Abstract
With advantages of multispatial resolutions, a high retrieval accuracy, and a high temporal resolution, the satellite-derived land surface temperature (LST) products are very important LST sources. However, the greatest barrier to their wide application is the invalid values produced by large quantities of cloudy pixels, especially for regions frequently swathed in clouds. In this study, an effective method based on the land energy balance theory and similar pixels (SP) method was developed to reconstruct the LSTs over cloudy pixels for the widely used MODIS LST (MOD11A1). The southwest region of China was selected as the study area, where extreme drought has frequently occurred in recent years in the context of global climate change and which commonly exhibits cloudy and foggy weather. The validation results compared with in situ LSTs showed that the reconstructed LSTs have an average error < 1.00 K (0.57 K at night and −0.14 K during the day) and an RMSE < 3.20 K (1.90 K at night and 3.16 K in the daytime). The experiment testing the SP interpolation indicated that the spatial structure of the LST has a greater effect on the SP performance than the size of the data-missing area, which benefits the LST reconstruction in the area frequently covered by large clouds.
1. Introduction
Land surface temperature (LST) is a key parameter in global climate change, extreme drought evaluation and prediction, and surface energy and water balance research [1,2,3,4]. Since the land surface is complex and the LST shows strong heterogeneous characteristics, the limited number of spatially noncontinuous ground station measurements has been inadequate for recent studies on regional or even global scales [5]. LST products retrieved from satellite-based thermal infrared (TIR) data provide the possibility of obtaining spatially continuous LST over large areas. A large number of LST products have been successively released since the 1970s [6,7,8,9], and the algorithms focusing on the LST retrieval from TIR data have developed to a mature stage [10,11,12,13,14,15]. As part of these products, the LST products retrieved by the generalized split-window algorithm [14,16] depending on the TIR data of the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) have recently become an important and widely used satellite-based LST product. However, the nature of TIR remote sensing is vulnerable to cloud contamination, which leads to its failure in observing LST information through a layer of cloud cover. The pixels below the clouds in these LST products are filled with invalid values, and as a result, the incomplete spatial and temporal data of these LST products greatly limit their subsequent applications, especially during monsoons or in humid zones.
The reconstruction of information missing over cloudy pixels in satellite-based LST products has been one of the hot issues to address for breakthroughs in the TIR remote sensing field at present [17,18,19,20,21]. A series of studies have focused on exploring reconstruction algorithms, which can be grouped into four general types: the spatial interpolation algorithm, temporal interpolation algorithm, spatiotemporal method, and multi-complementary reconstruction, which consider the physical geographical process. The popular algorithm of the first type is geostatistical interpolation, such as the Kriging method, Co-kriging based on multiple variables, and adjusted Kriging [17,18]. These geostatistical methods rely on the spatial correlations of the neighboring cloud-free pixels, which limits their applicability for images with large numbers of pixels with missing data. Therefore, several other spatial methods were developed to fill this gap, such as the network-based IDW interpolation and regression models established by several other relative factors [22,23,24]. Since the cloudy areas are often blurred by using spatial interpolation methods, temporal interpolation methods were explored to resort to the multi-temporal information. Based on the recognition of the periodical daily or seasonal change in LST under cloud-free conditions, several reconstruction models were developed, depending on the temporal periodical function of the LST using multi-temporal LST data in clear-sky conditions. Based on the seasonal periodic variation of the LST, the Harmonic Analysis of Time Series (HANTS) was employed by Wang, et al. [25] to estimate the cloudy pixels in MODIS LST for the Yangtze River Delta region, which effectively removes the invalid values contaminated by clouds. A robust regression was developed by Zeng, et al. [26] with the multitemporal information from the clear-sky similar pixels distinguished by a multi-temporal classification. Some spatiotemporal methods were also developed to get the most out of the spatial and temporal information to overcome the dense cloud cover conditions, such as the Gradient and Weiss interpolation [27] and the empirical orthogonal functions (DINEOF)-based spatiotemporal data interpolating [28]. According to the spatiotemporal autocorrelation of the LST, a spatial and multi-temporal phase method was developed by Evgenieva, et al. [29] to reconstruct clear-sky LST values for missing pixels of MODIS LST products. An empirical comparison of the three types of methods above was implemented by Pede and Mountrakis [27], and comparison results found evidence that the spatial interpolation algorithm and spatiotemporal method were more effective at reconstructing the cloudy LST in the MODIS LST than the temporal interpolation, even under extremely heavy cloud cover (>80%), without regard to the time of day or season. In summary, there is a critical defect of the first three methods in that the LST values reconstructed by them are the theorical LST values in clear-sky conditions, rather than the cloudy-sky LST values influenced by the clouds.
Generally, the LST values in the daytime under clouds are lower than the LST values in the clear sky, since clouds obscure solar radiation. Multi-complementary reconstruction considers the physical geographical process explored to reconstruct the real LST under clouds. Focusing on the implication factors, a series of auxiliary datasets were generated to help improve LST retrieval and reconstruction with the presence of cloud, including near-real-time estimation of the water vapor column from MSG_SEVIRI [30] and global atmospheric profiles from reanalysis (GSPRI) [31]. Considering the land surface energy balance theory, Jin [19] proposed a neighboring-pixel (NP) interpolation method. In Jin’s approach, the LSTs over cloudy areas were estimated by the LSTs in the neighboring cloud-free areas based on multi-complementary relative information, especially the net solar radiation information. Based on Jin’s theory, Lu, Venus, Skidmore, Wang and Luo [20] developed a temporal NP to reconstruct the cloudy pixels in the LST products retrieved from the data of the geostationary Meteosat Second Generation. Then, Yu, et al. [32] developed a spatiotemporal NP interpolation to estimate the LSTs over cloudy pixels of daily MODIS LST products. To limit the major dependence on local ground-based measurements, a two-step framework was developed for reconstructing satellite-based LSTs contaminated by clouds [21]. With the advancement of this method, the LST reconstruction work of satellite-based LST products has achieved great progress. The air temperature, which usually varies with elevation at a lapse rate of −6.5 K/km when estimated under standard circumstances [33], is closely related to LST and can potentially impact the LST retrieval as well. In addition, LST has been indicated to be strongly impacted by topography, and the topographic-namely illumination and elevation-effects over mountainous areas are even more complex compared to air temperature [34]. However, all of those aforementioned methods only place emphasis on land cover and climatic factors, without addressing the topographic factors, which limits the reconstruction accuracy over significant reliefs or topographically complex regions.
