Spatial–Temporal Wetland Landcover Changes of Poyang Lake Derived from Landsat and HJ-1A/B Data in the Dry Season from 1973–2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
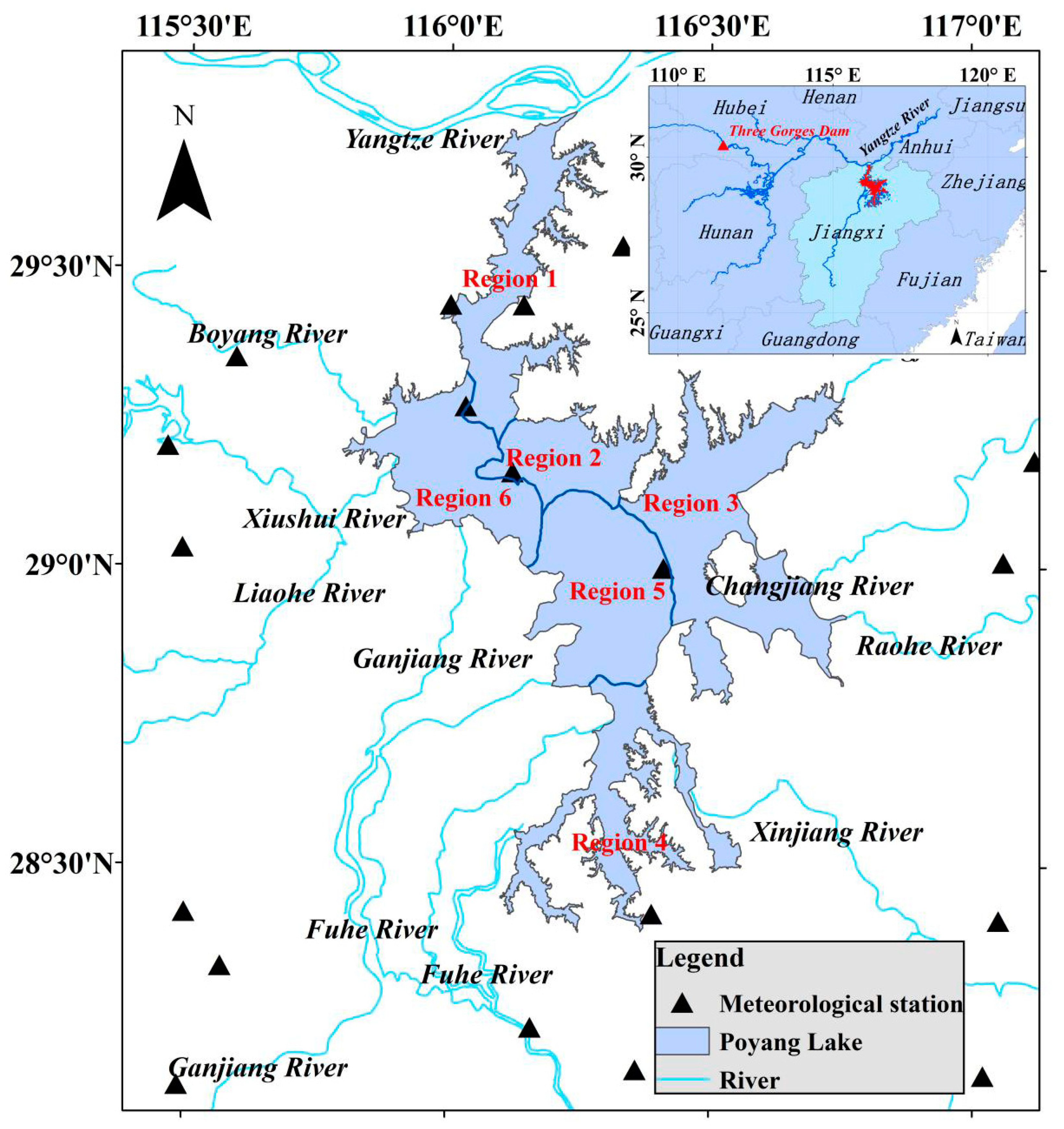
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
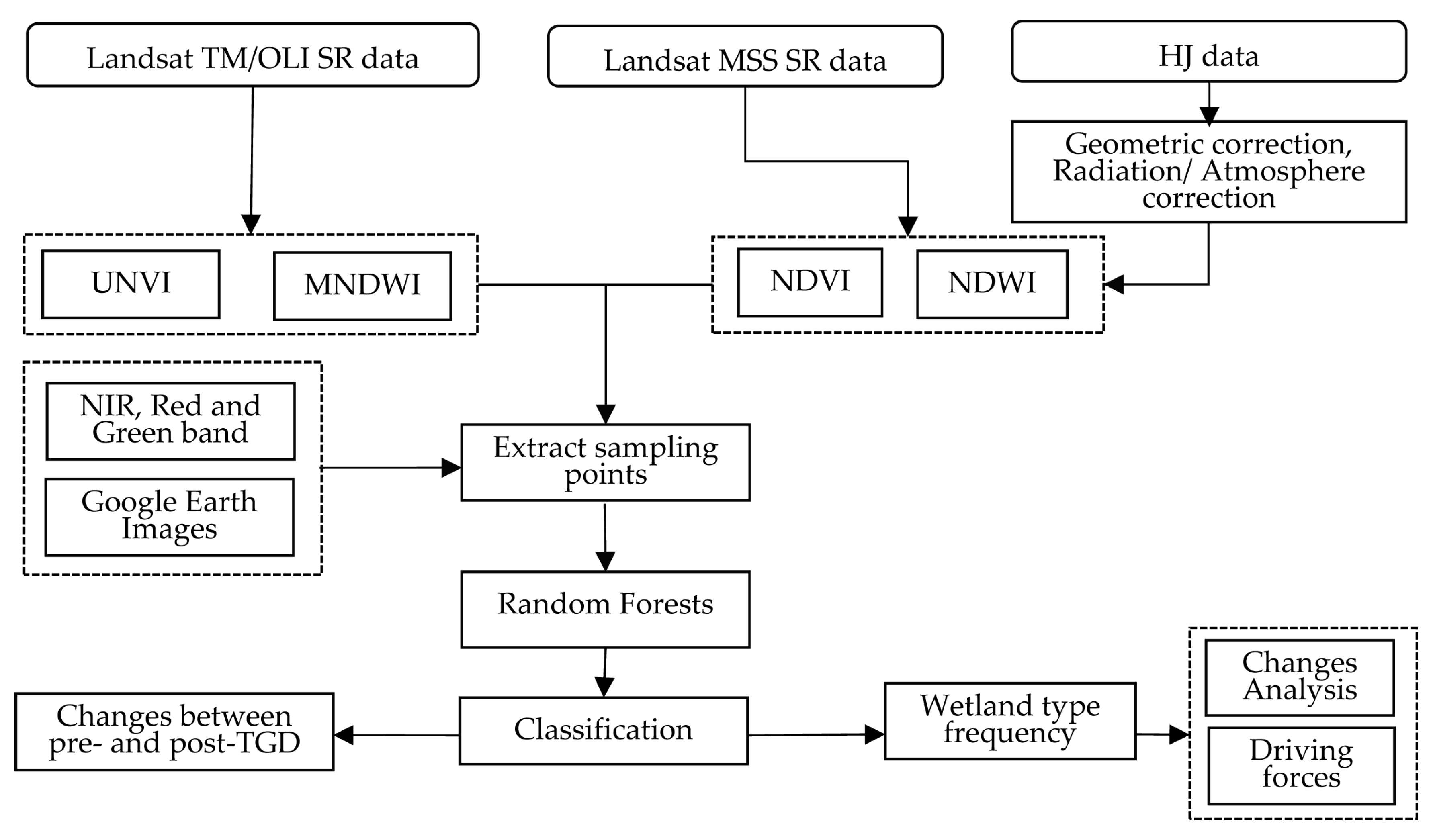
2.3. Image Classification
2.4. GeoDetector Model
3. Results: Long-Term Landcover Changes
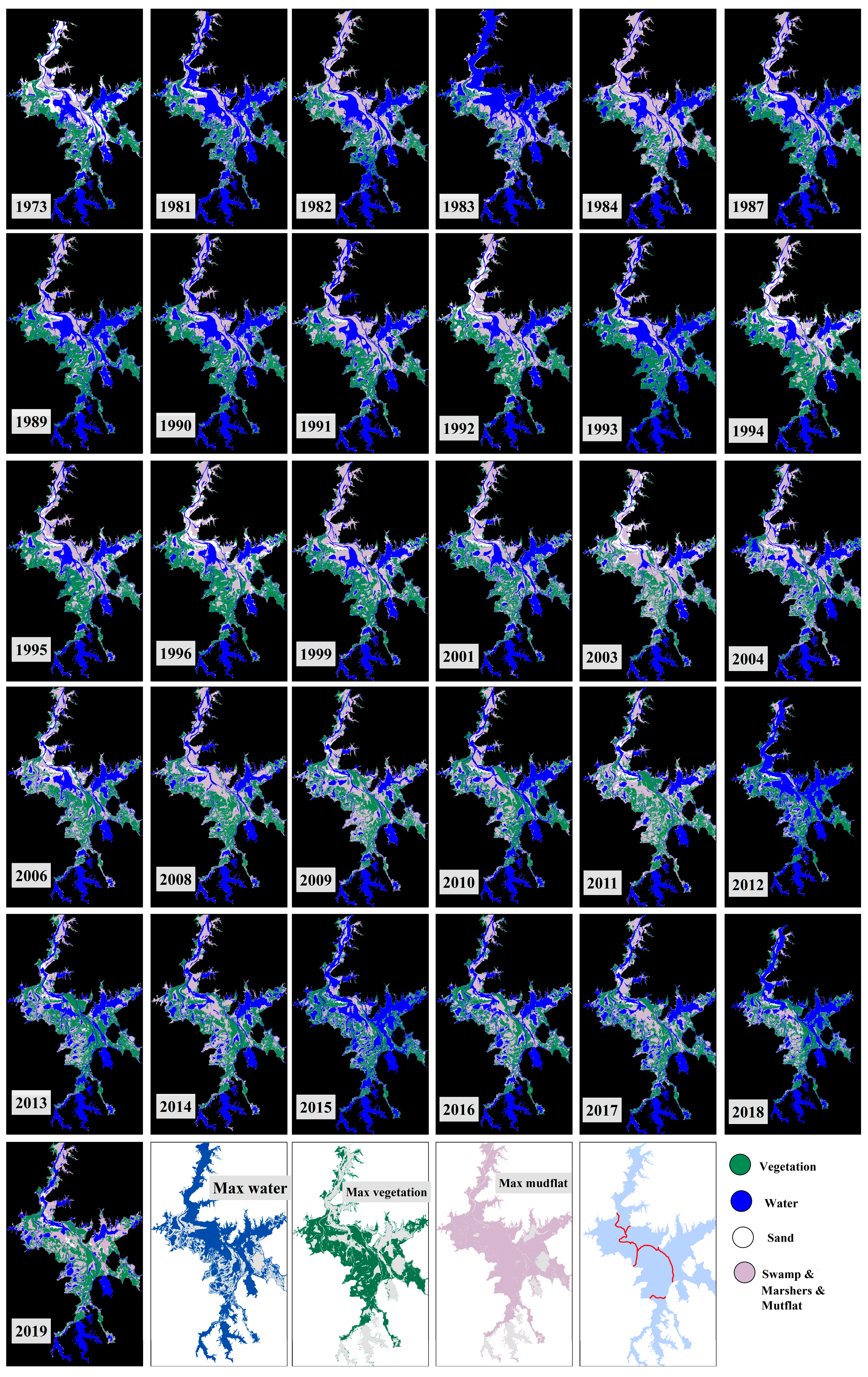
3.1. Image Classification
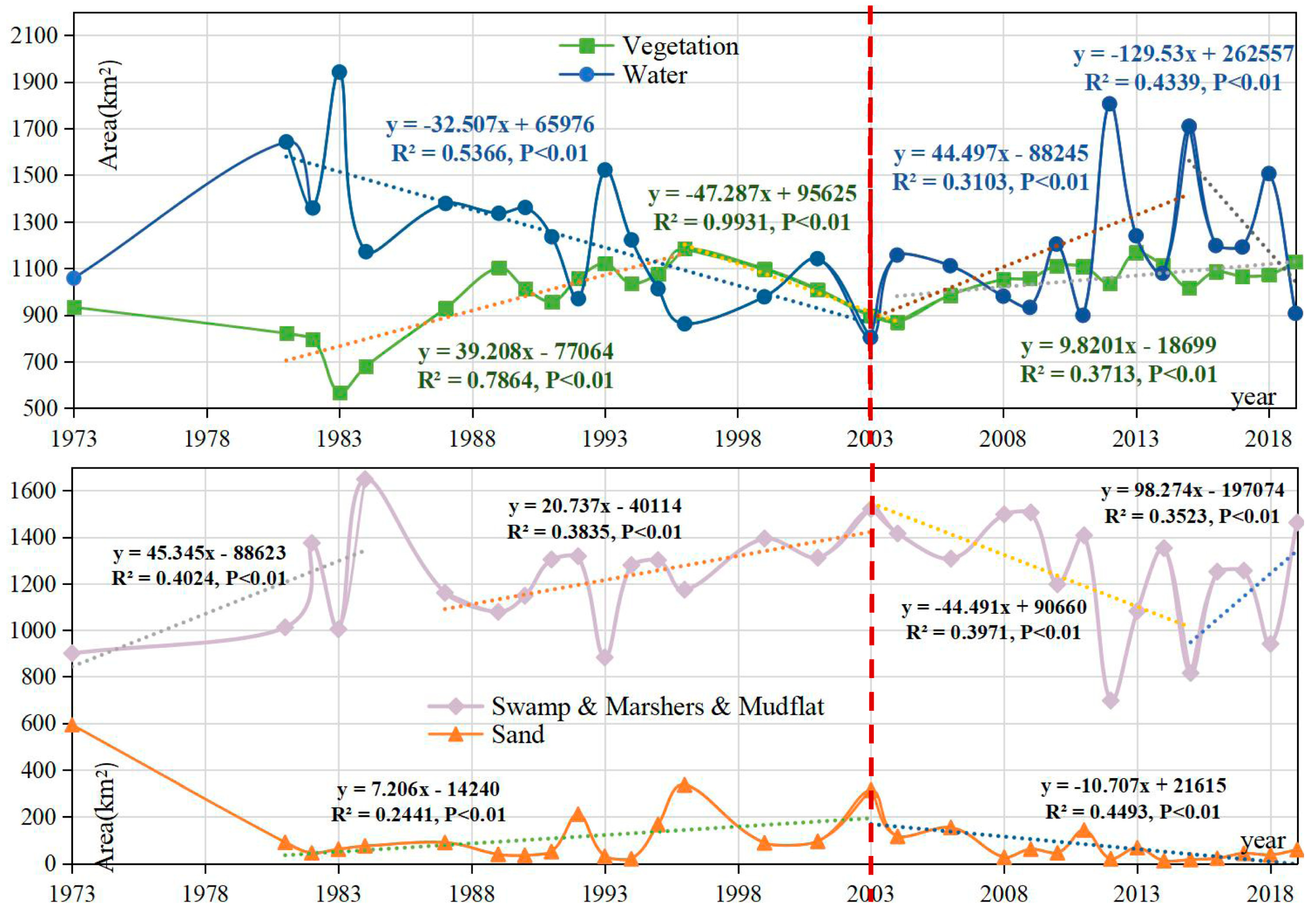
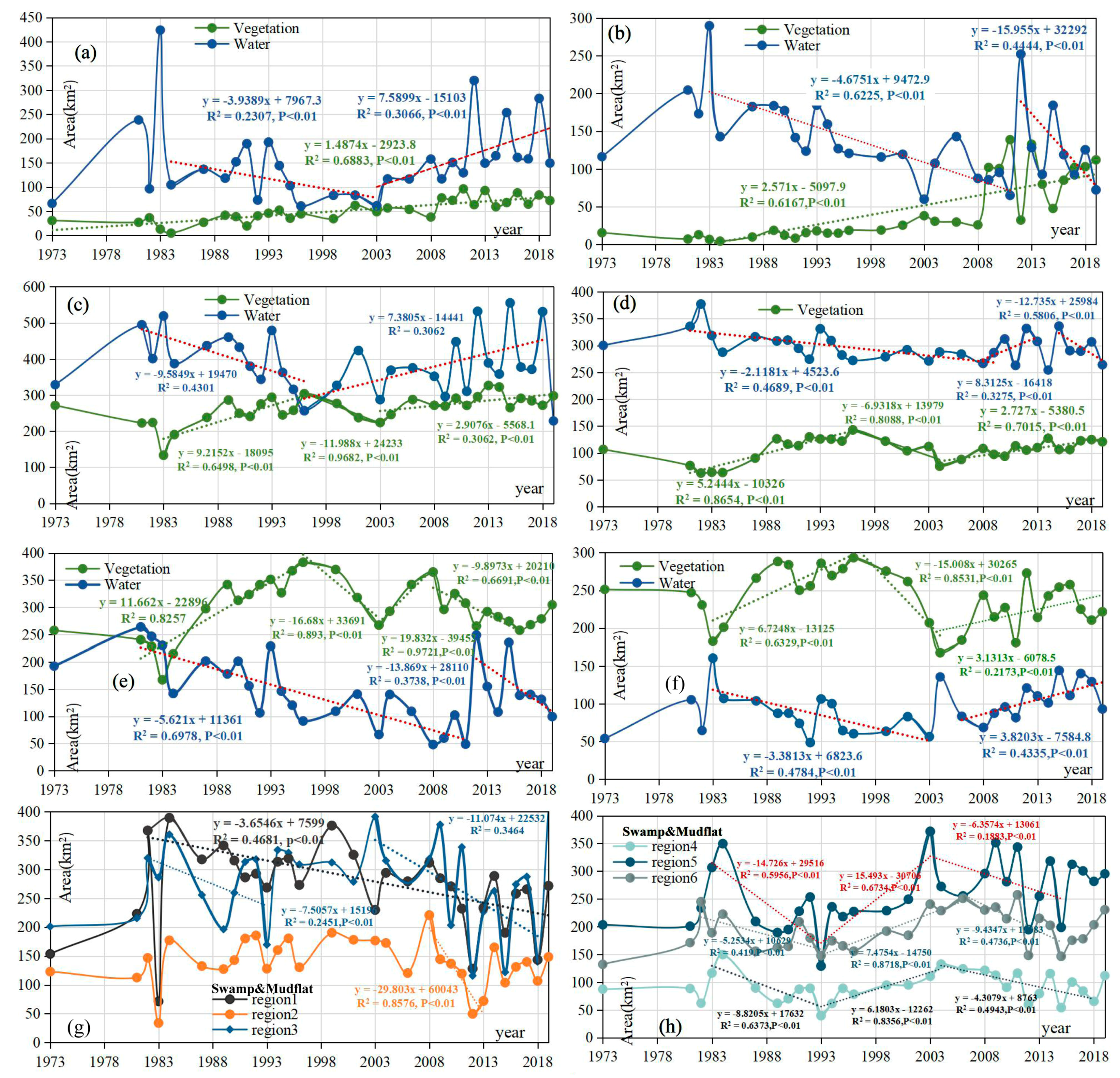
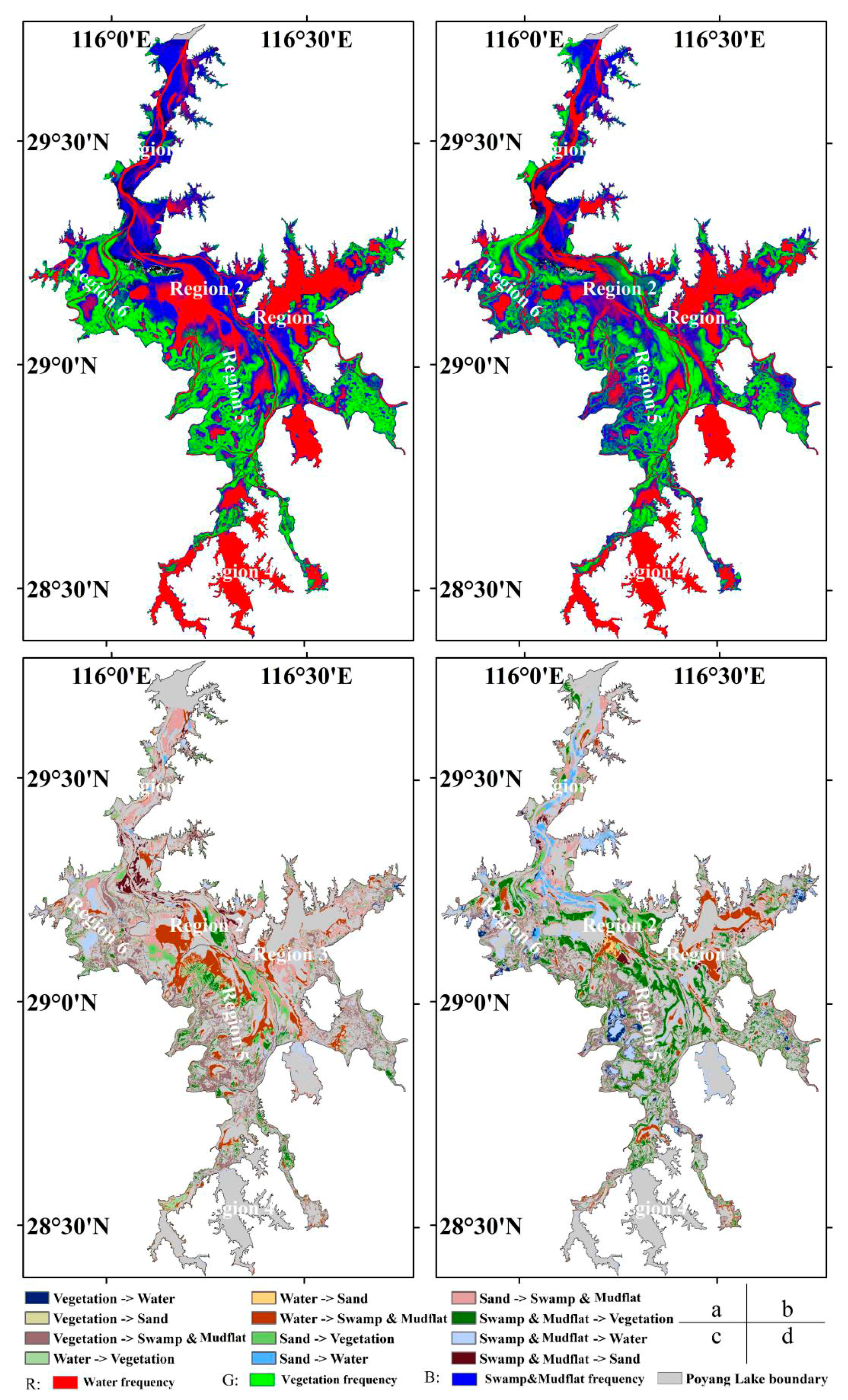
3.2. Spatial-Temporal Change Analysis
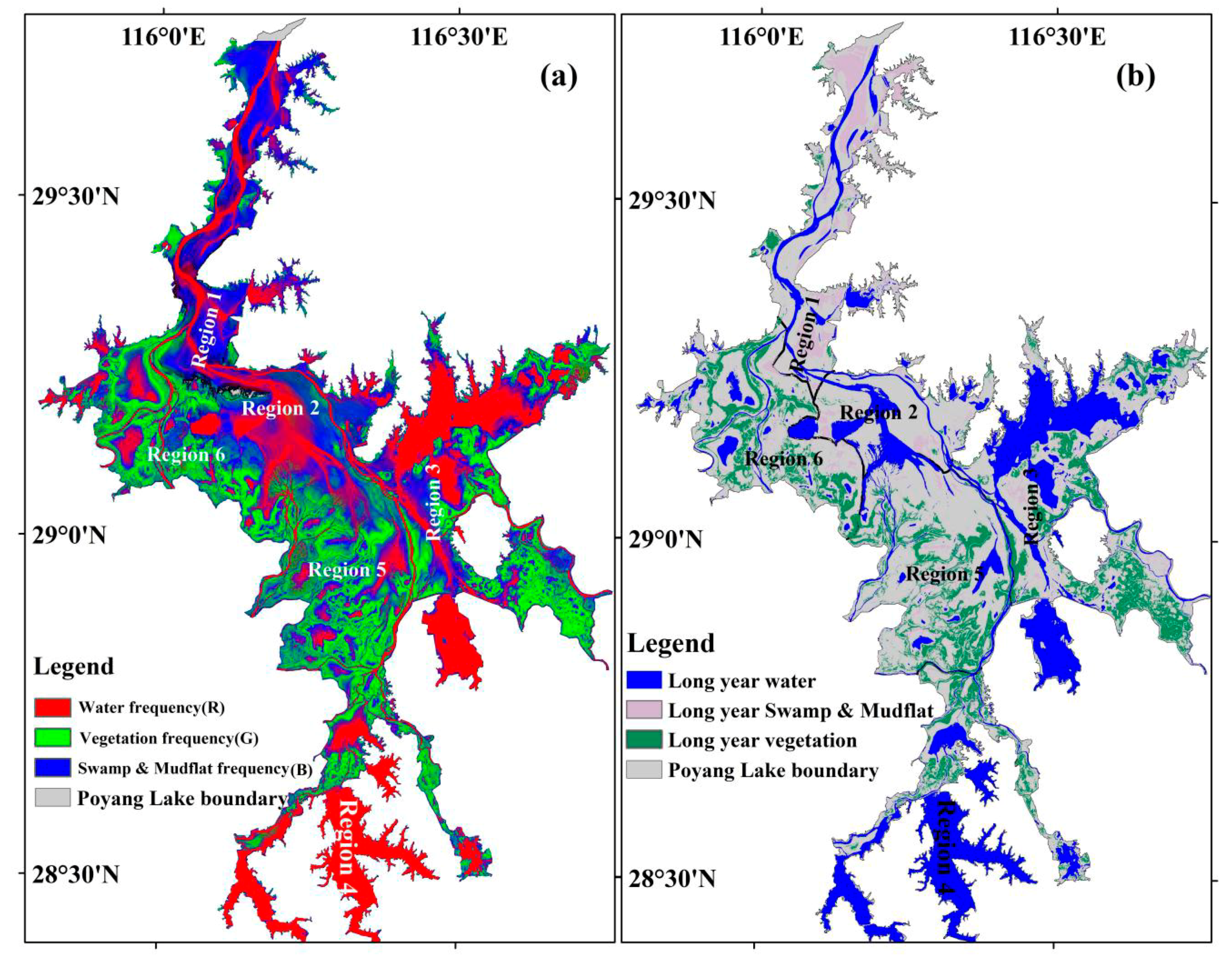
3.3. Wetland Landcover Variation Frequency of Poyang Lake
4. Discussion
4.1. Wetland Landcover Changes before and after the TGD Period
4.2. Driving Forces
4.2.1. Climate and Topography
4.2.2. Human Activities and Policies
4.3. Uncertainty of the Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pinay, G.; Clement, J.C.; Naiman, J.N. Basic principles and ecological consequences of changing water regimes on nitrogen cycling in fluvial systems. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Jiang, J.; Gao, H.; Zeng, B. Abundance, Distribution and Diversity Variations of Wintering Water Birds in Poyang Lake, Jiangxi Province, China. Pakistan J. Zool. 2014, 42, 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, C.; Keddy, P.A. Predictability of Change in Shoreline Vegetation in a Hydroelectric Reservoir, Northern Sweden. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1988, 45, 1896–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Chen, X.; Feng, L. Four decades of winter wetland changes in Poyang Lake based on Landsat observations between 1973 and 2013. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, E.; Mutanga, O.; Rugege, D. Multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing for identification and mapping of wetland vegetation: A review. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 18, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Fan, H.; Xu, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Yao, Z. Poyang Lake Wetland Ecosystem Health Assessment of Using the Wetland Landscape Classification Characteristics. Water 2019, 11, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, J.B.; Kercher, S. Wetland Resources: Status, Trends, Ecosystem Services, and Restorability. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2005, 30, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.J.; Kutser, T.; Hunter, P.D. Remote sensing of inland waters: Challenges, progress and future directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, D.; Guo, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Huang, H.; et al. China’s wetland change (1990–2000) determined by remote sensing. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Hoozemans, F.M.J.; Marchand, M. Increasing Flood Risk and Wetland Losses Due to Global Sea-Level Rise: Regional and Global Analyses. Glob. Environ. Chang. 