Modeling and Multi-Temporal Characterization of Total Suspended Matter by the Combined Use of Sentinel 2-MSI and Landsat 8-OLI Data: The Pertusillo Lake Case Study (Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
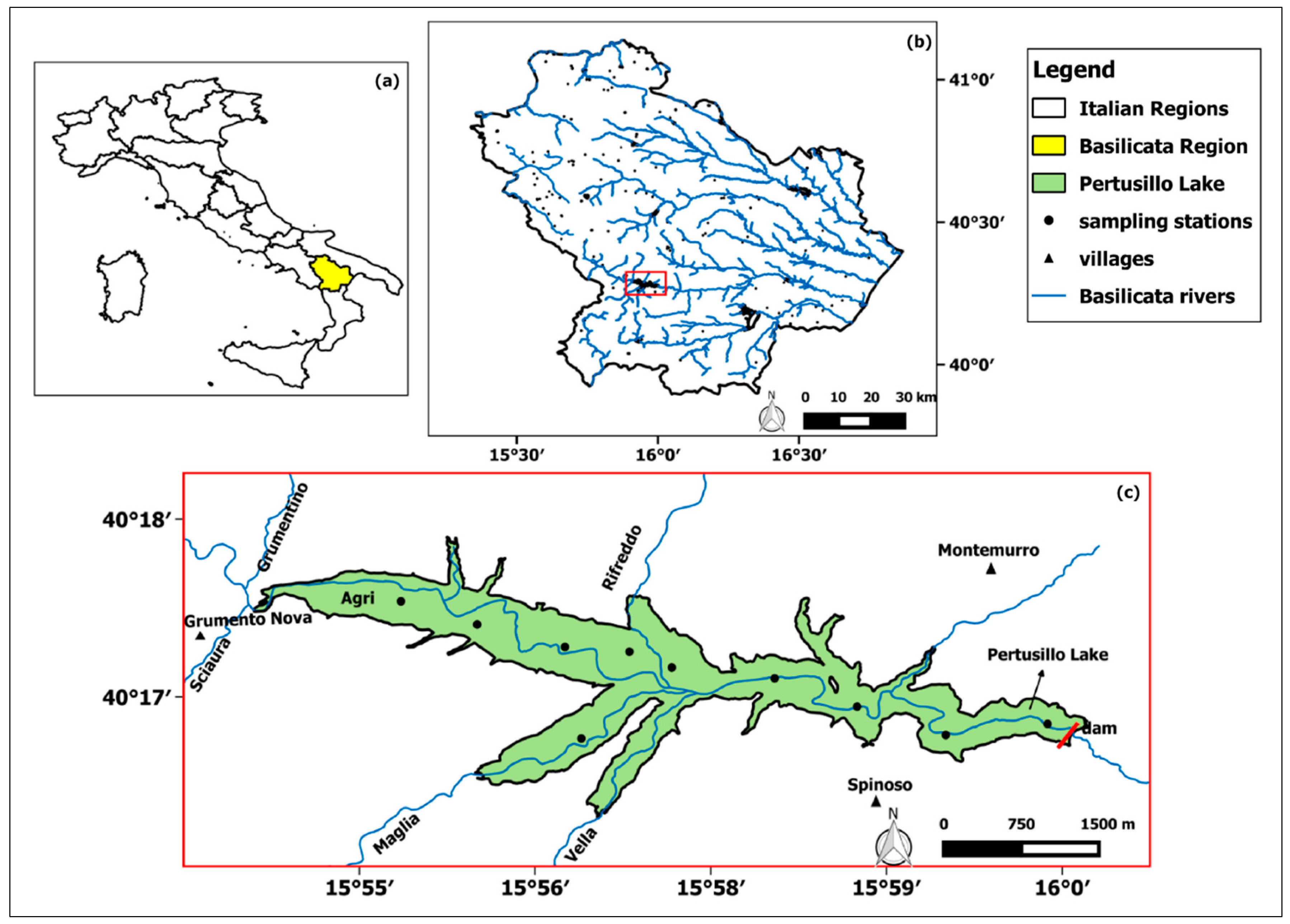
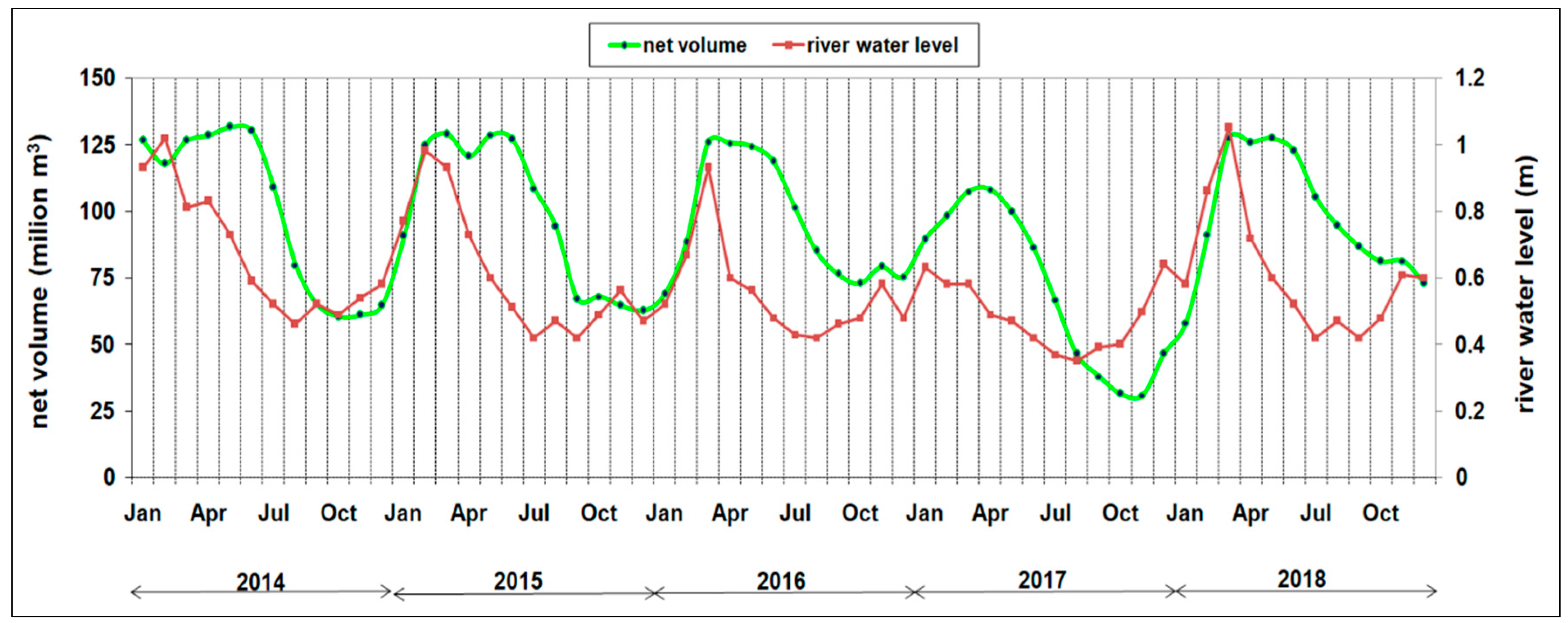
2.1. Study Area
2.2. In Situ Data Collection
In Situ TSM and Radiometric Rrs(λ)Measurements
2.3. Satellite Data
Atmospheric Correction and Data-Processing Scheme
2.4. Comparison between Satellite and In Situ Data
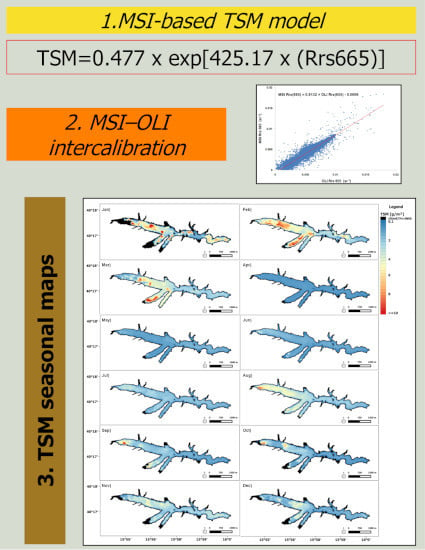
2.5. TSM Modeling Using MSI–OLI Combined Data
3. Results
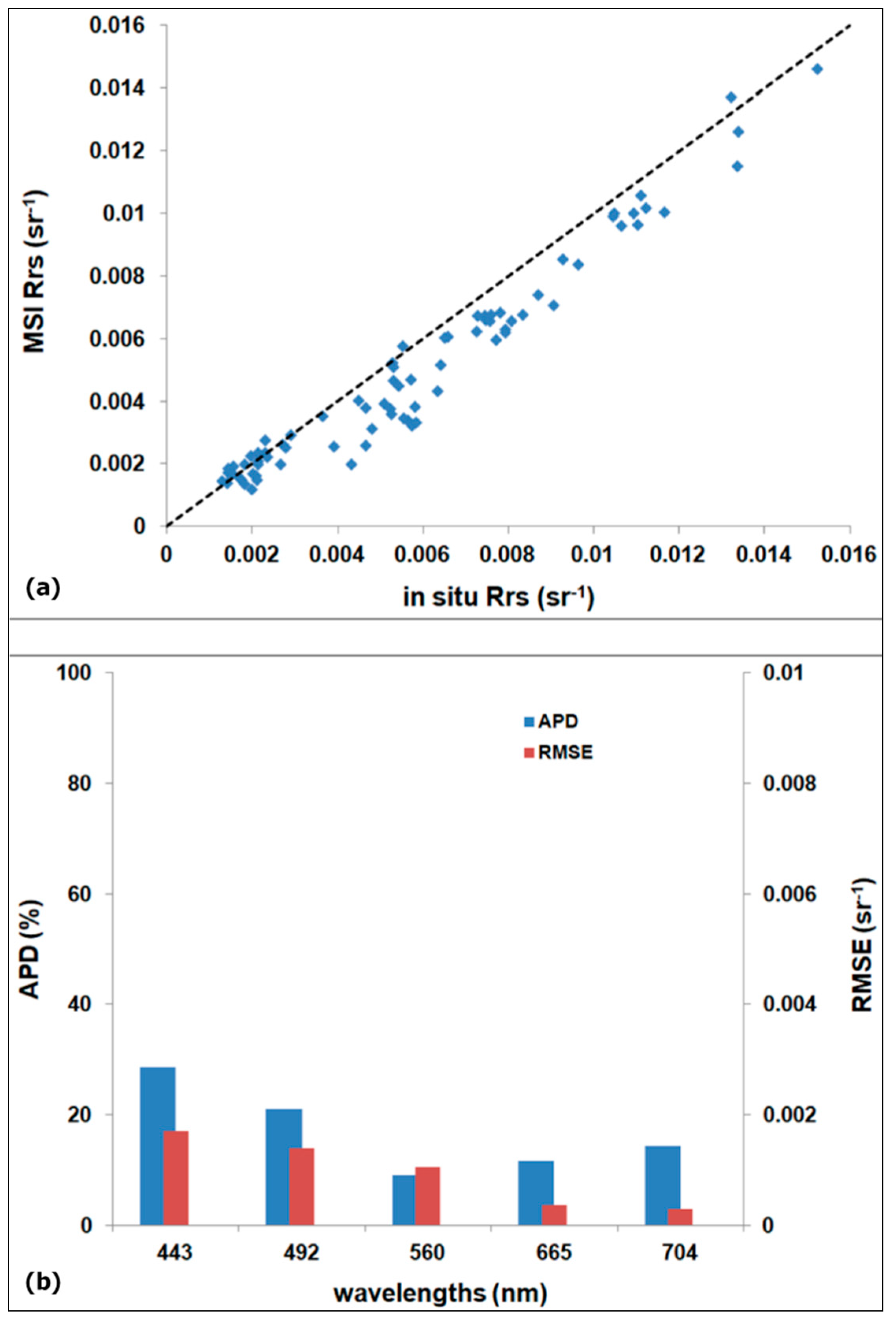
3.1. Accuracy Assessment of MSI-Derived Rrs(λ)
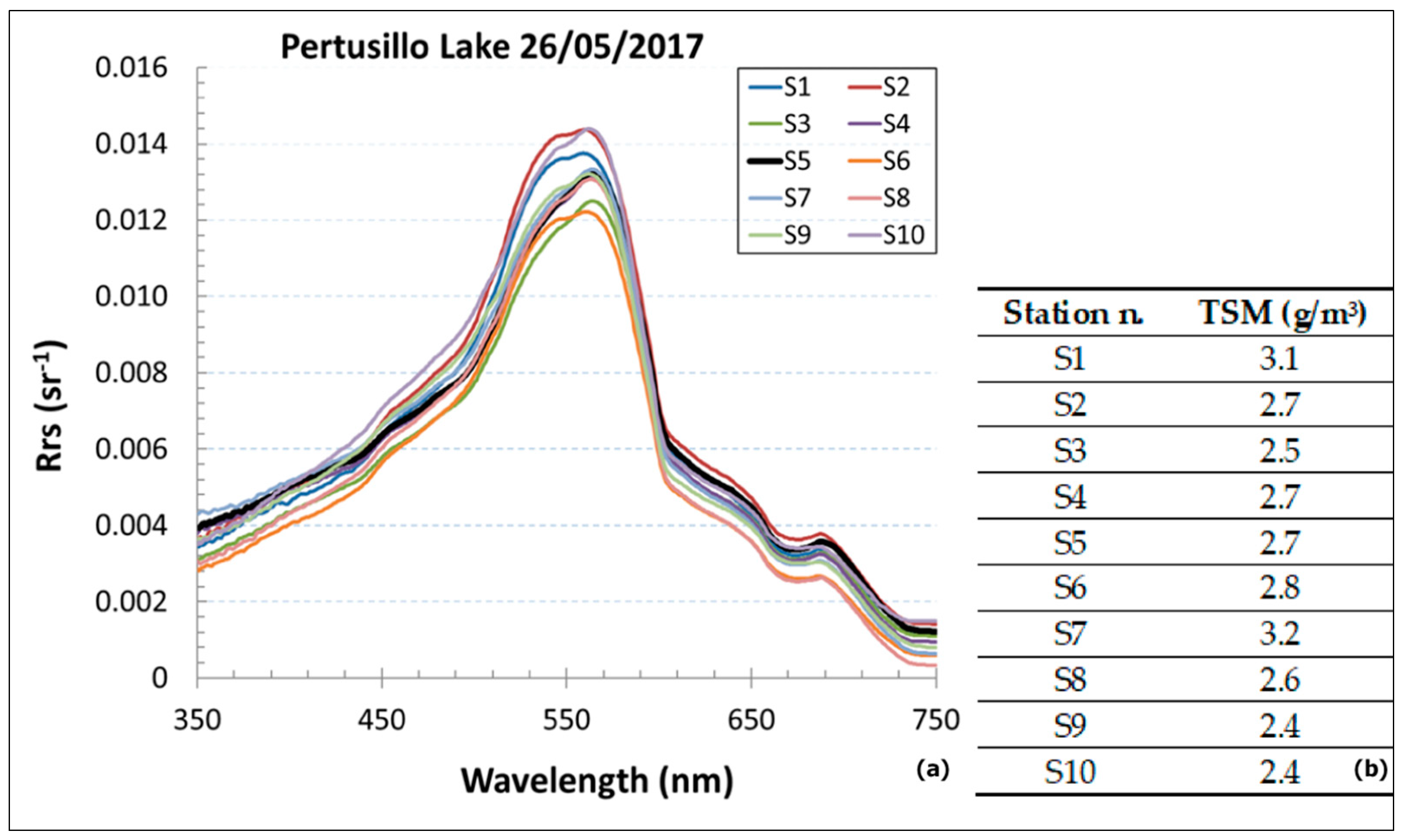
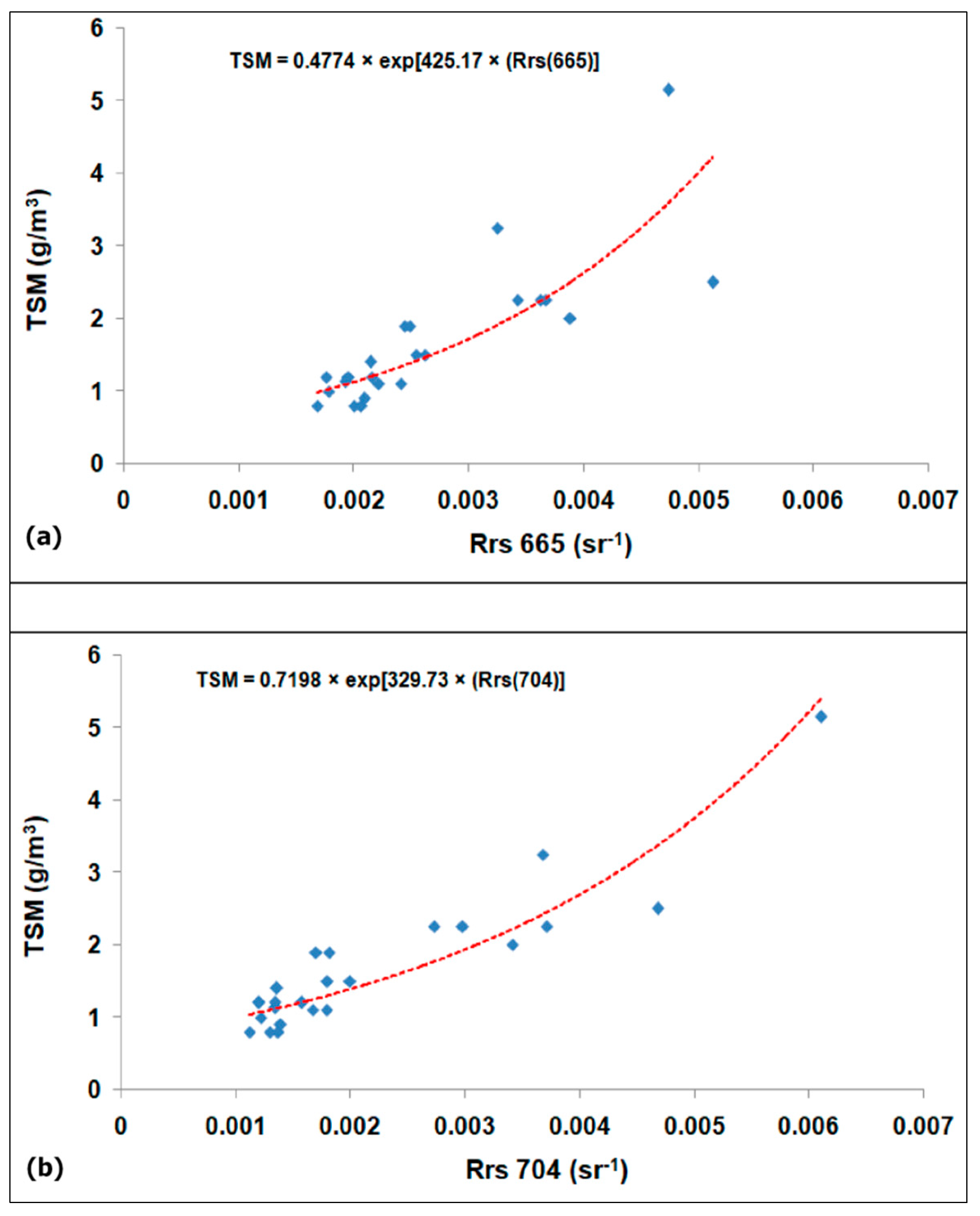
3.2. Calibration and Validation of a Locally Tuned TSM Model
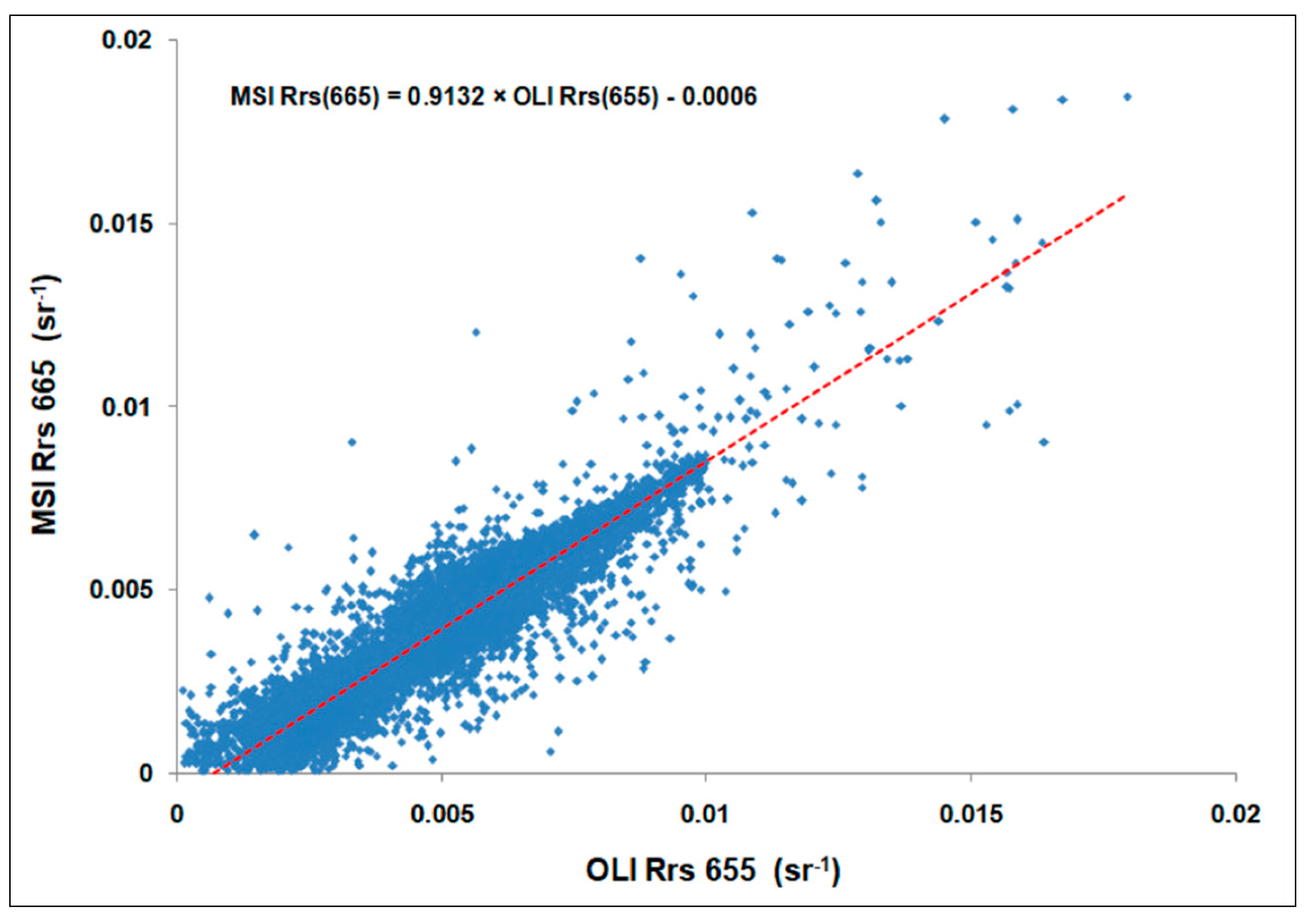
3.3. Intercalibration between MSI and OLI
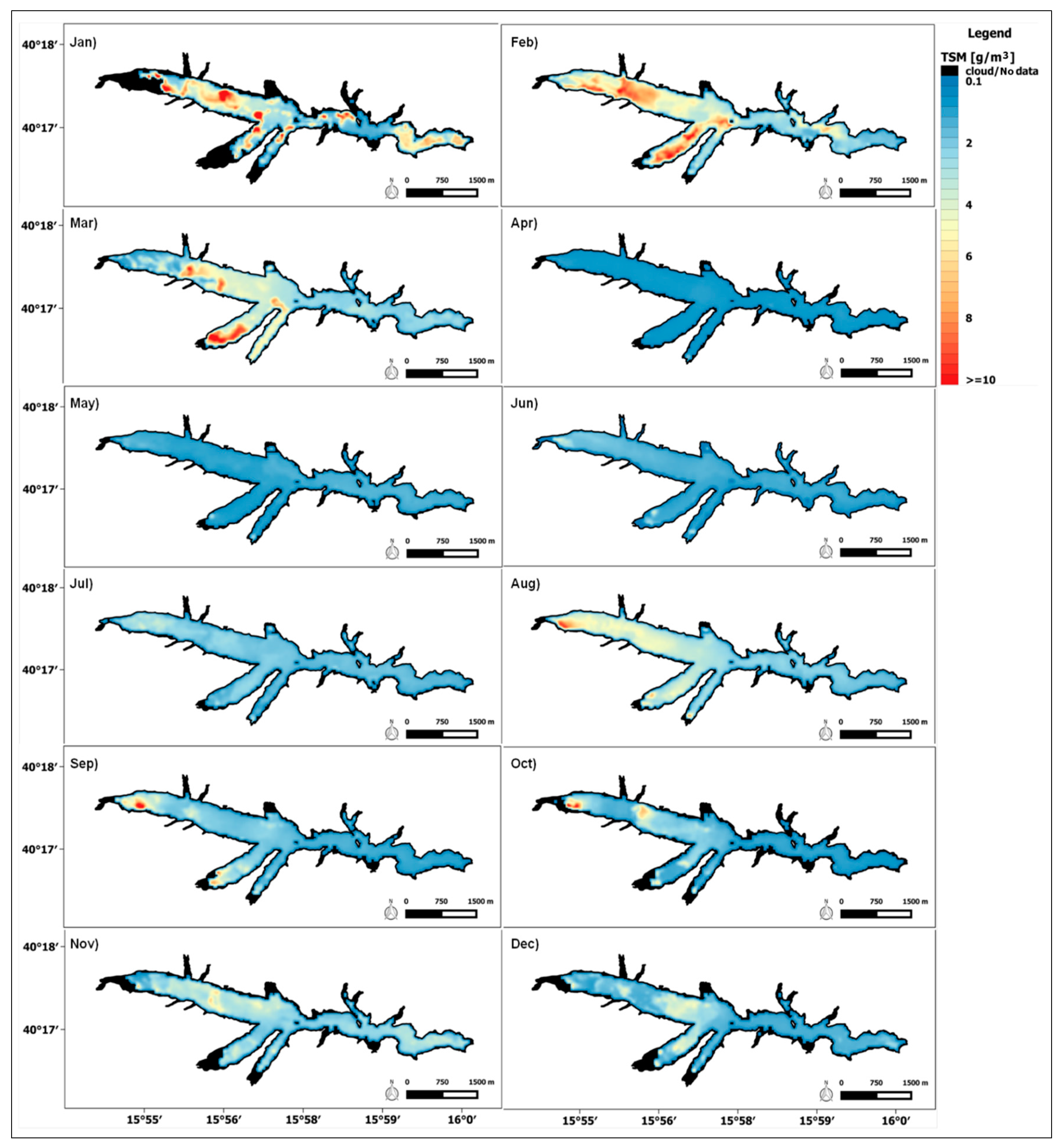
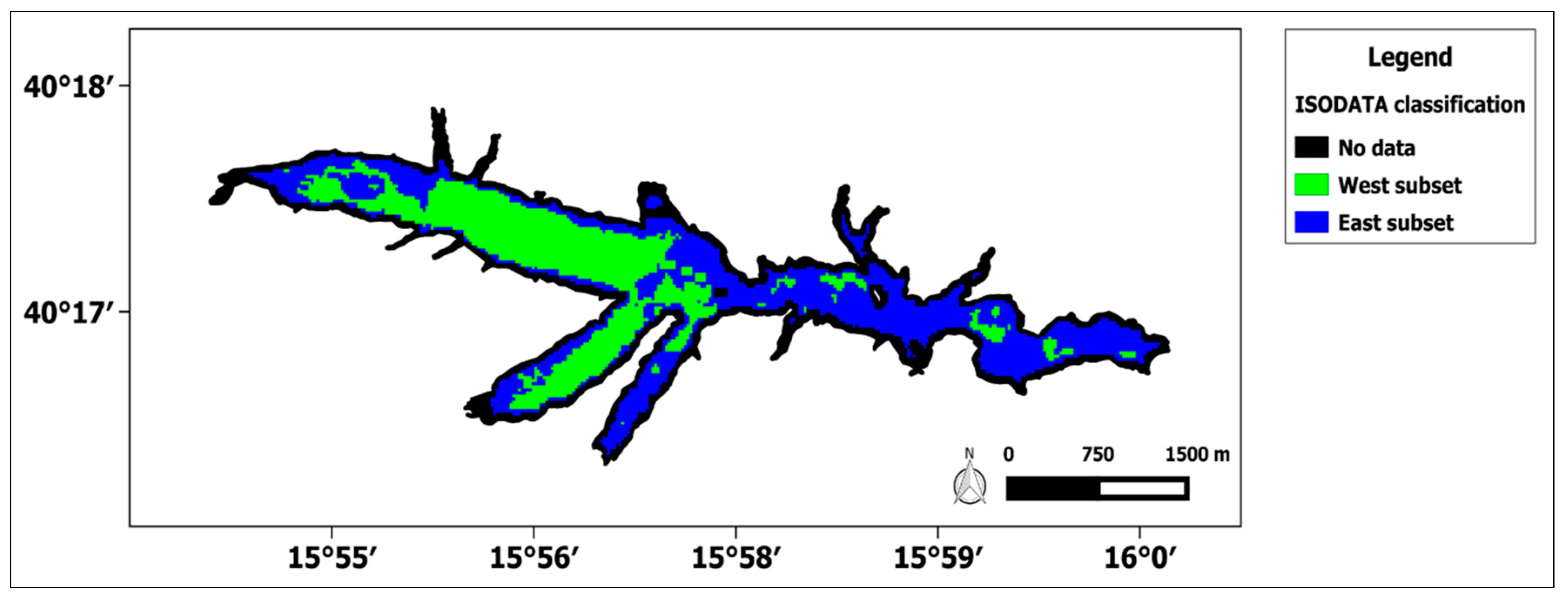
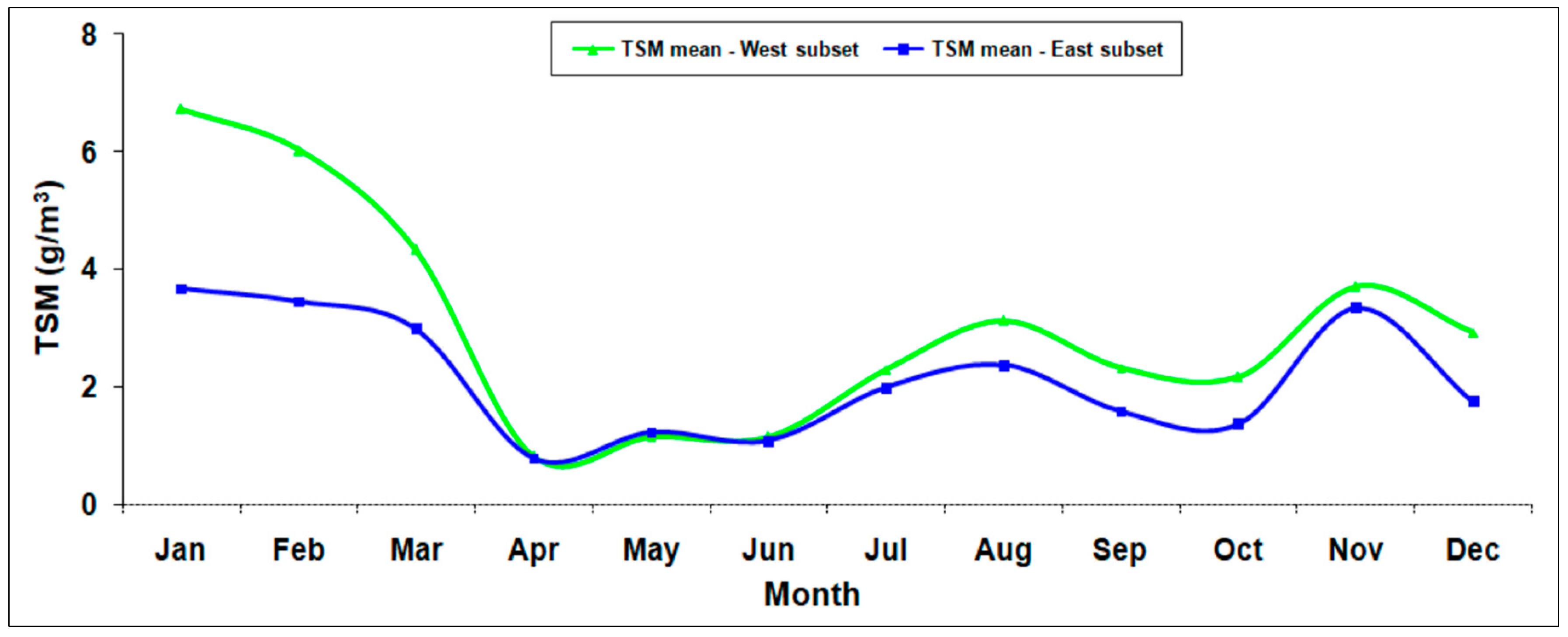
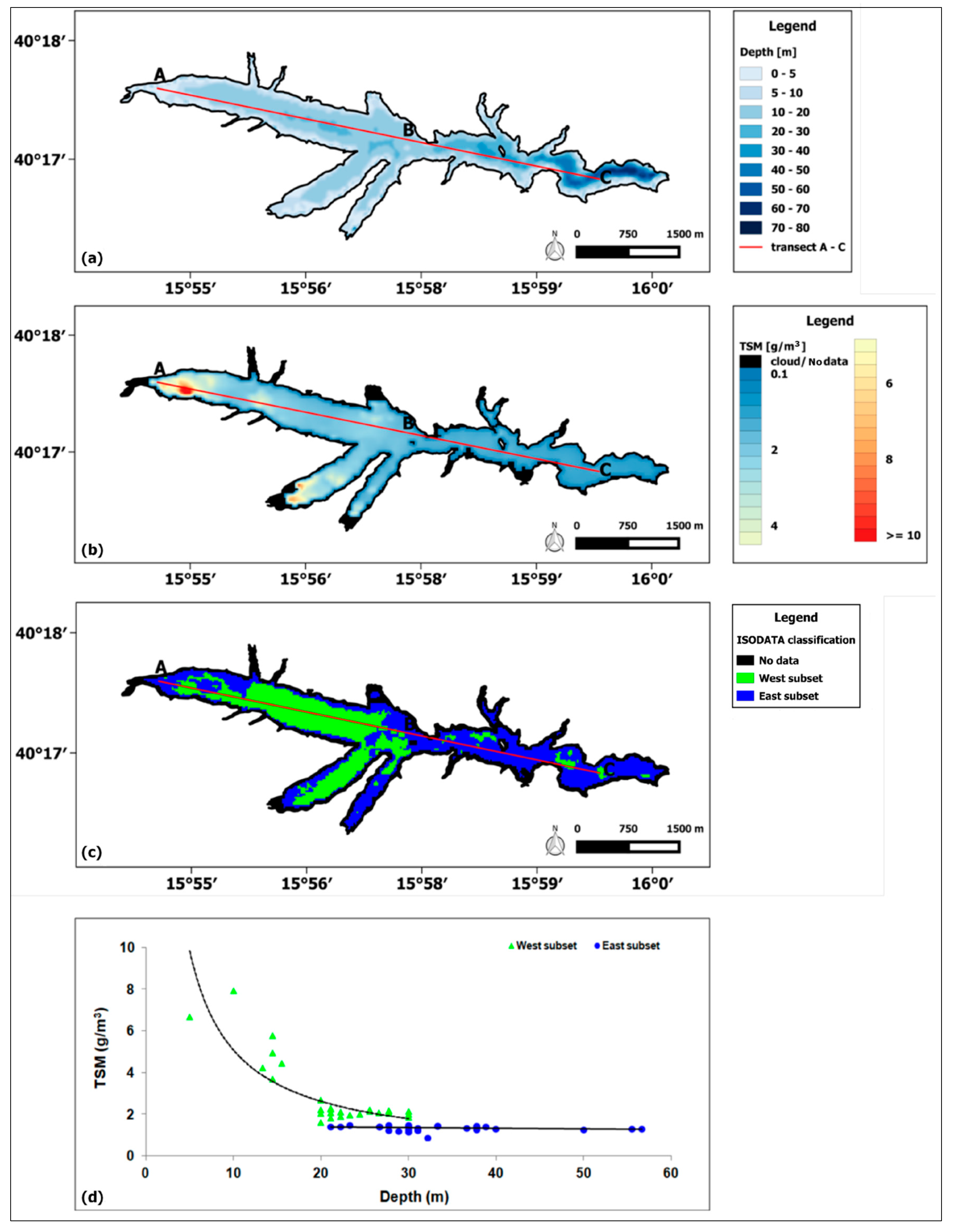
3.4. Seasonal TSM Variations
4. Discussion
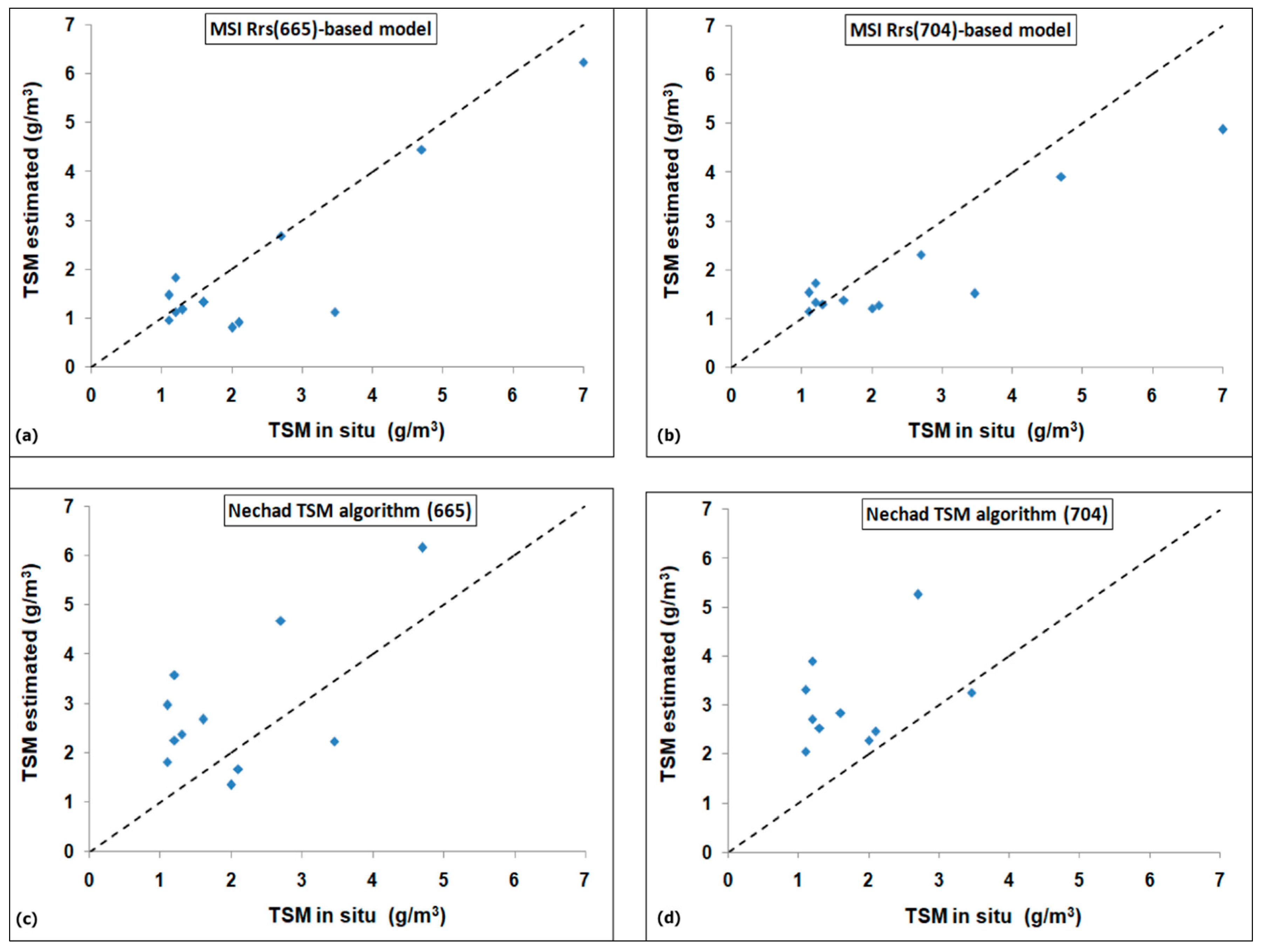
4.1. TSM Model Calibration and Validation
4.2. MSI–OLI Combined Dataset for TSM Seasonal Analysis
4.3. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Davies, P.M. Global Threats to Human Water Security and River Biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, R.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Zagarese, H.; Baines, S.B.; Hessen, D.O.; Keller, W.; Livingstone, D.M.; Sommaruga, R.; Straile, D.; Van Donk, E.; et al. Lakes as Sentinels of Climate Change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stendera, S.; Adrian, R.; Bonada, N.