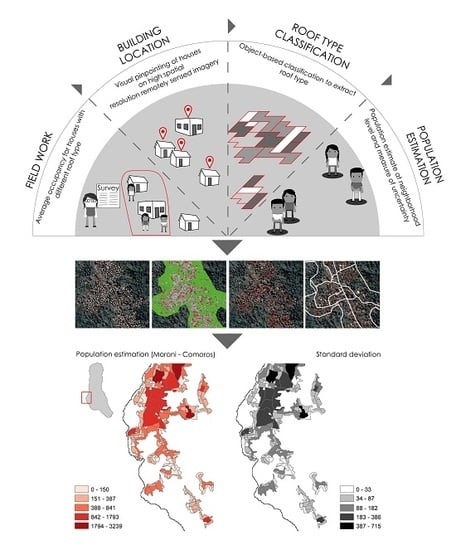
Mapping Population Distribution from High Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery in a Data Poor Setting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
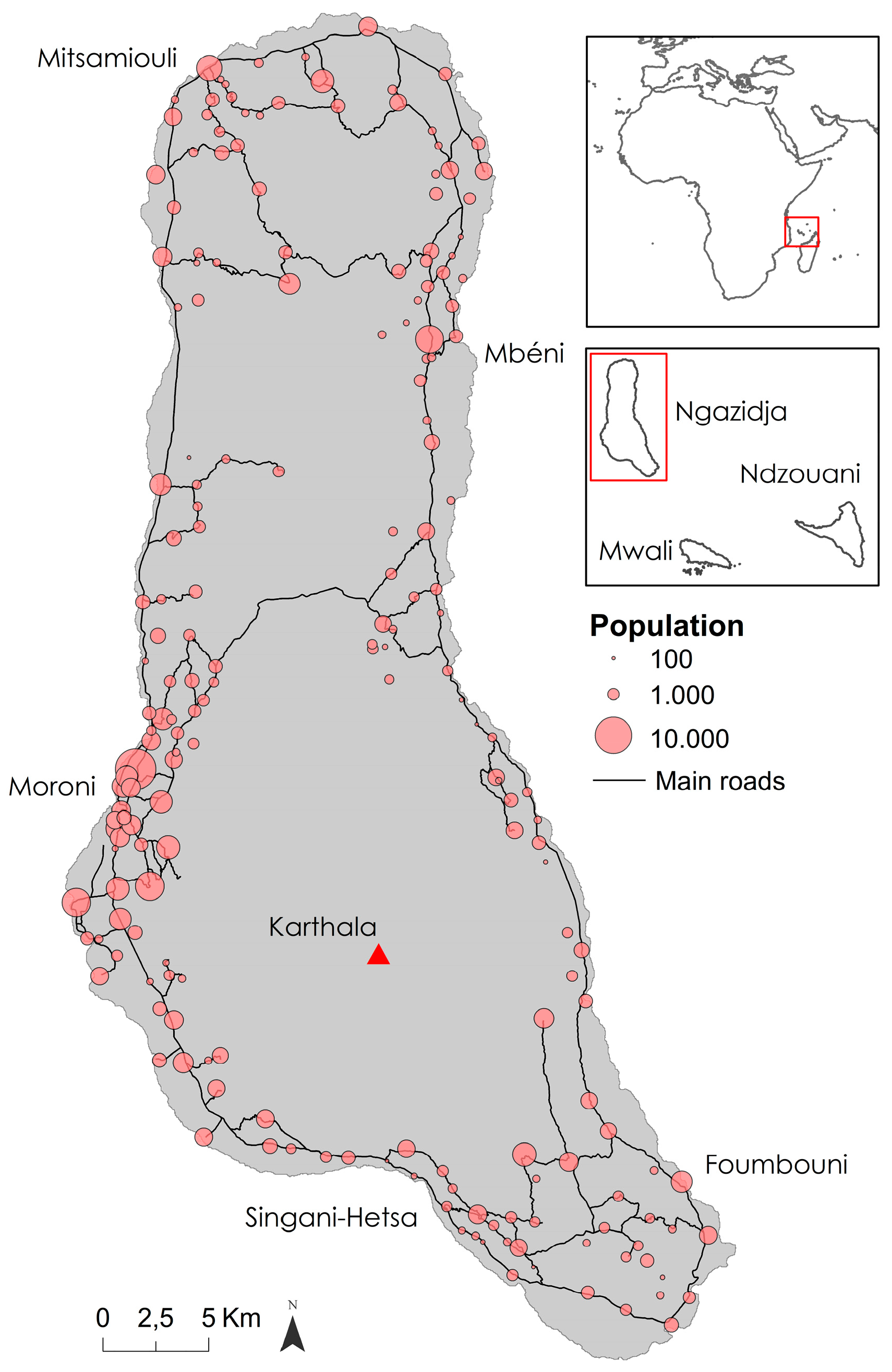
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Population Characteristics Based on the 2003 Census
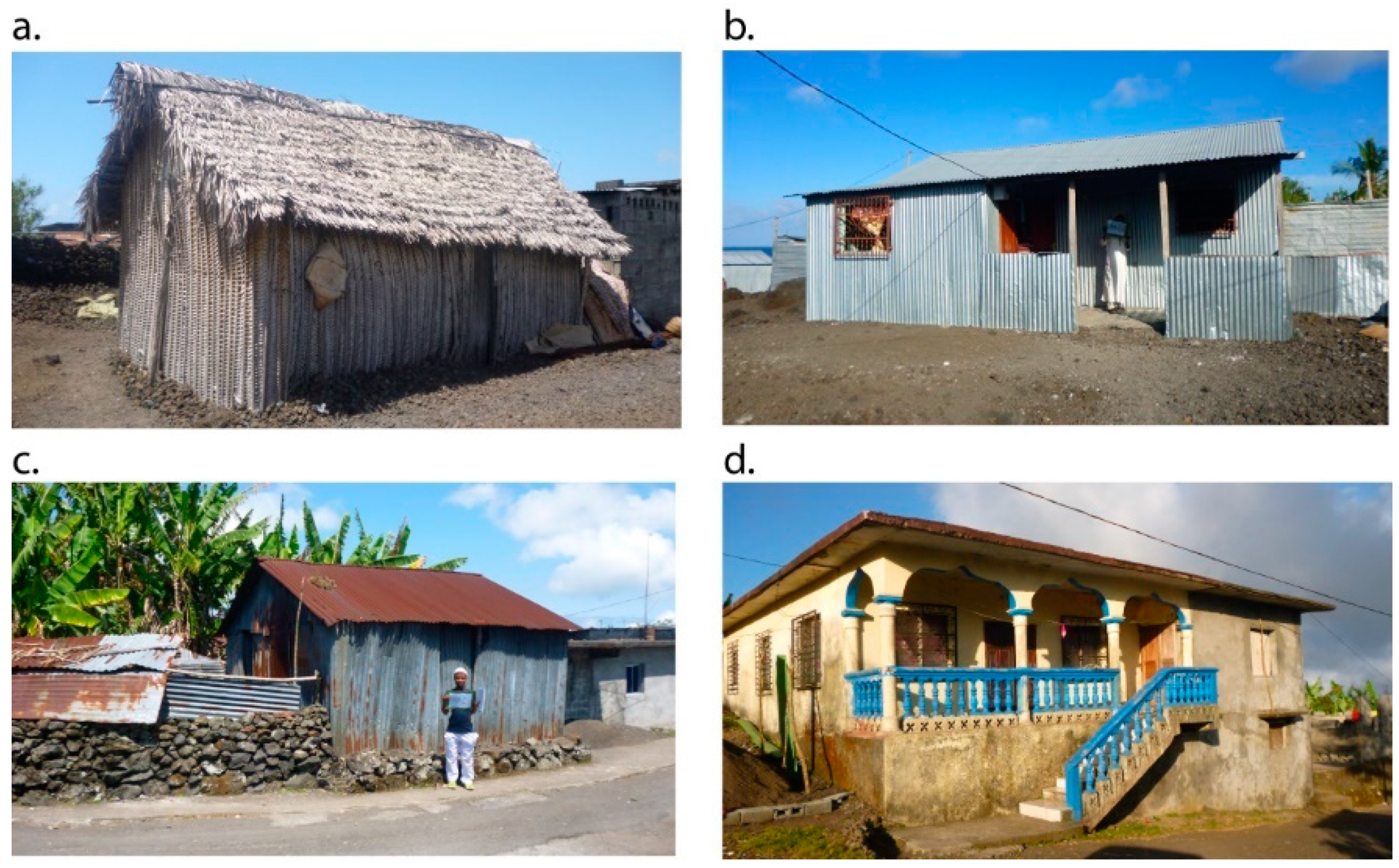