In this study, an effective reconstruction framework was developed to reconstruct the LST over cloudy pixels of satellite-based LSTs in southwest China. This advanced framework has two key advantages: it fully utilizes the satellite-based auxiliary data rather than the local measurements and adequately considers the main influences, especially the topographic factors. Based on this new developed method, the accuracy of the reconstructed LST and the usability of the satellite-based LST can be greatly increased, especially in mountainous areas that are frequently covered by clouds. First, the data and study area will be detailed, and then the new multifactor framework for the similar-pixel reconstruction will be systematically proposed. The results and discussion are demonstrated in the final section.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Southwest (SW) China (Figure 1) was selected as the study area to implement the reconstruction algorithm. The region (21°14′N–34°19′N, 97°21′E–112°05′E) includes Sichuan province, Guizhou province, Yunan province, Chongqing city, and Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. This area features a subtropical monsoon climate, and the weather in most parts is relatively moderate and rainy. Its topography is varied and complex, with towering mountains, basins of different sizes, undulating plateaus and hills, and wide karst areas. The SW is also a drought-prone region, and in recent years, fatal drought disasters in China have mostly taken place in the southwest region, as a probable regional response to global warming [35]. According to historical records, there were a total of 53 droughts that occurred from 1951 to 2011 [36]. While this region is frequently and extensively covered by clouds, it is also one with a relative elevation difference larger than 7000 m from the northwest to the southeast. As a result, the satellite-derived LST products are barely usable, which greatly impedes the regional studies in fields such as climate change, drought simulation, and loss estimation.
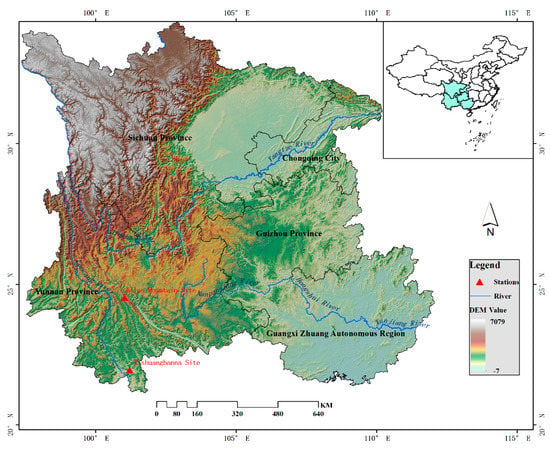
Figure 1.
The study area and location of validation stations.
2.2. Methods
According to the land surface balance theory, the relationship of energy fluxes follows this formula:
where G is the ground heat flux; is the net solar radiation at the surface; is the net longwave radiation; is the sensitive heat flux; and is the latent heat flux. Defining as the sum of and , the partial differential equation is derived with respect to the LST () as follows:
Based on previous research [19,32], and both have linear relationships with . Therefore, the relative in Equation (2) can be derived:
where is the slope of the linear relationship between and ; and b is the slope of the linear relationship between and . Additionally, according to the conventional force restoration theory:
in which is the soil thermal conductivity; is the depth of the subsurface layer; and is the temperature at the sublayer, which has been demonstrated to be less sensitive to skin surface insolation than the LST . Therefore, the terms in Equation (2) can be expressed as follows:
Combining Equations (3), (4), and (6) with (2) then gives
where . Based on (7), , the cloud-affected LST value could be calculated by the cloud-affected net shortwave solar radiation value (). Thus, for a given cloudy pixel, its real LST in the daytime can be constructed by two parts: the theoretical LST under clear-sky conditions () and the cloud-affected part ().
For the cloud-prone region, the neighboring-pixel method and other spatial interpolation would not apply for satellite-derived LST reconstruction because of the lack of the reference information over a huge area. Therefore, a similar pixel (SP) method is proposed to implement the reconstructing flow chart (Figure 2). In Figure 2, the selection of similar pixels for the cloudy pixel i is the first and most essential step for the whole reconstruction process, which is based on multiple effect factors, such as the digital elevation model (DEM), slope, normalized differential vegetation index (NDVI), aspect, and more. Since these factors are in different units, the following normalization function () is used:
where is a pixel value in the effect factor image; and and are the maximum and minimum value of the effect image, respectively. In a region with complex terrain like the study area in southwest China, under clear-sky conditions, the LST is synergistically impacted by location, vegetation, topography, microrelief, available surface radiation, weather information, and so on. Thus, these normalization factors () can be used to select the pixels similar to the cloudy pixel . Since the controlling factors may change with region, the most similar pixels, the set D, are identified by the similar threshold L using these normalized factors:
where S is the effect factor set of the LST, and its attribute is the nth factor; is all attributes of pixel i to be reconstructed; is all the attributes of another pixel j; and is the discriminant function of the similarity of the other pixels to the pixel i. To be easily implemented, d is simplified by the Euclidean distance form. Then, the most similar pixels in set D (pixels in green in Figure 2) are the desired pixels with a distance less than the similarity threshold L. Based on these similar clear-sky pixels, the two parts, including the theoretical LST under clear-sky conditions () and the cloud-affected parts () used to reconstruct the real LST of the cloudy pixels, are respectively calculated by the (b) and (c) processes in Figure 2.
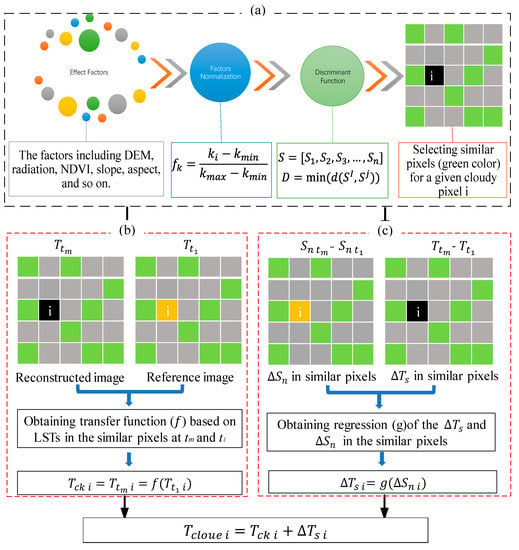
Figure 2.
Flow chart of the LST reconstruction process for the cloudy pixels in the satellite-derived LST products. (a) the process of selecting the similar pixels (the green color pixels) for a given cloudy pixel i; (b) the theoretical clear-sky LST () calculation for the cloudy pixel i; and (c) the cloud-affected parts () calculation for cloudy pixel i.
In the (b) process, assuming that the pixels in set D have the same LST changes in time and , a transfer function () is regressed from the LST pairs in set D at and . Then, the theoretical LST value (), namely, ) of the cloudy pixel i in the image can be derived by the following equation based on its value () in the reference image:
In set D, since all the pixels have similar environmental and surface conditions, all the pixels show a similar relationship between the and based on Equation (7), and the process (c) was proposed to obtain the cloud-affected parts (). The (namely, ) dataset is calculated by the pairs in set D at time and reference , and the (namely, ) dataset is calculated by the pairs in set D at time and reference . Then, the relationship (g) between the dataset and dataset is regressed to obtain the cloud-affected part of cloudy pixel i from the corresponding . Finally, the LST value of cloudy pixel i is reconstructed by the sum of the corresponding theoretical LST under clear-sky conditions () and the cloud-affected parts (). To obtain the effective function and g, the size of the area to select the similar pixels and the threshold L to determine similar pixels could be rationally adjusted by the regional condition of the satellite-derived LST products. Those similar pixels were selected from all clear-sky pixels in the whole study area because of frequent and severe cloud contamination in the SW region. Since there is no net solar radiation information in the nighttime along with relatively weaker spatial and temporal heterogeneity, the reconstruction process for the cloudy pixel of nighttime MODIS LST products only includes the (a) and (b) processes in Figure 2, compared to the reconstructed LST process implemented for the daytime products.
