On the Methods for Recalibrating Geostationary Longwave Channels Using Polar Orbiting Infrared Sounders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Measurements
2.1. Geostationary Satellite Observations
2.2. Reference Satellite Observations
3. Methods and Results
- (1)
- Selecting and preparing reference instruments on polar orbiting satellites;
- (2)
- Adjusting for spectral differences between LEO and GEO measurements and handling spectral gaps in AIRS spectra;
- (3)
- Collocating and filtering GEO and LEO measurements;
- (4)
- Computing of recalibration coefficients;
- (5)
- Anchoring recalibration coefficients to a prime reference.
3.1. Selecting and Preparing the Reference Data
3.2. Spectral Band Adjustment
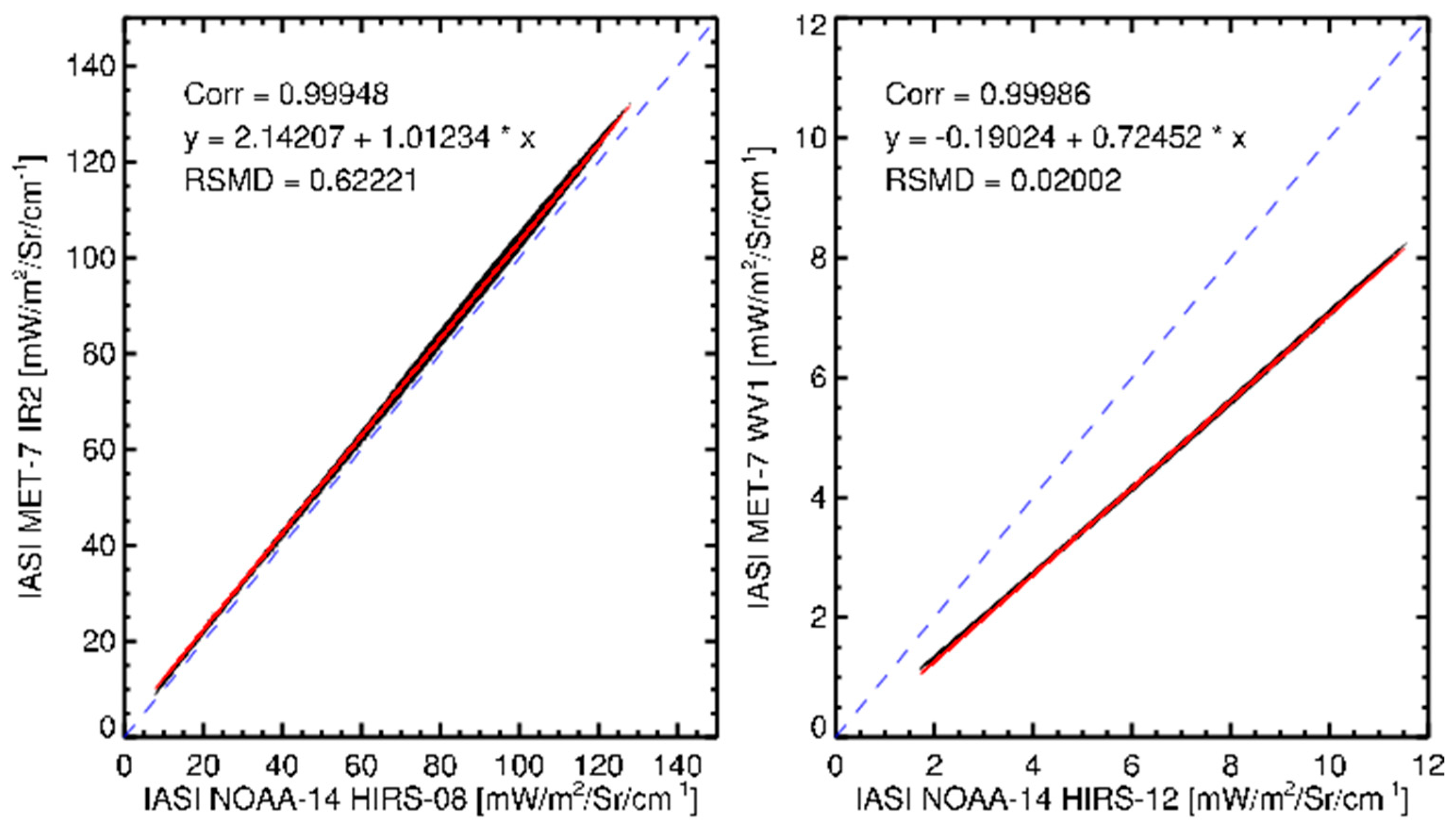
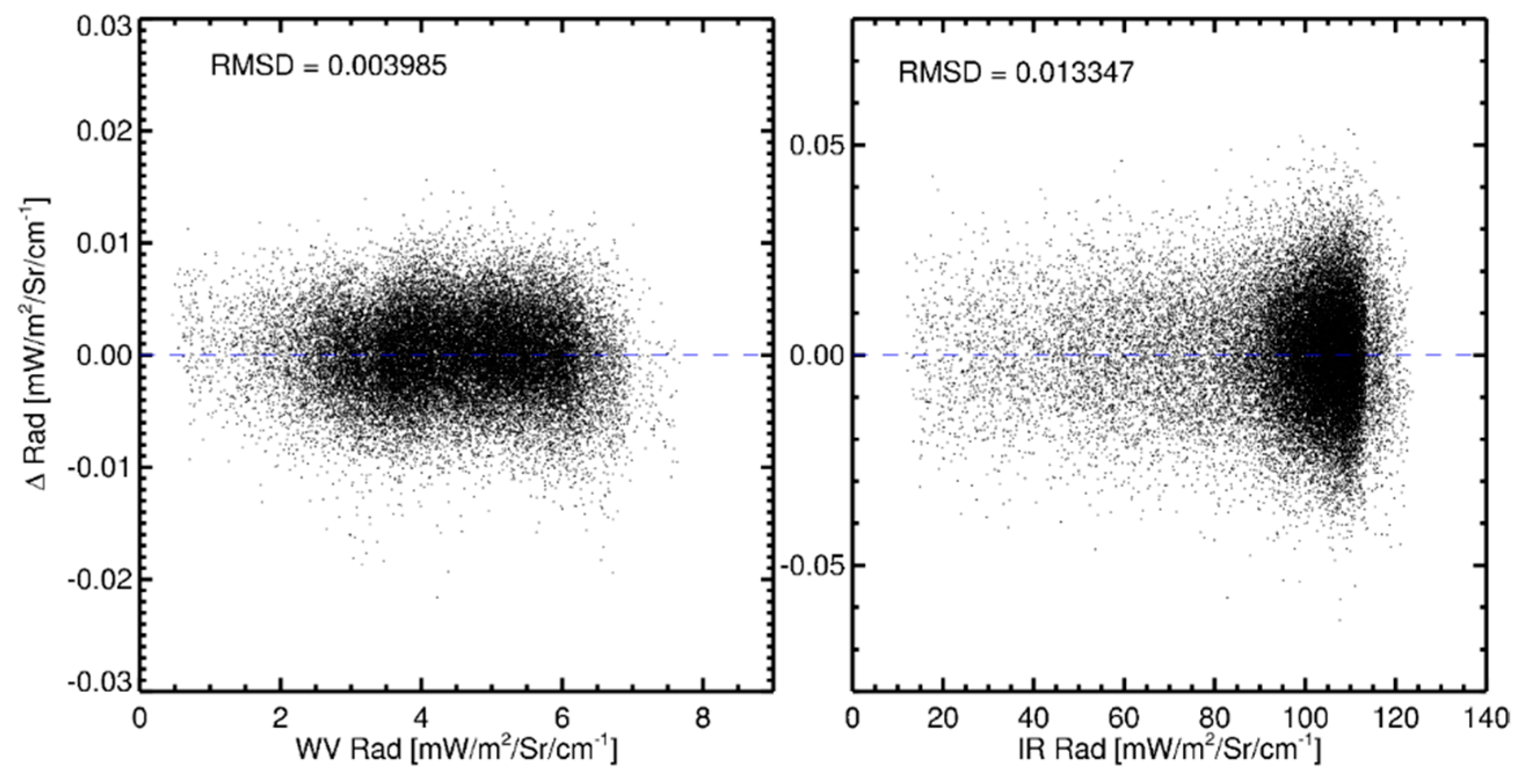
3.2.1. Spectral Band Adjustment for IASI
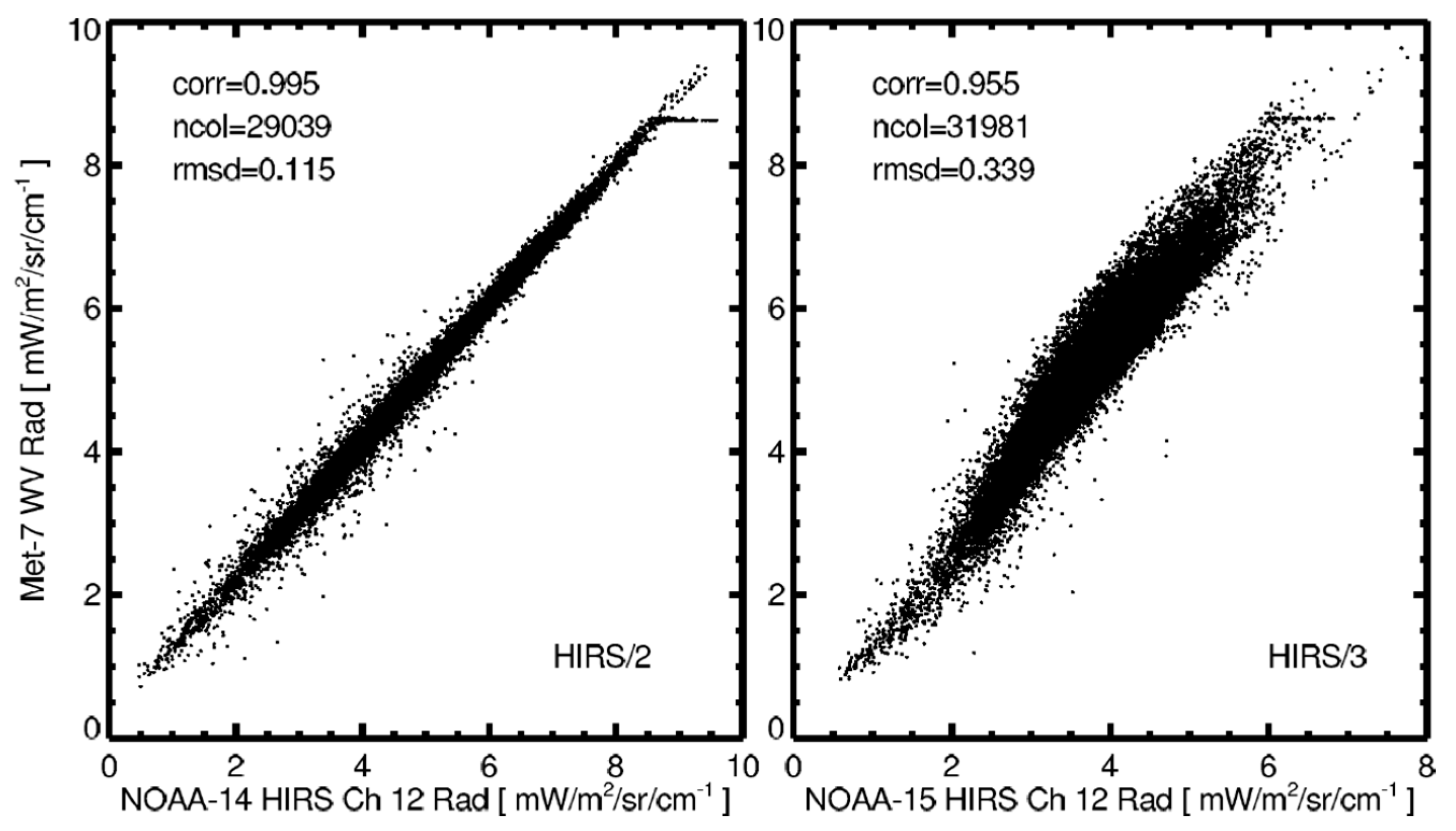
3.2.2. Spectral Band Adjustment for HIRS
3.2.3. Spectral Band Adjustment for AIRS
- (1)
- We simulated the broadband measurements of IR and WV channels with the same set of IASI spectra as is used in the HIRS SBAF. We also simulated AIRS radiances by convolving the IASI spectra with AIRS channel SRFs.
- (2)
- We determined the predictors, which varied from granule to granule, to compute the simulated broadband radiances of IR and WV channels from the simulated “good AIRS channel” radiances (≈260 channels in the IR band and ≈210 channels in the WV band) using multiple linear regression.
