Abstract
Urbanization and air pollution are major anthropogenic impacts on Earth’s environment, weather, and climate. Each has been studied extensively, but their interactions have not. Urbanization leads to a dramatic variation in the spatial distribution of air pollution (fine particles) by altering surface properties and boundary-layer micrometeorology, but it remains unclear, especially between the centers and suburbs of metropolitan regions. Here, we investigated the spatial variation, or inhomogeneity, of air quality in urban and rural areas of 35 major metropolitan regions across China using four different long-term observational datasets from both ground-based and space-borne observations during the period 2001–2015. In general, air pollution in summer in urban areas is more serious than in rural areas. However, it is more homogeneously polluted, and also more severely polluted in winter than that in summer. Four factors are found to play roles in the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution between urban and rural areas and their seasonal differences: (1) the urban–rural difference in emissions in summer is slightly larger than in winter; (2) urban structures have a more obvious association with the spatial distribution of aerosols in summer; (3) the wind speed, topography, and different reductions in the planetary boundary layer height from clean to polluted conditions have different effects on the density of pollutants in different seasons; and (4) relative humidity can play an important role in affecting the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution despite the large uncertainties.
1. Introduction
The worldwide trend in urbanization has been ongoing for decades, altering landscapes and modifying the air quality. Urbanization is a key contributor to emissions of greenhouse gases and aerosol particles and changes in land cover, which has a significant effect on regional and temporal climate changes [1,2,3,4]. Although urbanization has brought about rapid economic growth, it has adverse impacts on air quality and human health [5,6,7,8,9]. Rapid urbanization can lead to the destruction of cultivated land, overcrowding, complex infrastructures, and extreme weather disasters [10].
Reduced vegetation in urban areas, urban construction materials and structures, and anthropogenic heat emissions are among the major factors leading to the urban heat island (UHI) [11,12,13]. Urban regions are generally warmer than their rural surroundings because of the surfaces changing from permeable and moist to impermeable and dry. The effect is proportional to the urban size and varies considerably due to the great differences in numerous influential factors [14,15]. The UHI can alter surface evaporation, atmospheric circulations, the surface absorption rate of solar radiation, and surface properties. These factors can either delay or enhance urban precipitation and significantly change the spatial pattern of precipitation between urban and rural areas [16,17].
Air pollution is closely tied to such factors as pollutant emissions, atmospheric transport, atmospheric chemistry, and meteorological conditions. Aerosols reduce the amount of solar radiation reaching the ground and influence horizontal visibility due to their scattering and absorption. A variety of aerosols such as sulfates, nitrates, and ammonium are strong scattering aerosols, while black carbon and dust are light-absorbing aerosols that can change the vertical temperature gradient and even generate inversion layers [18,19]. Consequently, the atmospheric stability and planetary boundary layer (PBL) development are affected [20,21,22,23,24]. Urban areas with abundant particulate pollutants, an important source of aerosol emissions, have a significant effect on radiation and convection [25]. Severe air pollution episodes tend to occur under stable meteorological conditions, which favor the accumulation of primary and secondary pollutants in the atmosphere near the surface. The key player in this respect is the PBL, which is the lowest atmospheric layer immediately affected by the land surface [21].
There are significant and intricate interactions between urbanization and air pollution. Besides the strong cooling effect during the daytime, aerosols may increase longwave radiation at night due to infrared emissions. The daytime cooling effect and nighttime heating effect combine to change daytime and nighttime surface temperatures [26,27,28]. Urbanization has caused serious air pollution in urbanized regions [29], where urban characteristics may impact emissions and the spatial distribution of local-scale air pollution. For instance, numerical modeling studies have shown that increasing the urban area reduces near-surface aerosol concentrations over urban regions and increases particle concentrations at higher altitudes over the surrounding rural areas, mainly due to the urban-induced enhancement of the instability of the PBL [30]. During the past 40 years, rapid urbanization in China has generated intense anthropogenic emissions leading to severe air pollution, especially in metropolitan areas. Many urban populations in China are exposed to poor air quality that does not meet national standards, especially during wintertime [31].
Previous studies were mainly based on single data source to analyze the transfer of air pollution between rural and urban areas in China [32,33]. Given that different data sources (e.g., ground-based and space-borne observations) have different advantages and disadvantages, multiple datasets convey richer information to gain further insight and enhance the credibility of a study. Few studies have compared the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution between urban and rural areas (SIAP) in different seasons in China, which is important for analyzing the effect of air pollution on the UHI, precipitation, clouds, among others for they all have strong seasonality. Moreover, the factors affecting the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution in different seasons are still not clear.
This study employs multiple datasets generated from multiple satellite sensors and ground-based observations to analyze seasonal changes in the SIAP in 35 cities across China and the underlying factors in an attempt to understand the mechanism driving temperature differences between rural and urban areas. Section 2 introduces the study areas, datasets, and the methods for selecting the research windows and calculating the planetary boundary layer height (PBLH). Section 3 presents the different urbanization effects on the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution in summer and winter, followed by a discussion on the causes. The key findings are summarized in Section 5.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas and Data
The study areas comprise 35 medium to large cities located across China (Figure 1). Landsat data were first used to identify urban areas. Different data sources were then used to analyze the urban–rural inhomogeneity of air pollution. Finally examined were four potential factors accounting for the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution. Emission data, urban contours data, building density data, sounding data, land use data, wind speed, topography, and relative humidity (RH) data were used.
Figure 1.
Locations of the 35 cities selected as study areas.
Satellite datasets used in this study include those from the Land Satellite Thematic Mapper/Enhanced Thematic Mapper (Landsat), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer [MODIS; aerosol optical depth (AOD)], and the Cloud–Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation (CALIPSO) satellite [34]. Ground-based observation data include meteorological stations, hourly fine-particulate matter (PM2.5) concentration measurements, and daily sounding data.
The spatial resolution of Landsat data is 30m, only summertime (June, July, and August) images before 2000 or in 2000, in 2010, and in 2015 are used to extract urban impervious surfaces and outline urban contours.