2.3. All Materials Involved in the Reconstruction and Results Validation
The MODIS daily LST Collection 6 MOD11A1 data retrieved by the refined generalized split-window algorithm from Terra satellite thermal infrared data were selected to implement the reconstruction process in this study [16]. The data quality control flags were employed to evaluate the raw data quality to determine the cloudy pixels and other low-accuracy pixels (mainly the pixels with an error of average emissivity larger than 0.04, or with an average LST error larger than 2 K) to be constructed. The daytime and nighttime images from all of 2012 were chosen to examine the LST validity in southwest China. Figure 3 shows the spatial distribution of the days without high-quality LST in 2012 during the daytime (Figure 3a) and nighttime (Figure 3b). Figure 3a,b clearly indicate that a large area is missing LST data in both the daytime and nighttime, that the data missing from each pixel in this region cover between 126 and 357 days in 2012, and that the distribution of days without data shows clear bounds similar to the trend of topography (Figure 1). The area with extensive missing data is located in the eastern part of the study region, with a lower elevation. Since the reference images are necessary for the reconstruction process proposed above, to reasonably select reference images, Figure 4 is used to measure the change in pixels percentage without good quality LST in the daytime (the black dotted line) and nighttime (the red dotted line) MODIS products throughout 2012. Figure 4 shows that the trend of invalid data percentage in the daytime and nighttime is almost the same as the day changes, and the amount of data missing from the study area is serious, with an average of 72.74% in the daytime and 67.92% at night, along with several days at 100%. Moreover, the chance of data missing on warm days is obviously greater than on cold days. Considering the diurnal and seasonal variations of the thermal infrared regime, it would be better to reconstruct the LST over cloudy pixels by separately treating images according to daytime, nighttime, and different seasons. Therefore, the reference images are also selected separately depending on the statistical results in Figure 4, and the amount of missing data on the selected reference images is less than 20%. In the SW region, reference images are selected in different seasons of the year 2012 and in those images with a higher percentage of valid-LST pixels. Specifically, the daytime images from the 322nd and the 93rd days and nighttime image from the 322nd and the 140th days, with percentage values of 81.2%, 82.6%, 80.1%, and 84.1%, respectively, are selected as reference images. For a given cloudy daytime MODIS LST, between the two candidate daytime references, the temporal-closer one was taken as the reference image (see in Figure 2), and a similar strategy was also applied to determine the nighttime reference image.
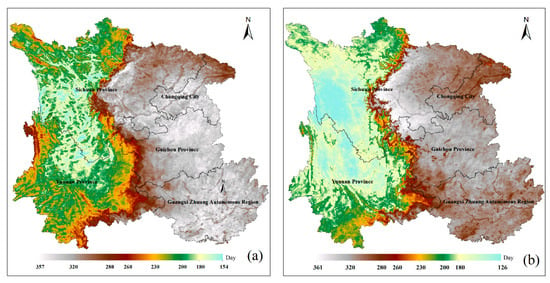
Figure 3.
Distributions of days without high-quality LST in 2012 in the study area. (a) the days in the daytime MODIS LST products, and (b) the days in the nighttime MODIS LST products.
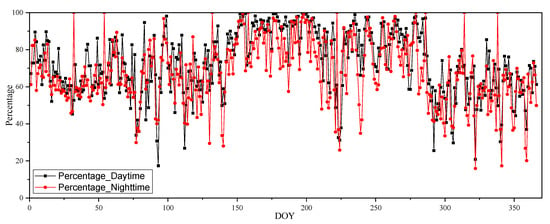
Figure 4.
Percentage of MODIS LST pixels with invalid values in the study area and their change with the day of the year (DOY).
The effect factors are essential input data used to identify similar pixels to implement the whole reconstruction process, including DEM, slope, aspect, NDVI, and theoretical radiation. The 1-km DEM input data for the SW region were clipped from global SRTM DEM data downloaded from the CGIAR-CSI site (http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/index.asp). According to the DEM data, the slope data and aspect data were also calculated further to express the terrain factor. To measure the vegetation conditions of this region, the 16-day period NDVI products were collected from NASA V006 MOD13A2, which has the best pixel value with low clouds, a low view angle, and the highest NDVI value in a 16-day period. Theoretical clear-sky solar radiation was simply obtained from the responding incident angle totally depending on time, location, terrain, and the diffuse and reflected radiation [37].
The MODIS net shortwave solar radiation value (NSSR) is a key input parameter to estimate the cloud-affected part . To take full advantage of the MODIS multiband information, the narrowband-to-broadband albedo conversion method proposed by Tang, et al. [38] was used for NSSR retrieval based on the narrowband data from MODIS. The parameterization method proposed by Li, et al. [39] was employed in the retrieval process. Compared to these methods based on radiative transfer models, which is complex and necessary to input cloud and aerosol information, this method makes it easier to simplify the calculation and to achieve better retrieval of the NSSR. Therefore, in this study, this method was implemented to obtain daily 1-km NSSR data in 2012 from MOD021KM, MOD03, and MOD05_L2 MODIS product files. The previous study of Yu et al. [32] has reported that the average difference between the retrieved NSSR and ground-based measurements was 35.5 Wm−2 at a daily pixel resolution, mainly attributed to random error. Since only the cloud-affected NSSR (, the difference between the cloudy pixel and responding similar pixels) is needed in the reconstruction process, the NSSR retrieved by this method meets the accuracy requirement of the reconstruction process.