- (3)
- We predicted the broadband radiances of IR and WV channels from real AIRS spectra by applying the predictors determined in Step 2.
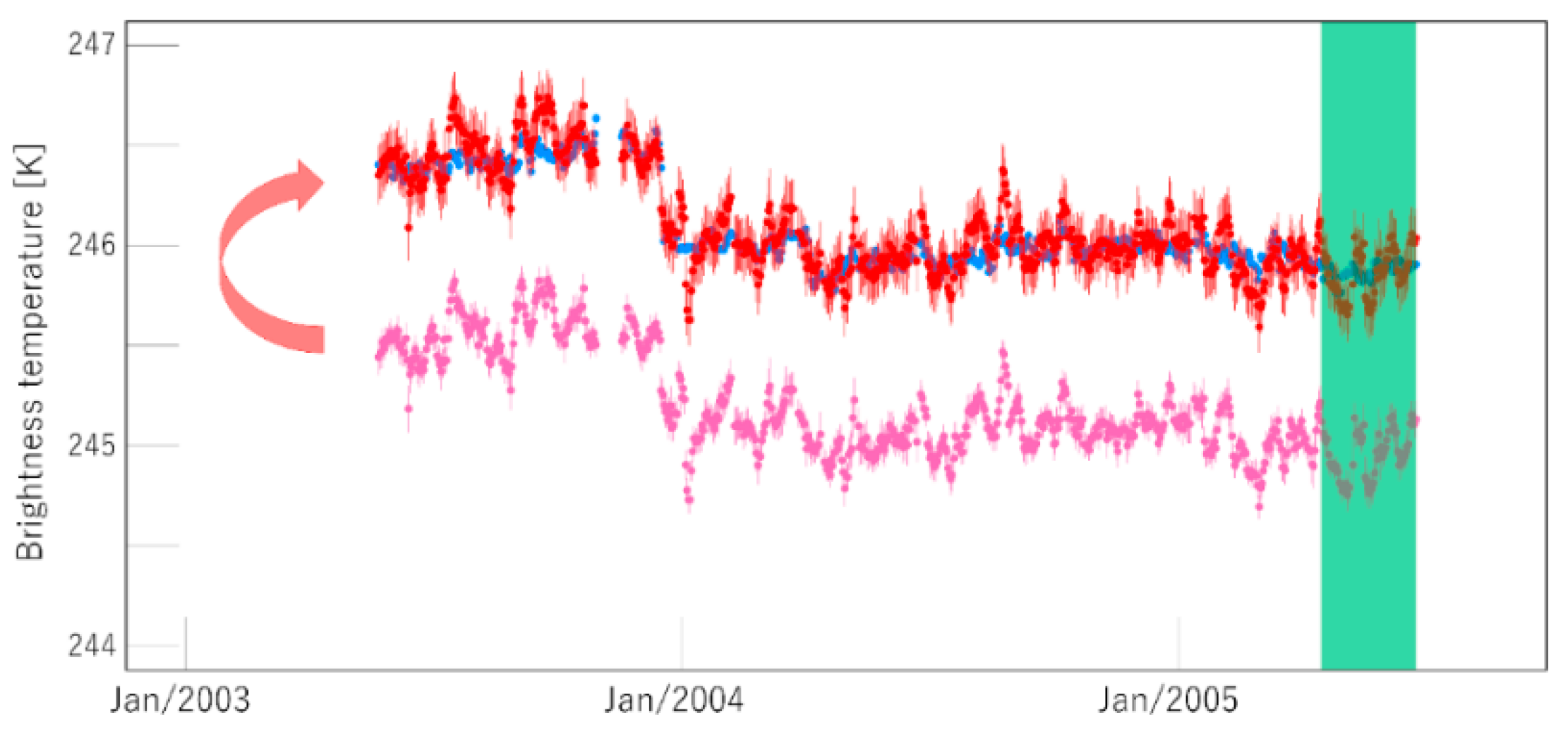
3.3. Finding Match-Ups between Refernce and Monitored Measurements
3.3.1. Collocation in Space
3.3.2. Collocation in Time
3.3.3. Collocation in Viewing Geometry
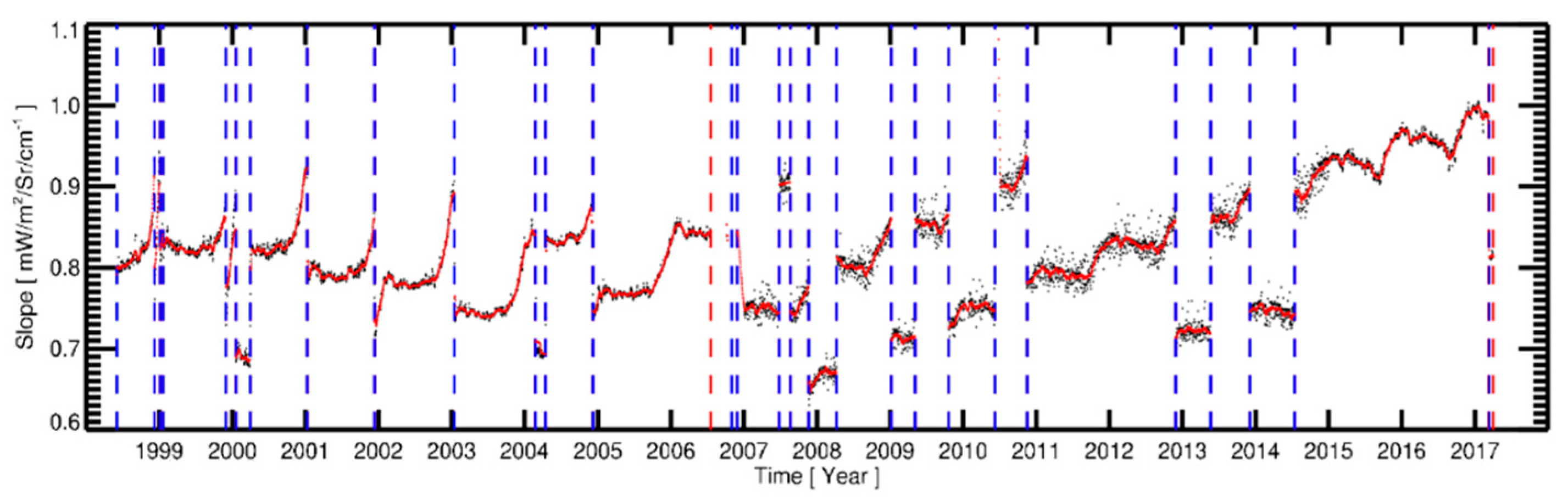
3.4. Determination of Calibration Coefficients
3.5. Anchoring Recalibration Coefficients to a Prime Reference
4. Validation
4.1. Comparison against Operational Calibrated and GSICS-Corrected Radiances
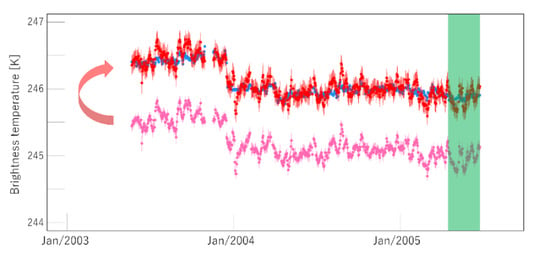
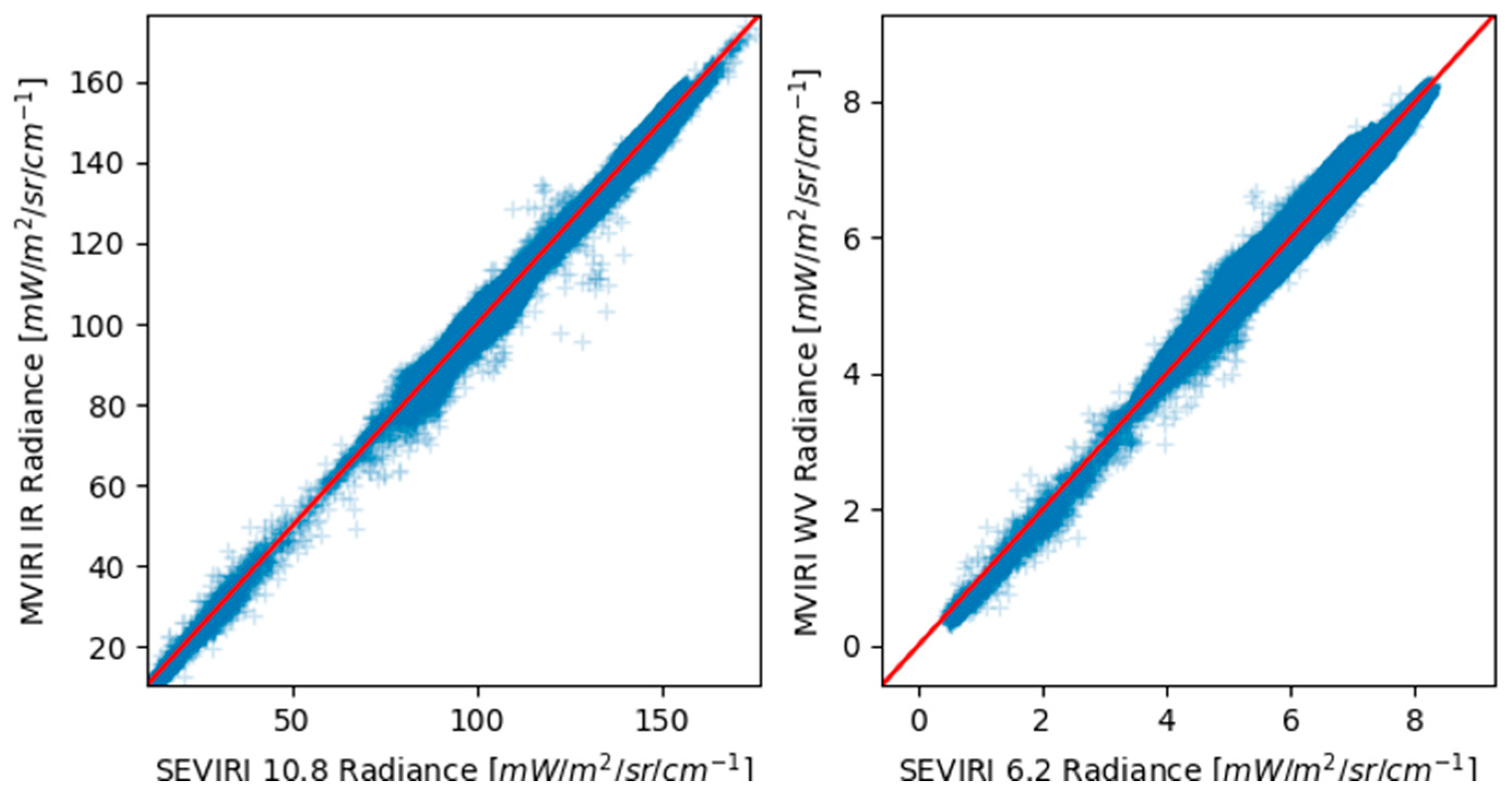
4.2. Comparison against SEVIRI Measurements
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions, Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIRS | Atmospheric Infrared Sounder |
| DN | Digital Number |
| EUMETSAT | European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites |
| FCDR | Fundamental Climate Data Record |
| FoR | Field of Regard |
| FoV | Field of View |
| GCOS | Global Climate Observing System |
| GEO | Geostationary |
| GMS | Geostationary Metrological Satellite |
| GOES | Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system |
| GSICS | Global Space-Based Inter-Calibration System |
| HIRS | High Resolution Infrared Radiation Sounder |
| IASI | Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer |
| IOGEO | Inter-Calibration of Imager Observations from Time-Series of Geostationary Satellites |
| IR | Infrared |
| JAMI | Japanese Advanced Meteorological Imager instrument |
| JMA | Japan Meteorological Agency |
| LEO | Low Earth Orbit |
| MFG | Meteosat First Generation |
| MVIRI | Meteosat Visible and InfraRed Imager |
| MSG | Meteosat Second Generation |
| MSICC | Multi Sensor Infrared Channel Calibration |
| MTSAT | Multi-Functional Transport Satellite |
| MVIRI | Meteosat Visible and Infrared Imager (onboard MFG satellites) |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| NCEP | National Centers for Environmental Prediction |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| OSCAR | Observing Systems Capability Analysis and Review Tool |
| REF | Reference |
| RMSD | Root Mean Square Difference |
