Estimation of Soil Heavy Metal Content Using Hyperspectral Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
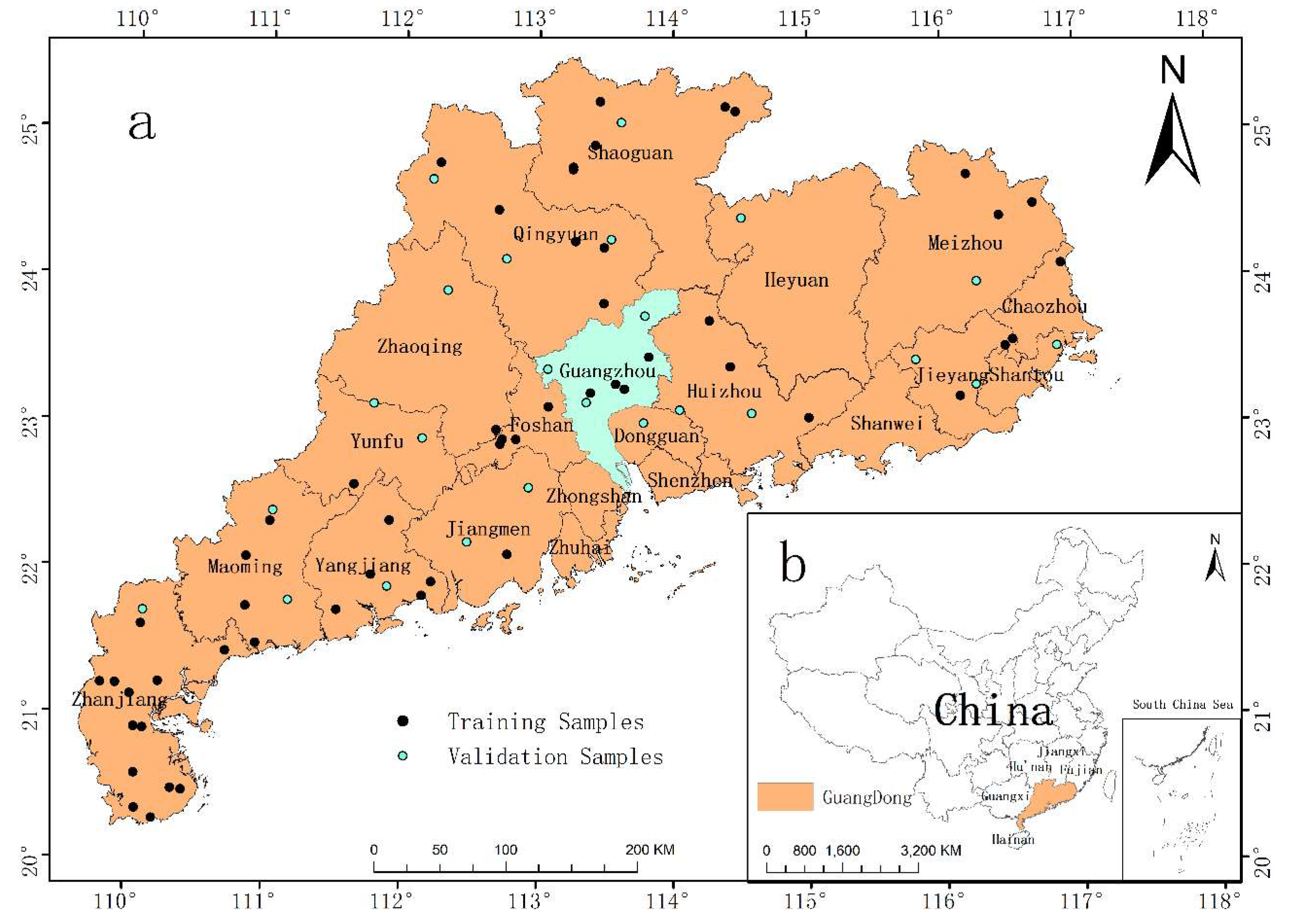
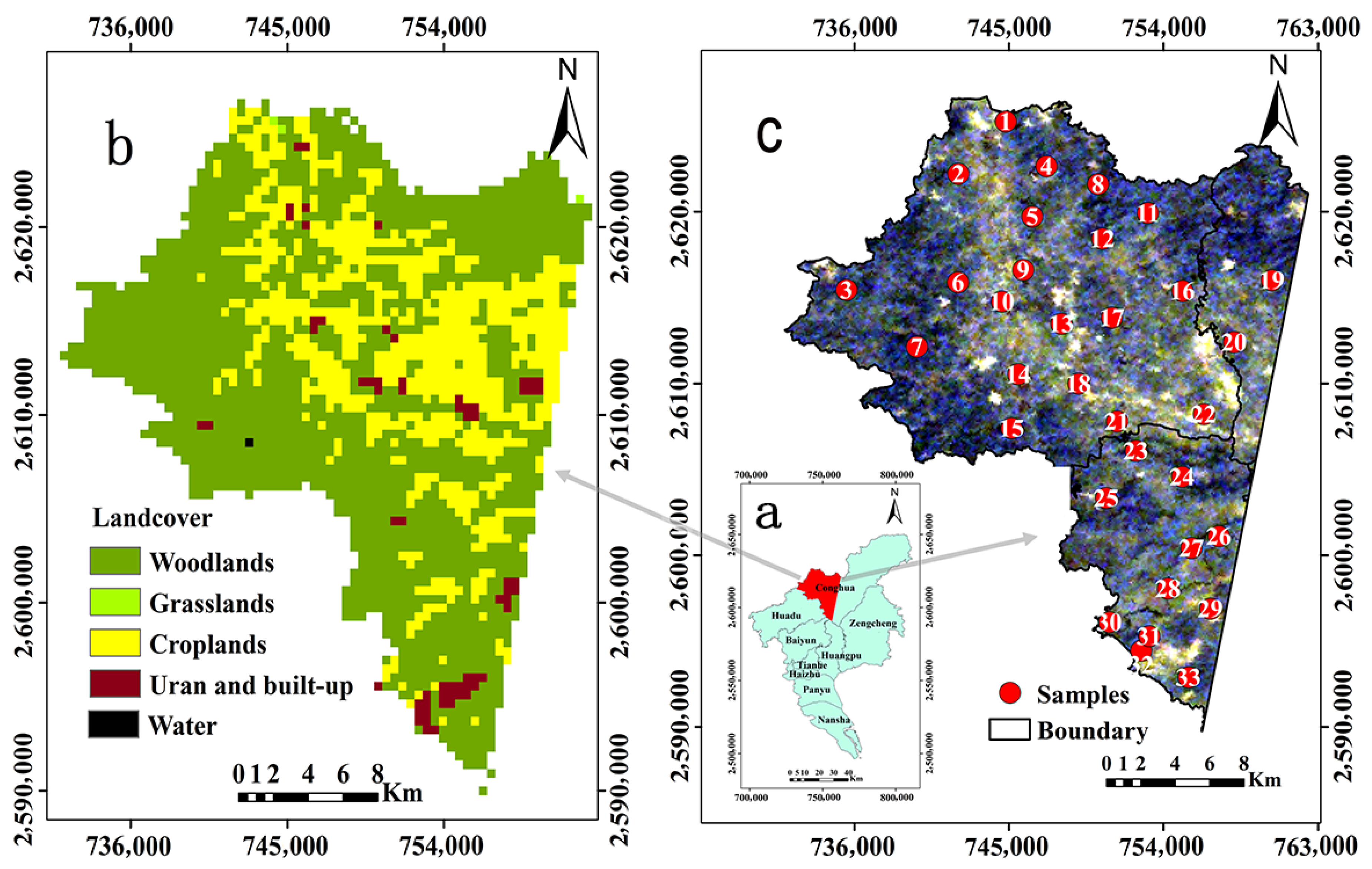
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Soil Samples
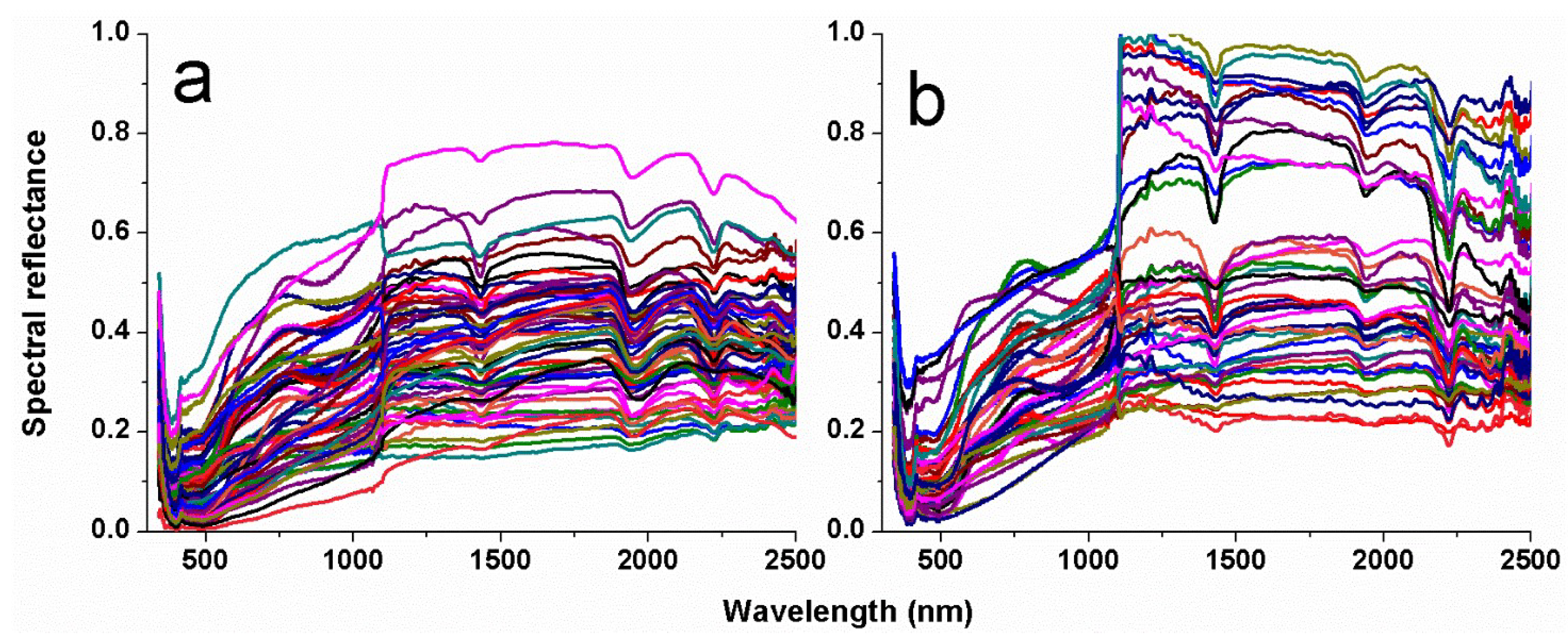
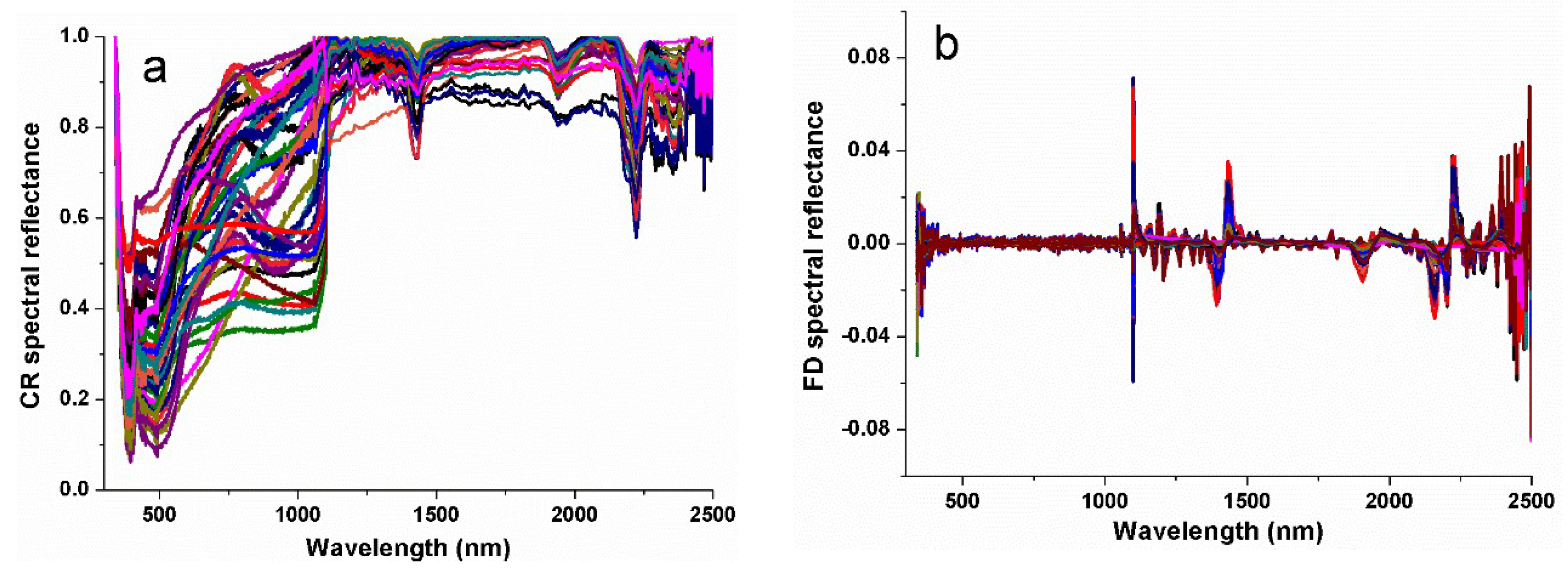
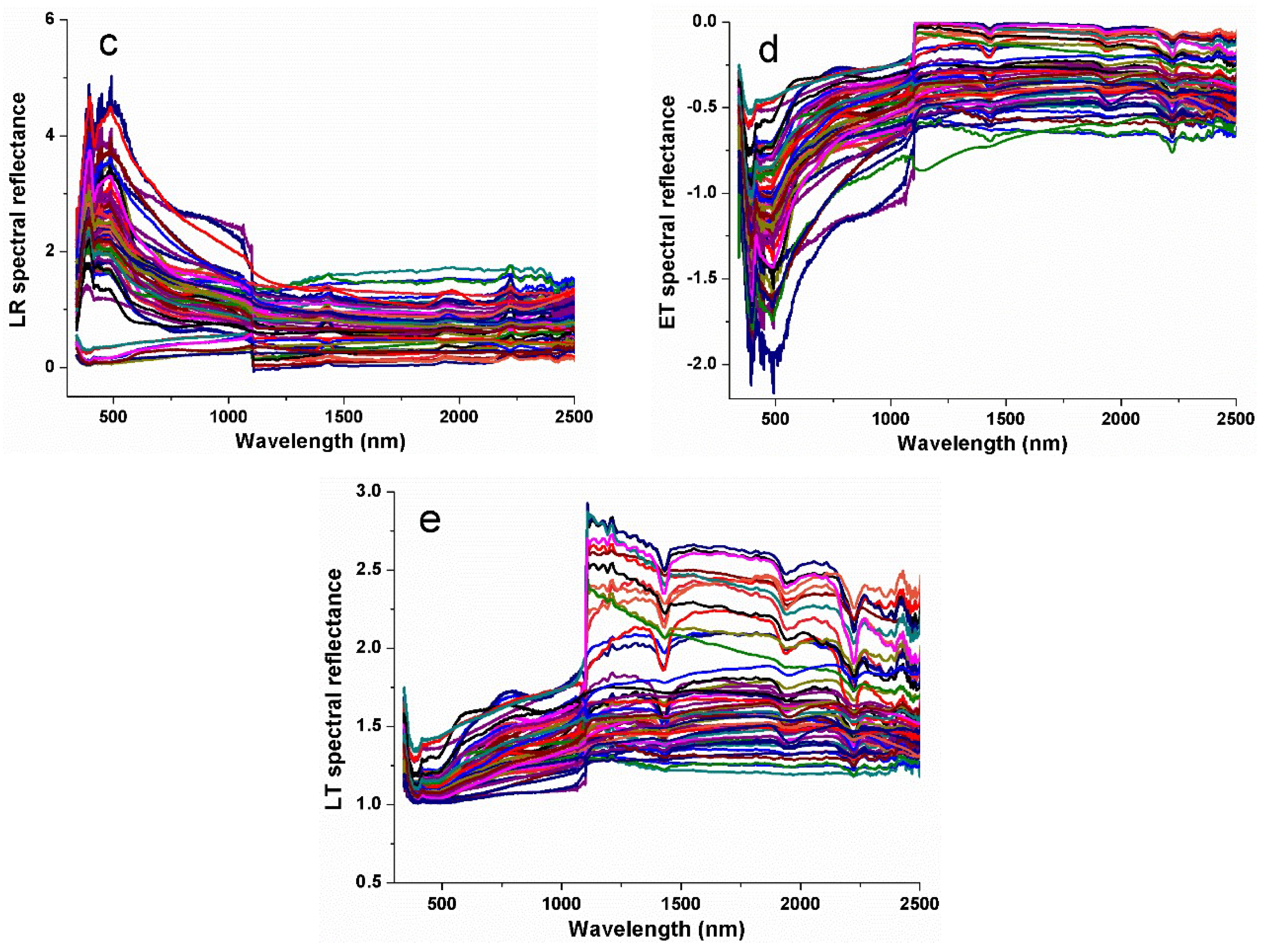
2.3. Spectral Measurements and Preprocessing
2.4. Methods
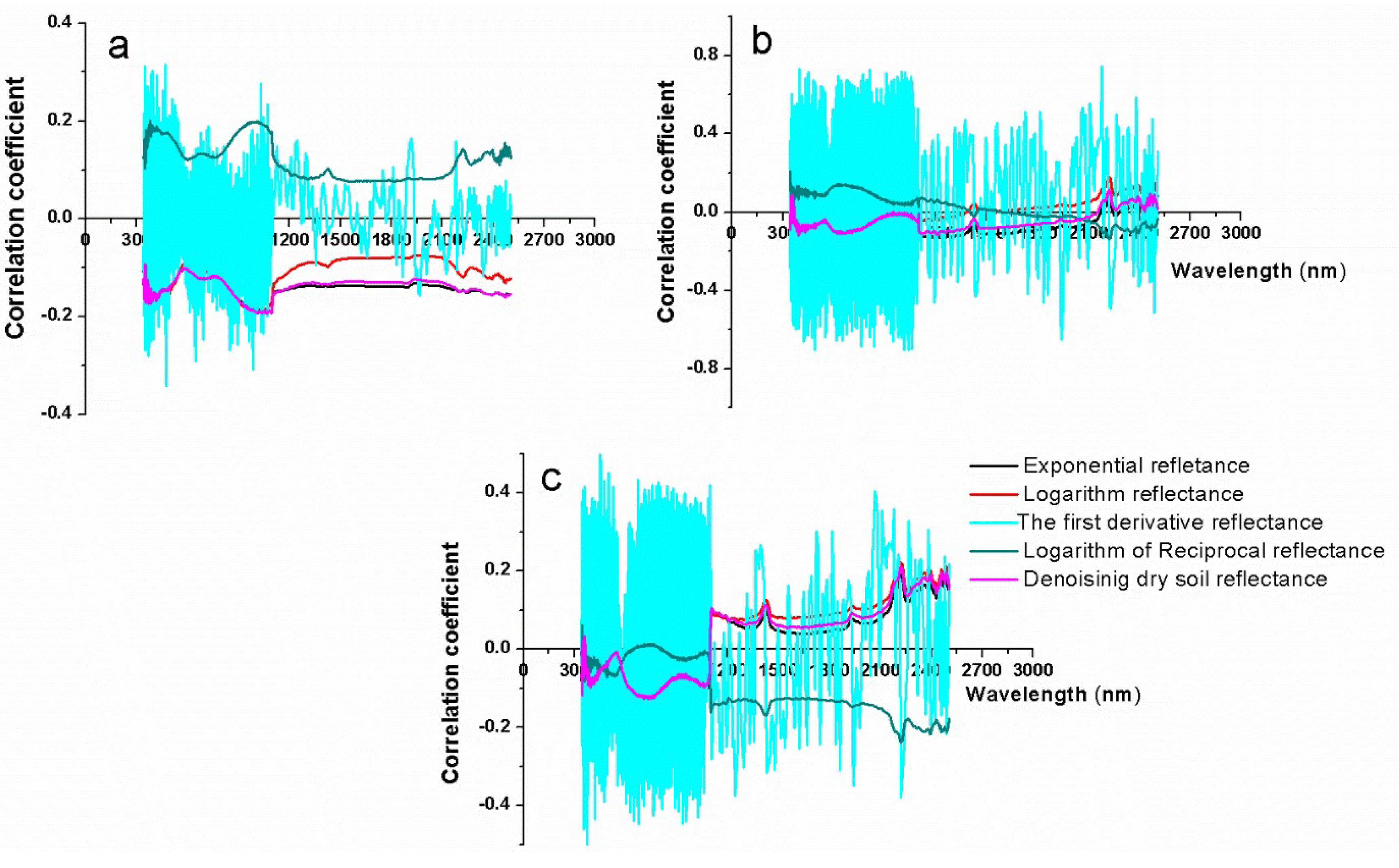
2.4.1. Selecting the Spectral Characteristic Indices of Dry Soil
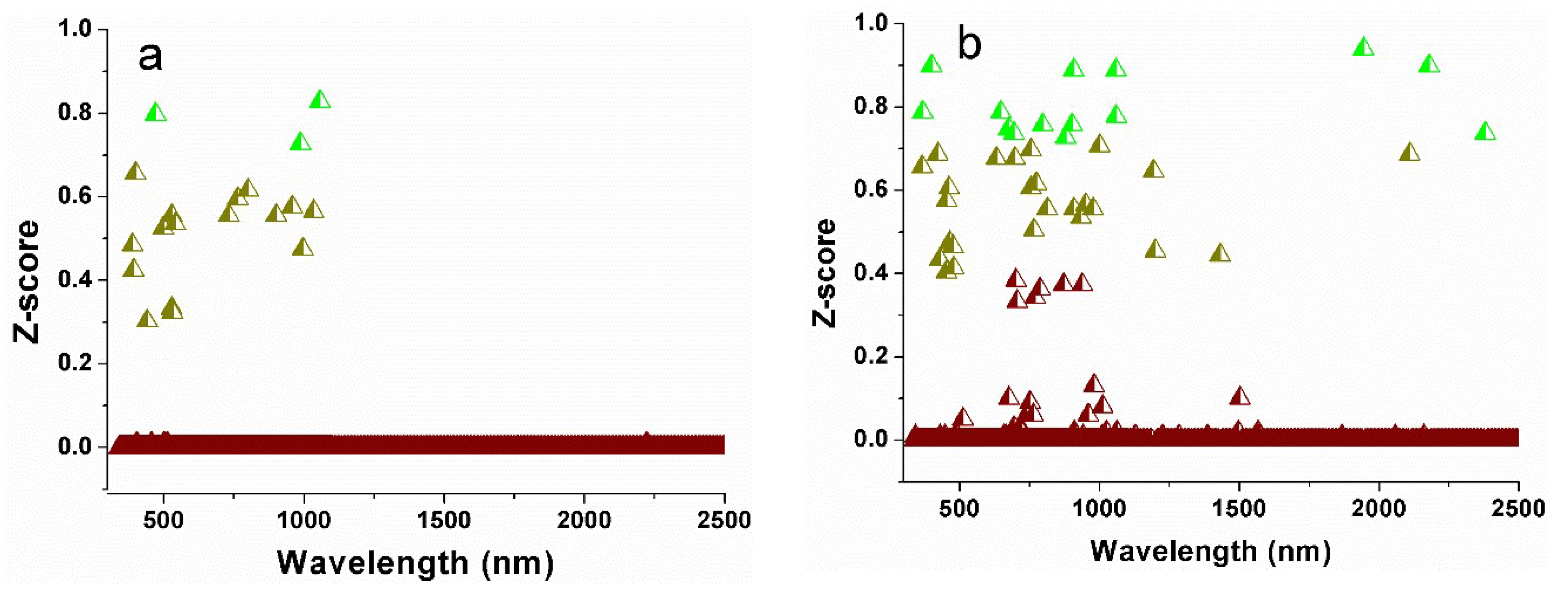
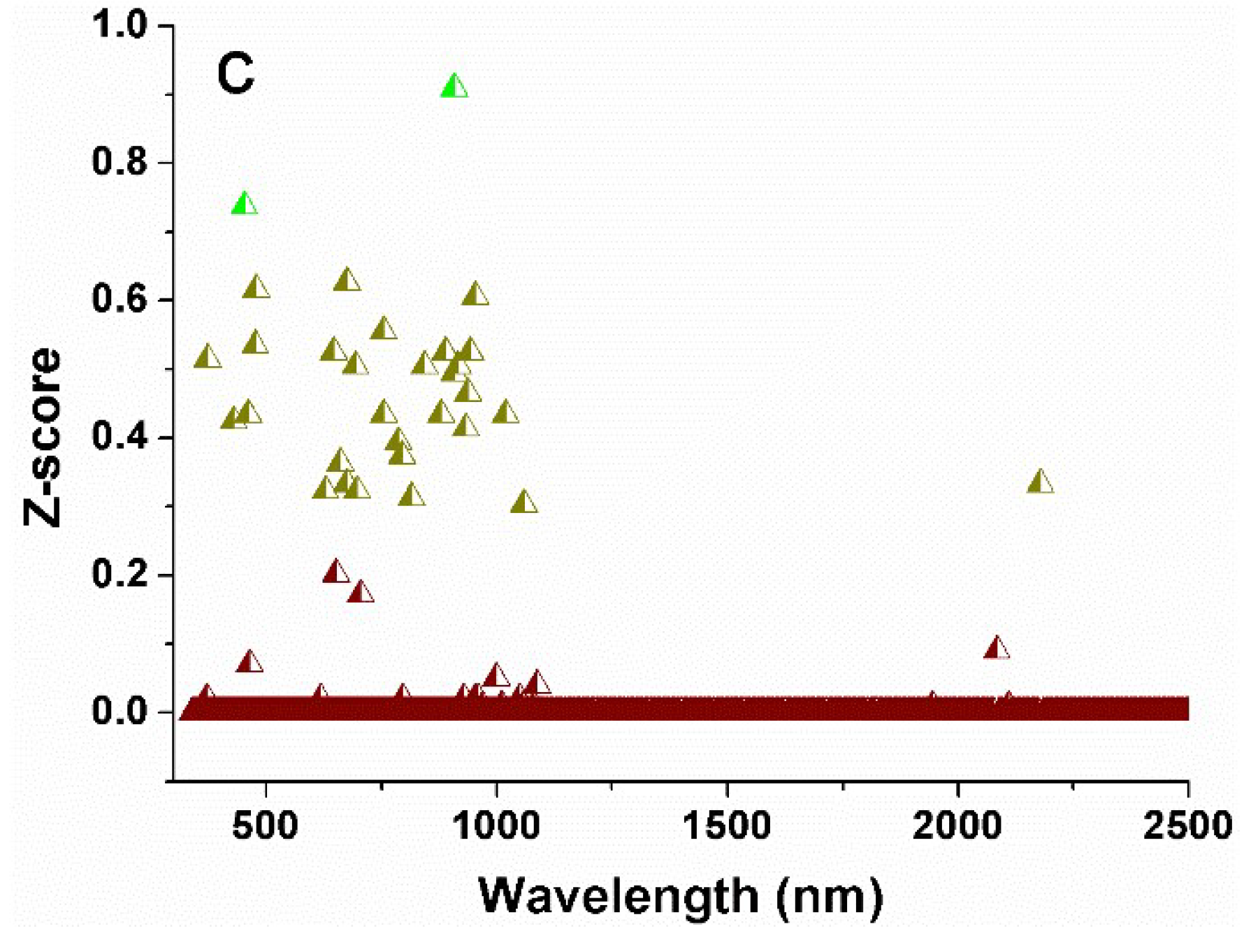
2.4.2. Selecting the Optimal Spectral Variables from the Spectral Indexes of Dry Soil
2.4.3. Model Development and Validation for Estimating Dry Soil Heavy Metal Contents
2.4.4. The Spectral Relationship Model Between Dry Soil and Moist Soil
3. Results
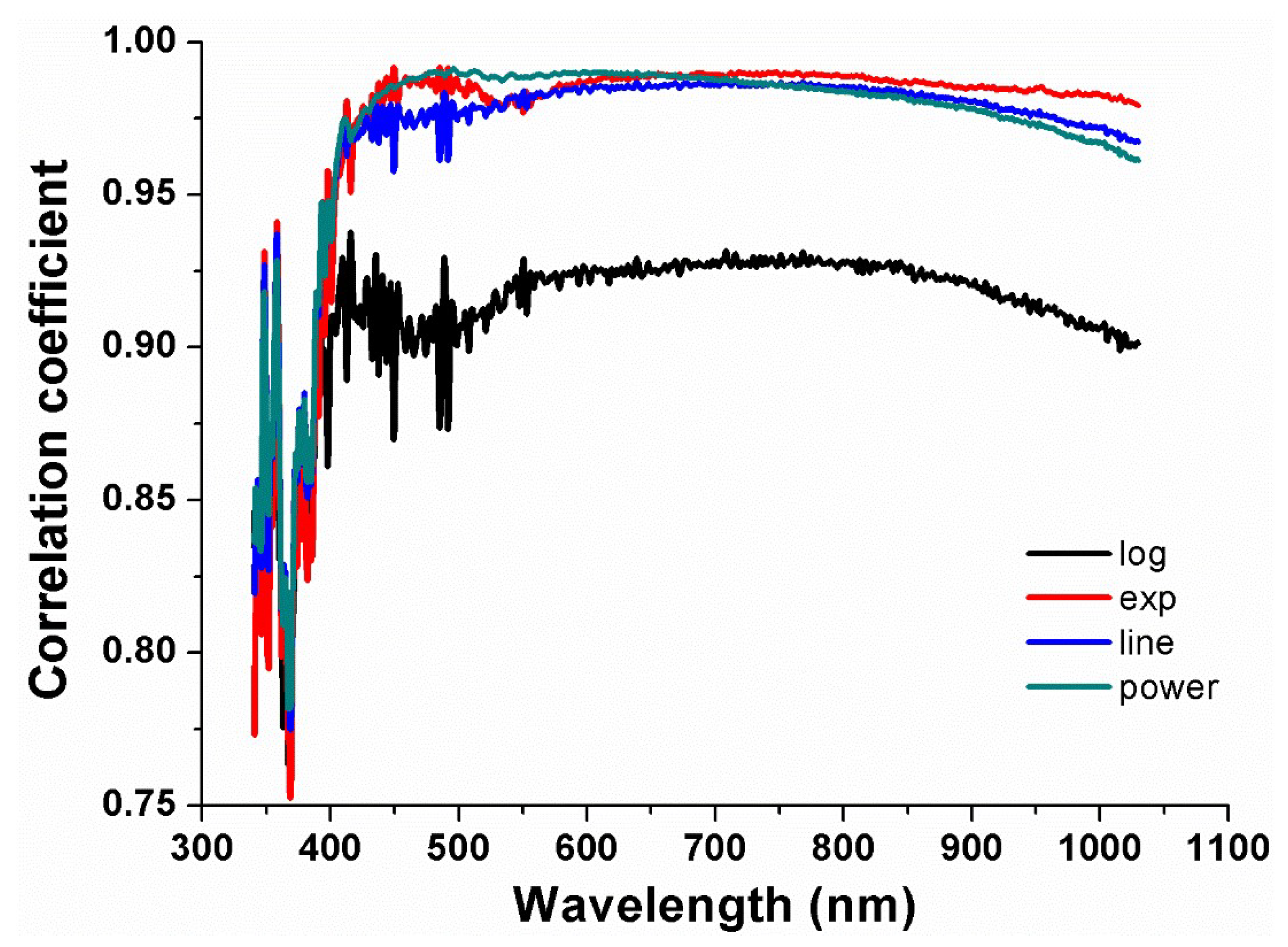
3.1. Selecting Spectral Indexes of Dry Soil
3.2. Selection of Optimal Relevant Spectral Variables
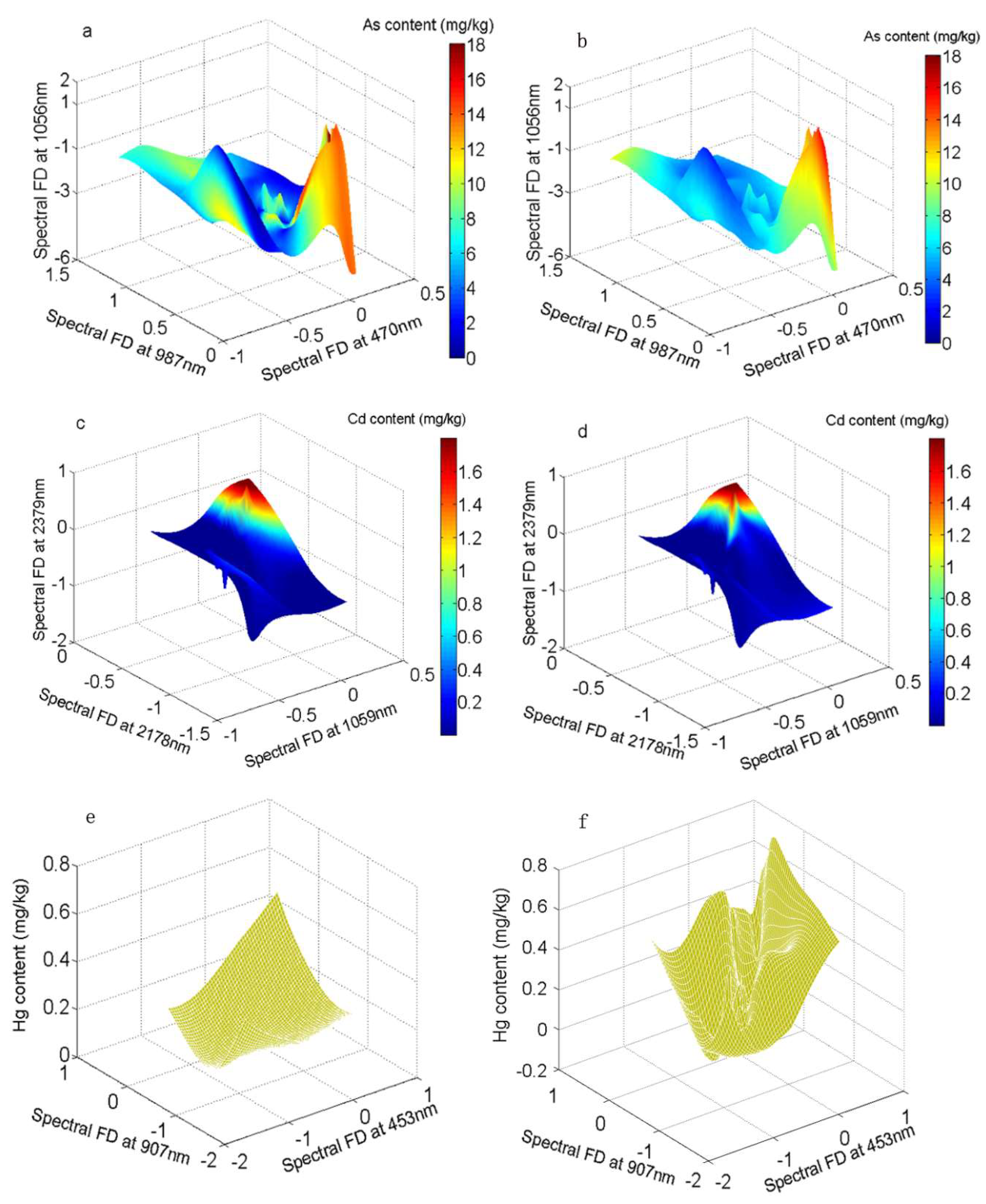
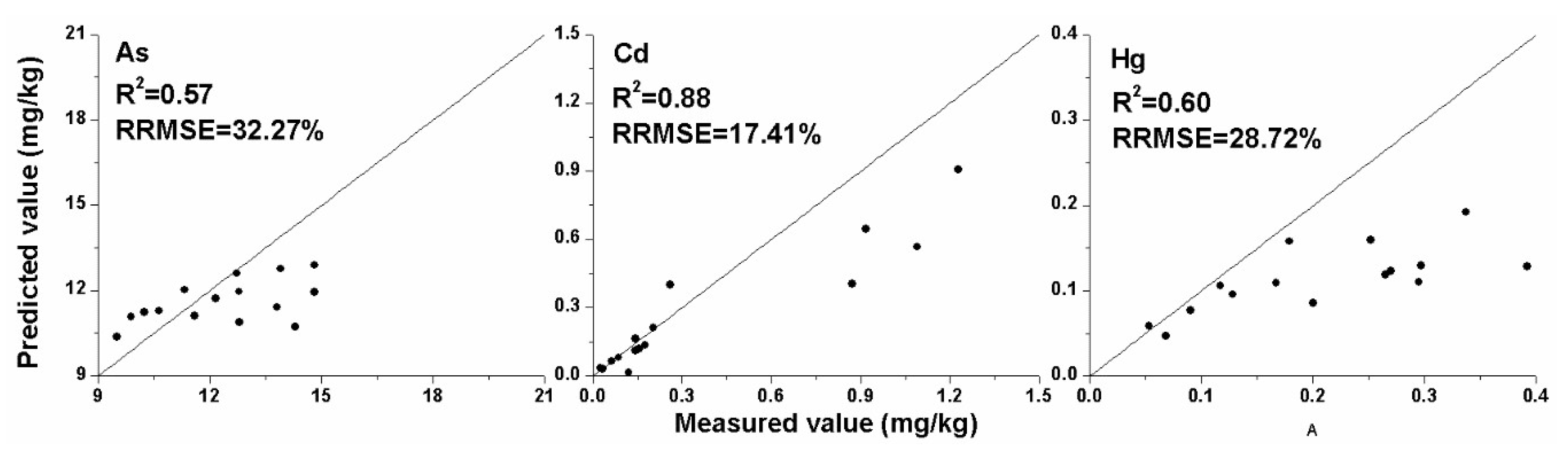
3.3. Estimation Models of Soil Heavy Metal Contents and Accuracy Assessment
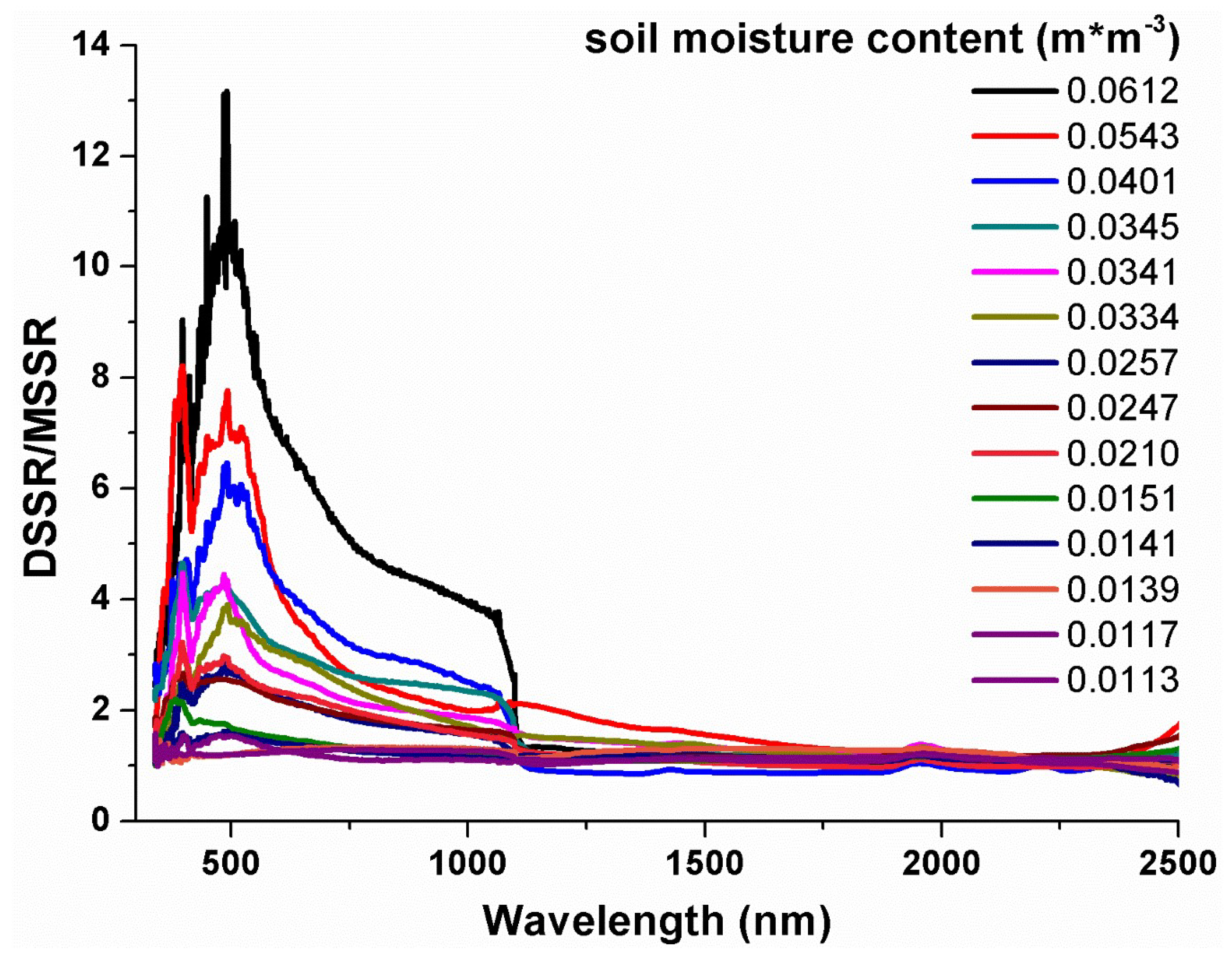
3.4. The Spectral Ratio Model of Dry Soil to Moisture Soil
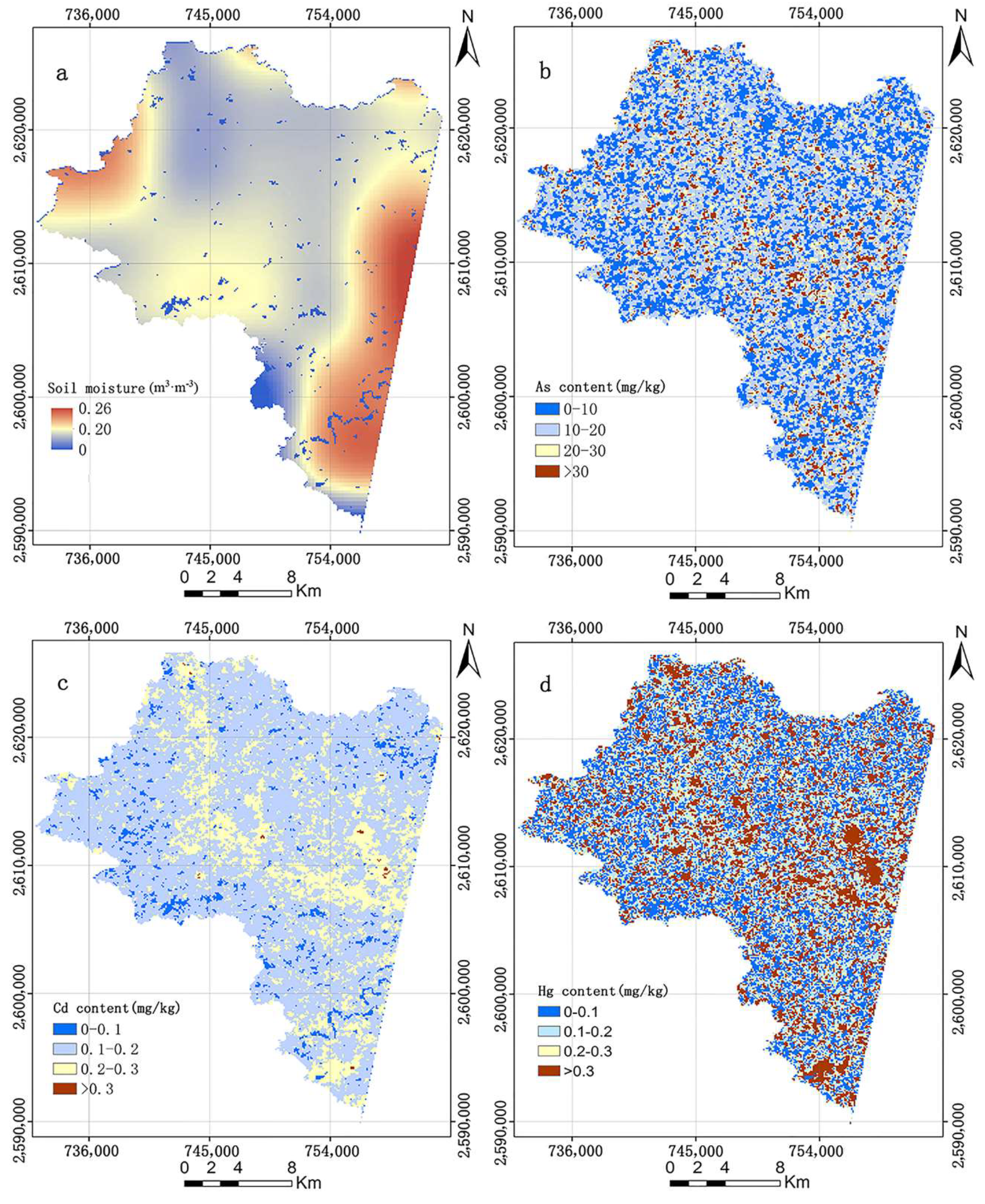
3.5. Regional-Scale Soil Heavy Metal Contents Retrieved from HJ-1A hyperspectral Data
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, M.; Wu, L. Extraction of rice heavy metal stress signal features based on long time series leaf area index data using ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Ding, C. Regional heavy metal pollution in crops by integrating physiological function variability with spatio-temporal stability using multi-temporal thermal remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 51, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; BI, R.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Chai, M.; Guo, Z. Source apportionment analysis of trace metal contamination in soils of Guangdong province, China. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 704–714. [Google Scholar]