The longwave radiation data from two meteorological stations (marked in Figure 1) in the study area were collected to validate the reconstruction results. Two sites, including the Ailao Mountain flux observation site and the Xishuangbanna flux observation site belonging to the Chinese FLUX observation and Research Network (ChinaFLUX) frame (http://www.chinaflux.org/enn/index.aspx), were employed to validate the reconstruction results. The Ailao flux observation site is located in the Ailao Nature Reserve (ALS, 24°32′N, 101°01′E, and 2476 m elevation) covered by forest with a stand age that exceeds 300 years. The Xishuangbanna flux is in the Xishuangbanna Tropical Rainforest Ecosystem Station (XSB, 21°57′N, 101°12′E, and 756 m elevation), which is covered by tropical seasonal rain forest with an average canopy height over 35 m. According to the thermal radiation transfer theory, the ground-based LST data can be calculated from stations’ longwave radiation measurements by the following equation:
where and are upwelling and downwelling longwave radiation, respectively; is the surface broadband emissivity; δ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (5.67 × 10−8 Wm−2 K−4); and is the LST used for validation. According to previous studies [40,41,42], MODIS narrowband emissivity products retrieved by the day/night LST algorithm can be regressed to estimate the broadband emissivity through the following form:
where , , and are the narrowband emissions of MODIS bands 29, 31, and 32, respectively; and , , and are regression coefficients. In this study, we used the set of coefficients provided by Wang and Liang [41] for the calculated broadband emissivity, which has demonstrated a stable accuracy over different types of materials except for ice, water, and snow. It has been indicated that satellite-based broadband emissivity agrees quite well with the ground measurements, with a standard deviation of 0.0085 and a bias of 0.0015, compared with three-year ground-based emissivity at the Gaize site (32.20°N, 84.06°E, 4420 m) [36].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Validation Results of the Reconstructed LSTs
Based on the LST measurements (LST_Insitu) of the ALS and XSB stations, the reconstructed LST results (LST_interp) in daytime and nighttime are validated, respectively. The validation scatter plots and difference distribution histograms of the two sites are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively. Figure 5 indicates that most of the points in the figure crowded around the 1:1 line (the red dashed line in Figure 5). Moreover, the reconstructed LSTs agreed more strongly with the in situ-based LST at night (Figure 5b,d) than that during the day (Figure 5a,c). When compared with the reconstructed LSTs in XSB, the reconstructed LSTs in ALS have a slightly higher precision, with fitted lines (the black solid line in the scatter plots) closer to the 1:1 line. Figure 6 shows the distribution histogram of the differences (LST_Insitu–LST_interp) in daytime and nighttime and indicates that the differences of most reconstructed LSTs are close to 0.00 K and concentrated in a range from −2.00 K to 2.00 K, although there were a few existing reconstructed LSTs with a larger difference. The percentage of the difference in the range from −2.00 K to 2.00 K is larger than 50.0%, with 51.2% (ALS) and 50.4% (XSB) in the daytime and 72.7% (ALS) and 72.3% (XSB) at night. Compared to the difference histogram of ALS with a peak area very close to the 0.00 K point, the peak of the difference histogram of XSB is close to −1.00 K. Therefore, the reconstruction results of the ALS site had a slightly greater accuracy than the XSB site in total (in the daytime and nighttime). Since the two sites are both covered by forest, the slightly higher accuracy is probably caused by a narrow range of LST change in the ALS site (namely, a weaker LST heterogeneity). The difference in the local microclimate and a relatively higher elevation of the ALS site (2476 m) than that of the XSB site (756 m) can strongly influence their LST range.
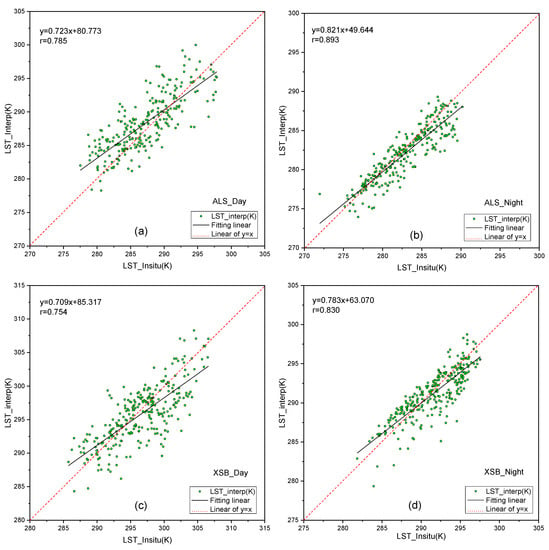
Figure 5.
The validation scatter of reconstruction results based on the in situ LST measurements. (a) and (b) are the daytime and nighttime validations in the ALS. (c) and (d) are the daytime and nighttime validations in the XSB.
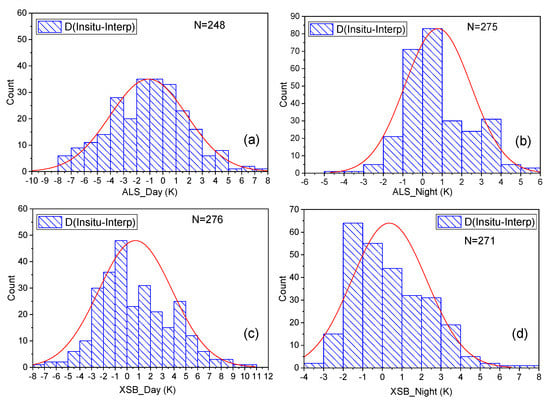
Figure 6.
The distribution histogram of the difference between in situ-based measurements of LST and reconstructed LSTs for the cloudy MODIS LST (D(In situ-Interp)). (a) and (b) are the daytime and nighttime distribution histograms in ALS. (c) and (d) are the daytime and nighttime distribution histograms in XSB.
The accuracy of the reconstructed LST in the ALS and XSB stations is summarized by the bias (Bias_Re, LST_Insitu- LST_interp) between the in situ-based LST and reconstructed LST and their root mean square error (RMSE) in Table 1. Table 1 shows that the accuracy of the reconstructed LST is relatively high at nighttime, with a bias of 0.57 K < 1.00 K (0.78 K in ALS and 0.35 K in XSB) and an RMSE of 1.90 K < 2.00 K (1.85 K in ALS and 1.88 K in XSB). For the reconstructed daytime LST, the overall bias is −0.14 K < 1.00 K, ranging from −1.09 K (in ALS) to 0.72 K (in XSB), with a total RMSE of 3.16 K < 3.20 K (2.96 K in ALS and 3.20 K in XSB). In total, the validation results of the reconstructed LSTs at nighttime had an average error < 1.00 K on the yearly scale, and the absolute errors of most reconstructed LSTs are in the range of < 2.00 K on the daily scale. For the cloudy daytime LST, which is more difficult to construct, the bias over the whole year was very close to 1.00 K, and the daily reconstruction results concentrate in a range of < 3.50 K, although a small proportion of outliers exist.

Table 1.
Summary of the validation results of reconstructed LSTs for the cloudy pixels in MODIS LST products (MOD11A1) in the ALS and XSB stations.
Based on the study of Jin [19], the occurrence of rainfall is probably the primary factor behind the small proportion of outliers in the validation results, and it is extremely difficult to estimate the effects of rainfall on the LST, even if the spatial rainfall information can be attained synchronously. The clear-sky LSTs in original MODIS LST products (MOD_LST) were validated using the ground-based LSTs from ALS and XSB and then compared with the reconstructed LSTs. As shown in Table 1, the bias of MOD_LST (Bias_MOD, LST_Insitu–MOD_LST) is less than 1.00 K (−0.45 K in ALS and −0.89 K in XSB) and the RMSE is less than 2.00 K (1.38 K in ALS and 1.57 K in XSB) in the daytime. In comparison, at nighttime, the bias is also less than 1.00 K (0.29 K in ALS and −0.78 K in XSB) and the RMSE is less than 1 K (0.83 K in ALS and 0.84 K in XSB). Considering the validation results, the LST_interp is almost in line with MOD_LST in terms of bias, but with a larger RMSE of 1 K–2 K (a greater RMSE of 1 K at nighttime, a greater RMSE of 1.5 K–2 K at daytime). The cloud-improved LSTs were produced on the basis of the clear-sky MODIS LSTs product and its associated cloud-mask information, including two parts: the original clear-sky MODIS LST and reconstructed LST for the cloud-sky MODIS LST. The comparison of the original MODIS LST product and the cloud-improved LST reconstructed by the presented method is shown in Figure 7. As a case, cloud-improved LST on the 214th day of 2012, relatively far from these days reference image selected, was randomly selected. Figure 7 indicates that the cloud-improved LST images have great spatial continuities compared with the original ones contaminated by swathes of clouds. Moreover, the distributions of reconstructed LST in both Figure 7a (the cloud-improved LST at daytime) and Figure 7c (the cloud-improved LST at nighttime) reasonably detailed the LST trend matching the elevation information (in the Figure 1). In the cloud-improved LST, a smooth transition is also observed from the original clear-sky LSTs in MODIS LST to reconstructed LST. Therefore, the cloud-improved LST products from MODIS LST benefit from a relatively great accuracy and spatiotemporal continuous LST information, which could meet most of the regional research in SW, where valid satellite-derived LST is extremely flawed and ground-based LST is highly limited.