| RTTOV | Radiative Transfer for TOVS |
| SBAF | Spectral Band Adjustment Factor |
| SCOPE-CM | Sustained and Coordinated Processing of Environmental Satellite Data for Climate Monitoring |
| SEVIRI | Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (onboard MSG satellites) |
| SNR | Signal to Noise Ratio |
| SRF | Spectral Response Function |
| SSP | Sub-Satellite Point |
| SST | Sea Surface Temperature |
| TIR | Thermal Infrared |
| TIROS | Television Infrared Observation Satellite |
| TOVS | TIROS Operational Vertical Sounder |
| VISSR | Visible and Infrared Spin Scan Radiometer |
| WMO | World Meteorological Organization |
| WV | Water Vapour |
References
- Schmetz, J.; Menzel, W.P. A Look at the Evolution of Meteorological Satellites: Advancing Capabilities and Meeting User Requirements. Weather Clim. Soc. 2015, 7, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GCOS. The Global Observing System for Climate: Implementation Needs. 2016. Available online: https://ane4bf-datap1.s3-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/wmocms/s3fs-public/programme/brochure/GCOS-200_OnlineVersion.pdf?PlowENiCc1RGh9ReoeAoGBT0QhnJYm6_ (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- Schmetz, J. Operational calibration of the METEOSAT water vapor channel by calculated radiances. Appl. Opt. 1989, 28, 3030–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Berg, L.C.J.; Schmetz, J.; Whitlock, J. On the calibration of the Meteosat water vapor channel. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 21069–21076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gube, M.; Gaertner, V.; Schmetz, J. Analysis of the Operational Calibration of the Meteosat Infrared-Window Channel. Meteorol. Appl. 1996, 3, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, M.; Jamieson, M.; Fulton, N.; Chen, Y.; Johnson, J.X.; Bremer, J.; Smith, C.; Baucom, J. Operational calibration of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-8 and -9 imagers and sounders. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 6895–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuno, M.; Itaya, H.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kurihara, S. Calibration of VISSR on board GMS-5. Adv. Space Res. 1997, 19, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, T.; John, V.O.; Roebeling, R.A.; Hewison, T.; Schulz, J. Recalibration of over 35 years of infrared and water vapor channel radiances of the JMA geostationary satellites. Remote Sens. under review.
