1. Introduction
In recent years, research interest in lightning has increased thanks to improved monitoring technology, which makes a huge amount of high-precision data available on an increasing temporal range. Interest is mainly related to scientific aspects, nature and the development of the phenomenon itself [
1,
2], associated hazards [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7], the relationship between weather and climate features [
8,
9,
10], and innovation in detection approaches [
11,
12]. In fact, cloud–ground lightning causes damage to buildings, infrastructures, and facilities, wildfires, and even casualties [
1]. On a global scale, thousands of deaths and injuries are caused by lightning every year, and occurrence is more frequent in developing countries where, on average, 150–200 casualties are registered per year. However, lightning causes many losses even in industrialized western countries: in the United States, about 100 people die of a lightning stroke every year [
13].
In this paper, we use the term “lightning” to generically indicate atmospheric discharges correlated to convective activity, while we use the term “flash” to indicate the more specific process of a discharge forming from a stepped-leader–return-stroke process (for cloud-to-ground events). Each flash can present one or more single currents named “strokes”, usually flowing in the same channel as the first stroke, and sometimes striking the ground at different points [
1]. For cloud-to-cloud discharges we generically use the term “cloud-cloud events”, without distinction between cloud-to-cloud, intracloud, or cloud-to-air processes.
The Mediterranean Sea is one of the most intense electric-activity areas of the Northern Hemisphere [
14] and, consequently, is one of the highest meteohydrological-risk areas of the world due to its highly vulnerable elements. On average, lightning claims between 5 and 10 victims per year per country [
15].
Several studies approached the spatial and temporal distribution of lightning in the Mediterranean region: activity largely prevails on the sea surface in winter and on land in spring and summer [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20], following the seasonal cycle of surface warming. The identification of convective systems into complex meteorological structures such as hurricanes [
21], mesoscale systems, and local thunderstorms needs continuous lightning monitoring. Adequate surveying is also crucial for civil-protection action plans and to adopt appropriate risk-mitigation strategies.
In the Mediterranean area, floods and flash floods with disastrous consequences are often associated with intense rain events [
6,
7]. Considering the period starting from the year 2000, 73 floods/flash floods occurred [
22] along all the seasons, but with higher frequency (over 45%) in October and November. The Italian peninsula and the French Mediterranean coastline are among the most affected areas, with 23 and 11 events, respectively [
22], happening during the entire year and primarily in fall (over 56%). In the last 50 years, in the central Liguria region, one of the most exposed areas, some authors [
23,
24] evidence that floods have progressively assumed flash-flood features due to rainfall-event duration, from 3–12 h to 24–72 h.
The relationship of lightning with climate change has largely been discussed [
21,
25,
26], and many authors agree in considering a positive correlation between increasing surface temperatures and lightning activity [
27,
28,
29], but such correlation does not find general agreement. Finney et al. [
30] expect a reduction in lightning to be correlated with an increase in surface temperature due to modifications in ice-cloud fluxes. Thus, a longtime series study appears crucial for a deeper comprehension of the relationship between lightning and climate change, and of the relationship with natural hazards. Nowadays, high-precision lightning ground detection systems allow the monitoring of long-distance activities, even on a large scale, contributing to large databases on wide geographical areas [
19,
31,
32]. Some global-scale databases are committed to the spatial distribution of thunderstorm cells [
33].
Some studies focused on studying the relationship between lightning and surface morphology and land use: generally, there is good correlation with orography [
34], especially in the presence of steep slopes that enhance the rapid uplift of unstable air masses, while even urbanization appears to affect the local increase of lightning [
35]. Orographic influence is particularly important in coastal areas, as underlined by many authors [
1,
5].
Many other research efforts [
1] have been devoted to studying atmospheric factors driving lightning activity, and stressing the connection between lightning and available convective potential energy. If surface warming is the basic element that is strictly correlated with atmospheric instability, more work is needed to investigate the relationship between lightning, sea-surface temperature, and land temperature, like the work of Kotroni and Lagouvardos [
9].
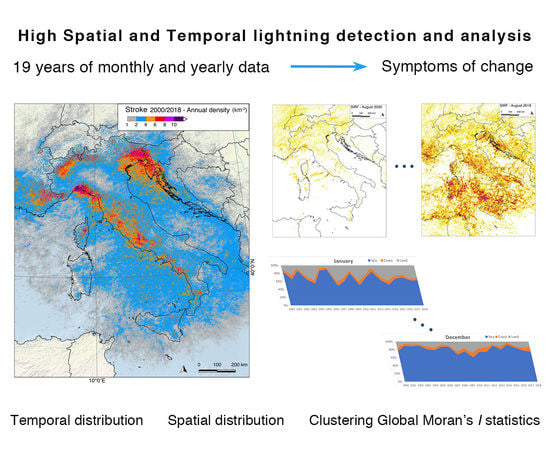
This research focuses on giving a preliminary characterization of cloud–ground strokes across the Mediterranean area surrounding the Italian peninsula based on the Italian Lightning Detection System SIRF, which is part of the European EUCLID network and uses ground-based sensors. The 19-year SIRF database (2000–2018) was used to analyze the strokes’ spatial and temporal distribution in the central Mediterranean area in order to: a) integrate existing studies with longer annual and monthly series, supporting further meteorological and climatic research; b) assess a possible relationship between surface warming and lightning activity or a possible trend in time, which would contribute to assessing future scenarios of the eventual increase of extreme meteorological events.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Area of Interest
The area under study is centered over the Italian peninsula (
Figure 1) and covers about 2,000,000 km
2; it is defined by longitude 4.04128E, latitude 34.6403N; and longitude 21.5229E, latitude 48.6584N. The surface is almost equally distributed between land and sea, 52% and 48%, respectively; the coastal zone, within 10 km from the seashore, is about 8% of the total land area.
The area (
Figure 1) includes the entire Alps and Apennines chains, the Po plain, the western Balkan peninsula, and the northeast termination of the Atlas Mountains; altitudes are between sea level and 4810 m.
According to the Köppen [
36] classification, the type of climate ranges between alpine, boreal, warm temperate, and arid [
37]. General atmospheric circulation is dominated by humid western currents. with the seasonal influences of the Azores and North African anticyclones; in winter, the central Mediterranean is sporadically affected by currents from the Balkans or from Scandinavia [
38]. The strong thermic contrast between air masses in such a complex and heterogeneous area contributes to generating high electric activity and heavy rains with a high-intensity rate: the highest value of 180 mm/h was measured in 2011 in the central Ligurian Apennines (Point 1 in
Figure 1B), when a flash flood caused 6 casualties [
39], but a rate of 140 mm/h was reached in the same area during a 2014 flash-flood event [
40,
41]. In the last 20 years, several floods and flash floods hit the whole Italian peninsula [
22].
2.2. Dataset
The lightning data used in this study were provided by the Italian Lightning Location System (SIRF), owned by CESI (Italian Electrotechnical Experimental Center) S.p.A. SIRF covers the entirety of Italy and Italian seas, with homogeneous performances. SIRF is the Italian member in EUCLID, a cooperation between national Lightning Location Systems (LLS) operators who joined their systems in one larger and uniform pan-European network. Thanks to this cooperation, lightning data over all of Italy and the bordering seas have been continuously located and archived since 2000, not only with the contribution of SIRF’s own national sensors, but potentially with the contribution of more than 140 sensors over Europe, mainly involving around 30 sensors over Italy and the border countries in data calculation [
42,
43].