- Von Steiger, B.; Webster, R.; Schulin, R.; Lehmann, R. Mapping heavy metals in polluted soil by disjunctive kriging. Environ. Pollut. 1994, 94, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenaers, H.; Okx, J.P.; Burrough, P.A. Employing elevation data for efficient mapping of soil pollution on floodplains. Soil Use Manag. 1990, 6, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, T.; Sommer, S. Estimate of heavy metal contamination in soils after a mining accident using reflectance spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2742–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmer, T.; Vohland, M.; Lilienthal, H.; Schnug, E. Estimation of some chemical properties of an agricultural soil by spectroradiometric measurements. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouazen, A.; Maleki, M.; De Baerdemaeker, J.; Ramon, H. On-line measurement of some selected soil properties using a VIS-NIR sensor. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 93, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawut, R.; Kasim, N.; Abliz, A.; Hu, L.; Yalkun, A.; Maihemuti, B.; Qingdong, S. Possibility of optimized indices for the assessment of heavy metal contents in soil around an open pit coal mine area. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, X. Estimating soil zinc concentrations using reflectance spectroscopy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Ding, W.; Wu, L. Monitoring stress levels on rice with heavy metal pollution from hyperspectral reflectance data using wavelet-fractal analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Su, Y.-C.; Shang, J.; Sha, J.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Ji, J.; Jin, B. Geographically Weighted Regression Effects on Soil Zinc Content Hyperspectral Modeling by Applying the Fractional-Order Differential. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Dai, W.; Xu, J.; Li, S. Spectral estimation model construction of heavy metals in mining reclamation areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, E.; van der Meer, F.; van Ruitenbeek, F.; van der Werff, H.; de Smeth, B.; Kim, K.W. Mapping of heavy metal pollution in stream sediments using combined geochemistry, field spectroscopy, and hyperspectral remote sensing: A case study of the Rodalquilar mining area, SE Spain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3222–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wen, J. Band Selection Method for Retrieving Soil Lead Content with Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data. SPIE 2010, 7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Shin, J.H. Spectral Responses of As and Pb Contamination in Tailings of a Hydrothermal Ore Deposit: A Case Study of Samgwang Mine, South Korea. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.-Y.; Zhuang, D.; Singh, A.N.; Pan, J.; Qiu, D.; Shi, R. Estimation of As and Cu Contamination in Agricultural Soils Around a Mining Area by Reflectance Spectroscopy: A Case Study. Pedosphere 2009, 19, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, Q.; Nie, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, D.; Hu, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y. Hyperspectral inversion of heavy metal content in reclaimed soil from a mining wasteland based on different spectral transformation and modeling methods. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mplecular Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 211, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X. Evaluation of MLSR and PLSR for estimating soil element contents using visible/near-infrared spectroscopy in apple orchards on the Jiaodong peninsula. Catena 2016, 137, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhao, S. Inversion of heavy metals content with hyperspectral reflectance in soil of well-facilitied capital farmland construction areas. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 230–239. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Ye, Y.; Cao, Q.; Du, P.; Dong, J. Estimation of arsenic contamination in reclaimed agricultural soils using reflectance spectroscopy and ANFIS model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2540–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, F. Prediction of heavy metals contamination in the groundwater of Arak region using artificial neural network and multiple linear regression. J. Tethys 2015, 3, 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhimathi, A.; Meenambal, T. Spatial prediction of heavy metal pollution for soils in Coimbatore, India based on ANN and kriging model. Eur. Sci. J. ESJ 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G. Visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy—An alternative for monitoring soil contamination by heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 265, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhaochang, L.; Yongfeng, N.; Lansheng, Z.; Zhansheng, W.; Qingzhong, B.; Chongjie, Y. Translocation and transformation of heavy metals in water logged aeration zone of soil. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 1990, 10, 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wen, J.; Zhao, D. SPIE Proceedings [SPIE Remote Sensing—Toulouse, France (Monday 20 September 2010)] Earth Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing/GIS Applications—Band selection method for retrieving soil lead content with hyperspectral remote sensing data. SPIE 2010, 7831, 78311K. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Patkin, K.; Banin, A.; Karnieli, A. Mapping of several soil properties using DAIS-7915 hyperspectral scanner data—A case study over clayey soils in Israel. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1043–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagacherie, P.; Baret, F.; Feret, J.B.; Netto, J.M.; Robbez-Masson, J.M. Estimation of soil clay and calcium carbonate using laboratory, field and airborne hyperspectral measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hbirkou, C.; Pätzold, S.; Mahlein, A.K.; Welp, G. Airborne hyperspectral imaging of spatial soil organic carbon heterogeneity at the field-scale. Geoderma 2012, 175–176, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C.; Lagacherie, P.; Coulouma, G. Regional predictions of eight common soil properties and their spatial structures from hyperspectral Vis–NIR data. Geoderma 2012, 189–190, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C.; Rossel, R.A.V.; McBratney, A.B. Soil organic carbon prediction by hyperspectral remote sensing and field vis-NIR spectroscopy: An Australian case study. Geoderma 2008, 146, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, Z.H.; Hu, Y.M.; Shi, Z.; Pan, Y.C.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.X. Integrating a Hybrid Back Propagation Neural Network and Particle Swarm Optimization for Estimating Soil Heavy Metal Contents Using Hyperspectral Data. Sustainability 2019, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Orueta, A.; Ustin, S.L. Remote Sensing of Soil Properties in the Santa Monica Mountains, I. Spectr. Anal. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cui, L.; Gao, W.; Shi, T.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y. Prediction of low heavy metal concentrations in agricultural soils using visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 2014, 216, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. The zonal differentiation of soil environmental background values and critical (4) contents in Guangdong. J. South China Agric. Univ. (China) 1996, 17, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, G. Improving the prediction of arsenic contents in agricultural soils by combining the reflectance spectroscopy of soils and rice plants. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimbye, Z.E.; Cho, M.A.; Nell, J.P.; Declercq, J.P.; Van, A.; Turner, D.P. Model-Based Integrated Methods for Quantitative Estimation of Soil Salinity from Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study of Selected South African Soils. Pedosphere (Beijing) 2012, 22, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yao, X.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Laboratory assessment of three quantitative methods for estimating the organic matter content of soils in China based on visible/near-infrared reflectance spectra. Geoderma 2013, 202–203, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Wang, J.; Lin, Z.; Cheng, Y. Spectral Features of Soil Organic Matter. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2006, 31, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Fei, B.; Yang, Z. The effect of spectral pretreatment on the prediction of wood cellulose crystallinity by near infrared spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2007, 27, 435–438. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Bai, Y.L.; Lu, Y.L.; Wang, H. Effect on retrieval precision for corn N content by spectrum data transformation. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2011, 26, 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Sankaran, S.; Maja, J.M.; Buchanon, S.; Ehsani, R. Huanglongbing (citrus greening) detection using visible, near infrared and thermal imaging techniques. Sensors 2013, 13, 2117–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, L. An alternative approach for machine learning seismic interpretation and its application in Daqing oilfield. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2018; pp. 2201–2205. [Google Scholar]
- Kursa, M.B.; Rudnicki, W.R. Feature selection with the Boruta package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicki, W.R.; Wrzesień, M.; Paja, W. All Relevant Feature Selection Methods and Applications. Stud. Comput. Intell. 