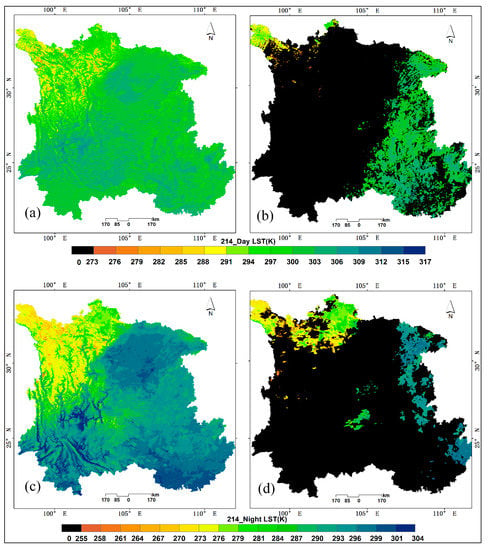
Figure 7.
Comparison of the cloud-improved LST and original MODIS product. (a) and (c) are the cloud-improved LSTs. (b) and (d) are corresponding original MODIS LSTs.
3.2. An Experiment Testing the Accuracy of the theorical Clear-Sky LST () Estimated by the SP Interpolation Method
For the daytime reconstruction process, several factors could affect the accuracy of the reconstructed LSTs. However, the SP method for interpolating the theoretical clear-sky LST of the cloudy pixels ((a) and (b) in Figure 2) and the precision of key input parameters, net solar radiation ((c) in Figure 2), which directly influence cloud estimates, have strong effects on the final reconstruction of the real LST under clouds. For the nighttime reconstruction process, the SP method for interpolating the process is the most important component, due to the lack of solar radiation information when the satellites pass by. Therefore, to test the SP interpolation method’s performance, an experiment was designed for the images with large continuous valid LST data. In the experiment, the three images, the daytime LST images from the 112nd day and 306th day and the nighttime LST image from the 341st day, with more valid LST pixels based on the statistical results of invalid pixels percentage in the study area shown in Figure 4, were selected from the MODIS LST dataset by excluding the reference LST images. Then, the LSTs were removed from the area with continuous LST in a series of circular area buffers with diameters of 50 km, 100 km, 150 km, 200 km, and 250 km in the selected LST images. The centers (the red point) of these circles are shown in Figure 8 for the three tests, where the black circular areas have a diameter (D) of 250 km, representing the maximum area to remove in the interpolation experiment. According to the NDVI in Figure 8, the sub-area of the experiments (Test 1 and Test 2) was selected in a relatively heterogeneous land surface (in the image from the 306th day for Test 2) and a relatively simple land surface (in the image from the 112th day for Test 1) for the interpolation experiment in the daytime. The sub-area for the nighttime interpolation experiment (in the image from 341st day for Test 3) is the most complicated one possible for a good test, since there is relatively weaker heterogeneity in the LST in the nighttime compared to that in the daytime.
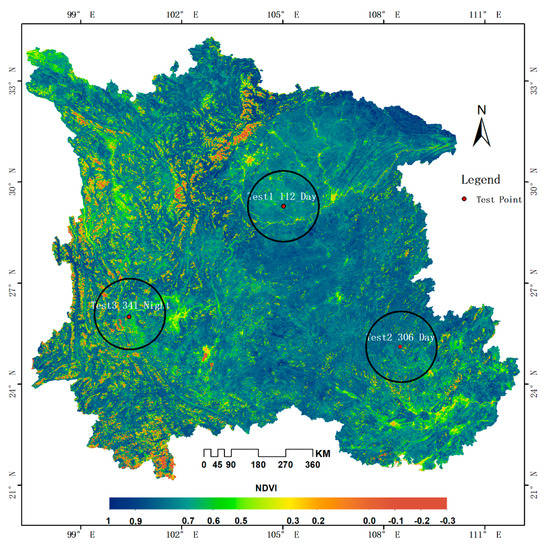
Figure 8.
The location of testing area for the SP performance experiment. The red points are centers of a series of circular area buffers to remove for the performance experiment with diameters of 50 km, 100 km, 150 km, 200 km, and 250 km; the black circles indicate the area with a maximum diameter.
The initial LSTs in the largest selected circle area of D = 250 km in three tests implemented in three images are shown in Figure 9, and their centers are the three points marked in Figure 8. Figure 9 indicates that for the two tests in daytime interpolation experiments, the LSTs in the largest removed area in Test 1 show weaker heterogeneous structural characteristics than those in Test 2, but have a higher absolute LST value. The LST for the nighttime interpolation experiment in Test 3 has a relative complementary structure and an LST difference of 21.04 K, representing the largest LST difference in the three test areas with D = 250 km. After implementing SP interpolation replaced LST in the series of diameters of 50 km, 100 km, 150 km, 200 km, and 250 km, the difference in the initial and SP interpolated LSTs was calculated for the three tests, and the difference images are shown in Figure 10. In Figure 10, the different results for Test 1, Test 2, and Test 3 are given in the columns, and D = 50 km, 100 km, 150 km, 200 km, and 250 km are given in the rows from top to bottom. The title of each subfigure gives the information about the day of the year of the test images and the circle diameter (such as 2012112 D = 50). Compared to the subfigures of Test 2 and Test 3 in Figure 10, the subfigures of Test 1 from D = 50 km to D = 250 km indicate that the SP interpolation method performs better in Test 1, since the values of the difference image pixels in Test 1 are much closer to 0.00 K. Meanwhile, the subfigures in Test 2 and Test 3 reveal that the SP interpolation method may tend to weaken the heterogeneity of the LST by underestimating in the high LST area and overestimating in the low LST area. Therefore, to interpolate the theoretical clear-sky LST, SP performs well in the weak heterogeneous surface and may weaken the special high or low LST. When comparing the subfigures with different diameters in the three tests, it is clear that in the same removed area, the interpolation results are very similar, although they are interpolated in images with different amounts of missing data.
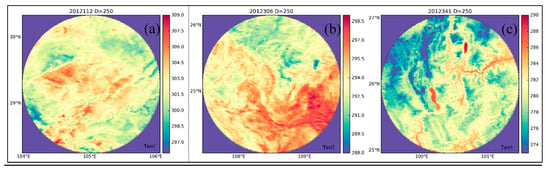
Figure 9.
