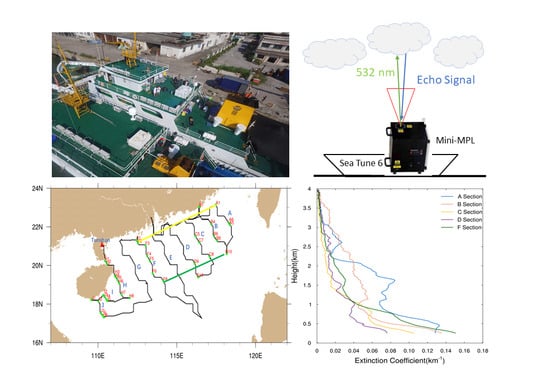
Micro-Pulse Lidar Cruising Measurements in Northern South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Observation Experiments and Methodology
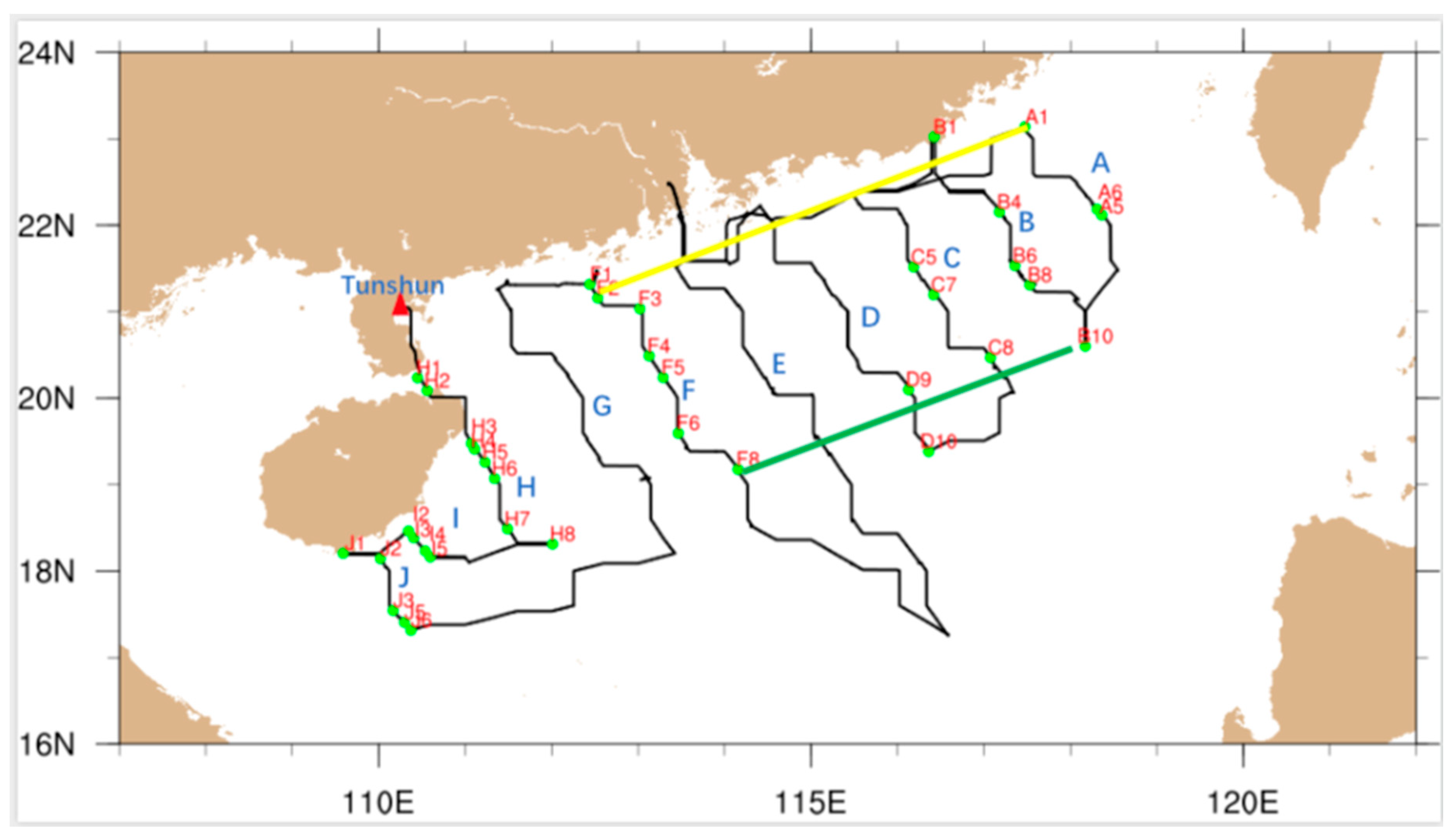
2.1. Cruise and Instrument
2.2. Quality Control and Preprocessing
- It was discontinuous due to technical difficulties, e.g., ship instability or typhoon avoidance.