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Hugueny, B.; Januschke, K.; Pletterbauer, F.; Hering, D. Drivers and Stressors of Freshwater Biodiversity Patterns Across Different Ecosystems and Scales: A Review. Hydrobiologia 2012, 696, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Borja, A.; Carstensen, J.; Carvalho, L.; Elliott, M.; Feld, C.K.; Heiskanen, A.S.; Johnson, R.K.; Moe, J.; Pont, D.; et al. The European Water Framework Directive at the Age of 10: A Critical Review of the Achievements with Recommendations for the Future. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4007–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa, S.; Doxaran, D.; Ody, A.; Vanhellemont, Q.; Lafon, V.; Lubac, B.; Gernez, P. Atmospheric Corrections and Multi-Conditional Algorithm for Multi-Sensor Remote Sensing of Suspended Particulate Matter in Low-to-High Turbidity Levels Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxaran, D.; Lamquin, N.; Park, Y.J.; Mazeran, C.; Ryu, J.H.; Wang, M.; Poteau, A. Retrieval of the Seawater Reflectance for Suspended Solids Monitoring in the East China Sea Using MODIS, MERIS and GOCI Satellite Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 146, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.Y.; Zhu, G.W.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhao, L.L.; Gu, Z. Estimation of the Algal-Available Phosphorus Pool in Sediments of a Large, Shallow Eutrophic Lake (Taihu, China) Using Profiled SMT Fractional Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Leermakers, M.; Osan, J.; Torok, S.; Baeyens, W. Heavy Metals in Lake Balaton: Water Column, Suspended Matter, Sediment and Biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 340, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Polito, C.; Ciancia, E.; Coviello, I.; Doxaran, D.; Lacava, T.; Pergola, N.; Tramutoli, V. On the Potential of Robust Satellite Techniques Approach for SPM Monitoring in Coastal Waters: Implementation and Application Over the Basilicata Ionian Coastal Waters Using MODIS-Aqua. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Stroppiana, D.; Oggioni, A.; Morabito, G. Optical Remote Sensing of Lakes: An Overview on Lake Maggiore. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, Y. Long-Term Remote Monitoring of Total Suspended Matter Concentration in Lake Taihu Using 250 m MODIS-Aqua Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnhöfer, K.; Göritz, A.; Gege, P.; Pflug, B.; Oppelt, N. Water Constituents and Water Depth Retrieval from Sentinel-2A—A first Evaluation in an Oligotrophic Lake. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxaran, D.; Castaing, P.; Lavender, S.J.; Castaign, P.; Lavender, S.J. Monitoring the Maximum Turbidity Zone and detecting Fine Scale Turbidity Features in the Gironde estuary Using High Spatial Resolution Satellite Sensor (SPOT HRV, Landsat ETM) Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 2303–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; McKee, B.A. Using MODIS Terra 250 m Imagery to Map Concentrations of Total Suspended Matter in Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Song, Q. Influence of the Three Gorges Dam on Total suspended Matters in the Yangtze Estuary and its Adjacent Coastal Waters: Observations from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petus, C.; Marieu, V.; Novoa, S.; Chust, G.; Bruneau, N.; Froidefond, J.M. Monitoring Spatio-Temporal Variability of the Adour River Turbid Plume (Bay of Biscay, France) with MODIS 250-m Imagery. