High-Rankness Regularized Semi-Supervised Deep Metric Learning for Remote Sensing Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A new semi-supervised deep metric learning model is presented to characterize vast RS image collections in an end-to-end manner, using a reduced amount of annotated data. Specifically, the proposed method has been designed to learn (based on CNN models) a metric space that jointly preserves the discrimination capability for labelled and unlabelled RS scenes.
- A new loss function, based on the normalized softmax loss with margin and the high-rankness regularization, is proposed to enhance the feature learning ability under a semi-supervised assumption. Additionally, an optimization mechanism is also defined to produce consistent features within each training epoch.
- The extensive experimental evaluation (based on three different RS applications) conducted in this paper compares the performance of the proposed method against different state-of-the-art methods using several datasets. The codes of this paper are publicly available to the research community (https://github.com/jiankang1991).
2. Related Work
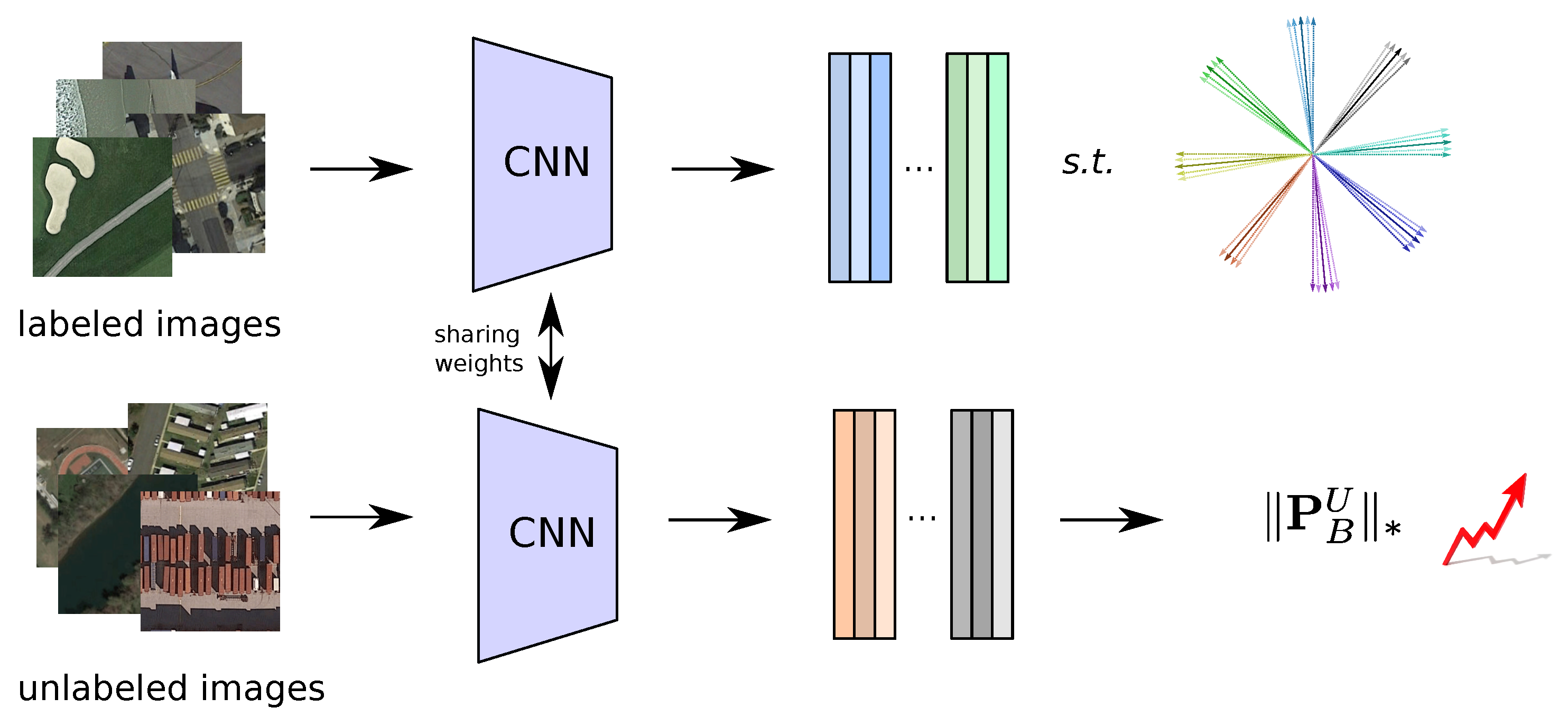
3. Proposed Semi-Supervised Deep Metric Learning for Remote Sensing
3.1. Normalized Softmax Loss with Margin
3.2. High-Rankness Regularization
| Algorithm 1 Optimization for HR-S2DML |
| Require:, , and |
| 1: Initialize , m, and D |
| 2: for to do |
| 3: Sample mini-batches from training and test sets, and . |
| 4: and based on and , respectively. |
| 5: Aggregate the two loss terms into a joint loss . |
| 6: Calculate the gradients and do back-propagation. |
| 7: end for |
| Ensure: |
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset Description
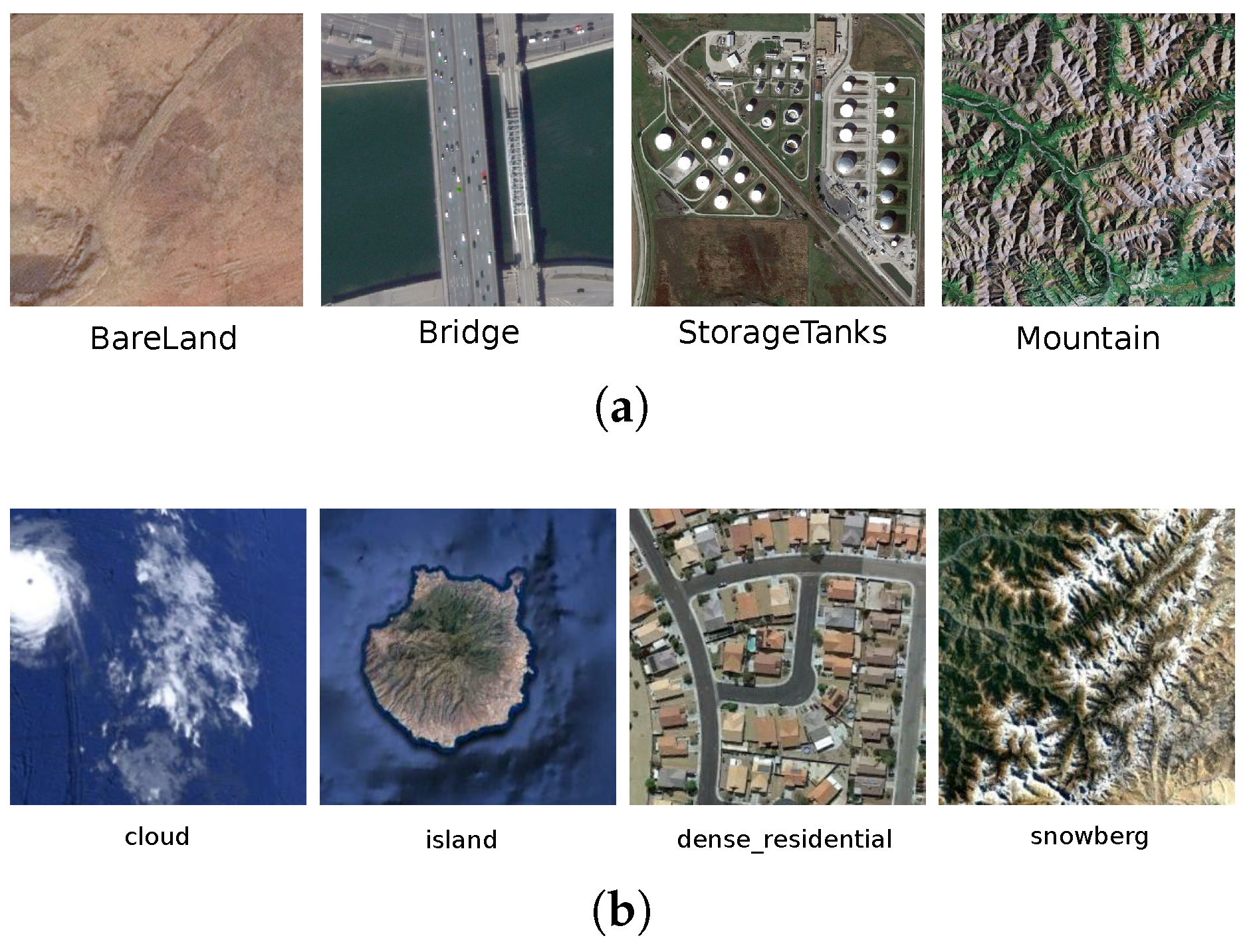
- Aerial Image Dataset (AID) [69]: This dataset has been specifically designed for RS image classification and retrieval tasks. Specifically, it contains a total of 10,000 images belonging to the following 30 semantic classes: airport, bare land, baseball field, beach, bridge, center, church, commercial, dense residential, desert, farmland, forest, industrial, meadow, medium residential, mountain, park, parking, playground, pond, port, railway station, resort, river, school, sparse residential, square, stadium, storage tanks, and viaduct. Figure 3a shows some of its images for illustrative purposes. All the images have a size of pixels in the RGB space, with a spatial resolution ranging from 8 to 0.5 meters, and each semantic class contains from 220 to 420 images. This collection is available online (AID: https://captain-whu.github.io/AID/).