Only satellite-based AOD was used here. The MODIS Multi-Angle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC) algorithm is an advanced algorithm which uses time series analyses and a combination of pixel- and image-based processing to improve the accuracies of cloud detection, aerosol retrievals, and atmospheric correction [35,36]. Its spatial and temporal resolutions are 1 km and 1 day, respectively. Linear interpolation is used to fill the missing values based on existing values when the data coverage is greater than 30%. For each city, five zones were selected based on the distance to the urban geometric center: Zone 1: 0–10 km, Zone 2: 11–20 km, Zone 3: 21–30 km, Zone 4: 31–40 km, and Zone 5: 41–50 km. The average AOD for each zone was then calculated.
The Cloud–Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP) is a two-wavelength polarization lidar that performs global profiling of aerosols and clouds in the troposphere and lower stratosphere. CALIOP is the primary instrument onboard the CALIPSO satellite, which has flown with the NASA A-train constellation of satellites since May 2006 [34].
The global emission inventory dataset called PKU-FUEL produced by Peking University was used to study emission differences between urban and rural areas. The inventory includes CO2, CO, PM2.5, PM10, BC, OC, SO2, NOx, NH3, total suspended particles, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. This global emission inventory has been developed using a bottom-up approach with a 0.1° × 0.1° (about 10 km) spatial resolution and a monthly temporal resolution, covering the period from 1960 to 2014 [37]. For each city, one urban window (0.1° × 0.1°) inside urban contour in 2000 and four rural windows (0.1° × 0.1°) that are not affected by urban expansion and outside urban contour in 2015.
Two sets of meteorological stations and stations were selected in each city: one set located in the urban area of the city and the other set located in the rural area near the city. Meteorological parameters such as visibility, surface wind speed, temperature, and precipitation were observed at three-hourly intervals at each meteorological station. Hourly concentrations were measured at each measurement site (shown in Figure S1) from the Chinese national monitoring network. Hourly PM2.5 data are published in real time by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (http://106.37.208.233:20035). The PM2.5 concentration is measured by tapered element oscillating microbalance (TEOM) or beta attenuation monitor. High correlation between the satellite-based AOD and ground-based PM2.5 observations were reported in previous studies [38,39,40]. One urban and one rural meteorological station was selected for each city. Meteorological (1100 and 1400 BJT) and PM2.5 concentration (1300 and 1400 BJT) observed at near 1330 Beijing time (BJT) were linearly interpolated to the MODIS imaging time (1330 BJT) for matching purposes. According to the evaluation standard of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China, urban concentration are classified into three levels of air quality: light pollution (), moderate pollution (), and heavy pollution (). The classification is based on 2-hour means of PM2.5 concentration, different from other standards using annual mean or 24-hour mean (e.g., the standards of WHO, US, EU).
Four sounding stations, representative of their respective regions, were selected, i.e., Shenyang, Beijing, Xi’an, and Nanjing. The high-resolution radiosonde network of the L-band sounding system, developed by the China Meteorological Administration in 2011, provides fine-resolution profiles of temperature, pressure, RH, wind speed, and wind direction twice a day at 0800 BJT and 2000 BJT. The sounding quality was strictly controlled and adequate to characterize PBL features in China [41,42]. Unless noted otherwise, 2000 BJT soundings were used in this study, given our focus on the daytime effect.
2.2. Urban Impervious Surfaces and Urban Contours
Many previous studies have used nighttime stable-light data to extract urban areas, but their low spatial resolution limits the extraction accuracy. So here, the Landsat data were used to accurately identify urban impervious surfaces and outline urban contours. The difference between the normalized difference build-up index (NDBI) and the soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI), i.e., , is used to extract urban impervious surfaces because this difference can effectively differentiate urban impervious surfaces from other land-use types [43]:
where L is the soil adjustment factor whose value is 0.5, and ρn is the nth Landsat reflectance band. Urban impervious surfaces were extracted using different thresholds ranging from 0.1 to 0.3, then urban boundaries were determined based on the urban impervious surfaces. Google Earth and a land-use map with a 1:100,000 scale from the Resource and Environment Science Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences verified the results. The physical contours of urban areas were extracted based on the difference in the underlying surfaces of urban and rural areas. Urban contours in three periods were outlined at each city, which were used to distinguish urban and rural areas. Figure 2 shows an example diagram of Nanjing.
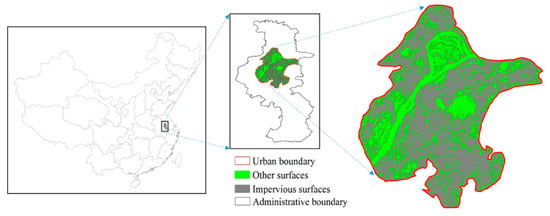
Figure 2.
Urban area of Nanjing in 2010. The red contour outlines the urban boundary. Green areas are other surfaces, for instance, water, vegetation, or soil. Gray areas are impervious surfaces.
2.3. Urban Shape
The Boyce-Clark shape index (SBC) has been used to reveal the urban morphology through comparisons with a standard shape [44]. The principle behind this index is to compare the urban shape with a standard circle, then calculate a relative shape index. This is also called the radius shape index on account of radii being involved in the algorithm, expressed as follows:
where is the length from the vantage point to the boundary, and n is the number of radii with an equal-angle difference. The vantage point of urban areas can be the central business district or the centroid of the urban contour. For example, when n is equal to 16, the angle between adjacent radii is 22.5°, and when n is equal to 32, the angle between adjacent radii is 11.25°. The minimum SBC is 0, which is the SBC of a standard circle. It represents the highest land-use efficiency and the most compact urban area. Larger SBC values generally mean lower land-use efficiencies and less compact urban areas. Urban contours of 35 cities extracted from Landsat in 2015 were used to calculate SBC here.
2.4. Research Windows for Cloud–Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation (CALIPSO)
CALIPSO data can provide vertical variation information, unlike MODIS data. Two metropolitan clusters were selected as research areas for CALIPSO: the Greater Beijing Metropolitan Area (GBMA) and the Yangtze River Delta (YRD). Both GBMA and YRD have experienced dramatic economic development and rapid urbanization over the past three decades. The GBMA includes Beijing, Tianjin, and some industrial cities in Hebei province, and the YRD region includes Shanghai, Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Zhenjiang, Yangzhou, Nanjing, and five other prosperous cities [45,46]. Each research area has one urban research window and one rural research window.