Both SIRF and EUCLID are based on the most recent and precise available technology for lightning detection, with sensors using a combined method of calculation (time of arrival plus direction finding) for the impact point on the ground. A sophisticated algorithm of waveform recognition is used to discriminate between cloud–ground and cloud–cloud events.
Each lightning is detected by multiple sensors in the LLS; information coming from each sensor is received and elaborated by central analyzers to calculate the main parameters for each lightning strike: the point of impact on the ground, the date and time of impact, peak current amplitude and polarity, and type (cloud–ground or cloud–cloud). The network is able to detect each stroke of a cloud–ground flash event, with its own characteristics, and each stroke is saved in the LLS database, available for subsequent analysis.
An algorithm assigns each stroke to a flash event if it is at a distance of less than 10 km and 1 s from the first event, with an interstroke time of less than 500 ms; each flash is saved in a separate database.
The network EUCLID performances have been extensively analyzed over the last decade against ground-truth data collected by either direct measurements on Gaisberg Tower or high-speed video and field recording system (VFRS). The resulting Detection Efficiency (DE) was determined to be 97% for flashes containing at least one stroke with a peak current greater than 5 kA, and 80% for strokes with peak currents greater than 10 kA [
44]. The median value of absolute location accuracy (LA) was measured at Gaisberg Tower in 2014 to reach a median value of 90 m, which is consistent with the results obtained at larger scales based on VFRS data [
39]. SIRF being homogeneous in technology, calibration, and mean baseline with the rest of the EUCLID network, these performances can also be inferred for the SIRF system.
The performances mentioned here for the SIRF system are homogeneous all over Italy and the bordering seas. The Adriatic Sea being narrow enough, sensors on both the Italian and the Balkan side assure the same kind of coverage and performance over its surface. The western side of the Italian Mediterranean waters under analysis are covered by sensors of the Italian mainland, Sardinia, Sicily, Corsica, and the Balearic Islands, presenting the same performance level from Sardinia toward the east. On the other hand, south of the Italian coast, in the absence of more sensors, one may expect degrading performance further from the coast [
43]. Although a limited part of the area under study is involved, this may be considered a limitation of the present study.
In this work, we used cloud–ground stroke data, with no filter on peak current. The aim of the study was to provide preliminary analysis of 19 years of measurements, between 2000 and 2018, detected and located by SIRF and EUCLID in the Italian basin. The database includes a total of more than 67 million cloud–ground strokes.
Analysis was performed aggregating (counting) stroke impact points in space, using a homogeneous 1 × 1 km grid. This is sensible due to extreme precision of the LLS in localization, with mean location accuracy being much lower than 1 km. Due to computational limits, data were then grouped in a 5 × 5 km grid to perform cluster analysis (per year or per month).
2.3. Methodology
Considering the peculiar nature of lightning, spatial autocorrelation analysis was performed on monthly and yearly aggregated data through global Moran’s
I statistics, which gives a measure of data clustering. The basis is given by Tobler’s first law of geography [
45,
46] that states: “everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things”. Then, global Moran’s
I statistics [
47,
48] transpose the autocorrelation concept to spatially distributed data, measuring spatial dependency. Moran’s
I index is defined as follows:
where:
n is the number of geographic entities, that is, the number of cells;
is the spatial feature at the location I, that is, the count of stroke per cell;
is the mean value;
is the spatial weight between features i and j;
Calculations were done using inverse distance for the weight matrix with a Euclidian metric; results were tested at 99% confidence level, as the null hypothesis was the random spatial distribution of strokes.
Index I may assume values in the range of , extremes corresponding, respectively, to situations of total dispersion and total clustering, and the 0 value to total randomness. Results of monthly and yearly calculations are presented in the following paragraphs.
In addition, spatial local autocorrelation was performed in order to evaluate local clustering through the Getis–Ord local statistic [
49] that is defined as follows:
where:
n is the number of geographic entities, that is, the number of cells;
is the attribute for spatial feature i, that is, the count of stroke per cell;
is the mean value;
is the spatial weight between features i and j;
Calculation was performed in ArcGIS (ESRI. Redlans, CA, USA) using inverse distance for the weight matrix with a fixed threshold value of 30 km and with a Euclidian metric; the combination of the obtained z-score and p-value allowed to identify a confidence level of 90%, 95%, and 99%, as indicated in
Table 1. This approach allows to identify local clusters of lightning strokes; preliminary statistical first evaluations are shown in the present work.
In order to assess a possible temporal trend, the nonparametric Mann–Kendall test [
50,
51] was performed at a spatial scale of a 5 × 5 km grid. Every monthly-series cell was tested and the results mapped in order to identify areas with statistically significant increasing or decreasing strokes within the studied period, considering three confidence levels: 90%, 95%, and 99%. The calculation was performed for every monthly series through the 19 years of measurements, and results are shown in the following paragraph.
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Distribution
The statistics in
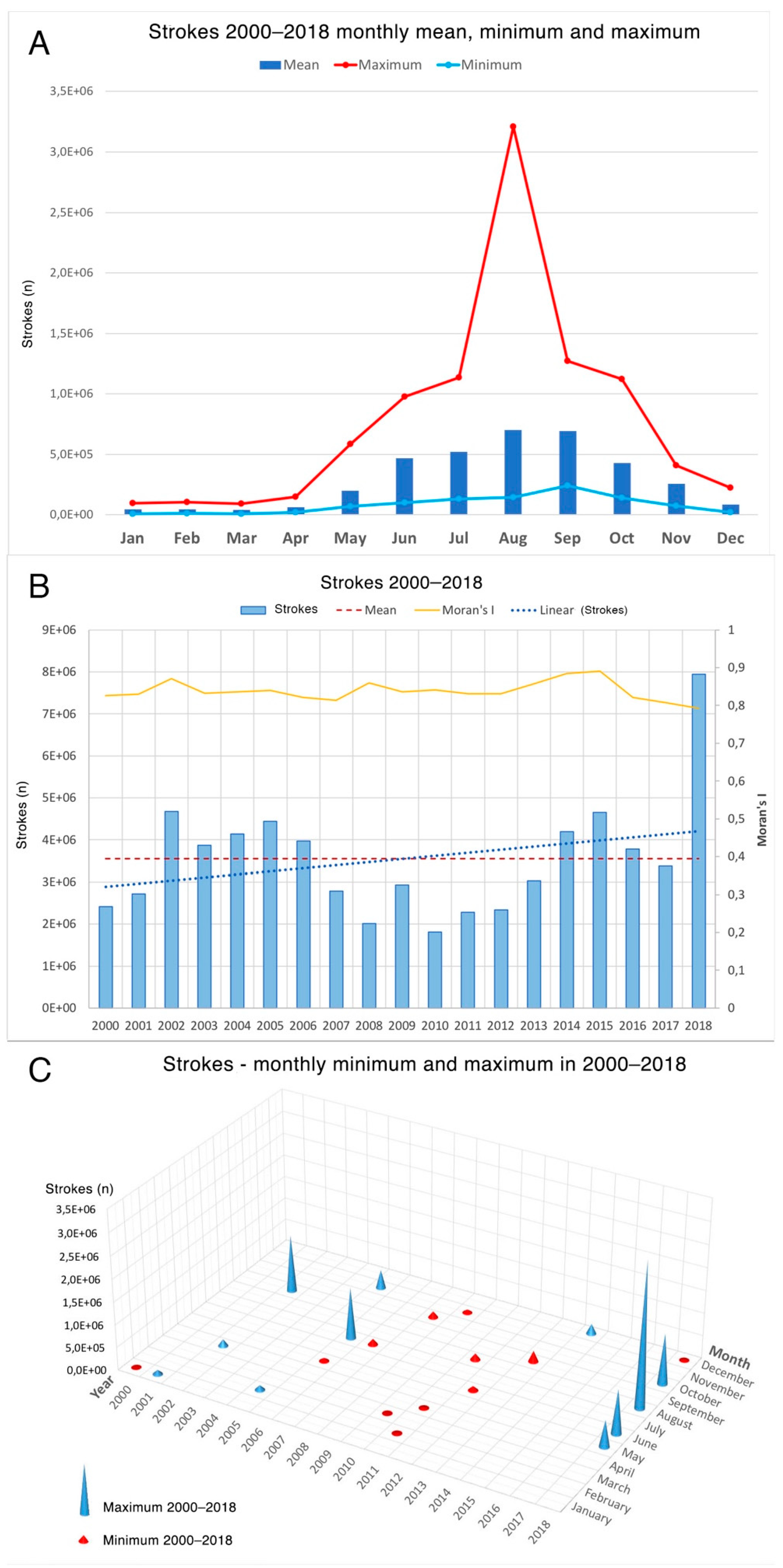
Figure 2A show the mean, maximum, and minimum total number of cloud–ground strokes per month over the whole geographic area of interest, calculated over the 19-year period: mean higher counts occurred in August and September, followed by June, July, and October according to the seasonal climate cycle. May and November may be considered as transitional periods from/towards the low activity that develops between December and April. Peak count in maximum values was reached in August. Considering the mean values, differences between the highest (August) and lowest (January) activity period were about 16 times. The maximum value in the series, registered in August, is more than three times the mean value of the same month, and correspond to August 2018.