2.1.2. House Characteristics
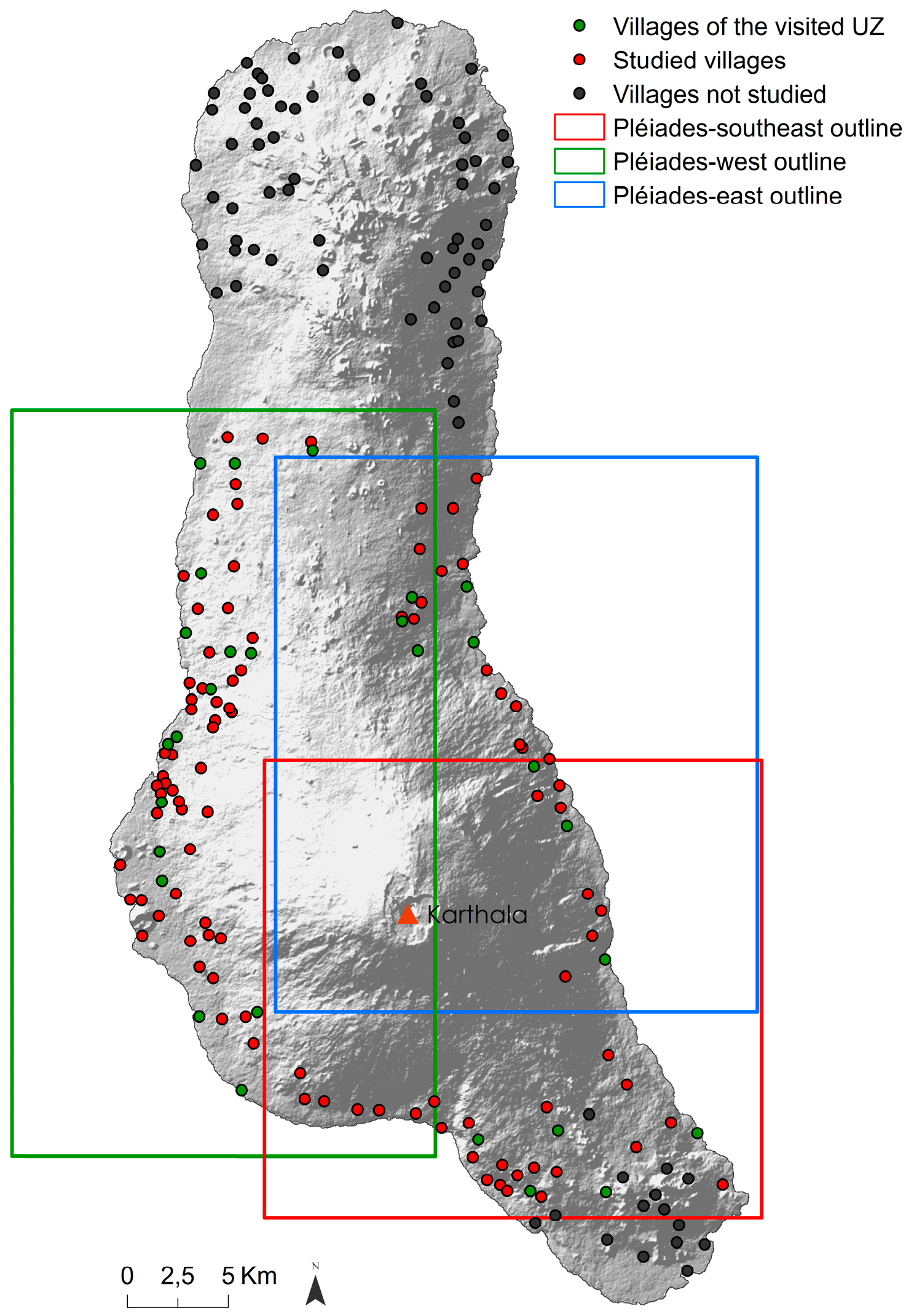
2.2. Collection of Field Data
2.3. Preprocessing of Pléiades Imagery
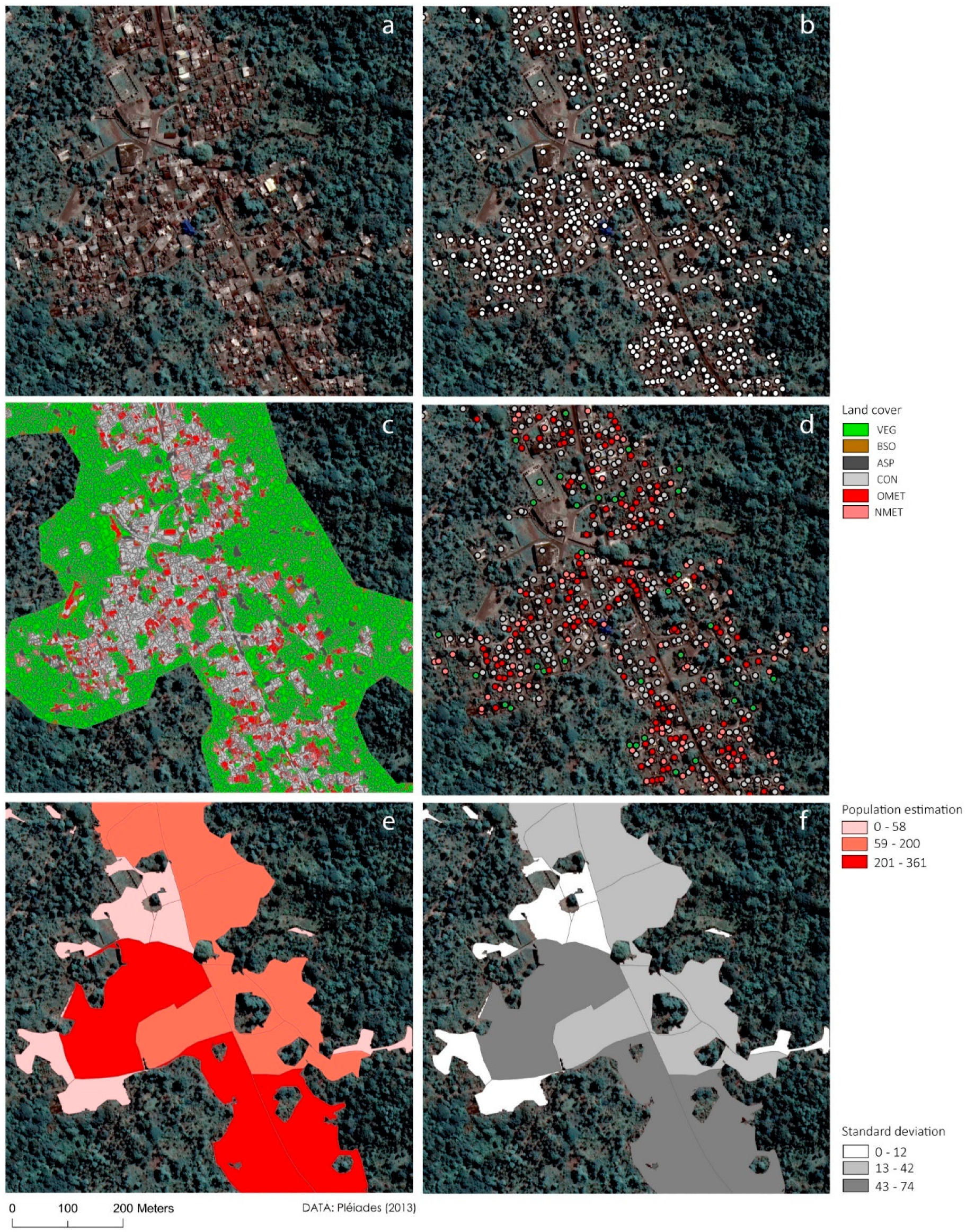
2.4. Building Layer Definition
2.5. Roof Type Characterization
2.6. Population Estimation Model
3. Results
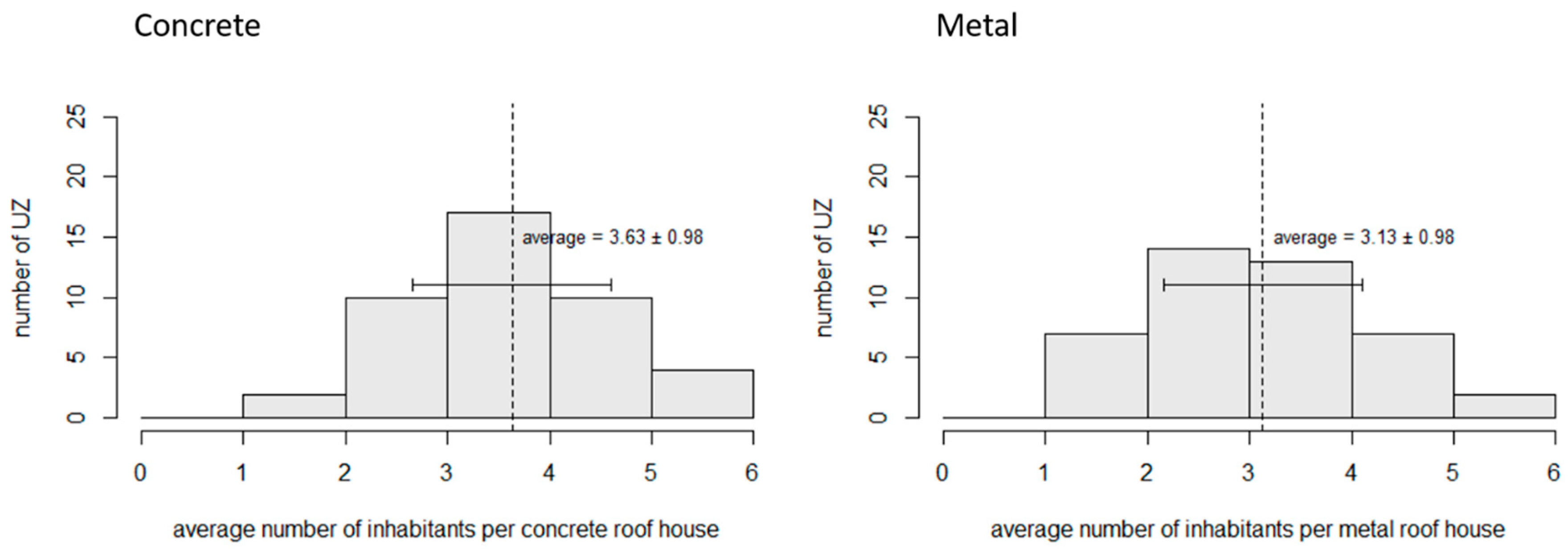
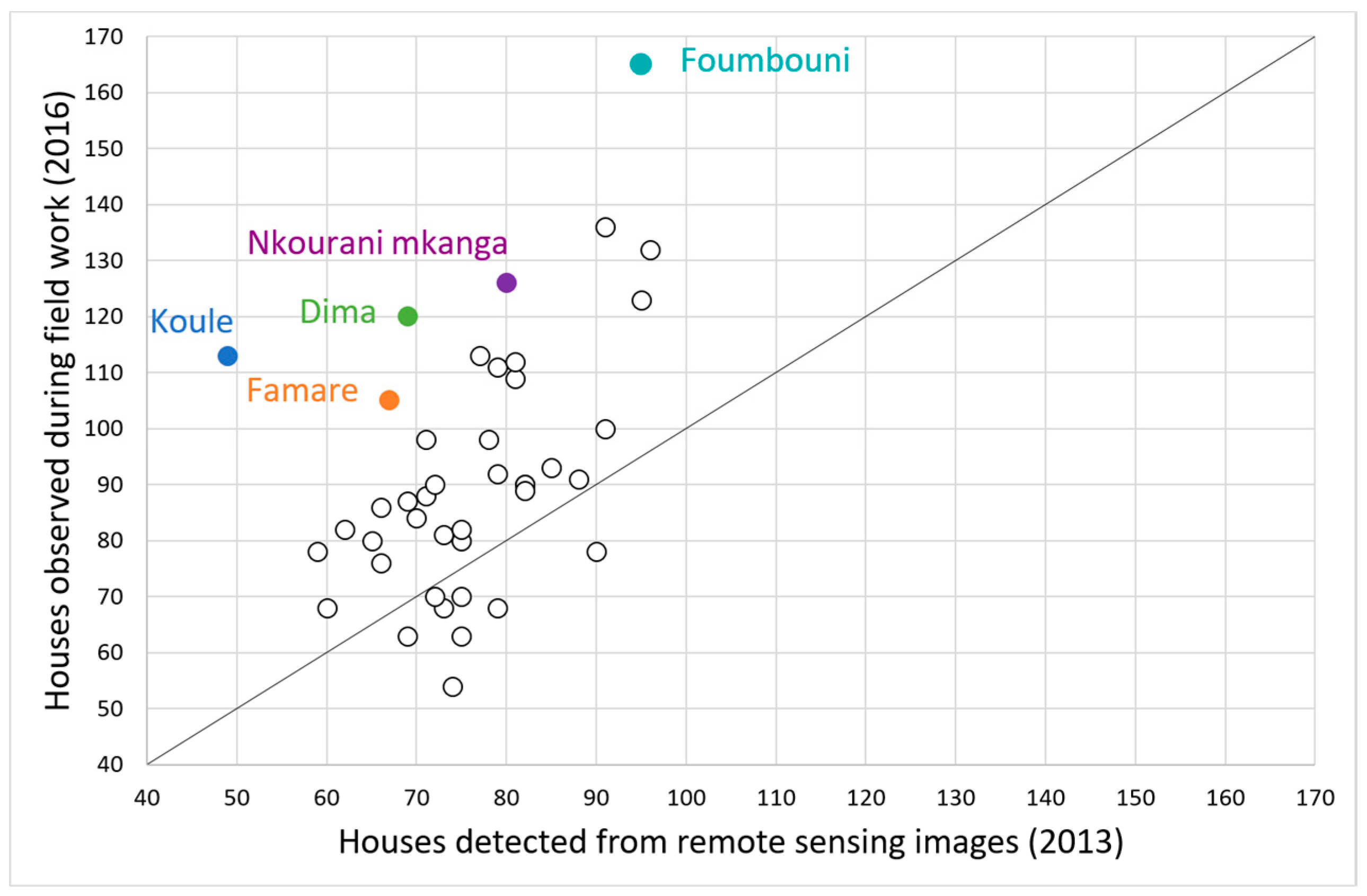
3.1. Relation between Number of Residents and Building Type
