Satellite-Based Models Need Improvements on Simulating Annual Gross Primary Productivity: A Comparison of Six Models for Regional Modeling of Deciduous Broadleaf Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Flux Tower Data
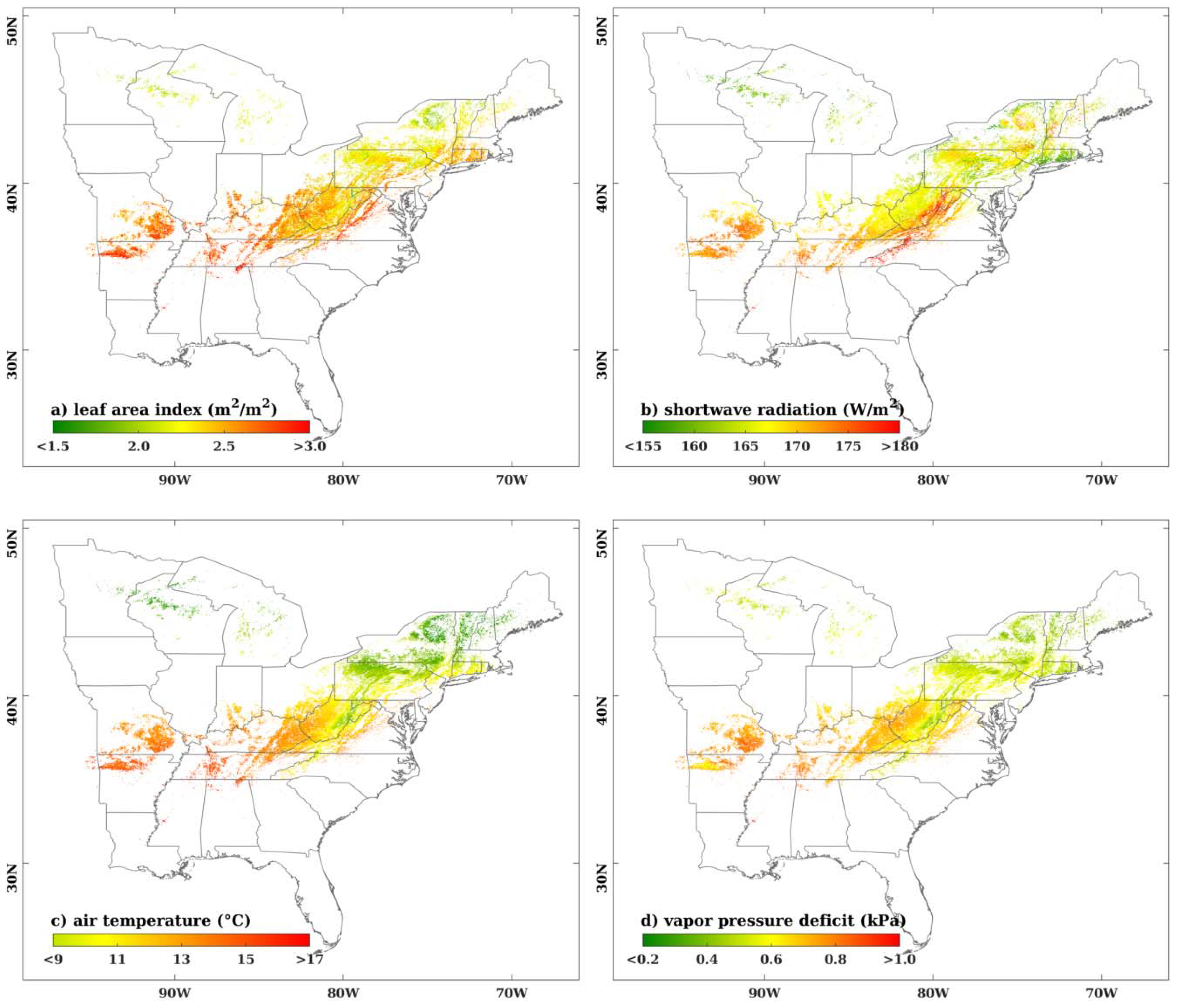
2.2. Climate Data
2.3. MODIS Data
3. Methods
3.1. The MODIS GPP Product
3.2. Two-Leaf Light Use Efficiency Model
3.3. Vegetation Photosynthesis Model
3.4. The Growing Production Day Model
3.5. The Breathing Earth System Simulator Product
3.6. The Eddy Covariance and MODIS Data-Driven Model
3.7. Model Implementation and Comparison
4. Results
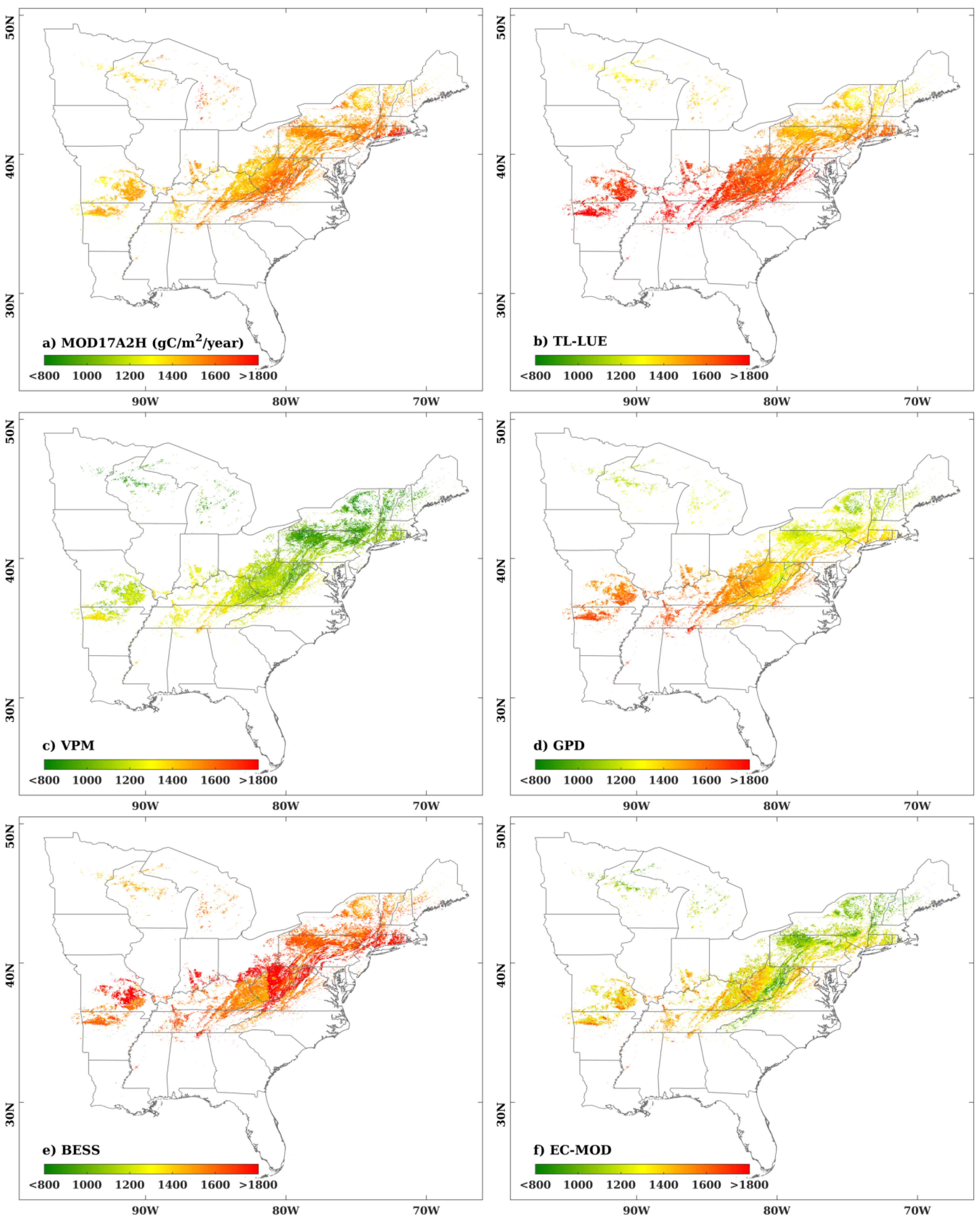
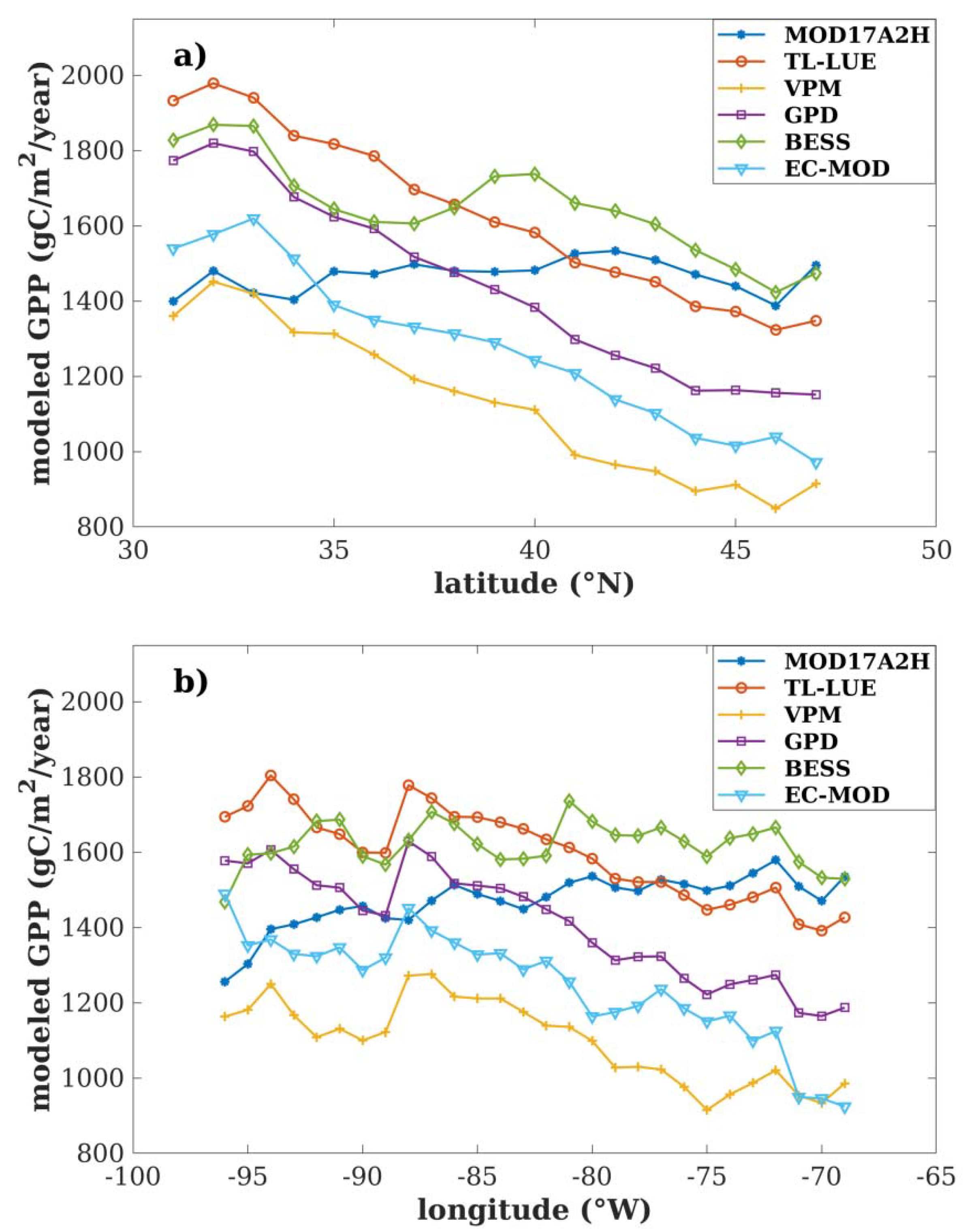
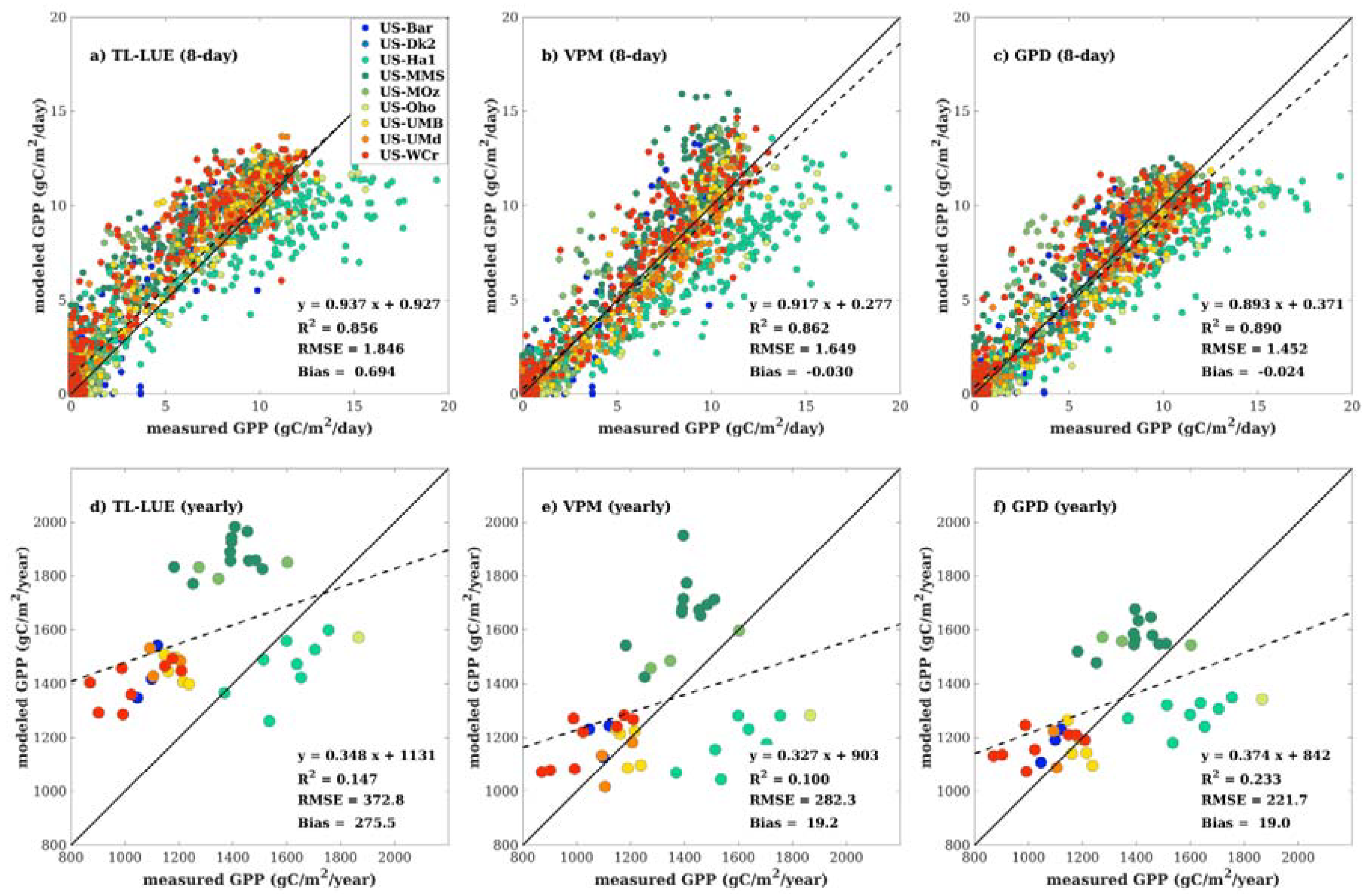
4.1. Regional-Scale Model Comparisons
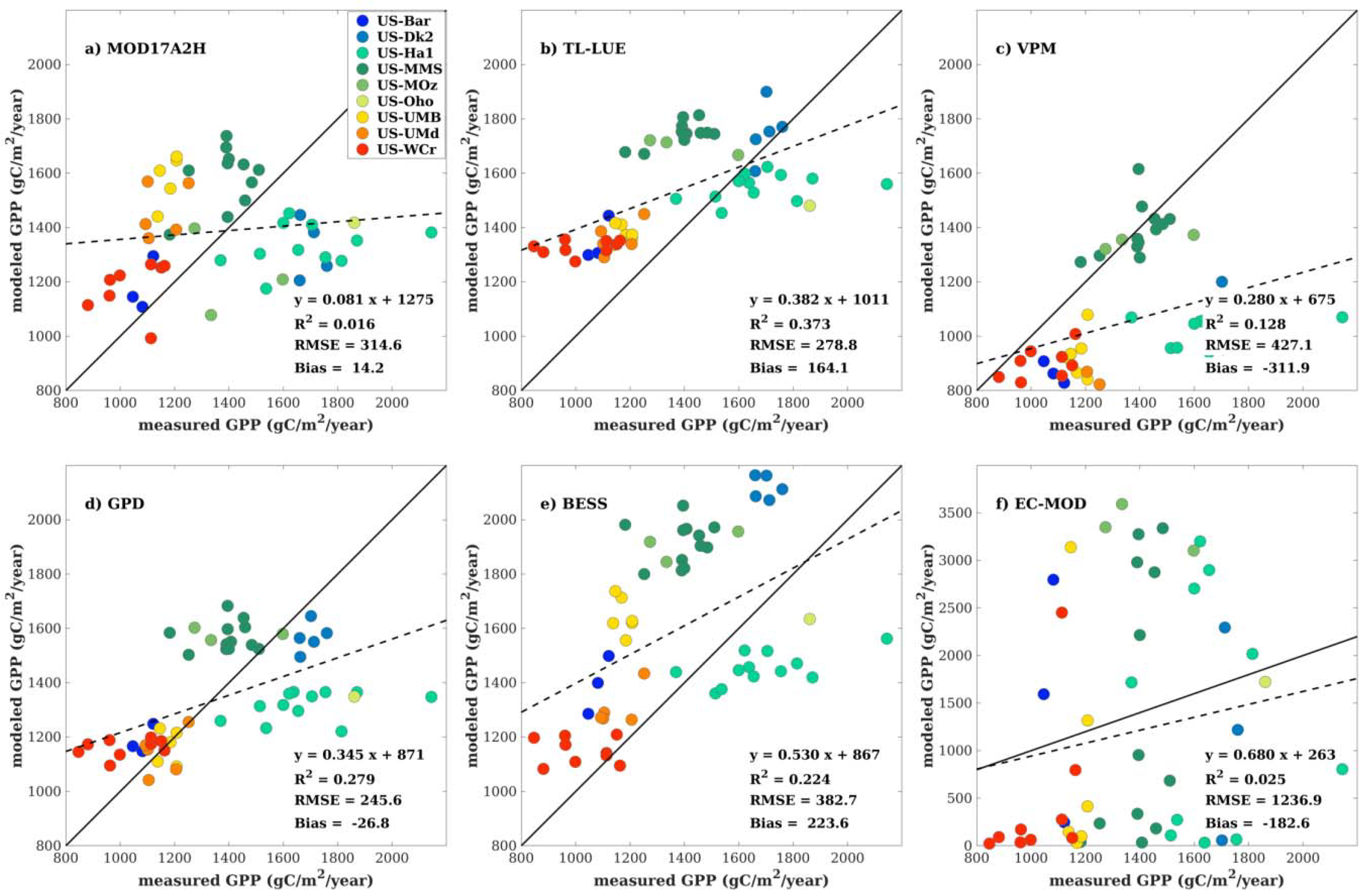
4.2. Site-Scale Model Comparisons
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciais, P.; Sabine, C.; Bala, G.; Bopp, L.; Brovkin, V.; Canadell, J.; Chhabra, A.; DeFries, R.; Galloway, J.; Heimann, M. Carbon and other biogeochemical cycles. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 465–570. [Google Scholar]
- Le Quéré, C.; Andrew, R.M.; Canadell, J.G.; Sitch, S.; Korsbakken, J.I.; Peters, G.P.; Manning, A.C.; Boden, T.A.; Tans, P.P.; Houghton, R.A. Global carbon budget 2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, C.; Reichstein, M.; Tomelleri, E.; Ciais, P.; Jung, M.; Carvalhais, N.; Roedenbeck, C.; Arain, M.A.; Baldocchi, D.; Bonan, G.B.; et al. Terrestrial Gross Carbon Dioxide Uptake: Global Distribution and Covariation with Climate. Science 2010, 329, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Niu, S.; Ciais, P.; Janssens, I.A.; Chen, J.; Ammann, C.; Arain, A.; Blanken, P.D.; Cescatti, A.; Bonal, D. Joint control of terrestrial gross primary productivity by plant phenology and physiology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2788–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yebra, M.; van Dijk, A.I.; Leuning, R.; Guerschman, J.P. Global vegetation gross primary production estimation using satellite-derived light-use efficiency and canopy conductance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Coops, N.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Black, T.A.; Guy, R.D. The use of remote sensing in light use efficiency based models of gross primary production: A review of current status and future requirements. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anav, A.; Friedlingstein, P.; Beer, C.; Ciais, P.; Harper, A.; Jones, C.; Murray-Tortarolo, G.; Papale, D.; Parazoo, N.C.; Peylin, P. Spatiotemporal patterns of terrestrial gross primary production: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 785–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, G.B. Ecological Climatology: Concepts and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; 678p. [Google Scholar]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Gamon, J.A. The need for a common basis for defining light-use efficiency: Implications for productivity estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Liu, S.; Yu, G.; Bonnefond, J.-M.; Chen, J.; Davis, K.; Desai, A.R.; Goldstein, A.H.; Gianelle, D.; Rossi, F. Global estimates of evapotranspiration and gross primary production based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1416–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Dai, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Gong, P.; Richardson, A.D. A steady-state approximation approach to simulate seasonal leaf dynamics of deciduous broadleaf forests via climate variables. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Drought-induced reduction in global terrestrial net primary production from 2000 through 2009. Science 2010, 329, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhuang, Q.; Cook, D.R.; Coulter, R.; Pekour, M.S.; Scott, R.L.; Munger, J.; Bible, K. Quantification of terrestrial ecosystem carbon dynamics in the conterminous United States combining a process-based biogeochemical model and MODIS and AmeriFlux data. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 2665–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liang, S.; Yu, G.; Yuan, W.; Cheng, X.; Xia, J.; Zhao, T.; Feng, J.; Ma, Z.; Ma, M. Estimation of gross primary production over the terrestrial ecosystems in China. Ecol. Model. 2013, 261, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, K.; Schwalm, C.R.; Williams, C.; Arain, M.A.; Barr, A.; Chen, J.M.; Davis, K.J.; Dimitrov, D.; Hilton, T.W.; Hollinger, D.Y.; et al. A model-data comparison of gross primary productivity: Results from the North American Carbon Program site synthesis. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2012, 117, G03010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D.D. Assessing the eddy covariance technique for evaluating carbon dioxide exchange rates of ecosystems: Past, present and future. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, A.D.; Arneth, A.; Kiang, N.Y.; Lomas, M.; OgÉE, J.; RÖDenbeck, C.; Running, S.W.; Santaren, J.-D.; Sitch, S.; Viovy, N.; et al. FLUXNET and modelling the global carbon cycle. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 610–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ryu, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of global gross primary productivity and evapotranspiration products derived from Breathing Earth System Simulator (BESS). Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 528–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöström, M.; Ardö, J.; Arneth, A.; Boulain, N.; Cappelaere, B.; Eklundh, L.; de Grandcourt, A.; Kutsch, W.L.; Merbold, L.; Nouvellon, Y. Exploring the potential of MODIS EVI for modeling gross primary production across African ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Munger, J.W.; Niu, Z.; Kuang, D. Comparison of multiple models for estimating gross primary production using MODIS and eddy covariance data in Harvard Forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2925–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, H.; Huang, N.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ding, Z.; Xie, J. A comprehensive assessment of MODIS-derived GPP for forest ecosystems using the site-level FLUXNET database. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5907–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.P.; Urbanski, S.; Bremer, D.; Wofsy, S.C.; Meyers, T.; Gower, S.T.; Gregory, M. A cross-biome comparison of daily light use efficiency for gross primary production. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Cai, W.; Xia, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Dong, W.; Merbold, L.; Law, B.; Arain, A.; Beringer, J.; et al. Global comparison of light use efficiency models for simulating terrestrial vegetation gross primary production based on the LaThuile database. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 192–193, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements-FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300, p. 6541. [Google Scholar]
