Global Distribution of Column Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth to Surface PM2.5 Relationships
Abstract
1. Introduction
Methods for Estimating Surface PM2.5 from Satellite AOD
2. Data
2.1. Satellite AOD Product
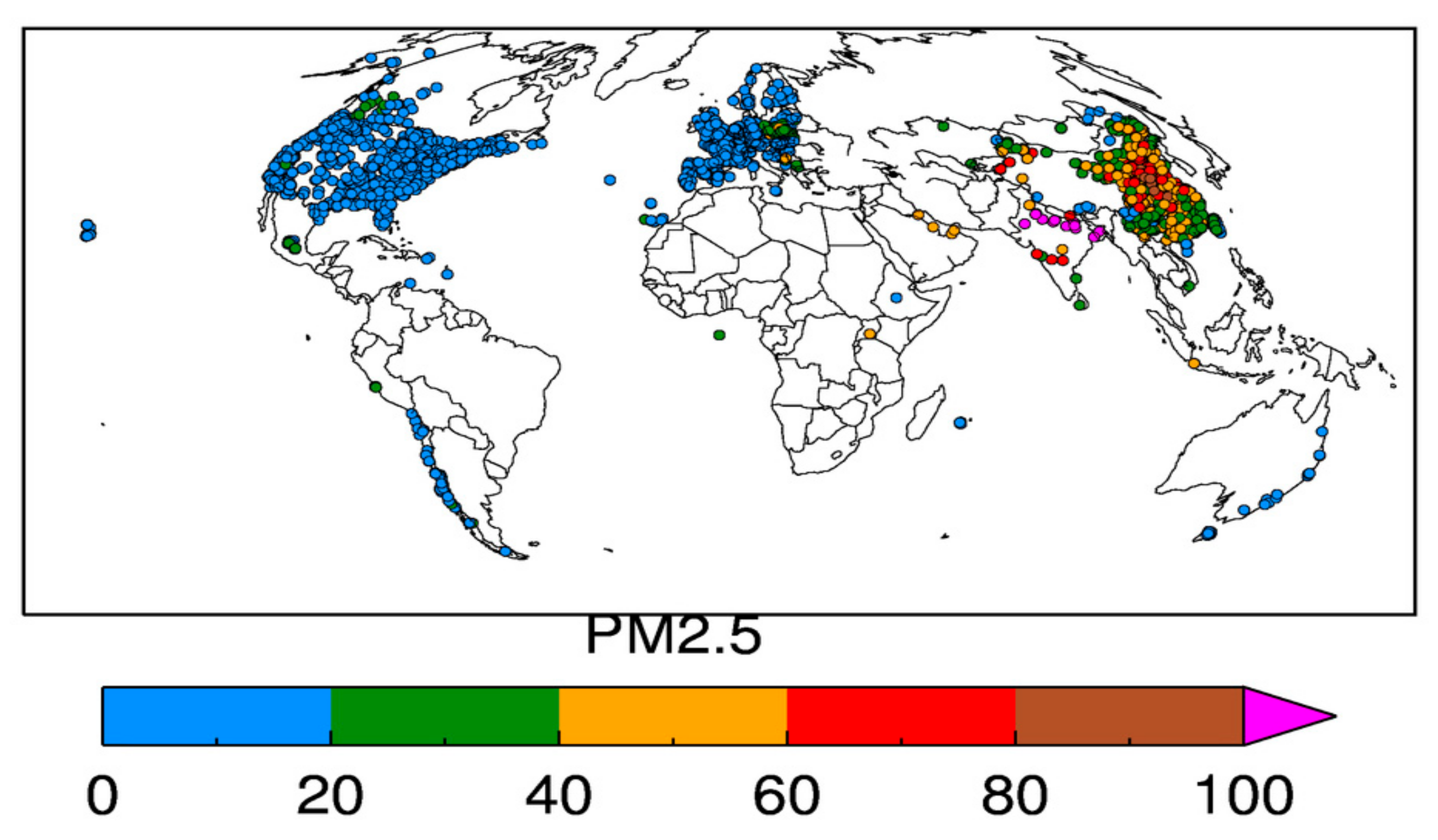
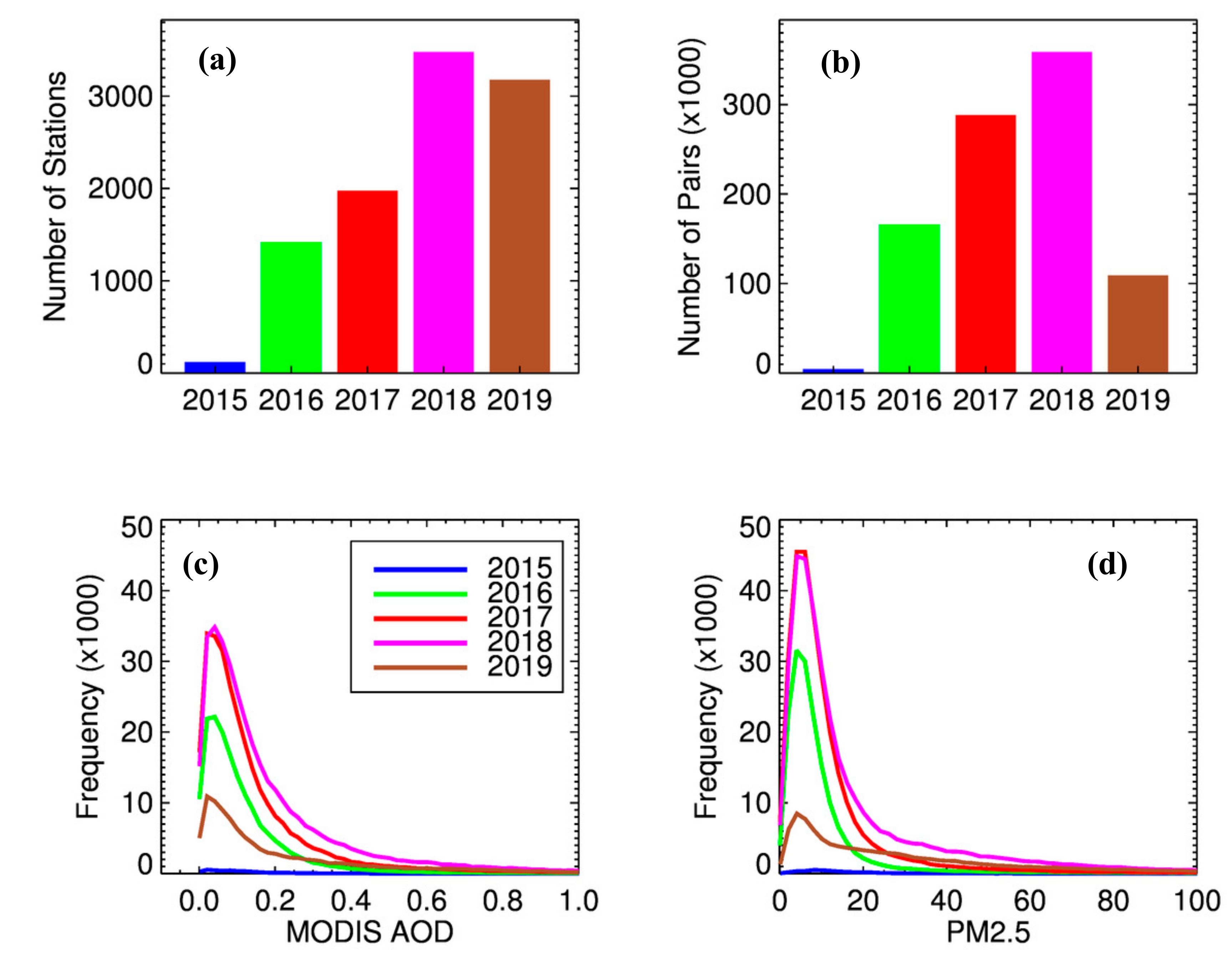
2.2. Surface PM2.5
3. Methods
- We first used the level 2 AOD at 0.1 × 0.1-degree spatial resolution to match with the PM2.5 data from global point locations both in space and time. For simplicity, 24-h averaged PM2.5 values are collocated with daily AOD values. The spatial collocation is performed by selecting the nearest satellite grid to the surface monitor.