- NWPU-RESISC45 [19]: This archive is a large-scale RS dataset, which is made of 31,500 images which are uniformly distributed in the following 45 semantic classes: airplane, airport, baseball diamond, basketball court, beach, bridge, chaparral, church, circular farmland, cloud, commercial area, dense residential, desert, forest, freeway, golf course, ground track field, harbor, industrial area, intersection, island, lake, meadow, medium residential, mobile home park, mountain, overpass, palace, parking lot, railway, railway station, rectangular farmland, river, roundabout, runway, sea ice, ship, snow-berg, sparse residential, stadium, storage tank, tennis court, terrace, thermal power station, and wetland. Figure 3b illustrates some examples of this collection. All the images have a size of pixels in the RGB space, with a spatial resolution varying from 30 to 0.2 m. This dataset is also available online (NWPU-RESISC45: http://www.escience.cn/people/JunweiHan/NWPU-RESISC45.html).
4.2. Evaluation Tasks
4.2.1. KNN Classification
4.2.2. Clustering
4.2.3. Image Retrieval
4.3. Experimental Setup
4.4. Experimental Results
4.4.1. KNN Classification
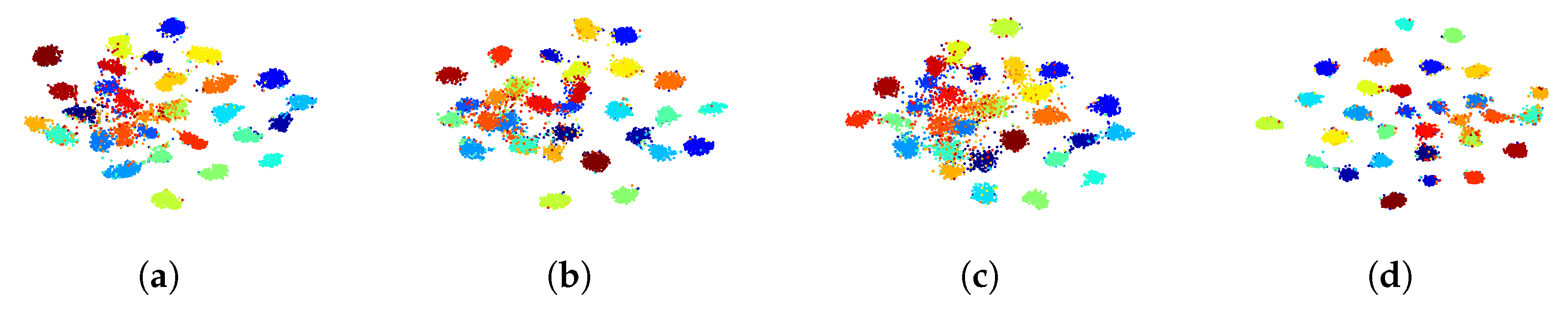
4.4.2. Clustering
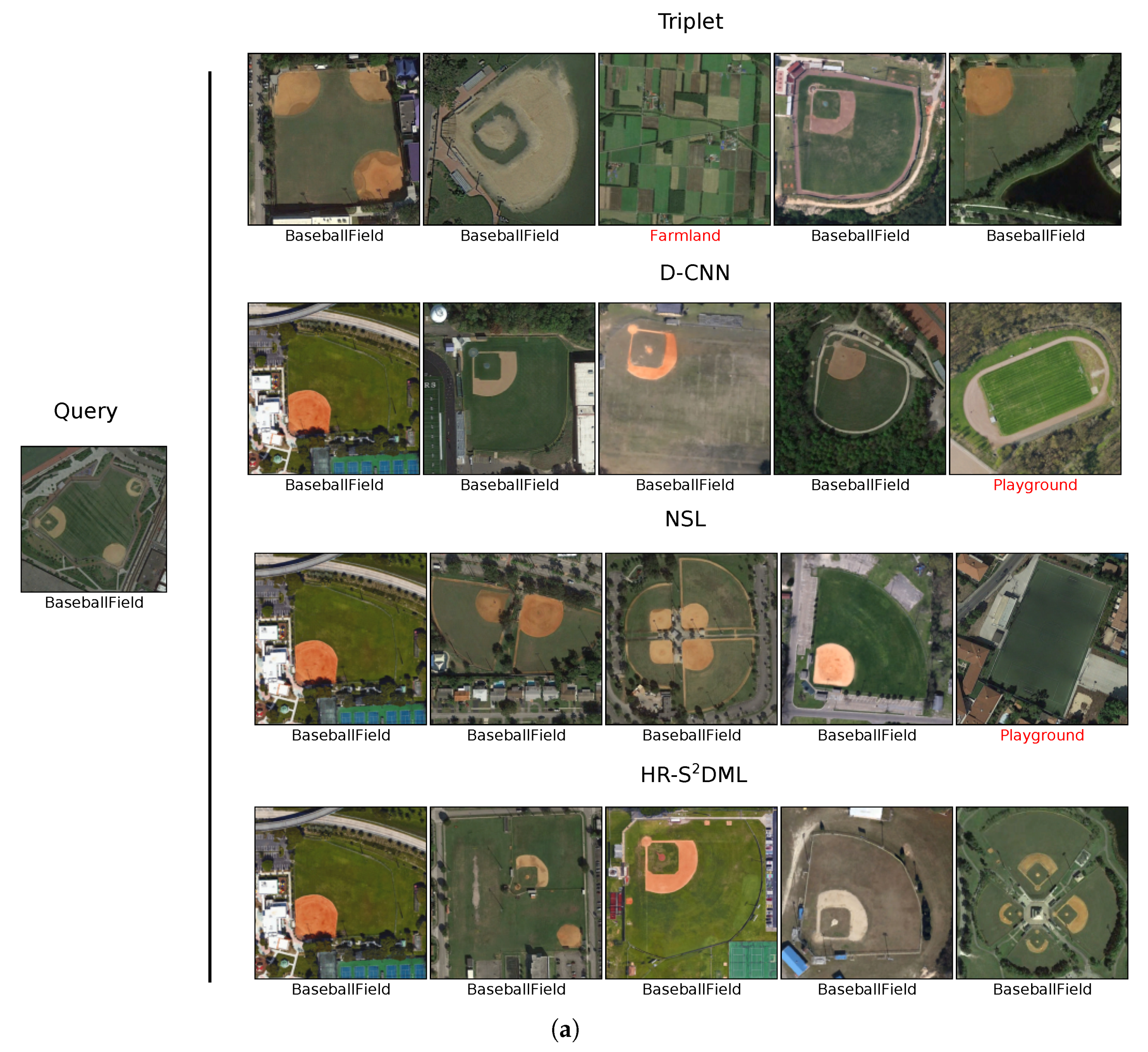
4.4.3. Image Retrieval
4.4.4. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, B.; Zhao, B.; Song, Y. Urban land-use mapping using a deep convolutional neural network with high spatial resolution multispectral remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantakumar, L.N.; Kumar, S.; Schneider, K. SUSM: A scenario-based urban growth simulation model using remote sensing data. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, J.; Qiu, C.; Shi, Y.; Kang, J.; Mou, L.; Bagheri, H.; Haberle, M.; Hua, Y.; Huang, R.; et al. So2Sat LCZ42: A Benchmark Dataset for Global Local Climate Zones Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Plaza, A.; Plaza, J.; Pla, F. Hyperspectral unmixing based on dual-depth sparse probabilistic latent semantic analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6344–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Jiao, L. Large-Scale Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Based on Semi-Supervised Adversarial Hashing. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Demir, B.; Pla, F.; Plaza, A. Unsupervised Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Using Probabilistic Latent Semantic Hashing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, H. End-to-end change detection for high resolution satellite images using improved unet++. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S.; Zhan, Z. Change Detection Based on Artificial Intelligence: State-of-the-Art and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, M.; Kang, J.; Hong, D.; Xu, J.; Zhu, X. Estimation of pmx concentrations from landsat 8 oli images based on a multilayer perceptron neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Pla, F.; Plaza, A. Endmember Extraction From Hyperspectral Imagery Based on Probabilistic Tensor Moments. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Su, Y.; Hu, T.; Chen, J.; Guo, Q. An Object-Based Strategy for Improving the Accuracy of Spatiotemporal Satellite Imagery Fusion for Vegetation-Mapping Applications. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Pla, F.; Plaza, A. Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3 Intersensor Vegetation Estimation via Constrained Topic Modeling. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Körner, M.; Wang, Y.; Taubenböck, H.; Zhu, X.X. Building instance classification using street view images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.J.; Wang, Y.; Werner, M.; Kang, J.; Zhu, X.X. Model Fusion for Building Type Classification from Aerial and Street View Images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratasanu, D.; Nedelcu, I.; Datcu, M. Bridging the semantic gap for satellite image annotation and automatic mapping applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, B.; Ranjan, R.; Zomaya, A.; Jie, W. Remote sensing big data computing: Challenges and opportunities. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2015, 51, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Latorre-Carmona, P.; Pla, F. Single-frame super-resolution in remote sensing: A practical overview. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 314–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Z.; Peng, D.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Liu, B.; Zou, L.; Li, J.; Plaza, A. Remotely sensed big data: Evolution in model development for information extraction [point of view]. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 2294–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Lu, X. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Chen, C.; Tian, L.; Du, Q. Fusing local and global features for high-resolution scene classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Tsou, J.Y.; Liu, D.; Lu, X. Assessing texture features to classify coastal wetland vegetation from high spatial resolution imagery using completed local binary patterns (CLBP). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, C.; Tan, Y.; Shang, K.; Tian, J. Unsupervised multilayer feature learning for satellite image scene classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Haut, J.M.; Paoletti, M.E.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A.; Pla, F. Multimodal probabilistic latent semantic analysis for sentinel-1 and sentinel-2 image fusion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Xia, G.S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. Transferring deep convolutional neural networks for the scene classification of high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14680–14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hang, R.; Song, H.; Li, Z. Learning multiscale deep features for high-resolution satellite image scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.Y.; Xia, G.S.; Hu, F.; Zhong, Y.; Datcu, M.; Zhang, L. Exploiting deep features for remote sensing image retrieval: A systematic investigation. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Diao, W.; Fu, K. FMSSD: Feature-Merged Single-Shot Detection for Multiscale Objects in Large-Scale Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 3377–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, C.; Jia, X.; Ghamisi, P. Deep Feature Extraction and Classification of Hyperspectral Images Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6232–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, B. Deep learning for remote sensing data: A technical tutorial on the state of the art. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, W.; Cui, Y.; Cai, M. An End-to-End Local-Global-Fusion Feature Extraction Network for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires de Lima, R.; Marfurt, K. Convolutional Neural Network for Remote-Sensing Scene Classification: Transfer Learning Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Yang, C.; Yao, X.; Guo, L.; Han, J. When deep learning meets metric learning: Remote sensing image scene classification via learning discriminative CNNs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2811–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhu, R.; Mo, N.; Liu, Y. Cross-Domain Distance Metric Learning Framework With Limited Target Samples for Scene Classification of Aerial Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3840–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.S.; Nam, W.J.; Lee, S.W. Coarse-to-Fine Deep Metric Learning for Remote Sensing Image Retrieval. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Plaza, A.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sun, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhu, Y. Big data for remote sensing: Challenges and opportunities. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, B.; Hong, D.; Hang, R.; Ghamisi, P.; Kang, X.; Chanussot, J.; Benediktsson, J.A. Feature Extraction for Hyperspectral Imagery: The Evolution from Shallow to Deep. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.02822. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Newsam, S. Spatial pyramid co-occurrence for image classification. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Barcelona, Spain, 6 November 2011; pp. 1465–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Itti, L. Saliency and gist features for target detection in satellite images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 2017–2029. [Google Scholar]
- Aptoula, E. Remote sensing image retrieval with global morphological texture descriptors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3023–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, B.; Ghamisi, P.; Ulfarsson, M. Hyperspectral Feature Extraction Using Sparse and Smooth Low-Rank Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheriyadat, A.M. Unsupervised feature learning for aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Haut, J.M.; Paoletti, M.E.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A.; Pla, F. Remote Sensing Image Fusion Using Hierarchical Multimodal Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4982–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Du, P.; Samat, A.; Meng, Y.; Che, M. Mid-level feature representation via sparse autoencoder for remotely sensed scene classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, Z.; Han, J.; Yao, X.; Guo, L. Exploring hierarchical convolutional features for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6712–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Xia, J.; Du, P.; Lin, C.; Samat, A. Integrating multilayer features of convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5653–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piramanayagam, S.; Saber, E.; Schwartzkopf, W.; Koehler, F.W. Supervised classification of multisensor remotely sensed images using a deep learning framework. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, K.; Penatti, O.A.; dos Santos, J.A. Towards better exploiting convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penatti, O.A.; Nogueira, K.; dos Santos, J.A. Do deep features generalize from everyday objects to remote sensing and aerial scenes domains? In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Boston, MA, USA, 7 June 2015; pp. 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Lu, J.; Tan, Y.P. Deep transfer metric learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7 June 2015; pp. 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Hadsell, R.; Chopra, S.; LeCun, Y. Dimensionality reduction by learning an invariant mapping. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), New York, NY, USA, 17 June 2006; Volume 2, pp. 1735–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Qiu, G. Enhancing remote sensing image retrieval with triplet deep metric learning network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.05818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Ye, Z.; Tong, X.; Ghamisi, P.; Plaza, A. Deep Metric Learning Based on Scalable Neighborhood Components for Remote Sensing Scene Characterization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Efros, A.A.; Yu, S.X. Improving generalization via scalable neighborhood component analysis. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8 September 2018; pp. 685–701. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.; Yokoya, N.; Xia, G.S.; Chanussot, J.; Zhu, X.X. X-ModalNet: A Semi-Supervised Deep Cross-Modal Network for Classification of Remote Sensing Data. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Duan, P.; Liu, S.; Plaza, A. Deep Unsupervised Embedding for Remotely Sensed Images based on Spatially Augmented Momentum Contrast. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Krishnan, D.; Isola, P. Contrastive multiview coding. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.05849. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Luo, R.; Shang, F.; Meng, X.; Gou, S.; Hou, B. Semi-Supervised Deep Metric Learning Networks for Classification of Polarimetric SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Xue, N.; Zafeiriou, S. Arcface: Additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16 June 2019; pp. 4690–4699. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.; Wang, S.; Zhuo, J.; Li, L.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Q. Towards Discriminability and Diversity: Batch Nuclear-norm Maximization under Label Insufficient Situations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12237. [Google Scholar]