- There were 10-m wind speed above 9 m/s or when it was raining. From cruise weather records, the profile was judged to be visibly contaminated by clouds or excessive humidity. The profile was considered contaminated by excessive humidity when both visibility was less than 7 km and the signal-to-noise ratio was less than 20 below 3 km.
- The raw signal was overshooting.
2.3. Calculation of Extinction Coefficient
2.4. Calculation of Depolarization Ratio
2.5. Calculation of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height (ABLH)
2.6. Back-Trajectories
3. Results
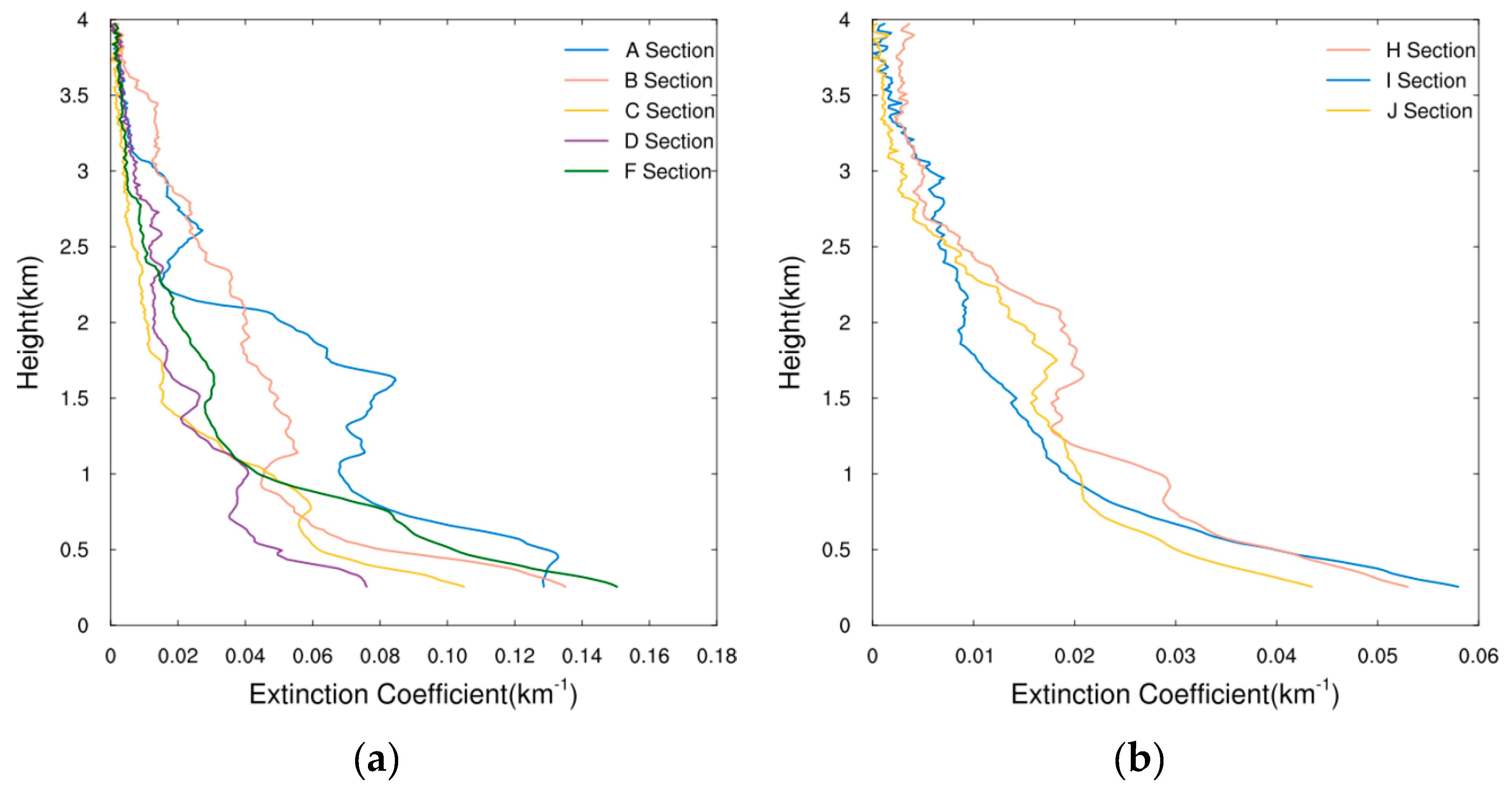
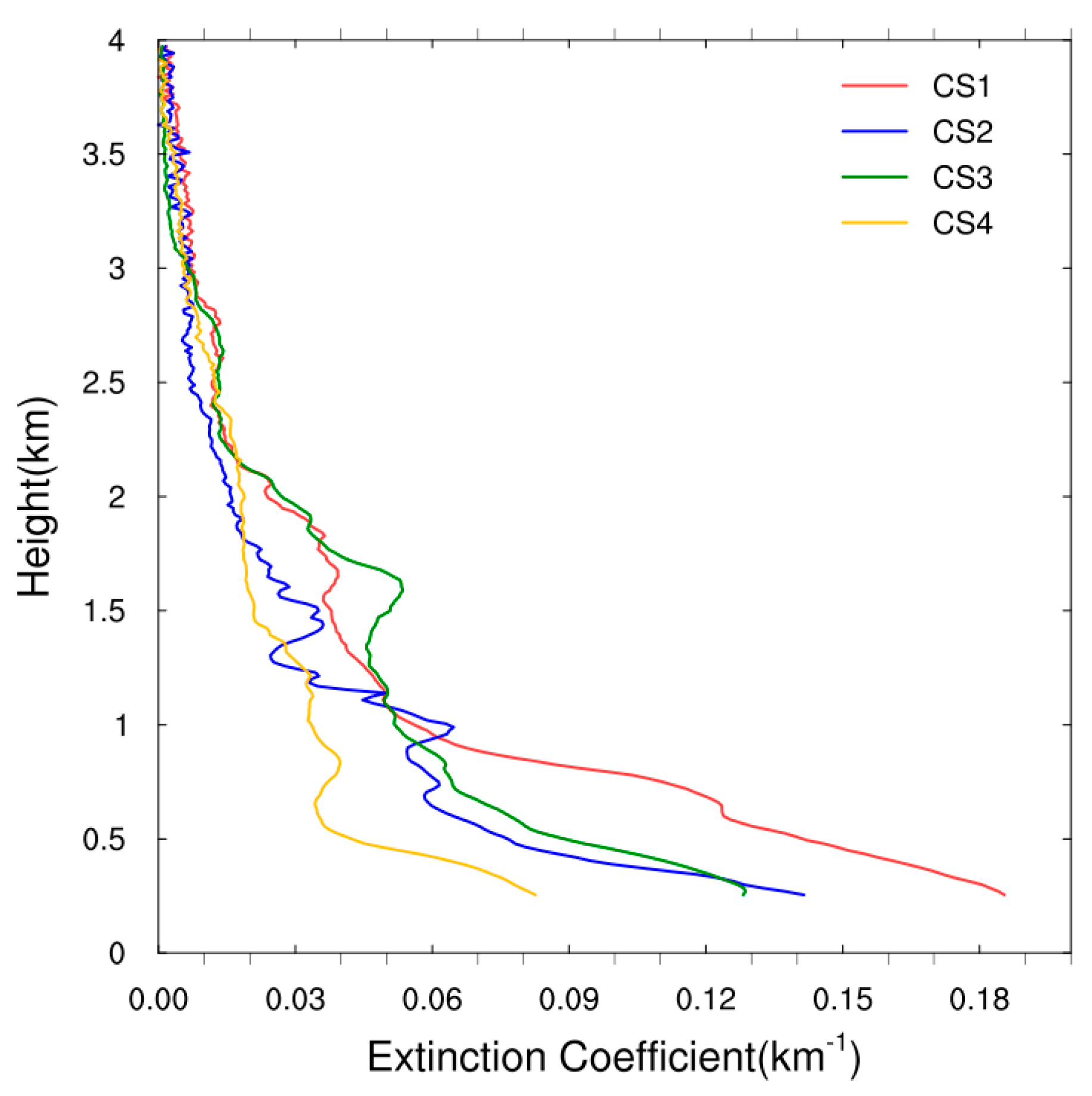
3.1. Vertical Structure of Extinction Coefficient
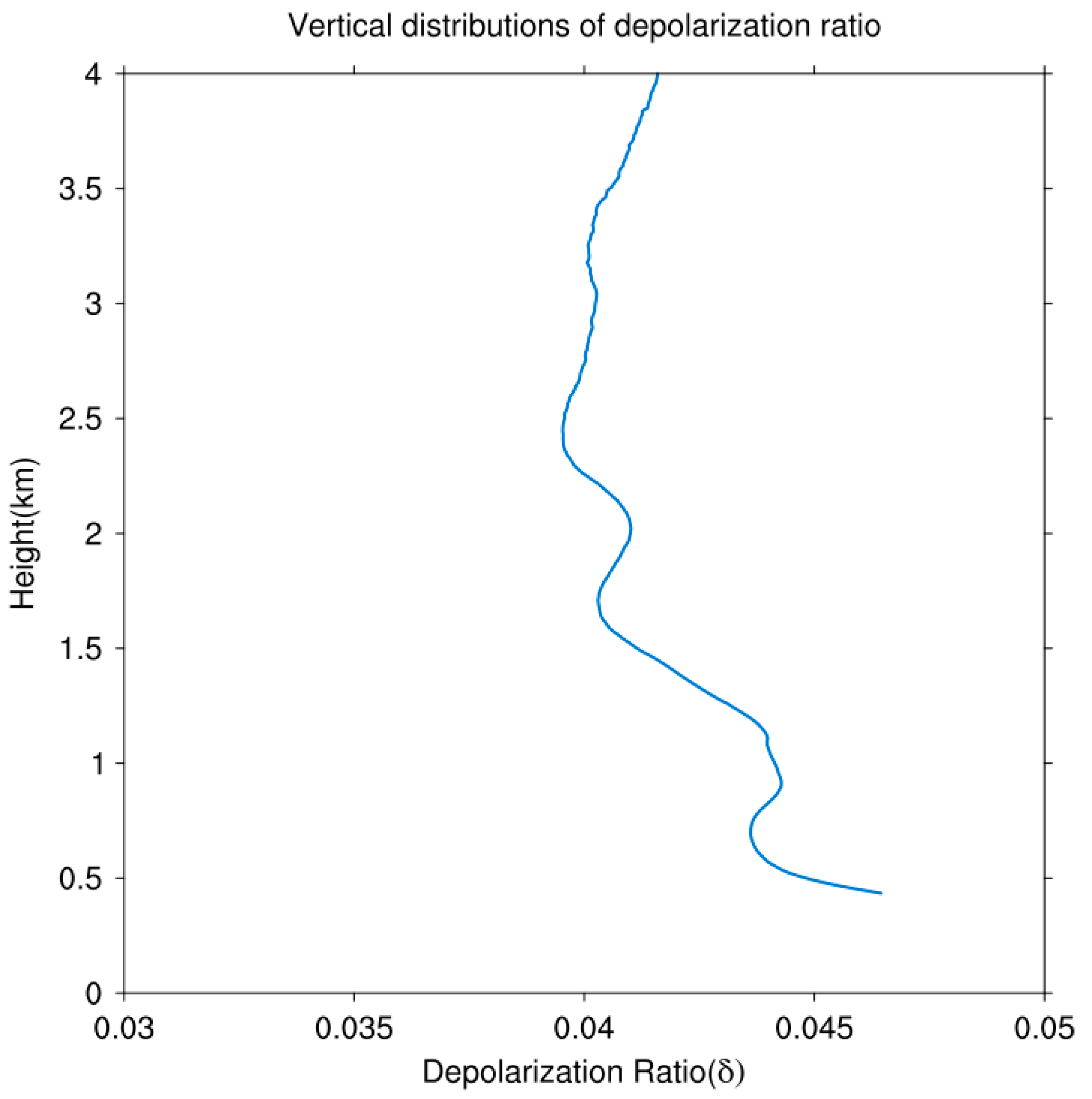
3.2. Depolarization Ratio
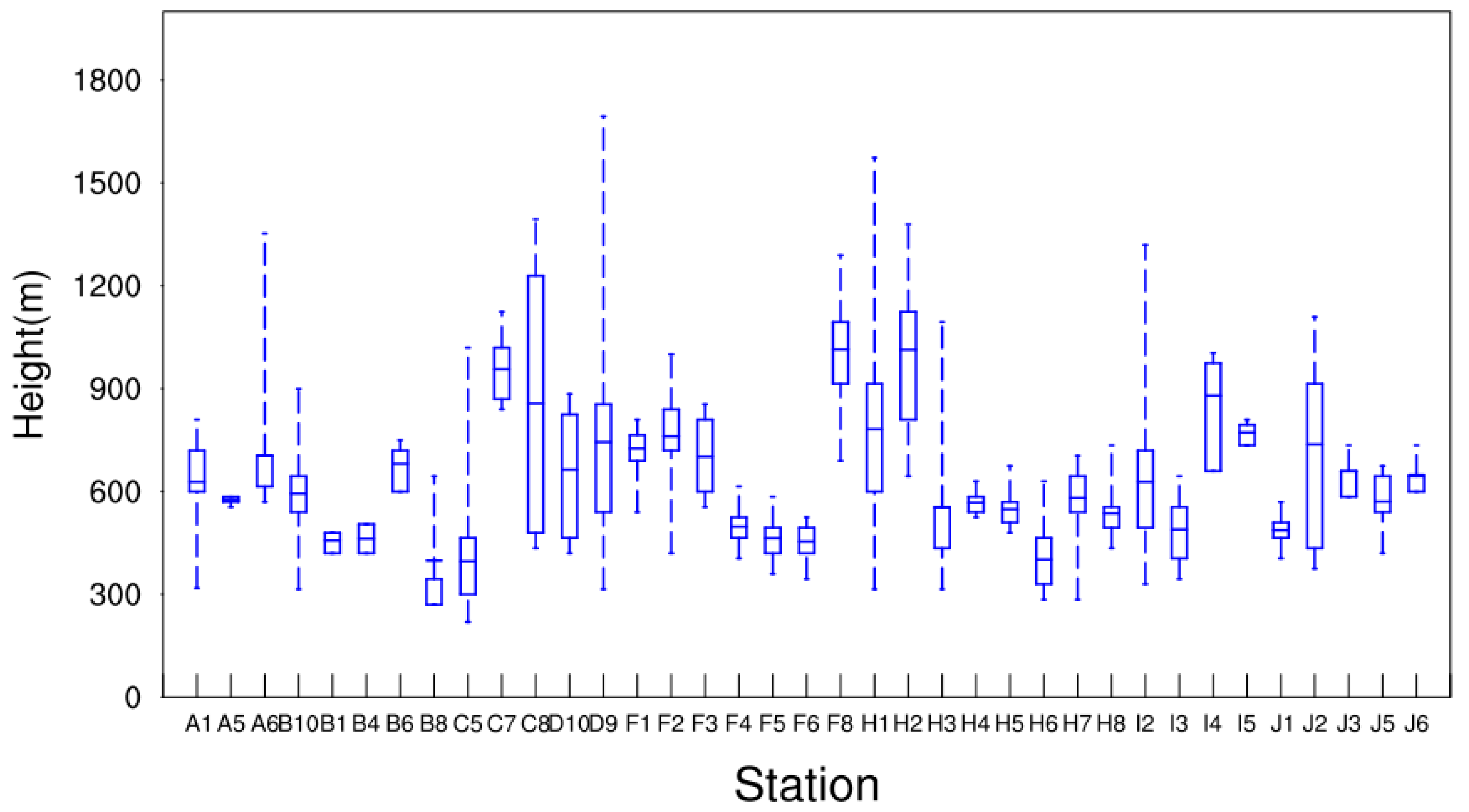
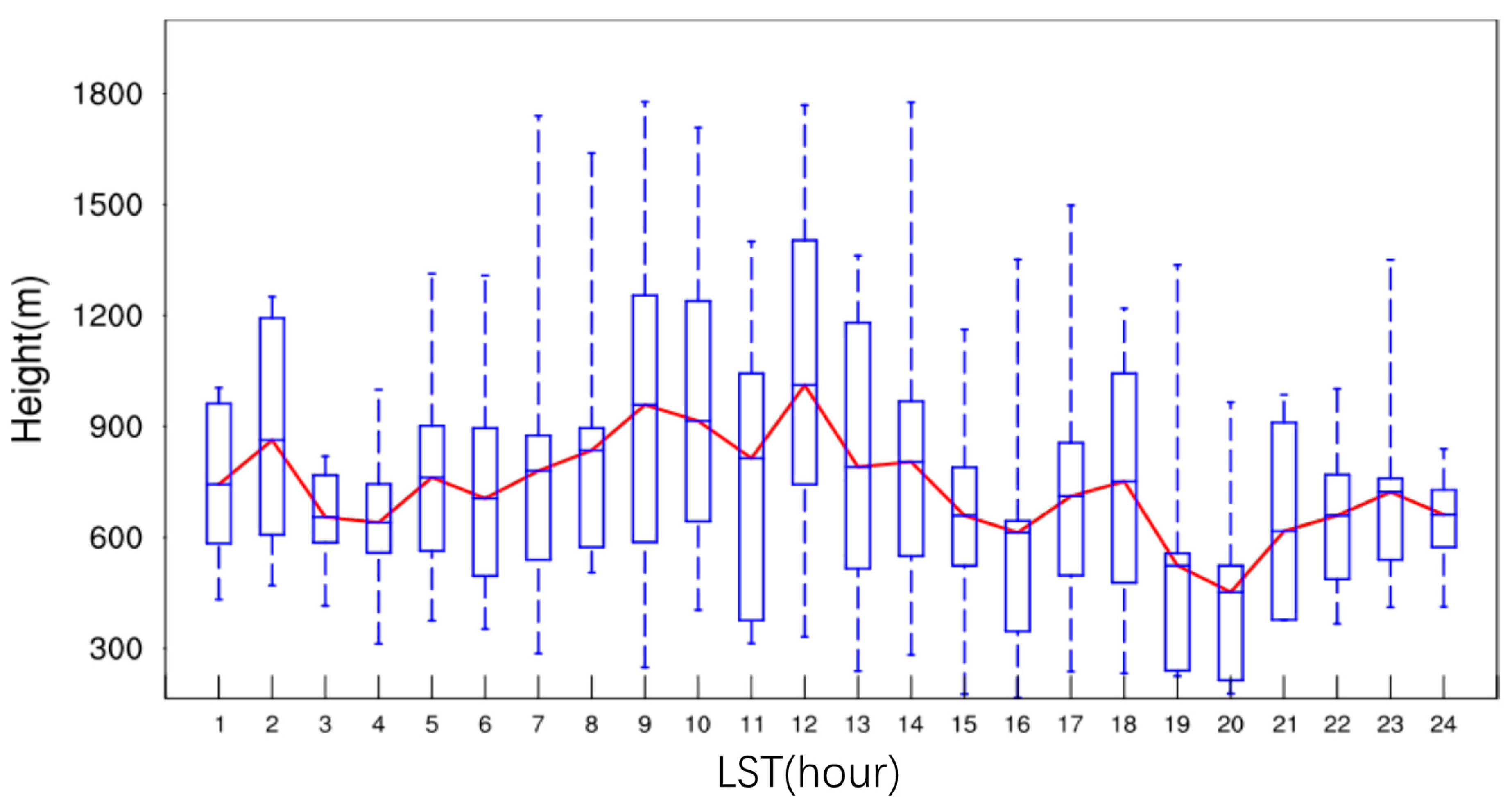
3.3. Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height (ABLH)
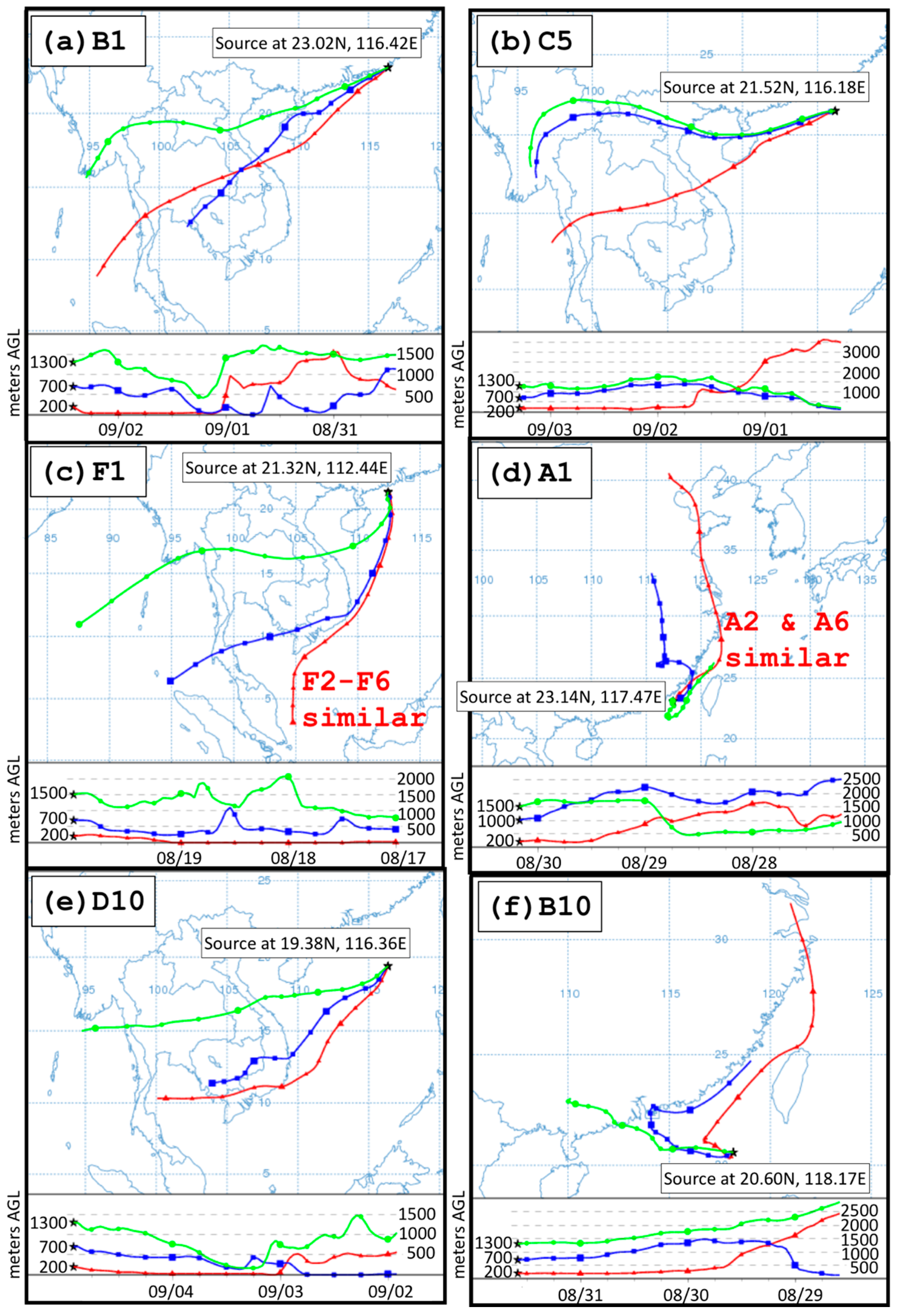
3.4. Back-Trajectories
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meinrat, O.A.; Paul, J.C. Atmospheric Aerosols: Biogeochemical Sources and Role in Atmospheric Chemistry. Science 1997, 276, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Gordon, H.R.; Nakajima, T.; Lenoble, J.; Frouin, R.; Grassl, H.; Herman, B.M.; King, M.D.; Teillet, P.M. Passive remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol and atmospheric correction for the aerosol effect. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16815–16830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréon, F.M.; Tanré, D.; Generoso, S. Aerosol effect on cloud droplet size monitored from satellite. Science 2002, 295, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutzen, P.J.; Andreae, M.O. Biomass Burning in the Tropics: Impact on Atmospheric Chemistry and Biogeochemical Cycles. Science 1990, 250, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC, Climate Change. The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lang-Yona, N.; Lehahn, Y.; Herut, B.; Burshtein, N.; Rudich, Y. Marine aerosol as a possible source for endotoxins in coastal areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkikas, A.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Torres, O. Characterization of aerosol episodes in the greater Mediterranean Sea area from satellite observations (2000–2007). Atmos. Environ. 2016, 128, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.P.; Chen, L.Q.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, S.H.; Li, L.; Zhu, D.Y. Marine Aerosol Using On-board Aerosol Mass Spectrometry. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 2629–2636. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tsunogai, S.; Kondo, T. Sporadic transport and deposition of continental aerosols to the Pacific Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1982, 87, 8870–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yan, L. Multi-angular polarized characteristics of ocean aerosol. Spectrosc. Spectra. Anal. 2013, 33, 600–607. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.W.; Sheng, L.F.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.Z. Impact of marine-atmospheric process on aerosol number size distribution in the south China sea. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 2443–2452. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bellouin, N.; Boucher, O.; Haywood, J.; Reddy, M.S. Global estimate of aerosol direct radiative forcing from satellite measurements. Nature 2005, 438, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Chen, L.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, M. Effect of typhoon on atmospheric aerosol particle pollutants accumulation over Xiamen, China. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Chen, B.; Ming, J.; Lynn, B.H.; Yang, M.J. Aerosol Impacts on the Structure, Intensity, and Precipitation of the Landfalling Typhoon Saomai (2006). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.Y. Climatological characteristics on the onset of the South China Sea southwest monsoon. Chin. Meteorol. Sci. 1997, 55, 174–180. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Li, C.; He, J.; Chen, L.; Gan, Z.; Qian, Y.; Xu, J. South China sea monsoon experiment (SCSMEX) and the East Asian monsoon. Chin. Meteorol. Sci. 2004, 20, 159. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guan, F.; Xie, Q. The statistical characteristics of typhoon in the South China Sea. Marine Sci. Bull. 1984, 3, 19–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Wu, D.; Bi, X. Measurement and study of aerosol optical depth over northern South China Sea. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2006, 25, 21–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.Z.; Tian, L.Q.; Yang, J.K.; Chen, C.C. Study of aerosol optical thickness over Northern South China Sea. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2008, 24, 205–208. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Vaughan, M.; Uno, I.; Sugimoto, N.; Kittaka, C.; Trepte, C.; Wang, Z.; Hostetler, C.; et al. Airborne dust distributions over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas derived from the first year of CALIPSO lidar observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5045–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, J. Using the MIE theory to calculate aerosol optical characterization. J. Atomic Mol. Phys. 2005, 22, 701–707. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.T.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, M.H. Summary comment on research of atmospheric aerosol in China. Chin. Meteorol. Sci. 2002, 60, 625–634. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Powell, D.M.; Reagan, J.A.; Rubio, M.A.; Erxleben, W.H.; Spinhirne, J.D. ACE-2 multiple angle micro-pulse lidar observations from Las Galletas, Tenerife, Canary Islands. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2000, 52, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, E.J.; Voss, K.J.; Quinn, P.K.; Flatau, P.J.; Markowicz, K.; Campbell, J.R.; Spinhirne, J.D.; Gordon, H.R.; Johnson, J.E. Measurements of aerosol vertical profiles and optical properties during INDOEX 1999 using micropulse lidars. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, W.; Gao, F.; Tang, J. Ground surface observation of aerosol optical thickness over Yellow Sea region. Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 2003, 20, 635–640. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duflot, V.; Royer, P.; Chazette, P.; Baray, J.L.; Courcoux, Y.; Delmas, R. Marine and biomass burning aerosols in the southern Indian Ocean: Retrieval of aerosol optical properties from shipborne lidar and Sun photometer measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, S.; Tesche, M.; Freudenthaler, V.; Toledano, C.; Wiegner, M.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Seefeldner, M. Characterization of Saharan dust, marine aerosols and mixtures of biomass-burning aerosols and dust by means of multi-wavelength depolarization and Raman lidar measurements during SAMUM 2. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 706–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, I.; Savov, P.; Kaprielov, B.; Parvanov, O.; Simeonov, V. Lidar observation of the nocturnal boundary layer formation over Sofia, Bulgaria. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 3223–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Lacis, A.A.; Fung, I. The influence on climate forcing of mineral aerosols from disturbed soils. Nature 1996, 380, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, X.M.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, T. Atmosphere boundary layer height (ABLH) determination under multiple-layer conditions using micro-pulse lidar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavers, D.A.; Beljaars, A.; Richardson, D.S.; Rodwell, M.J.; Pappenberger, F. A Forecast Evaluation of Planetary Boundary Layer Height Over the Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 4975–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, L.R. Sensitivity analysis of lidar inversion algorithms. Appl. Opt. 1986, 25, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New Lidar Product: The Mini-MPL Launched By Sigma Space. Available online: http://www.sigmaspace.com/blog-post/new-lidar-product-minimpl-launched-sigma-space (accessed on 23 June 2010).