1999, 9, S69–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q. Four Decades of Estuarine Wetland Changes in the Yellow River Delta Based on Landsat Observations Between 1973 and 2013. Water 2018, 10, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Gong, P. Suitability mapping of global wetland areas and validation with remotely sensed data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Brown, D.G.; Tian, Q.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, T.; Bergen, K.A. Inundation Extent and Flood Frequency Mapping Using LANDSAT Imagery and Digital Elevation Models. GISci. Remote Sens. 2009, 46, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, D.; Keim, B.D.; Song, J. Flood frequency in China’s Poyang Lake region: Trends and teleconnections. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, D.; Liang, Q. Landscape changes and increasing flood frequency in China’s Poyang Lake region. Prof. Geogr. 2003, 55, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Di, M.; Wang, J. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in water, sediments, and wild fish from Poyang Lake, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhao, X.; Cai, H. Reality and Conservation of Wetland in Poyang Lake. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis Nat. Sci. Ed. 2003, 25, 943–947. [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson, M.; Harris, J.; McCartney, M.; Lew, Y.; Zhang, C. Report on Ramsar visit to Poyang Lake Ramsar Site, P.R. China. Ramsar Convention. Available online: https://www.ramsar.org/sites/default/files/documents/pdf/Poyang_lake_report_v8.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Hu, Q.; Yao, B.; Liu, Y. Analysis on Changes of Man-Land Relationship and Associated driving force in Poyang Lake Region. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin. 2010, 19, 628–633. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, F.; Xie, Z. Study on Land Reclamation around Poyang Lake in the Abandoned Farmland in the Context of the Policy for Converting Farmland to Lake. China Land Sci. 2017, 31, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, J.; Ma, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Dynamic monitoring of Poyang Lake water body area using MODIS images between 2000 and 2014. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Earth Observing and Applications, Guilin, China, 23–24 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Han, X.; Hu, C.; Chen, X. Four decades of wetland changes of the largest freshwater lake in China: Possible linkage to the Three Gorges Dam? Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Song, Q. Influence of the Three Gorges Dam on total suspended matters in the Yangtze Estuary and its adjacent coastal waters: Observations from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Qi, S. Was the trend of the net sediment flux in Poyang Lake, China, altered by the Three Gorges Dam or by sand mining? Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Dai, Z.; Du, J.; Chen, J. Linkage between Three Gorges Dam impacts and the dramatic recessions in China’s largest freshwater lake, Poyang Lake. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S. Effects of the Three Gorges Dam on Yangtze River flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003–2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416–417, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Assessment of the Hydro-Ecological Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on China’s Largest Freshwater Lake. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Tian, L.; Gan, W. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, X.; Dai, S.; Zhao, B. Long-Term Dynamic of Poyang Lake Surface Water: A Mapping Work Based on the Google Earth Engine Cloud Platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yésou, H. Remote Sensing of Floodpath Lakes and Wetlands: A Challenging Frontier in the Monitoring of Changing Environments. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Schmitt, M.; Li, L.; Zhu, X.X. Analysing changes of the Poyang Lake water area using Sentinel-1 synthetic aperture radar imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 7041–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, L.; Huang, B.; Michishita, R.; Xu, B. Dynamic monitoring of the Poyang Lake wetland by integrating Landsat and MODIS observations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Yao, X.; Dai, X. Mapping Aboveground Biomass of Four Typical Vegetation Types in the Poyang Lake Wetlands Based on Random Forest Modelling and Landsat Images. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Han, X.; Chen, X.; Qi, L. Long-Term Distribution Patterns of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in China’s Largest Freshwater Lake: MERIS Full-Resolution Observations with a Practical Approach. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yin, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H. Relationship between the hydrological conditions and the distribution of vegetation communities within the Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve, China. Ecol. Inform. 2012, 11, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, J.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, X.; Liu, H. Hydrodynamic and Inundation Modeling of China’s Largest Freshwater Lake Aided by Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4858–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Luo, Z.; Tangdamrongsub, N.; Zhou, Z.; He, L.; Xu, C.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y. Identifying Flood Events over the Poyang Lake Basin Using Multiple Satellite Remote Sensing Observations, Hydrological Models and In Situ Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Hou, X. How important are the wetlands in the middle-lower Yangtze River region: An ecosystem service valuation approach. Ecosyst. Serv. 2014, 10, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanonckelen, S.; Lhermitte, S.; Van Rompaey, A. The effect of atmospheric and topographic correction methods on land cover classification accuracy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 24, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, J.G.; Huang, C.; Wolfe, R.; Cohen, W.; Hall, F.; Kutler, J.; Nelson, P. North American forest disturbance mapped from a decadal Landsat record. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2914–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Franch, B. Preliminary analysis of the performance of the Landsat 8/OLI land surface reflectance product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Cao, C.; Chen, l. Atmospheric correction on CCD data of HJ-1 satellite and analysis of its effect. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 15, 709–713. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Tian, L.; Feng, L. Tracking radiometric responsivity of optical sensors without on-board calibration systems-case of the Chinese HJ-1A/1B CCD sensors. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 1829–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dronova, I.; Gong, P.; Wang, L. Object-based analysis and change detection of major wetland cover types and their classification uncertainty during the low water period at Poyang Lake, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3220–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; He, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Landsat-TM Data Based Study on Dynamic Changes of the Typical Wetlands of Poyang Lake. Remote Sens. Inform. 2010, 32, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, D.R.; Edwards, T.C.; Beard, K.H.; Cutler, A.; Hess, K.T.; Gibson, J.; Lawler, J.J. Random Forests for Classification in Ecology. Ecology 2007, 88, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Linden, S.; Rabe, A.; Held, M.; Jakimow, B.; Leitao, P.J.; Okujeni, A.; Schwieder, M.; Suess, S.; Hostert, P. The EnMAP-Box-A Toolbox and Application Programming Interface for EnMAP Data Processing. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11249–11266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariana, B.; Dragut, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and futuredirections. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, B. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Furumi, S.; Muramatsu, K.; Fujiwara, N.; Daigo, M.; Zhang, L. A new vegetation index based on the universal pattern decomposition method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, N.; Baig, M.H.A.; Huang, C.; Lv, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z. Monitoring vegetation dynamics using the universal normalized vegetation index (UNVI): An optimized vegetation index-VIUPD. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A Study on Information Extraction of Water Body with the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI). J. Remote Sens. 2005, 9, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Defries, R.