3.2. Building and Roof Type Mapping
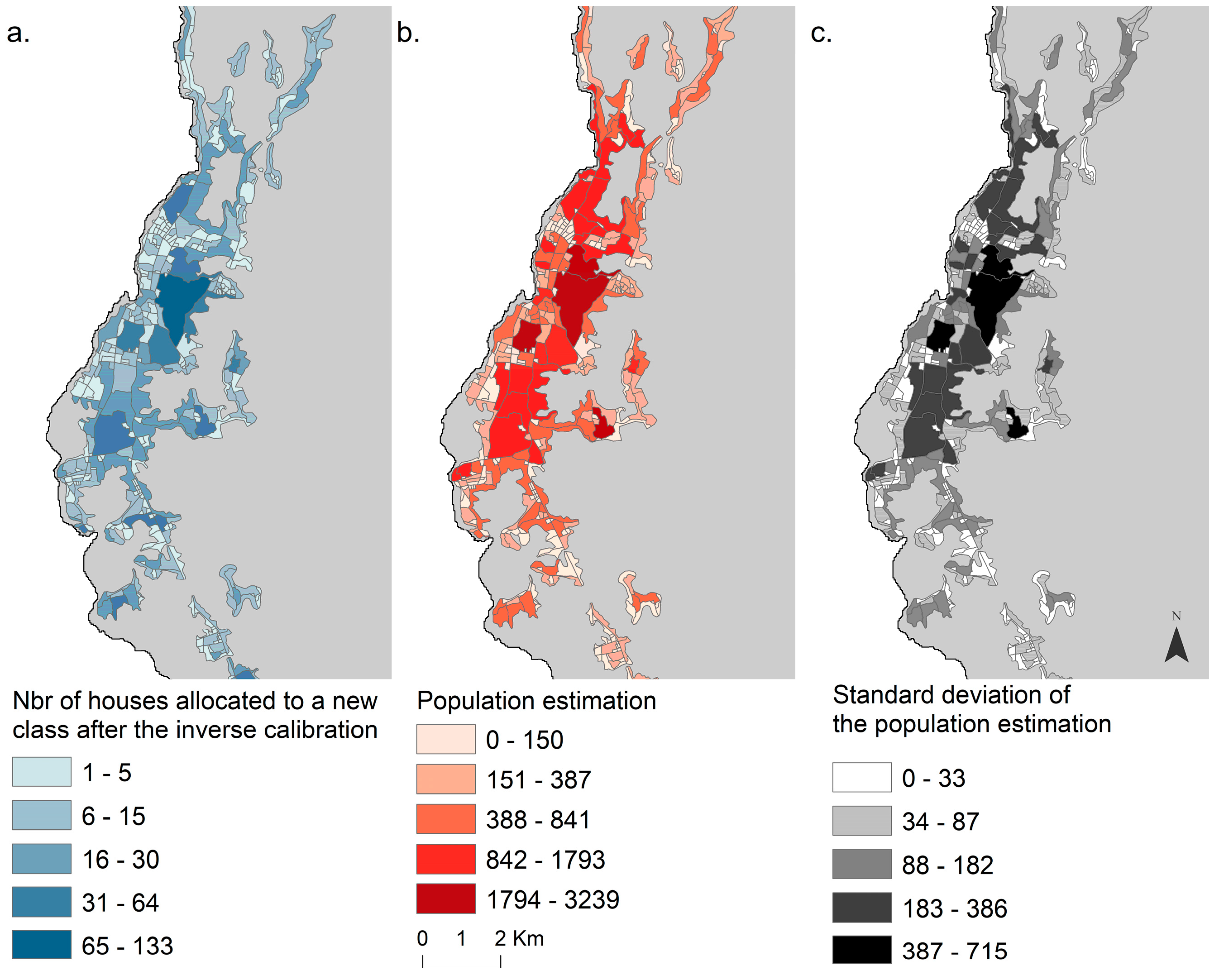
3.3. Population Estimation
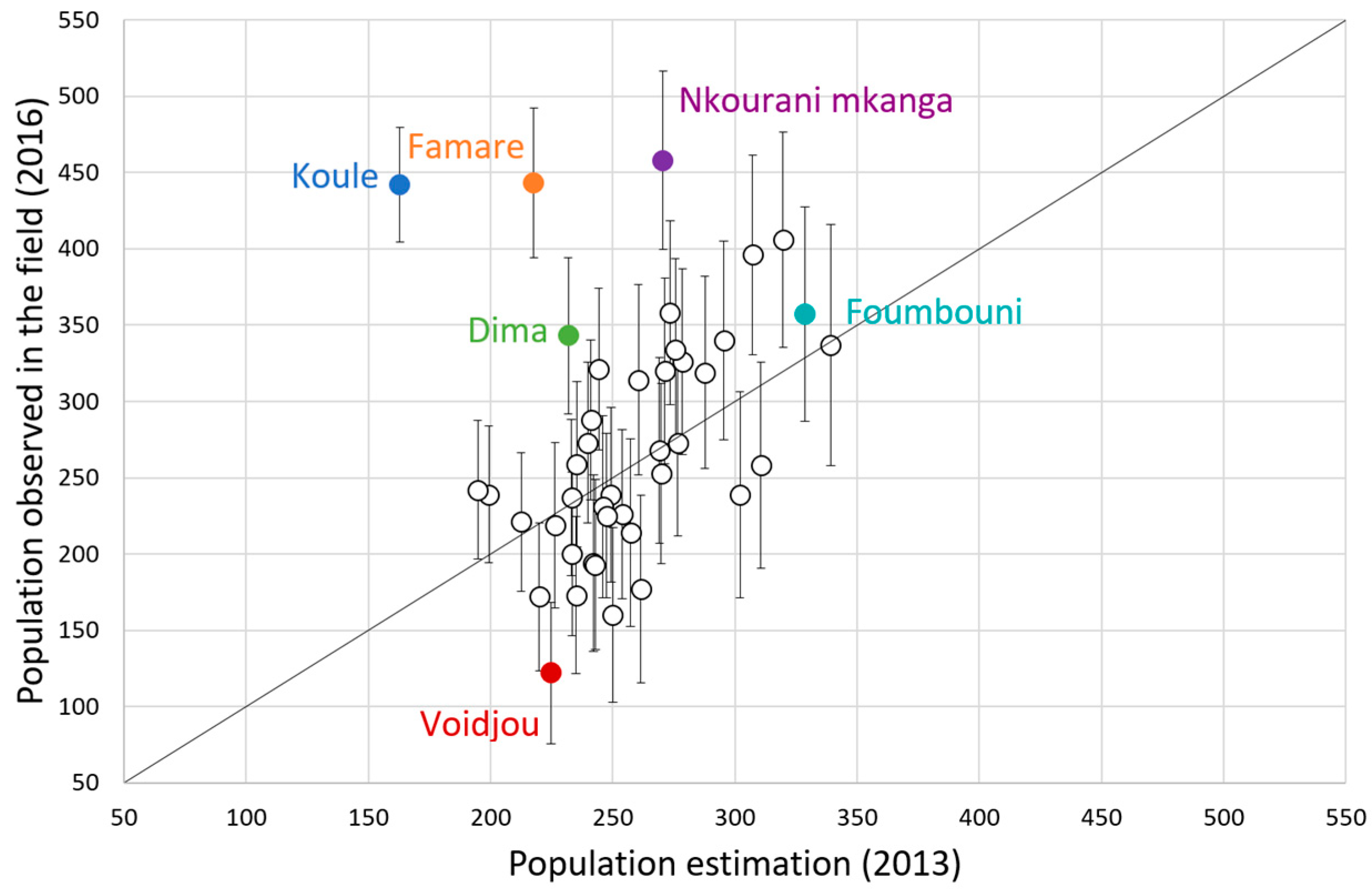
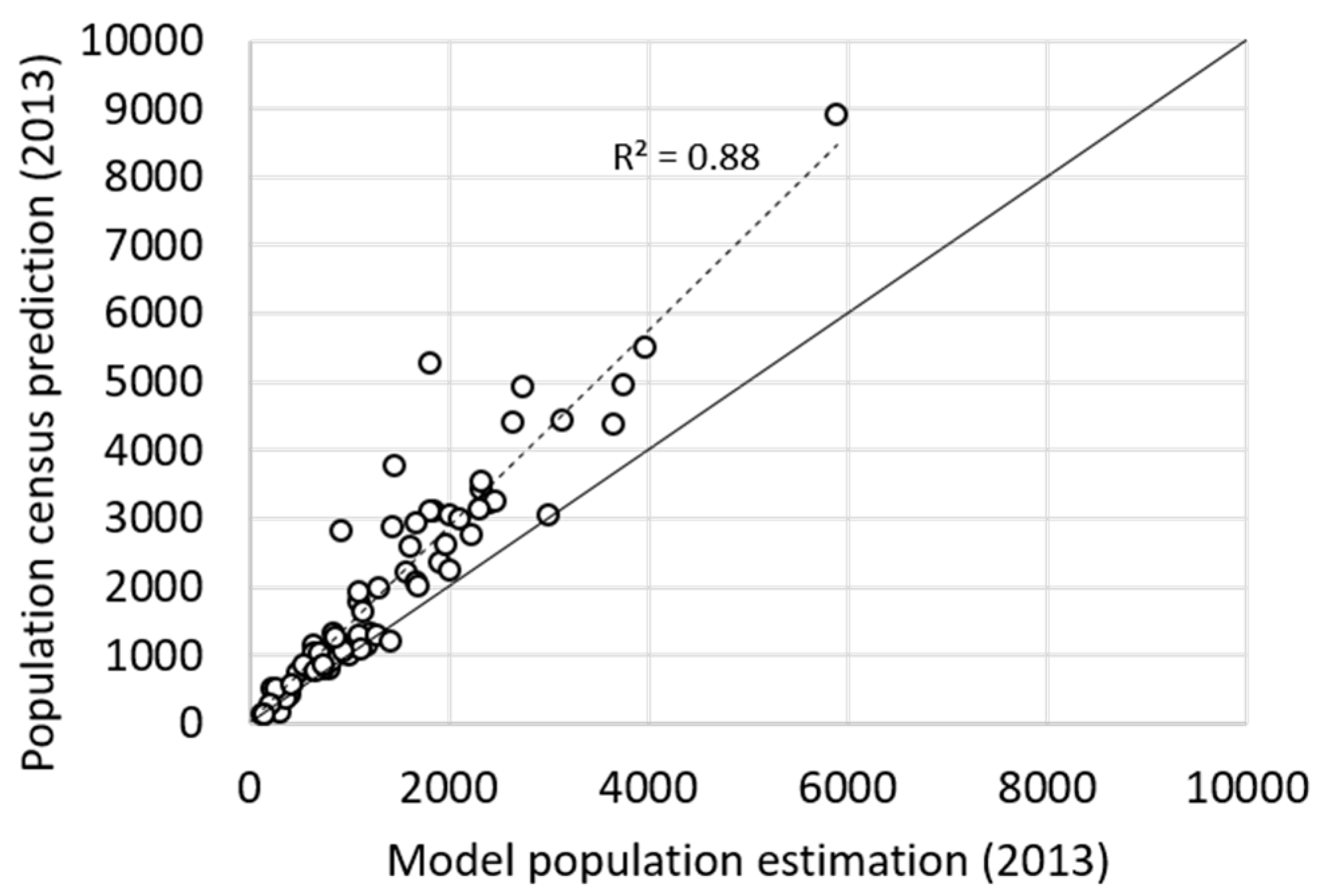
3.4. Model Extrapolation and Comparison with Census Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, K.; McAneney, J.; Blong, R.; Leigh, R.; Hunter, L.; Magill, C. Defining area at risk and its effect in catastrophe loss estimation: A dasymetric mapping approach. Appl. Geogr. 2004, 24, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayembe wa Kayembe, M.; Ngoy Ndombe, A.; Makanzu Imwangana, F.; Mpinda, M.; Misilu Mia Nsokimieno, E.; Wolff, E. Contribution of Remote Sensing in the Estimation of the Populations Living in Areas with Risk of Gully Erosion in Kinshasa (D. R. Congo). Case of Selembao Township. Am. J. Geosci. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, L.; Fonseca, L.; Almeida, C.; Leonardi, F.; Pereira, M. Urban population estimation based on residential buildings volume using IKONOS-2 images and lidar data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Ramesh, S.; Nepali, A. Evaluation of small-area population estimation using LiDAR, Landsat TM and parcel data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 5571–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Principles and Recommendations for Population and Housing Censuses; United Nations Publication: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 67, ISBN 978-92-1-161597-5. [Google Scholar]
- Statistics Netherlands. Dutch Census 2011: Analysis and Methodology; Statistics Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 9789035719484.