Figure 2B shows the total number of cloud–ground strokes counted per each year over the whole area of interest for the entire period under study: values are quite variable from one year to the other and look dominated by the high count that occurred during 2018, which was more than twice higher than the mean value of the entire period. In the same figure, the results of global Moran’s
I statistics are shown: values are always high (
I > 0.8), denoting strong spatial data clustering along the whole series. The year 2018, with the highest number of strokes, shows a relatively low value of I, indicating more diffuse activity in the area. In
Figure 2B, the linear trend for number of strokes per year is also shown: the high variability, strongly influenced by the 2018 value, did not show an increasing trend that would need to eventually be assessed in further measurement years. A statistic of monthly extremes in stroke counts per year is shown in
Figure 2C: 2018 appears to be singular again, including maximum values for May, June, August, and October, that is, most of the higher-activity period. Maximum values for the remaining months were registered in the 2001–2007 period, while the minimum values are concentrated in the central part of the series between 2007 and 2013.
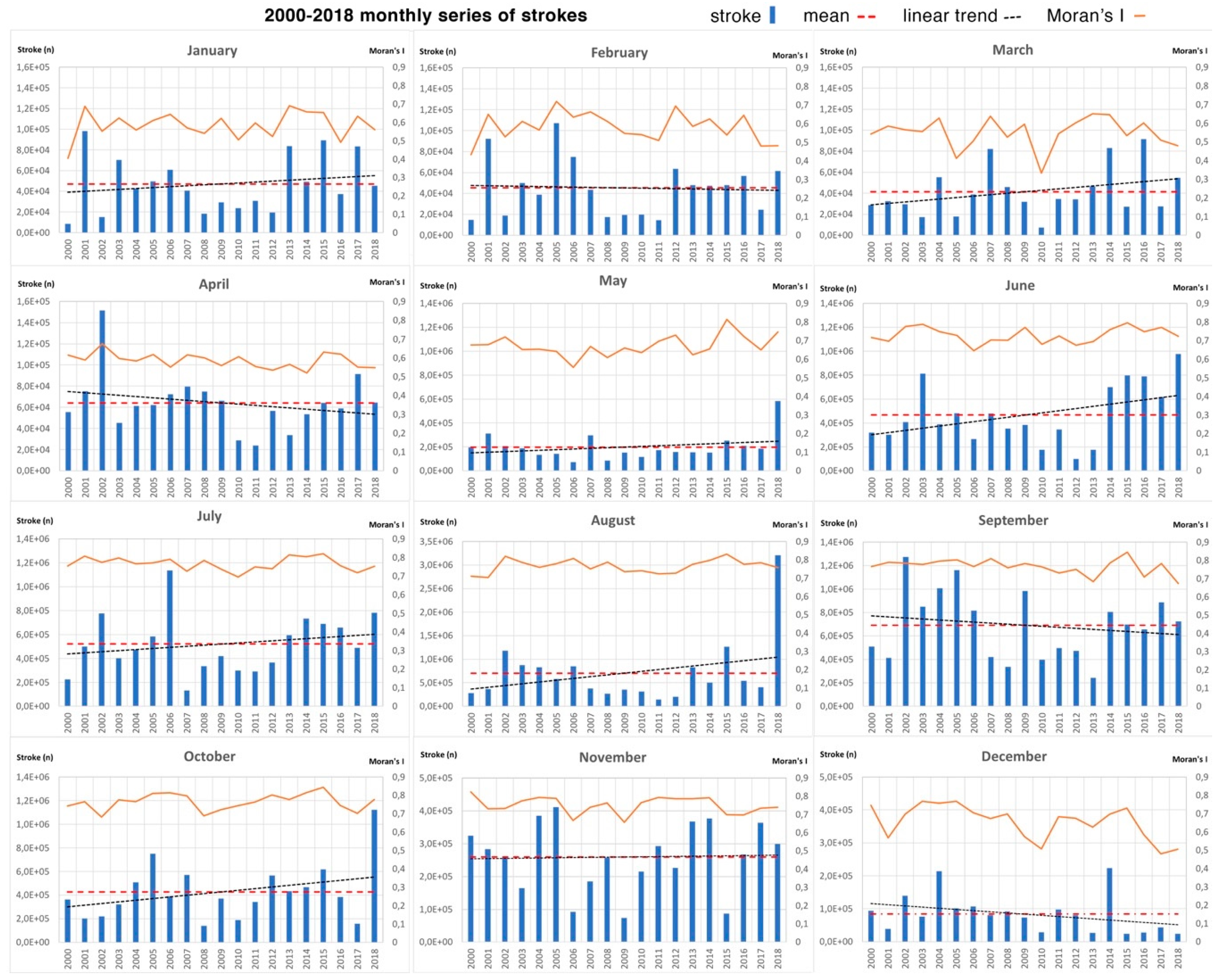
Figure 3 shows the monthly series, the total number of cloud–ground strokes per each month of each year, together with the respective global Moran’s
I values; the mean value and the linear trend are shown as well. The large variability of lightning-stroke activity is evident for every monthly series, with a single month value frequently twice or three times higher than the monthly mean. This tendency is particularly evident in August when, in 2018, the total stroke count was three times higher than the mean value, while in 2011 and 2012 the respective counts were about one-third of the mean. This extreme variability is always in agreement with the high value of Moran’s
I, which means that clustering is present anyway; even in August 2018, diffuse high activity presented a high clustering level. An exceptionally high number of lightning in 2018 months occurred even in May and October, denoting a general tendency for the entire year.