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 74, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.; Odermatt, D.; Hunter, P.D.; Brockmann, C.; Présing, M.; Balzter, H.; Tóth, V.R. Satellite Remote Sensing of Phytoplankton Phenology in Lake Balaton Using 10 years of MERIS Observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binding, C.E.; Greenberg, T.A.; Watson, S.B.; Rastin, S.; Gould, J. Long Term Water Clarity Changes in North America’s Great Lakes from Multi-Sensor Satellite Observations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1976–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, I.; Odermatt, D.; Anneville, O.; Wüest, A.; Bouffard, D. Application of Remote Sensing for the Optimization of In-Situ Sampling for Monitoring of Phytoplankton Abundance in a Large Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.C.; Kutser, T.; Hunter, P.D. Remote Sensing of Inland Waters: Challenges, Progress and Future Directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnhöfer, K.; Oppelt, N. Remote Sensing for Lake Research and Monitoring—Recent Advances. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 64, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernez, P.; Doxaran, D.; Barillé, L. Shellfish Aquaculture from Space: Potential of Sentinel2 to Monitor Tide-Driven Changes in Turbidity, Chlorophyll Concentration and Oyster Physiological Response at the Scale of an Oyster Farm. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Shi, T.; Hu, S.; Wu, G.; Zhou, Q. Application of Sentinel 2 MSI Images to Retrieve Suspended particulate matter concentrations in Poyang Lake. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Laas, A.; Sepp, M.; Paavel, B.; Nõges, T. First Experiences in Mapping Lake Water Quality Parameters with Sentinel-2 MSI Imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, E.; Dörnhöfer, K.; Gege, P.; Schenk, K.; Klinger, P.; Wenzel, J.; Gruber, N. Analysis of Mineral-Rich Suspended Matter in Glacial Lakes Using Simulations and Satellite Data. In Living Planet Symposium; Ouwehand, L., Ed.; ESA Communications: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 740. [Google Scholar]
- Manzo, C.; Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Braga, F.; Bassani, C. Sensitivity Analysis of a Bio-Optical Model for Italian Lakes Focused on Landsat-8, Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 48, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrova, O.Y.; Soloviev, D.M.; Strochkov, M.A.; Bocharova, T.Y.; Kashnitsky, A.V. River plumes investigation using Sentinel-2A MSI and Landsat-8 OLI data. In Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9999, p. 99990G. [Google Scholar]
- Pahlevan, N.; Chittimalli, S.K.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Vellucci, V. Sentinel-2/Landsat-8 Product Consistency and Implications for Monitoring Aquatic Systems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, A.; Fortunato, E. The Sedimentary Infill of the Pertusillo Freshwater Reservoir (Val d’Agri, Southern Italy). Feb Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 23, 824–830. [Google Scholar]