2.5. Calculation of the Planetary Boundary Layer Height
Five cities with sounding stations that are part of the China Meteorological Administration’s radiosonde network of L-band sounding systems were selected: Beijing, Shenyang, Chengdu, Xi’an, and Nanjing. Radiosonde profiles from 1 January 2013 to 31 December 2015 were analyzed. The bulk Richardson number () has been used to estimate the PBLH [41,47,48], which is also done here. The is defined as the ratio of turbulence associated with buoyancy to that induced by mechanical shear and is expressed as
where denotes the height above the ground, denotes the surface, is the acceleration due to gravity, is the virtual potential temperature, are the components of wind speed, and is the surface friction velocity. Here, can be ignored because its magnitude is small [48]. Previous theoretical and laboratory studies [49] have suggested that when is smaller than the critical value (0.25), the laminar flow becomes unstable. The lowest level at which interpolated crosses the critical value of 0.25 is thus referred to as the PBLH in this study, similar to the criterion used by others [41].
3. The Spatial Inhomogeneity of Air Pollution in Summer and Winter
3.1. Visibility Differences between Urban and Rural Areas
Figure 3a shows detailed mean visibilities of each city in urban and rural areas in summer and winter under polluted conditions. Figure 3b shows the overall mean visibilities of all cities. Only visibilities associated with RH levels less than 85% were analyzed to eliminate the influence of water vapor. Urban visibilities of less than 10 km are considered as grossly polluted in summer (June, July, and August) and winter (December, January, and February).
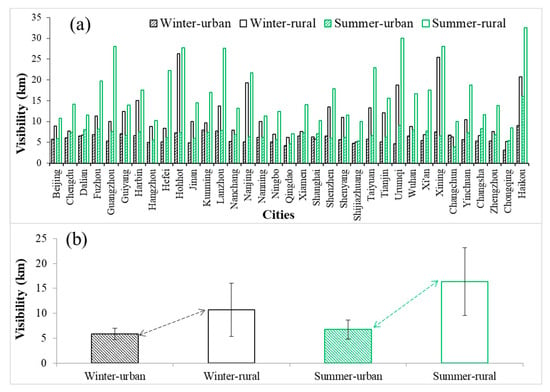
Figure 3.
Wintertime (in black) and summertime (in green) mean visibilities (unit: km) calculated based on observational data from meteorological stations in urban (shaded bars) and rural (unfilled bars) areas of (a) each city and (b) all cities when the air is polluted. Data are from 2001 to 2015.
Averaging over all cities, the wintertime urban mean visibility under polluted conditions is ~5.8 km (standard deviation, or std, = 1.1 km), and the wintertime rural mean visibility is ~10.7 km (std = 5.3 km). In the summertime, the urban mean visibility is ~7.0 km (std = 1.9 km), and the rural mean visibility is ~16.4 km (std = 6.8 km). The overall differences in visibility between urban and rural areas are ~9.4 km and ~4.9 km for summertime and wintertime, respectively.
3.2. Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Differences between Urban and Rural Areas
Figure 4 shows the mean difference in AOD () between the urban and rural areas of each city and all cities. Summertime s are larger than those in winter in all cities except for Chongqing. Figure 5 shows the variation trends of mean AOD as a function of distance from the urban geometrical center of each city in winter and summer. As the distance from the urban geometrical center increases, summertime AODs decrease more rapidly than wintertime AODs. The range of the decrease in summer is greater than that in winter. Figure 4 and Figure 5 indicate that the in summer is larger than that in winter. The overall mean s are 0.175 in summer and 0.07 in winter, and the relative difference between summer and winter is 0.105. Moreover, the AOD variations of different cities in Figure 5 are inconsistent, because of the joint complex effects of meteorological conditions, topography, and aerosol types.
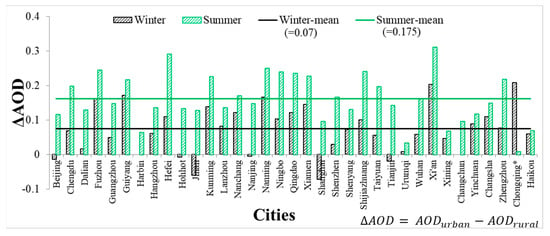
Figure 4.
The spatial differences in aerosol optical depth (AOD) () between the urban and rural areas in and around the 35 cities based on MODIS AOD. Black and green bars represent in winter and summer, respectively. The overall mean calculated using data in winter and summer are shown as black and green lines, respectively. The city marked with an asterisk (Chongqing) shows results opposite to those of the other cities.
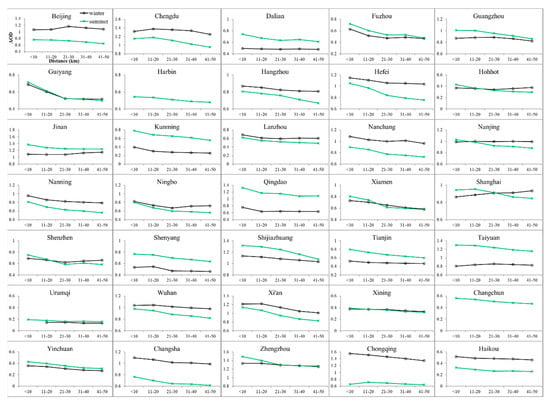
Figure 5.
Mean AOD as a function of distance from the urban geometrical center of each city in winter (black curves with open circles) and summer (green curves with crosses). Note that wintertime AOD data are not available at cities Harbin and Changchun. The distance ranges are <10 km, 11–20 km, 21–31 km, 31–40 km, and 41–50 km from the urban geometrical center.
The spatial difference in CALIPSO aerosol distributions from urban to rural areas was also analyzed. Figure 6 shows the frequency of occurrence of aerosols at different altitudes over the GBMA and YRD regions from 2006 to 2015. In both regions, the occurrence frequency differs more in summer than in winter, consistent with the column total AOD from MAIAC. Aerosols reach higher into the atmosphere in summer than in winter, i.e., higher than 3 km (GBMA) and 2.5 km (YRD) in summer, and lower than 2 km over both regions in winter. The occurrence frequency as determined by CALIPSO at lower altitudes (<1.5 km) is larger in urban areas than in rural areas in summer (Figure 6a,c). This is not as obvious in winter (Figure 6b,d). In rural areas, larger occurrence frequencies in summer are located at higher altitudes (0.5–2.5 km), whereas they are at lower altitudes (<1 km) in winter. The rural frequency of occurrence is close to, or even larger than, the urban frequency of occurrence at higher altitudes in summer. Urban–rural circulation may explain this. Because of higher temperatures, urban areas act as convergence zones, bringing in near-surface pollutants from rural areas that are then lifted by updrafts to higher altitudes and dispersed to rural surrounding areas, especially in summer. This is more clearly seen at the border between urban and rural areas (Figure 6a,c) This process diminishes the vertical gradient of pollution in the boundary areas of a city. Since updrafts are stronger in summer than in winter, pollutants can be carried to higher altitudes, leading to more aerosols at higher altitudes in summer than in winter.