- Kathilankal, J.; O’Halloran, T.; Schmidt, A.; Hanson, C.; Law, B. Development of a semi-parametric PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation) partitioning model for the United States, version 1.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 2477–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q. A risk-benefit model to simulate vegetation spring onset in response to multi-decadal climate variability: Theoretical basis and applications from the field to the Northern Hemisphere. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 228–229, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.; Richardson, A.D.; Braswell, B.; Ollinger, S.V.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Smith, M.-L. Refining light-use efficiency calculations for a deciduous forest canopy using simultaneous tower-based carbon flux and radiometric measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 143, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, A.C.; Oren, R.; Stoy, P.C. Estimating components of forest evapotranspiration: A footprint approach for scaling sap flux measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1719–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanski, S.; Barford, C.; Wofsy, S.; Kucharik, C.; Pyle, E.; Budney, J.; McKain, K.; Fitzjarrald, D.; Czikowsky, M.; Munger, J. Factors controlling CO2 exchange on timescales from hourly to decadal at Harvard Forest. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2007, 112, G02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoni, D.; Schmid, H.P.; Wayson, C.A.; Potter, H.; Grimmond, C.S.B.; Randolph, J.C. Evidence of increased net ecosystem productivity associated with a longer vegetated season in a deciduous forest in south-central Indiana, USA. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Meyers, T.; Pallardy, S.G.; Hanson, P.J.; Yang, B.; Heuer, M.; Hosman, K.P.; Riggs, J.S.; Sluss, D.; Wullschleger, S.D. Direct and indirect effects of atmospheric conditions and soil moisture on surface energy partitioning revealed by a prolonged drought at a temperate forest site. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, G.; Chu, H.; Noormets, A.; Ouyang, Z.; John, R.; Wan, S.; Guan, W. Long-term variability and environmental control of the carbon cycle in an oak-dominated temperate forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 313, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, C.M.; Hardiman, B.S.; Nave, L.E.; Bohrer, G.; Maurer, K.D.; Vogel, C.S.