.926 | 12.76 | 2344 | 0.979 | 147 | 0.794 | 4.00 |
| 492.5 | 31 | 43.48 | 99.76 | 101.60 | −0.70 | −4914.37 | 0.389 | 36.73 | 6745 | 0.980 | 136 | 0.582 | 4.38 |
| CS | Estimated | Substitute | Significant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | A and P | I, A, and P | Parameter | ||
| NRMSE[%] | NRMSE[%] | NRMSE[%] | NRMSE[%] | ||
| 721.1 | 12.96 | −1.02 | −2.13 | +0.65 | Roughness |
| 702.4 | 19.24 | +3.19 | +3.97 | +7.24 | Roughness |
| 698.8 | 70.69 | +5.03 | −49.11 | −47.87 | Bathymetry |
| 694.7 | 28.43 | −2.72 | +0.30 | −2.31 | Roughness |
| 683.9 | 17.34 | −2.58 | −4.90 | −3.79 | Roughness |
| 599.4 | 23.42 | −9.76 | −11.25 | −6.09 | All |
| 591.1 | 23.83 | −9.96 | −10.69 | +4.24 | Roughness |
| 580.9 | 47.27 | +13.40 | −14.32 | −30.78 | Bathymetry |
| 576.0 | 13.26 | +8.42 | −0.27 | +16.95 | Roughness |
| 564.8 | 21.92 | −6.60 | +0.29 | +17.76 | Roughness |
| 492.5 | 36.73 | −14.84 | +2.46 | −12.23 | Gradient |
| 471.4 | 12.76 | +19.92 | +3.84 | +24.11 | Roughness |
| 460.9 | 12.86 | +9.80 | -1.51 | +18.72 | Roughness |
| 439.4 | 10.95 | −0.47 | +3.49 | +1.03 | Roughness |
| 427.5 | 12.97 | +1.27 | +10.77 | +7.67 | Roughness |
| 416.9 | 12.12 | +1.47 | +8.50 | +3.06 | Roughness |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scherer, D.; Schwatke, C.; Dettmering, D.; Seitz, F. Long-Term Discharge Estimation for the Lower Mississippi River Using Satellite Altimetry and Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12172693
Scherer D, Schwatke C, Dettmering D, Seitz F. Long-Term Discharge Estimation for the Lower Mississippi River Using Satellite Altimetry and Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(17):2693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12172693
Chicago/Turabian StyleScherer, Daniel, Christian Schwatke, Denise Dettmering, and Florian Seitz. 2020. "Long-Term Discharge Estimation for the Lower Mississippi River Using Satellite Altimetry and Remote Sensing Images" Remote Sensing 12, no. 17: 2693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12172693
APA StyleScherer, D., Schwatke, C., Dettmering, D., & Seitz, F. (2020). Long-Term Discharge Estimation for the Lower Mississippi River Using Satellite Altimetry and Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 12(17), 2693. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12172693