- Faruolo, M.; Coviello, I.; Filizzola, C.; Lacava, T.; Pergola, N.; Tramutoli, V. A Satellite-Based Analysis of the Val d’Agri Oil Center (Southern Italy) Gas Flaring Emissions. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 2783–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Emilio, M.; Coluzzi, R.; Macchiato, M.; Imbrenda, V.; Ragosta, M.; Sabia, S.; Simoniello, T. Satellite Data and Soil Magnetic Susceptibility Measurements for Heavy Metals Monitoring: Findings from Agri Valley (Southern Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Gao, P. Heavy Metal Research in Lacustrine Sediment: A Review. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2007, 25, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoniello, T.; Coluzzi, R.; Imbrenda, V.; Lanfredi, M. Land Cover Changes and Forest Landscape Evolution (1985–2009) in a Typical Mediterranean Agroforestry System (High Agri Valley). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autorità Di Bacino Della Basilicata. Available online: http://www.adb.basilicata-it/adb/risorseidriche/diaginv.asp?invaso=Pertusillo (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- Centro Funzionale Basilicata. Available online: http://centrofunzionalebasilicata.it/it/scaricaDati (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- Capozza, F. Influenza del fattore geomorfologico e litoloco sul trasporto solido del Fiume Agri a monte della diga del Pertusillo. Rass. Lav. Pubblici 1963, 12, 1235–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Anselmi, B.; Blasi, L.; Cautilli, F.; Crovato, C.; Grauso, S. La sedimentazione nell’invaso artificiale del Pertusillo (Fiume Agri, Basilicata). Geol. Tec. Ambient. 1996, 4, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Strickland, J.D.; Parsons, T.R. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis; Journal of Fisheries Research Board of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Protocols for the Joint Global Ocean Flux Study (JGOFS) Core Measurements; UNESCO-IOC: Paris, France, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, J.L.; Fargion, G.S.; McClain, C.R. Ocean Optics Protocols for Satellite Ocean Color Sensor Validation. In Technical Memorandum TM-2003-21621/Revision 5; NASA Goddard Space Flight Space Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ViewSpec Pro Software Manual, ASD Inc. 2008. Available online: http://www.grss-ieee.org/lep4/project_materials_for_web/viewspecpro_manual.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- Lee, Z. Remote Sensing of Inherent Optical Properties: Fundamentals, Tests of Algorithms, and Applications; International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group: Hanover, NH, Canada, 2006; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Zibordi, G.; Voss, K. Protocols for Satellite Ocean Color Data Validation: In Situ Optical Radiometry; IOCCG Protocols Document; IOCCG: Hanover, NH, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Coluzzi, R.; Imbrenda, V.; Lanfredi, M.; Simoniello, T. A First Assessment of the Sentinel-2 Level 1-C Cloud Mask Product to Support Informed Surface Analyses. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Acolite for Sentinel-2: Aquatic applications of MSI imagery. In Proceedings of the 2016 ESA Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- United States Geological Survey (USGS) Web Portal. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov (accessed on 18 July 2019).
- ESA’s Science Hub Web Portal. Available online: https://scihub.copernicus.eu (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- ACOLITE Software. Available online: https://odnature.naturalsciences.be/remsem/acolite-forum (accessed on 24 April 2020).