- Tjemkes, S.A.; König, M.; Lutz, H.-J.; van de Berg, L.; Schmetz, J. Calibration of Meteosat water vapor channel observations with independent, satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 5199–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogniez, H.; Roca, R.; Picon, L. A clear-sky radiance archive from METEOSAT ‘water vapor’ observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D21109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosema, A.; Foppes, S.; van der Woerd, J. Meteosat Derived Planetary Temperature Trend 1982–2006. Energy Environ. 2013, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.; Ohring, G.; Butler, J.; Cao, C.; Datla, R.; Doelling, D.; Gaertner, V.; Hewison, T.; Iacovazzi, B.; Kim, D.; et al. The global space-based inter-calibration system (GSICS). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewison, T.J.; Wu, X.; Yu, F.; Tahara, Y.; Hu, X.; Kim, D.; Koenig, M. GSICS Inter-Calibration of Infrared Channels of Geostationary Imagers using Metop/IASI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmetz, J.; Pili, P.; Tjemkes, S.; Just, D.; Kerkmann, J.; Rota, S.; Ratier, A. An Introduction to Meteosat Second Generation (MSG)—and supplements. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2002, 83, 977–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JMA. Preliminary Validation Report on MTSAT-1R Imagery Data, CGMS33 JMA-WP-11. In Proceedings of the 33th Meeting of the Coordination Group for Meteorological Satellites (CGMS), Tokyo, Japan, 1–4 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, F.; Armante, R.; August, T.; Barnet, C.; Bouchard, A.; Camy-Peyret, C.; Capelle, V.; Clarisse, L.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.F.; Collard, A. Hyperspectral Earth observation from IASI: Five years of accomplishments. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2012, 93, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Bates, J.; Shi, L. Three decades of intersatellite-calibrated High-Resolution Infrared Radiation Sounder upper tropospheric water vapour. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D04108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, Y.; Koji, K. New Spectral Compensation Method for Intercalibration Using High Spectral Resolution Sounder. Meteorol. Satell. Cent. Tech. Note 2009, 52, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, K.R. Calibration Assessment of ISCCP Geostationary Infrared Observations Using HIRS. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, V.O.; Holl, G.; Buehler, S.A.; Candy, B.; Saunders, R.W.; Parker, D.E. Understanding intersatellite biases of microwave humidity sounders using global simultaneous nadir overpasses. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D02305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolksy, S.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B. Numerical Recipes in FORTRAN 77: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts, Y.M.; Rüthrich, F.; John, V.O.; Quast, R. Climate Data Records from Meteosat First Generation Part I: Simulation of Accurate Top-of-Atmosphere Spectral Radiance over Pseudo-Invariant Calibration Sites for the Retrieval of the In-Flight Visible Spectral Response. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojanowski, J.S.; Stöckli, R.; Duguay-Tetzlaff, A.; Finkensieper, S.; Hollmann, R. Performance Assessment of the COMET Cloud Fractional Cover Climatology across Meteosat Generations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckli, R.; Bojanowski, J.S.; John, V.O.; Duguay-Tetzlaff, A.; Bourgeois, Q.; Schulz, J.; Hollmann, R. Cloud Detection with Historical Geostationary Satellite Sensors for Climate Applications. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguay–Tetzlaff, A.; Stöckli, R.; Bojanowski, J.; Hollmann, R.; Fuchs, P.; Werscheck, M. CM SAF Land SUrface Temperature Dataset from METeosat First and Second Generation, 1st ed.; Satellite Application Facility on Climate Monitoring: Offenbach, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Köpken, C. Solar Stray Light Effects in Meteosat Radiances Observed and Quantified Using Operational Data Monitoring at ECMWF. J. Appl. Meteor. 2004, 43, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Channel | Spatial Sampling at Nadir (km) | Central Wavelength (µm) | SNR (K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MVIRI (Meteosat-2, -3, -4, -5, -6, -7); 1981–2017 | |||