More generally, and comparing the monthly series, high variability in monthly totals was registered both during the high-activity seasonal period and in low and transitional ones. Global Moran’s I always denotes clustering in the data, but values are lower and more variable for low stroke activity periods, denoting a general higher clustering tendency from June to October, with the exception of August 2018.
A linear trend is drawn on every monthly diagram but, again, due to the great variability of values in every series, results do not show any significant long-term tendency.
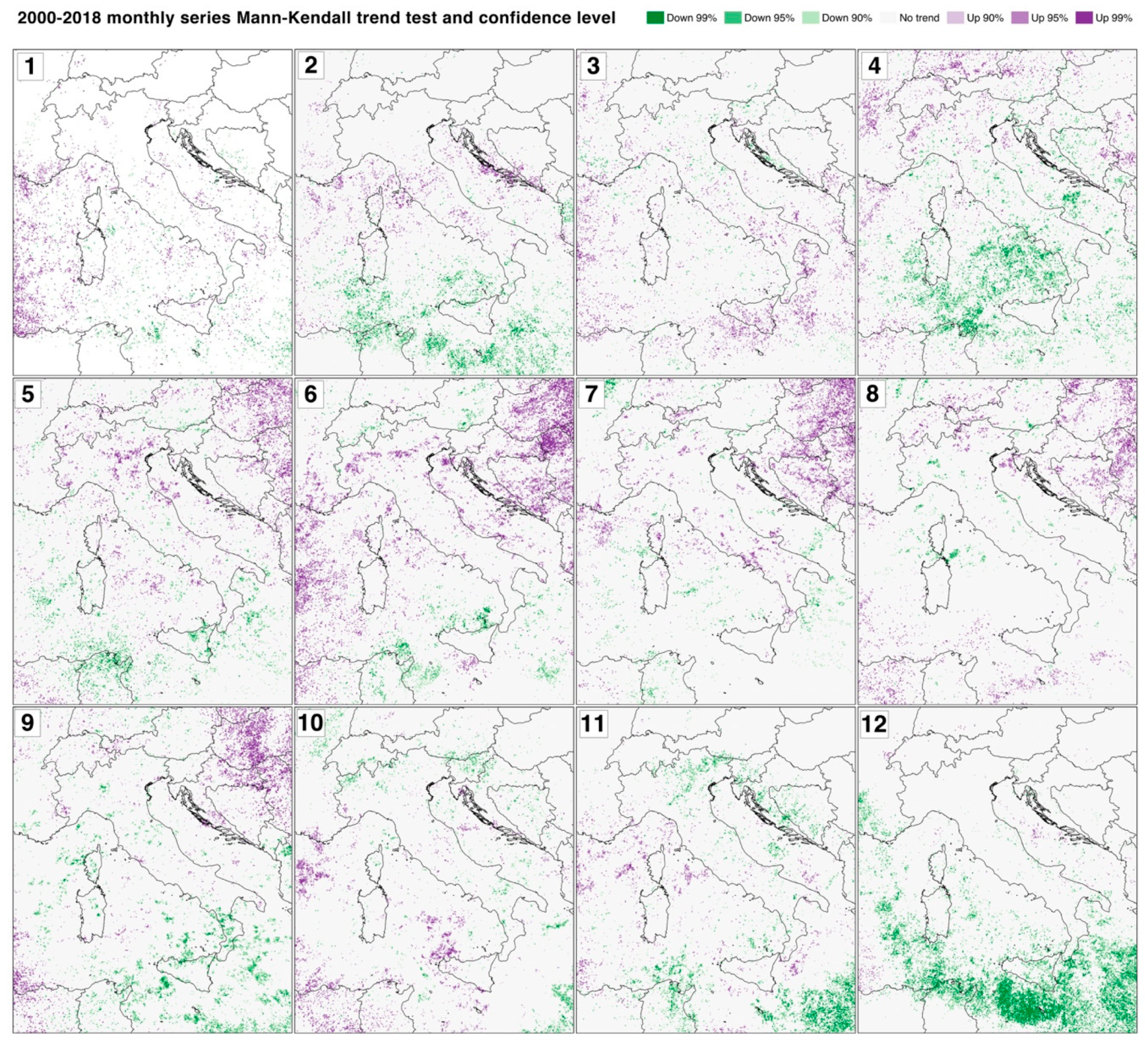
The results of the Mann–Kendall trend test are shown in
Figure 4 for every monthly series. Increasing trends in the 19-year measurements are identified as follows:
January: along the French coastline and the North African coastline, in the sea west to Sardinia and Corsica, in the sea between Corsica and Ligurian and in the central and northern Tyrrhenian Sea;
February: in the sea surrounding Corsica and along the Balkan coastline;
March: in southern Italy, in Sicily, and sporadically along the Apennines and the Tyrrhenian Sea;
April: along the French coastline, the central–western Alps, in the strip North of the Alps, and in the inner south Balkans;
May: in the northern and central inner Balkans, in North–Central and East Italy, in the western Alps, and sparsely in the central and northern Tyrrhenian Sea;
June: in the northern and central inner Balkans, along the western, central, and eastern Alps, in the central and northern Adriatic Sea, in the sea surrounding Corsica, in Provence, and in the sea west of Corsica and Sardinia;
July: in the northern and central inner Balkans, in the Tyrrhenian and Adriatic south of Italy, in inner Corsica, and along the French coastline and facing the sea;
August: in the northern and central inner Balkans, in the northern Adriatic Sea, and in the eastern and northern Alps;
September: in the northern and central inner Balkans, along the central Balkan coastline, northern to western Liguria region, and in the western extreme of North Africa in the study area;
October: in the central Tyrrhenian Sea and northern to western Sicily, in Africa comprising the study area, along the French coastline, and facing the sea;
November: sporadic areas in the sea surrounding Corsica and in the sea south of Italy;
December: a small and limited area only emerged in the central Adriatic Sea.
Decreasing trends mainly in February, April, May, September, November, and December in the southern Tyrrhenian Sea, in the northern African coast, and in the sea south to Sicily. Sporadic reduction areas were even present in northern Italy and the surrounding areas in October and November.
3.2. Spatial Distribution
Analysis of a large amount of data allowed to point out spatial features of cloud–ground strokes along the 19 years of measurements. Preliminary visual analysis was performed, while a more statistical–mathematical approach will be developed in future studies.
Figure 1 shows the mean stroke density per square km over each year: there are some differences in stroke patterns from year to year depending on the meteorological behavior in that year. Nonetheless, some areas were consistently more exposed to strokes, as can also be inferred from
Figure 1: higher values were localized in the northeastern part of Italy together with the interior of the Capodistrian peninsula along the northern Tyrrhenian coastline, that is, the central and eastern Liguria region of Italy, and along the western–central Alps. Other areas of high stroke density were located in the southern slopes of the Maritime Alps, in Provence, in Corsica, and in the central Tyrrhenian–Italian border (western side of the Apennines chain).