The initial LSTs in the largest selected circular area with a diameter of 250 km for the interpolation experiment. (a), (b) and (c) are the initial LSTs of Test 1, Test 2 and Test 3, respectively.
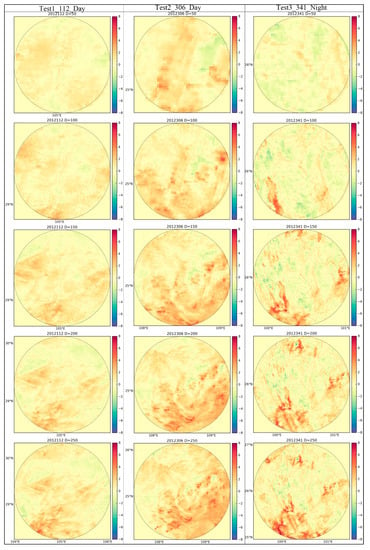
Figure 10.
The spatial distribution of the difference between the initial LST and interpolation LST in the area removed with a diameter from 50 km to 250 km.
To quantitatively analyze the performance of the SP interpolation method, the average of the difference (or bias) between the initial LST and interpolation LST and the standard deviation (SD) of the three tests is shown in Figure 11. Based on difference plots of the three tests (see Figure 10), a total RMSE of the whole removed area and its corresponding sub RMSE of the sub circle area with a diameter of 50 km (the same as the smallest removed area of each test) are calculated and shown in Figure 12. Figure 11 indicates that most of the biases of the interpolation LST concentrate in the range from −1 K to 1 K. Likewise, the values of biases are slightly increased by 0.228 K in Test 1, 0.385 K in Test 2, and 0.913 K in Test 3 with the size of the missing-data area from D = 50 km to D = 250 km, respectively. According to the SD bars in Figure 11, the SDs from D = 50 km to 250 km are all in the range of SD < 1.5 K, with SD from 0.558 K to 0.939 K in Test 1, SD from 0.937 K to 1.139 K in Test 2, and SD from 0.722 K to 1.368 K in Test 3. The SDs in the three tests increase from D = 50 km to 150 km and then maintain relative stability. Based on the total RMSE of the whole removed area of each test (shown in Figure 12) with diameter ranging from 50 km to 250 km, errors of the interpolation LSTs is less than 1.80 K in general, which is caused by the SP interpolation method. Similarly, with SD, the total RMSEs in the three tests also rapidly increase from 50 km to 150 km, and then slow down. Therefore, for a certain area to be interpolated, when the size of an area with missing data reaches a specific range, the SD and RMSE of the SP interpolation method may achieve stability. The sub RMSE, as shown in Figure 12, indicates that in the selected sub circle area of each test, the largest difference between the maximum sub RMSE and its corresponding minimum sub RMSE is about 0.04 K, and the trend of sub RMSE is negligible with the increase of the LST-missing area. Therefore, in most cases, for a certain area, the accuracy of the SP interpolation barely changes over the size of the entire LST-missing area, because for a certain pixel or a certain area, the relationships regressed from a larger number of similar pixels in interpolated images and reference images are relatively stable. Moreover, based on Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12, it is clear that Test 2 has the greatest LST heterogeneity among the three tests and the other two tests both display a greater LST difference. Despite this, the biases and total RMSEs of Test 2 are larger than those of the other two tests. Therefore, the spatial structure of the LST distribution has a greater impact on SP interpolation performance than the size of the area missing data and the absolute LST value in the area missing data.
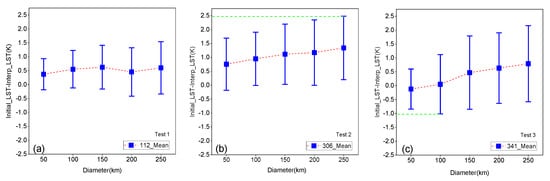
Figure 11.
The bias and standard deviation (SD) between the interpolation LST and the removed LST in the experiment. The blue point is the bias (removed LST—interpolated LST), and the blue bars from the blue point are the SDs. (a), (b) and (c) are bias and SD figures of Test 1, Test 2 and Test 3, respectively.
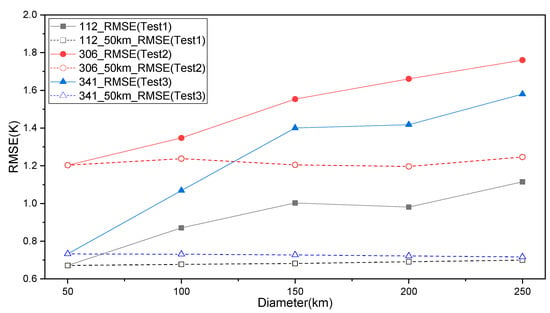
Figure 12.
The RMSE between the interpolation LST and the removed LST in the experiment. The 112_RMSE(Test1), 306_RMSE(Test2), and 341_RMSE(Test3) are total RMSEs of the whole removed area; the 112_50km_RMSE(Test1), 306_50km_RMSE(Test2), and 341_50km_RMSE(Test3) are sub RMSEs within a sub circle area with a 50 km diameter (the same as the smallest removed area of each test) from the whole removed area.
3.3. Topography Sensitivity Testing
To test the topography sensitivity of the SP interpolation, the biggest removed area in Test 3 with mixed topography was selected to implement an SP interpolation without the DEM factor. The difference image between initial SP interpolation (Initial_SP) and the DEM-removed SP interpolation (DEM-removed_SP), and the biases from the difference images (the difference image between Initial_SP and removed LST, and the difference image between DEM-removed_SP and removed LST) within different classes of DEM are calculated and shown in Figure 13. From Figure 13a,b, the DEM-removed_SP is with obvious high interpolated LSTs (the negative value area colored with blue and green in Figure 13b) in the high elevations. Figure 13c indicated, in most cases, that the Initial_SP has a lower bias than DEM-removed_SP, especially in the higher elevation area, which is with a lower LST in the testing area. Less biased areas of DEM-removed_SP are within the DEM from 2.5 km–3.0 km, including the average elevation (about 2.7 km) of the around removed area. Compared to the total bias (0.79 K) and RMSE (1.58 K) of the Initial_SP, DEM-removed_SP has larger bias and RMSE of 1.27 K and 2.67 K, respectively. Therefore, judging from the overall accuracy and the performance in different elevations, Initial_SP generally outperforms DEM-removed_SP. Furtherly, the SP interpolation method is sensitive to the DEM factor, namely, the addition of the topography factor improved the accuracy of reconstructed LST over significant reliefs or topographically complex regions.
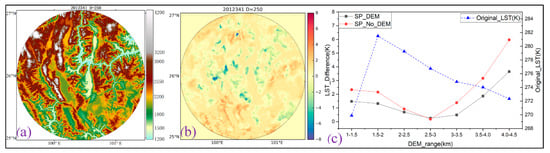
Figure 13.