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. NDVI-derived land cover classifications at a global scale. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 3567–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, M.; Fasbender, D.; Rembold, F.; Atzberger, C.; Klisch, A. Near real-time vegetation anomaly detection with MODIS NDVI: Timeliness vs. accuracy and effect of anomaly computation options. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.V.; Setia, R.; Sahoo, S.; Prasad, A.; Pateriya, B. Evaluation of NDWI and MNDWI for assessment of waterlogging by integrating digital elevation model and groundwater level. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; Lei, J. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Vegetation NDVI Changes and the Driving Forces in Mongolia during 1982–2015. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, Z. Environmental factors influencing spatial variability of soil total phosphorus content in a small watershed in Poyang Lake Plain under different levels of soil erosion. Catena 2020, 187, 104357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J. A long-term site study for the ecological risk migration of landscapes and its driving forces in the Sanjiang Plain from 1976 to 2013. Acta Ecol. Sinica 2018, 38, 3729–3740. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Cao, E.; Gong, J. Impact factors of soil phosphorus loss in watershed based on geographical detector. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 4814–4822. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Spatial quantitative analysis of the potential driving factors of land surface temperature in different “Centers” of polycentric cities: A case study in Tianjin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiang, J. Distribution of Typical Vegetation Communities along Elevation in Poyang Lake Wetlands. Wetl. Sci. 2016, 14, 506–515. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Stein, A.; Chen, X.L. Monitoring the dynamics of wetland inundation by random sets on multi-temporal images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 706, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S. Brief introduction of “83.7” flood in Poyang Lake. J. Hydrol. 1988, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Qi, S.; Liao, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, J.; Xiong, M. Hydrological and sediment effects from sand mining in Poyang Lake during 2001-2010. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 837–845. [Google Scholar]

| Year 1 | Acquisition Time | Sensor Type | Spatial Resolution (m) | Year 1 | Acquisition Time | Sensor Type | Spatial Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1973 | 1973/12/24 | MSS | 60 | 2003 | 2004/02/15 | TM | 30 |
| 1981 | 1981/12/09 | MSS | 60 | 2004 | 2004/12/15 | TM | 30 |
| 1982 | 1983/01/28 | MSS | 60 | 2006 | 2006/12/21 | TM | 30 |
| 1983 | 1983/11/28 | MSS | 60 | 2008 | 2008/12/10 | TM | 30 |