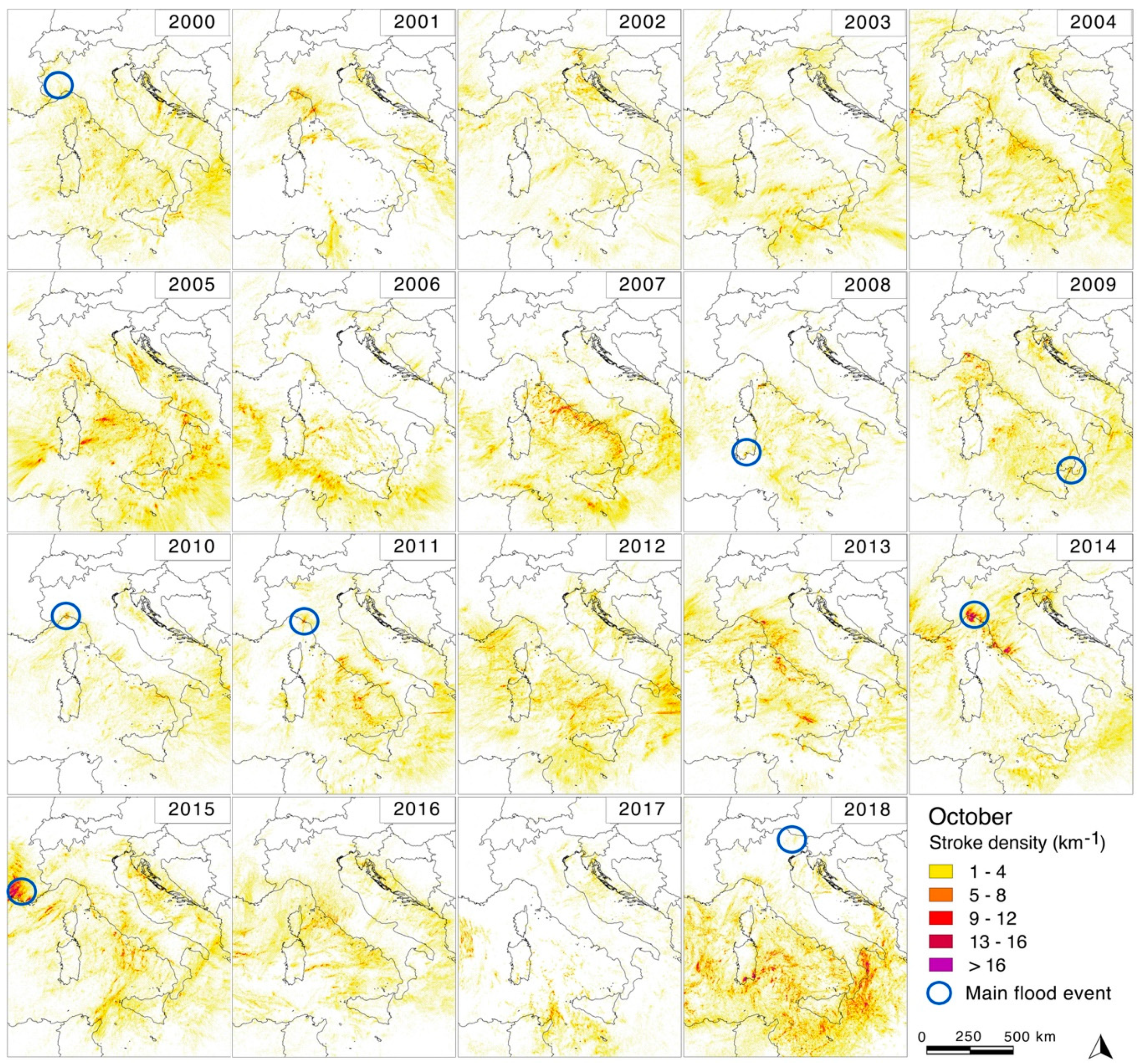
In
Figure 5,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7 the series for August, October, and November are shown, displaying the spatial distribution of strokes in various months. Great variability in activity and clustering appears evident even in the monthly series. In the same figures, the main flood events [
22] that happened in the corresponding months are highlighted that largely correspond to high stroke density. The lack of relationship may be attributed to two reasons: the contemporary display of floods and flash floods in
Figure 5,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7, and the temporal resolution used in analysis. The first is the case for the October and November 2000 events in Northwest Italy: in those situations, floods usually happened after long and intense rainy periods, a different process compared to that of flash floods. Monthly temporal resolution of analysis performed in the present research does not allow to perfectly discriminate local very high density that may have only happened for a few hours in respect to the absence of activity in the rest of the month: preliminary statistical analysis was executed during the 19 years of monitoring activity, and further research will be dedicated to investigating the correlation of events on a daily temporal scale as high-precision data allow.
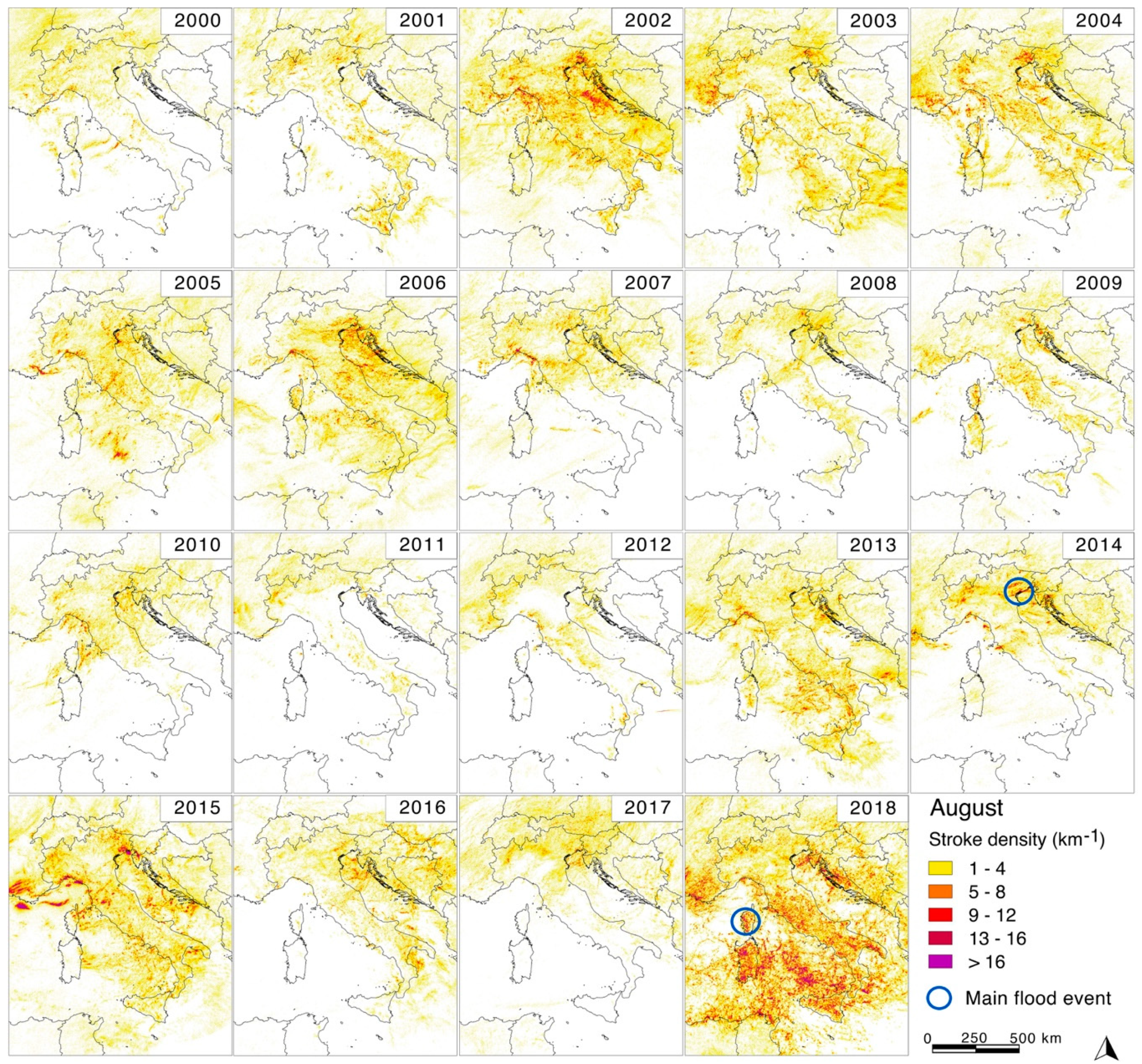
Activity was largely diffused on land and sea in August (
Figure 5) for the years 2002–2006, 2010, 2013–2016, and 2018. In August 2010 and 2014, activity was concentrated in the northern part of Italy and the corresponding sea and coasts, while in 2016 activity was mainly in the eastern part of the peninsula. High and widespread activity was first evident in 2018 and, second, in 2002 and 2015.