The experiment for testing the topography sensitivity. (a) is the DEM of the testing area; (b) is the difference between the initial SP interpolation and DEM-removed SP interpolation; and within the different classes of DEM, the average value of the removed LST (Original_LST in (c)), average difference values of the removed LST with initial SP interpolation (SP_DEM in (c)), and the DEM-removed SP interpolation (SP_No_DEM in (c)), are calculated and shown in (c).
3.4. Other Factors Effect on LST Reconstruction
Along with the performance of the SP interpolation method and the effect of topography, some other factors may also impact the final reconstruction results. For the daytime reconstruction process, the accuracy of the net solar shortwave radiation (NSSR) retrieval is an important factor influencing the estimation of the cloud-affected part (). The accuracy of the NSSR retrieved by the method in this study has been validated in previous studies by ground-based measurements and has an average error of 35.5 Wm−2 at a daily pixel resolution, which is mostly attributed to random errors [32]. In the reconstruction process, the NSSR difference () of the similar pixels between the NSSR value in the reconstructed day and their corresponding NSSR values in the reference day is a required parameter, which can completely remove systematic error and decrease the error caused by the accuracy of NSSR retrieval in the final LST reconstruction. According to the study by Jin, the parameter K in Equation (7) is typically 140 Wm−2K−1, as the root mean square of LSTs is a minimum when simulated by Equation (7) [19]. Therefore, the average error introduced by the NSSR retrieval is approximately 0.253 K (35.5 Wm−2/140 Wm−2K−1). According to the surface energy balance equation, the LST difference between a given cloudy pixel and its similar pixels is due to the differences in energy fluxes. In the transformation form of surface energy balance Equation (2), and , which are not available from satellite remote sensing, are parameterized by for daytime to obtain the cloud-affected part (). According to the study of Jin [19], the effect of uncertainty caused by their parameterization on the final reconstruction results is about 1.50 K–1.96 K. Jin [19] also indicated that the parameterization can provide an adequate LST estimation accuracy of about 1 K–2 K, with the knowledge of .
The similarity threshold L is key to identifying similar pixels to implement the entire reconstruction. The Euclidean distances between pixel i and other pixels with valid LSTs were calculated based on attributes including the DEM, slope, aspect, NDVI, and theoretical solar radiation. Therefore, the threshold L is a distance threshold to restrain the attribute distance: the smaller L is set, the more similar the selected pixels will be to pixel i, which should produce optimized regression functions and g. However, there is a high risk of being unable to acquire enough pixels to obtain functions and g, especially for areas with large, frequent clouds, which leads to the existence of null value pixels in the reconstructed LST data, limiting its application. Certainly, a dynamic and appropriate L can be selected by a condition loop in the reconstructing code to reconstruct all the cloudy pixels in MODIS LST. In practice, the loop starts with L = 0, step at 0.1, and to implement reconstructing code on cloudy-covered MODIS LST. When encountering an incomplete reconstructed image, this specific loop is stopped and proceeds to the next loop with L + 0.1. The L completely reconstructing all MODIS LST in SW is considered the appropriate L to ensure the integrity of LST data, but not the optimal L for the best accuracy of reconstructed LST.
In this study, which was limited by the ground-based measurement of LST, two forest sites were employed to validate the reconstructed LST. However, from the NDVI distribution of the SW regions in Figure 8, the rate of the area covered by dense vegetation is very high. Based on the MODIS land cover products (MCD12Q1) in 2012, the total area covered by the forest and Savannas (mainly forest mixed grassland in SW) makes up about 72.4 percent of the SW region. Therefore, the validation results may not represent all landscapes, but cover most areas in the SW region. Clearly, more validation work should be done to fully evaluate the performance of the SP reconstruction results in the future, if more ground-based measurements become available.
5. Conclusions
To reconstruct the LST for MODIS cloudy pixels, an effective method based on the energy balance and similar pixels algorithm was proposed in this study. Based on the similar pixels, the cloudy-sky LST under clouds was calculated by the theoretical clear-sky LST and the cloud-affected part. This reconstruction method has been validated against ground-based measurements of LST, and the results show that the average error of the reconstructed LST is less than 1.00 K, and the RMSE is less than 3.50 K in the daytime and even close to 2.00 K at nighttime. Moreover, the cloud-improved LST products from MODIS LST, with a relatively high accuracy and spatiotemporal continuous LST information, could satisfy most of the regional research in SW, where valid satellite-derived LST is extremely flawed and the ground-based LST is limited. Despite the uncertainty in the reconstruction algorithm, this work provides an effective guideline for reconstructing satellite-derived LST products in areas, e.g., the SW region, that are frequently covered by large clouds.
SP interpolation is the key step in the whole reconstruction process used to estimate the theoretical clear-sky LST part. Its performance has been examined in the daytime and nighttime images by a data removing experiment that included three tests. The analyses indicated that the RMSE led by the SP interpolation is less than 1.8 K in an interpolation area of <= 49,000 km2. Because of the lack of solar shortwave radiation information, the accuracy of LST reconstruction at nighttime is mainly dependent on the performance of SP interpolation. Besides, the distinct advantage of the SP interpolation is that the size of the null data area hardly influences its performance in a certain pixel or a certain area, which could support the reconstruction of frequently cloudy regions. Moreover, compared with the performance of the three tests, the complexity of the LST structure effect was larger than the absolute difference in the LST in the reconstructed region. Compared to the initial LST, the SP interpolation slightly flattened the heterogeneity of the LST in the removed area. The topography sensitivity testing indicated that the inclusion of topography can greatly improve the accuracy of the reconstructed LST in the topographically complex regions.
Depending on properties including the DEM, slope, aspect, NDVI, and the theoretical solar radiation, the Euclidean distances between the cloudy pixels and other pixels with valid LST in the reference images were calculated. A similar threshold was set to select the most similar pixels, and the threshold could be adjusted to control the similarity of the pixels selected. According to the condition of data missing in the satellite-derived LST products, the adjustable and dynamic threshold can help optimize the accuracy of the interpolation and the integrity of the constructed LST for a certain area, which lets the reconstruction method have potential for a wider range of application backgrounds.
As is well known, no study is perfect, and this paper is no exception. Limited by the ground-based measurements, it lacks a complete validation focus for all land cover types (LCT) in the study area. Nevertheless, a complete-LCT validation will be implemented for the SP reconstruction method when more ground-based LSTs are available, which will probably in turn feed back into the improvement for this reconstruction process. Moreover, the existence of extreme cases with differences up to 8–10 K in the cloudy pixels is probably caused by strong convection systems, and usually occurs with events of heavy precipitation, strong wind, and rapid transition among the air masses, etc., which largely alter the LST. Identification of extreme cases in the reconstruction results, a common and tough problem in most reconstruction or interpolation methods developed for satellite-derived LST-usually the weather condition under clouds that is hard to access now, is necessary information. In addition to weather conditions, some other more complex factors, such as hill shade, illumination, and soil moisture, are expected to be suitably considered in future reconstructions for cloudy pixels in satellite-derived LST to improve current methods, including the SP reconstruction method presented in this research.