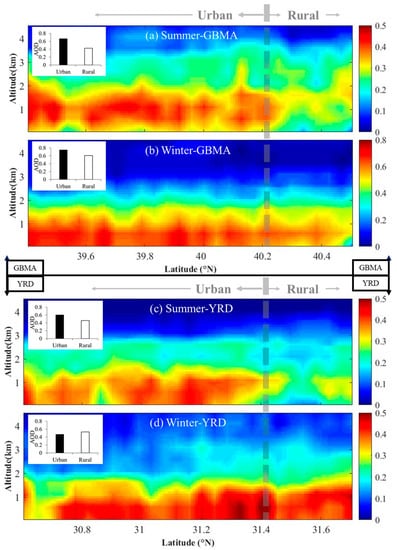
Figure 6.
The Cloud–Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation (CALIPSO)-retrieved occurrence frequency of aerosols at different altitudes from urban to rural areas for the data period of 2006 to 2015 for (a) the Greater Beijing Metropolitan Area (GBMA) in summer, (b) the GBMA in winter, (c) the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) in summer, and (d) the YRD in winter. The color bars represent the occurrence frequencies of aerosols. The histograms located in the upper-left corner of each panel show the overall mean AODs in rural and urban areas.
3.3. Differences between Urban and Rural Areas
Figure 7a–c shows detailed differences for each city. Figure 7d shows summertime and wintertime overall differences () at each pollution level of all cities using data from 2013 to 2015. Summertime differences are generally larger than wintertime differences, with greater increases in magnitude than wintertime differences as increases.
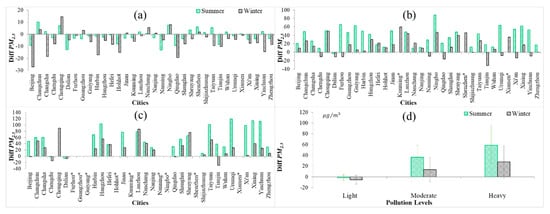
Figure 7.
differences (, unit: μg / m3) in different concentration bins based on surface observations: (a) 0–50 μg/m3 (light pollution), (b) 100–150 μg / m3 (moderate pollution), and (c) >200 μg/m3 (heavy pollution). (d) the mean spatial differences in all cites for different levels. Green and black bars represent summertime and wintertime PM2.5 differences, respectively. Asterisks mark those cities with insufficient numbers of samples.
The results of Section 3 indicate that the SIAP is found to exhibit a pronounced seasonality that is not recognized before, namely, that summertime SIAP > wintertime SIAP, it can reveal the linkage of air pollution to the urban heat island, clouds, and precipitation, among others. Combining multi-source datasets shows the 3-D distribution of air pollution between urban and rural areas that have rarely been investigated before (mostly 2-D), and this is important for validating future model simulations.
4. Potential Reasons for the Seasonal Differences in the Spatial Inhomogeneity of Air Pollution
4.1. Emission Effect
Figure 8 presents the spatial distribution of total PM2.5 emissions in the urban and rural areas of each city in summer and winter. For all cities, urban PM2.5 emissions are larger than rural emissions in both winter and summer. Summertime PM2.5 emissions from most cities located south of are slightly larger than in winter. The opposite is the case for cities located north of where emissions from heating in winter may make a difference. For most cities, urban–rural differences in PM2.5 emissions in summer are slightly larger than in winter. Figure 9 shows the urban–rural emission differences of precursors (including NOx, SO2, and NH3), which promote the formation of particulate matter. Results also show that the urban–rural differences in precursors in summer are larger than in winter in most cities. Overall, the seasonal differences are not obvious, suggesting that the emission difference is a factor but not the only one causing the different spatial inhomogeneities of air pollution in different seasons. It should be noted that the AOD differences in a few cities are inconsistent with emission differences, because AOD is not only affected by PM2.5, but also by PBL height, RH, and larger particles (e.g., PM10, dust).
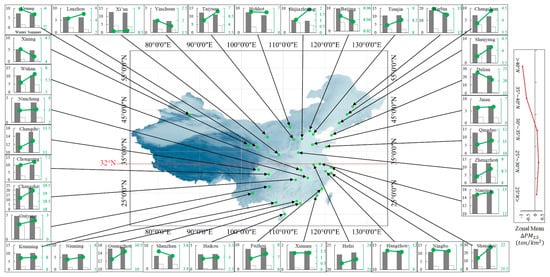
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of mean PM2.5 emissions (unit: ton/km2) in the urban (filled bars) and rural (unfilled bars) areas of each city in summer and winter, and PM2.5 differences (green dots, unit: ton / km2) between the urban and rural areas of each city in summer and winter. The in right panel is the urban differences between summer and winter. Data are from 2010 to 2014.
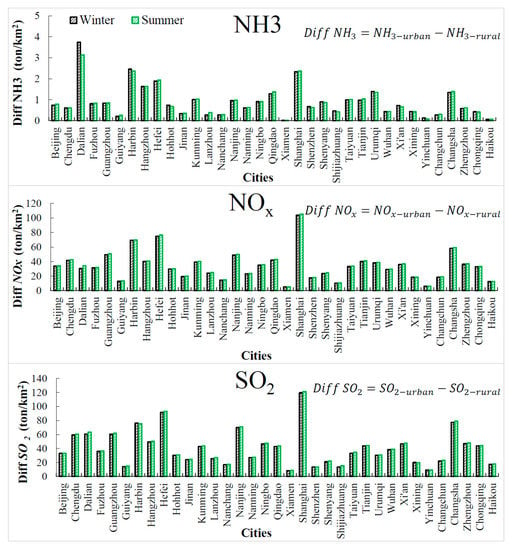
Figure 9.
Wintertime (in black) and summertime (in green) NH3, NOx, and SO2 emission differences (unit: ton/km2) between the urban and rural areas of each city. Data are from 2010 to 2014.