- Fazel, S.M. Matrix Rank Minimization with Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Wang, Y.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X.X. Object-based multipass InSAR via robust low-rank tensor decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3062–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, S.; Xi, F.; Liu, Z. Interferometric Phase Retrieval for Multimode InSAR via Sparse Recovery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Hong, D.; Liu, J.; Baier, G.; Yokoya, N.; Demir, B. Learning Convolutional Sparse Coding on Complex Domain for Interferometric Phase Restoration. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.X. Multipass SAR Interferometry Based on Total Variation Regularized Robust Low Rank Tensor Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 5354–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X. Reweighted Tensor Factorization Method for SAR Narrowband and Wideband Interference Mitigation Using Smoothing Multiview Tensor Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 3298–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.S.; Hu, J.; Hu, F.; Shi, B.; Bai, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X. AID: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, C.D.; Raghavan, P.; Schütze, H. Introduction to Information Retrieval; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, CA, USA, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 8024–8035. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, A.; Wu, H.Y. Classification is a Strong Baseline for Deep Metric Learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.12649. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Wong, Y.; Kankanhalli, M.; Zhao, Q. G-Softmax: Improving Intraclass Compactness and Interclass Separability of Features. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
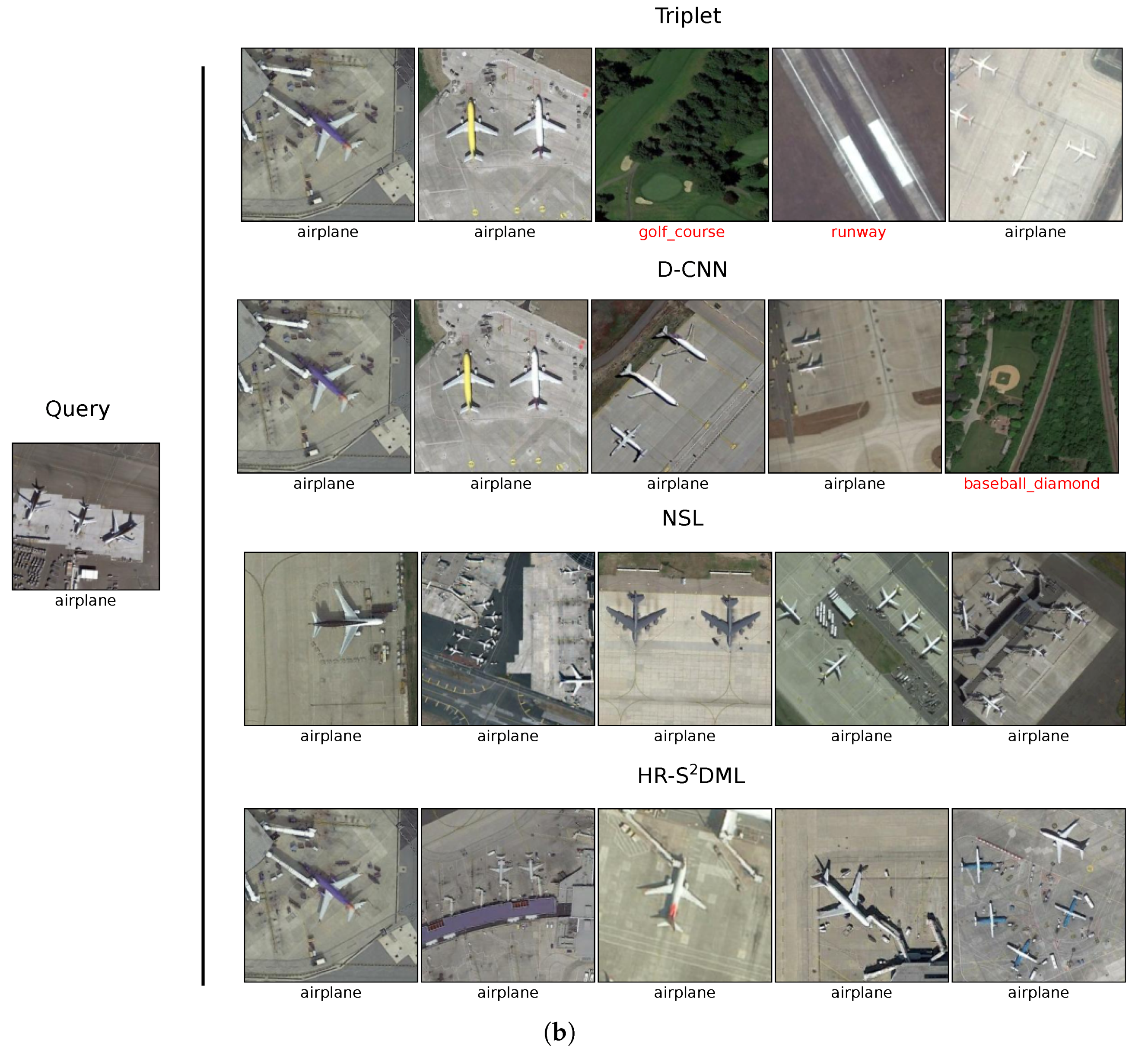



| AID | NWPU-RESISC45 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | |
| D-CNN | 80.03 | 86.62 | 90.22 | 91.61 | 80.08 | 86.06 | 89.21 | 90.75 |
| Triplet | 79.46 | 85.72 | 89.47 | 91.24 | 78.08 | 84.43 | 87.43 | 89.58 |
| NSL | 73.92 | 82.71 | 86.78 | 89.55 | 73.92 | 82.71 | 86.78 | 89.55 |
| HR-S2DML | ||||||||
| AID | NWPU-RESISC45 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | |
| D-CNN | 72.90 | 79.87 | 82.95 | 86.04 | 72.73 | 79.11 | 81.62 | 84.24 |
| Triplet | 74.90 | 80.97 | 84.30 | 85.68 | 73.06 | 78.57 | 81.05 | 83.41 |
| NSL | 67.31 | 75.66 | 79.77 | 83.72 | 65.94 | 73.44 | 77.98 | 80.77 |
| HR-SDML | ||||||||
| AID | NWPU-RESISC45 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | |
| D-CNN | 73.87 | 82.26 | 85.91 | 86.24 | 73.67 | 81.66 | 84.38 | 86.30 |
| Triplet | 77.93 | 82.38 | 85.73 | 90.08 | 72.82 | 80.87 | 82.89 | 85.60 |
| NSL | 66.61 | 78.63 | 80.59 | 88.48 | 56.80 | 62.16 | 67.12 | 69.36 |
| HR-SDML | ||||||||
| AID | NWPU-RESISC45 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | |
| D-CNN | 79.93 | 86.93 | 90.36 | 92.24 | 81.86 | 87.56 | 91.05 | 92.37 |
| Triplet | 77.11 | 84.90 | 88.46 | 90.69 | 77.33 | 83.85 | 87.15 | 89.18 |
| NSL | 69.86 | 79.92 | 84.74 | 88.40 | 69.86 | 79.92 | 84.74 | 88.40 |
| HR-SDML | ||||||||
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90.44 | 90.58 | 91.34 | 91.38 | 91.40 | |
| 90.90 | 91.01 | 91.59 | 92.11 | 91.40 | |
| 90.70 | 91.38 | 91.21 | 91.27 | 91.27 | |
| 91.11 | 90.88 | 90.81 | 91.40 | 91.04 | |
| 89.85 | 90.10 | 90.08 | 89.95 | 90.38 |
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 88.50 | 89.00 | 89.26 | 90.05 | 89.71 | |
| 89.29 | 89.77 | 89.95 | 89.53 | 89.54 | |
| 89.71 | 89.55 | 89.40 | 89.06 | 88.70 | |
| 89.33 | 89.21 | 89.41 | 89.04 | 88.95 | |
| 88.59 | 88.79 | 88.70 | 88.60 | 88.52 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.; Fernández-Beltrán, R.; Ye, Z.; Tong, X.; Ghamisi, P.; Plaza, A. High-Rankness Regularized Semi-Supervised Deep Metric Learning for Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162603
Kang J, Fernández-Beltrán R, Ye Z, Tong X, Ghamisi P, Plaza A. High-Rankness Regularized Semi-Supervised Deep Metric Learning for Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(16):2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162603
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jian, Rubén Fernández-Beltrán, Zhen Ye, Xiaohua Tong, Pedram Ghamisi, and Antonio Plaza. 2020. "High-Rankness Regularized Semi-Supervised Deep Metric Learning for Remote Sensing Imagery" Remote Sensing 12, no. 16: 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162603
APA StyleKang, J., Fernández-Beltrán, R., Ye, Z., Tong, X., Ghamisi, P., & Plaza, A. (2020). High-Rankness Regularized Semi-Supervised Deep Metric Learning for Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sensing, 12(16), 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12162603