| WV | 5.0 | 6.4 | 1.00 K @ 250 K |
| IR | 5.0 | 11.5 | 0.50 K @ 300 K |
| SEVIRI (Meteosat-8, -9, -10, -11); 2003– | |||
| WV | 3.0 | 6.25 | 0.75 K @ 250 K |
| IR | 3.0 | 10.8 | 0.25 K @ 300 K |
| VISSR (GMS, GMS-2, -3, -4); 1978–1995 | |||
| IR | 5.0 | 11.5 | ≤0.5 K @ 300 K |
| VISSR (GMS-5); 1995–2003 | |||
| WV | 5.0 | 6.75 | ≤0.22 K @ 300 K |
| IR | 5.0 | 11.0 | ≤0.35 K @ 300 K |
| JAMI (MTSAT-1R); 2005–2014 | |||
| WV | 4.0 | 6.75 | 0.15 K @ 300 K |
| IR | 4.0 | 10.8 | 0.18 K @ 300 K |
| IMAGER (MTSAT-2); 2009–2016 | |||
| WV | 4.0 | 6.75 | 0.11 K @ 300 K |
| IR | 4.0 | 10.8 | 0.12 K @ 300 K |
| Imager (GOES-9); 2003–2005 | |||
| WV | 8.0 | 6.75 | 0.09 K @ 300 K |
| IR | 4.0 | 10.7 | 0.11 K @ 300 K |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
John, V.O.; Tabata, T.; Rüthrich, F.; Roebeling, R.; Hewison, T.; Stöckli, R.; Schulz, J. On the Methods for Recalibrating Geostationary Longwave Channels Using Polar Orbiting Infrared Sounders. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101171
John VO, Tabata T, Rüthrich F, Roebeling R, Hewison T, Stöckli R, Schulz J. On the Methods for Recalibrating Geostationary Longwave Channels Using Polar Orbiting Infrared Sounders. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(10):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101171
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohn, Viju O., Tasuku Tabata, Frank Rüthrich, Rob Roebeling, Tim Hewison, Reto Stöckli, and Jörg Schulz. 2019. "On the Methods for Recalibrating Geostationary Longwave Channels Using Polar Orbiting Infrared Sounders" Remote Sensing 11, no. 10: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101171
APA StyleJohn, V. O., Tabata, T., Rüthrich, F., Roebeling, R., Hewison, T., Stöckli, R., & Schulz, J. (2019). On the Methods for Recalibrating Geostationary Longwave Channels Using Polar Orbiting Infrared Sounders. Remote Sensing, 11(10), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101171