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Franch, B. Preliminary Analysis of the Performance of the Landsat 8/OLI Land Surface Reflectance Product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric Correction of Metre-Scale Optical Satellite Data for Inland and Coastal Water Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q. Adaptation of the Dark Spectrum Fitting Atmospheric Correction for Aquatic Applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 Archives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J. A Multi-Sensor Approach for the On-Orbit Validation of Ocean Color Satellite Data Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Bakelants, L.; Solana, C.; Canters, F.; Kervyn, M. Dating Lava Flows of Tropical Volcanoes by Means of Spatial Modeling of Vegetation Recovery. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.G.; Park, Y. Calibration and Validation of a Generic Multisensor Algorithm for Mapping of Total Suspended Matter in Turbid Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of Constituent Retrieval in Optically Deep and Complex Waters from Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tou, J.T.; Gonzalez, R.C. Pattern Recognition Principles; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Valentini, E.; Gasperini, L.; Bolpagni, R.; Brando, V.E. Airborne hyperspectral Data to Assess Suspended Particulate Matter and Aquatic Vegetation in a Shallow and Turbid Lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, E.T.; Franken, R.J.; Jeppesen, E.; Moss, B.; Bécares, E.; Hansson, L.A.; Nõges, T. Assessing Ecological Quality of Shallow Lakes: Does Knowledge of Transparency Suffice? Basic Appl. Ecol. 2009, 10, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E.; Vincent, W.F.; Smol, J.P. Lakes and Reservoirs as Sentinels, Integrators, and Regulators of Climate Change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Lee, Z.; Wei, J.; Schaaf, C.B.; Schott, J.R.; Berk, A. On-Orbit Radiometric Characterization of OLI (Landsat-8) for Applications in Aquatic Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Schott, J.R. Leveraging EO-1 to Evaluate Capability of New Generation of Landsat Sensors for Coastal/Inland Water Studies. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandanici, E.; Bitelli, G. Preliminary Comparison of Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 Imagery for a Combined Use. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Sarkar, S.; Franz, B.A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; He, J. Sentinel-2 MultiSpectral Instrument (MSI) Data Processing for Aquatic Science Applications: Demonstrations and Validations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Schott, J.R.; Franz, B.A.; Zibordi, G.; Markham, B.; Bailey, S.; Strait, C.M. Landsat 8 Remote Sensing Reflectance (Rrs) Products: Evaluations, Intercomparisons, and Enhancements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverie, M.; Ju, J.; Masek, J.G.; Dungan, J.L.; Vermote, E.F.; Roger, J.C.; Justice, C. The Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 Surface Reflectance Data Set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Zhu, Z. Harmonizing Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2: A Time-Series-Based Reflectance Adjustment Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.R.; Ogashawara, I.; Gitelson, A.A. Bio-Optical Modeling and Remote Sensing of Inland Waters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, W.J.; Sterckx, S.; Montes, M.J.; De Keukelaere, L.; Knaeps, E. Chapter 3-Atmospheric Correction for Inland Waters. In Bio-Optical Modeling and Remote Sensing of Inland Waters; Mishra, R.D., Ogashawar, I., Gitelson, A.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 69–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of Water-Leaving Radiance and Aerosol Optical Thickness Over the Oceans with SeaWiFS: A Preliminary Algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M. Remote sensing of the ocean contributions from ultraviolet to near-infrared using the shortwave infrared bands: Simulations. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doxaran, D.; Froidefond, J.M.; Lavender, S.; Castaing, P. Spectral Signature of Highly Turbid Waters: Application with SPOT Data to Quantify Suspended Particulate Matter Concentrations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacava, T.; Ciancia, E.; Di Polito, C.; Madonia, A.; Pascucci, S.; Pergola, N.; Tramutoli, V. Evaluation of MODIS—Aqua Chlorophyll-a Algorithms in the Basilicata Ionian Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lee, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Z. Remote Sensing of Secchi Depth in Highly Turbid Lake Waters and Its Application with MERIS Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, Z.; Sun, D.; Shen, X.; Zhang, H. Light Beam Attenuation and Backscattering Properties of Particles in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea with Relation to Biogeochemical Properties. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 3955–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Roy, D.P. A Global Analysis of Sentinel-2A, Sentinel-2B and Landsat-8 Data Revisit Intervals and Implications for Terrestrial Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 902. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, S.L.; Wiley, K.B. Great Lakes Toxic Sediments and Climate Change: Implications for Environmental Remediation. Glob. Environ. Chang. 1993, 3, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coops, H.; Beklioglu, M.; Crisman, T.L. The role of water-level fluctuations in shallow lake ecosystems–workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leira, M.; Cantonati, M. Effects of Water-Level Fluctuations on Lakes: An Annotated Bibliography. In Ecological Effects of Water-Level Fluctuations in Lakes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Premazzi, G.; Dalmiglio, A.; Cardoso, A.C.; Chiaudani, G. Lake Management in ITALY: The Implications of the Water Framework Directive. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2003, 8, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruolo, M.; Lacava, T.; Pergola, N.; Tramutoli, V. The VIIRS-Based RST-FLARE Configuration: The Val d’Agri Oil Center Gas Flaring Investigation in Between 2015–2019. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sampling Days | Number of Samples | Type of Measurements |
|---|---|---|
| 10 May 2017 | 10 | TSM, chl-a, aCDOM(440), Rrs(λ) |
| 26 May 2017 | 10 | TSM, chl-a, aCDOM(440), Rrs(λ) |
| 14 June 2017 | 10 | TSM, chl-a, aCDOM(440), Rrs(λ) |
| 15 June 2017 | 10 | TSM, chl-a, aCDOM(440), Rrs(λ) |
| 19 September 2017 | 9 | TSM, chl-a, aCDOM(440) |
| 12 October 2017 | 8 | TSM, chl-a, aCDOM(440), Rrs(λ) |
| 21 November 2017 | 8 | TSM, chl-a, aCDOM(440), Rrs(λ) |
| 17 May 2018 | 10 | TSM, chl-a, aCDOM(440), Rrs(λ) |
| Sensor | Blue1 | Blue2 | Green | Red1 | Red2 | Red3 | Red4 | NIR1 | NIR2 | SWIR1 | SWIR2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSI | 443 (60 m) | 492 (10 m) | 560 (10 m) | 665 (10 m) | 704 (20 m) | 740 (20 m) | 783 (20 m) | 833 (20 m) | 865 (20 m) | 1614 (20 m) | 2202 (20 m) |
| OLI | 443 (30 m) | 483 (30 m) | 561 (30 m) | 655 (30 m) | 865 (30 m) | 1609 (30 m) | 2201 (30 m) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciancia, E.; Campanelli, A.; Lacava, T.; Palombo, A.; Pascucci, S.; Pergola, N.; Pignatti, S.; Satriano, V.; Tramutoli, V. Modeling and Multi-Temporal Characterization of Total Suspended Matter by the Combined Use of Sentinel 2-MSI and Landsat 8-OLI Data: The Pertusillo Lake Case Study (Italy). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132147
Ciancia E, Campanelli A, Lacava T, Palombo A, Pascucci S, Pergola N, Pignatti S, Satriano V, Tramutoli V. Modeling and Multi-Temporal Characterization of Total Suspended Matter by the Combined Use of Sentinel 2-MSI and Landsat 8-OLI Data: The Pertusillo Lake Case Study (Italy). Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(13):2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132147
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiancia, Emanuele, Alessandra Campanelli, Teodosio Lacava, Angelo Palombo, Simone Pascucci, Nicola Pergola, Stefano Pignatti, Valeria Satriano, and Valerio Tramutoli. 2020. "Modeling and Multi-Temporal Characterization of Total Suspended Matter by the Combined Use of Sentinel 2-MSI and Landsat 8-OLI Data: The Pertusillo Lake Case Study (Italy)" Remote Sensing 12, no. 13: 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132147
APA StyleCiancia, E., Campanelli, A., Lacava, T., Palombo, A., Pascucci, S., Pergola, N., Pignatti, S., Satriano, V., & Tramutoli, V. (2020). Modeling and Multi-Temporal Characterization of Total Suspended Matter by the Combined Use of Sentinel 2-MSI and Landsat 8-OLI Data: The Pertusillo Lake Case Study (Italy). Remote Sensing, 12(13), 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132147