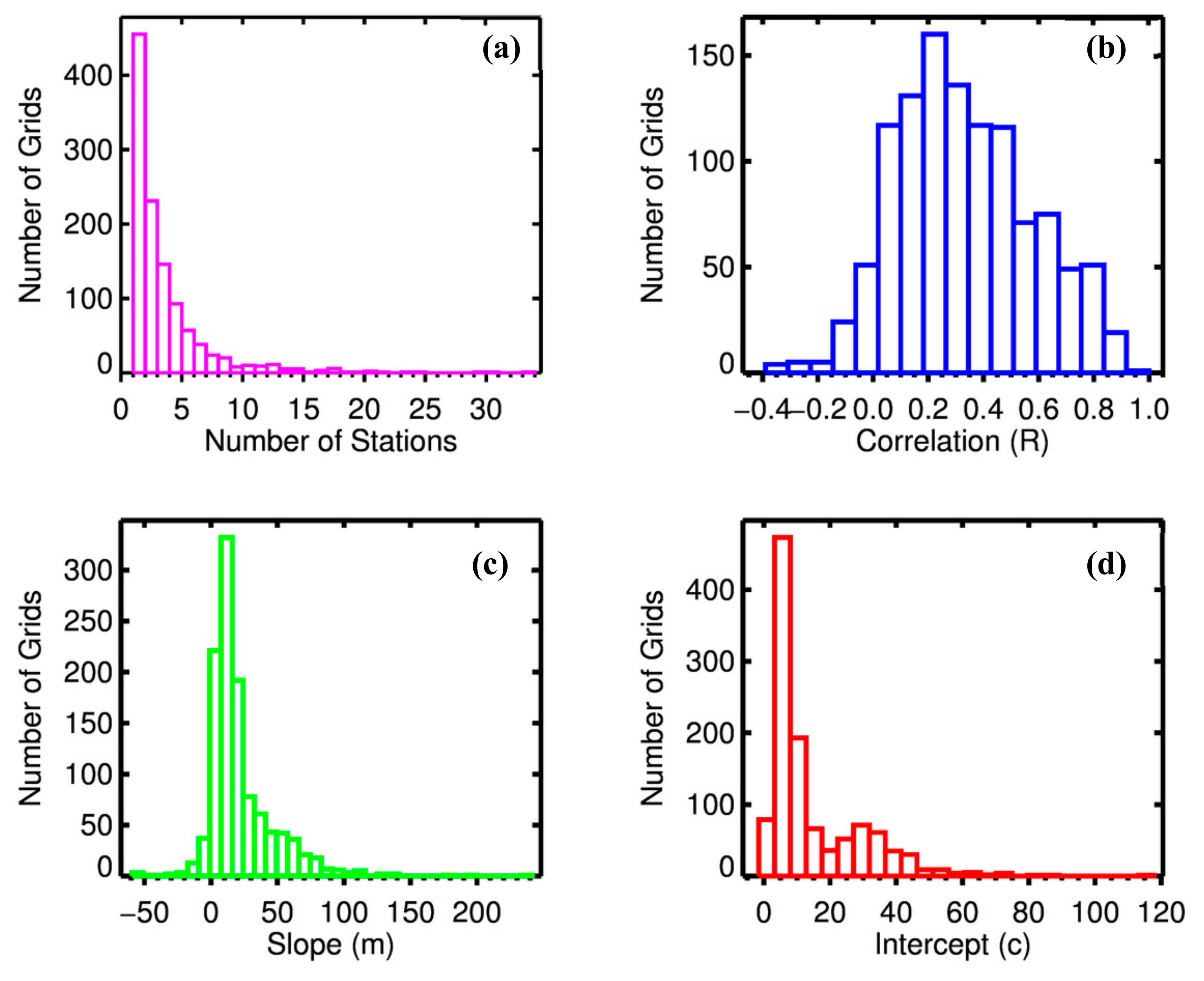
- Then we averaged the AOD data over 3 × 3 grids centered around the nearest grid to obtain an AOD value for a given day at a given PM2.5 locations. This way, we have spatial–temporal collocated AOD–PM2.5 data sets for 3352 ground monitors.
- We then present our results acquired at individual stations but grouped in 1 × 1 degree grids.
4. Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Ramaswamy, V.; Collins, W.; Haywood, J.; Lean, J.; Mahowald, N.; Myhre, G.; Naik, V.; Shine, K.P.; Soden, B.; Stenchikov, G.; et al. Radiative Forcing of Climate: The Historical Evolution of the Radiative Forcing Concept, the Forcing Agents and their Quantification, and Applications. Meteorol. Monogr. 2018, 59, 14.1–14.101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, R.M.; Christopher, S.A.; Hidy, G.; Sharma, P.; Poulsen, T.; Kalluri, P.; Hoff, S.; Bundy, D.; Nelson, M.; Zelle, B.; et al. Remote Sensing of Particulate Pollution from Space: Have We Reached the Promised Land? J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.N.; Power, S.A.; Jarraud, N.; Agrawal, M.; Davies, C. The effects of air pollution on urban ecosystems and agriculture. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2011, 18, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: an analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R. Global Estiamtes of mortality associaed with long erm exposure to outdoor fine particulate matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9592–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease; RePEc: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- West, J.J.; Cohen, A.; Dentener, F.; Brunekreef, B.; Zhu, T.; Armstrong, B.; Bell, M.; Brauer, M.; Carmichael, G.R.; Costa, D.L.; et al. What We Breathe Impacts Our Health: Improving Understanding of the Link between Air Pollution and Health. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4895–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balluz, L.; Wen, X.-J.; Town, M.; Shire, J.D.; Qualter, J.; Mokdad, A. Ischemic Heart Disease and Ambient Air Pollution of Particulate Matter 2.5 in 51 Counties in the U.S. Public Health Rep. 2007, 122, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.; Sioutas, C.; Koutrakis, P.; Reiss, R.; Lurmann, F.W.; Roberts, P.T. Evaluation of the TEOM method for measurement of ambient particulate mass in urban areas. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1997, 47, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feenstra, B.; Papapostolou, V.; Hasheminassab, S.; Zhang, H.; Der Boghossian, B.; Cocker, D.; Polidori, A. Performance evaluation of twelve low-cost PM2.5 sensors at an ambient air monitoring site. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 216, 116946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudnovsky, A.A.; Kostinski, A.; Lyapustin, A.; Koutrakis, P. Spatial scales of pollution from variable resolution satellite imaging. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudnovsky, A.; Tang, C.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. A critical assessment of high resolution aerosol optical depth (AOD) retrievals for fine particulate matter (PM) predictions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 14581–14611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Strandgren, J.; Rozanov, V.; Vountas, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Wang, Y. A study of the impact of spatial resolution on the estimation of particle matter concentration from the aerosol optical depth retrieved from satellite observations. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2019, 40, 7084–7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Intercomparison between satellite-derived aerosol optical thickness and PM2.5mass: Implications for air quality studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Paciorek, C.; Koutrakis, P. Estimating Regional Spatial and Temporal Variability of PM2.5 Concentrations Using Satellite Data, Meteorology, and Land Use Information. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Li, C.; Burnett, R.T. Regional Estimates of Chemical Composition of Fine Particulate Matter Using a Combined Geoscience-Statistical Method with Information from Satellites, Models, and Monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2595–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Diner, D.J. Multi-Angle Imager for Aerosols: A Satellite Investigation to Benefit Public Health. Public Health Rep. 2017, 132, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelemeijer, R.; Homan, C.; Matthijsen, J. Comparison of spatial and temporal variations of aerosol optical thickness and particulate matter over Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5304–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Lu, H.; Lu, Y.; Mao, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, N.; Ren, M.; et al. A Review on Predicting Ground PM2.5 Concentration Using Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A. Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological products: Multiple regression approach. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Park, R.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Li, Q.; Kilaru, V.; A Sarnat, J. Mapping annual mean ground-level PM2.5concentrations using Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol optical thickness over the contiguous United States. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Liu, Y.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. A novel calibration approach of MODIS AOD data to predict PM2.5 concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 7991–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloog, I.; Nordio, F.