Figure 6 and
Figure 7 show the registered situation in October and November, respectively, which are particularly important because of the relevant transitional periods from summer to winter when high-intensity solar radiation diminishes. During October and November, floods also happen more frequently in the area under study [
22].
In October, strokes are highly concentrated on the sea and along the coastlines, and only episodically on land: this is the case for 2005, 2013, 2014, 2015, and 2018. The high density of strokes for 2018 was confirmed even during October, creating clustering in the central and southern part of the coast and sea.
In November, general stroke activity tends to decrease compared to previous warmer months, and it is mainly concentrated on the sea and along the coastline. High-density levels have been locally registered, reaching the highest values along the Tyrrhenian Sea, except for the years 2003, 2006, 2009, and 2015. Activity on the Adriatic Sea has always been registered as low except in 2000.
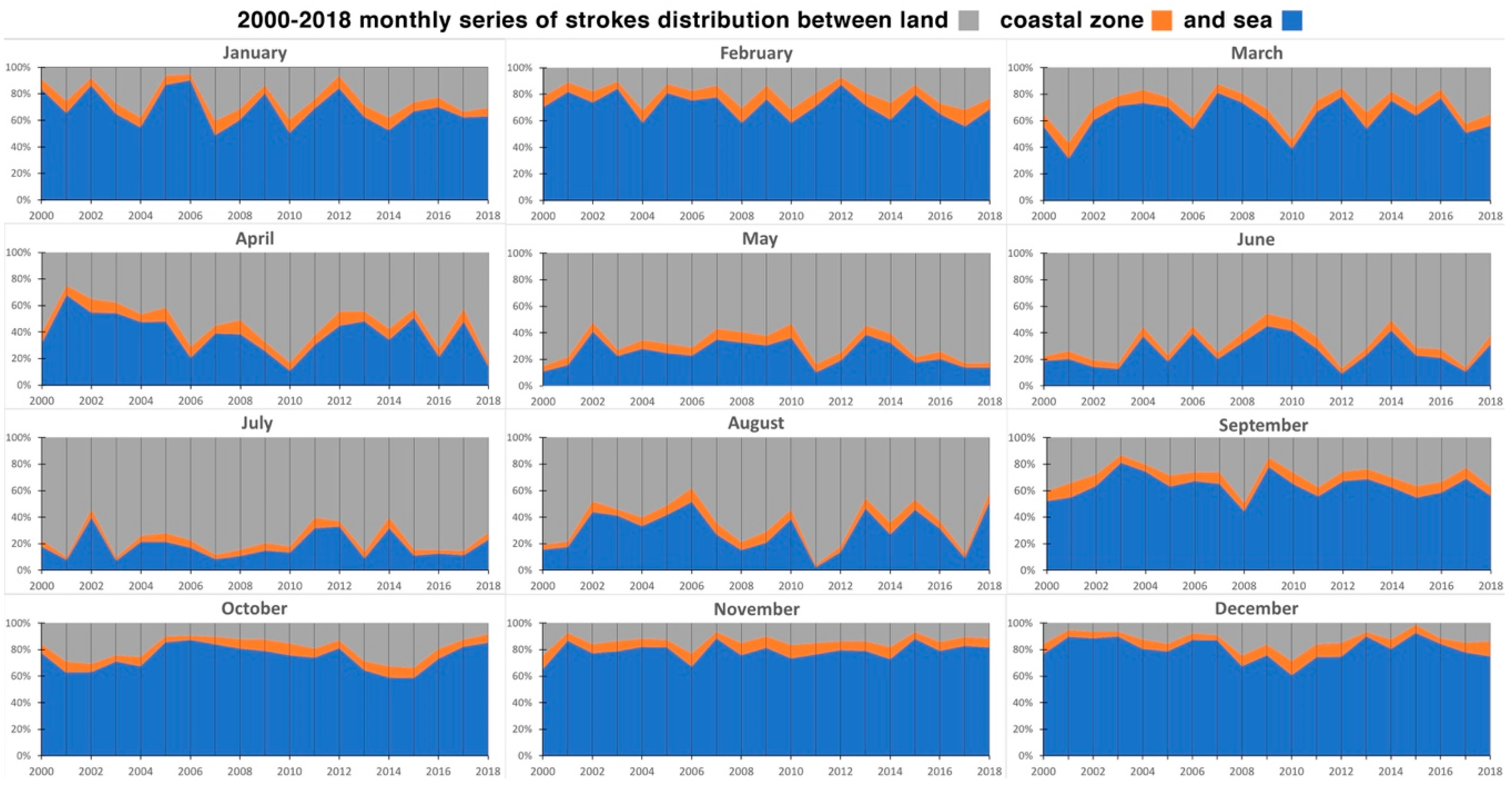
In order to quantify the spatial distribution of cloud-ground strokes, the study area was divided into three parts: sea surface, land, and a coastal buffer 10 km from the shore. In the relevant calculation, the land area does not include the coastal strip. The distribution of the total number of cloud–ground strokes per month was calculated for the three different areas, and the results are shown in
Figure 8, expressed in total percentage. During the fall and winter months, the data are mainly concentrated on the sea while, as ground-surface warming proceeds, the situation tends to invert: during spring and summer, activity prevails over land. The coastal zone is hit by about 4%–13% of strokes, with a higher percentage in fall and winter. The January, February, April, and May series show an increasing percentage of strokes on land at the expense of the sea.