4.2. Urban Structure Effect
Figure 10a,b show the relationship between SBC and in summer and winter, respectively. In summer, decreases as SBC increases. In winter, there is no clear relationship between them. Figure 10c shows the extent of changes in AOD every 10 km as a function of SBC. Results show that the extent of decreases in AOD reduces with increasing SBC in summer. The extent of decreases in AOD with increasing SBC barely changes in winter. Figure 10d shows the relationship between PM2.5 concentration and building density. PM2.5 concentrations first increase then decrease as the building density increases in both summer and winter, but the correlation in summer is more significant than in winter. The above results indicate that urban structure has a more obvious relationship with the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution in summer than in winter. Low SBC values indicate simpler shapes and more compact urban areas, which serve as a barrier against pollutants being transported elsewhere, causing greater differences between the pollution levels of urban and rural areas. High SBC values indicate more complex shapes and less compact urban areas, which favors the dispersion of pollutants, leading to lower differences in the pollution levels between urban and rural areas [50,51]. The urban structure affects the spatial distribution of air pollution in the summer because the compactness of urban areas plays an important role in the dispersion of pollutants in the more active PBL. In winter, the PBL is very stable, so the influence of the compactness of urban areas likely weakens, lessening the effect.
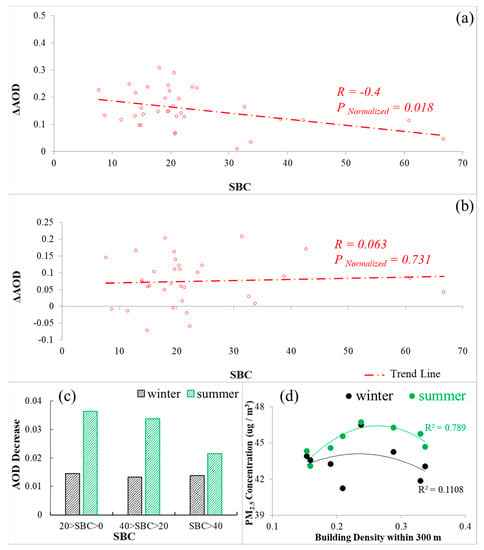
Figure 10.
The relationships between the Boyce-Clark shape index (SBC) and in summer (a) and winter (b) at 35 cities in 2015. The red dashed lines are the linear least-squares-fit lines. (c) The extent of changes in AOD every 10 km from the urban geometrical center as a function of SBC. The AOD decrease is calculated based on Figure 5. (d) The relationship between PM2.5 concentration and building density within 300 m around the PM2.5 sites in Beijing (unit: μg/m3). The building density information is extracted using the ArcMap application.
4.3. Meteorological and Topographical Effect
To gain further insight into the impact of the PBL on air quality, their relationship is investigated more rigorously. Note that pollutants mainly exist within the PBL. A lower (higher) PBLH means less (more) space available for aerosols, so changes in the PBLH will affect the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution to varying degrees [21,52].
Figure 11a–d show the mean PBLHs in summer and winter at four cities at three pollution levels. Figure 11e shows PBLH differences between clean and heavy polluted conditions in the four cities in summer and winter. The PBLH decreases persistently as the air quality changes from clean, moderately polluted to heavily polluted, and the extent of changes in PBLH is more in summer (~0.2–0.9 km) than in winter (<0.4 km). In absolute terms, the PBLH decreases in summer (~0.54–0.99 km) are more than twice that in winter (<0.35 km) at these four cities when air quality changes from clean to polluted conditions. In relative terms, the PBLH decreases 51%, 50%, 52%, and 35% in summer at the four cities, respectively, but 21%, 30%, 38%, and 26% in winter. A greater PBLH reduction leads to greater PM2.5 concentrations within the PBL. The greater reduction in the PBLH in summer enhances the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution more significantly than that in winter.
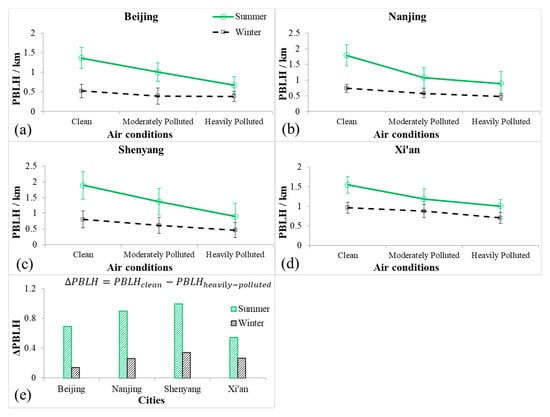
Figure 11.
Planetary boundary layer height (PBLH, unit: km) under different pollution conditions calculated based on sounding data in (a) Beijing, (b) Nanjing, (c) Shenyang, and (d) Xi’an. The green lines are summertime and the black lines are wintertime. (e) is the PBLH difference under clean and heavy pollution conditions at each city.
Figure 12 shows the variation of ΔPM2.5 with wind speed. In Beijing, ΔPM2.5 increases with increasing wind speed in summer, but decreases in winter. The prevailing southeast wind in summer carries pollutants from surrounding area to urban area, and the northwest mountain areas prevent diffusion of urban pollutants. This process facilitates the accumulation of pollutants in urban areas and increase urban–rural pollution difference. However, in winter, the prevailing northwest wind from mountain area is cleaner and pushes urban pollutants to surrounding areas, reducing urban–rural pollution differences. The prevailing wind directions in Xi’an are same as that in Beijing in summer and winter. There are also mountains near Xi’an, but they are situated south of the urban area. So the combined effects of wind and topography in Xi’an is opposite to that in Beijing. There is no continuous mountain area around Nanjing. Winds from any directions help disperse urban pollutants and decrease urban–rural pollution differences. In Shenyang, the prevailing winds in summer and winter are southeast wind and northeast wind, respectively. The cleaner winds from eastern mountain area help remove urban pollutants. The above results indicate that the combination of wind and topography can affect the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution.
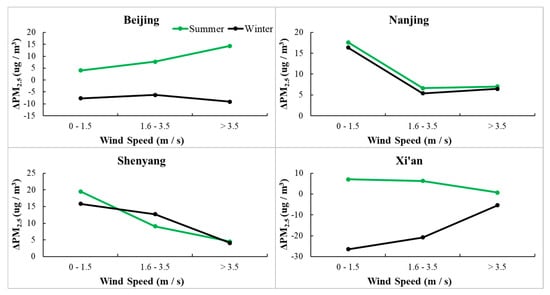
Figure 12.