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J. Incorporating Local Land Use Regression And Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth In A Hybrid Model Of Spatiotemporal PM2.5Exposures In The Mid-Atlantic States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11913–11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckerman, B.S.; Jerrett, M.; Serre, M.L.; Martin, R.V.; Lee, S.-J.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Ross, Z.; Su, J.; Burnett, R.T. A Hybrid Approach to Estimating National Scale Spatiotemporal Variability of PM2.5in the Contiguous United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7233–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Crosson, W.L.; Mauric, G.E., Jr.; Estes, S.M.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Sarnat, J.A.; Liu, Y. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the southeastern U.S. using geographically weighted regression. Environ. Res. 2013, 121, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jia, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. A satellite-based geographically weighted regression model for regional PM2.5 estimation over the Pearl River Delta region in China. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A. Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological products: 2. A neural network approach. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, H.; Li, Q.; Wu, C.; Qi, Y.; Mo, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Sachdeva, S.; Kaimian, H. Evaluation of Different Machine Learning Approaches to Forecasting PM2.5 Mass Concentrations. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Belle, J.; Meng, X.; Wildani, A.; Waller, L.A.; Strickland, M.J.; Liu, Y.; Kelly, J.T.; Jang, C.J.; Timin, B.; et al. Estimating PM2.5Concentrations in the Conterminous United States Using the Random Forest Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6936–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, U.; Ma, J.; Ryu, U.; Ryom, K.; Juhyok, U.; Pak, K.; Pak, C. Deep learning-based PM2.5 prediction considering the spatiotemporal correlations: A case study of Beijing, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 699, 133561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Levy, R.; Remer, L.; Patadia, F.; Christopher, S.A. High Resolution Gridded Level 3 Aerosol Optical Depth Data from MODIS, to be submitted to Geoscience Data Journal, 2020, to be submitted.
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L.A. MODIS 3 km aerosol product: algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Remer, L.A.; Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S. Validation of MODIS 3 km land aerosol optical depth from NASA’s EOS Terra and Aqua missions. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3145–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L. MODIS Collection 6.1 aerosol optical depth products over land and ocean: validation and comparison. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.; Gupta, P. Satellite remote sensing of particulate matter air quality: the cloud-cover problem. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Region Number | Region | Number of Stations | Number of Pairs | R | m | c | Mean AOD | Mean PM2.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | North America | 1056 | 507,092 | 0.55 | 24.4 | 6.0 | 0.149 | 9.6 |
| 2 | Europe | 775 | 188,769 | 0.12 | 8.9 | 12.6 | 0.153 | 13.9 |
| 3 | Asia | 1508 | 159,440 | 0.49 | 55.0 | 33.0 | 0.435 | 57.0 |
| 4 | South America | 90 | 49,163 | 0.10 | 19.4 | 17.8 | 0.100 | 19.8 |
| 5 | Africa | 30 | 5728 | 0.56 | 65.4 | 7.9 | 0.265 | 25.0 |
| 6 | Australia | 61 | 15,237 | 0.55 | 45.2 | 3.9 | 0.091 | 8.0 |
| Global | 3352 | 925,817 | 0.55 | 54.1 | 8.6 | 0.19 | 19.3 |
| Season | Numbers of Stations | Numbers of Pairs | R | m | c | Mean AOD | Mean PM2.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DJF | 3321 | 175,387 | 0.65 | 81.8 | 14.1 | 0.20 | 30.6 |
| MAM | 3432 | 230,443 | 0.62 | 62.0 | 5.5 | 0.19 | 17.6 |
| JJA | 2127 | 242,477 | 0.46 | 22.5 | 7.3 | 0.22 | 12.2 |
| SON | 3469 | 277,510 | 0.59 | 58.9 | 9.3 | 0.18 | 19.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christopher, S.; Gupta, P. Global Distribution of Column Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth to Surface PM2.5 Relationships. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121985
Christopher S, Gupta P. Global Distribution of Column Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth to Surface PM2.5 Relationships. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(12):1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121985
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristopher, Sundar, and Pawan Gupta. 2020. "Global Distribution of Column Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth to Surface PM2.5 Relationships" Remote Sensing 12, no. 12: 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121985
APA StyleChristopher, S., & Gupta, P. (2020). Global Distribution of Column Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth to Surface PM2.5 Relationships. Remote Sensing, 12(12), 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121985