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Curtis, P.S. Sustained carbon uptake and storage following moderate disturbance in a Great Lakes forest. Ecol. Appl. 2013, 23, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, A.R.; Noormets, A.; Bolstad, P.V.; Chen, J.; Cook, B.D.; Davis, K.J.; Euskirchen, E.S.; Gough, C.; Martin, J.G.; Ricciuto, D.M. Influence of vegetation and seasonal forcing on carbon dioxide fluxes across the Upper Midwest, USA: Implications for regional scaling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 288–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, P.; Thornton, M.; Mayer, B.; Wei, Y.; Devarakonda, R.; Vose, R.; Cook, R. Daymet: Daily Surface Weather Data on a 1-km Grid for North America, Version 3; Oak Ridge National Laboratory Distributed Active Archive Center: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, R.B.; Hoffman, S.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Privette, J.L.; Glassy, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Smith, G.R.; et al. Global products of vegetation leaf area and fraction absorbed PAR from year one of MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; El Saleous, N.Z.; Justice, C.O. Atmospheric correction of MODIS data in the visible to middle infrared: First results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Tan, B.; Schneider, A.; Ramankutty, N.; Sibley, A.; Huang, X. MODIS Collection 5 global land cover: Algorithm refinements and characterization of new datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, S.; Zhao, M. User’s guide daily GPP and annual NPP (MOD17A2/A3) products NASA earth observing system MODIS land algorithm. Version 2015, 3, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. Fitting autoregressive models for prediction. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1969, 21, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Friedl, M.A.; Xin, Q.; Gray, J.; Pan, Y.; Frolking, S. Mapping Crop Cycles in China Using MODIS-EVI Time Series. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2473–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Babu, J.Y.; Salas, W.; Moore, B., III. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in South and Southeast Asia using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Heinsch, F.A.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Improvements of the MODIS terrestrial gross and net primary production global data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Ju, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; He, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Guan, D.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Development of a two-leaf light use efficiency model for improving the calculation of terrestrial gross primary productivity. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 173, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Braswell, B.; Urbanski, S.; Boles, S.; Wofsy, S.; Moore, B.; Ojima, D. Modeling gross primary production of temperate deciduous broadleaf forest using satellite images and climate data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Kobayashi, H.; Ingen, C.; Li, J.; Black, T.A.; Beringer, J.; Gorsel, E.; Knohl, A.; Law, B.E. Integration of MODIS land and atmosphere products with a coupled-process model to estimate gross primary productivity and evapotranspiration from 1 km to global scales. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2011, 25, GB4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Ollinger, S.V.; Frolking, S.; Hurtt, G.C.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Davis, K.J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Deng, F.; Chen, J. Data-driven diagnostics of terrestrial carbon dynamics over North America. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 197, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Cihlar, J.; Goulden, M. Daily canopy photosynthesis model through temporal and spatial scaling for remote sensing applications. Ecol. Model. 1999, 124, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, X.; Ju, W.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Yuan, W.; Andrew Black, T.; Jassal, R.; Ibrom, A. Global parameterization and validation of a two-leaf light use efficiency model for predicting gross primary production across FLUXNET sites. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 1045–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ju, W.; Zhou, Y.; He, M.; Law, B.E.; Black, T.A.; Margolis, H.A.; Cescatti, A.; Gu, L.; Montagnani, L. Performance of linear and nonlinear two-leaf light use efficiency models at different temporal scales. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2238–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Gong, P.; Li, W. Modeling photosynthesis of discontinuous plant canopies by linking the Geometric Optical Radiative Transfer model with biochemical processes. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 3447–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Gong, P.; Suyker, A.E.; Si, Y. Effects of the partitioning of diffuse and direct solar radiation on satellite-based modeling of crop gross primary production. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 50, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhuang, Q.; Law, B.E.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Chen, J.; Richardson, A.D.; Melillo, J.M.; Davis, K.J.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Wharton, S. Assessing net ecosystem carbon exchange of US terrestrial ecosystems by integrating eddy covariance flux measurements and satellite observations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parazoo, N.C.; Bowman, K.; Fisher, J.B.; Frankenberg, C.; Jones, D.; Cescatti, A.; Pérez-Priego, Ó.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Montagnani, L. Terrestrial gross primary production inferred from satellite fluorescence and vegetation models. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3103–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, T.F.; Baker, I.; Barr, A.; Ciais, P.; Davis, K.; Dietze, M.; Dragoni, D.; Gough, C.M.; Grant, R.; Hollinger, D.; et al. Terrestrial biosphere model performance for inter-annual variability of land-atmosphere CO2 exchange. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 1971–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.P.; Ritts, W.D.; Cohen, W.B.; Gower, S.T.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W.; Wofsy, S.C.; Urbanski, S.; Dunn, A.L.; Munger, J. Scaling gross primary production (GPP) over boreal and deciduous forest landscapes in support of MODIS GPP product validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhuang, Q.; Law, B.E.; Chen, J.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Cook, D.R.; Oren, R.; Richardson, A.D.; Wharton, S.; Ma, S. A continuous measure of gross primary production for the conterminous United States derived from MODIS and AmeriFlux data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Site Code | Site Name | Lat (°N) | Lon (°W) | Elev (m) | Years | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US-Bar | Bartlett Experimental Forest | 44.0646 | −71.2881 | 272 | 2004–2006 | Jenkins et al. [27] |
| US-Dk2 | Duke Forest Hardwoods | 35.9736 | −79.1004 | 168 | 2001–2005 | Oishi et al. [28] |
| US-Ha1 | Harvard Forest Environmental Measurement Station Tower | 42.5378 | −72.1715 | 340 | 2001–2012 | Urbanski et al. [29] |
| US-MMS | Morgan Monroe State Forest | 39.3231 | −86.4131 | 275 | 2001–2012 | Dragoni et al. [30] |
| US-MOz | Missouri Ozark | 38.7441 | −92.2000 | 219 | 2005–2007 | Gu et al. [31] |
| US-Oho | Oak Openings | 41.5545 | −83.8438 | 230 | 2005 | Xie et al. [32] |