| 1984 | 1984/12/08 | MSS | 60 | 2009 | 2010/01/14 | TM | 30 |
| 1987 | 1987/12/17 | TM | 30 | 2010 | 2010/12/31 | HJ-1A | 30 |
| 1989 | 1990/01/23 | TM | 30 | 2011 | 2011/12/24 | HJ-1A | 30 |
| 1990 | 1990/12/09 | TM | 30 | 2012 | 2012/12/08 | HJ-1A | 30 |
| 1991 | 1991/11/10 | TM | 30 | 2013 | 2013/12/24 | OLI | 30 |
| 1992 | 1993/01/31 | TM | 30 | 2014 | 2014/12/17 | HJ-1A | 30 |
| 1993 | 1993/12/17 | TM | 30 | 2015 | 2016/02/16 | OLI | 30 |
| 1994 | 1994/12/04 | TM | 30 | 2016 | 2016/12/16 | OLI | 30 |
| 1995 | 1995/12/07 | TM | 30 | 2017 | 2017/12/19 | OLI | 30 |
| 1996 | 1997/01/10 | TM | 30 | 2018 | 2019/01/23 | OLI | 30 |
| 1999 | 1999/12/18 | TM | 30 | 2019 | 2019/12/06 | HJ-1A | 30 |
| 2001 | 2002/01/08 | TM | 30 |
| Type | Vegetation | Water | Sand | Swamp & Mudflat | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation | 294 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 294 |
| Water | 0 | 292 | 0 | 7 | 299 |
| Sand | 0 | 0 | 139 | 0 | 139 |
| Swamp & Mudflat | 6 | 8 | 11 | 293 | 318 |
| total | 300 | 300 | 150 | 300 | 1050 |
| Prod. accuracy% | 98.00% | 97.33% | 92.67% | 97.67% | |
| Overall accuracy = 96.95% | Kappa coefficient = 0.96 | ||||
| Prod. Accuracy | Vegetation | Water | Sand | Swamp & Mudflat | All | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNVI, MNDWI, NIR, Red, and Green | 98.00% | 97.33% | 92.67% | 97.67% | 96.95% | 0.96 |
| NDVI, NDWI, NIR, Red, and Green | 94.00% | 98.33% | 91.33% | 95.00% | 95.14% | 0.94 |
| Type | Unchanged (km2) | Declined (km2) | Increased (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation | 534.106 | 399.152 | 597.376 |
| Water | 558.302 | 499.127 | 350.706 |
| Sand | 24.137 | 568.542 | 34.717 |
| Swamp and Mudflat | 465.296 | 434.621 | 1008.187 |
| Region | Long-year Water (km2) | Long-year Vegetation (km2) | Long-year Swamp and Mudflat (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 81.03 | 14.89 | 119.76 |
| 2 | 91.68 | 4.75 | 19.97 |
| 3 | 322.20 | 175.05 | 45.01 |
| 4 | 273.08 | 63.09 | 12.97 |
| 5 | 72.27 | 146.48 | 30.33 |
| 6 | 50.64 | 136.29 | 25.64 |
| Poyang Lake | 891.01 | 540.80 | 254.42 |
| Type | E | Slope | Aspect | C | T | MAXT | MINT | P | DP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poyang Lake | V | 0.387 ** | 0.426 ** | 0.266 ** | 0.250 ** | 0.011 ** | 0.012 ** | 0.027 ** | 0.017 ** | 0.040 ** |
| W | 0.226 ** | 0.306 ** | 0.216 ** | 0.202 ** | 0.057 ** | 0.045 ** | 0.112 ** | 0.029 ** | 0.018 ** | |
| S | 0.031 ** | 0.033 ** | 0.000 | 0.004 ** | 0.028 ** | 0.059 ** | 0.021 ** | 0.020 ** | 0.024 ** | |
| S&M | 0.103 ** | 0.009 ** | 0.000 | 0.007 ** | 0.094 ** | 0.074 ** | 0.113 ** | 0.041 ** | 0.044 ** | |
| Region 1 | V | 0.329 ** | 0.273 ** | 0.201 ** | 0.242 ** | 0.019 ** | 0.021 ** | 0.009 ** | 0.061 ** | 0.108 ** |
| W | 0.112 ** | 0.089 ** | 0.069 ** | 0.095 ** | 0.183 ** | 0.019 ** | 0.032 ** | 0.053 ** | 0.046 ** | |
| S | 0.014 ** | 0.013 ** | 0.005 | 0.006* | 0.122 ** | 0.104 ** | 0.147 ** | 0.047 ** | 0.019 ** | |