2015, 584, 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- Suykens, J.A.; Vandewalle, J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process. Lett. 1999, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancheva, R.; Georgiev, G. Assessing Cd-induced stress from plant spectral response. SPIE 2014, 9239, 923926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Research on the method for retrieving soil moisture using thermal inertia model. Sci. China Ser. D 2006, 49, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Zha, Y. Hyperspectral sensing of heavy metals in soil and vegetation: Feasibility and challenges. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 136, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.S.; Saleh, A.M.; Belal, A.B.; Allah, A. Application of near-infrared reflectance for quantitative assessment of soil properties. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2017, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, Y.M.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Z.H.; Pan, Y.C.; Shi, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.X. Estimation Methods for Soil Mercury Content Using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Alnasrallah, M.; Wong, D.; Beaird, H.; Logue, E. Impacts of scale on geographic analysis of health data: An example of obesity prevalence. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2014, 3, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]


| Metal | Minimum (mg/kg) | Maximum (mg/kg) | Mean (mg/kg) | Standard Deviation (mg/kg) | CV (%) | Background Value [35] (mg/kg) | Health Standard (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.003 | 1.937 | 0.109 | 0.103 | 94.50 | 0.034 | 0.3 |
| Hg | 0.018 | 1.326 | 0.128 | 0.111 | 86.72 | 0.078 | 0.3 |
| As | 1.230 | 34.797 | 7.912 | 6.951 | 87.85 | 10.50 | 30 |
| Soil Heavy Metals | The First Derivative Spectral Variables |
|---|---|
| As | FD 470 nm FD 987 nm FD 1056 nm |
| Cd | FD 1059 nm FD 2178 nm FD 2379 nm |
| Hg | FD 453 nm FD 907 nm |
| Heavy Metal | As | Cd | Hg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Field Data | Estimates | Field Data | Estimates | Field Data | Estimates | |
| Mean | 7.12 | 7.11 | 1.33 | 1.35 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Stdev | 4.26 | 3.30 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.13 | 0.11 |
| RRMSE (%) | 45.92 | 11.51 | 40.29 | |||
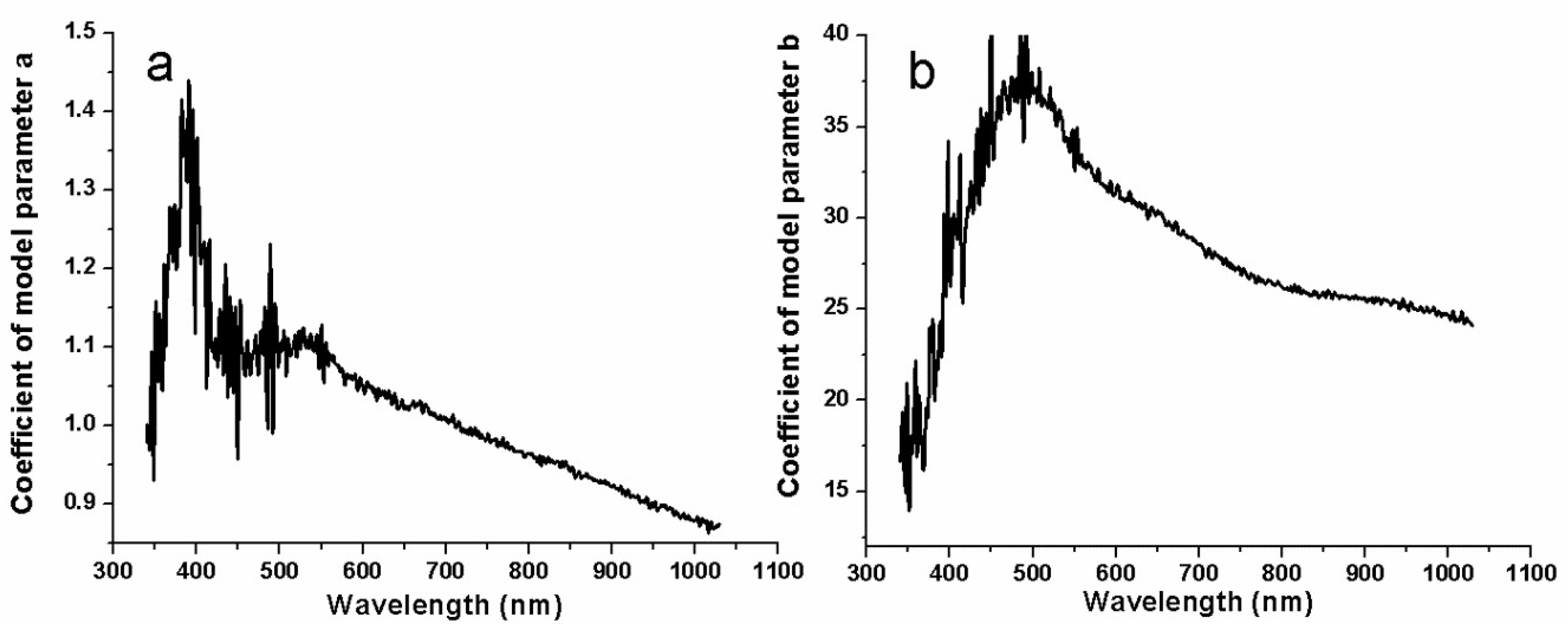