| US-UMB | Univ. of Mich. Biological Station | 45.5598 | −84.7138 | 234 | 2001–2006 | Gough et al. [33] |
| US-UMd | Univ. of Mich. Biological Station Disturbance | 45.5625 | −84.6975 | 239 | 2008–2012 | Gough et al. [33] |
| US-WCr | Willow Creek | 45.8060 | −90.0798 | 515 | 2001–2012 | Desai et al. [34] |
| Model Name | Equations |
|---|---|
| Canopy radiative transfer | |
| Leaf photosynthesis | |
| Leaf conductance | |
| Leaf transpiration | |
| Soil evaporation |
| Models | AAGPP as a Function of Latitude | AAGPP as a Function of Longitude | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Function | R2 | Slope p Value | Regression Function | R2 | Slope p Value | |
| MOD17A2H | y = 2.270x + 1379 | 0.070 | 0.304 | y = 6.797x + 2031 | 0.636 | <0.0001 |
| TL-LUE | y = −43.619x + 3330 | 0.980 | <0.0001 | y = −12.797x + 541.9 | 0.787 | <0.0001 |
| VPM | y = −38.550x + 2632 | 0.950 | <0.0001 | y = −10.381x + 242.4 | 0.627 | <0.0001 |
| GPD | y = −46.933x + 3271 | 0.970 | <0.0001 | y = −16.273x + 65.21 | 0.852 | <0.0001 |
| BESS | y = −21.962x + 2508 | 0.724 | <0.0001 | y = 0.100x + 1629 | 0.0002 | 0.944 |
| EC-MOD | y = −40.233x + 2844 | 0.963 | <0.0001 | y = −15.598x − 42.2 | 0.787 | <0.0001 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xin, Q. Satellite-Based Models Need Improvements on Simulating Annual Gross Primary Productivity: A Comparison of Six Models for Regional Modeling of Deciduous Broadleaf Forests. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071008
Li L, Zhao Y, Fu Y, Xin Q. Satellite-Based Models Need Improvements on Simulating Annual Gross Primary Productivity: A Comparison of Six Models for Regional Modeling of Deciduous Broadleaf Forests. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(7):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071008
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Le, Yaolong Zhao, Yingchun Fu, and Qinchuan Xin. 2018. "Satellite-Based Models Need Improvements on Simulating Annual Gross Primary Productivity: A Comparison of Six Models for Regional Modeling of Deciduous Broadleaf Forests" Remote Sensing 10, no. 7: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071008
APA StyleLi, L., Zhao, Y., Fu, Y., & Xin, Q. (2018). Satellite-Based Models Need Improvements on Simulating Annual Gross Primary Productivity: A Comparison of Six Models for Regional Modeling of Deciduous Broadleaf Forests. Remote Sensing, 10(7), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071008