- Deng, C.; Wu, C.; Wang, L. Improving the housing-unit method for small-area population estimation using remote-sensing and GIS information. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 5673–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, F. Using Landsat imagery and census data for urban population density modeling in Port-au-Prince, Haiti. GISci. Remote Sens. 2012, 49, 228–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Weng, Q. Using Landsat ETM+ imagery to measure population density in Indianapolis, Indiana, USA. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.P. Zone-Based Estimation of Population and Housing Units from Satellite-Generated Land Use/Land Cover Maps; Victor, M., Ed.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 0415260450. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.P.; Chan, H.F. Rural population estimation from aerial photographs. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1980, 46, 337–345. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q.; Li, G. Residential population estimation using a remote sensing derived impervious surface approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3553–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, E.M.; Seaman, V.Y.; Stewart, R.N.; Bird, T.J.; Tatem, A.J.; McKee, J.J.; Bhaduri, B.L.; Moehl, J.J.; Reith, A.E. Census-independent population mapping in northern Nigeria. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Qiu, X.; Wang, L. Population estimation methods in GIS and remote sensing: A review. GISci. Remote Sens. 2005, 42, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagoub, M.M. Application of remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to population studies in the gulf: A case of Al Ain city (UAE). J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2006, 34, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fu, B. Estimating the population distribution in a county area in China based on impervious surfaces. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahabir, R.; Croitoru, A.; Crooks, A.; Agouris, P.; Stefanidis, A. A Critical Review of High and Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing Approaches for Detecting and Mapping Slums: Trends, Challenges and Emerging Opportunities. Urban Sci. 2018, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R. Slums from Space—15 Years of Slum Mapping Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F. Monitoring population evolution in China using time-series DMSP/OLS nightlight imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.K.; Arunachalam, A.; Diwakar, P.G. Potential of High Resolution Satellite Data for Human Population Estimation. Asian J. Geoinf. 2015, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ayila, A.E.; Paul Babatunde, B.; Yohanna, J.P. Population estimation and census track demarcation in Hwolshe, Plateau State, Nigeria: A geospatial approach. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2018, 10, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, D.J.; Gulliver, J.; Fecht, D.; Vienneau, D.M. Dasymetric modelling of small-area population distribution using land cover and light emissions data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Xin, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Xiang, W. Modeling population density based on nighttime light images and land use data in China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 90, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Clarke, K.; Herold, M. Population density and image texture: A comparison study. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillson, R.; Alejandre, J.D.; Jacobsen, K.H.; Ansumana, R.; Bockarie, A.S.; Bangura, U.; Lamin, J.M.; Malanoski, A.P.; Stenger, D.A. Methods for Determining the Uncertainty of Population Estimates Derived from Satellite Imagery and Limited Survey Data: A Case Study of Bo City, Sierra Leone. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veljanovski, T.; Urša, K.; Pehani, P.; Oštir, K.; Kovačič, P. Object-Based Image Analysis of VHR Satellite Imagery for Population Estimation in Informal Settlement Kibera-Nairobi, Kenya. Intech Open 2018, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checchi, F.; Stewart, B.T.; Palmer, J.J.; Grundy, C. Validity and feasibility of a satellite imagery-based method for rapid estimation of displaced populations. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2013, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T.; Gueguen, L.; Soille, P. Automatic information retrieval from meter and sub-meter resolution satellite image data in support to crisis management. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. 2010, 25, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shao, G. Object-based land-cover mapping with high resolution aerial photography at a county scale in midwestern USA. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11372–11390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füreder, P.; Hölbling, D.; Tiede, D.; Zeil, P.; Lang, S. Monitoring refugee camp evolution and population dynamics in Dagahaley, Kenya, based on VHR satellite data. In Proceedings of the 9th Internation Conference African Association Remote Sensing Environment, El Jadida, Morocco, 29 October–2 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Chapman, M.A.; Rüther, H. Small Format Digital Imaging for Informal Settlement Mapping. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiede, D.; Lang, S.; Hölbling, D.; Füreder, P. Transferability of obia rulesets for idp camp analysis in darfur. Geobia 2010, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, S.; Andersson, N.; Ansari, N.M.; Omer, K.; Soberanis, J.L.; Cockcroft, A. Equity and vaccine uptake: A cross-sectional study of measles vaccination in Lasbela District, Pakistan. BMC Int. Health Hum. Rights 2009, 9 (Suppl. 