| Model Coefficients | The Central Wavelength of Selected Spectral Bands (nm) from HJ-1A Image | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 470 | 472 | 477 | 479 | 481 | 484 | 486 | 491 | 493 | |
| a | 35.79 | 36.44 | 36.47 | 37.48 | 36.87 | 39.76 | 40.18 | 40.95 | 38.29 |
| b | 1.11 | 1.10 | 1.12 | 1.09 | 1.12 | 1.07 | 1.06 | 1.03 | 1.11 |
| Plot # | As Content (mg/kg) | Cd Content (mg/kg) | Hg Content (mg/kg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observation | Estimate | Error | Observation | Estimate | Error | Observation | Estimate | Error | |
| 1 | 13.72 | 16.76 | 3.04 | 0.19 | 0.18 | −0.01 | 0.15 | 0.12 | −0.03 |
| 2 | 5.48 | 7.52 | 2.04 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.11 | −0.06 |
| 3 | 5.58 | 5.15 | −0.43 | 0.09 | 0.08 | −0.01 | 0.09 | 0.04 | −0.05 |
| 4 | 4.15 | 6.17 | 2.02 | 0.18 | 0.14 | −0.04 | 0.18 | 0.14 | −0.04 |
| 5 | 24.56 | 17.89 | −6.67 | 0.22 | 0.19 | −0.03 | 0.44 | 0.27 | −0.17 |
| 6 | 5.14 | 5.2 | 0.06 | 0.1 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.03 |
| 7 | 5.33 | 6.06 | 0.73 | 0.11 | 0.09 | −0.02 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.07 |
| 8 | 4.09 | 6.56 | 2.47 | 0.17 | 0.15 | −0.02 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.01 |
| 9 | 5.7 | 9.85 | 4.15 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.1 | −0.02 |
| 10 | 4.03 | 7.06 | 3.03 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.07 |
| 11 | 5.65 | 8.85 | 3.2 | 0.21 | 0.18 | −0.03 | 0.2 | 0.18 | −0.02 |
| 12 | 11.93 | 17.83 | 5.9 | 0.21 | 0.17 | −0.04 | 0.18 | 0.27 | 0.09 |
| 13 | 6.4 | 7.98 | 1.58 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0 |
| 14 | 4.03 | 6.44 | 2.41 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.05 |
| 15 | 10.38 | 14.94 | 4.56 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.01 |
| 16 | 4.3 | 6.26 | 1.96 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.03 |
| 17 | 5.61 | 7.96 | 2.35 | 0.15 | 0.13 | −0.02 | 0.2 | 0.18 | −0.02 |
| 18 | 8.06 | 7.56 | −0.5 | 0.22 | 0.19 | −0.03 | 0.23 | 0.22 | −0.01 |
| 19 | 5.22 | 8.08 | 2.86 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.16 | −0.01 |
| 20 | 4.3 | 7.42 | 3.12 | 0.19 | 0.17 | −0.02 | 0.19 | 0.14 | −0.05 |
| 21 | 8.28 | 7.39 | −0.89 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.02 |
| 22 | 18.92 | 18.77 | −0.15 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.2 | 0.07 |
| 23 | 3.98 | 5.46 | 1.48 | 0.23 | 0.21 | −0.02 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.04 |