- Campbell, J.R.; Hlavka, D.L.; Welton, E.J.; Flynn, C.J.; Turner, D.D.; Spinhirne, J.D.; Stanley, S.; Hwang, I.H. Full-time, eye-safe cloud and aerosol lidar observation at atmospheric radiation measurement program sites: Instruments and data processing. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collis, R.T.H. Lidar: A new atmospheric probe. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1966, 92, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, J.D. Lidar inversion with variable backscatter/extinction ratios. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reba, M.N.M.; Rocadenbosch, F.; Sicard, M.; Kumar, D.; Tomás Martínez, S. On the lidar ratio estimation from the synergy between aeronet sun-photometer data and elastic lidar inversion. In Proceedings of the 25th International Laser Radar Conference (Conference on Advances in Lidar Components and Techniques), Saint Petersburg, Russia, 5–9 July 2010; pp. 1102–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Cattrall, C.; Reagan, J.; Thome, K.; Dubovik, O. Variability of aerosol and spectral lidar and backscatter and extinction ratios of key aerosol types derived from selected Aerosol Robotic Network locations. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2005, 110, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Kittaka, C.; Vaughan, M.A.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Rogers, R.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.P.; et al. The CALIPSO automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.S.; Li, C.C.; Mao, J.T.; Lau, A.K.H.; Li, P.R. A study on the aerosol extinction-to-backscatter ratio with combination of micro-pulse LIDAR and MODIS over Hong Kong. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3243–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Franke, K.; Wagner, F.; Althausen, D.; Ansmann, A.; Heintzenberg, J.; Verver, G. Vertical profiling of optical and physical particle properties over the tropical Indian Ocean with six-wavelength lidar 2. Case studies. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 28577–28595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, K.W.; Meskhidze, N.; Josset, D.; Gassó, S. Spaceborne observations of the lidar ratio of marine aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3241–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, L.; Flamant, C.; Pelon, J.; Flamant, P.H. Urban boundary-layer height determination from lidar measurements over the Paris area. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, I.M. Finding boundary layer top: Application of a wavelet covariance transform to lidar backscatter profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawbridge, K.B.; Snyder, B.J. Planetary boundary layer height determination during Pacific 2001 using the advantage of a scanning lidar instrument. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 5861–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. Noaa’s hysplit atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Stunder, B. Real-time environmental applications and display sYstem: READY. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Tsay, S.C.; Lin, N.H.; Hsu, N.C.; Bell, S.W.; Li, C.; Ji, Q.; Jeong, M.J.; Hansell, R.A.; Welton, E.J.; et al. First detailed observations of long-range transported dust over the northern South China Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4804–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wang, F.; Min, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L. Extinction effects of atmospheric compositions on return signals of space-based lidar from numerical simulation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 210, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Lee, S.-Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dong, W. Micro-Pulse Lidar Cruising Measurements in Northern South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101695
Li Y, Wang B, Lee S-Y, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Dong W. Micro-Pulse Lidar Cruising Measurements in Northern South China Sea. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(10):1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101695
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuan, Baomin Wang, Shao-Yi Lee, Zhijie Zhang, Ye Wang, and Wenjie Dong. 2020. "Micro-Pulse Lidar Cruising Measurements in Northern South China Sea" Remote Sensing 12, no. 10: 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101695
APA StyleLi, Y., Wang, B., Lee, S.-Y., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., & Dong, W. (2020). Micro-Pulse Lidar Cruising Measurements in Northern South China Sea. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101695