1), S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adah, M.I.; Taiwo, A.T. Multidimensional Poverty in Rural Kogi State, Nigeria: A Subjective Wellbeing (SWB) Approach. Science 2017, 5, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- The Housing Development Agency. Working for Integration—Annual Report 2012–2013; The Housing Development Agency: Limpopo, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- DGSP; ICF. Enquête Démographique et de Santé et à Indicateurs Multiple aux Comores 2012; DGSP: Moroni, Comoros, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Commissariat Général au Plan. Analyse des Données du Recensement Général de la Population et de L’habitat 2003: Ménages et Habitations; Commissariat Général au Plan: Moroni, Comoros, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Trimble eCognition. Developer 9.0 Reference Book; Trimble eCognition: Munich, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–266. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, E.; Boykin, K.; Valdez, R. Multispectral and Texture Feature Application in Image-Object Analysis of Summer Vegetation in Eastern Tajikistan Pamirs. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohn, R.C.; Autrey, B.C.; Lane, C.R.; Reif, M. Segmentation and object-oriented classification of wetlands in a karst Florida landscape using multi-season Landsat-7 ETM+ imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 1471–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roeck, T.; Van de Voorde, T.; Canters, F. Full hierarchic versus non-hierarchic classification approaches for mapping sealed surfaces at the rural-urban fringe using high-resolution satellite data. Sensors 2009, 9, 22–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witharana, C.; Civco, D.L.; Meyer, T.H. Evaluation of data fusion and image segmentation in earth observation based rapid mapping workflows. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 87, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaplewski, R.L.; Catts, G.P. Calibration of remotely sensed proportion or area estimates for misclassification error. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 39, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.A.; Burk, T.E. Calibration of satellite classifications of land area. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 46, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canters, F. Evaluating the uncertainty of area estimates derived from fuzzy land-cover classification. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 403–414. [Google Scholar]
- Cockx, K.; Canters, F. Incorporating spatial non-stationarity to improve dasymetric mapping of population. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, J. Gestion Institutionnelle et Réponses des Populations Face Aux Crises Volcaniques: Études de Cas à La Réunion et en Grande Comore; Université de la Réunion: La Réunion, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]


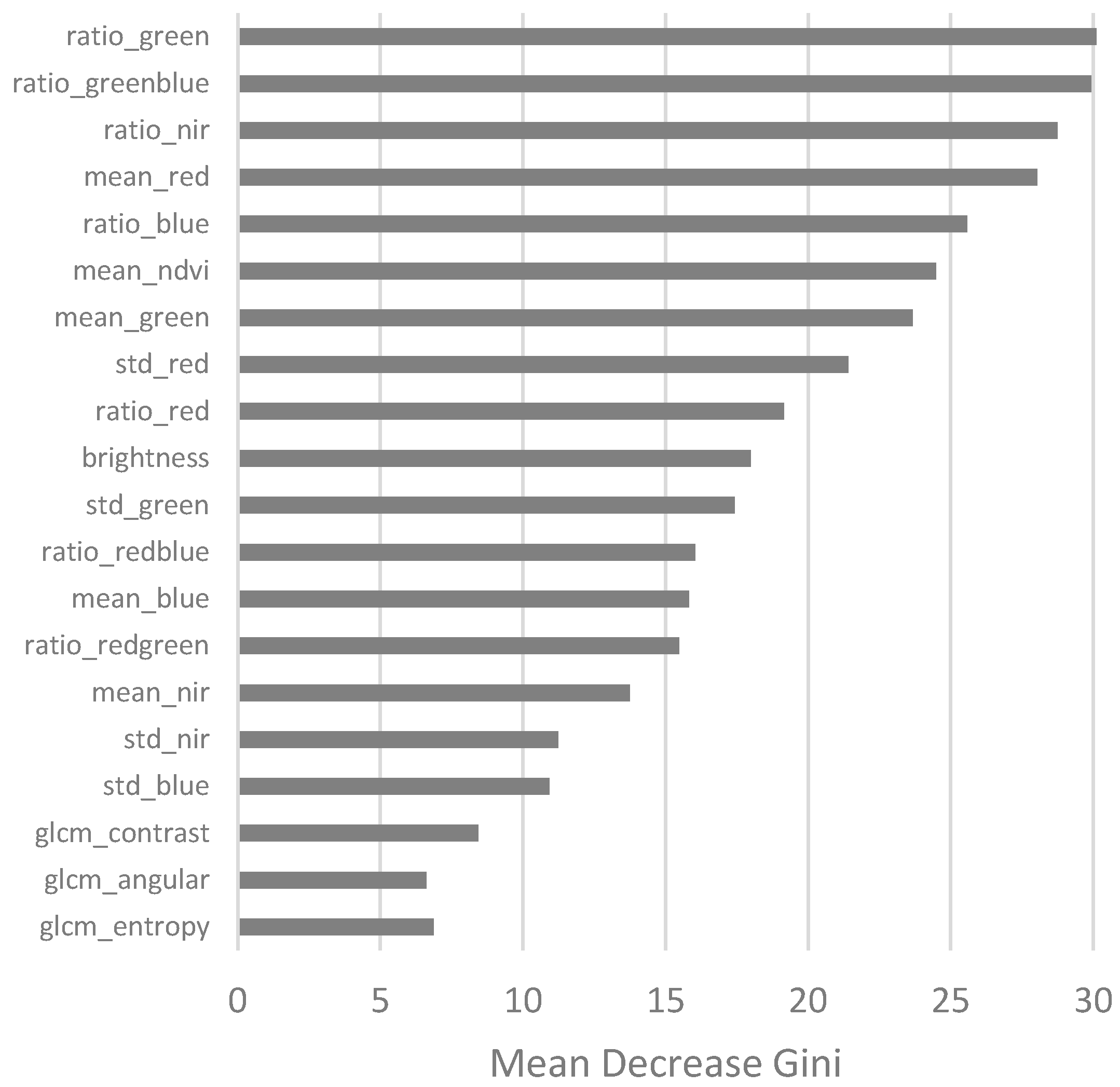
| Variables | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | blue, green, red, NIR | Mean of the values in the spectral band, calculated over all pixels within the segment |
| NDVI | Mean of (NIR-red)/(NIR + red) within the segment | |
| Ratio | blue, green, red, NIR | Ratio between the mean of the spectral band and the sum of the mean values in each band within the segment |
| green/blue, red/blue, red/green | Mean of one spectral band divided by the mean of the other band within the segment | |
| Standard deviation | blue, green, red, NIR | Standard deviation of all pixel values in the spectral band within the segment |
| Brightness | Sum of the mean values in each spectral band | |
| Grey Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) | Angular second moment | Reflects the degree of homogeneity present in the spectral band within the segment |
| contrast | Reflects the contrast present in all spectral bands within the segment | |
| entropy | Reflects the randomness in the spatial arrangement of all spectral bands values within the segment |
| Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Cover Classes | CON | OMET | NMET | ||
| Classification | VEG | 1 | 0 | 2 | |
| BSO | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| ASP | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| CON | 76 | 5 | 23 | ||
| OMET | 7 | 14 | 2 | ||
| NMET | 9 | 2 | 70 | Overall Accuracy | |
| Producer’s Accuracy | 0.80 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.75 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mossoux, S.; Kervyn, M.; Soulé, H.; Canters, F. Mapping Population Distribution from High Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery in a Data Poor Setting. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091409
Mossoux S, Kervyn M, Soulé H, Canters F. Mapping Population Distribution from High Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery in a Data Poor Setting. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(9):1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091409
Chicago/Turabian StyleMossoux, Sophie, Matthieu Kervyn, Hamid Soulé, and Frank Canters. 2018. "Mapping Population Distribution from High Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery in a Data Poor Setting" Remote Sensing 10, no. 9: 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091409
APA StyleMossoux, S., Kervyn, M., Soulé, H., & Canters, F. (2018). Mapping Population Distribution from High Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery in a Data Poor Setting. Remote Sensing, 10(9), 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091409