| S&M | 0.027 ** | 0.019 ** | 0.009* | 0.024 ** | 0.051 ** | 0.028 ** | 0.050 ** | 0.029 ** | 0.028 ** | |
| Region 2 | V | 0.239 ** | 0.173 ** | 0.163 ** | 0.140 ** | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.014 ** | 0.060 ** | 0.060 ** |
| W | 0.139 ** | 0.110 ** | 0.110 ** | 0.096 ** | 0.008 ** | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.019 ** | 0.013 ** | |
| S | 0.500 ** | 0.290 ** | 0.120 ** | 0.143 ** | 0.012 ** | 0.002 | 0.095 ** | 0.007 | 0.010 ** | |
| S&M | 0.034 ** | 0.020 ** | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.010 ** | 0.004 | 0.019 ** | 0.005 | 0.002 | |
| Region 3 | V | 0.589 ** | 0.493 ** | 0.312 ** | 0.281 ** | 0.072 ** | 0.042 ** | 0.056 ** | 0.049 ** | 0.125 ** |
| W | 0.524 ** | 0.485 ** | 0.351 ** | 0.309 ** | 0.069 ** | 0.019 ** | 0.038 ** | 0.054 ** | 0.101 ** | |
| S | 0.014 ** | 0.009 ** | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.020 ** | 0.033 ** | 0.034 ** | 0.029 ** | 0.032 ** | |
| S&M | 0.074 ** | 0.064 ** | 0.029 ** | 0.037 ** | 0.013 ** | 0.001 | 0.009 ** | 0.040 ** | 0.025 ** | |
| Region 4 | V | 0.337 ** | 0.413 ** | 0.244 ** | 0.293 ** | 0.126 ** | 0.039 ** | 0.191 ** | 0.000 | 0.013 ** |
| W | 0.494 ** | 0.563 ** | 0.385 ** | 0.412 ** | 0.193 ** | 0.074 ** | 0.289 ** | 0.002 | 0.008 ** | |
| S | 0.016 ** | 0.017 ** | 0.007 | 0.019 ** | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.000 | |
| S&M | 0.315 ** | 0.322 ** | 0.205 ** | 0.243 ** | 0.117 ** | 0.043 ** | 0.163 ** | 0.007 ** | 0.000 | |
| Region 5 | V | 0.502 ** | 0.379 ** | 0.190 ** | 0.176 ** | 0.038 ** | 0.011 ** | 0.040 ** | 0.006 ** | 0.003* |
| W | 0.400 ** | 0.307 ** | 0.159 ** | 0.146 ** | 0.045 ** | 0.013 ** | 0.057 ** | 0.011 ** | 0.008 ** | |
| S | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.017 ** | 0.000 | 0.016 ** | 0.011 ** | 0.002 | |
| S&M | 0.114 ** | 0.050 ** | 0.025 ** | 0.026 ** | 0.030 ** | 0.000 | 0.022 ** | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Region 6 | V | 0.360 ** | 0.228 ** | 0.112 ** | 0.101 ** | 0.038 ** | 0.023 ** | 0.027 ** | 0.036 ** | 0.033 ** |
| W | 0.294 ** | 0.186 ** | 0.099 ** | 0.094 ** | 0.043 ** | 0.057 ** | 0.028 ** | 0.072 ** | 0.055 ** | |
| S | 0.056 ** | 0.045 ** | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.112 ** | 0.063 ** | 0.078 ** | 0.179 ** | 0.047 ** | |
| S&M | 0.097 ** | 0.041 ** | 0.023 ** | 0.023 ** | 0.007* | 0.011 ** | 0.006 * | 0.007 | 0.005 | |
| Type | Dominant Interaction 1, q | Dominant Interaction 2, q | Dominant Interaction 3, q | Dominant Interaction 4, q | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poyang Lake | V | E ∩ Slope, 0.558 | E ∩ C, 0.487 | E ∩ MINT, 0.486 | Slope ∩ C, 0.462 |
| W | E ∩ Slop, 0.450 | E ∩ MINT, 0.421 | Slope ∩ MINT, 0.415 | Slope ∩ MAXT, 0.398 | |
| S | MAXT ∩ MINT, 0.169 | MAXT ∩ Slope, 0.163 | MAXT∩E, 0.114 | MAXT ∩ T, 0.114 | |
| S&M | E ∩ MINT, 0.207 | E ∩ T, 0.204 | E ∩ MAXT, 0.192 | E ∩ P, 0.184 | |
| Region 1 | V | E ∩ DP, 0.564 | E ∩ P, 0.533 | E ∩ MINT, 0.522 | E ∩ T, 0.499 |