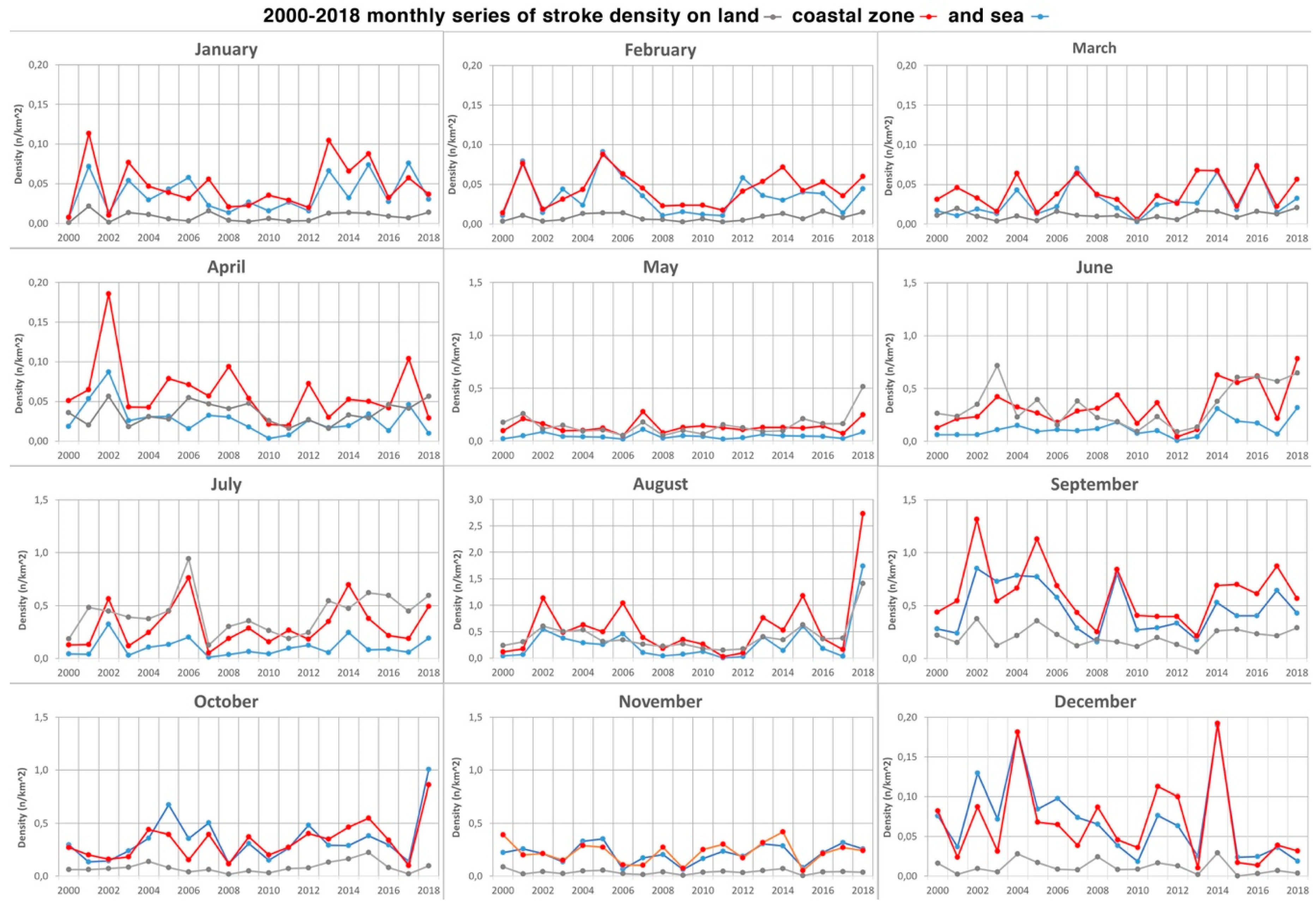
Further calculation regards the density of cloud–ground strokes with respect to the three total areas (
Figure 9) per each year. Diagrams show how stroke density is always high in the coastal zone that, being a transition area from sea to land, is exposed both to high fall/winter activity on the sea and to spring/summer activity on land. High variability in density emerged from the monthly diagrams, particularly in January, April, June, July, September, and December. The singularity of August 2018 emerged with exceptionally high-density value in the relative diagram, especially for the coastal zone. Density trends in this figure reflect the alternate seasonal lightning behavior on the land and sea surface, as recognized in previous percentage analysis.
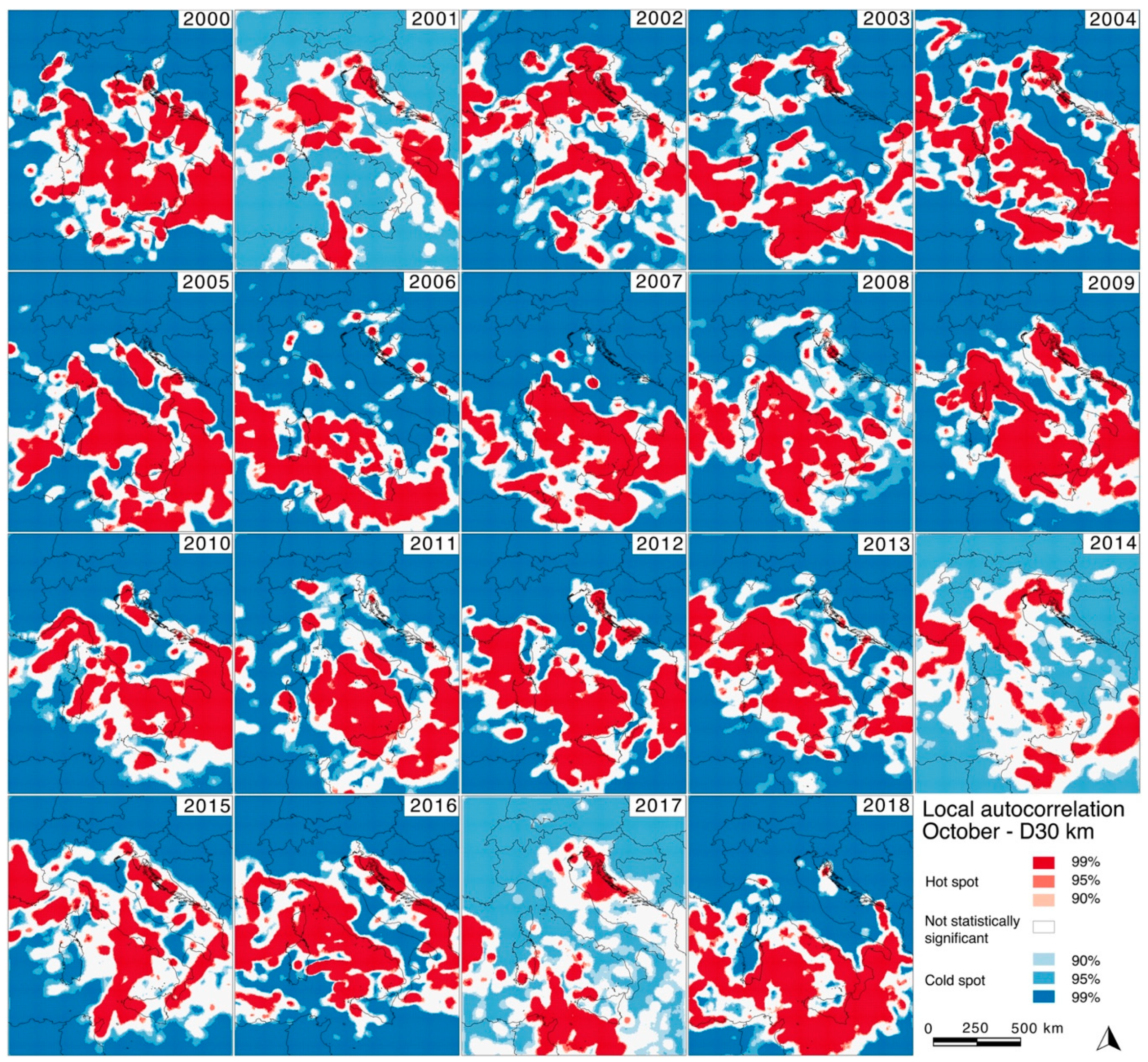
Preliminary spatial local autocorrelation analysis was performed for every month in the 19 years of measurements: in
Figure 10, the results for October are shown. Analysis allows to identify the hot and cold spots, that is, a clustering of high- and low-density values. Clustering is localized in the Tyrrhenian Sea and in the sea south of Italy, evidencing particular strong activity along all the Tyrrhenian–Italian coastlines; more discontinuous clustering affected even the Provence area and the northern Adriatic Sea. Smaller clustering areas happened in October 2001, 2014, and 2017. Further analysis will be conducted in future studies.