Variations in ΔPM2.5 concentration (unit: ug/m3) as a function of wind speed in Beijing, Nanjing, Shenyang, and Xi’an in summer (green curves) and winter (black curves). The ΔPM2.5 concentration is the difference in PM2.5 concentration between urban and rural areas.
Figure 13 shows the ΔAODs of different terrain cities. The results show that the ΔAODs in summer are larger than in winter in all such cities. Comparing different categories of cities in Figure 13, ΔAOD has smaller changes in summer than in winter. This indicates that the effect of topography in winter is more obvious than that in summer.
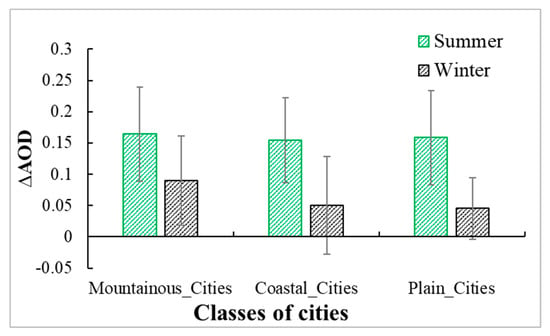
Figure 13.
The ΔAODs of mountainous cities, coastal cities, and plain cities in summer (green bars) and winter (black bars).
4.4. Humidity Effects
Humidity facilitates both particle growth and new particle formation, having a stronger effect when RH levels are high [53,54,55]. New particle formation is highly localized and extremely tiny (from nano- to tens of nano-meter). This process tends to have little effect on AOD and PM2.5 that are most strongly influenced by particles >0.1 m. However, particle growth can largely enhance the scattering efficiency and increase particle size and AOD, also affecting nucleation and coagulation, and thus dry and wet depositions, which would influence the mass concentration. Humidity exerts a considerable influence on aerosols and generally increases both AOD and PM2.5 [54,56,57]. Due to the spatial variation in RH, humidity can influence the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution in terms of mass concentration, particle diameter, and optical depth [55,58,59,60].
Table 1 summarizes the correlation coefficients between and for all cities. Twenty-eight cities have positive relationships between and in summer, while only eleven cities have positive relationships in winter. Figure 14 shows the variations in ΔPM2.5 concentration as a function of RH in Beijing, Nanjing, Shenyang, and Xi’an. Results indicate that ΔPM2.5 continuously increases as RH increases in summer in all cities, while the variations in ΔPM2.5 differ with different values of RH in winter. In winter, the ΔPM2.5 variations in Beijing and Xi’an are different from other cities. ΔPM2.5 changes at high RH in Xi’an are opposite to those in Beijing, which may be caused by different aerosol compositions and properties between urban and rural areas. Urban particles grow more than rural particles under high RH in Beijing, which is contrary to Xi’an. This may lead to different relationship between ∆AOD and ΔRH in different seasons in Table 1 in a few cities. Figure 15 shows the mean RH in each city in summer and winter. Twenty-seven cities have higher RHs in summer than in winter. The other eight cities, mainly located in the northernmost and southernmost parts of China, have lower RHs in summer than in winter. Previous studies have shown that urban aerosols are more hygroscopic than rural aerosols, especially in summer, because of the higher proportion of inorganic aerosols and higher RH in summer (shown in Figure 15). The spatial inhomogeneity of AOD or pollutants in summer is thus more sensitive to the effects of RH [61,62,63,64,65]. Furthermore, the differences in aerosol hygroscopicity can affect the spatial inhomogeneity of AOD between urban and rural areas. Differences in RH affect the process of particle growth, serving as a potential factor explaining the spatial differences in aerosol loading. Note that the effects of humidity on aerosols are still highly uncertain.

Table 1.
The correlation coefficients between normalized ∆AOD and ΔRH between urban and rural areas at all cities, where “*” and “**” means passing the significance test at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively. ‘NAN’ means no data.
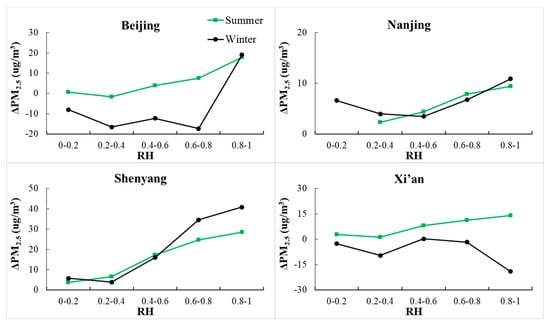
Figure 14.
Variations in ΔPM2.5 concentration (unit: μg/m3) as a function of relative humidity (RH) in Beijing, Nanjing, Shenyang, and Xi’an in summer (green curves) and winter (black curves). The ΔPM2.5 concentration is the difference in PM2.5 concentration between urban and rural areas.
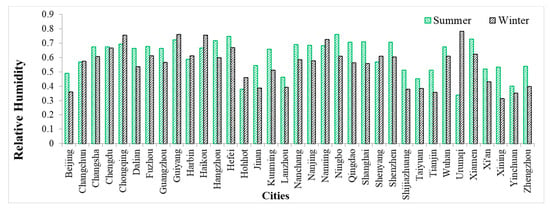
Figure 15.
Comparisons of mean RH in each city in summer (green bars) and winter (black bars).
In summary, the above analyses suggest that the effects on seasonal SIAP are complex, likely driven by multi-factors that vary with season, including emission, urban structure, PBL, and relative humidity.
4.5. Discussion for Potential Factors
The interaction mechanism between urbanization and air pollution is very complicated. Here, the four potential factors we proposed provide new insights into this subject. Meanwhile, they raise more questions than what can be addressed in this study, due to the limitations of currently available observational data. For the sake of a future study, the limitations of the approach and uncertainties or ambiguities in the interpretation of the results are stated here. (1) For the emission effect, the spatial resolution of the emission data is about 10 km. While it is higher than some related products, it is still not fine enough to resolve any variations on urban–rural scales for which higher resolution data would be needed. (2) For the urban structure effect, the relationship between SBC and ΔAOD is faint. It is thus impossible to solely extract the urban effects, as other factors disturb the signal of urban structures. Resolving this issue entails model simulations (e.g., LES—Large eddy simulation or WRF—Chem simulation) [66]. (3) While the influences of PBLH, wind speed, and topography are analyzed here, quantification of their respective importance is still wanting. (4) For the humidity effect, a handful of studies have been conducted, there still exit large uncertainties, especially concerning urban–rural difference. Understanding the effects of humidity merit further comprehensive observations of aerosol chemical composition between urban and rural areas.