| 24 | 3.22 | 7.23 | 4.01 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.1 |
| 25 | 8.11 | 5.12 | −2.99 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.14 | −0.04 |
| 26 | 15.22 | 10.35 | −4.87 | 0.19 | 0.2 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.05 |
| 27 | 18.98 | 24.12 | 5.14 | 0.23 | 0.2 | −0.03 | 0.2 | 0.24 | 0.04 |
| 28 | 25.59 | 27.87 | 2.28 | 0.2 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.16 | −0.02 |
| 29 | 57.22 | 32.51 | −24.71 | 0.1 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 0.1 |
| 30 | 6.66 | 7.49 | 0.83 | 0.25 | 0.21 | −0.04 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.02 |
| 31 | 3.51 | 7.6 | 4.09 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.01 |
| 32 | 21.06 | 26.83 | 5.77 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.39 | 0.23 | −0.16 |
| 33 | 7.56 | 7.35 | −0.21 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.12 | −0.02 |
| Average (mg/kg) | 10.36 | 11.20 | 0.844 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.001 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.003 |
| STDEV (mg/kg) | 10.52 | 7.43 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | |||
| CV (%) | 101.54 | 37.22 | 45.90 | ||||||
| RMSE (mg/kg) | 5.34 | 0.03 | 0.06 | ||||||
| RRMSE (%) | 51.55 | 17.1 | 36.34 | ||||||
| Spectral variables | FD367 | FD400 | FD647 | FD675 | FD693 | FD796 | FD879 | FD902 |
| VIF | 2.99 | 6.26 | 10.82 | 26.57 | 19.87 | 16.90 | 51.63 | 31.87 |
| Spectral variables | FD907 | FD1008 | FD1059 | FD1943 | FD2178 | FD2379 | ||
| VIF | 9.96 | 19.87 | 16.90 | 51.63 | 31.87 | 9.96 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, G.; Hu, Y. Estimation of Soil Heavy Metal Content Using Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121464
Liu Z, Lu Y, Peng Y, Zhao L, Wang G, Hu Y. Estimation of Soil Heavy Metal Content Using Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(12):1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121464
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhenhua, Ying Lu, Yiping Peng, Li Zhao, Guangxing Wang, and Yueming Hu. 2019. "Estimation of Soil Heavy Metal Content Using Hyperspectral Data" Remote Sensing 11, no. 12: 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121464
APA StyleLiu, Z., Lu, Y., Peng, Y., Zhao, L., Wang, G., & Hu, Y. (2019). Estimation of Soil Heavy Metal Content Using Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121464