4. Discussion
Preliminary analysis of the spatial and temporal high-resolution stroke database for the Central Mediterranean area in the 2000–2018 period allowed to obtain the first result: high variability both in time and space is a common feature for the distribution of total strokes both per month and per year during the examined period. Such high temporal variability has been found in Africa, then in a different climatic context, by Price and Asfur [
52] who studied a fifty-year series. Year-by-year variability seems to prevent identifying any statistically significative general trend in the data, implying that there is no evidence of a steady rising or descending number of strokes over time.
Exceptionally intense activity throughout most of 2018 is another important. The year 2018 has been documented as the fourth warmest year globally from 1880 after, 2016, 2017, and 2015, respectively [
53]. On the European scale, August 2018 was the third warmest after August 2016 and 2017. Some authors agree in finding a positive correlation between increasing temperature and lightning activity on the global scale [
21,
26], even if a long-term trend in lightning activity has still not emerged [
52]. As mentioned, no increasing trend in the last 19 years of stroke detection has been clearly found in the area under study here, where the exceptional numbers found in 2018, the last year of the series, could be occasional. An explanation of the lack of a linear general trend, apart from the large variability of the phenomenon itself, may be found in a nonlinear relationship between warming and cloud electrification and, then, lightning activity [
26]. Future measurements may allow to point out a clear tendency if global warming proceeds at a similar rate.
Spatial analysis, combined with temporal analysis, allowed to outline a more complicated condition, with some emerging local trends. Preliminary analysis allows to obtain some conclusions, but further research is needed to confirm and better delineate tendencies.
An interesting result has emerged applying global Moran’s I analysis to stroke data as a new possible approach to lightning studies. Moran’s I clearly indicates data clustering, as expected for stroke data. Strong clustering was demonstrated as a common feature for all the considered data series, both for more populated and for sparser ones. When stroke activity has been at the maximum, in August 2018 cloud–ground strokes were spread almost all over the studied area, but higher densities were strongly clustered anyway.
Dedicated analysis was performed in order to find eventual different spatial distribution of strokes between land, sea, and coastal zones; at the global scale, the proportion between strokes on land and on the oceans is 10:1 [
21]. In the study area, examining the monthly data, this ratio looks to be affected by the seasonal cycle, coherently with previous studies [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. In fall and winter, strokes are prevalent on the sea, while in spring and summer, that is, the higher activity period, on land. This results in a proportion of about 1:1 between land and sea occurrence considering the total amount of strokes in the whole study period. This behavior could be related to the climatic peculiarity of the Mediterranean Sea and the regional area in respect to the tropical zone, where two-thirds of global lightning activity is concentrated [
14].
The percentage of strokes on land appears to increase in January, February, April, and May with respect to that on the sea. Sunlight warms the sea and land surface differently due to the different thermal properties of the two: higher thermal inertia of the sea mass causes it to warm slower as the season moves from winter to spring and summer, and causes it to cool slower from the hot to the cold season. As a consequence, lightning activity being related to updraft velocities [
54], lightning and stroke counts are considerably higher in the second part of spring and in summer than in winter and late fall; similarly, the progressively higher warming in spring in recent years suggests a possible relationship with an increasing percentage of lightning on land in spring. Quicker warming on land may induce higher lightning activity than on the sea. This process may be considerably enhanced by the orographic effect [
34] that may partially explain the high density measured in the central Ligurian coastline (
Figure 1).
Then, even if it is not possible to identify a statistically significant general trend in the data for the studied period and area, many symptoms of possible change emerged from analysis: the Mann–Kendall trend test on the monthly series at the cell scale evidences areas with statistically significant increments of activity along all months except December, which showed very limited activity. At the same time, areas with decreasing activity were identified.
Increasing local activity may be related to intense precipitative events and flash floods that hit many coastal areas of Italy and of Provence in France in October and November, which are the transitional months from the warm to the cold season: the strong contrast between cold-air masses coming from the north with a still-warm sea induces high convective activity and subsequent lightnings and large thunderstorms [
55]. These local trends are coherent with data regarding the increase in sea-surface temperatures revealed by Pastor et al. [
56], and as underlined by Kotroni and Lagouvardos [
9].
Many flash-flood events associated with high lightning activity happened under these conditions: in Liguria in 2010, 2011, and 2014; in the northern Tyrrhenian coastline in 2012 and 2014; in Corsica in 2014 and 2016; in Sicily in 2011 and 2018; and in coastal Provence in 2015. The possible relationship with the increasing trend of stroke density in the same areas requires further and more detailed analysis, but spatial local autocorrelation in October allows to clearly identify clustering in the Tyrrhenian Sea and along the Italian coastlines, from north to south, and the Provence coastline: clustering gives evidence of concentrated activity in the same areas hit by intense rainfall events and associated flash floods. If the local increasing trend identified through the Mann–Kendall test is confirmed in the future, then a possible increase of intense precipitation could happen.
5. Conclusions
Analysis allowed to evidence the behavior of cloud–ground strokes during 19 years of measurements over the central Mediterranean, stressing particular features both in space and time: a record of more years will eventually allow to confirm the emerging indications that could be related to surface warming.
The performed analysis emphasizes the importance of high-resolution stroke detection and the collection of a long-term series database. Despite the lack of agreement in considering lightning activity as increasing with rising surface temperatures, the results contribute, at a local scale, to the study of the relationship with climate change. The Mediterranean is a spatially constrained sea with a composite relationship between land and sea areas due to the complex physiography of the coastlines. Thus, it may not be considered as a representative region on a global scale but, for the same reasons, it is considered as one of the more susceptible areas of change [
57]. Although two-thirds of global lightning originates in tropical regions [
14], the results arising from long-term series analysis seem to suggest a possible relationship with increasing temperatures, despite the lack of a statistically significant general trend that emerges from preliminary analysis. Considering spatial distribution, some local increasing trends emerge in areas recently affected by intense precipitation and flash floods, while no relation seems to affect normal floods.
Global Moran’s I analysis allowed to evidence the strong clustering of stroke activity in the examined period, and the peculiar features in the yearly series between monthly stroke count and the respective I value. These results suggest that future investigations on the clustering properties of strokes through space and time are required.
In general, the use of high temporal- and spatial-resolution data will substantially contribute to the progress of this research. The next evolution may be supported by analysis of lightning intensity and clustering features to better investigate possible future trends and the relationship with floods and, particularly, flash floods with not-negligible morphological effects on the mainland and coastland. The present research is a first step toward a possible identification of spatial and temporal trends that would allow to elaborate possible future scenarios of higher activity, which may be related to extreme events like flash floods: coastal areas could be the ones that are most exposed.