5. Conclusions
Satellite data and ground-based observation data from multiple sources were used to analyze the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution between the urban and rural areas of 35 cities in China in different seasons. The results obtained from these multi-source datasets are consistent and provide observational analysis support for previous model simulation work [30]. Results show that the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution between urban and rural areas is larger in summer than in winter. Urban pollution is often more severe than rural pollution in summer. However, in winter, both urban and rural pollution are severe, and rural pollution is even more severe than urban pollution in few cities.
Emissions, urban structures, meteorology and topography, and humidity are the potential reasons for why the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution is larger in summer:
(1) For most cities, the urban–rural differences in PM2.5 and precursor-gas emissions in summer are larger than in winter but not obviously. This indicates that besides the emission effect, there are also other factors causing different spatial inhomogeneities of air pollution in different seasons.
(2) The effect of the urban structure is more significant in summer than in winter. The compactness of urban areas has a more obvious effect on the dispersion of pollutants in summer because of an active planetary boundary layer, but not in winter.
(3) The reduction in planetary boundary layer height over urban areas is larger in summer than in winter from clean to heavy polluted conditions. This causes more significant influence on urban pollution concentrations in summer than in winter, as is its impact on the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution. Moreover, both wind speed and topography affect the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution.
(4) For most cities, higher relative humidity can cause the larger spatial inhomogeneities of air pollution in summer and winter due to particle growth.
Note that these explanations are not independent, i.e., there are interactions between them, influencing each other. However, their respective importance cannot be quantitatively assessed by analyzing observation data alone. Numerical simulations will be conducted to gain further insights. This study mainly focused on physical factors. Synchronous experiments of urban and rural areas are needed in the future to gain a deep insight into related problems. The chemical transformation of pollutants and socioeconomic factors also need to be investigated to understand their impacts on the spatial inhomogeneity of air pollution.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/12/14/2320/s1, Figure S1: The spatial distribution of 1680 PM2.5 sites in China until 2015.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L. and W.H.; methodology, Z.L. and W.H.; validation, Z.L., W.H. and J.G.; formal analysis, W.H.; resources, Z.L. and J.G.; data curation, J.G., T.S. and T.C.; writing—original draft preparation, W.H.; writing—review and editing, Z.L, W.H., J.G., J.W. and M.C.; supervision, Z.L.; project administration, Z.L.; funding acquisition, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (grant number 2017YFC1501702), and the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant number 91544217 and 41771399).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the provision of PM2.5 data by the Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China and for the provision of meteorological and radiosonde data by the China Meteorological Administration. We extend our sincerest thanks to the NASA team for their satellite datasets and the PKU-FUEL team for their emission dataset.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mahmood, R.; Li, S. Remote influence of South Asian black carbon aerosol on East Asian summer climate. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Olsen, S.C.; Dubey, M.K.; He, J. CCSM3 simulated regional effects of anthropogenic aerosols for two contrasting scenarios: Rising Asian emissions and global reduction of aerosols. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chan, A.; Lau, G.N.C.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yim, S.H.L. Effects of urbanization and global climate change on regional climate in the Pearl River Delta and thermal comfort implications. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 2984–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yim, S.H.L.; Yang, Y.; Morin, C.W. The effect of urbanization and climate change on the mosquito population in the Pearl River Delta region of China. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yim, S. The air quality and health impacts of domestic trans-boundary pollution in various regions of China. Environ. Int. 2016, 97, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wong, T.W.; Law, C.; Dong, G.H.; Ho, K.F.; Yang, Y.; Yim, S.H.L. Impacts of sectoral emissions in China and the implications: Air quality, public health, crop production, and economic costs. Eniviron. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 084008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Yim, S.H.; Shen, H.; Ho, H.C.; Li, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. High-Spatial-Resolution Population Exposure to PM2. 5 Pollution Based on Multi-Satellite Retrievals: A Case Study of Seasonal Variation in the Yangtze River Delta, China in 2013. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.H.; Lee, G.L.; Lee, I.H.; Allroggen, F.; Ashok, A.; Caiazzo, F.; Eastham, S.D.; Malina, R.; Barrett, S.R. Global, regional and local health impacts of civil aviation emissions. Eniviron. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.H.L.; Wang, M.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Dong, G.; Li, Q. Effect of urbanization on ozone and resultant health effects in the Pearl River Delta region of China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 11568–11579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habitat, U. Urbanization and development emerging futures. In World Cities Report; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Christen, A.; Vogt, R. Energy and radiation balance of a central European city. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 1395–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, D.J.; Fan, H. Modeling the diurnal variability of effective albedo for cities. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G. Urbanization as a major driver of urban climate change. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2017, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniello, C.; Morgan, K.; Busbey, A.; Newland, L. Mapping micro-urban heat islands using Landsat TM and a GIS. Comput. Geosci. 1995, 21, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, H. Urban climates and heat islands: Albedo, evapotranspiration, and anthropogenic heat. Energy Build. 1997, 25, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lee, X.; Smith, R.B.; Oleson, K. Strong contributions of local background climate to urban heat islands. Nature 2014, 511, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, E.M.; Thomas, R.M.; Praveen, P.S.; Pistone, K.; Bender, F.A.-M.; Ramanathan, V. Black carbon solar absorption suppresses turbulence in the atmospheric boundary layer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11794–11799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, S.; Ma, X.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, X.; Xie, T. The spatial and temporal distributions of absorbing aerosols over East Asia. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.; Hales, J.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.J.; Hansen, J.; Hofmann, D. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Ding, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Xue, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B. Aerosol and boundary-layer interactions and impact on air quality. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 810–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, Y.; Fang, Z.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Li, Y. On the summertime planetary boundary layer with different thermodynamic stability in China: A radiosonde perspective. J. Climatol. 2018, 31, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Tie, X.; Lin, Y. A possible positive feedback of reduction of precipitation and increase in aerosols over eastern central China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Shen, C.; Tan, W.; Wei, J.; Guo, J. The significant impact of aerosol vertical structure on lower atmosphere stability and its critical role in aerosol–planetary boundary layer (PBL) interactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3713–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givati, A.; Rosenfeld, D. Quantifying precipitation suppression due to air pollution. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1038–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Lee, X.; Liu, S.; Schultz, N.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L. Urban heat islands in China enhanced by haze pollution. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, T.; Riemer, N.; Chen, P.; Li, M.; Li, S. Urban heat island impacted by fine particles in Nanjing, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yim, S.Y.; Roth, M.; Ren, G.; Gao, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, Q.; Shi, C.; Ning, G. PM2.5 Pollution Modulates Wintertime Urban Heat Island Intensity in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Megalopolis, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Qian, Y.; Sarangi, C.; Zhao, C.; Leung, R.; Wang, H.; Yan, H.; Yang, T.; Yang, B. Urbanization effect on winter haze in the Yangtze River Delta region of China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 6710–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W. City clusters in China: Air and surface water pollution. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 4, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Streets, D.G.; Yim, S.H.L. Assessing outdoor air quality and public health impact attributable to residential black carbon emissions in rural China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 159, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Ru, M.; Du, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, H.; Yun, X.; Meng, W.; Liu, J. Impacts of air pollutants from rural Chinese households under the rapid residential energy transition. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO mission and CALIOP data processing algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Martonchik, J.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Korkin, S. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 1. Radiative transfer basis and look-up tables. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Kahn, R.; Korkin, S.; Remer, L.; Levy, R.; Reid, J. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 2. Aerosol algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Su, S.; Chen, Y.; Lin, N.; Zhuo, S.; Zhong, Q. Quantification of global primary emissions of PM2. 5, PM10, and TSP from combustion and industrial process sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13834–13843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Xia, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Lou, M.; He, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, F.; Min, M. Impact of diurnal variability and meteorological factors on the PM2.5-AOD relationship: Implications for PM2.5 remote sensing. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Fu, D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xia, X.; He, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, R.; Che, H. Diurnal and seasonal variability of PM2.5 and AOD in North China plain: Comparison of MERRA-2 products and ground measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M.; Huang, W.; Xue, W.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Improved 1 km resolution PM2.5 estimates across China using enhanced space–time extremely randomized trees. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3273–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Bian, L. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13309–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhai, P. Planetary boundary layer height from CALIOP compared to radiosonde over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9951–9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Extraction of urban built-up land features from Landsat imagery using a thematicoriented index combination technique. Photogramm. Eng. Rem. Sens. 2007, 73, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.R.; Sallee, G.T. A method of measuring shape. Geogr. Rev. 1970, 60, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, X. Impact of city belt in Yangtze River Delta in China on a precipitation process in summer: A case study. Atmos. Res. 2013, 125, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Leung, R.; Yang, X.Q. A case study of urbanization impact on summer precipitation in the Greater Beijing Metropolitan Area: Urban heat island versus aerosol effects. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 10903–10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Cohen, J.B.; Li, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, H.; Liu, L.; Yin, J.; Hu, K.; Zhai, P. Shift in the temporal trend in boundary layer height trend in China using long-term (1979–2016) radiosonde data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 6080–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelezang, D.; Holtslag, A. Evaluation and model impacts of alternative boundary-layer height formulations. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1996, 81, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, D.; Ma, Q. The relationship between urban form and air pollution depends on seasonality and city size. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15554–15567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Effects of China’s urban form on urban air quality. Urban Stud. 2016, 53, 2607–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Chen, D.; Miao, Y.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Ma, S. On the relationship between aerosol and boundary layer height in summer in China under different thermodynamic conditions. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Hu, M.; Zamora, M.L.; Peng, J.; Shang, D.; Zheng, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, Z.; Shao, M.; Zeng, L. Elucidating severe urban haze formation in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17373–17378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Gomez, M.E.; Yang, L.; Zamora, M.L.; Hu, M.; Lin, Y.; Peng, J.; Guo, S.; Meng, J. Persistent sulfate formation from London Fog to Chinese haze. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13630–13635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, C.; Yan, P. A review of atmospheric chemistry research in China: Photochemical smog, haze pollution, and gas-aerosol interactions. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 1006–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bei, N.; Hu, B.; Liu, S.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Feng, T.; Liu, Z. Is water vapor a key player of the wintertime haze in North China Plain? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8721–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, C.; Göbel, T.; Hallbauer, E.; Nowak, A.; Ran, L.; Xu, W.; Deng, Z.; Ma, N.; Mildenberger, K. Hygroscopic properties of aerosol particles at high relative humidity and their diurnal variations in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3479–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L.; Cribb, M. Estimating 1-km-resolution PM2.5 concentrations across China using the space-time random forest approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Sun, L.; Huang, W.; Xue, W.; Fan, T.; Cribb, M. Satellite-derived 1-km-resolution PM1 concentrations from 2014 to 2018 across China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13265–13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Chu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L. The evolution of springtime water vapor over Beijing observed by a high dynamic Raman lidar system: Case studies. IEEE J-STARS 2017, 10, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhuang, G.; Cheng, S.; Li, J. The mineral aerosol and its impact on urban pollution aerosols over Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7533–7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shao, L.; Zhang, D.; Ro, C.-U.; Hu, M.; Bi, X.; Geng, H.; Matsuki, A.; Niu, H.; Chen, J. A review of single aerosol particle studies in the atmosphere of East Asia: Morphology, mixing state, source, and heterogeneous reactions. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1330–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Salmon, L.G.; Zheng, M. Source apportionment of PM2. 5 in Beijing using principal component analysis/absolute principal component scores and UNMIX. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 372, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ji, D.; Li, Y.; Gao, M.; Tian, S.; Wen, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, P.; Jiang, C. The impact of relative humidity on the size distribution and chemical processes of major water-soluble inorganic ions in the megacity of Chongqing, China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 192, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Pan, X.; Tang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, L. Hygroscopic growth of aerosol scattering coefficient: A comparative analysis between urban and suburban sites at winter in Beijing. Particuology 2009, 7, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Li, Z.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Su, T.; Cribb, M.; Fan, J.; Chen, T.; Wei, J. The mechanisms and seasonal differences of the impact of aerosols on daytime surface urban heat island effect. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6479–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).