Author Contributions
W.Y. outlined the research topic and methodology and also handled the analysis work and wrote the manuscript. J.T. assisted with the outline of the research topic and preprocessed the data. M.M. gave helpful advice and assisted with manuscript writing. X.L., X.S., and Z.S. collected and preprocessed the data.
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41601448, No. 41830648, No. 41701420, and No. 41771453). This work is also jointly supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (No. SWU117063).
Acknowledgments
In the study, all the MODIS data were acquired from the Level-1 and Atmosphere Archive & Distribution System (LAADS) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC), located in the Goddard Space Flight Greenbelt, Maryland (http://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov/). The ground-based measurement data were obtain from the Chinese FLUX observation and Research Network (ChinaFLUX) frame (http://www.chinaflux.org/enn/index.aspx).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Anderson, M.C.; Allen, R.G.; Morse, A.; Kustas, W.P. Use of landsat thermal imagery in monitoring evapotranspiration and managing water resources. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenstein, O.; Qin, Z.; Derimian, Y.; Karnieli, A. Derivation of land surface temperature for landsat-8 tirs using a split window algorithm. Sensors 2014, 14, 5768–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.-C.; Yeh, H.-H. Analysis of atmospheric turbidity levels at taichung harbor near the taiwan strait. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.L. Quantitative remote sensing of land surface; John Wiley & Sons, INC., Publication: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillin, L.M. Estimation of sea surface temperatures from two infrared window measurements with different absorption. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 5113–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinker, R.T.; Sun, D.; Hung, M.-P.; Li, C.; Basara, J.B. Evaluation of satellite estimates of land surface temperature from goes over the united states. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, P.N.; Biggar, S.F.; Thome, K.J.; Gellman, D.I.; Spyak, P.R. Vicarious radiometric calibrations of eos sensors. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1996, 13, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Li, Z.-L. A physics-based algorithm for retrieving land-surface emissivity and temperature from eos/modis data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 980–996. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C. Land surface temperature retrieval from thermal infrared data: An assessment in the context of the surface processes and ecosystem changes through response analysis (spectra) mission. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, L.F.; DaCamara, C.C. Land surface temperature and emissivity estimation based on the two-temperature method: Sensitivity analysis using simulated msg/seviri data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.-h.; Karnieli, A.; Berliner, P. A mono-window algorithm for retrieving land surface temperature from landsat tm data and its application to the israel-egypt border region. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3719–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.S.; Rokugawa, T.; Matsunaga, J.; Cothern, S.; Hook, A.K. A temperature and emissivity separation algorithm for advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer(aster) images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.M.; Dozier, J. A generalized split-window algorithm for retrieving land-surface temperature from space. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 892–905. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.-l. Validation of the land-surface temperature products retrieved from terra moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z. New refinements and validation of the collection-6 modis land-surface temperature/emissivity product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neteler, M. Estimating daily land surface temperatures in mountainous environments by reconstructed modis lst data. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, S.W.; S⊘rensen, R.; Stendahl, J.; Seibert, J. Using landscape characteristics to define an adjusted distance metric for improving kriging interpolations. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M. Interpolation of surface radiative temperature measured from polar orbiting satellites to a diurnal cycle 2. Cloudy-pixel treatment. J. Geopys. Res. 2000, 105, 4061–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Venus, V.; Skidmore, A.; Wang, T.; Luo, G. Estimating land-surface temperature under clouds using msg/seviri observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Long, D.; Shen, H.; Wu, P.; Cui, Y.; Hong, Y. A two-step framework for reconstructing remotely sensed land surface temperatures contaminated by cloud. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 141, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Nan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wu, T.; Zhao, L. An effective interpolation method for modis land surface temperature on the qinghai–tibet plateau. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4539–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. Recovering missing pixels for landsat etm+ slc-off imagery using multi-temporal regression analysis and a regularization method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiode, N.; Shiode, S. Street-level spatial interpolation using network-based idw and ordinary kriging. Trans. Gis 2011, 15, 457–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z. Long-term observations of aerosol optical properties at wuhan, an urban site in central china. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Shen, H.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, P. Reconstructing modis lst based on multitemporal classification and robust regression. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pede, T.; Mountrakis, G. An empirical comparison of interpolation methods for modis 8-day land surface temperature composites across the conterminous unites states. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 142, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, B.; Shi, J. Reconstructing spatial–temporal continuous modis land surface temperature using the dineof method. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 046016. [Google Scholar]
- Evgenieva, T.; Iliev, I.; Kolev, N.; Sobolewski, P.; Pieterczuk, A.; Holben, B.; Kolev, I. Optical characteristics of aerosol determined by cimel, prede, and microtops ii sun photometers over belsk, poland. In Proceedings of the 15th International School on Quantum Electronics: Laser Physics and Applications, Bourgas, Bulgaria, 15 December 2008; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Julien, Y.; Sobrino, J.A.; Mattar, C.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C. Near-real-time estimation of water vapor column from msg-seviri thermal infrared bands: Implications for land surface temperature retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4231–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattar, C.; Durán-Alarcón, C.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Santamaría-Artigas, A.; Olivera-Guerra, L.; Sobrino, J.A. Global atmospheric profiles from reanalysis information (gapri): A new database for earth surface temperature retrieval. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 5045–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ma, M.; Wang, X.; Tan, J. Estimating the land-surface temperature of pixels covered by clouds in modis products. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J.; Outcalt, S.I. An approach toward energy balance simulation over rugged terrain. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 11, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbéteau, Y.; Merlin, O.; Gascoin, S.; Gastellu, J.P.; Mattar, C.; Olivera-Guerra, L.; Khabba, S.; Jarlan, L. Normalizing land surface temperature data for elevation and illumination effects in mountainous areas: A case study using aster data over a steep-sided valley in morocco. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 189, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, J.C.; Casinière, A.D.L.; Cabot, T. Atmospheric turbidity analyzed by means of standardized linke’s turbidity factor. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1995, 34, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscà, J.V.; Pinazo, J.M.; Cañada, J.; Ruiz, V. Ångström’s turbidity coefficient in seville, spain in the years 1990 and 1991. Int. J. Ambient Energy 1996, 17, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elminir, H.K.; Hamid, R.H.; El-Hussainy, F.; Ghitas, A.E.; Beheary, M.M.; Abdel-Moneim, K.M. The relative influence of the anthropogenic air pollutants on the atmospheric turbidity factors measured at an urban monitoring station. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Li, Z.-L.; Zhang, R. A direct method for estimating net surface shortwave radiation from modis data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Leighton, H.G.; Masuda, K.; Takashima, T. Estimation of sw flux absorbed at the surface from toa reflected flux. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wan, Z.; Wang, P.; Sparrow, M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Haginoya, S. Estimation of surface long wave radiation and broadband emissivity using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (modis) land surface temperature/emissivity products. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D11109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liang, S. Evaluation of aster and modis land surface temperature and emissivity products using long-term surface longwave radiation observations at surfrad sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Schmugge, T.; Jacob, F.; French, A. Estimation of land surface window (8–12 μm) emissivity from multi-spectral thermal infrared remote sensing—A case study in a part of sahara desert. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).