| W | E ∩ P, 0.167 | E ∩ DP, 0.165 | E ∩ MINT, 0.154 | C ∩ DP, 0.149 | |
| S | MINT ∩ P, 0.243 | MINT ∩ C, 0.242 | MINT ∩ Slope, 0.23 | MINT ∩ E, 0.228 | |
| S&M | MINT ∩ DP, 0.188 | T ∩ DP, 0.186 | P ∩ MINT, 0.173 | P ∩ T, 0.172 | |
| Region 2 | V | E ∩ C, 0.320 | E ∩ Slope, 0.304 | E ∩ Aspect, 0.298 | E∩DP, 0.282 |
| W | E ∩ C, 0.163 | E ∩ Aspect, 0.160 | E ∩ Slope, 0.158 | E ∩ P, 0.156 | |
| S | E ∩ MINT, 0.637 | E ∩ T, 0.588 | E ∩ DP, 0.576 | E ∩ C, 0.562 | |
| S&M | E ∩ T, 0.088 | E ∩ MINT, 0.067 | E ∩ DP, 0.067 | E ∩ Aspect, 0.057 | |
| Region 3 | V | E ∩ Slope, 0.658 | E ∩ C, 0.634 | E ∩ DP, 0.622 | E ∩ P, 0.622 |
| W | E ∩ Slope, 0.604 | E ∩ DP, 0.598 | E ∩ P, 0.594 | E ∩ Aspect, 0.587 | |
| S | E ∩ T, 0.081 | E ∩ DP, 0.067 | Slope ∩ DP, 0.065 | C ∩ DP, 0.063 | |
| S&M | E ∩ DP, 0.170 | E ∩ P, 0.166 | E ∩ Slope, 0.164 | E ∩ T, 0.159 | |
| Region 4 | V | E ∩ Slope, 0.554 | E ∩ MINT, 0.547 | E ∩ C, 0.517 | C ∩ Slope, 0.480 |
| W | E ∩ MINT, 0.719 | E ∩ Slope, 0.693 | E ∩ C, 0.672 | MINT ∩ Slope, 0.666 | |
| S | C ∩ Slope, 0.047 | C ∩ E, 0.041 | C ∩ T, 0.040 | C ∩ Aspect, 0.039 | |
| S&M | E ∩ Slope, 0.439 | E ∩ Slope, 0.432 | E ∩ MINT, 0.425 | Slope ∩ MINT, 0.418 | |
| Region 5 | V | E ∩ Slope, 0.570 | E ∩ MINT, 0.560 | E ∩ T, 0.558 | E ∩ P, 0.557 |
| W | E ∩ Slope, 0.479 | E ∩ T, 0.476 | E ∩ MINT, 0.472 | E ∩ DP, 0.465 | |
| S | E ∩ MINT, 0.053 | E ∩ T, 0.050 | Slope ∩ T, 0.041 | Aspect ∩ T, 0.040 | |
| S&M | E ∩ T, 0.211 | E ∩ MINT, 0.210 | E ∩ DP, 0.157 | E ∩ P, 0.156 | |
| Region 6 | V | E ∩ P, 0.453 | E ∩ Slope, 0.440 | E ∩ MAXT, 0.440 | E ∩ T, 0.440 |
| W | E ∩ Slope, 0.440 | E ∩ P, 0.428 | E ∩ MAXT, 0.409 | E ∩ T, 0.407 | |
| S | P ∩ Slope, 0.375 | P ∩ E, 0.329 | MAXT ∩ E, 0.320 | MAXT ∩ Slope, 0.295 | |
| S&M | P ∩ E, 0.181 | MAXT ∩ E, 0.179 | T ∩ E, 0.165 | MINT ∩ E, 0.163 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Han, X.; Zhang, L. Spatial–Temporal Wetland Landcover Changes of Poyang Lake Derived from Landsat and HJ-1A/B Data in the Dry Season from 1973–2019. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101595
Wang S, Zhang L, Zhang H, Han X, Zhang L. Spatial–Temporal Wetland Landcover Changes of Poyang Lake Derived from Landsat and HJ-1A/B Data in the Dry Season from 1973–2019. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(10):1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101595
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Sa, Lifu Zhang, Hongming Zhang, Xingxing Han, and Linshan Zhang. 2020. "Spatial–Temporal Wetland Landcover Changes of Poyang Lake Derived from Landsat and HJ-1A/B Data in the Dry Season from 1973–2019" Remote Sensing 12, no. 10: 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101595
APA StyleWang, S., Zhang, L., Zhang, H., Han, X., & Zhang, L. (2020). Spatial–Temporal Wetland Landcover Changes of Poyang Lake Derived from Landsat and HJ-1A/B Data in the Dry Season from 1973–2019. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101595






